0% found this document useful (0 votes)
110 views1 pageThe Running Times: O (log (n) ) O (n) O (α (n) ) O (log (n) ) O (log (n) ) O (log (n) ) O (log (n) )
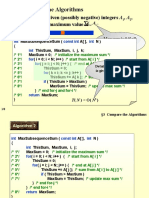
The document contains running times for various algorithms:
1. Common operations on maps, heaps, and disjoint sets have logarithmic or constant time complexity, such as deleting from a map (O(log(n))), pop from a heap (O(log(n))), and union on a disjoint set (O(1)).
2. Sorting algorithms like insertion sort and bubble sort have quadratic time complexity (O(n^2)), while heap sort, multiset sort, and STL sort are faster at O(n log n).
3. Operations on heaps like creating a heap from a vector and push/pop can be done in linear or logarithmic time respectively.
Uploaded by
dinban1Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
110 views1 pageThe Running Times: O (log (n) ) O (n) O (α (n) ) O (log (n) ) O (log (n) ) O (log (n) ) O (log (n) )
The document contains running times for various algorithms:
1. Common operations on maps, heaps, and disjoint sets have logarithmic or constant time complexity, such as deleting from a map (O(log(n))), pop from a heap (O(log(n))), and union on a disjoint set (O(1)).
2. Sorting algorithms like insertion sort and bubble sort have quadratic time complexity (O(n^2)), while heap sort, multiset sort, and STL sort are faster at O(n log n).
3. Operations on heaps like creating a heap from a vector and push/pop can be done in linear or logarithmic time respectively.
Uploaded by
dinban1Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd