Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lifting Lug Calc - Vertical
Uploaded by
jahiranazriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lifting Lug Calc - Vertical
Uploaded by
jahiranazriCopyright:
Available Formats
MSET ENGINEERING CORPORATION SDN BHD
DOCUMENT TITLE: DESIGN CALCULATION DOC. REF. NO.: MSETe/M2-228/L4-104C SUBJECT: LIFTING LUG CALC DATE : 10/04/2013 REVISION: C JOB NO: M2-228
LIFTING LUG CALC(VERTICAL VESSEL) ( Ref: Compress & Pressure Vessel Handbook by Dennis Moss).
1.0 LIFTING LUG CALCULATION
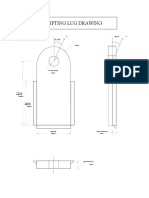
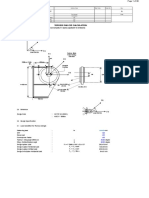
Figure 1: Lifting Lug Detail 1.1 Geometry Inputs Lifting Lug Material Length of Lifting Lug, L Width of Lifting Lug, B Thickness of Lifting Lug, t Pin Hole Diameter, d Lug Diameter at Pin, D Weld Size, tw Weld Length, b1 Weld Length, d2 Collar Thickness, tc Collar Diameter, Dc Width of Pad, Bp Length of Pad, Lp Pad Thickness, tp Pad Weld Size, twp Weld Length, L3 Length to Brace Plate, L1
: = = = = = = = = = = = = = = = =
SA 36 642 300 30 55 300 12 125 50 16 150 400 200 15.88 12 150 325
mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm
= =
5.50 cm 30.00 cm
32.50 cm
Page 2
Vessel Empty Weight Load Factor Design Lift Weight, W Dist. from C.O.G to Lifting Lug,l1 Dist. from C.O.G to Tailing Lug,l2 Dist. from Vessel C.L to Tailing Lug,l3 Yield Stress at amb Temp.,Sy Allow.Tensile Stress, t =0.6Sy Allow. Shear Stress, s = 0.4Sy Allow. Bearing Stress, p =0.9Sy Allow. Bending Stress, b =0.66Sy Allow. Weld Shear Stress,allow.
= = = = = = = = = = = =
22946 1.5 34419 3343 4166 940 2528.82 1517.292 1011.528 2275.938 1669.0212 1476.400
kg kg mm mm mm kg/cm2 kg/cm2 kg/cm2 kg/cm2 kg/cm2 kg/cm2
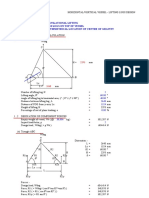
1.2 Lift Forces Lift force on lifting & tailing lug during rotational lift (0o 90o) 2*Ftop Ftail = = [W* ((l2*cos) +(l3*sin))] / [((l1*cos) + (l2*cos) + (l3*sin))] W - (2*Ftop) FT FL = = Ftop cos Ftop sin
o 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90
Figure 2: Lifting & Tailing Force-Loading Diagram (rad) Ftop (kgf) FT(top) (kgf) FL(top) (kgf) 0 9548 9548 0 0.0873 9631 9594 839 0.1745 9566 1687 9713 0.2618 9463 2536 9796 0.3491 9882 9286 3380 0.4363 9970 9036 4214 0.5236 10064 8716 5032 0.6109 10165 8327 5831 0.6981 10276 7872 6605 10400 7354 7354 0.7854 8076 0.8727 10542 6777 0.9599 10710 6143 8773 9451 1.0472 10913 5457 10123 1.1345 11169 4720 1.2217 11509 3936 10815 1.3090 3103 11579 11988 1.3963 2210 12535 12729 1225 14004 1.4835 14058 17210 1.5708 17210 0 17210 9594 17210
Max Force (kgf)
Table 1: Lifting Load at Various Lift Angle,
Page 3
Max. Lifting Load, Fv
17210 kgf
1.3 Lifting Lug Stress Calculation 1.3.1 Lug Pin Diameter based on Shear Stress. Pin Hole Required Diameter, dreqd : =
Pin Hole Required Dia. less than
(2*Fv /(*s))0.5
2.687 cm
26.87 mm
Sufficient
Geometry Input, So Pin Hole Dia. is
Pin Hole Area (on 2 Lifting Lug), A
: = : =
2*((/4)*d2)
4751.659 mm
2
2 47.52 cm
Shear Stress Required, reqd
Fv /A
362.179 kg/cm
2
Shear Stress Required
less than
Allowable Shear Stress, Stress on Hole is
Sufficient
1.3.2 Lug Thickness based on Tensile Stress. Lifting Lug Thickness Required, treqd : =
Thickness Required are less than
Fv /(D*t) 0.227 cm
2.27 mm
Sufficient
Geometry Input, Thickness used is
Lifting Lug Area, A
