Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Capacity Matrix Total Year 13-14
Uploaded by
api-2439094870 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views8 pagesOriginal Title
capacity matrix total year 13-14
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views8 pagesCapacity Matrix Total Year 13-14
Uploaded by
api-243909487Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
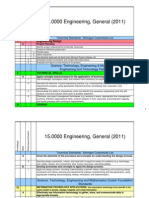
Pre-Calculus and Trigonometry Capacity Matrix
Purpose and Vision
Understanding and Applying Pre-Calculus and
Trigonometry
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
K
n
o
w
l
e
d
g
e
K
n
o
w
-
h
o
w
w
i
s
d
o
m
P
o
r
t
f
o
l
i
o
Unit Standard Capacity Breakdown
Review
Polynomials
A1.1.4
Add, subtract, multiply and simplify polynomials and
rational expressions
X X
Shot in the Dark
A1.2.5
Solve polynomial equations and equations involving rational
expressions
X X
Shot in the Dark
Unit Standard Capacity Breakdown
Review
Chapter 1
Sec 1.5 Use interval notation X
Sec 1.5 Solve and use properties of inequalities X X Piecewise
Sec 1.6 Solve equations involving Absolute Value X X Piecewise
Sec 1.6 Solve Inequalities involving Absolute Value X
Sec 1.7 Verbal descriptions into mathematical expressions X
Sec 1.7
Solve interest problems, uniform motion problems, mixture
problems and constant rate job problems
X
Unit Standard Capacity Breakdown
Functions and their
Graphs
Chapter 3
P1.1
Know and use a definition of a function to decide if a given
relation is a function
X X
Shot in the Dark
P1.2
Perform algebraic operations (including compositions) on
functions and apply transformations(translations,
reflections and rescaling)
X X
Shot in the Dark
P1.6
Identify and describe discontinuities of a function(greatest
integer function) and how these relate to the graph
X
P5.3
Know and apply the definition and geometric interpretation
of the difference quotient
X
P5.3
Simplify difference quotients and interpret them as rates of
change and slopes of secant lines
X
Sec 3.6
Translate written description of a real world problem into a
mathematical model
X
Sec 3.6
Assign independent and dependent variables Be able to find
minimum or maximum value in a real world problem
X X
Shot in the Dark
Pre-Calculus and Trigonometry Capacity Matrix
Purpose and Vision
Understanding and Applying Pre-Calculus and
Trigonometry
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
K
n
o
w
l
e
d
g
e
K
n
o
w
-
h
o
w
w
i
s
d
o
m
P
o
r
t
f
o
l
i
o
Unit Standard Capacity Breakdown
Linear and Quadratic
Functions
Chapter 4
P1.1
Know and use a definition of a function to decide if a
given relation is a function
X X
Shot in the Dark
P1.2
Perform algebraic operations on functions and apply
transformations(translations, reflections, and
rescaling)
X X
Shot in the Dark
P1.8
Explain how the rates of change of functions in
different families (ex. Linear functions and quadratics)
differ, referring to graphical representations
X
X
Shot in the Dark
P3.2
Apply quadratic functions and their graphs in context
of motion under gravity and simple optimization
problems
X X
Shot in the Dark
P3.3
find a quadratic function to model a given data set or
situation
X X
Shot in the Dark
Sec 4.4
Solve applied problems involving the law of demand
using the demand equation
Polynomials and Rational
Functions
Chapter 5
P4.1
Given a polynomial function whose roots are known or
can be calculated, find the intervals on which the
functions value are positive and those where it is
negative
P4.2
Solve polynomial equations and inequalities of degree
greater than or equal to three. Graph the polynomial
functions given in factored form using zeros and their
multiplicities, testing the sign-on intervals and
analyzing the functions large-scale behavior.
P4.3
Know and apply fundamental facts about polynomials: the
remainder theorem, the factor theorem, and the fundamental
theorem of algebra
X X
Shot in the Dark
Pre-Calculus and Trigonometry Capacity Matrix
Purpose and Vision
Understanding and Applying Pre-Calculus and
Trigonometry
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
K
n
o
w
l
e
d
g
e
K
n
o
w
-
h
o
w
w
i
s
d
o
m
P
o
r
t
f
o
l
i
o
Unit Standard Capacity Breakdown
Polynomials and Rational
Functions
Chapter 5
P5.1
Solve equations and inequalities involving rational
functions. Graph rational functions given factored
form using zeros, identifying asymptotes, analyzing
their behavior for large x values and testing intervals.
P5.2
Given vertical and horizontal asymptotes, find an
expression for a rational function with these functions.
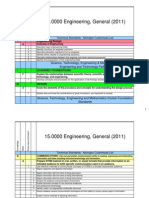
Unit Standard Capacity Breakdown
Exponential and
Logarithmic Functions
Chapter 6
P1.2
Know and use a definition of a function to decide if a given relation
is a function.
P1.3
Write an expression for the composition of one given function with
another and find domain, range and graph of the composite
function. Recognize components when a function is composed of
two or more elementary functions.
P1.4
Determine whether a function (given symbolically or graphically)
has an inverse and express the inverse if it exists. Know and
interpret the function notation for inverses
P1.5
Determine whether two given functions are inverses, using
composition.
P2.1
Use the inverse relationship between exponential and logarithmic
functions to solve equations and problems.
P2.2
Graph logarithmic functions. Graph translations and reflections of
these functions
P2.3
Solve exponential and logarithmic equations. For those that
cannot be solved analytically, use graphical methods to find
approximate solutions.
P2.4
Solve exponential and logarithmic equations when possible.
For those that cannot be solved analytically, use graphical
methods to find approximate solution.
Pre-Calculus and Trigonometry Capacity Matrix
Purpose and Vision
Understanding and Applying Pre-Calculus and
Trigonometry
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
K
n
o
w
l
e
d
g
e
K
n
o
w
-
h
o
w
w
i
s
d
o
m
P
o
r
t
f
o
l
i
o
Unit Standard Capacity Breakdown
Exponential and
Logarithmic functions
Chapter 6
P2.5
Explain how the parameters of an exponential or
logarithmic model relate to the data set or situation
being modeled. Find an exponential or logarithmic
function to model a given data set or situation. Solve
problems involving exponential growth and decay.
P3.1
Solve quadratic-type equations by substitution(eg. e
2x
-
4e
x+4
= 0)
P3.3
Explain how the parameters of an exponential or
logarithmic model relate to the data set or situation
being modeled. Find a quadratic function to model
given data or situation.
Unit Standard Capacity Breakdown
Trigonometric Functions
Chapter 7
P6.1
Define using the unit circle, graph and use all
trigonometric functions of any angle. Convert
between radian and degree measure. Calculate
arc length, and area of a sector in a given circle.
X
P6.2
Graph transformations of the sine and cosine functions
(involving changes in amplitude, period, midline and
phase changes) and explain the relationship between
constraints in the formula and transformed graph.
X
Sec 7.7
Graph transformations of tangent functions
X
P6.6
Prove trigonometric identities and derive some of
the basic ones. Know the fundamental identities.
X
P6.7
Find a sinusoidal function to model a given data
set or situation and explain how the parameters
of the model relate to the data set or situation.
X
Pre-Calculus and Trigonometry Capacity Matrix
Purpose and Vision
Understanding and Applying Pre-Calculus and
Trigonometry
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
K
n
o
w
l
e
d
g
e
K
n
o
w
-
h
o
w
w
i
s
d
o
m
P
o
r
t
f
o
l
i
o
Unit Standard Capacity Breakdown
Analytic Trigonometry
Chapter 8
P6.3
Know the basic properties of the inverse trigonometric
functions: sin
-1
x, cos
-1
x, tan
-1
x, including their domains
and ranges. Recognize their graphs.
P6.4
Know basic trigonometric identities for sine cosine and
tangent ( Fundamental, sum and difference, co
functions, double and half angle formulas)
X X Robot 101
P6.6
Prove trigonometric identities and derive some of the
basic ones ( double angle formulas from sum and
difference formulas, half angles formula from double
angle formula)
X
P6.5
Solve trigonometric equation using basic identities and
inverse trigonometric functions
X X Robot 101
CCSS
Prove the addition and subtraction formula for sine,
cosine, and tangent and use them to solve problems.
Unit Standard Capacity Breakdown
Miscellaneous
Application of
Trigonometric
Functions
Real world applications of problems involving
trigonometry such as the laws of sine and cosine.
X X Shot in the Dark
Unit Standard Capacity Breakdown
Polar Coordinates
Chapter 10
P9.1
Convert between polar and rectangular coordinates.
