0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views2 pagesECE 3600: 3-Phase Power Basics
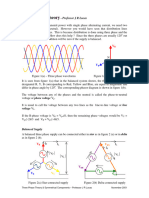
Three phase power uses three lines to transmit power in a balanced way where the ground return current is zero. It provides a constant power output unlike single phase power which pulses at 120 Hz. There are two main connection types for three phase power: wye and delta. In a wye connection, each load is connected between a line and ground while in a delta connection each load is connected between two lines. Proper phase sequencing is also important for three phase power.
Uploaded by
Aitzaz HussainCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views2 pagesECE 3600: 3-Phase Power Basics
Three phase power uses three lines to transmit power in a balanced way where the ground return current is zero. It provides a constant power output unlike single phase power which pulses at 120 Hz. There are two main connection types for three phase power: wye and delta. In a wye connection, each load is connected between a line and ground while in a delta connection each load is connected between two lines. Proper phase sequencing is also important for three phase power.
Uploaded by
Aitzaz HussainCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd