Professional Documents
Culture Documents
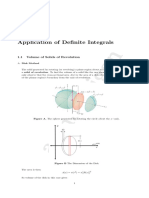
Introduction Definal 1
Uploaded by
Nurul HudaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction Definal 1
Uploaded by
Nurul HudaCopyright:
Available Formats
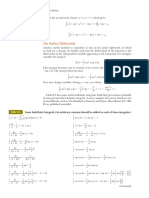
Integral Formulation for Numerical Solutions
OBJECTIVE: Use integral methods to obtain an approximate
solution to a physical problem.
EXAMPLE: Find a solution for a beam deflection.
H
M(x) = m
0
x
M(x)
EI
m
0
m
0
Differential
Equations
EI = beam stiffness
M(x) = bending moment
EI
d y
dx
M x
2
2
0 = ( )
x
*Approximate Beam deflection:
Integrating twice
*Exact Solution:
Using boundary conditions:
y(0) = y(H) = 0
y(0) = 0, x = 0 c
2
= 0
Exact
Solution.
d y
dx
M x
EI
2
2
=
( )
dy
dx
Mx
EI
c = +
y
Mx
EI
c x c = + +
2
1 2
2
0
2
2
1
= +
MH
EI
c H
c
MH
EI H
MH
EI
1
2
2 2
= =
y
Mx
EI
MHx
EI
=
2
2 2
y
MHx
EI
x H =
2
( )
y x
x
H
( ) sin =
VARIATIONAL METHOD
Given a differential equation such as:
The calculus of variations will generate a solution if the numerical
value of the integral is a minimum.
In other words, if a particular y = g(x) generates a minimum
for ; it is the solution of the differential equation.
D
d y
dx
Q
2
2
0 =
So, for the beam:
=
F
H
G
I
K
J
L
N
M
M
O
Q
P
P
z
EI dy
dx
M y dx
H
2
2
0
0
Consider the approximate function,
then evaluate .
Steps:
1. Write as a function of A
2. Minimize with respect to A
y x A
x
H
( ) sin =
y x A
x
H
( ) sin =
dy
dx
A
H
x
H
=
cos
VARIATIONAL METHOD
continued
=
L
N
M
O
Q
P
z
EI
M dx
H
2
2
0
0
b g
A
x
H
sin
A
H
x
H
cos
=
F
H
G
I
K
J
+
F
H
G
I
K
J
EI
H
A
M H
A
2
2
0
4
2
Minimizing :
=
F
H
G
I
K
J
+ =
A
EI
H
A
M H
2
4
2
0
2
0
A
M H
EI
=
4
0
2
3
y x
x
H
( ) sin =
4
0
2
3
M H
EI
Development of a Continuous Solution
in a 1 dimensional region
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
4 4 4
b g
b g
b g
b g
= + =
= + =
= + =
= + =
N N
N N
N N
N N
i i j j
i i j j
i i j j
i i j j
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
N N
N N
N N
N N
1
1
1 2
1
2
2
2
2 3
2
3
3
3
3 4
3
4
4
4
4 5
4
5
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
+
+
+
+
(1) (2) (3) (4)
1
2
3 4 5
(1) (2) (3) (4)
1
i
2
j
3
j
4
j
2
i
3
i
4
i
5
j
Apply shape
functions
concept to
each element
e
i
e
i j
e
j
N N
b g
= +
( ) ( )
General
Form
With Shape functions:
N
X x
X X
N
x X
X X
i
e
j
j i
j
e
i
j i
( ) ( )
=
&
Development of a Continuous Solution
in a 1 dimensional region
(continued)
(1) (2) (3) (4)
1
i
2
j
3
j
4
j
2
i
3
i
4
i
5
j
N N
2
1
2
2 ( ) ( )
Grid Summary:
element nodes
# i j
(1) 1 2
(2) 2 3
(3) 3 4
(4) 4 5
Note:
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Asme B30Document1 pageAsme B30Nurul Huda100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Complex Calculus Formula Sheet - 3rd SEMDocument6 pagesComplex Calculus Formula Sheet - 3rd SEMgetsam123100% (1)
- Calculus III Study GuideDocument23 pagesCalculus III Study Guideasipasi7No ratings yet
- Elastic BeaconsDocument9 pagesElastic BeaconsNurul HudaNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Marine Structures V Digital PDFDocument4 pagesAnalysis and Design of Marine Structures V Digital PDFNurul Huda0% (1)
- Designmodeler: Workshop 5.1 3D CurveDocument8 pagesDesignmodeler: Workshop 5.1 3D CurveNurul HudaNo ratings yet
- 25 Abaqus ODBDocument6 pages25 Abaqus ODBNurul HudaNo ratings yet
- Steel Pipes - Pipe Schedule ChartDocument3 pagesSteel Pipes - Pipe Schedule ChartNurul HudaNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Analysis Tool 1.0Document2 pagesFatigue Analysis Tool 1.0Nurul HudaNo ratings yet
- Spring Analysis Tool3Document4 pagesSpring Analysis Tool3Nurul HudaNo ratings yet
- Response Spectra GenerationDocument16 pagesResponse Spectra GenerationNurul HudaNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Finite Element Analysis of Wind Induced Buckling of Steel TankDocument4 pages3.4 Finite Element Analysis of Wind Induced Buckling of Steel TankNurul HudaNo ratings yet
