Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathological Fractures Types of Fracture: Limb Trauma - Mmap - 08/09/2010
Uploaded by
sharu4291Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pathological Fractures Types of Fracture: Limb Trauma - Mmap - 08/09/2010
Uploaded by
sharu4291Copyright:
Available Formats
Osteoporosis Metabolic bone disease - osteomalacia, hyperparathyroidism Generalised Bone Disease Paget's disease Myelomatosis Chronic infection Site:
bone fractures, part of bone (proximal, shaft, distal) Line: transverse, oblique, spiral, multi fragmentary Displacement: angulation, translation, rotation Tendon shears of a fragment of bone Typically in athletes Avulsion fracture Primary Malignant Reduction Immobilisation Rehab Usually need to correct rotational or valgus or varus deformity Reduction can be performed as either an open or closed procedure Immobilisation is required until fracture union Intraarticular fractures - to stabilise anatomical reduction Repair of blood vessels and nerves - to protect vascular and nerve repair Multiple injuries Elderly patients - to allow early mobilisation Long bone fractures Failure of conservative management Pathological fractures Fractures that require open reduction Unstable fractures Secondary Survey Infection Non-union Implant failure Refracture Acute trauma - open and unstable fractures Non union of fractures Correction of joint contracture Filling of segmental limb defects - trauma, tumour and osteomyelitis Limb lengthening Overdistraction Pin-tract infection Complications # Upper Limb Immediate: bleeding, organ injury, nerve or skin injury, vessel injury Later Local: skin necrosis, pressure sores, infection, delayed union Later General: venous / fat embolism, PE, pneumonia, renal stones Bleeding into fascial compartment Fluid loss, DIC and myoglobin release cause renal tubular necrosis - dialysis may be needed Causes vascular occulsion impairing blood supply, with potential for nerve damage and muscle death Limb and life threatening Compartment Syndrome Hip / Femur: external rotation, adduction and shortening Distal radius Indications External Clavicle: common in young from fall; complications include neurovascular injury and pneumothorax Scapula / Acramion: represent high energy transfer injuries Humerus: for example a child falling from an out stretched hand Colles: dorsal angulation and displacement; common in osteoporotic post menopausal women Smiths: forward / palmar displacement Complications Fixation Internal Indications Primary Survey General Airway + Oxygen + Check C-Spine Breathing + Ventilation Circulation + Haemorrhage Control Disability (check GCS and pupillary reflexes) Exposure (check and maintain body temperature) Principles Metastases Lung Breast Prostate GI Description Localised Benign Solitary bone cyst Fibrous cortical defect Chondroma Osteosarcoma Chondrosarcoma Ewing's tumour
Types of Fracture
Pathological Fractures
ATLS Protocol # Management
Adjuncts (to add life saving information)
Radiography: CXR, lateral C-Spine, and pelvis Urinary catheter (unless urethral injury) NGT (unless facial fracture) Oxygen sats and ABG Once pt is stabilised complete check from scalp to toe More focused imaging and examination
Limb Trauma
Scaphoid: common and easily missed on XR; resulting from falls on the hand; signs are swelling, pain and localised tenderness
Fractures
Typically 6 week healing - half as much in children Just below femoral head Intracapsular Circumflex artery supplies the head via the neck so with fracture there is risk of ischaemic necrosis Total hip replacement Between greater and lesser trochanters Extracapsular Typically 12 week healing - half as much in children Blood supply is not compromised Dynamic hip screw fixation
# Complications
# Lower Limb
Prompt fasciotomy is limb and life saving Results from skeletal muscle breakdown Release of contents into blood stream - myoglobin, potassium, phosphate, urate and CK Complications include hyperkalaemia and acute renal failure (myoglobi obstructs renal tubules) Causes: trauma, prolonged immobilisation, excessive exercise, drugs and toxins (statins, alcohol), infections (EBV, influenza), inherited muscle disorders Rhabdomylosis
