Professional Documents
Culture Documents
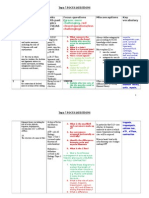
Topic 5 (Focus Questions)
Uploaded by
Saifulahmed49Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 5 (Focus Questions)
Uploaded by
Saifulahmed49Copyright:
Available Formats
Topic 5
Less
on
Area of
specifcation
covered
Links
with past
topics
GCSE/AS
level
Focus questions Misconceptions Ke
voca!ular
1
10. Explain that the
numbers and distribution of
organisms in a habitat are
controlled by biotic and
abiotic factors.
11. Describe how to carry
out a study on the ecology
of a habitat to produce valid
and reliable data (including
the use of uadrats and
transects to assess
abundance and distribution
of organisms and the
measurement of abiotic
factors! e.g. solar energy
input! climate! topography!
oxygen availability and
edaphic factors".
1#. Explain how the
concept of niche accounts
Ecosystem
Ecology
What affects the
distribution and
abundance of species in a
habitat?
What is the difference
between valid and
reliable?
What is succession?
How important is the role
of pioneer species in
succession?
Describe what you would
see in a climax community
What is the difference
between secondary
succession and deflected
succession?
What is a niche?
$hich sampling method to
use% transect&uadrat
$hich method to use to
measure abundance and
distribution
Explaining what is a niche
Succession
Habitat
Niche
Community
Biosphere
Ecosystem
opulation
Species
Biotic
!biotic
Edaphic
Topic 5
for distribution and
abundance of organisms in
a habitat.
1' Describe the concept of
succession to a climax
community.
#
(. )arry out calculations of
net primary productivity
and explain the relationship
between gross primary
productivity! net primary
productivity and plant
respiration.
*. )alculate the efficiency
of energy transfers between
trophic levels.
Ecology Do plants store all the
"lucose it produces?
Why is net primary
productivity less than
"ross primary
productivity?
Why is some ener"y lost
from one trophic level to
the next?
Why is the role of
decomposers important in
increasin" the efficiency of
ener"y transfer?
How can you increase the
efficiency of ener"y
transfer?
How do you calculate
efficiency?
Explain what is energy
stored a biomass+
Difference between gross
and net
Does all the sunlight which
falls on a leaf get absorbed
by the chlorophyll+
#ood chain
#ood web
$rophic level
Consumers
Herbivores
Carnivores
Decomposers
roducers
%
N
Ener"y
&espiration
Efficiency
' and , '() -utline the causes of
global warming. including
the role of greenhouse gases
/)0E global
warming
What is the difference
between "lobal warmin"
and the "reenhouse effect?
Explaining the difference
between global warming
and greenhouse effect
%lobal warmin"
%reenhouse effect
Carbon dioxide
Topic 5
(carbon dioxide and
methane" in the greenhouse
effect
'*. 1nalyse and interpret
different types of evidence
for global warming and its
causes (records of carbon
dioxide! temperature
records! pollen in peat bogs
and dendrochronolgy"
recognising correlations and
casual relationships
/reenhouse
effect
)arbon cycle
How do the "reenhouse
"ases stop infrared
radiation from escapin"?
What would be the
conse+uence of any chan"e
in the level of "reenhouse
"as?
How are "reenhouse "ases
produced?
Does a correlation mean a
cause?
How can you use carbon
dioxide and temperature
records to show evidence
for "lobal warmin"?
Why can you use pollen
"rains as evidence for
"lobal warmin"?
How is the width of tree
rin"s related to their
conditions of "rowth?
2ow does analysing peat
and tree ring studies show
evidence of changing
climate
,ethane
Dendrochronlo"y
Correlations
eat bo"
ollen
5 '() -utline the causes of
global warming. including
the role of greenhouse gases
(carbon dioxide and
methane" in the greenhouse
effect
/)0E global
warming
/reenhouse
effect
!ctivity -)'./ what are the
different parts of the
model correspondin" to?
0s your conclusion valid?
What are the limitations to
this model -)'.?
Explaining the difference
between valid and reliable
data+
3f one measurement of
temperature does not fit the
%lobal warmin"
%reenhouse "as
%reenhouse effect
Climate model
Extrapolation
#actors
Topic 5
'1) Describe that data can
be extrapolated to ma4e
predictions! that these are
used in models for future
global warming! and that
these models have
limitations
)arbon cycle
Why are climate models
bein" used?
