Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unreal Tenses and Subjunctives
Uploaded by
BMWuBCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unreal Tenses and Subjunctives
Uploaded by
BMWuBCopyright:
Available Formats
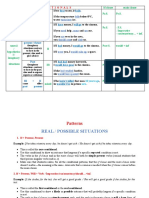
UNREAL TENSES AND SUBJUNCTIVES
WISHES wish + past simple/ past continuous This structure is used when we want to say that we would like something to be different in the present. e.g. I wish I had a car. (I dont have one now.) I wish you werent leaving. (You are leaving.) I wish I was going on holiday with you. (I am not going.) wish + past perfect This structure is used to express regret that something happened or did not happen in the past. e.g. I wish I hadnt eaten so much last night.(I ate too much.) wish + would/ could This structure is used: o for a polite imperative; o to express our desire for change in a situation or someones behavior. e.g. I wish you would leave. (would here means I decided to) I wish I could come on holiday with you next year. (I cant come.) I wish we could have been together. (We werent together.) I wish you wouldnt make such a mess. (would is often used to describe an annoying habit)
IF ONLY If only is used to add emphasis on hypothetical situations or to add the sense of regret (in past events). e.g. If only I had enough time! (I dont have enough time) If only I hadnt drunk too much! (I drank too much) HOPE hope + present or future tense This structure is used to expresses simple future events. e.g. I hope it doesnt rain tomorrow. I hope he will stop talking soon!
ITS TIME/ ITS HIGH TIME/ ITS ABOUT TIME Its time + past simple/ past continuous e.g. Its time we left. Its high time I was/were going. Its time + infinitive e.g. Its time to start work. (As a simple statement of fact.) Its time you started work! (You are being lazy and not working.)
HAD BETTER had better + bare infinitive This structure is used to: o give advice or to say what the best thing to do in a particular situation is. e.g. You had better book tour flight early. I had better not take out a loan; I wont be able to pay it back. Had better is more emphatic than should/ ought to, but it is not as emphatic as must. e.g. You must see a lawyer. (strong advice) You had better see a lawyer. (less emphatic than must) You should/ ought to see a lawyer. (less emphatic than had better)
WOULD RATHER/ WOULD SOONER When the subject of would rather/ sooner is also the subject of the following verb, we use the following construction: would rather + present bare infinitive (for future) e.g. Id rather do my shopping tomorrow. would rather + perfect bare infinitive (for past) e.g. Id rather not have gone to the dinner party last night. would rather + bare infinitive + than (+ bare infinitive) e.g. Id rather watch a comedy than (watch) a thriller. When the subject of would rather is different from the subject of the following verb, we use the following constructions: would rather + past tense (for present or future) e.g. Id rather Kate stayed with us tonight. would rather + past perfect (for past) e.g. Id rather Sam hadnt taken his fathers car yesterday. (WOULD) PREFER prefer + ing form + to + ing form (for general preference) e.g. I prefer playing tennis to playing squash. prefer + full infinitive + rather than + bare infinitive (for general preference) e.g. I prefer to eat fish rather than (eat)meat. prefer + noun + to + noun (for general preference) e.g. I prefer basketball to football. would prefer + full infinitive + rather than + bare infinitive (for specific preference) e.g. Id prefer to walk home rather than take bus. Id prefer to have juice rather than (have) Coke.
AS IF/ AS THOUGH When the situation is true we use the following construction: present tense + as if + present tense (future likely situation) e.g. It looks as if it is going to rain. It looks as if it is raining. present tense + as if + present perfect (present likely situation) e.g. He looks as if he hasnt slept enough. past tense + as if + past perfect (past likely situation) e.g. He looked as if he hadnt slept enough. When the situation is unreal we use the following construction: present tense + as if + past simple (present unlikely situation) e.g. He acts as if he was/ were a boss. (but he isnt) present tense + as if + past perfect (past unlikely situation) e.g. You look as if you had seen a ghost. (but he/ she didnt) SUPPOSE/ IMAGINE likely situation e.g. Imagine it rains lather, what will you do? unlikely situation e.g. Imagine we won a lot of money, what would we do? Supposing we had never met. Suppose someone told you I was a spy!
