Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scabies: What You Can Do Yourself
Uploaded by
AbdulAzees S DeenmohamedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Scabies: What You Can Do Yourself
Uploaded by
AbdulAzees S DeenmohamedCopyright:
Available Formats
COMMON CONDITIONS: SKIN, HAIR, AND NAIL PROBLEMS
35
Scabies
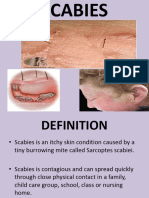
Scabies is an infestation caused by a mite that burrows just under the skin surface. At first you will have intense itching, which is worse at night. You may then notice little bumps and tiny, pencil-like lines (burrows); these usually develop between the fingers and toes and on the elbows and wrists, but may occur anywhere on your skin. Scabies is troublesome rather than serious. Anyone can catch it, regardless of age and personal hygiene, through any type of skin-to-skin contact or simply by sharing bedding, towels, or clothing.
Scabies infestation on a hand and fingers
See your doctor first
Make an appointment to see your doctor if you think that you have scabies. He or she will check if you have the condition and prescribe the appropriate medication.
DRUG REMEDIES Scabies lotions usually contain the antiparasitic drugs lindane or permethrin. Your doctor will prescribe an appropriate preparation. Usually, the treatment is applied to your entire body (but not your head and face). Trim your nails short and apply it under your nail tips. Babies under 2 years and elderly people may need their face and scalp to be treated as well. The preparation is usually left on overnight and then washed off in the morning. A second application may be necessary, depending on the type of lotion used and your symptoms. Antihistamines (see p.178) can help relieve itching. Sedative types make you drowsy, and are particularly useful at night. Calamine lotion (see p.179) helps relieve the itchiness that occurs in scabies.
What you can do yourself
For best results, start scabies treatment as soon as the symptoms appear. This may be anything up to 8 weeks after infestation, and the itching can last for several weeks. Use a prescription cream or lotion for treating scabies (see DRUG REMEDIES, right).
G
You can relieve itching with calamine lotion and/or take an antihistamine if itching is making it difficult for you to sleep (see DRUG REMEDIES, right).
G
Make sure other people in the home and close friends are treated, even if they are not showing signs of scabies. Ask your physician to provide enough treatment for all household members.
G G Scabies mites can live for 12 days in clothes and bedding. To kill the mites, wash clothes, bed linen, and towels in hot water and dry in a tumble dryer if possible. Wash personal items such as hairbrushes as well. G Vacuum carpets, rugs, furniture, and cushions because they may harbor the scabies mites. Use a disposable bag in your vacuum cleaner and discard the bag afterward. If you have a bagless vacuum cleaner, empty it and wash it out after use.
Relieving itching Itching can persist for several weeks after the infestation has cleared up, so you may need to continue using calamine and/or an antihistamine.
Seek further medical advice
Arrange to see your doctor if:
G You are still itching more than 2 weeks after finishing your course of treatment G The rash becomes sore and starts to ooze
36
COMMON CONDITIONS: SKIN, HAIR, AND NAIL PROBLEMS
Urticaria
Urticaria, or hives, is an intensely itchy rash of white or yellow swellings (wheals) surrounded by red, inflamed skin. It is usually caused by an allergic reaction, which can be triggered by a range of factors, such as certain foods or medicines, insect bites, or stings. People with hay fever or asthma are more susceptible. Hives can also be caused by stress, or have no obvious cause.
See also Anaphylactic shock, p.159.
WARNING
Seek immediate medical help if you have urticaria and:
G You become breathless or hoarse, or start to wheeze G Your lips or tongue swell and/or you have difficulty swallowing
See your doctor first
Make an appointment to see your doctor to confirm that you have urticaria and/or to check whether you are taking medication that could be triggering the attack.
DRUG REMEDIES Antihistamines (see p.178) control allergic
swelling and itching. You may need to try several types to find out which works best for you. The drug may need to be taken regularly for a prolonged attack of hives. Ask your pharmacist for advice.
What you can do yourself
Urticaria is extremely uncomfortable, but the following measures will help relieve irritation and soothe the skin. Attacks are usually short-lived, but some people have persistent symptoms. Take an antihistamine to reduce itching and swelling (see DRUG REMEDIES, right).
G
Calamine lotion (see p.179) is a soothing
preparation with a cooling effect. Using a cotton ball, dab it onto the rash 23 times a day.
NATURAL REMEDIES Oatmeal products (see p.187) are often effective for soothing itchy skin. Add oatmeal oil to lukewarm bath water and soak for 1020 minutes.