How can climate models
be used to ma2e
predictions?
What are the problems of
usin" climate models?
Why is it difficult to ma2e
an accurate prediction?
Explain how other
variables affect "lobal
mean surface
temperature?
What assumptions are you
ma2in" when you are
extrapolatin" data?
pattern! do you disregard the
whole set of data+ )an there
be an explanation for this+
Drawing lines to extrapolate
data
Explaining how the
different factors on page ,5
affect the temperature
(activity 5.15! ,"
&eliability
Carbon dioxide
$rends
3alidity
5 .4) describe the way in
which scientific conclusions
about controversial issues!
such as what actions should
be ta4en to reduce global
warming or the degree to
which humans are affecting
global warming! can
sometimes depend on who
is reaching the conclusions
/)0E%
)ase study%
creating
arguments and
reaching a
conclusion
based on the
evidence
!ctivity -)'5/ describe some
stron" data which proves a lin2
between carbon dioxide and
"lobal warmin"
Why is there controversy
surroundin" the issue of "lobal
warmin"?
Why can the same data be
interpreted differently by
different people? %ive some
examples
How can you use the
2ow to identify wea4nesses
in data&strong data (5.1'"
$hy there is controversy
surrounding the issue of
global warming
Explaining how the same
data can be interpreted in
different ways.
Controversy
Ethical ar"ument
$heory
Evidence
predictions
Topic 5
discrepancies between surface
temperature and upper air
temperature to 6ustify the case of
"lobal warmin"?
What impact do sulphate
particles have on climate
fluctuation?
What are the evidences for "lobal
warmin" and how do they prove a
lin2?
( '7) Explain the effect of
increasing temperature on
the rate of en6yme activity
in plants! animals! micro.
organisms
/)0E
En6ymes!
7ates of
reaction
8se scientific explanation to
explain your hypothesis)
What are the ha9ards associated
with this experiment and what
are the precautions you will ta2e?
How have you chan"ed your
method after conductin" the
preliminary experiment and why?
How did you ensure that the data
you collected was valid?
How do you 2now that your data
is reliable?
How did you decide whether or
not you had any anomalous
results?
Explain why you may have "ot
$hen carrying out ris4
assessment also thin4ing
about the products being
produced and how best to
dispose of the products.
2ave they chosen a good
range of temperatures which
will allow them to see a
clear pattern and ma4e a
strong conclusion about
what is the optimum
temperature+
Ensuring that the catalase!
hydrogen peroxide reach the
Hypothesis
Ha9ards
recautions
3ariables
&an"e
3alid
&eliable
!nomalous
:imitations
Topic 5
some anomalous results)
What are the limitations of the
method used?
How can you improve the method
and how will this affect the
results?
How does temperature affect the
en9yme activity of en9ymes found
in animals and microor"anisms?
%ive examples
desired temperature before
starting experiment.
$hy students shouldn8t
swirl the boiling tube during
the experiment! or ma4e
sure they do swirl in all
temperatures
* ';) Describe how to
investigate the effects of
temperature on the
development of organisms
(e.g. seedling growth rate!
brine shrimp hatch rates"
9lanning
experiments
What are the ethical issues arisin"
from the use of livin" or"anisms?
How have you considered the well
bein" of the or"anisms used?
How did you ensure that the data
you collected was valid?
How can you ensure that the
results are reliable?
What other factors could affect
the hatchin" success? Why?
What is the difference between
random errors and systematic
errors?
What are the random and
systematic errors that can arise
from this experiment?
How does this experiment help to
prove the effects of "lobal
warmin"?
$hat impact is the
temperature having on the
life cycle of the organism
and how does this lin4 in
with climate change+
To be aware that it may not
be possible to control all the
variables.
&andom errors
Systematic errors
Ethical issues
3alid
&eliable
:ife cycle
Climate chan"e
henolo"y
Topic 5
What impact has climate chan"e
had on the development of
or"anisms? "ive specific examples
What are the problems with e""s
hatchin" too early?
: '-) Describe the effects of
global warming (rising
temperature! changing
rainfall patterns and
changes in seasonal cycles"
on plants and animals
(distribution of species!
development and life
cycles"
En6ymes How will an increase in
temperature affect the rate of
photosynthesis?