IF/ WHETHER/ WHATEVER e.g. If/ Whether he (should) agree/agrees or not, we are going to have to go ahead. Whatever his reasons be/are, they are insufficient to excuse him.
FORMAL SUBJUNCTIVES After verbs such as demand, insist, suggest, require, request, order recommend, propose, think which involve an implied obligation, the subjunctive can be used in formal style. This has only the infinitive form. e.g. I suggest that you should study harder. (informal) I suggest you study harder. (formal) The police insisted that the car should be removed.(informal) The police insisted the car be removed. (formal) They demand that he should study harder. (informal) They demand he study/ studies hard. (formal) After expressions such as it is advisable/necessary/essential/important/desirable/preferable/ urgent that e.g. It is urgent that he should do it immediately. (informal) It is urgent he do it immediately. (formal) FORMALIC SUBJUNCTIVES God save the Queen! Heaven help us! Heaven forbid! Curse this fog! So be it. Be that as it may Suffice it to say Far it be from me Come what may
You might also like
- Conditionals, Variations & SubjunctiveDocument6 pagesConditionals, Variations & SubjunctiveLuz RicoNo ratings yet
- The SubjunctiveDocument2 pagesThe SubjunctiveMaritzaNo ratings yet
- Gerund or Infinitive INGDocument5 pagesGerund or Infinitive INGAndrezecoNo ratings yet
- Vocabulario EoiDocument13 pagesVocabulario EoiVirginia Madrid ParaísoNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument13 pagesConditionalsapi-276622834No ratings yet
- Repaso Gramática Inglés.Document19 pagesRepaso Gramática Inglés.MARIANo ratings yet
- Grammar-Use of English - Theory Test 2Document16 pagesGrammar-Use of English - Theory Test 2cosme.fulanitaNo ratings yet
- Tense Active Voice Passive VoiceDocument7 pagesTense Active Voice Passive Voicestaff roomNo ratings yet
- Wishes and Regrets ExercisesDocument2 pagesWishes and Regrets ExercisesMaría PereiraNo ratings yet
- Past Simple or Past PerfectDocument4 pagesPast Simple or Past PerfectAna KosNo ratings yet
- Conjugaciones de Tiempos en InglesDocument10 pagesConjugaciones de Tiempos en InglesLina Johana Mejía Castillo100% (1)
- Cae Reading Part 3Document9 pagesCae Reading Part 3Mila GracaninNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument28 pagesEnglish Tensesapi-3756381No ratings yet
- Future Tenses ChartDocument2 pagesFuture Tenses ChartSonia GabaldonNo ratings yet
- Participle Clauses: 1. Present Participle: Gerund (-Ing)Document2 pagesParticiple Clauses: 1. Present Participle: Gerund (-Ing)ADRIAN MARTINEZ SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- c1 - Grammar LessonsDocument78 pagesc1 - Grammar Lessonskcsaba27No ratings yet
- Writing - Grammar - CaeDocument12 pagesWriting - Grammar - Caehi5deborav vlNo ratings yet
- Business English Negotiating Phrases Error Correction Pairwork PDFDocument6 pagesBusiness English Negotiating Phrases Error Correction Pairwork PDFEleniDesliNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument7 pagesModal VerbsbelbachirNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense - EnglishClubDocument3 pagesPast Perfect Continuous Tense - EnglishClubidahashimNo ratings yet
- I2ci Grammar 8 Verbs Ing or InfinitiveDocument15 pagesI2ci Grammar 8 Verbs Ing or InfinitiveDanielSánchezMartínezNo ratings yet
- The Passive 2012Document90 pagesThe Passive 2012jljloneNo ratings yet
- Conditionals PatternsDocument6 pagesConditionals PatternsOleseaNo ratings yet
- Proficiency - InversionDocument36 pagesProficiency - InversionLindsey CottleNo ratings yet
- I Wish If Only British StudentDocument4 pagesI Wish If Only British StudentFayçal SerhaniNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and Infinitives: - GerundDocument20 pagesGerunds and Infinitives: - GerundpenggemarsherinaNo ratings yet
- C1 Advanced Writing Cheat SheetDocument1 pageC1 Advanced Writing Cheat SheetalNo ratings yet
- CAE Reading and Use of English Parts 1 - 2 - 3 - TEST - 2 - ANSWERSDocument2 pagesCAE Reading and Use of English Parts 1 - 2 - 3 - TEST - 2 - ANSWERSNevena Halevacheva0% (1)
- Reported Speech Grammar Guide PDFDocument2 pagesReported Speech Grammar Guide PDFRobertMaldiniNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple: A Link To The PresentDocument18 pagesPresent Perfect Simple: A Link To The PresentOlga Vainali100% (1)
- Dependent PrepositionsDocument2 pagesDependent PrepositionsToritusdutNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument7 pagesModal VerbsElena MartínNo ratings yet
- Tenses ReviewDocument2 pagesTenses ReviewClaudia SilvaNo ratings yet
- Absolute Constructions & Loose Participles (2022)Document2 pagesAbsolute Constructions & Loose Participles (2022)Camila CarelliNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument3 pagesGerunds and Infinitivesdjumbirko1No ratings yet
- Countries and Nationalities: Learning GoalDocument13 pagesCountries and Nationalities: Learning GoalAna MayoriNo ratings yet
- How To Succeed in Writing ISE IDocument19 pagesHow To Succeed in Writing ISE IDomingo100% (1)
- Past PerfectDocument9 pagesPast PerfectBenedito Rodrigues Bitencort JuniorNo ratings yet
- Beginnings: Informal LetterDocument6 pagesBeginnings: Informal Lettermoni_76No ratings yet
- Grammar Review 4. Past and Present SubjunctiveDocument10 pagesGrammar Review 4. Past and Present SubjunctiveNguyen Quang MinhNo ratings yet
- FCE Modal VerbsDocument3 pagesFCE Modal VerbsMRG 1DNo ratings yet
- FCE Grammar TestsDocument14 pagesFCE Grammar TestsAnonymous Ef74S6d9No ratings yet
- Say Tell Speak TalkDocument8 pagesSay Tell Speak TalkgalwaympNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect TenseDocument6 pagesPast Perfect TenseRosaLovaNo ratings yet
- Comparative and Superlative AdjectivesDocument5 pagesComparative and Superlative AdjectivesalopemouNo ratings yet
- Used To Vs Be Used ToDocument4 pagesUsed To Vs Be Used ToAnna VonblonNo ratings yet
- 5 - FCE Preposition With AdjectiveDocument3 pages5 - FCE Preposition With AdjectiveAlba Fortuny HueteNo ratings yet
- Participle ClausesDocument8 pagesParticiple ClausesMarina GotalskayaNo ratings yet
- Common Regular Verbs in EnglishDocument1 pageCommon Regular Verbs in EnglishCarlos TorresNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo Use of EnglishDocument75 pagesCuadernillo Use of EnglishLuis Miguel Mejias RamosNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Grammar & VocabularyDocument5 pagesUnit 6 - Grammar & VocabularyHai AnhNo ratings yet
- Adjectives Ending in Ed and IngDocument2 pagesAdjectives Ending in Ed and IngKat_23No ratings yet
- Compounds PDFDocument1 pageCompounds PDFIrina PelteaNo ratings yet
- The ApostropheDocument4 pagesThe ApostropheSHarliza RamliNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs: English Level 2Document16 pagesModal Verbs: English Level 2jorge913No ratings yet
- Unreal Tenses and SubjunctivesDocument3 pagesUnreal Tenses and SubjunctivesBình LươngNo ratings yet
- Unreal Past 1Document4 pagesUnreal Past 1gdydj2wrjtNo ratings yet
- Unreal Past FileDocument2 pagesUnreal Past FileDora ChandraNo ratings yet
- Have GotDocument12 pagesHave GotAlejandraNo ratings yet
- Unreal Time and SubjunctivesDocument17 pagesUnreal Time and SubjunctivesMilica StojkovićNo ratings yet
- PrepositionsDocument4 pagesPrepositionsBMWuBNo ratings yet
- The Man Who Made FemenDocument2 pagesThe Man Who Made FemenBMWuBNo ratings yet
- Indefinite or Definite ArticleDocument4 pagesIndefinite or Definite ArticleBMWuBNo ratings yet
- Oxford UniversityDocument1 pageOxford UniversityBMWuBNo ratings yet
- The Passive Voice: To Be + Verb IIIDocument4 pagesThe Passive Voice: To Be + Verb IIIadriandobre2014No ratings yet
