Professional Documents
Culture Documents
08 Deforming Solids 08
Uploaded by
Ashani0001Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
08 Deforming Solids 08
Uploaded by
Ashani0001Copyright:
Available Formats
8 Worksheet (AS)
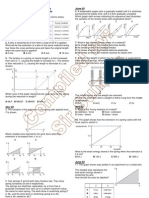
Data needed to answer questions can be found in the Data, formulae and relationships sheet. 1 Two springs X and Y have spring constants k and 2k respectively. Spring X is stretched by a force F and spring Y is stretched by a force 2F. Each spring obeys Hookes law during the extension. The work done in stretching spring X is WX and the work done in stretching spring Y is WY. What is the relationship between WX and WY?
1 WX 2 B WY = WX C WY = 2WX D WY = 4WX
[1]
A WY =
Four wires A, B, C and D have diameters, lengths and are stretched by forces as shown. All the wires are made of the same material. Which wire has the smallest extension? A B C D [1]
2d
2d 2l
F 2F
2F
The force on a sample of a material is slowly increased and then slowly decreased. The forceextension graph is shown in the diagram.
Which area represents the net work done on the sample during the complete process? A P+Q B Q+R C P+QR D P+Q+R
[1]
AS and A Level Physics
Original material Cambridge University Press 2010
8 Worksheet
Which statement is true about rubber, a polymeric material? A A normal rubber band breaks when the strain is greater than 1. B A normal rubber band breaks when the strain is less than 10%. C When a small amount of sulfur is added, to provide cross-links between molecules in rubber, the elastic limit is reduced. D When a small amount of sulfur is added, to provide cross-links between molecules in rubber, the ultimate tensile stress is reduced.
[1]
What is equal to the Young modulus? A B C D The area between a forceextension graph and the extension axis. The area between a stressstrain graph and the stress axis. The gradient of a forceextension graph. The gradient of a stressstrain graph.
[1]
6 7
Springs and wires obey Hookes law. State Hookes law. A spring has a natural length of 2.5 cm. A force of 4.0 N extends the spring to a length of 6.2 cm. a What is the extension of the spring? b Determine the force (spring) constant k for the spring in N m1. c Calculate the extension of the spring when a tensile force of 6.0 N is applied. You may assume that the spring has not exceeded its elastic limit.
[1]
[1] [3] [2]
The diagram shows the stressstrain graphs for two wires A and B made from different materials.
The wires have the same length and cross-sectional area. Explain which of the materials is: a brittle b stiffer c stronger. [1] [1] [1]
AS and A Level Physics
Original material Cambridge University Press 2010
8 Worksheet
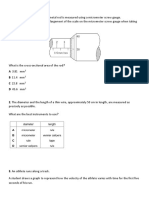
9 A graph of force F against extension x is shown for a spring.
a Use the graph to determine the force (spring) constant k of the spring. b Calculate the energy stored (elastic potential energy) in the spring when its extension is 5.0 cm. 10 A length of cable of diameter 1.2 mm is under a tension of 150 N. Calculate the stress in the cable. 11 A metal wire of diameter 0.68 mm and natural length 1.5 m is fixed firmly to the ceiling at one end. When a 6.8 kg mass is hung from the free end, the wire extends by 2.8 mm. Calculate: a the stress in the wire b the Young modulus of the material of the wire. 12 The diagram shows two springs X and Y connected in series and supporting a weight of 8.0 N. The force constants of the springs are shown on the diagram. a Calculate the extension of each spring. b Determine the force (spring) constant for the combination. c According to a student, the force constant for the springs in series is the sum of the force constants of the individual springs. Is the student correct? [2] [2]
[2] [3] [3]
[3] [4]
[1]
AS and A Level Physics
Original material Cambridge University Press 2010
8 Worksheet
13 A 180 g trolley is placed on a frictionless air track. One end of the trolley is attached to a spring of force constant 50 N m1. The trolley is pushed against a fixed support so that the compression of the spring is 8.0 cm. The trolley is then released. a What is the initial acceleration of the trolley when it is released? b What is the initial energy stored in the spring? c Calculate the final speed of the trolley along the air track. You may assume that there is 100% transfer of energy from the spring to the trolley. 14 The forceextension graph for a length of metal wire is shown below. a The gradient of the graph is equal to the force constant k of the wire. Show that the force constant k is given by: EA k= l where E is the Young modulus of the metal, A is the cross-sectional area of the wire and l is the natural length of the wire. [4] b Explain how the gradient of the forceextension graph would change for a wire of the same material but: i twice the length [1] ii twice the radius. [1] [3] [3] [2]
Total:
49
Score:
AS and A Level Physics
Original material Cambridge University Press 2010
You might also like
- G11 - Assignment As Chapter Wise TestDocument5 pagesG11 - Assignment As Chapter Wise TestccNo ratings yet
- 8 Worksheet (AS) Deformation: 2dd 2d 2lDocument3 pages8 Worksheet (AS) Deformation: 2dd 2d 2lMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 08Document4 pagesWorksheet 08Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Deformation MCQDocument4 pagesDeformation MCQCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- As-1 WS - 7 Matter and Material 2020-2021Document8 pagesAs-1 WS - 7 Matter and Material 2020-2021MFNo ratings yet
- Winter Break Holiday HW - PhysicsDocument3 pagesWinter Break Holiday HW - PhysicsAkshat KumarNo ratings yet
- Deformation of SolidsDocument24 pagesDeformation of SolidsSaeed AkhtarNo ratings yet
- The Matters and Materials ExaminationDocument8 pagesThe Matters and Materials ExaminationHartono Wijaksono SantosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of SolidsDocument49 pagesChapter 9 Mechanical Properties of SolidsNitish MehraNo ratings yet
- Springs Understanding Hooke S Law Calculation SheetDocument4 pagesSprings Understanding Hooke S Law Calculation Sheetmarkmattesz06No ratings yet
- Worksheet 25 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 25 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (2)
- A-Level Exam (2001) Papers and AnswersDocument46 pagesA-Level Exam (2001) Papers and AnswersAston Hamilton100% (3)
- Pastpaper QuestionDocument27 pagesPastpaper Questionmostafa67100% (1)
- Deformation of SolidDocument37 pagesDeformation of SolidEllen Koh100% (1)
- STPM 2014 p1 TrialDocument13 pagesSTPM 2014 p1 Trialshinichi_kesian6117No ratings yet
- T6 Deformation of SolidsDocument4 pagesT6 Deformation of SolidsyanasakaranNo ratings yet
- Spring 2010 Qualifying ExamDocument7 pagesSpring 2010 Qualifying ExamrujintoNo ratings yet
- EEE 43 Problem Set 1Document3 pagesEEE 43 Problem Set 1Ruben_Aldave_4254No ratings yet
- Physics Electric Current and Direct Current Circuit NotesDocument118 pagesPhysics Electric Current and Direct Current Circuit NoteskumuthaNo ratings yet
- Topic C: Energy - Examples SPRING 2014: V V V V e 0.0 e 0.5 e 1.0Document9 pagesTopic C: Energy - Examples SPRING 2014: V V V V e 0.0 e 0.5 e 1.0ettypasewangNo ratings yet
- Phys 1011 Assignment IIDocument3 pagesPhys 1011 Assignment IIDanielNo ratings yet
- Practise Problems Set04Document5 pagesPractise Problems Set04rohit kumarNo ratings yet
- g481 1 3 4 Springs and MaterialsDocument9 pagesg481 1 3 4 Springs and Materialsapi-236179294No ratings yet
- QLM of SOMDocument4 pagesQLM of SOMatulkumargaur26No ratings yet
- MG Section 1 HWDocument8 pagesMG Section 1 HWAnonymous 9OUMMmSBHNo ratings yet
- HOOKES LAW - Docx MCQDocument4 pagesHOOKES LAW - Docx MCQfarogh hamid100% (2)
- Hooke's LawDocument5 pagesHooke's LawDanelle EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Revision Test (Waves, Mechanical Properties of Solid)Document3 pagesRevision Test (Waves, Mechanical Properties of Solid)ShioNo ratings yet
- Physics 10Document17 pagesPhysics 10minyahilsafeneNo ratings yet
- SJPO Special Round 2010 Sample PDFDocument7 pagesSJPO Special Round 2010 Sample PDFziwei_from_chinaNo ratings yet
- VLFXZ 7 C Bs GOCa SL5 V Iw PDocument8 pagesVLFXZ 7 C Bs GOCa SL5 V Iw PTaruna MishraNo ratings yet
- Kings: Engineering MechanicsDocument16 pagesKings: Engineering Mechanicsgovind4ever5No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Magnetic CircuitsDocument10 pagesLecture 3 Magnetic CircuitsJojo KawayNo ratings yet
- G12 Phy Pa2 Q.PDocument8 pagesG12 Phy Pa2 Q.PnjragavendaraNo ratings yet
- AS Trial - 2004 Sep - P1Document14 pagesAS Trial - 2004 Sep - P1Syafiq ShazwanNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam IdeaDocument419 pagesPhysics Exam IdeaAditya50% (2)
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 2.10-2.12 - Teacher'sDocument10 pagesForm 4 Physics Chapter 2.10-2.12 - Teacher'sPavithiran100% (1)
- You May Not Start To Read The Questions Printed On The Subsequent Pages of This Question Paper Until Instructed That You May Do So by The InvigilatorDocument5 pagesYou May Not Start To Read The Questions Printed On The Subsequent Pages of This Question Paper Until Instructed That You May Do So by The InvigilatorSpringOrchidNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 ExercisesDocument6 pagesUnit 7 ExercisesBao Hoang LeNo ratings yet
- As Revision 2016Document3 pagesAs Revision 2016Gayathri GananathapillaiNo ratings yet
- Ebook College Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3Rd Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument39 pagesEbook College Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3Rd Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFStevenMillersqpe100% (11)
- TMP B4 A0Document6 pagesTMP B4 A0FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Simple StrainDocument36 pagesSimple StrainMartina CelsoNo ratings yet
- RMPH 2017 PT3 QuestionDocument2 pagesRMPH 2017 PT3 QuestionUguumur TsagaanbayarNo ratings yet
- BME - MOD I QuestionsDocument4 pagesBME - MOD I QuestionsGaurav ThakareNo ratings yet
- Model Questions For PracticeDocument4 pagesModel Questions For PracticeRohan SahanaNo ratings yet
- 1ELASTICITYDocument6 pages1ELASTICITYtttomtiaNo ratings yet
- Long Answer QuestionsDocument19 pagesLong Answer QuestionsGorima GoonNo ratings yet
- BPhO Round 1 2013 PRT 1Document6 pagesBPhO Round 1 2013 PRT 1Karn KumarNo ratings yet
- Assigment 1Document2 pagesAssigment 1Pankhuri Kumari0% (1)
- 2.12 Understanding ElasticityDocument10 pages2.12 Understanding ElasticityBid HassanNo ratings yet
- Program Studi Fisika: A. QuestionsDocument2 pagesProgram Studi Fisika: A. QuestionsCho KocokNo ratings yet
