Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bartholin'S Cyst and Abscess: North Dakota Family Planning Program Protocols - Reproductive Diseases
Uploaded by
Milanisti22Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bartholin'S Cyst and Abscess: North Dakota Family Planning Program Protocols - Reproductive Diseases
Uploaded by
Milanisti22Copyright:
Available Formats
NORTH DAKOTA FAMILY PLANNING PROGRAM PROTOCOLS REPRODUCTIVE DISEASES
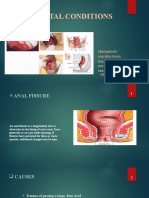
BARTHOLIN'S CYST AND ABSCESS
DEFINITION A post-inflammatory pseudocyst that forms proximally to the obstructed duct of a Bartholin's gland. The cyst may become infected and an abscess may develop in the gland. The flora is usually a mixture of aerobic and anerobic from the vagina, with chlamydia trachomatis and n. gonorrhoeae cultured in approximately 10% of the cases. Predominant pathogens leading to abscess are gonococcus and chlamydial organisms. May include: 1. Painful swollen lump in the vaginal area. 2. Difficulty sitting or walking due to severe pain and swelling. 3. History of infected Bartholin's gland, with or without antibiotic treatment. 4. History of sexually transmitted disease. 5. Fever 6. Dyspareunia May include: 1. No symptoms. 2. Cyst is characteristically located in the lower half of the labia with its inner wall immediately adjacent to the lower vaginal wall. 3. Lesions may vary in size from 1-10 cm. 4. The involved area may be painfully tender and erythemic. May include: 1. Vaginitis/cervicitis screening, as appropriate. Bartholin's Cyst Treatment options may include: 1. Asymptomatic cyst may require no treatment 2. Abscesses require antibiotic treatment. A. Doxycycline 100 mg PO bid x 7d, OR B. Cephalexin 500 mg PO bid x 7d, OR C. Cephalexin 250 mg PO qid x 7d, OR D. Ampicillin 500 mg PO qid x 7d. E. Advise sitz baths qid for 30 minutes for relief of pain. F. Advise OTC analgesic (ASA or NSAID) q4h prn for pain. 3. If cyst has increased in size or there is no change in size after 3 days of antibiotic therapy, a physician referral may be needed. 4. Symptomatic cysts and gland abscesses may require drainage. Bartholins Cyst RD-
SUBJECTIVE
OBJECTIVE
LABORATORY
ASSESSMENT PLAN
Page 1 of 2 15
CLIENT EDUCATION CONSULT / REFER TO PHYSICIAN Revised 07/10
1. Provide client education handout(s). Review symptoms, treatment options, and medication side effects. 2. Advise to avoid intercourse until completion of medication. 1. If above treatment under plan is ineffective refer to a physician.
References: 1. Hawkins, Joellen W.; Roberto-Nichols, Diane M.; Stanley-Haney, J. L. (2000). Protocols for Nurse Practitioners in Gynecologic Settings (7th ed.). New York: Tiresias Press, Inc. pp.149-150. 2. Omole, F., Simmons, B.J. & Hacker, Y. (2003) Management of Bartholins Duct Cyst and Gland Abscess. American Family Physician. 68 (1). pp. 135-40. 3. Bartholin Cyst (2010). Retrieved April 1, 2010 from http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/bartholin-cyst/DS00667 4. Bartholin Cyst and Abscess. 2009 Marx: Rosens Emergency Medicine (7th ed.). Retrieved from www.mdconsult.com . 5. Bartholins Abscess. (2010). Retrieved April1, 2010 from http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001489.htm.
Page 2 of 2 15
Bartholins Cyst
RD-
You might also like
- 4 Appendectomy Nursing Care PlansDocument8 pages4 Appendectomy Nursing Care PlansMarin Andrei100% (2)
- Project Proposal - MEDICAL SUPPLIES & EQUIPMENTDocument3 pagesProject Proposal - MEDICAL SUPPLIES & EQUIPMENTRogelio Ladiero100% (5)
- ATI Med Surg SPRING 2019 Post ReviewDocument11 pagesATI Med Surg SPRING 2019 Post ReviewQuincey Hamilton43% (7)
- rd-15 Bartholin Cyst and Abscess 10-12 PDFDocument2 pagesrd-15 Bartholin Cyst and Abscess 10-12 PDFdevidanthonyNo ratings yet
- Case Study On AppendicitisDocument15 pagesCase Study On AppendicitisKristelle BonitaNo ratings yet
- Questions: Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument11 pagesQuestions: Peptic Ulcer DiseaseNahanNo ratings yet
- Case 1Document8 pagesCase 1Vineth MartinNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Management and Nursing Care PlanDocument37 pagesAppendicitis Management and Nursing Care PlanAlva AlfaNo ratings yet
- Abcesso e Fistula AnoretalDocument5 pagesAbcesso e Fistula AnoretalDani SNo ratings yet
- Title: Antibiotic Guideline For Acute Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument5 pagesTitle: Antibiotic Guideline For Acute Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseresortbabeNo ratings yet
- Peri TonsilLar AbscessDocument6 pagesPeri TonsilLar Abscessrivan90No ratings yet
- Assignment: Applied MedicineDocument10 pagesAssignment: Applied MedicineKhadija BakhtawarNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic GuidDocument11 pagesAntibiotic Guidlaur_rbNo ratings yet
- DIVERTICULOSISDocument21 pagesDIVERTICULOSISTiffany AdriasNo ratings yet
- Final Meq Ss OncoDocument10 pagesFinal Meq Ss OncoRoadtogot 2023No ratings yet
- Pulmonary TBDocument13 pagesPulmonary TBAmanda ScarletNo ratings yet
- Respi, GI, GU, Repro DiseasesDocument6 pagesRespi, GI, GU, Repro DiseasesAngela OngNo ratings yet
- Botulism: Physical ExamDocument13 pagesBotulism: Physical ExamAlexandria P. OrcajadaNo ratings yet
- SBARDocument2 pagesSBARJason Kai Poth100% (1)
- Anorectal Conditions: Prepared By: Manisha Thapa Roll No: 6 BSN 2 Year Presented To: Ms. Shristhi ShresthaDocument25 pagesAnorectal Conditions: Prepared By: Manisha Thapa Roll No: 6 BSN 2 Year Presented To: Ms. Shristhi ShresthaManjesh Mishra XettriNo ratings yet
- Med Surg ReviewDocument6 pagesMed Surg ReviewSabhi Sandhu75% (4)
- Ix. Discharge PlanDocument8 pagesIx. Discharge PlanLyra LizetteNo ratings yet
- NCP and DrugsDocument13 pagesNCP and DrugsApRil ANn ChUa BingcangNo ratings yet
- Case Pres Abstract Intro Disch PLNDocument7 pagesCase Pres Abstract Intro Disch PLNMheaye JheaaNo ratings yet
- Journal AbssDocument5 pagesJournal AbssMilanisti22No ratings yet
- Fungal Infection Case StudiesDocument4 pagesFungal Infection Case StudiesJape GarridoNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On LeiomyomasDocument4 pagesA Case Study On LeiomyomasGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- Gis Pih Ud 2023 09Document2 pagesGis Pih Ud 2023 09ahimsam552No ratings yet
- Oncologic DrugsDocument8 pagesOncologic DrugsMiden AlbanoNo ratings yet
- Ob Management Septic AbortionDocument8 pagesOb Management Septic AbortionspringdingNo ratings yet
- SKENARIO 2 - Pelvic Inflammatory Disease REVISIDocument7 pagesSKENARIO 2 - Pelvic Inflammatory Disease REVISILidya IryaniNo ratings yet
- OB-GYN 101: Vaginal DischargeDocument8 pagesOB-GYN 101: Vaginal Dischargemadmax500No ratings yet
- Resume Materi Presentasi EnglishDocument6 pagesResume Materi Presentasi EnglishBunda SyifaNo ratings yet
- Format Latar Belakang Dan AppendicitisDocument5 pagesFormat Latar Belakang Dan AppendicitisBisturi 2022No ratings yet
- Anal Fissure: A Frequent Reason of Anal Pain: Dr. Bhavin KothariDocument3 pagesAnal Fissure: A Frequent Reason of Anal Pain: Dr. Bhavin KotharisebastixmasterNo ratings yet
- LP Hemoroid BedahDocument11 pagesLP Hemoroid BedahakunbinNo ratings yet
- UGI DisordersDocument108 pagesUGI DisorderssafeheavenNo ratings yet
- Pharma Module 4Document4 pagesPharma Module 4Chelsy Sky SacanNo ratings yet
- I. IntroductionDocument11 pagesI. IntroductionnsgcareplannerNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument17 pagesAppendicitisAhmed Halaby100% (1)
- Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis Case SampleDocument3 pagesAcute Uncomplicated Cystitis Case SampleElmery Gem Galapon EstorqueNo ratings yet
- Marsupial IzationDocument2 pagesMarsupial IzationMuhammadUsriYusranNo ratings yet
- AppendicitisDocument5 pagesAppendicitisSalma NazarNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis SampleDocument15 pagesAppendicitis SampleChiqui Lao DumanhugNo ratings yet
- Anorectal Conditions: Manisha Thapa Roll No: 06 BSN 2 YearDocument11 pagesAnorectal Conditions: Manisha Thapa Roll No: 06 BSN 2 YearManjesh Mishra XettriNo ratings yet
- By Amente J. (B.Pharm, MSC) : For Clinical Pharmacy Students (4 Year)Document38 pagesBy Amente J. (B.Pharm, MSC) : For Clinical Pharmacy Students (4 Year)Mohamed IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi DifteriDocument11 pagesPatofisiologi DifteriicorrrNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Appendicitis Post OperativeDocument17 pagesNursing Care Plan For Appendicitis Post OperativeOkaRizukiramanNo ratings yet
- Case Study Indirect Inguinal Hernia Left IncauceratedDocument6 pagesCase Study Indirect Inguinal Hernia Left Incauceratedstudent_019No ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument2 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseasejayinthelongrunNo ratings yet
- Stomach Ulceration Leaflet and Drugs Used To Treat Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument4 pagesStomach Ulceration Leaflet and Drugs Used To Treat Peptic Ulcer DiseasePrisma TridaNo ratings yet
- Rd-15 Bartholin Cyst and Abscess 10-12Document2 pagesRd-15 Bartholin Cyst and Abscess 10-12Chong Hui ChekNo ratings yet
- 4 Most Common Types of CancerDocument20 pages4 Most Common Types of CancerAce ENo ratings yet
- Basilio Aya Nov 12 2016: ReadingDocument5 pagesBasilio Aya Nov 12 2016: ReadingAyaBasilioNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On (Pud) Peptic Ulcer Disease: Presented by Pharm D InternDocument28 pagesCase Presentation On (Pud) Peptic Ulcer Disease: Presented by Pharm D InternAntoNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer (Nursing Care)Document5 pagesLung Cancer (Nursing Care)heiyuNo ratings yet
- A.Disorder Includes Inflammation, Infection, Neoplastic Lesions B. PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesA.Disorder Includes Inflammation, Infection, Neoplastic Lesions B. PathophysiologySr.Jasmin LarizaNo ratings yet
- A. Definition: Santos, Jianne Kyra E. BSN Iii-BDocument5 pagesA. Definition: Santos, Jianne Kyra E. BSN Iii-BLiza AingelicaNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument14 pagesHirschsprung DiseaseFlordelyn Anuales100% (2)
- NCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!From EverandNCLEX: Pharmacology for Nurses: 100 Practice Questions with Rationales to help you Pass the NCLEX!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Diverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandDiverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol) Dosing ChartDocument1 pageAcetaminophen (Tylenol) Dosing ChartMilanisti22No ratings yet
- Chronic Rhinosinusitis - An Overview: N.V Deepthi, U.K. Menon, K. MadhumitaDocument6 pagesChronic Rhinosinusitis - An Overview: N.V Deepthi, U.K. Menon, K. MadhumitaMilanisti22No ratings yet
- Indications, Efficacy, and Safety of Intranasal Corticosteriods in RhinosinusitisDocument4 pagesIndications, Efficacy, and Safety of Intranasal Corticosteriods in RhinosinusitisMilanisti22No ratings yet
- Otitis Externa Swimmers EarDocument2 pagesOtitis Externa Swimmers EarMilanisti22No ratings yet
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Document2 pagesP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Milanisti22No ratings yet
- Recurrent Tonsillitis: Information For PatientsDocument1 pageRecurrent Tonsillitis: Information For PatientsMilanisti22No ratings yet
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Document5 pagesP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Milanisti22No ratings yet
- Sinusitis in ChildrenDocument1 pageSinusitis in ChildrenMilanisti22No ratings yet
- Otitis Media and Sinusitis I. Otitis MediaDocument5 pagesOtitis Media and Sinusitis I. Otitis MediaMilanisti22No ratings yet
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Document3 pagesP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Milanisti22No ratings yet
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Document2 pagesP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Milanisti22No ratings yet
- Acute Sinusitis in Adults: Key HighlightsDocument3 pagesAcute Sinusitis in Adults: Key HighlightsMilanisti22No ratings yet
- Walgreen Online PharmacyDocument64 pagesWalgreen Online PharmacyWalgreen Online PharmacyNo ratings yet
- Policy Brief For Philippine Senate - 05.17.2023 (With Summary)Document27 pagesPolicy Brief For Philippine Senate - 05.17.2023 (With Summary)rh4v0cNo ratings yet
- Manual of Laboratory MedicineDocument436 pagesManual of Laboratory MedicineUlfat NiazyNo ratings yet
- 2009 - BTS Guidelines For Home Oxygen in Children Quick Reference GuideDocument8 pages2009 - BTS Guidelines For Home Oxygen in Children Quick Reference GuideblueicelandNo ratings yet
- Organistional Study: at V.S.M HospitalDocument10 pagesOrganistional Study: at V.S.M HospitalBinsa ThomasNo ratings yet
- AbortionDocument5 pagesAbortionYlenol HolmesNo ratings yet
- Final Ger Syllbus Jan16 Bridging 2016 After DR ModificationDocument2 pagesFinal Ger Syllbus Jan16 Bridging 2016 After DR ModificationHaneenNo ratings yet
- Thromboangiitis ObliteransDocument17 pagesThromboangiitis Obliteransmu_crNo ratings yet
- 340b Topic DiscussionDocument3 pages340b Topic Discussionapi-550597190No ratings yet
- Non Admissible ExpensesDocument7 pagesNon Admissible ExpenseskumarmtNo ratings yet
- HDF3Document36 pagesHDF3tateNo ratings yet
- Final Scientific Program EORCAPS 2013 For StudentsDocument3 pagesFinal Scientific Program EORCAPS 2013 For StudentsdrgauravkguptaNo ratings yet
- The Diagnosis and Treatment of Hair PDFDocument11 pagesThe Diagnosis and Treatment of Hair PDFSpica AdharaNo ratings yet
- Buntis Congress Report 2021Document24 pagesBuntis Congress Report 2021Giselle ArenasNo ratings yet
- Sulfa Zala ZineDocument7 pagesSulfa Zala ZineAkira EphanophythaNo ratings yet
- EB001Document10 pagesEB001Giselle MillsNo ratings yet
- Question NEURODocument39 pagesQuestion NEUROjondelacruz19100% (1)
- Fiziologie Aplicata - 2019Document16 pagesFiziologie Aplicata - 2019RaduNo ratings yet
- CHN1 Lec Session 8 SASDocument8 pagesCHN1 Lec Session 8 SASFrances PaqueoNo ratings yet
- Caring For Surgical Wounds at Home - Information For PatientsDocument8 pagesCaring For Surgical Wounds at Home - Information For PatientsleewfNo ratings yet
- Flapless Implant SurgeryDocument5 pagesFlapless Implant SurgerysharifNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based MedicineDocument55 pagesEvidence Based MedicineHelen SusantoNo ratings yet
- Nicu PPT - PPTX NewDocument65 pagesNicu PPT - PPTX Newvineeta.ashoknagarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Patient - S Medical Chart (2012) PDFDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Patient - S Medical Chart (2012) PDFFrancinetteNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Prosthodontic Treatment On Alveolar Bone Loss - A Review of The LiteratureDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Prosthodontic Treatment On Alveolar Bone Loss - A Review of The LiteratureNathawat PleumsamranNo ratings yet
- Syllabus FUNDADocument12 pagesSyllabus FUNDATuTitNo ratings yet
- Jurnal MaternitasDocument11 pagesJurnal MaternitasEndyNo ratings yet
- Reimplantation of Avulsed Tooth - A Case StudyDocument3 pagesReimplantation of Avulsed Tooth - A Case Studyrahul sharmaNo ratings yet
- Headache Behind The Ear - Causes, Treatment, and MoreDocument12 pagesHeadache Behind The Ear - Causes, Treatment, and Morethe conquerorNo ratings yet