100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views2 pagesGear Pump
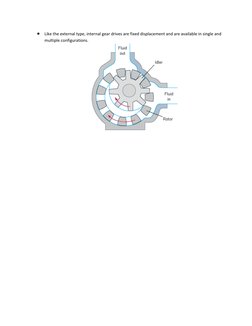
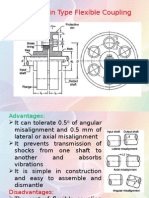
Gear pumps use two meshed gears to develop fluid flow. The drive gear is powered by a drive shaft and turns the idler gear, forming pumping chambers between the gear teeth that are enclosed by the pump housing. External gear pumps place the gears side by side to draw fluid into the chambers as the gears unmesh and force it out as they mesh again. Internal gear pumps have an external gear that meshes with teeth on the inside of a larger gear, with pumping chambers formed between the teeth and a seal separating the inlet and outlet. Both external and internal gear pumps are fixed displacement designs.
Uploaded by
01parthCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views2 pagesGear Pump
Gear pumps use two meshed gears to develop fluid flow. The drive gear is powered by a drive shaft and turns the idler gear, forming pumping chambers between the gear teeth that are enclosed by the pump housing. External gear pumps place the gears side by side to draw fluid into the chambers as the gears unmesh and force it out as they mesh again. Internal gear pumps have an external gear that meshes with teeth on the inside of a larger gear, with pumping chambers formed between the teeth and a seal separating the inlet and outlet. Both external and internal gear pumps are fixed displacement designs.
Uploaded by
01parthCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Gear Pumps: Explains the mechanism of gear pumps, external and internal gear pump types with advantages and diagrammatic representations.