Why does the rate of
photosynthesis affect the
development of plants?
Why will the distribution of
species be affected due to climate
chan"e? What problems may this
"ive rise to?
What will be the affect of pests
and diseases spreadin" to
different areas?
How mi"ht plant species be
dispersed to a different area?
Comment and explain on the time
ta2en for a species to distribute to
another area?
What are the problems with e""s
hatchin" too early?
The effect on
photosynthesis if the
temperature increases above
the optimum temperature
3s temperature the only
limiting factor when it
comes to the rate of
photosynthesis
The effect of shorter life
cycle on other organisms
and availability of food.
The effect of species
distribution on the current
inhabitants.
Dominant
Distribution
Dispersal
Competition
&ate
En9ymes
:ife cycle
hotoperiod
Development
10
#1. Describe how evolution
;utation How can allele fre+uency chan"e
over time?
Explaining evolution using
4ey concepts
Evolution
Natural selection
Topic 5
(a change in the allele
freuency" can come about
through gene mutation and
natural selection.
#'. Describe the role of the
scientific community in
validating new evidence
(including molecular
biology! e.g. D<1!
proteomics" supporting the
accepted scientific theory of
evolution (scientific
=ournals! the peer review
process! scientific
conferences".
Evolution
<atural
selection
What is natural selection?
Why is it important to present
scientific findin"s in conferences?
What are the advanta"es and
disadvanta"es of publishin"
scientific ideas directly online?
What are reasons for havin" a
paper peer reviewed?
How has "enomics and
proteomics provided evidence for
evolution?
What are the different types of
molecular evidence supportin"
the theory of evolution?
$hy should ideas be peer
reviewed+
roteomics
%enomics
eer review
DN!
Hybridi9ation
DN! profilin"
DN! and protein
se+uencin"
DN! molecular
cloc2s
11
##. Explain how
reproductive isolation can
lead to speciation
<atural
selection
Define species
What is reproductive isolation?
What is the impact of havin"
individuals separated by a
"eo"raphical feature?
Why mi"ht the individuals face
different selection pressures?
Will the evolution of both the
populations be the same?
What are the reasons why two
species may not be able to
interbreed?
$hy two populations may
face different selection
pressures+
$hy may the two
populations be unable to
interbreed! which is a
conseuence of the random
mutations accumulating
$riting long answer
uestions on speciation
Speciation
&eproductive
isolation
$emporal
Ecolo"ical
Behavioural
hysical
incompatibility
Hybrid inviability
Hybrid sterility
Topic 5
1#
:. Discuss how
understanding the carbon
cycle can lead to methods
to reduce atmospheric
levels of carbon dioxide
(including the use of
biofuels and reforestation".
)arbon cycle What are the ways in which
carbon is incorporated into the
atmosphere?
What are the ways in reducin"
the amount of carbon from the
atmosphere?
0s there a balance?
What is the reasonin" for usin"
biofuels for maintainin" carbon
dioxide?
0s usin" biofuels an effective
solution?
$hy may different countries differ
about the views on biofuels+
How can we maintain the carbon
dioxide balance by reforestation?
Will reforestation really wor2?
Why?
3s the transport of biofuels
carbon neutral+
2ow much carbon dioxide
can the trees ta4e in! is there
a limit to the rate of
photosynthesis+
hotosynthesis
&espiration
Decay <
decomposition=
Biomass
Combustion
Carbon sin2
Deforestation
&eforestation
Biofuel
Bio"as
1'
#. Describe the structure of
chloroplasts in relation to
their role in photosynthesis.
'. Describe the overall
reaction of photosynthesis
as reuiring energy from
light to split apart the strong
bonds in water molecules!
storing the hydrogen in a
fuel (glucose" by combining
)hloroplast
function
photosynthesis
How are the thyla2oid
membranes adapted for the li"ht
dependent reactions?
How is the stoma adapted for the
li"ht independent reactions?
Why are starch "rains present in
chloroplasts?
What is the role of hydro"en in
photosynthesis?
What is N!D?