- Ebook College Physics A Strategic Approach 3Rd Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument44 pagesEbook College Physics A Strategic Approach 3Rd Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFkennethalandlj1f100% (13)
- College Physics A Strategic Approach 3rd Edition Knight Test BankDocument23 pagesCollege Physics A Strategic Approach 3rd Edition Knight Test Bankpaullanb7nch100% (32)
- RevisionDocument3 pagesRevisionKaifkhanNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- WBI04 01 MSC 20140306Document23 pagesWBI04 01 MSC 20140306Ashani0001No ratings yet
- T/S I/Microa LN (I) 0 100 4.60517 10 68 4.219508 20 47 3.850148 30 32 3.465736 40 22 3.091042 50 15 2.70805 60 10 2.302585Document2 pagesT/S I/Microa LN (I) 0 100 4.60517 10 68 4.219508 20 47 3.850148 30 32 3.465736 40 22 3.091042 50 15 2.70805 60 10 2.302585Ashani0001No ratings yet
- PH CalculationsDocument4 pagesPH CalculationsVanandiNo ratings yet
- Eng Science Vol1Document219 pagesEng Science Vol1hackermikeNo ratings yet
- 2002 JUNE Unit 2Document12 pages2002 JUNE Unit 2Ashani0001No ratings yet
- HairDocument3 pagesHairAshani0001No ratings yet
- Brain Treatments AyurvedicDocument5 pagesBrain Treatments AyurvedicAshani0001No ratings yet
- 04 Forces Vectors and Moments 04..Document3 pages04 Forces Vectors and Moments 04..Ashani0001100% (1)
- 28lattiDocument4 pages28lattifaizana_8No ratings yet
- Matter and Antimatter PosterDocument1 pageMatter and Antimatter PosterAshani0001No ratings yet
- Biopraguen 12Document54 pagesBiopraguen 12Ashani0001No ratings yet
- Corrected Projectile Motion PDFDocument13 pagesCorrected Projectile Motion PDFRitwik KumarNo ratings yet
- 15 Superposition of Waves 15Document5 pages15 Superposition of Waves 15Ashani0001100% (1)
- As Equations and DefinitionsDocument23 pagesAs Equations and DefinitionsAshani0001No ratings yet
- A1 Bonding WS5Document13 pagesA1 Bonding WS5Ashani0001No ratings yet
- Practicals Recap Type IIDocument2 pagesPracticals Recap Type IIAshani0001No ratings yet
- Physics Revision Notes - Electricity: Acetate Rod With A Cloth, It Becomes Positively ChargedDocument1 pagePhysics Revision Notes - Electricity: Acetate Rod With A Cloth, It Becomes Positively ChargedAshani0001No ratings yet
- 9701 Chemistry Applications BookletDocument161 pages9701 Chemistry Applications BookletZain RehanNo ratings yet
- Predator PreyDocument14 pagesPredator PreyAshani0001No ratings yet
- Thin Layer ChromatographyDocument22 pagesThin Layer ChromatographyAshani0001No ratings yet
- M Schemes 04Document3 pagesM Schemes 04Pathmanathan Nadeson0% (2)
- A1 Equilibria WS5Document6 pagesA1 Equilibria WS5Ashani0001No ratings yet
- A1 Bonding WS5Document13 pagesA1 Bonding WS5Ashani0001No ratings yet
- Capacitors in DDocument2 pagesCapacitors in DAshani0001No ratings yet
- 022 - Protein Synthesis I - Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pages022 - Protein Synthesis I - Nucleic Acidslastjoe71100% (1)
- Stationary WavesDocument10 pagesStationary WavesAshani0001No ratings yet
- 6CH02 MS 2011Document20 pages6CH02 MS 2011areyouthere92No ratings yet
- Unit 4 CoreDocument31 pagesUnit 4 CoreAhmed SolimanNo ratings yet
- Refraction Diagrams: Select The Correct Ray in Each of The Diagrams Below. A 1Document1 pageRefraction Diagrams: Select The Correct Ray in Each of The Diagrams Below. A 1Ashani0001No ratings yet
- EE40 Basic Electrical Engineering (DC Series-Parralel Circuit)Document45 pagesEE40 Basic Electrical Engineering (DC Series-Parralel Circuit)jason sutanaNo ratings yet