: = : =
D*t 9000 mm Fv /A 191.217 kg/cm
2 2
2 90.00 cm
Tensile Stress Required, reqd
Tensile Stress Required
less than
Allowable Tensile Stress, Stress on Lug is
Sufficient
1.3.3 Lug Thickness based on Bearing Stress. Lifting Lug Thickness (Including Collar Plate) T : = Lifting Lug Thickness Required, Treqd : =
t + (2*tc) 62.0 mm Fv /(d*p) 3.093 cm
30.93 mm
Sufficient
Thickness Required are
less than
Geometry Input, Thickness used is
Collar Required Thickness, tc reqd
: =
max(0, 0.5*(Treqd -t)) 0.47 mm
Sufficient
Collar Thick. Required
less than
Geometry Input, Thickness used is
Bearing Area, Abearing
: = : =
(d*(t+2tc))
3410.00 mm
2
2 34.10 cm
Bearing Stress Required, reqd
Fv /Abearing
504.677 kg/cm
2
Bearing Stress Required
less than
Allowable Bearing Stress, Stress on Lug is
Sufficient
Page 4
1.3.4 Lug Thickness based on Shear Stress.
( Ref: Pressure Vessel Design Manual Handbook by Dennis Moss pg 417).
Net Section at top of Lug(2 lugs), An
: = : =
2[t(D-d/2)] + [2tc (Dc-d/2)] 2 10390.00 mm FT(top)/An
92.341 kg/cm
2
2 103.90 cm
Shear Stress at top of lug, s
Shear Stress Required
less than
Allowable Shear Stress, Stress on Lug is
Sufficient
1.3.5 Weak Axis Bending Stress Section Modulus of Lug, Z : = : = = = = = B*t2 /6
45000.00 mm
3
3 45.00 cm
Bending Stress, b b Max. lift cable angle from Vertical,
M/Z , Where F = 0.5W/cos Fsin *L1 /Z ,Where sin/cos = tan 0.5W(sin/cos)*L1/Z arctan((b*Z)/(0.5WL1))
0.18 rad 10.38 deg
1.4 Weld Stress Calculation
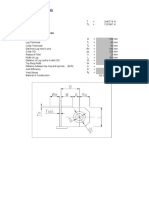
Figure 3: Lifting Lug Weld Area. Maximum weld shear stress occurs at lift angle, = From Table 1, lift force,FL(TOP) = Lifting Lug Weld Area, Aweld : = = : = : =
90.00 deg 17209.50 kgf
1.5708
rad
A1 + A2 + A3 + A4(Brace Plate) 0.707*tw[(d1+b1)+(2d2+b2)+(d3+b3) + L1] 2 8696.10 mm = FL(TOP) cos/ A weld 2 0.00 kgcm FL(TOP)/ A weld
2 197.90 kgcm
2 86.96 cm
Max. weld Shear Stress, t
Max. weld Shear Stress, s
Page 5
1.4.1 Torsional Shear: Weld Centrod: Weld Areas, Ai : 0.707 *tw*Li Location Area(mm2) A1 1272.60 A2 1060.5 A3 424.20 A4 424.20 A5 424.20 A6 1060.50 A7 1272.60 A8 2545.20 (Weld at Brace Plate) Ai (mm2) 8484.00
Table 2: Weld Torsion Area Weld Centroid Location: x1 = 0.00 x2 = 62.50 x3 = 50.00 x4 = 150.00 x5 = 175.00 x6 = 237.50 x7 = 300.00 x8 = 150.00 Xbar : = (Ai*Xi)/Ai 146.25 mm : mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm : mm mm4 mm4 mm4 mm4 mm4 mm4 mm4 : = (Ji + Ai*ri2) 437455918 mm4
4
mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm
y1 y2 y3 y4 y5 y6 y7 y8 Ybar
= = = = = = = = : =
75.00 0.00 25.00 50.00 25.00 0.00 75.00 467.00 (Ai*Yi)/Ai
mm mm mm mm mm mm mm mm
(Location at Brace)
167.60 mm
Radius to Centroid Locations, ri r1 = 173.10 r2 = 187.36 r3 = 172.04 r4 = 117.66 r5 = 145.47 r6 = 190.83 r7 = 179.48 r8 = 299.42 Polar Moment Area, Ji J1 = 2386125.00 J2 = 1380859.38 J3 = 88375.00 J4 = 88375.00 J5 = 88375.00 J6 = 1380859.38 J7 = 2386125.00 J8 = 19089000.00 Parrallel axis theorem, J
sqrt((Xbar -xi)2 +(Ybar-yi)2)
0.707 *tw*(Li3)/12
Page 6
Radial distance from centroid to weld: r : = : = = : = = = : =
sqrt(Xbar2 +((L3+L-L1)- Ybar)2) 333.21 mm arctan(((L3+L-L1)-Ybar)/Xbar) 1.12 rad 63.97 deg M*r/J (Fr*cos*(L+L3-Ybar))*r/J 2 0.00 kg/mm 2 0.00 kg/cm sqrt[(t +2sinr)2 + (s + 2cosr)2] 2 197.90 kg/cm
Sufficient
total
Weld Shear Stress Reqd.