Graph functions given in polar coordinates
P9.2
Write complex numbers in polar form. Know and use
De Moivres Theorem
P9.3
Evaluate parametric equations for given values of
parameter
P9.4 Convert between parametric and rectangular forms of
Pre-Calculus and Trigonometry Capacity Matrix
equations
Purpose and Vision
Understanding and Applying Pre-Calculus and
Trigonometry
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
K
n
o
w
l
e
d
g
e
K
n
o
w
-
h
o
w
w
i
s
d
o
m
P
o
r
t
f
o
l
i
o
Polar Coordinates
Chapter 10 P9.5
Graph curves described by parametric equation
and find parametric equations for a given graph
P9.6
Use parametric equations in applied contexts to
model situations and solve problems
CCSS
Represent complex numbers on the complex
plane in rectangular and polar form (including real
and imaginary numbers), and explain why the
rectangular and polar forms of a given complex
number represent the same number.
Unit Standard Capacity Breakdown
Vectors, Matrices, and
Systems of Equations
Chapter 12
P7.1
Perform operations (addition, subtraction, and
multiplication by scalars) on vectors in the plane. Solve
applied problems using vectors.
X
P7.2
Know and apply the algebraic and geometric definitions of
the dot product using vectors
P7.3
Know the definitions of matrix addition and multiplication.
Add, subtract, and multiply matrices. Multiply a vector by a
matrix.
X
P7.5
Define the inverse of a matrix and compute the inverse of
two-by-two and three-by-three matrices when they exist
X
P7.6
Explain the role of determinants in solving systems of linear
equation using matrices and compute determinants of two-
by-two and three-by-three matrices. Use Crammers Rule
X X Robot 101
P7.7
Write systems of two and three equations in matrix form.
Solve such systems using Gaussian elimination or inverse
matrices.
X
Pre-Calculus and Trigonometry Capacity Matrix
P7.8
Represent and solve systems of inequalities in two variable
and apply these methods in linear
programming situations to solve problems
Purpose and Vision
Understanding and Applying Pre-Calculus and
Trigonometry
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
K
n
o
w
l
e
d
g
e
K
n
o
w
-
h
o
w
w
i
s
d
o
m
P
o
r
t
f
o
l
i
o
Sequences, Series and
Math Induction
Chapter 13
P8.1 Know, explain and use sigma and factorial notation
P8.2
Given arithmetic, geometric, or recursively defined
sequence, write an expression for the nth term when
possible. Write a particular term of a sequence when given
the nth term.
P8.3
Understand, explain and use the formulas for the sums of
finite arithmetic and geometric sequences
P8.4
Compute the sums of infinite geometric series. Understand
and apply the convergence criterion for geometric series.
P8.5
Understand and explain the principle of mathematical
induction and prove statements using mathematical
induction
P8.6
Prove the binomial theorem using mathematical induction.
Show its relationship to Pascals Triangle and to
combinations. Use the binomial theorem to find terms in
the expansion of a binomial to a power greater than 3.
Analytical Geometry
Chapter 11
P9.7
Know, explain, and apply the locus definitions of parabolas,
ellipses and hyperbolas and recognize conic sections in
applied situations
P9.8
Identify parabolas, ellipses and hyperbolas from equations,
write the equations in standard form, and sketch an
appropriate graph of the conic section
P9.9
Derive equation for a conic section from given geometric
information. Identify key characteristics of a conic section
form its equation or graph.
P9.10
Identify conic sections whose equations are in polar or
parametric form.