- Soft Starter Working Principle - Electrical Solution & TechnologyDocument8 pagesSoft Starter Working Principle - Electrical Solution & TechnologyanuragpugaliaNo ratings yet
- GOVERNMENT POLYTECHNIC BHUJ FinalDocument15 pagesGOVERNMENT POLYTECHNIC BHUJ FinalManan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ramaite Mbuso Fikile 2013Document87 pagesRamaite Mbuso Fikile 2013Saby Lisbeth Eugenio PonceNo ratings yet
- Wmo - 266 v1 enDocument198 pagesWmo - 266 v1 enAcademia GustavoNo ratings yet
- Lumped Load Editor - Short-Circuit PDFDocument3 pagesLumped Load Editor - Short-Circuit PDFNMulyonoNo ratings yet
- AsdddDocument54 pagesAsdddSyazwan HafidziNo ratings yet
- Answerkey FullTest2 SankalpEducationDocument16 pagesAnswerkey FullTest2 SankalpEducationDkNo ratings yet
- Hookes LawDocument23 pagesHookes LawAman Singh100% (1)
- Nss College of Engineering: Bachelor of Technology Electrical and Electronics Engineering University of CalicutDocument33 pagesNss College of Engineering: Bachelor of Technology Electrical and Electronics Engineering University of CalicutNidhiNo ratings yet
- BobiSoft Short Description 2017Document11 pagesBobiSoft Short Description 2017felixNo ratings yet
- ProjectileDocument2 pagesProjectileMmonster GirirajNo ratings yet
- Cabluri Date Tehnice Mecanice PrysmianDocument22 pagesCabluri Date Tehnice Mecanice Prysmianiulian17dNo ratings yet
- Introduction TNB SubstationDocument1 pageIntroduction TNB SubstationShyanyoon TehNo ratings yet
- SP015 Topic2 1819 PDFDocument120 pagesSP015 Topic2 1819 PDFnurul nuhaNo ratings yet
- Grid-Connected Wind Photo Voltaic Cogeneration Using Back To Back Voltage Source ConvertersDocument84 pagesGrid-Connected Wind Photo Voltaic Cogeneration Using Back To Back Voltage Source ConvertersThulasi Prasad0% (1)
- Beata J. Dąbrowska-Wüster Et Al - Multicomponent Gap Solitons in Spinor Bose-Einstein CondensatesDocument11 pagesBeata J. Dąbrowska-Wüster Et Al - Multicomponent Gap Solitons in Spinor Bose-Einstein CondensatesPomac232No ratings yet
- BM - Lec 4 - Conservation of Angular Momentum and Projectile MotionDocument50 pagesBM - Lec 4 - Conservation of Angular Momentum and Projectile MotionBhavya PanchalNo ratings yet
- Emf Seri̇si̇ İngi̇li̇zce El Ki̇tabiDocument11 pagesEmf Seri̇si̇ İngi̇li̇zce El Ki̇tabialperemirNo ratings yet
- Physics Laboratory Apparatuses PDFDocument7 pagesPhysics Laboratory Apparatuses PDFRomeo Nicolas I. NungayNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines & Measurement B.E. 4 SemesterDocument4 pagesElectrical Machines & Measurement B.E. 4 Semestersameerpatel15770No ratings yet
- Linear Momentum: Question Paper 3Document14 pagesLinear Momentum: Question Paper 3Mulei KithyaNo ratings yet
- CE 320 - Fluid Mechanics - Module 1 Lesson 1 PDFDocument14 pagesCE 320 - Fluid Mechanics - Module 1 Lesson 1 PDFMichael Christ IcagoyNo ratings yet
- (L6) - (JLD 3.0) - NLM - 22nd June.Document63 pages(L6) - (JLD 3.0) - NLM - 22nd June.Aditya BiswasNo ratings yet
- Important TermsDocument45 pagesImportant TermsrameshsmeNo ratings yet
- Buoyancy, Flotation and StabilityDocument13 pagesBuoyancy, Flotation and StabilityDenzel Edward CariagaNo ratings yet
- Vibration MonitoringDocument6 pagesVibration MonitoringankitsarvaiyaNo ratings yet
- Telangana Junior Inter Physics Text BookDocument120 pagesTelangana Junior Inter Physics Text BookASNMURTYNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Notes (Jan-2022)Document10 pagesOptical Fiber Notes (Jan-2022)mandar desurkarNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Review Grade 7 3rd QuarterDocument4 pagesCurriculum Review Grade 7 3rd QuarterJohn EviotaNo ratings yet