- Karim - Teacher BAC Cours ExDocument17 pagesKarim - Teacher BAC Cours ExTaoufik RadiNo ratings yet
- The Simple Present Tense and Frequency AdverbsDocument5 pagesThe Simple Present Tense and Frequency AdverbsBrayan Ramirez0% (1)
- Focus-BrE4 StudentsBook Unit1GrammarFocusDocument2 pagesFocus-BrE4 StudentsBook Unit1GrammarFocusValentina NelkovskaNo ratings yet
- Mixed Exercises7 PDFDocument9 pagesMixed Exercises7 PDFYanii CoronelNo ratings yet
- English 4 VCDocument32 pagesEnglish 4 VCJavier CastelblancoNo ratings yet
- Grammar 2 Syllabus Ngay 23 Thang 5 Word 97 Dang SuaDocument78 pagesGrammar 2 Syllabus Ngay 23 Thang 5 Word 97 Dang SuaThanh BlueNo ratings yet
- I 11 2prim E Term2Document71 pagesI 11 2prim E Term2JFJannahNo ratings yet
- Infinitive PDFDocument53 pagesInfinitive PDFАлина Марченко-ТихоноваNo ratings yet
- 1.1 VERB Patterns: 9 Quarter Group 1 Aeronautics Advanced PlusDocument8 pages1.1 VERB Patterns: 9 Quarter Group 1 Aeronautics Advanced PlusCesar AguirreNo ratings yet
- Verb PatternsDocument14 pagesVerb Patternssayenshan0205No ratings yet
- GERUNDSDocument13 pagesGERUNDSCarlos MelendezNo ratings yet
- Peringkasan Noun ClauseDocument4 pagesPeringkasan Noun Clauseria.janitaNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice and Other Grammar Topics 4Document158 pagesPassive Voice and Other Grammar Topics 4rocio silfaNo ratings yet
- Indirect Questions at Work + QuizDocument5 pagesIndirect Questions at Work + QuizManuel PargaNo ratings yet
- Gerund and InfinitiveDocument3 pagesGerund and InfinitiveCarmen María MolinaNo ratings yet
- Mubarak Abdessalami: Put The Verb Betwe en Brackets in The Correct FormDocument7 pagesMubarak Abdessalami: Put The Verb Betwe en Brackets in The Correct FormMubarak Abdessalami100% (9)
- Would Like, Would Prefer, Would RatherDocument18 pagesWould Like, Would Prefer, Would RatheringridblancoNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Vs Past Perfect SimpleDocument3 pagesSimple Past Vs Past Perfect SimpleFredy Jesus Choque HinojoNo ratings yet
- Ephesians-Exegetical Commentary-KregelDocument50 pagesEphesians-Exegetical Commentary-KregelNate Perkins100% (2)
- Chapter Four: Stative VerbsDocument8 pagesChapter Four: Stative Verbssteffen han100% (2)
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument9 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesNithyanandan MavilapatharaNo ratings yet
- Appendix:English Catenative Verbs: Playing Tennis More OftenDocument10 pagesAppendix:English Catenative Verbs: Playing Tennis More OftenHabib ZaherNo ratings yet
- Reflection EssayDocument23 pagesReflection EssayPheakdeyNo ratings yet
- Appendix 10 Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument10 pagesAppendix 10 Gerunds and Infinitivesteacher sabirNo ratings yet
- High Five! 5 High Five! 5: Wh-Questions and Relative PronounsDocument18 pagesHigh Five! 5 High Five! 5: Wh-Questions and Relative PronounsEsterNo ratings yet
- αἰσθάνομαι verb conjugationDocument5 pagesαἰσθάνομαι verb conjugationthersitesslaughter-1No ratings yet
- Copy of CSAT - Compendium General English PDFDocument393 pagesCopy of CSAT - Compendium General English PDFSatyajeet RoutNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice With Reporting VerbsDocument4 pagesPassive Voice With Reporting VerbsTijana CurcicNo ratings yet
- Verbal PhrasesDocument3 pagesVerbal PhrasesKianna Shane HirabanNo ratings yet
- Summary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: How to Know a Person: The Art of Seeing Others Deeply and Being Deeply Seen By David Brooks: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- How Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideFrom EverandHow Not to Write a Novel: 200 Classic Mistakes and How to Avoid Them—A Misstep-by-Misstep GuideNo ratings yet