Take a cool shower to reduce the redness and heat of the rash. Alternatively, hold a cool compress (a clean washcloth soaked in cool water and wrung out) against the rash for a few minutes at a time. Keep reapplying for about 30 minutes.
G
PREVENTION Preventing urticaria If you have
recurrent attacks, try these measures of prevention. Keep a diary of attacks, and try to identify any foods, medicines, or other factors that may trigger them. Once you find a trigger, you can try to avoid it. G If you think stress is a contributory factor, try self-help techniques (see STRESS, pp.2021).
G
You can also relieve itching with calamine lotion (see DRUG REMEDIES, right).
G
Try an oatmeal bath oil (see NATURAL REMEDIES, right) to relieve itchy skin.
G G Minimize irritation by wearing loose-fitting, lightweight clothes made of natural fibers.
Seek further medical advice
Arrange to see your doctor again if:
G
Urticaria is not responding to treatment
You might also like
- FACIAL WORK BOOK - UpdatedDocument48 pagesFACIAL WORK BOOK - UpdatedVivienne Lawrence100% (6)
- Dermatologia, 3a Edicao - Jean Bolognia - DesbloqueadoDocument4,324 pagesDermatologia, 3a Edicao - Jean Bolognia - DesbloqueadoCarla Puppim100% (1)
- Eczema Diet: Itch No More! End Skin rashes, skin irritation & reduce inflammation with A Low Inflammation Diet & Proven foods that work! BONUS know what to avoid!From EverandEczema Diet: Itch No More! End Skin rashes, skin irritation & reduce inflammation with A Low Inflammation Diet & Proven foods that work! BONUS know what to avoid!No ratings yet
- Shingles: What You Can Do YourselfDocument2 pagesShingles: What You Can Do YourselfAbdulAzees S DeenmohamedNo ratings yet
- Excessive Sweating: What You Can Do YourselfDocument2 pagesExcessive Sweating: What You Can Do YourselfAbdulAzees S DeenmohamedNo ratings yet
- What Causes Nettle Rash?Document2 pagesWhat Causes Nettle Rash?Ardave Laurente100% (1)
- Management of Insect Bites and Stings: Description IDocument4 pagesManagement of Insect Bites and Stings: Description IElvisNo ratings yet
- First Aid Group 1Document29 pagesFirst Aid Group 1Veramel ValenzonaNo ratings yet
- Nodular Prurigo Update May 2016 - Lay Reviewed April 2016 (Revised July 2016)Document5 pagesNodular Prurigo Update May 2016 - Lay Reviewed April 2016 (Revised July 2016)ranz ibonkNo ratings yet
- What Is ShingleDocument8 pagesWhat Is ShingleAkinsoun MotunrayoNo ratings yet
- Burns and Electric Shock - Home Treatment: Immediate First Aid For BurnsDocument7 pagesBurns and Electric Shock - Home Treatment: Immediate First Aid For BurnsAira Grace AtabayNo ratings yet
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) - Diagnosis and Treatment - Mayo ClinicDocument1 pageAtopic Dermatitis (Eczema) - Diagnosis and Treatment - Mayo ClinicHarry LeNo ratings yet
- Pertussis: What You Can Do YourselfDocument2 pagesPertussis: What You Can Do YourselfAbdulAzees S DeenmohamedNo ratings yet
- Patient Education - Dermatitis (The Basics) - UpToDateDocument4 pagesPatient Education - Dermatitis (The Basics) - UpToDateRadu BalanNo ratings yet
- First Aid For Your BabyDocument5 pagesFirst Aid For Your BabyDevyNo ratings yet
- How To Take The Sting Out of A Burn (With Pictures)Document12 pagesHow To Take The Sting Out of A Burn (With Pictures)DtftftfrNo ratings yet
- Gatal Pada KulitDocument3 pagesGatal Pada KulitDessi NataliaNo ratings yet
- Contact DermatitisDocument4 pagesContact DermatitisHieu MinhNo ratings yet
- These Guidelines Can Help You Care For Minor Cuts and LacerationsDocument2 pagesThese Guidelines Can Help You Care For Minor Cuts and LacerationsMark Dennis AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Skin AsthmaDocument7 pagesSkin AsthmaShin AbonalNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid TrainingDocument32 pagesBasic First Aid Trainingtukaram patilNo ratings yet