less than
Allow. Weld Shear Stress. So, Stress is
1.4.2 Collar Weld Stress: Collar Weld Area, Aweld : =
2Dc*0.707tw
2 7995.98 mm
2 79.96 cm
Collar Weld Stress, c
: =
Fv/Aweld
2 215.23 kg/cm
Collar Weld Shear Stress Required Sufficient
less than
Allow. Weld Shear Stress. So, Stress is
1.4.3 Pad Weld Stress:
Figure 4: Pad Weld Area. Direct Shear:
Pad Weld Area, Aweld
: = : = : =
0.707twp * (2Lp +Bp)
2 6787.20 mm
2 67.87 cm
Max. weld Shear Stress, t
FT(TOP) cos/ A weld 2 0.00 kgcm FT(TOP) sin/ A weld
2 253.56 kgcm
Max. weld Shear Stress, s
Page 7
1.4.4 Torsional Shear: Weld Centrod: Weld Areas, Ai Location Area(mm2) A1 1696.80 A2 3393.6 A3 1696.80 Ai (mm2) 6787.20 : 0.707 *twp*Li
Table 3: Weld Torsion Area Weld Centroid Location: x1 = 0.00 x2 = 200.00 x3 = 400.00 Xbarp : = (Ai*Xi)/Ai 200.00 mm : mm mm mm : 0.707 *twp*(Li3)/12
mm mm mm
y1 y2 y3 Ybarp
= = = : =
100.00 0.00 100.00 (Ai*Yi)/Ai
mm mm mm
50.00 mm
Radius to Centroid Locations, ri r1 = 206.16 r2 = 50.00 r3 = 206.16
sqrt((Xbar -xi)2 +(Ybar-yi)2)
Polar Moment Area, Ji J1 = 5656000 mm4 J2 = 45248000.00 mm4 J3 = 5656000 mm4 Parrallel axis theorem, J
: =
(Ji + Ai*ri2) 209272000 mm4 sqrt(Xbarp2 +((Lp- Ybarp)2) 250.00 mm arctan(((Lp)-Ybar)/Xbar) 0.64 rad 36.87 deg M*rp/Jp (Fr*cos*(L+Lp-Ybarp))*rp/Jp 2 0.00 kg/mm 2 0.00 kg/cm sqrt[(t +2sinr)2 + (s + 2cosr)2] 2 253.56 kg/cm
Sufficient
Radial distance from centroid to weld: r : = : = = : = = = : =
total
Weld Shear Stress Reqd.