Pre-Calculus and Trigonometry Capacity Matrix
You might also like
- Smart Watch User Manual: Please Read The Manual Before UseDocument9 pagesSmart Watch User Manual: Please Read The Manual Before Useeliaszarmi100% (3)
- NUET 2022 Mathematics SpecificationDocument9 pagesNUET 2022 Mathematics SpecificationАдина Сагнаева100% (1)
- Stress Management PPT FinalDocument7 pagesStress Management PPT FinalAdarsh Meher100% (1)
- Calculation of The Current Transformer Accuracy Limit FactorDocument14 pagesCalculation of The Current Transformer Accuracy Limit FactorWeiKiat Goh67% (3)
- Sermo 13 de Tempore (2 Feb in Praes)Document1 pageSermo 13 de Tempore (2 Feb in Praes)GeorgesEdouardNo ratings yet
- QTM - Soap Battle CaseDocument7 pagesQTM - Soap Battle CaseAshish Babaria100% (1)
- Calculus Capcity Matrixssecondssememster113 14Document8 pagesCalculus Capcity Matrixssecondssememster113 14api-243626014No ratings yet
- Algebra 2 CriticalDocument10 pagesAlgebra 2 Criticalapi-115680157No ratings yet
- Algebra 2Document7 pagesAlgebra 2api-262893996No ratings yet
- Algebra II Honors Common Core Standards: Greenville CountyDocument4 pagesAlgebra II Honors Common Core Standards: Greenville CountyStephanie ClareyNo ratings yet
- North Carolina Standard Course of Study North Carolina Math 3Document8 pagesNorth Carolina Standard Course of Study North Carolina Math 3Alex WellmanNo ratings yet
- NC Math 1 2016-17Document7 pagesNC Math 1 2016-17api-236042577No ratings yet
- A Visual Inspection of The Real Roots of A Polynomial FunctionDocument10 pagesA Visual Inspection of The Real Roots of A Polynomial FunctionxcrunitccNo ratings yet
- Application and Interpretations Standard Level SyllabusDocument6 pagesApplication and Interpretations Standard Level SyllabusTheTrolLordNo ratings yet
- Ut3 ConceptsDocument2 pagesUt3 Conceptsapi-261139685No ratings yet
- Module 7Document18 pagesModule 7shaina sucgangNo ratings yet
- Algebric Modeling Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013Document3 pagesAlgebric Modeling Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013api-70433300No ratings yet
- Cbse 11th Class Maths SyllabusDocument8 pagesCbse 11th Class Maths Syllabussanjeev kumarNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Syllabus 2014-2015Document5 pagesMath 7 Syllabus 2014-2015api-266524097No ratings yet
- Alg 2 Polynomial UnitDocument3 pagesAlg 2 Polynomial Unitapi-368100366No ratings yet
- Algebra I Pacing Guides 2015-2016 1Document9 pagesAlgebra I Pacing Guides 2015-2016 1api-252392763No ratings yet
- Calculus Capcity Matrix Second Sememster 13 14Document8 pagesCalculus Capcity Matrix Second Sememster 13 14api-245300570No ratings yet
- 8th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapDocument6 pages8th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapMarcos ShepardNo ratings yet
- BK Chap07Document78 pagesBK Chap07Osama_Othman010% (1)
- 11th MathsDocument4 pages11th Mathsavinash mishraNo ratings yet
- The Big 50 Revision C3Document5 pagesThe Big 50 Revision C3Jithin RajanNo ratings yet
- Learning Competency DirectoryDocument3 pagesLearning Competency DirectoryRaymond Gorda88% (8)
- Coordinate Algebra Unit 3Document8 pagesCoordinate Algebra Unit 3crazymrstNo ratings yet
- Unit - Unit 4 - Quadratic Equations and Functions - 20200503161254Document5 pagesUnit - Unit 4 - Quadratic Equations and Functions - 20200503161254Alex WellmanNo ratings yet
- FEM AssignmentDocument8 pagesFEM AssignmentVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- MHF4U OutlineDocument10 pagesMHF4U OutlineFrederick Zhang100% (1)
- Mccrs-Compacted Math 8Document7 pagesMccrs-Compacted Math 8api-318685719No ratings yet
- Algebra 2 UnitsDocument12 pagesAlgebra 2 Unitsxedef17No ratings yet
- CS240A: Databases and Knowledge BasesDocument20 pagesCS240A: Databases and Knowledge BasesJohnZNo ratings yet
- C-14 Dme-Iv SemDocument39 pagesC-14 Dme-Iv SemsivaenotesNo ratings yet
- Ut4 ConceptDocument1 pageUt4 Conceptapi-261139685No ratings yet
- SL Year Plans DP 2024Document6 pagesSL Year Plans DP 2024Elias GranditsNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus: Updated 09/15/04Document14 pagesPre-Calculus: Updated 09/15/04Neha SinghNo ratings yet
- Domain Dependence in Parallel Constraint SatisfactionDocument6 pagesDomain Dependence in Parallel Constraint Satisfactionmax9467No ratings yet
- Math RB RL GR12 PreCalculus30Document4 pagesMath RB RL GR12 PreCalculus30arg456No ratings yet
- RJournal 2012-2 Kloke+McKeanDocument8 pagesRJournal 2012-2 Kloke+McKeanIntan PurnomosariNo ratings yet
- Math Unit 3 Plan TollesonDocument2 pagesMath Unit 3 Plan TollesonLindseyNo ratings yet
- MAT114 Multivariable Calculus and Differential Equations ETH 1.01 AC34Document2 pagesMAT114 Multivariable Calculus and Differential Equations ETH 1.01 AC34Karan DesaiNo ratings yet
- Foundation Year Program Entrance Tests Mathematics Specification For Nufyp Set 2020Document9 pagesFoundation Year Program Entrance Tests Mathematics Specification For Nufyp Set 2020Даниал ГабдоллаNo ratings yet
- 1608cbb682872f - 48646037354Document4 pages1608cbb682872f - 48646037354Hamza GhaffarNo ratings yet
- R O M H A H A: Educed Rder Odeling Ybrid Pproach Ybrid PproachDocument30 pagesR O M H A H A: Educed Rder Odeling Ybrid Pproach Ybrid PproachLei TuNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 StandardsDocument6 pagesAlgebra 1 Standardsapi-306943671No ratings yet
- Individual Development Profile Report: Muhammad, TalibahDocument5 pagesIndividual Development Profile Report: Muhammad, TalibahGlamrockFreddy TLCNo ratings yet
- Describe The Structure of Mathematical Model in Your Own WordsDocument10 pagesDescribe The Structure of Mathematical Model in Your Own Wordskaranpuri6No ratings yet
- 1.1 Arrangements: C C F F C CDocument18 pages1.1 Arrangements: C C F F C CAhmed SalimNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Fractional CalculusDocument29 pagesAn Introduction To Fractional CalculusFredrik Joachim GjestlandNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Algebra Common Core WorkbooksDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Algebra Common Core WorkbooksLindaNo ratings yet
- MATH 150 Course OutlineDocument5 pagesMATH 150 Course OutlinePerter K MNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Ni RobyDocument9 pagesSyllabus Ni RobyRoby PadillaNo ratings yet
- Algebra II Unit 1 PlanningDocument7 pagesAlgebra II Unit 1 PlanningAdam LadjNo ratings yet
- Calculus and Vectors - Chapter 1Document6 pagesCalculus and Vectors - Chapter 1myobNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document86 pagesClass 1allan surasepNo ratings yet
- Core Competencies - Math Iv Advanced Algebra, Trigonometry and Statistic First Quarter A. FunctionsDocument5 pagesCore Competencies - Math Iv Advanced Algebra, Trigonometry and Statistic First Quarter A. FunctionsFrederichNietszcheNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument33 pagesFunctionsIrene Mae BeldaNo ratings yet
- Honors Final ReviewDocument7 pagesHonors Final ReviewVivian HoNo ratings yet
- ADA - Question - BankDocument6 pagesADA - Question - Bankananyanalawade2004No ratings yet
- CPNA Course SyllabusDocument5 pagesCPNA Course SyllabusTorNo ratings yet
- Semester:-Sem VI Branch: - Computer Science and Engineering Subject: - Design and Analysis of AlgorithmDocument16 pagesSemester:-Sem VI Branch: - Computer Science and Engineering Subject: - Design and Analysis of AlgorithmVaibhav DewdheNo ratings yet
- The Calculi of Lambda-Conversion (AM-6), Volume 6From EverandThe Calculi of Lambda-Conversion (AM-6), Volume 6Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Linear Algebra and Linear Operators in Engineering: With Applications in Mathematica®From EverandLinear Algebra and Linear Operators in Engineering: With Applications in Mathematica®No ratings yet
- Seminars s1 2015Document2 pagesSeminars s1 2015api-243909487No ratings yet
- Internship PresentationDocument3 pagesInternship Presentationapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Tours s1 14 15 SeniorsDocument2 pagesTours s1 14 15 Seniorsapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Internship SummaryDocument1 pageInternship Summaryapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Ela Capacity MatrixDocument18 pagesEla Capacity Matrixapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Projects s1 13 14Document1 pageProjects s1 13 14api-243909487No ratings yet
- Alloy PresentationDocument16 pagesAlloy Presentationapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Cost and Price SheetDocument2 pagesCost and Price Sheetapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Employability Skills Matrix 09 10Document2 pagesEmployability Skills Matrix 09 10api-243909487No ratings yet
- The CompanyDocument1 pageThe Companyapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Time ChartsDocument1 pageTime Chartsapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Project Planning StandardsDocument19 pagesProject Planning Standardsapi-245213984No ratings yet
- Mentor Page 1 13 14Document2 pagesMentor Page 1 13 14api-243909487No ratings yet
- OutlineDocument6 pagesOutlineapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Engineering Graphical Communications StandardsDocument5 pagesEngineering Graphical Communications Standardsapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Overview of Engineering StandardsDocument12 pagesOverview of Engineering Standardsapi-244914824No ratings yet
- ThegoalisleanDocument3 pagesThegoalisleanapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering StandardsDocument1 pageElectrical Engineering Standardsapi-244958549No ratings yet
- Design Processes-Problem Solving StandardsDocument8 pagesDesign Processes-Problem Solving Standardsapi-244958549No ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Technologies StandardsDocument1 pageCivil Engineering Technologies Standardsapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Materials and Engineering StandardsDocument1 pageMaterials and Engineering Standardsapi-244958549No ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering StandardsDocument1 pageMechanical Engineering Standardsapi-245297609No ratings yet
- Logistical Engineering StandardsDocument1 pageLogistical Engineering Standardsapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Engineering Ethics StandardsDocument4 pagesEngineering Ethics Standardsapi-245297609No ratings yet
- Thermal Dynamic Principals StandardsDocument1 pageThermal Dynamic Principals Standardsapi-244954731No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Assembly and Fabrication StandardsDocument1 pageManufacturing Assembly and Fabrication Standardsapi-244954731No ratings yet
- Color Codes and Irregular MarkingDocument354 pagesColor Codes and Irregular MarkingOscarGonzalezNo ratings yet
- Wjec Biology SpectificaionDocument93 pagesWjec Biology SpectificaionLucy EvrettNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Lecture NoteDocument15 pagesEpilepsy Lecture Notetamuno7100% (2)
- Tamil NaduDocument64 pagesTamil Nadushanpaga priyaNo ratings yet
- Pi 0614 Hiblack f890b en WebDocument2 pagesPi 0614 Hiblack f890b en Web王偉仲No ratings yet
- NDTDocument2 pagesNDTRoop Sathya kumarNo ratings yet
- 10 - Enzymes - PPT - AutoRecoveredDocument65 pages10 - Enzymes - PPT - AutoRecoveredFaith WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Monk - Way of The Elements RevisedDocument3 pagesMonk - Way of The Elements Revisedluigipokeboy0% (1)
- 2UEB000487 v1 Drive On GeneratorDocument19 pages2UEB000487 v1 Drive On GeneratorSherifNo ratings yet
- Movimiento Circular, Momentun Lineal y EnergíaDocument92 pagesMovimiento Circular, Momentun Lineal y EnergíaJulio César Macías ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Transformations of Tschirnhaus, Bring and Jerrard4s++Document5 pagesPolynomial Transformations of Tschirnhaus, Bring and Jerrard4s++wlsvieiraNo ratings yet
- Taper Lock BushesDocument4 pagesTaper Lock BushesGopi NathNo ratings yet
- Master Key Utbk Saintek 2022 (Paket 3) Bahasa InggrisDocument5 pagesMaster Key Utbk Saintek 2022 (Paket 3) Bahasa InggrisRina SetiawatiNo ratings yet
- Augocom Micro 768 Battery Tester User ManualDocument29 pagesAugocom Micro 768 Battery Tester User ManualJorge PontonNo ratings yet
- 173 EvidenceDocument6 pages173 EvidenceSantiago RubianoNo ratings yet
- Lab Centre of Pressure Ecw341Document4 pagesLab Centre of Pressure Ecw341danialNo ratings yet
- Module 12. Big Issues Lesson 12a. Reading. Pages 140-141: No Words TranslationDocument4 pagesModule 12. Big Issues Lesson 12a. Reading. Pages 140-141: No Words TranslationLeonardo Perez AlegriaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument11 pagesChemistry Notesraifaisal9267% (12)
- TA308 616configurationDocument1 pageTA308 616configurationJesus AvilaNo ratings yet
- Afectiuni Si SimptomeDocument22 pagesAfectiuni Si SimptomeIOANA_ROX_DRNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: W-Series WSI 6/LD 10-36V DC/ACDocument12 pagesData Sheet: W-Series WSI 6/LD 10-36V DC/ACLUIS FELIPE LIZCANO MARINNo ratings yet
- Logistics Operation PlanningDocument25 pagesLogistics Operation PlanningLeonard AntoniusNo ratings yet
- Avionic ArchitectureDocument127 pagesAvionic ArchitectureRohithsai PasupuletiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Steel Structure Concepts: 2 MonthsDocument4 pagesAdvanced Steel Structure Concepts: 2 MonthsAnkit SoniNo ratings yet
- Amc 20-21Document33 pagesAmc 20-21Vasco M C SantosNo ratings yet