- Insects, Stings and BitesDocument5 pagesInsects, Stings and BitesDian ariefNo ratings yet
- When To Visit Your GPDocument12 pagesWhen To Visit Your GPJohn EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Pigsa, Letteg Ken Busali... The Three BossDocument8 pagesPigsa, Letteg Ken Busali... The Three Bossjojazz74No ratings yet
- What Is It? Points To Remember About Atopic Dermatitis: BasicsDocument6 pagesWhat Is It? Points To Remember About Atopic Dermatitis: BasicsRiya potbhareNo ratings yet
- Male Genital EczemeDocument4 pagesMale Genital EczemewandalexNo ratings yet
- Neuro DermatitisDocument19 pagesNeuro DermatitisAiman Tymer100% (1)
- Week 2Document19 pagesWeek 2Christina MalayaoNo ratings yet
- Atopic EczemaDocument3 pagesAtopic EczemaMr JohnNo ratings yet
- Common Injuries and IlnnessDocument4 pagesCommon Injuries and IlnnessSLIDENo ratings yet
- Hand-Foot Syndrome During TreatmentDocument2 pagesHand-Foot Syndrome During TreatmentzainabativeNo ratings yet
- Home Remedies: The Painful Irritation of Eczema: by Dana SparksDocument6 pagesHome Remedies: The Painful Irritation of Eczema: by Dana SparksFrancois Cyrus EsletaNo ratings yet
- Hives: What Are Hives? TreatmentDocument2 pagesHives: What Are Hives? TreatmentAlisha RangaNo ratings yet
- BMG PCHA EczemaDocument2 pagesBMG PCHA EczemaBobby DebNo ratings yet
- Insects, Stings and BitesDocument5 pagesInsects, Stings and BitesHans Alfonso ThioritzNo ratings yet
- Introduction To First Aid: American Red Cross St. John AmbulanceDocument5 pagesIntroduction To First Aid: American Red Cross St. John AmbulanceВалентина Василівна Банилевська0% (1)
- IntroductionDocument21 pagesIntroductionfarmasi_hmNo ratings yet
- Banish Hives Forever EbookDocument29 pagesBanish Hives Forever EbookSarah BayaNo ratings yet
- Unicystic Ameloblastoma 2 2Document8 pagesUnicystic Ameloblastoma 2 2osama slmanNo ratings yet
- Fast First Aid Tips For 4 Common Accidents: Cut or ScrapeDocument2 pagesFast First Aid Tips For 4 Common Accidents: Cut or ScrapeЮлия ДаниловаNo ratings yet
- TreatmentDocument11 pagesTreatmentsanyassandhuNo ratings yet
- HivesDocument4 pagesHivesAlfie PanisanNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Clinical SurjeryDocument26 pagesAssignment of Clinical SurjeryMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaNo ratings yet
- Co3rd21 22Document16 pagesCo3rd21 22keira ygotNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument5 pagesFirst AidCitra Zea FichellaNo ratings yet
- Scabies 160908065024Document12 pagesScabies 160908065024Syed NoorNo ratings yet
- ACEP First Aid KitDocument2 pagesACEP First Aid KitThe DoctorNo ratings yet
- Rubella: What You Can Do YourselfDocument2 pagesRubella: What You Can Do YourselfAbdulAzees S DeenmohamedNo ratings yet
- Acne - Get Rid of It Naturally With Homeopathy - DR Batra'sDocument6 pagesAcne - Get Rid of It Naturally With Homeopathy - DR Batra'snadee.ak2023No ratings yet
- HivesDocument3 pagesHivessashi5kalaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Hand Foot SyndromesDocument5 pagesJurnal Hand Foot Syndromesari marliyanaNo ratings yet
- Allergies Hives Rashes Handout 509kDocument2 pagesAllergies Hives Rashes Handout 509kIndu SinghNo ratings yet
- InjuryDocument2 pagesInjuryKuiper TenneyNo ratings yet
- Home Kit: A Household First Aid Kit Should Include These ItemsDocument7 pagesHome Kit: A Household First Aid Kit Should Include These ItemsRonny Fardian SetiadarmaNo ratings yet
- Peh 12 w2Document15 pagesPeh 12 w2api-613352174No ratings yet
- Good-Cause Emergency First Aid ForPetsDocument53 pagesGood-Cause Emergency First Aid ForPetsAmandla XokiNo ratings yet
- DM 14 Skin Prick Testing ENT Trust Print v1Document4 pagesDM 14 Skin Prick Testing ENT Trust Print v1niyatihopesNo ratings yet
- Bathing Guide en WebDocument20 pagesBathing Guide en WebkupitiroNo ratings yet