- Body Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.From EverandBody Language: Decode Human Behaviour and How to Analyze People with Persuasion Skills, NLP, Active Listening, Manipulation, and Mind Control Techniques to Read People Like a Book.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- Stonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonFrom EverandStonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Wordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageFrom EverandWordslut: A Feminist Guide to Taking Back the English LanguageRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (429)
- Writing to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllFrom EverandWriting to Learn: How to Write - and Think - Clearly About Any Subject at AllRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (83)
- Win Every Argument: The Art of Debating, Persuading, and Public SpeakingFrom EverandWin Every Argument: The Art of Debating, Persuading, and Public SpeakingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (78)
- Surrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSurrounded by Idiots: The Four Types of Human Behavior and How to Effectively Communicate with Each in Business (and in Life) (The Surrounded by Idiots Series) by Thomas Erikson: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageFrom EverandThe Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates LanguageRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (916)
- Everything You'll Ever Need: You Can Find Within YourselfFrom EverandEverything You'll Ever Need: You Can Find Within YourselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (41)
- Idioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsFrom EverandIdioms in the Bible Explained and a Key to the Original GospelsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- Learn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn Spanish with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Spanish Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (136)
- The Art of Writing: Four Principles for Great Writing that Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandThe Art of Writing: Four Principles for Great Writing that Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- 1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundFrom Everand1000 Words: A Guide to Staying Creative, Focused, and Productive All-Year RoundRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- Learn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn French with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: French Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- Abominations: Selected Essays from a Career of Courting Self-DestructionFrom EverandAbominations: Selected Essays from a Career of Courting Self-DestructionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Writing Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsFrom EverandWriting Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsNo ratings yet
- Messages: The Communication Skills BookFrom EverandMessages: The Communication Skills BookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- The Emotional Craft of Fiction: How to Write the Story Beneath the SurfaceFrom EverandThe Emotional Craft of Fiction: How to Write the Story Beneath the SurfaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (35)
- Learn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachFrom EverandLearn Mandarin Chinese with Paul Noble for Beginners – Complete Course: Mandarin Chinese Made Easy with Your 1 million-best-selling Personal Language CoachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (15)
- Spanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesFrom EverandSpanish Short Stories: Immerse Yourself in Language and Culture through Short and Easy-to-Understand TalesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)