less than
Allow. Weld Shear Stress. So, Stress is
Page 8
You might also like
- Anchor Bolt (CSA) Rev1.1Document10 pagesAnchor Bolt (CSA) Rev1.1coolkaisyNo ratings yet
- Lifting LugDocument8 pagesLifting LugAzwan ShahNo ratings yet
- Clip PlatformDocument24 pagesClip Platformwisnu_bayusaktiNo ratings yet
- Pveng: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDDocument5 pagesPveng: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDBruno TrujilloNo ratings yet
- SKID LIFTING LUG CALCULATIONSDocument5 pagesSKID LIFTING LUG CALCULATIONSinnovativekarthiNo ratings yet
- Lifting Lug Calculation: Equipment: Housing Gas Filter (Simplex)Document1 pageLifting Lug Calculation: Equipment: Housing Gas Filter (Simplex)Tejas ShahNo ratings yet
- Sight Glass Flange AnalysisDocument4 pagesSight Glass Flange AnalysisOmil Rastogi0% (2)
- Studding Outlet Calculation - PV Elite 2016Document8 pagesStudding Outlet Calculation - PV Elite 2016Liu YangtzeNo ratings yet
- ASME Horizontal Vessel AnalysisDocument10 pagesASME Horizontal Vessel AnalysisSyedZainAliNo ratings yet
- Lifting Lug CalculationsDocument6 pagesLifting Lug CalculationsAwais Hameed100% (1)
- Vessel lifting lug design data and stress analysisDocument3 pagesVessel lifting lug design data and stress analysismiteshpatel191100% (1)
- Design of large diameter slip on flangeDocument6 pagesDesign of large diameter slip on flangeAKSHAY BHATKARNo ratings yet
- LIFTING LUG Weld Check KGDocument4 pagesLIFTING LUG Weld Check KGjoerijiNo ratings yet
- Lifting Lug CalculationsDocument1 pageLifting Lug CalculationsshazanNo ratings yet
- Tailing Lug - 173004-05Document1 pageTailing Lug - 173004-05shazan100% (1)
- Water Tank DesignDocument58 pagesWater Tank DesignMoHaMmAd WaHeEd88% (17)
- Water Tank DesignDocument58 pagesWater Tank DesignMoHaMmAd WaHeEd88% (17)
- FORMWORK DESIGNDocument28 pagesFORMWORK DESIGNsubhananya50% (4)
- Lifting Lug Design CalculationsDocument17 pagesLifting Lug Design CalculationsSiva baalan100% (1)
- Lifting LugDocument5 pagesLifting LugFarid Tata100% (1)
- Trunnion AnalysisDocument45 pagesTrunnion AnalysisChiragJansariNo ratings yet
- Calculation of left and right saddle supports for offshore tankerDocument12 pagesCalculation of left and right saddle supports for offshore tankerrustamriyadiNo ratings yet
- HORIZONTAL VESSEL STRESS CALCULATIONSDocument12 pagesHORIZONTAL VESSEL STRESS CALCULATIONSSanket BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Davit Cal 2251B Davit Arm CalculationDocument4 pagesDavit Cal 2251B Davit Arm Calculationnitin400No ratings yet
- #754 v-3103 Spreader & Lifting 60 DegreeDocument12 pages#754 v-3103 Spreader & Lifting 60 DegreeHafizi HZnumismatic100% (1)
- Vdocuments - MX Rectangular Tank CalculationDocument34 pagesVdocuments - MX Rectangular Tank CalculationAtilla TekinNo ratings yet
- Base Ring Fillet Size CalculationDocument4 pagesBase Ring Fillet Size Calculationmiteshpatel191No ratings yet
- LIFTING LUG AND LIFTING COVER DESIGN REFERENCEDocument4 pagesLIFTING LUG AND LIFTING COVER DESIGN REFERENCERohith V VNo ratings yet
- Lifting Lug CalculationsDocument6 pagesLifting Lug CalculationsYash RamiNo ratings yet
- Calculation For Lifting Lug DesignDocument6 pagesCalculation For Lifting Lug DesignErin JohnsonNo ratings yet
- U-V-673 - Manual Flange and GussetDocument8 pagesU-V-673 - Manual Flange and GussetDarshan PanchalNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Lifting ForcesDocument9 pagesCalculation of Lifting ForcesprantikduarahNo ratings yet
- Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Lifting Trunnion Common Practices PDFDocument4 pagesBoiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Lifting Trunnion Common Practices PDFAlexandru AsmarandeiNo ratings yet
- Platform Cleat CalculationDocument1 pagePlatform Cleat Calculationmiteshpatel191No ratings yet
- Lifting Lug DesignDocument7 pagesLifting Lug DesignadammzjinNo ratings yet
- 2.a) Davit CalculationDocument11 pages2.a) Davit CalculationneelNo ratings yet
- Skid LiftDocument2 pagesSkid LiftAmi PutraNo ratings yet
- Sample8 NozzleProDocument17 pagesSample8 NozzleProjahiranazriNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Lifting LugDocument1 pageHorizontal Lifting LugTushar MangratiNo ratings yet
- Studding Flange Calculations Gasket SelectionDocument6 pagesStudding Flange Calculations Gasket SelectionDarshan PanchalNo ratings yet