- First Aid Treatments "Someone Faints & Burn by Hot Water"Document8 pagesFirst Aid Treatments "Someone Faints & Burn by Hot Water"riandini pandansariNo ratings yet
- Diaper Rash GuideDocument5 pagesDiaper Rash GuideLaras Ciingu SyahrezaNo ratings yet
- ShinglesDocument5 pagesShinglesklinik mandiriNo ratings yet
- Palmoplantar Pustulosis: What Are The Aims of This Leaflet?Document5 pagesPalmoplantar Pustulosis: What Are The Aims of This Leaflet?Muhammad SaifulNo ratings yet
- 1 Jyothi Sanjeevini Full DetailsDocument161 pages1 Jyothi Sanjeevini Full DetailsPramodNo ratings yet
- Lumps and Ulcer, Sebaceous Cyst, Lipoma, Dermoid CystDocument88 pagesLumps and Ulcer, Sebaceous Cyst, Lipoma, Dermoid CystAbdulsalam DostNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris IIIDocument3 pagesBahasa Inggris IIIAfifah TyasNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Skin InfectionsDocument9 pagesBacterial Skin InfectionskateverdadNo ratings yet
- Regular Discounted Price Price: Descripti0N Exp. Date As of Jan. 14, 2021Document1 pageRegular Discounted Price Price: Descripti0N Exp. Date As of Jan. 14, 2021Angela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Stock 21 November 2022Document17 pagesStock 21 November 2022Rhesa GuttamaNo ratings yet
- Lesi Multipel Akut (Infeksi Virus & Bakteri)Document19 pagesLesi Multipel Akut (Infeksi Virus & Bakteri)Icha AnviniNo ratings yet
- Fungal Skin Infections: Education GapDocument17 pagesFungal Skin Infections: Education GapAncuta CalimentNo ratings yet
- Dermatita SeboreicaDocument4 pagesDermatita SeboreicaFlorian MaghearNo ratings yet
- Ex 15 2Document29 pagesEx 15 2aya essamNo ratings yet
- Ringworm (Tinea Corporis) : How Ringworm Is DiagnosedDocument2 pagesRingworm (Tinea Corporis) : How Ringworm Is DiagnosedBudiMulyanaNo ratings yet
- Photosensitive Diseases: 1. Solar Dermatitis, SunburnDocument8 pagesPhotosensitive Diseases: 1. Solar Dermatitis, SunburnOliver RomaineNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary LesionsDocument7 pagesPrimary and Secondary LesionsCoral Srinivasa Ramalu50% (2)
- Morsicatio Labiorum-LinguarumDocument3 pagesMorsicatio Labiorum-LinguarumPaola SilvaNo ratings yet
- Dry Skin Relief and Treatment Products CeraVeDocument1 pageDry Skin Relief and Treatment Products CeraVeArham SohailNo ratings yet
- What You Need To Know About AcneDocument5 pagesWhat You Need To Know About AcnerichardgomezNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Skin Disorders: Prepared by Dr. Darin MathkorDocument33 pagesPediatric Skin Disorders: Prepared by Dr. Darin MathkorArwa HakamiNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus - Dr. Annisa Putri SiregarDocument17 pagesLaporan Kasus - Dr. Annisa Putri Siregaramka chanNo ratings yet
- Microneedling AftercareDocument2 pagesMicroneedling AftercareRuth ann Micol RiveraNo ratings yet
- Dermatology MDMSDocument64 pagesDermatology MDMSDipesh Shrestha0% (1)
- The Differential Diagnosis of Psoriasis Vulgaris 2376 0427 1000245Document2 pagesThe Differential Diagnosis of Psoriasis Vulgaris 2376 0427 1000245Oktavianti Prisilia SoumokilNo ratings yet
- Scabies Home Remedies Treatment and ImagesDocument3 pagesScabies Home Remedies Treatment and ImagesIyan DwiNo ratings yet
- Manager Pharmaceutical Sales Representative in Sacramento CA Resume Robert RoedigerDocument3 pagesManager Pharmaceutical Sales Representative in Sacramento CA Resume Robert RoedigerRobertRoedigerNo ratings yet
- Basic Information About DermatologyDocument52 pagesBasic Information About DermatologymohdNo ratings yet
- Barang Istana CosmeticDocument7 pagesBarang Istana CosmeticlisaririNo ratings yet
- Cosmeticology semVIDocument3 pagesCosmeticology semVIRamchandra Keny50% (4)
- Non-Odontogenic Tumors of The JawsDocument5 pagesNon-Odontogenic Tumors of The JawsSaman SadeghiNo ratings yet
- 82-Article Text-254-4-10-20200220Document8 pages82-Article Text-254-4-10-20200220Ari PurnamayasaNo ratings yet