What is the difference between
$here are the en6ymes
located for the light
dependent and independent
stages
$hat is <1D9 and how
does it become reduced
;ain products needed for
light independent stage is
reduced <1D9 and 1T9
hotosynthesis
,icroscope
Chloroplast
Stroma
$hyla2oid
!$
Hydro"en
&eduction
N!D
En9ymes
Topic 5
it with carbon dioxide and
releasing oxygen into the
atmosphere.
reduced N!D and N!D?
Explain what is meant by the
reduction of carbon dioxide?
)arbon dioxide and water
have no direct contact
1, , Describe the light.
dependent reactions of
photosynthesis including
how light energy is trapped
by exciting electrons in
chlorophyll and the role of
these electrons in
generating 1T9! and
reducing <1D9 in
photophosphorylation and
producing oxygen through
photolysis of water.
5. Describe how
phosphorylation of 1D9
reuires energy and how
hydrolysis of 1T9 provides
an immediate supply of
energy for biological
processes.
)hloroplast
function
9hotosynthesis
7eduction
1T9
What are the useful products of
the li"ht dependent reaction?
How is li"ht involved in this first
sta"e?
Has any "lucose been produced at
this sta"e?
What does the electron transport
chain consist of?
How will the electron transport
chain be affected if one of the
carriers had a mutation?
What will be the result if all the
coen9yme N!D were reduced?
How will the reaction be effected
if no water was available?
What is needed for the photolysis
of water? 0s an en9yme involved?
Why is !$ an important ener"y
transfer molecule?
What happens durin" the
phosphorylation of !D?
How does the hydrolysis of !$
provide ener"y?
3f no <1D9 were present
the electrons would not be
accepted from the electron
transport chain and it will
stop
<1D9 must be regenerated
from reduced <1D9
Electrons must from the
splitting of water must
replace the electrons lost
from the chlorophyll
En6yme 1T9ase involved in
hydrolysis of 1T9
The role of water molecules
in releasing energy
(hydrolysis of 1T9"
hotophosphoryla
tion
!$
Hydrolysis
hotolysis
Excited
hotosystem
Electron
transport chain
N!D
:i"ht dependant
reaction
En9ymes
Electron
Hydro"en
Topic 5
15 , Describe the light.
dependent reactions of
photosynthesis including
how light energy is trapped
by exciting electrons in
chlorophyll and the role of
these electrons in
generating 1T9! and
reducing <1D9 in
photophosphorylation and
producing oxygen through
photolysis of water.
)hloroplast
function
photosynthesis
What is the name of the molecule
reduced in the li"ht dependent
sta"e?
What is a reducin" a"ent?
Will DC0 decolourise if left in
the dar2?
Will DC0 decolourise if there is
no chloroplast in the tube?
0f DC0 chan"es colour what
does this show? Where have the
electrons come from?
What molecule involved in
photosynthesis is DC0 behavin"
li2e?
How will the li"ht dependent
sta"es of photosynthesis be
affected if no carbon dioxide was
present?
$hat is a reducing agent+
$hat happens to the
reducing agent+
D)939 is behaving li4e
<1D9
Tube containing chloroplast
and D)939 in the light
should decolourise
DC0
&educin" a"ent
Electron acceptor
:i"ht dependent
reaction
15
5.Describe the light.
independent reactions as
reduction of carbon dioxide
using the products of the
light.dependent reactions
(carbon fixation in the
)alvin cycle! the role of /9!
/1>9! 7u?9 and
7@?30)-" and describe
the products as simple
sugars that are used by
)hloroplast
function
photosynthesis
What is carbon fixation?
Where is !$ needed in the
Calvin cycle?
Can the cycle occur in the absence
of reduced N!D?
What is the role of en9ymes in the
Calvin cycle?
How does !$ provide ener"y for
the reactions?
Can the cycle continue in the
dar2? Why?
2ow will the other products
in the cycle be affected if
one of the en6ymes has a
mutation+
The cycle cannot occur
without the products from
light dependent reaction
(1T9! reduced <1D9"
@nderstanding the numbers
Carbon fixation
En9yme
%
%!:
&uB
&8B0SC>
!$
&educed N!D
Su"ars
hosphorylation
Topic 5
plants! animals and other
organisms in respiration
and the synthesis of new
biological molecules
(including polysaccharides!
amino acids! lipids and
nucleic acids".
What are the products of the li"ht
independent sta"e and what are
their uses?