- Computer Science EngineeringDocument16 pagesComputer Science EngineeringChinmay MokhareNo ratings yet
- Gate XeDocument3 pagesGate XeAbhinav MathurNo ratings yet
- MATB42 Formula SheetDocument3 pagesMATB42 Formula SheetSunny RochiramaniNo ratings yet
- How Is Numerical Integration Programmed in S7-SCL and STEP 7Document2 pagesHow Is Numerical Integration Programmed in S7-SCL and STEP 7Anderson PereiraNo ratings yet
- B.SC Mathmatics BooksDocument26 pagesB.SC Mathmatics Books22bspc002hyNo ratings yet
- Applications of Numerical MethodsDocument54 pagesApplications of Numerical Methodstarun gehlotNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument598 pagesClass NotesjackNo ratings yet
- Demidovich Mathematical AnalysisDocument100 pagesDemidovich Mathematical AnalysisMafteiDanNo ratings yet
- New Syllabus For B.E Department of Information Technology 1 Year 1 SemesterDocument50 pagesNew Syllabus For B.E Department of Information Technology 1 Year 1 SemesterRavikGangulyNo ratings yet
- Calculus (Bradley & Smith) - Instructor's EditionDocument1,107 pagesCalculus (Bradley & Smith) - Instructor's EditionmathchanNo ratings yet
- C3 Integration PDFDocument5 pagesC3 Integration PDFRokonuddin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Drexel - Math 123 - FinalExamReviewDocument2 pagesDrexel - Math 123 - FinalExamReviewPeterNaranjoNo ratings yet
- Course Planner: Subject Wise Syllabus PlanDocument2 pagesCourse Planner: Subject Wise Syllabus PlanRavi KantNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus I PDFDocument2 pagesIntegral Calculus I PDFrenzon272No ratings yet
- BSMaSS 2 1Document4 pagesBSMaSS 2 1Daniela Mardini GonzálezNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL: Multiple Integrals: Dxdy X e yDocument6 pagesTUTORIAL: Multiple Integrals: Dxdy X e yArsene LupinNo ratings yet
- DTDP SyllabusDocument97 pagesDTDP SyllabusSreeniza BhamidiNo ratings yet
- Aamarasigan: Application of Definite IntegralsDocument20 pagesAamarasigan: Application of Definite IntegralsCyruz Lapinas100% (1)
- Differentiation, Interdependence and Performance in Formal OrganizationsDocument15 pagesDifferentiation, Interdependence and Performance in Formal OrganizationsMayara Benicio De Barros SouzaNo ratings yet
- JEE APRIL 2025 Final TrackerDocument1 pageJEE APRIL 2025 Final TrackerjhasureshchandNo ratings yet
- Integration by Substitution: Review of Basic Integration FormulasDocument8 pagesIntegration by Substitution: Review of Basic Integration FormulasMyka ManingdingNo ratings yet
- BCA (R) Session 2012-13 - 15 - 16 (1) - 23 - 7 - 18Document27 pagesBCA (R) Session 2012-13 - 15 - 16 (1) - 23 - 7 - 18Md Tabrez AlamNo ratings yet
- Apendix-B-IntegralsRaymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett - Physics For Scientists and Engineers With Modern Physics (2013, Cengage Learning)Document2 pagesApendix-B-IntegralsRaymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett - Physics For Scientists and Engineers With Modern Physics (2013, Cengage Learning)Edwin PenroseNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Dynamic Relaxation Algorithm For Non-Linear Hyperelastic StructuresDocument19 pagesAdaptive Dynamic Relaxation Algorithm For Non-Linear Hyperelastic StructuresJoaquin VieraNo ratings yet
- R17 Mechatronics Syllabus PDFDocument112 pagesR17 Mechatronics Syllabus PDFScientist SakthivelNo ratings yet
- Master HH Crash Worthiness P 2Document72 pagesMaster HH Crash Worthiness P 2Jonatan Pozo Palacios100% (1)
- Code MATH Course Details PDFDocument80 pagesCode MATH Course Details PDFAnees RahmanNo ratings yet
- 11 ProductionDocument95 pages11 ProductionSubashNo ratings yet