Limb Trauma.mmap - 08/09/2010 -
You might also like
- Complicationsoffractures 120127084025 Phpapp02Document62 pagesComplicationsoffractures 120127084025 Phpapp02Aaliyah ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Avascular NecrosisDocument49 pagesAvascular NecrosisvhugalabudeliNo ratings yet
- Presenter: Dr. J. W. Kinyanjui Moderator: Prof. Mulimba J. A. O. 22 July 2013Document32 pagesPresenter: Dr. J. W. Kinyanjui Moderator: Prof. Mulimba J. A. O. 22 July 2013Santomi Pratama100% (1)
- Intracranial Complications of OMDocument30 pagesIntracranial Complications of OMAhmed Bin KamarulzamanNo ratings yet
- You Answered Trans Metatarsal AmputationDocument98 pagesYou Answered Trans Metatarsal AmputationOstazNo ratings yet
- Complications of FracturesDocument13 pagesComplications of FracturesmilananandNo ratings yet
- Review Sistem GerakDocument63 pagesReview Sistem GerakDanur AdiNo ratings yet
- Alterations Related To Musculoskeletal Trauma: Lisa M. Dunn MSN/Ed, RN, CCRN, CNEDocument83 pagesAlterations Related To Musculoskeletal Trauma: Lisa M. Dunn MSN/Ed, RN, CCRN, CNEjayvee2012No ratings yet
- Avascular NecrosisDocument41 pagesAvascular NecrosisMohd Johari Mohd Shafuwan100% (1)
- Case of Back PainDocument55 pagesCase of Back PainaayceeNo ratings yet
- Complications of FracturesDocument68 pagesComplications of FracturesChenna Kesava100% (1)
- ARTHRITIS TB KNEE HIP BPTDocument84 pagesARTHRITIS TB KNEE HIP BPTMiso100% (1)
- Sickle Cell and HemophiliaDocument38 pagesSickle Cell and HemophiliacorneliusNo ratings yet
- Sss Orthopedicemergencies 2012 Final Samuel-WongDocument38 pagesSss Orthopedicemergencies 2012 Final Samuel-WongMuhammad Irham FananiNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Emergency EnglishDocument64 pagesOrthopedic Emergency EnglishmegaNo ratings yet
- Pariyuth-Limb Injuries For EMedDocument75 pagesPariyuth-Limb Injuries For EMedDia Inggrit PNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal ProblemsDocument22 pagesMusculoskeletal ProblemsShauki AliNo ratings yet
- Pagetsdiseaseofthebone 180107110929Document28 pagesPagetsdiseaseofthebone 180107110929Lolo TotoNo ratings yet
- DR - Rieva Kuliah 7 November - 2018Document38 pagesDR - Rieva Kuliah 7 November - 2018Nisrina100% (1)
- Anaesthetic Management of Joint Replacement SurgeriesDocument55 pagesAnaesthetic Management of Joint Replacement SurgeriesRaguNo ratings yet
- General Principles of FractureDocument31 pagesGeneral Principles of Fractureamel015No ratings yet
- Orthopedic EmergencyDocument94 pagesOrthopedic EmergencyZenith100% (1)
- MF2 - Spinal Cord InjuryDocument43 pagesMF2 - Spinal Cord InjuryAnnbe BarteNo ratings yet
- 2009.10.09 Legg Calve Perthes Disease 2Document43 pages2009.10.09 Legg Calve Perthes Disease 2AnItaNo ratings yet
- Avn and Perthes DiseaseDocument29 pagesAvn and Perthes DiseaseRoopa Lexmy MuniandyNo ratings yet
- General Bone DiseasesDocument3 pagesGeneral Bone DiseasesMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Disorders Care of Client With Fall 2005Document41 pagesMusculoskeletal Disorders Care of Client With Fall 2005mara5140100% (3)
- Discuss Nursing Interventions That Prevent Complications of ImmobilityDocument19 pagesDiscuss Nursing Interventions That Prevent Complications of ImmobilityLilly Ann Vaughan50% (2)
- Dr. Abdul Rashad Senior Lecturer DPT, Mphill (Opt) Mppta United College of Physical TherapyDocument32 pagesDr. Abdul Rashad Senior Lecturer DPT, Mphill (Opt) Mppta United College of Physical Therapypasha100% (1)
- Lect 8 - Internal Fixation - IIDocument21 pagesLect 8 - Internal Fixation - IIAnkit LakshyaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal TraumaDocument63 pagesMusculoskeletal Traumarobby pardiansyahNo ratings yet
- Legg Calve PerthesDocument7 pagesLegg Calve PerthesNelhbenson LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Closed Fracture of Midshaft Femur FracturesDocument33 pagesClosed Fracture of Midshaft Femur FracturesLana AdilaNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument4 pagesIlovepdf Mergedallkhusairy6tuansiNo ratings yet
- Muskuloskeletal Disorders: Submitted By: Jho Ann Labor Bsn-Iv Submitted To: Mrs. Dapnhny HatudDocument9 pagesMuskuloskeletal Disorders: Submitted By: Jho Ann Labor Bsn-Iv Submitted To: Mrs. Dapnhny HatudjhoanNo ratings yet
- Name: Biadsi Odey Group:M1560 SUBJECT: Rheumatology (Patenit Presentation) - Data: 31/03/2019Document10 pagesName: Biadsi Odey Group:M1560 SUBJECT: Rheumatology (Patenit Presentation) - Data: 31/03/2019Galina LozovanuNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spondylosis: Muhammad Yafidy Pembimbing: Dr. S. Dohar AL Tobing, SP - OT (K)Document31 pagesCervical Spondylosis: Muhammad Yafidy Pembimbing: Dr. S. Dohar AL Tobing, SP - OT (K)yafidyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To OrthopaedicsDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Orthopaedicsgus_lions100% (1)
- Complications of FracturesDocument19 pagesComplications of Fracturesمحمد رأفتNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis & Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument60 pagesOsteoarthritis & Rheumatoid ArthritisSaya MenangNo ratings yet
- Trauma Musculoskeletal - Spine FKK UMJ1Document92 pagesTrauma Musculoskeletal - Spine FKK UMJ1Hendra Hash AwoNo ratings yet
- Avascular Necrosis of Femoral HeadDocument50 pagesAvascular Necrosis of Femoral HeadStar CruiseNo ratings yet
- Arthritis: Prepared By: Salini D/O Vasudevan Supervisor: DR JaneDocument73 pagesArthritis: Prepared By: Salini D/O Vasudevan Supervisor: DR Janeumanantini06No ratings yet
- 2.299224 - Initial Assessment Musculoskeletal TraumaDocument63 pages2.299224 - Initial Assessment Musculoskeletal TraumaMuhammad GilangNo ratings yet
- Ortho 26 Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesOrtho 26 Exam Questionsmehmi123100% (6)
- All Previous Essay SurgeryDocument170 pagesAll Previous Essay Surgeryalsfyabdullah2021No ratings yet
- Rthopaedics Ed Flag Emergencies: Staph Aureus, H. Influenzae and Enterobacter (In Children)Document13 pagesRthopaedics Ed Flag Emergencies: Staph Aureus, H. Influenzae and Enterobacter (In Children)rocitaho1458No ratings yet
- In The Name of Allah The Beneficent and The MercifulDocument29 pagesIn The Name of Allah The Beneficent and The Merciful81.Ghazala NawazNo ratings yet
- Vascular Disease Approach 11-7-13Document65 pagesVascular Disease Approach 11-7-13Dian PuspaNo ratings yet
- Limping 12.10.2018Document32 pagesLimping 12.10.2018Emily Eresuma100% (1)
- Complication of FractureDocument38 pagesComplication of FractureAshok BalwadaNo ratings yet
- Vascular Overview May 2009Document60 pagesVascular Overview May 2009BryndenNo ratings yet
- Oite 2006Document823 pagesOite 2006dastroh100% (1)
- Student Fracture OrthoDocument27 pagesStudent Fracture OrthoChristian Roy GanancialNo ratings yet
- Fracture PresentationDocument53 pagesFracture Presentationrahul yadav100% (7)
- Spinal Cord Injury: Cedric Muceros BSN 3CDocument4 pagesSpinal Cord Injury: Cedric Muceros BSN 3CJanelle Cabida SupnadNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury: Cedric Muceros BSN 3CDocument4 pagesSpinal Cord Injury: Cedric Muceros BSN 3CJanelle Cabida SupnadNo ratings yet
- Case Report (Ola)Document44 pagesCase Report (Ola)amel015No ratings yet
- Orthopedics Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandOrthopedics Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- UW Path NoteDocument218 pagesUW Path NoteSophia Yin100% (4)
- Comparison CarsDocument5 pagesComparison Carssharu4291No ratings yet
- Renal Urology HistoryDocument131 pagesRenal Urology Historysharu4291No ratings yet
- Molecules 18 08976Document18 pagesMolecules 18 08976sharu4291No ratings yet
- ChoiDocument19 pagesChoiLuciana RafaelNo ratings yet
- Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome: R. Venkatraman and Sunit C. SinghiDocument6 pagesHyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome: R. Venkatraman and Sunit C. Singhisharu4291No ratings yet
- Approach To A Case of Hyperuricemia: Singh V, Gomez VV, Swamy SGDocument7 pagesApproach To A Case of Hyperuricemia: Singh V, Gomez VV, Swamy SGsharu4291No ratings yet
- ABC Emergency Differential DiagnosisffDocument3 pagesABC Emergency Differential Diagnosisffsharu4291No ratings yet
- Chapter 23: Hyperuricemia and Gout: BackgroundDocument2 pagesChapter 23: Hyperuricemia and Gout: Backgroundsharu4291No ratings yet
- ABC Emergency Differential DiagnosisdrererDocument3 pagesABC Emergency Differential Diagnosisdrerersharu4291No ratings yet
- ABC Emergency Differential DiagnDocument3 pagesABC Emergency Differential Diagnsharu4291No ratings yet
- Prospectus MDMSJULY2015Document39 pagesProspectus MDMSJULY2015sharu4291No ratings yet
- ABC Emergency Differential DiagnosisewwwwweDocument3 pagesABC Emergency Differential Diagnosisewwwwwesharu4291No ratings yet
- ABC Emergency Differential Diagnosis1Document4 pagesABC Emergency Differential Diagnosis1sharu4291No ratings yet
- Intern ACOG Bulletin Episiotomy and Repair3Document3 pagesIntern ACOG Bulletin Episiotomy and Repair3sharu4291No ratings yet
- CNS Case Sheet FinalDocument12 pagesCNS Case Sheet FinalKamal SnkNo ratings yet
- PiOS Sample (CH 2)Document39 pagesPiOS Sample (CH 2)Ramyasree BadeNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing ExamsDocument37 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing ExamsJheanAlphonsineT.Means100% (9)
- Project Proposal For Improving The Health and Socializing Conditions of Senior Citizens in Sto 1Document8 pagesProject Proposal For Improving The Health and Socializing Conditions of Senior Citizens in Sto 1Yrrem Ubagan100% (3)
- All The Truth About EPSDocument3 pagesAll The Truth About EPSCarlo PizarroNo ratings yet
- Animals: Clinical Practice Guidelines: An Opinion of The Legal Implication To Veterinary MedicineDocument13 pagesAnimals: Clinical Practice Guidelines: An Opinion of The Legal Implication To Veterinary MedicinesamiNo ratings yet
- Detoxify For Healthy LivingDocument15 pagesDetoxify For Healthy LivingUmesh SisodiaNo ratings yet
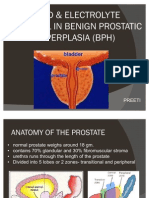
- Electrolytes in BPHDocument74 pagesElectrolytes in BPHPreeti Gehlaut NaraNo ratings yet
- GOOVCATX ProtocolDocument7 pagesGOOVCATX Protocolthanh ngôNo ratings yet
- 06 Collection and Handling of Biopsy SpecimensDocument7 pages06 Collection and Handling of Biopsy SpecimensAudrey CobankiatNo ratings yet
- Liquid BiopsyDocument217 pagesLiquid BiopsymanasagcNo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument3 pagesPrednisoneapi-3797941100% (1)
- Portal Hypertension: IntroductionDocument13 pagesPortal Hypertension: IntroductionGaoudam NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - 1ST Monthly TestDocument2 pagesScience 9 - 1ST Monthly TestMaria JocosaNo ratings yet
- Cis Self-Study Lesson Plan: Otolaryngological InstrumentationDocument4 pagesCis Self-Study Lesson Plan: Otolaryngological Instrumentationjerimiah_manzonNo ratings yet
- Protein TherapeuticsDocument14 pagesProtein TherapeuticsSumanth Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Pancreatitis, Acute: Clinical PresentationDocument26 pagesPancreatitis, Acute: Clinical Presentationapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Diseases of Salivary Glands: Prepared By: Dr. Ahlam A. AlesayiDocument96 pagesDiseases of Salivary Glands: Prepared By: Dr. Ahlam A. AlesayiWaqas Iqbal100% (1)
- Blood Coagulation Overview and Inherited Hemorrhagic Disorders Questions 2Document25 pagesBlood Coagulation Overview and Inherited Hemorrhagic Disorders Questions 2John M. Hemsworth50% (2)
- 2009 Cone Nonprofit Power Brand 100 - Full ReportDocument35 pages2009 Cone Nonprofit Power Brand 100 - Full ReportZiba CranmerNo ratings yet
- Punjab Cancer StatsDocument4 pagesPunjab Cancer StatsPranjul SainiNo ratings yet
- Public Health Nursing and Community Health NursingDocument9 pagesPublic Health Nursing and Community Health NursingKreme Labb100% (1)
- Tumor Flash Cards - Osteochondroma and Multiple Hereditary ExostosisDocument23 pagesTumor Flash Cards - Osteochondroma and Multiple Hereditary Exostosislaxge54No ratings yet
- Bone Marrow AspirationDocument43 pagesBone Marrow AspirationDr. Pawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Biology MCQs SSBCrack PDFDocument39 pagesBiology MCQs SSBCrack PDFPRASHANT MARKANNo ratings yet
- Quetions Step 1Document948 pagesQuetions Step 1Noel David100% (2)
- BibliographyDocument21 pagesBibliographyapi-204960846No ratings yet
- Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Chirosis HepatisDocument48 pagesAsuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Chirosis HepatisRheni WidyaNo ratings yet