What will happen to the number
of &uB if there was a mutation
in en9yme &uB0SC>?
How will this affect the rest of the
cycle?
of carbon atoms involved in
the cycle
You might also like
- BiOLOGY Unit 4 NEW Revision NotesDocument37 pagesBiOLOGY Unit 4 NEW Revision NotesChinuNo ratings yet
- The Global Carbon Cycle and Climate Change: Scaling Ecological Energetics from Organism to the BiosphereFrom EverandThe Global Carbon Cycle and Climate Change: Scaling Ecological Energetics from Organism to the BiosphereNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement On Global WarmingDocument6 pagesThesis Statement On Global Warmingsheenawhiteoverlandpark100% (2)
- IX General Sc.Document3 pagesIX General Sc.Kulachi Hansraj Model School100% (1)
- Handbook of Environmental Economics: Environmental Degradation and Institutional ResponsesFrom EverandHandbook of Environmental Economics: Environmental Degradation and Institutional ResponsesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Cold Kills, Warmth Gives Life: There is More to Climate Change Than Global WarmingFrom EverandCold Kills, Warmth Gives Life: There is More to Climate Change Than Global WarmingNo ratings yet
- Lab Review 13 LabsDocument37 pagesLab Review 13 LabsPurePureMilkNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Andecosystem FunctioningDocument16 pagesBiodiversity Andecosystem FunctioningScorpion official gamingNo ratings yet
- Envisci PrelimDocument3 pagesEnvisci PrelimSecuretech Security Systems PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Check Your UnderstandingDocument4 pagesCheck Your UnderstandingSonia HajiyaniNo ratings yet
- 2012 APES Mid-Term Study GuideDocument6 pages2012 APES Mid-Term Study Guideinvisible_winterNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Kinetics 4 Biological Science - HammesDocument180 pagesThermodynamics Kinetics 4 Biological Science - Hammeshsteele2013No ratings yet
- Scientific Method Lab ReportDocument37 pagesScientific Method Lab ReportRituparn SinghNo ratings yet
- PDF DatastreamDocument53 pagesPDF DatastreamANGELCLYDE GERON MANUELNo ratings yet
- Principles of Environmental Physics: Plants, Animals, and the AtmosphereFrom EverandPrinciples of Environmental Physics: Plants, Animals, and the AtmosphereNo ratings yet
- Scientific Uncertainties: Unscientific ArgumentsDocument8 pagesScientific Uncertainties: Unscientific ArgumentsbillpaparounisNo ratings yet
- Dissertation UcrDocument5 pagesDissertation UcrBuyCollegePapersUK100% (1)
- Pisa Science QuestionDocument12 pagesPisa Science QuestionDira KadirNo ratings yet
- Global Change and the Terrestrial Biosphere: Achievements and ChallengesFrom EverandGlobal Change and the Terrestrial Biosphere: Achievements and ChallengesNo ratings yet
- BIO 111 Exam 1 TopicsDocument2 pagesBIO 111 Exam 1 Topicspanzmo01No ratings yet
- Philosophy and Fundamental ConceptsDocument63 pagesPhilosophy and Fundamental ConceptsSarah Wulan SariNo ratings yet
- The Helix Charter HS Lab ReportDocument19 pagesThe Helix Charter HS Lab ReportChristian AlvarezNo ratings yet
- A Scientific Paper in Subject of "Applied Ethics" Topic: "What Is Climate Change, Why and How Can We Save Our Environment?"Document14 pagesA Scientific Paper in Subject of "Applied Ethics" Topic: "What Is Climate Change, Why and How Can We Save Our Environment?"Aki ĆivokatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 and 02 Book AnswersDocument76 pagesChapter 01 and 02 Book Answersfilip78fNo ratings yet
- Cien Años de Ecologia Del PaisDocument19 pagesCien Años de Ecologia Del PaisEdwin L Ayala PNo ratings yet