- LiftingLug TrunnionDocument22 pagesLiftingLug Trunnionrichardchiam100% (2)
- Lifting Lug Calculation For Small Horizontal VesselDocument2 pagesLifting Lug Calculation For Small Horizontal VesselshaishavNo ratings yet
- Base Plate Hinged - Moment On Anchors Adjusted 09-06-2021Document2 pagesBase Plate Hinged - Moment On Anchors Adjusted 09-06-2021ahmed osmanNo ratings yet
- Design of base plate for columnDocument6 pagesDesign of base plate for columnsoumyaNo ratings yet
- Design of Fixed Base Connection (BP) : Reactions Input Material PropertiesDocument10 pagesDesign of Fixed Base Connection (BP) : Reactions Input Material PropertiesAnand.5No ratings yet
- Sfex Pad Eyes Calculations 35T - 32MMDocument1 pageSfex Pad Eyes Calculations 35T - 32MMJohn Rom CabadonggaNo ratings yet
- Flat Plate - Roark & YoungDocument15 pagesFlat Plate - Roark & YoungPrasad Pingle0% (1)
- Padeye DolphinDocument38 pagesPadeye DolphinMuhammad FadelNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Lifting Lug CalculationDocument2 pagesPressure Vessel Lifting Lug Calculationtekstep767% (3)
- FVC Catalog - UnlockedDocument80 pagesFVC Catalog - UnlockedhumbubbleNo ratings yet
- LIFTING LUG CALCULATIONDocument2 pagesLIFTING LUG CALCULATIONhuangjlNo ratings yet
- Sample FLG CalcDocument6 pagesSample FLG CalcameyyammaiNo ratings yet
- Lifting and Tailing StackDocument42 pagesLifting and Tailing StackSudar MyshaNo ratings yet
- Lifting Lug Calculation For Small Horizontal VesselDocument2 pagesLifting Lug Calculation For Small Horizontal VesselshaishavNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Tank (With Horizontal Stiffner)Document5 pagesRectangular Tank (With Horizontal Stiffner)DURGAIRAJ100% (1)
- Large Horizontal Vessel Supported by Two Saddles Stress AnalysisDocument7 pagesLarge Horizontal Vessel Supported by Two Saddles Stress AnalysisSiva baalanNo ratings yet
- PV Elite Vessel Analysis Program HorizontalDocument55 pagesPV Elite Vessel Analysis Program HorizontalMarizta Perdani PutriNo ratings yet
- Spreader Beam (Planning)Document28 pagesSpreader Beam (Planning)AKSHAY BHATKARNo ratings yet
- Jn1399 - 71t Lifting LugDocument5 pagesJn1399 - 71t Lifting LugRiyan EsapermanaNo ratings yet
- Design of Circular Flat Endplate With Stiffeners - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-TipsDocument2 pagesDesign of Circular Flat Endplate With Stiffeners - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-Tipsisrar khanNo ratings yet
- Trunnion 6 TonDocument3 pagesTrunnion 6 TonEngr Khurram Jaan RamayNo ratings yet
- Fe Report of Base SkidDocument16 pagesFe Report of Base SkidpawanNo ratings yet
- 8 Padeye - Spreadsheet Check1Document4 pages8 Padeye - Spreadsheet Check1oluomo1No ratings yet
- Cone Weight CalculationDocument10 pagesCone Weight CalculationRajesh OwaiyarNo ratings yet
- Ga & Transportation DWGDocument2 pagesGa & Transportation DWGjahiranazriNo ratings yet
- Sloshing DSFGSD GDocument20 pagesSloshing DSFGSD GjahiranazriNo ratings yet
- Mset M2-228 L4-301D Mto 006Document1 pageMset M2-228 L4-301D Mto 006jahiranazriNo ratings yet
- PV Elite Vessel Analysis Program: Input DataDocument90 pagesPV Elite Vessel Analysis Program: Input DatajahiranazriNo ratings yet
- Installation & Maintenance ManualDocument9 pagesInstallation & Maintenance ManualjahiranazriNo ratings yet
- M2-237a Nozzle On Obround PlateDocument1 pageM2-237a Nozzle On Obround PlatejahiranazriNo ratings yet
- Base Block Sdsdsdasd Asda Dasdqaweqe SadDocument3 pagesBase Block Sdsdsdasd Asda Dasdqaweqe Sadjahiranazri100% (1)
- Theories of FailureDocument62 pagesTheories of FailureAjith MosesNo ratings yet
- Connection 2 CalculationsDocument5 pagesConnection 2 CalculationsNguyễn Văn BanNo ratings yet
- M4-228-M4-102-Calc-Rev ADocument64 pagesM4-228-M4-102-Calc-Rev AjahiranazriNo ratings yet
- Linear Vs Non-Linear Contact Analysis 082207Document9 pagesLinear Vs Non-Linear Contact Analysis 082207Senthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Sloshing DSFGSD GDocument20 pagesSloshing DSFGSD GjahiranazriNo ratings yet
- Bernoulliwoochangchung 1213360646168171 9Document21 pagesBernoulliwoochangchung 1213360646168171 9jahiranazriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 98Document34 pagesChapter 5 98masturaabdulrahimNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Wave Generation in a TankDocument24 pagesSimulation of Wave Generation in a Tankjoputa15No ratings yet