- Preparation, Characterization, Properties, and Application of NanofluidFrom EverandPreparation, Characterization, Properties, and Application of NanofluidNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Quarter 1 Common LabDocument4 pagesChemistry Quarter 1 Common LabLynsey WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 5d83b684c0fa4b974de9b431 - HS Biology 1 - Course #2000310Document7 pages5d83b684c0fa4b974de9b431 - HS Biology 1 - Course #2000310Lerante LaubaxNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry PDFDocument283 pagesPhysical Chemistry PDFzerocool86No ratings yet
- Thermal and Energetic Studies of Cellular Biological SystemsFrom EverandThermal and Energetic Studies of Cellular Biological SystemsA. M. JamesNo ratings yet
- Investigating Factors Affecting The Rate of Photosynthesis: QuestionsDocument3 pagesInvestigating Factors Affecting The Rate of Photosynthesis: QuestionsChin CustodioNo ratings yet
- Biology SyllabusDocument6 pagesBiology Syllabusapi-268326026No ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction Lab Report PDFDocument15 pagesRate of Reaction Lab Report PDFRemuz G. EbuengaNo ratings yet
- Rod Ö F. A. Comfn Global ClimateDocument303 pagesRod Ö F. A. Comfn Global ClimatecbfodrtfNo ratings yet
- gr5 Science ImpactearthDocument2 pagesgr5 Science Impactearthapi-251387344No ratings yet
- Teaching Scheme - A2 ConceptDocument7 pagesTeaching Scheme - A2 Conceptaby251188No ratings yet
- CCV Tutwk4 Attribution Extremeevents 2014Document3 pagesCCV Tutwk4 Attribution Extremeevents 2014David CrowhurstNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Environmental Data and Ecological Parameters: Environmental Sciences and ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Environmental Data and Ecological Parameters: Environmental Sciences and ApplicationsS. E. JørgensenNo ratings yet
- Intro To ChemDocument5 pagesIntro To ChemJabadiah SlippersNo ratings yet
- Physiological Ecology of Forest Production: Principles, Processes and ModelsFrom EverandPhysiological Ecology of Forest Production: Principles, Processes and ModelsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 12-13 Apes Study Guide 2Document2 pages12-13 Apes Study Guide 2btec jNo ratings yet
- ) Anilin PDFDocument1,616 pages) Anilin PDFAnisa RachmadaniNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Ecosystem FunctioningDocument15 pagesBiodiversity and Ecosystem FunctioningsabanNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 On The Wild Side Revision QuestionsDocument2 pagesTopic 5 On The Wild Side Revision QuestionsDhruti MysoreNo ratings yet
- Standard of LivingDocument7 pagesStandard of LivingSaifulahmed49No ratings yet
- Balance of PaymentDocument4 pagesBalance of PaymentSaifulahmed49No ratings yet
- Topic 7 Focus QuestionsDocument17 pagesTopic 7 Focus QuestionsSaifulahmed49No ratings yet
- 2 Calculating Energy Change For An Experimental ReactionDocument5 pages2 Calculating Energy Change For An Experimental ReactionSaifulahmed49No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Revision Business StudiesDocument19 pagesUnit 3 Revision Business StudiesSaifulahmed49No ratings yet
- 1-Enthalpy Intro DefinitionsDocument6 pages1-Enthalpy Intro DefinitionsSaifulahmed49No ratings yet
- Mod 1 Revision Guide Organic2Document6 pagesMod 1 Revision Guide Organic2Saifulahmed49No ratings yet
- As Unit 2 June 2012 Exam PaperDocument36 pagesAs Unit 2 June 2012 Exam Paperapollo3605693No ratings yet
- Optical Isomerism - Edexcel Chemistry Unit 2Document9 pagesOptical Isomerism - Edexcel Chemistry Unit 2Da GuyNo ratings yet
- On The Wild Side: A Extensions 5.4 To 5.7Document5 pagesOn The Wild Side: A Extensions 5.4 To 5.7Saifulahmed49No ratings yet
- Infections, Immunity and Forensics: A Extensions 6.7 To 6.11Document4 pagesInfections, Immunity and Forensics: A Extensions 6.7 To 6.11Saifulahmed49No ratings yet
- Forest Fires: Causes and Impact On Environment: October 2020Document4 pagesForest Fires: Causes and Impact On Environment: October 2020JorgeNo ratings yet
- Namba Park Sub by - SoorajDocument25 pagesNamba Park Sub by - SoorajsoorajNo ratings yet
- Mangrove Rehabilitation Guide BookDocument68 pagesMangrove Rehabilitation Guide BookHolid Mrys0% (1)
- Philo From Abella L4Document6 pagesPhilo From Abella L4Elexis CastilloNo ratings yet
- Sahara Desert - Science PioloDocument6 pagesSahara Desert - Science PioloEsperanza M. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Allamanda CatharticaDocument2 pagesAllamanda CatharticaShivansh Singh GautamNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity AssessmentDocument13 pagesBiodiversity Assessmentphilippe Giblot DucrayNo ratings yet
- Geron, Salazar, Halili, Terui, AndesDocument6 pagesGeron, Salazar, Halili, Terui, AndesAint YanyanNo ratings yet
- Forest Stewardship Council (FSC)Document13 pagesForest Stewardship Council (FSC)Akanksha kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Values of Biodiversity, Threats To BiodiversityDocument34 pagesValues of Biodiversity, Threats To BiodiversityMarilyn Castro LaquindanumNo ratings yet
- Water Hyacinth Removing MachineDocument23 pagesWater Hyacinth Removing MachineGaikwad shrikrushnaNo ratings yet
- Land ClassificationDocument21 pagesLand Classificationsilessingh0% (1)
- Crop Ecology - Productivity and Management in Agricultural Systems - (2011) Queensland RecomendationDocument569 pagesCrop Ecology - Productivity and Management in Agricultural Systems - (2011) Queensland RecomendationYecid Fernando Guerrero PiracocaNo ratings yet
- Cebe 2016 Artigo Water Quality Modelling in Kas BayDocument27 pagesCebe 2016 Artigo Water Quality Modelling in Kas BayJoão Paulo Mendes FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Aarrttss & & Lleeiissuurree: ""Ccaalliiffoorrnniiaa'Ss Bbeesstt - Pprreesseerrvveedd V Viiccttoorriiaann V Viillllaaggee""Document1 pageAarrttss & & Lleeiissuurree: ""Ccaalliiffoorrnniiaa'Ss Bbeesstt - Pprreesseerrvveedd V Viiccttoorriiaann V Viillllaaggee""ferndaleenterpriseNo ratings yet
- CVEN4705 Lec Week1 T32020Document73 pagesCVEN4705 Lec Week1 T32020Cynthia OuyangNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Water ManagementDocument187 pagesSustainable Water ManagementGlen GurayNo ratings yet
- SMLXLDocument3 pagesSMLXLDenisa BalajNo ratings yet
- Harvard Business School Tragedy of The CommonsDocument4 pagesHarvard Business School Tragedy of The CommonsjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- Test On ECOLOGY NEET BIOLOGYDocument4 pagesTest On ECOLOGY NEET BIOLOGYSadananda KumbhakarNo ratings yet
- Capture D'écran . 2023-02-10 À 7.33.44 PMDocument1 pageCapture D'écran . 2023-02-10 À 7.33.44 PMMoussa SouléNo ratings yet
- Summary of Fishing Regulations: Note 1: This Pamphlet Does Not Relate To The West Coast PenaltiesDocument2 pagesSummary of Fishing Regulations: Note 1: This Pamphlet Does Not Relate To The West Coast PenaltiesJeremy JNo ratings yet
- Cultural Landscape Framework Study 160317Document104 pagesCultural Landscape Framework Study 160317Rekha VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- EvseDocument100 pagesEvseJanarthanan SuriyaNo ratings yet
- Response of Water Resources Systems To Climate ChangeDocument355 pagesResponse of Water Resources Systems To Climate ChangePat Prodanovic100% (5)
- San Lorenzo Ruiz Clup VolonethreeDocument269 pagesSan Lorenzo Ruiz Clup VolonethreearvinNo ratings yet
- Fishing Tourism in GreeceDocument1 pageFishing Tourism in GreeceDoina CocirtaNo ratings yet
- 040920145pfgj5jbannexurefinaleiareportwb Onn 2005 3Document193 pages040920145pfgj5jbannexurefinaleiareportwb Onn 2005 3saaisNo ratings yet
- Duong: My First English Test Was Not As Good As I Expected. ThomasDocument5 pagesDuong: My First English Test Was Not As Good As I Expected. Thomas36 Võ Ngọc Huyền TrânNo ratings yet
- Soil Health and Ecosystem ServicesDocument32 pagesSoil Health and Ecosystem ServicesNational Press FoundationNo ratings yet