Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Engg.: Panipat Thermal Power Station (A Unit of H.P.G.C.L., Haryana)
Uploaded by
dinesh66jattOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Engg.: Panipat Thermal Power Station (A Unit of H.P.G.C.L., Haryana)
Uploaded by
dinesh66jattCopyright:
Available Formats
Page | 1
ON
PANIPAT THERMAL POWER STATION
(A UNIT OF H.P.G.C.L., HARYANA)
Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the
Award of B.Tech in
Electrical Engg.
SUBMITED TO : Prepared By:
Er. Rishi Saroup Sharma Name: Jibin Chacko
H.O.D. ELE DEPTT. Roll No. 1211722
Page | 2
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In every step of achieving any concert, there is need of guidance, inspiration & help for better
result. I am hereby thankful to following persons for not only their valuable instructions that
they given me to prepare this project report but also for their cooperation during training
period.
1. ER. HIMANSHU GUPTA /XEN TRG
2. ER. RAMAN SOBTI/XEN SWITCHYARD
3. AEE P.K. DAHIYA/SWITCHYARD
I am equally thankful to all other workers who tried their best to help me & provided me
informations required for training and my friendswho directly or indirectly helped me for
completion of this project report.
Page | 3
INDEX
Introduction
Functional Description
6.6 kv supply system
Motor
o h.t.motors
o L.T motors
Transformers
o Switchyard Components
o Turbo Generator
Page | 4
INTRODUCTION
The salient features of the plant are as under:
CAPACITY 4X110MW+2X210MW+2X250MW
UNIT-1 01-11-1979
UNIT-2 27-03-1980
UNIT-3 01-01-1985
UNIT-4 11-01-1987
UNIT-5 28-03-1989
UNIT-6 04-07-2001
UNIT-7 16-10-2004
UNIT-8 02-02-2005
DAILY COAL
REQ.
15,000M.T.
Height Of Cooling
Towers
123.5 mtr. in stage 1&2
143.5 mtr. in stage 3&4
140 mtr. in stage 5&6
Page | 5
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The thermal power station burns fuel & uses the resultant to make the steam ,which
derives the turbo generator. The fuel i.e. Coal is burnt in pulverised form . The pressure
energy of the steam proudced is converted into mechanical energy with the help of
turbine . The mechanical energy is fed to the genertor where the magnets rotates inside
a set of stator winding & thus electricity is prouduced. In india 65% of total power is
generated by thermal power stations. To understand the working of the thermal power
station plant ,we can divide the whole process into following parts :
1.COAL FLOW:
In coal fired plants, raw material are air &water .in ptps ,coal is transported through
railway wagons from m\s. coal india& is kept reserved on a buffer stock .the brought
out to the station is unloded with the help of wagon tippler .after unloading ,the coal is
sent to crusher house with the helpof conveyor belts. the coal which is now resuced to
very small pieces,is sent to the coal bunkers with the help of conveyor belt .the raw coal
is fed to coal mills through raw coal feeders . raw coal feeders basically regulate raw
coal to pulverise mill. the raw pulverised coal is fed to the furnacewith the help of
primary fan through pulverised coal pipes .a porition of the primary air is heated
utilising the heat of the flue gases & then mixed with the cold air as per requirement by
the pulverised coal. normally the temp. of is maintainedat 60 to 70 degrees .the coal is
now burnt in the furnace using oil in the beginning, showerd through the nozzles at
different elevations in the furnace .to provide air for combution ,the heat of the flue
gases also heat it. the heat produced due to combution is utilised for the conversion of
water into steam .this water is stored in the boiler drum .there are two sets of pipes
attached to the drum ,one called riser& other known as down corner through which
the water comes to the ringheader& steam moves up due to the density difference of
Page | 6
water & steam . this steam is super heated using super heaters & meanwhile the flue
gases are throughout in the atmosphere through chimney.
2. Steam Flow:
The super heated steam is sent to the turbine through pipelines.there are three turbines
in the units, using this steam at different temp. & pressures. after passing through high
pressure turbine the steam is sent to the reheater for rising the temp. of the
steam.after reheating the steam is sent to the intermediate pressure turbine through
reheated line. here it losses most of its temp. & pressure, & finally sent to low
pressureturbine. the uses of three different turbines helps in increasing theefficiency
of the plant. the turbine in turn connecting with a generator produces electricity. then
this electricity is stepped upto 220 kv with the help of step up transformer & supplied to
various substations/grids.
Meanwhile, the steam through low pressure ( l.p.) turbine is condensed and the
condensed water is stored in hot well.
3.WATER FLOW:
The condensed water is extracted from the hot well through condensate extraction
pumps& sent to the boiler drum with the help of boilerfeed pump (b.f.p.) Before
passing through low pressure heater and deareter. While loss in water is made up from
c.s. Tank, which have d.m. Moor in it. The c.s tank is directly conneced to hot well.
The water used in condensor is sent to cooling tower for cooling . After cooling
this water is again sent to condensor with the help of circulating waterpump. The loss is
made up from raw water pump house through calorifier pump house.
Page | 7
BOILER FEED PUMP
Page | 8
BRIEF EXPLANATION
1.WAGON TIPPLER:-It is the machine which is used to tip the coal from the
wagon . the coal tipped is directly fed to conveyor belt. its capacity is 12 wagon per hour.
2.CRUSHER:-it crush the coal into small pieces.
3.COAL MILLS:-In it small pieces of coal are converted into pulverised form. they
are 6 in number.
4.FURNACE:-It is the chamber in which fuel burns & fire blows.
5.BOILER DRUM:-It Contains Water For Boiling.
6.ELECTROSTATIC PRECIPITATOR:-In this we have electrodes which
attracts fly ash and extract it from flue gases so that it cannot enter atmosphere.
7.CHIMNEY:-It is used to release flue gases into the atmosphere.
8.TURBINE:-Turbine is the part which revolves due to steam pressure.it is of three
types:
a).High Pressure Turbine
b).Intermediate Pressure Turbine.
c).Low Pressure Turbine.
Page | 9
9.TURBO GENERATOR:-It is the main machine which produces 210 mw
electricity. it is water and h2(hydrogen) gas cooled. therefore it is contained in
cylindrical chamber.
10.CONDENSOR:-It condense steam coming from low pressure turbine (l.p.t.) to hot
water.
11.COOLING WATER (C.W.) PUMP :-This pump send water from cooling
tower to condensor.
12.COOLING TOWER:-It is used to cool the water its height is near
about143.5mtr.
13.RAW WATER PUMP HOUSE:-Itsupplies raw water to the boiler.
14.CLEARIFIER PUMP HOUSE:-The water from raw is cleared at clearifier by
putting alum in it & filtering it & then supplied to the condensor.
15.CONDENSATE EXTRACTION PUMP:- C.E.P. pump is used to extract
the condense water from the hot well and supply to the dear eater after passing through
L.P. heater& economisier,so that high pressure steam in the cylinder can be created.
16.LOW PRESSURE HEATER:-It is used to increase the temperature of water,
in this way efficiency of system increases.
Page | 10
17.DEAREATER:-It is used to remove air from water,which is entrapped in the
water molecules. it is very important part because the entrapped air effect air drum badly.
18.BOILER FEED PUMP(B.F.P.):-It is the heaviest drive in the plant & supply
water to boiler drum from deareater.
19.HIGH PRESSURE HEATER(H.P.):-In this temperature of water increases,
thus efficiency further increases.
20.ECONOMISER:-In this flue gases exchange heat to the water to increase system
efficiency.
Page | 11
GENERAL WORKING DIAGRAM
6.6KV CIRCUIT BREAKER
A circuit breaker is a device which:-
Makes or breaks a circuit either manually or by remote control under normal
conditions.
Breaks a circuit automatically under fault conditions.
Thus a circuit breaker is just a switch which can be operated under normal & abnormal
conditions both automatic or manually. To perform this operation ,a circuit breaker is
Page | 12
essential consisting of fixed and moving contacts called electrodes. When a fault occurs on
power system, the trip coil of circuit breakers energized which pulls apart moving contacts,
thus open the circuit dc supply is used for the operation of circuit breaker. on the basis of
medium used for a extinction the circuit breaker are classified as :
1. Oil circuit breakers
2. Air blast circuit breaker
3. Sulpher hexafluoride circuit breaker.
OIL CIRCUIT BREAKER
It is well known that when a circuit carrying a large current is broken, an arc occurs at
that point where the contacts are separate, the arching is specially severe when high
voltages are involved and if a short circuit occurs on a high voltage cable which is
supplied from large power station. The arc would be powerful to bridge the contacts of
the switch and destroy it by burning. The device is employed as an oil breaker. An oil
breaker posses the property of always breaking an alternative current at its zero value.
These switches are suitable for a maximum voltage of 6.6 kv. The contacts of these
switches , which breaks high tension circuit, are immersed in oil to ensure rapid &
effective rapture of the circuit. When the arc occurs, the oil in its path is vaporized and
the gas thereby generated extract a pressure on the surrounding oil. This pressure is
utilised in arc controlled devices to cause a movement of fresh cool oil across the path of
the arc, thereby efficiently assisting its interruption.
Page | 13
SPECIFICATION:-
Low Oil Circuit Breaker
TYPE E7531/10.
1. Voltage:- 6.6/11KV
2. Current:- 3150 A.
3. Frequency:- 50HZ
4. Short Time Current:- 50/35KA FOR 1/3 S
5. Breaking Current:- 44/39.4KA
6. Weight:- 350KGS
TYPE:- E7512/10.
1. Voltage:- 6.6/11KV
2. Current:- 1250A
3. Frequency:- 50HZS
4. Short Time Current:- 50/40KA FOR 1/3S
5. Breaking Current:- 44/39.4KA
6. Weight:- 210KGS
TYPE:- E7525/10
1. Voltage:- 6.6/11 KV
2. Current:- 2500A
3. Frequency:- 50HZ
4. Short Time Current:- 50/35KA FOR 1/3S
5. Breaking Current:- 44/39.4KA
6. Weight:- 220KGS
Page | 14
INDEX
Incomer
Tie
Load
1250 a circuit breaker
2500 a circuit breaker
3150 a circuit breaker
III-A
1.DUMMY FOR TIE TO 5 A
2.TIE TO 5 A
3.DUMMY FOR TIE TO C-11-A
4.TIE TO C-II A
5.R.W.T. III
6.F.O.T. IIIA
7.BUS P.T
8.S.S.T. IIIA
9.S.B.T. IIA
10.TO C.H.S. IIIA
11.C.M.8A, 340KW, 325A
12.I.D.F.M. 5B, 130 KW, 147.5A
13.ASH WATER RECOVERY T/F.
14.H.P.W.P.M. IIIB, 260KW, 29A
15.H.P.W.P.M. IIIA, 260KW, 29A
16.C.W.P.M. 3C, 1265KW. 140A
17.A.H.T. IIIA.
Page | 15
18.C.L.M.T. IIIA.
19.B.C.W.P.M. IIIB, 135KW, 38A
20.B.C.W.P.M. IIIA, 335KW, 38A
21.INCOMER
22.DUMMY FOR INCOMER
23.TIE FOR UNIT 6A
III-B
1. TIE TO UNIT 6B
2. DUMMY FOR INCOMER
3. INCOMER
4. B.C.W.P.M. IIIC, 335 KW,38A.
5. B.C.W.P.M. IIID, 335KW, 38A
6. C.L.W.T. IIIB
7. A.H.T. IIIB
8. H.P.W.P.M. IIIC, 260KW, 29A.
9. H.P.W.P.M. IIID, 260KW, 29A.
10. H.P.W.P.M. IIIE, 260KW, 29A
11. SPARE MOTOR
12. E.P.T.
13. C.M. 8B, 340KW, 325A,
14. C.H.S.
15. S.B.T. IIIB
16. S.S.T. IIIB
17. BUS P.T.
18. F.O.T. IIIB
19. B.F.P.M. IIIB, 3500KW, 360A.
20. TIE TO C- II B
21. DUMMY FOR TIE TO C II B
22. TIE TO 5B
23. DUMMY FOR TIE TO 5B.
Page | 16
INDEX
5( A )
1. U.S.T.-5
2. E.P.T.-5A
3. BUS P.T.
4. B.F.P.M.-5 A,3500 KW,360
5. P.A.F.M-5 A,1250 KW,132 A
6. F.D.F.M.-5 A,750 KW,80.2 A
7. P.M.-5 A,340 KW,40.7 A
8. P.M.-5B,340 KW,40.7A
9. P.M.-5C,340KW,40.7A
10. I.D.F.M.-5A,1300KW,147.5A
11. RECT. T/F
12. C.W.M.-5A,500KW,525A
13.C.W.P.M.-5A,265KW,140A
14.INCOMER
15.DUMMY FOR INCOMER
16.TIE TO SSIII-A
17.DUMMY FOR TIE TO SSIII-A
5(B)
1. DUMMY FOR TIE TO SSIII-B
2. TIE TO SSIII-B
3. DUMMY FOR INCOMER
4. INCOMER
5. C.W.P.M.-5B,265KW,140A
6. C.P.M.-5B,500KW,525A
Page | 17
7. 11KW,TEMPORARY SUPPLY
8. I.D.F.M.-5C,1300KW,147.5A
9. P.M.-5D,340KW,40.7A
10. P.M.-5E,340KW,40.7A
11. P.M.-5F,340KW,40.7A
12. F.D.F.M.-5B,750KW,80.2A
13. P.A.F.M.-5B,1250KW,132A
14. B.F.P.M.-5C,3500KW,360A
15. BUS P.T.
16. E.P.T.-5B
17. SPARE MOTOR
Page | 18
MOTOR
A) HIGH TENSION MOTOR
HIGH TENSION MOTORS OPERATED AT HIGH VOLTAGES
In Tau Devi Lal thermal power station, these motors are operated at 6.6kv.
Some of these motors are as follows:-
I. CIRCULATING WATER(C.W.) PUMP MOTORS:-
a).SPECIFICATIONS:-
i. Maker b.h.e.l.
ii. Capacity(k.w.)-1265
iii. Rated voltage(volts)-6600
iv. Rated r.p.m.-493
v. Rated current-140a
vi. Connectins-star
vii. Duty- continuous
viii. Insulation class-f
ix. Installation position- vertical
x. Quantity-3
b).FUNCTION:- C.W. pump is used to circulate cooling water to the condensers so
that low pressure steam in the cylinder can be converted into water.
Page | 19
2.C.E.P. PUMP MOTOR:-
a).SPECIFICATIONS:-
MAKE- B.H.E.L.
CAPACITY-500KW
RATED VOLTAGE-6600V
RATED R.P.M.-1482
RATED CURRENT-52.8A
CONNECTIONS-STAR
DUTY-(2 WORKING,1STANDBY) CONTINUOUS
INSULATION CLASS-F
INSULATION POSITION-VERTICAL
QUANTITY-3
b).FUNCTION:-C.E.P.pump is used to extract the condense water from the
hot well and supply to the deareator after passing through l.p. Heater&
economisier,so that high pressure steam in the cylinder can be created.
3.BOILER FEED PUMP(B.F.P.) MOTOR:-
a).SPECIFICATIONS:-
MAKE- B.H.E.L.
CAPACITY-3500KW
RATED VOLTAGE-6600VOLTS
RATED CURRENT-360A
RATED R.P.M.-1481
CONNECTIONS- STAR
Page | 20
DUTY(2 WORKING,1 STANDBY)-CONTINUOUS
INSULATION CLASS-F
QUANTITY-3
b).FUNCTION:-Its function is to supply the water to the boiler drum. It takes water
from the deareator by creating strong suction. It is the biggest motor in the plant.
4.COAL MILL MOTOR:-
a). SPECIFICATIONS:-
MAKE-B.H.E.L.
RATED VOLTAGE-6600
CAPACITY-340KW
RATED R.P.M.-992
RATED CURRENT-40.7A
CONNECTIONS- STAR
DUTY- CONTINUOUS
INSULATION CLASS-F
INSTALLATION POSITION HORIZONTAL
QUANTITY-6
b).FUNCTIONS:-Its function is to grind the coal pieces to fine powder
(pulverised) form I.E. upto size of 25 micron.
Page | 21
5.COAL CRUSHER :-
i).MAKE-N.G.F.E
ii).CAPACITY-600KW
iii).RATED VOLTAGE-6600V
iv).RATED R.P.M.-747
v).RATED CURRENT-72A
vi). CONNECTIONS-STAR
vi).QUANTITY-2
b).FUNCTION:-Its function is to crush the big size coal pieces to a size of 25mili
meter square, which are then carried to bunkers through conveyor belt.
6. PRIMARY AIR FAN MOTOR:-
i).MAKE-B.H.E.L.
ii).CAPACITY (K.W.)-1250
iii).RATED VOLTAG (VOLTS)-6600
iv).RATED R.P.M.-1487
v).RATED CURRENT (AMPS)-132
vi).CONNECTIONS-STAR
vii).DUTY-CONTINUOUS
viii).INSULATION CLASS-F
ix).QUANTITY-3
b).FUNCTION:-Its function is to carry pulverized coal from the coal mill to the
furnace for its ignition. It creates strong draft of air that carries pulverized coal.
7). FORCE DRAUGHT (F.D.) FAN MOTOR:-
i).MAKE-B.H.E.L.
ii).CAPACITY-750KW
iii).RATED VOLTAGE-6600V
Page | 22
iv).RATED R.P.M.-1490
v).RATED CURRENT-80.2A
vi).CONNECTION-STAR
vii).DUTY-CONTINUOUS
viii).INSULATION CLASS-F
ix).QUANTITY-2
b).FUNCTION:-F.D. Fan is used to supply fresh air to the furnace for the proper
ignition of coal into the furnace.
8). INDUCED DRAFT (I.D.) FAN
i).MAKE-B.H.E.L.
ii).CAPACITY-1300KW
iii).RATED VOLTAGE-6600V
iv).RATED R.P.M.-750
v).RATED CURRENT-147.5A
vi).CONNECTION-STAR
vii).DUTY-CONTINUOUS
viii).INSULATION CLASS-F
ix).QUANTITY-3
b).FUNCTION:-Its function is to discharge flue gases to the atmosphere through the
chimney after passing through the precipitator.
9.BEARING COOLING WATER PUMP MOTOR:-
a).SPECIFICATION:-
i).MAKE-B.H.E.L.
ii).CAPACITY-335KW
iii)RATED VOLTAGE-6600V
iv).RATED R.P.M.-980
Page | 23
v).-CONNECTION-STAR
vi).INSULATION CLASS-F
vii).INSTALLATION POSITION-HORIZONTAL
b).FUNCTION:-It supply cooling water to the motor &other auxillary for cooling
puposes. & other auxillary for cooling puposes.
B)LOW TENSION MOTOR
Low tension motors are those which areof 415v. they are mainly used in h.t.motor
auxillary.
1. B.C.W. DRAIN MOTOR:-
a).SPECIFICATION:-
i).CAPACITY-136KW
ii).rated r.p.m.-987
iii).RATED CURRENT-43A
iv).FREQUENCY-50HZ
v).MAKE-KRILOSKER
vi).INSULATION CLASS-B
b)FUNCTION:-IT PUMP THE B.C. WATER TO THE SUMP.
Page | 24
2. SEAL WATER PUMP MOTOR:-
a).SPECIFICATION:-
i). CAPACITY-25KW
ii). RATED R.P.M.- 1479
iii) RATED CURRENT 43A
iv) FREQUENCY -50HZ
v). PHASE-3
vi). MAKE NGEF
vii). INSULATION CLASS B
b).FUNCTION It provides a layer of water to the lower position of boiler in order
to seal it from the entry of atmospheric air.
3. SEAL WATER VAPOUR EXHAUST FAN:-
a.) SPECIFICATIONS
i) CAPACITY 1.5 KW
ii) RATED R.P.M. 6205
iii) RATED CURRENT 3.1A
iv) FREQUENCY 50HZ
v) PHASE 3
vi) MAKE KIRLOSKER
vii) INSULATION CLASS B
Page | 25
a) FUNCTION-It prevents the entry of air bubbles in the turbine cylinder by providing
the opposite push.
4. CENTRIFUGE PUMP MOTOR:-
a). SPECIFICATIONS
i). CAPACITY 7.5KW
ii). RATED R.P.M-1440
iii). RATED CURRENT-14.
iv). FREQUENCY 50HZ
v). PHASE 3
vi). MAKE CROMPTON GREAVES
vii). INSULATION CLASS B
b). FUNCTION To centrifuge the vapour that enters by change in turbine
an remove them.
Page | 26
5. ASH SLURRY PUMP MOTOR:
a).SPECIFICATIONS
i) CAPACITY 100KW
ii) RATED R.P.M. 1485
iii) RATED CURRENT 176
iv) FREQUENCY 50HZ.
v) PHASE - 3
vi) MAKE NGEF
vii) INSULATION CLASS B
b). FUNCTION To pump ash slurry to the ash disposal area.
6. EMERGENCY OIL PUMP:
a). SPECIFICATIONS
1. CAPACITY 15 KW
2. RATED R.P.M. 1425
3. RATED CURRENT 125
4. FREQUENCY N.A. (DC)
5. PHASE NOT APPLICABLE
b).FUNCTION To provide oil to the shaft and bearing of the turbine if seal oil
pump and taking oil pump fails.
Page | 27
7. RAW WATER MOTOR PUMP:
a) SPECIFICATIONS-
i).CAPACITY-90KW
ii).RATED R.P.M.-1450
iii).RATED CURRENT-154A
iv).FREQUENCY-50HZ
vi).PHASE-3
vii).MAKE-KIRLOSKER
viii).INSULATION CLASS-B
b).FUNCTION-It is use to pump raw water from the lake to the plant.
8. INSTUMENT AIR COMPRESSOR:-
a).SPECIFICATIONS:-
i).CAPACITY-105KW
ii).RATED R.P.M-1485
iii).RATED CURRENT-184A
iv).FREQUENCY-50HZ
v).PHASE-3
vi).MAKE- KIRLOSKER
vii).INSULATION CLASS- B
b).FUNCTION- It is used to compress the air used to control pneumatic
controlled instruments at a pressure 6 to 7 kg/cm cube.
Page | 28
9.SERVICE AIR COMPRESSOR:-
a). SPECIFICATIONS-
i).CAPACITY-30KW
ii).RATED R.P.M.-1485
iii).RATED CURRENT-184A
iv).FREQUENCY-50HZ
v).PHSE-3
vi).MAKE-NGEF
vii).INSULATION CLASS-B
b).FUNCTION- Its Function Is Similar To Instrument Air
Compressor.
Page | 29
10.CLARIFIER WATER PUMP MOTOR-
a).SPECIFICATION-
i)CAPACITY-30KW
ii).RATED R.P.M-1470
iii).RATED CURRENT-53A
iv).FREQUENCY-50HZ
v).PHASE-3
vi).MAKE-CROMPTON
vii).INSULATION CLASS-B
b).FUNCTION-It pump the filtered water from clearifier to d.m. water
treatment plant.
TRANSFORMERS
The transformer is the most convenient & economical device for transfer of power
from one voltage to another voltage at the same frequency. it works on the
principle of electromagnetic induction. there is hardly any installation without a
transformer.due to this equipment,it has been possible to transmit bulk power to
load centers from far off power houses and to various machineries and
switchgears of the power plant. transformers are of two types:-
#STEP-UP TRANSFORMER - Which step-up the voltage at secondry
side called step-up transformer.
#STEP-DOWN TRNSFORMER- Which step-down the voltage at
secondry side are called step-down transformer.
Page | 30
MAIN PARTS OF POWER TRANSFORMERS
# PRIMARY WINDING
# SECONDRY WINDING
# OIL TANK
# DRAIN COKE
# CONSERVATOR
# BRETHER
# TUBES FOR COOLING
# TRNSFORMER OIL
# EARTH POINT
# EXPLOSION VENT
# TEMPERATURE GAUGE
# BUCHHOLZ RELAY
# PRIMARY TERMINALS
# SECONDARY TERMINALS
ACCESSORIES OF TRANSFORMERS
1.OIL CONSERVATOR:-
Oil conservator is a short of dum mounted on the top
of transformer. A level indicator is fixid to it, which gives alarm at low level.
Conservator is connected through a pipe to the transformer tank containing oil.
This oil expands & contract depending upon the heat produced & so the oil
level in conservator is left open to the atmosphere through a breather so that the
extra air may go out or come in.
Page | 31
2.BREATHER:-
The breather is a box containing calcium chloride or silica gel
to absorb moisture of our entering the conservator as it is well known fact that
the insulating property of the transformers oil is lost if a small amount of
moisture enter in it. So dry air is allowed to pass through the breather.
when oil levrl in oil conservator changes, air moes in & out of
the conservator. This action is known as breathing. dry silica gel is of the blue
color. it turns pale pink as it absorbs moisture . the wet silica gel can be
regenerated by drying.
3.BUCHHOLZ RELAY:-
This relay is a gas-actuated relay which is meant for the
protecting of oil immersed transformer from insulation failure, core heating or
any type of internal fault which may cause the heating of oil beyond the
specified temp.. due to any internal fault, oil is heated up & oil vapour so
formed causes either the alarm circuit(for less fault) or trip the circuit(for sever
fault).
4.EXPLOSION VENT:-
It is also a safety device of the transformer which
protects the transformer tank from gases induced by & any type of short circuit
in the transformer. this consist of a vertical pipe closed by a dia pharm made of
thin bakelite sheet. this diapharm burst or slides out in case of abnormal pressure
inside the tank. a diverter plate is used at the bottom of the explosion vent to ensure
that gases proudce inside the transformer are directed toward the buchholz relay &
dont get collected inside the ventilation and equilise the pressure on each side of the
diverter plate.
Page | 32
5.TEMP. INDICATOR:-
It is also a protective device fitted to the transformer to indicate temp.of transformer
oil. for measuring temp. of the oil, bulb of the vapour pressure type thermometer is
placed in the hot oil & dial of the thermometer is mounted outside the tank. two
indicating pointers black and red are provided. alarm contacts are also provided
which come into action when predetermined permissible higher temparature is
reached under abnormal operating conditions.
6.BUSHING:
The bushing serve as supports and insulation of the bus bars and transformer terminal.
the bushing consists of procelain shell body, upper and lower locating washer used for
fixing the position of bush bar and mounting flange with the hole drilled for fixing
bolt and it is supplied with an earthing bolt.
7. MAGANETIC OIL GAUGE:-
The maganetic oil level gauge supervises the level of oil in the conservator
tank. the oil level gauge is provided on the transformer are of dial type with
minimum and maximum level marking and a pointer which indicate the level of oil in
the conservater. sometime the scale is also graduated for oil temperature on the basis
of its level.
8. TAP CHANGER:
The voltage control of transmission and distribution systems is obtained by tap
changer. tap changer are either on load or off load tap changer. tap changer is fitted with the
transformer for adjusting secondary voltage.
Page | 33
IMPORTANT TRANSFORMERS IN THE PLANT
1. GENERATOR TRANSFORMER (240 MVA, 15.75 KV/220KV)
It converts 15.75 kv which is supplied from generator 220kv and supplied it to the bus bar/
grid.
2. STATION SERVICE TRANSFORMER (40MVA, 220KV/7KV)
It converts 220kv which is coming to station from bbmb to 7kv and fed to station auxiliary.
3. UNIT AUXILIARY TRANSFORMER (15MVA, 15.75KV/7KV)
It converts 15.75kv which is supplied from generator to 7kv to fed unit auxiliary.
Page | 34
SWITCHYARD COMPONENTS
1.SWITCH-GEAR
Switch gear is a control switch that control the operation of a power circuit. The two
function of a switch in power systems are
i). To permit the transmission lines to be convenient put into and taken out from service.
ii). To disable the some plant and lines when these become faulty, to be repidly and safely
isolated by automatic means.
The first of these can be served by relatively simple switches the second however
require circuit breakers, which are more robust & capable of breking the large value of fault
power that results in faults on major power system. since all plants and lines are liable to
develop faults as a results of mechanical damage, electrical breakdown, errors in operation
etc. the simple isolators switch in favour of automatic circuit breakers even for switching
function. the whole switchgear assembly consists of two parts:-
A.PANEL-Panel consists of protective relays, Mountig of potential transformer, current
transformer, ammeter, voltmeter & energy meter. the potential transformer is mounted on the
panel. the primary is connected to 11kv & the reduce voltage from the secondary is given to
energy meter as line voltages & for protective purposes.
B.TROLLY- The trolly consists of current Carying contacts called electrodes. these are
normally engaged but in predetermined conditions, separate to interrupt the circuit, when the
contacts are made.
Page | 35
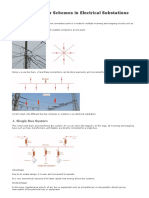
2 BUS BAR ARRANGEMENT
Conductors to which a number of circuits are connected called bus bars. in power plants,
shut down results disconnection of supply to a large area. hence to avoid shut down the major
plants should have elaborate bus bar arrangement with duplicate buses, alternative supply
arrangement section etc. the extra high voltage equipments such as isolators, circuit breaker
are generally costly hence unnecessary equipment should not be provided.
1. SINGLE BUS BAR ARRANGEMENT:-
The single arrangement consists of a single (three phase) bus bar to which various
feeders are connected. in case of fault or maintenance of bus, the entire bus bar has to be
de-energized and the total shutdown results. this scheme is most economical and simple.
2. DOUBLE BUS BAR ARRANGEMENT:-
The double bus systems provide additonal flexibility, continuity of supply and permit
periodic maintenance. In the event of fault on the bus bar the other can be used the
figure shows to the bus bar arrangement. there are two buses called main bus and
reserve bus . The coupler can be closed so as to connect two buses while transferring
the power to the reserve bus.
i) Closed bus coupler, the two buses are now at same potential.
ii) Closed isolator on reserve bus.
iii) Open isolator on main bus.
3 LIGHTING ARRESTER
A lighting arrester is device, which proves low impedence path for the flow of
current between the line and earth when the systems voltage increases more than the desire
value and regains its original properties of an insulator at normal voltage. It is connected
between line and earth at the swith yard near the transformer.
Page | 36
The lighting arresters are extensively used for protection of transformers, swith gears and
electrical equipments of over head lines, power houses and sub-station. These are also use to
protect the line and equipments from skylighting. following are the main type of lighting
arresters-
i) Horn gap lighting arrester.
ii) Expulsion type lighting arresters.
iii) Oxide film lighting arrester.
iv) Pellet lighting arrester
v) Thyrite lighting arrester.
vi) Auto value lighting arrester.
EXPULSION TYPE LIGHTING ARRESTER
It consists of
i) a tube made of fibre which is very effective gas evolving materials.
ii) an isolating spark gap ( or external series gap)
iii) an intrupting spark gap inside the fibre tube.
during operation, arc due to impulse spark or inside the fibrous tube
causes some fibre material of the tube voltise in form of gas, which is
expelled through a vent from the bottom of the tube, thus extinguishing
the arc just like in circuit breaker. since the gases generated have to be
expelled, one of the electrode is hollo and diverter is open at its lower
end.
Page | 37
Thyrite Lighting Arrester:-
This type of lighting arrester consists of number of discs of inorganic ceramic
compound. These discs are placed in a series having some gaps in between them and are
sealed in a porcelain tube. This tube has metallic cap and electrodes at its end. The
compound used for discs serve as an insulator but changes to a good conductor when
voltages across it rises to a certain predetermined value. It is used up to 220kv systems.
Page | 38
Lighting Arrester
210 MW TURBO GENERATOR
GENERAL:-
Modern features of direct cooling by water & hydrogen are incorporated in the 210 mw turbo
generator, thus evolve an economical & reliable design. the machine is provided with a fast
acting excitation system & dependable auxillary service to give prolonged trouble free
operation over the years. all the material that goes into the manufacture of this machine
subjected to various test as per national & international standards. each compononets
undergoes series of stagewise tests. description of various parts is given balow:-
Page | 39
1.STATOR WINDING AND INSULATION:-
The stator has a three phase, double layer, short chorded, bar type winding, having two
parallel pats. each coil side consists of glass insulated solid and hollow conductors with
cooling water passing through the patter. the elementary conductors are roebel transposed in
the slot poetion of winding to minimise eddy current losses.adequate protection is provided
to avoid corona & other discharges. in the slots, the sides are firmly held in the position by
fiborousslot wages, which are mechanically strong and have high dielectric properties. the
overhang portion of the coil is securely lashed with glass chord to bondage rings& special
breckets of non magnetic steel, which are in turn fixed to the core press rings. on short
circuits the forces betweenthe conductor tend to open the cone formed by overhang portion
of the coils , but the movement is effectively presented by supports & lashings.
2.DISTILLATE HEADERS OR STATOR WATER HEADER:-
Ring type water headers, made of copper are provided seperately for distillate inlet & outlet
in the stator on turbine side. the headers are supported on insulators and isolated from stator
body. the winding ends are soledly soldered into the coil lugs which are than ultrasonically
tested. individual bars are provided with water inlet/outlet connections made of p.t.f.e.
houses. the bar heads are insulated by fibre moulded corners. the winding scheme along with
the water connections. the complete water path assemblty is subjected to the rigid hydroatic
pneumatic tests at various stages to ensure water tightness and to detect blocking of the flows
paths.
3.TERMINAL BUSHINGS :-
Water colled terminal bushings are housed in the lower part of the stator on the slip ring side.
procelain insulators are provided to insulate the terminal bars from the stator body. effective
sealing is provided between the terminal bushingnand the statir bidy to avoid any possibility
of leakage of hydrogen. terminal bushing are housed inside a chamber made of non magnetic
Page | 40
steel plates. three phase terminals are brought out to facilitate external connections. the
terminal plate of the end terminals, where bus bar connections are made is silver plated.
the terminal bushings can be replaced without removing the stator from foundation. provision
is made for fixing the external bus ducts with the terminal plate.
4.ROTOR:-
The rotor is of cylindrical type shaft and body being forged in one piece from chromium,
nickel,molybdenum & vanadium steel. prior to matching, a series of comprehensive
ultrasonic examination and other tests are carried out on rotor byody and shsft portion to
ensure of any internal defects. the rotor with all the details assembled , dynamically balanced
to a high degree of accuracy and subjected to 20% over speeding for 2 minutes ensuring
mechanical strength.
5.FIELD WINDING:-
The field winding is made from hard drawn silver bearing copper. rotor winding is held in
position against centrifugal forces by dualism forces wedges in the slot portion & by non
magnetic steel retaining rings in the overhang portion . gap pick up system is employed for
direct hydrogen cooling of rotor winding. several groups of ventilation ducts are mulled on
the sides of the rotor coil for gas passage. the rotor slot wedges are of special profiles with
elliptical holes rolled in to match the ventilation ducts on the winding stacks. the end
windings are insulated from rings with the help of glass epoxy molded segments. Copper
segmental type damper winding is provided in the end zone of rotor morrows to prevent over
heating of returning ring s during asymmetrical & asynchronous operation.
6.SHAFT MOUNTED FANS:-
For circulating the cooling gas inside the generator, two propeller type fans are shaft
mounted on this & of rotor body. Fan hubs are made from alloy steel forging and are hot
Page | 41
fitted on the rotor shaft with sufficient interference . The alloy steel cast fan blades are
machined in the tail portion to suit the fan hub and held in position with the help of conical
pins. The blades can be easily removed from or assembled in the fan hub. Fan shields fixed
to the end shields, guide the flow of gas through the fan sections.
7.SLIP RINGS:-
The slip ring consists of helically grooved alloy steel rings shrunk on the rotor shaft &
insulated from it. For convenience in assembly both the rings are mounted on a single,
common steel bush, which has an insulated jacket pre molded on it. The complete bush with
slip ring is shrunk on the rotor shafts. The slip rings are provided with inclined holes for self-
ventilation. The helical grooves cut on the outer surface of the slip rings improves brush
performance.
Page | 42
TURBO GENERATOR RATINGS
CAPACITY IN KW- 210000
POWER FACTOR- 0.85
CAPACITY IN KVA- 247000
STATOR:-a).15750 V
b).90.60A
ROTOR:-a).310V.
b).2600A
ROTOR R.P.M.- 3000
FREQUENCY- 50HZ
PHASE- 3
CONNECTION- STAR
COOLENT- H2+H2O
NO. OF POLES- 2
Page | 43
TURBO GENERATOR
You might also like
- Industrial Training Report ON C & I Maintenance Division Unit-8 AT Panipat Thermal Power StationDocument27 pagesIndustrial Training Report ON C & I Maintenance Division Unit-8 AT Panipat Thermal Power StationAbhishek AroraNo ratings yet
- A Training Report (Thermal Power Plant) : Functional DiscriptionDocument26 pagesA Training Report (Thermal Power Plant) : Functional DiscriptionTrRihaNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report On NTPC Tanda, Ambedkar NagarDocument9 pagesSummer Training Report On NTPC Tanda, Ambedkar NagarAliraza7660% (5)
- Generation of Electric PowerDocument108 pagesGeneration of Electric Powermausam sharmaNo ratings yet
- Harduaganj Thermal Power Plant by Geetesh SharmaDocument66 pagesHarduaganj Thermal Power Plant by Geetesh Sharmageeteshaccurate100% (1)
- Project Report by Manish YadavDocument53 pagesProject Report by Manish Yadavmanish yaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- Brief Description of Tanda Thermal Project: 1.1 Geographical LocationDocument22 pagesBrief Description of Tanda Thermal Project: 1.1 Geographical Locationcoolvipin1988No ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant - EeDocument20 pagesThermal Power Plant - EePrabhat Chandra100% (1)
- CSEB (Chhattisgarh State Electricity Board) Korba East Vocational Training Presentation I IDocument44 pagesCSEB (Chhattisgarh State Electricity Board) Korba East Vocational Training Presentation I Ihaxxo24No ratings yet
- NTPCDocument32 pagesNTPC12 EC ATUL KUMAR SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
- Power Plant FamiliarisationDocument110 pagesPower Plant FamiliarisationmrdipakwaghNo ratings yet
- NTPCDocument33 pagesNTPCSubodh DuhanNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Report On NTPC Tanda Ambedkar NagarDocument9 pagesSummer Training Report On NTPC Tanda Ambedkar NagarNaman ShahNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engg.: Report On Industrial TrainingDocument44 pagesMechanical Engg.: Report On Industrial TrainingSakshi SanghiNo ratings yet
- Gajendra KumarDocument23 pagesGajendra KumarGAJENDRA KUMARNo ratings yet
- NTPC ReportDocument47 pagesNTPC ReportUpendra Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Full Mechanical Degree Updated On 2 7 2010Document54 pagesFull Mechanical Degree Updated On 2 7 2010Balwan Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chandrapur CTPS 15 Days Training ReportDocument21 pagesChandrapur CTPS 15 Days Training ReportUday Wankar0% (1)
- Report #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantDocument41 pagesReport #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantKian TecsonNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant: Shubham Thakur 13BME8149 5MEL3 Mechanical EngineeringDocument34 pagesThermal Power Plant: Shubham Thakur 13BME8149 5MEL3 Mechanical EngineeringMos MohNo ratings yet
- Amulya Gaikwada ProjectDocument34 pagesAmulya Gaikwada ProjectHarikrishna NethaNo ratings yet
- TPS Internship ReportDocument34 pagesTPS Internship Reportmkhalil1148No ratings yet
- Thermal PlantDocument4 pagesThermal PlantHanan Tariq QasuriaNo ratings yet
- AES Thermal Power Plant, Lalpir, District Muzaffargarh: Prepared byDocument25 pagesAES Thermal Power Plant, Lalpir, District Muzaffargarh: Prepared byIrfan UllahNo ratings yet
- Thermal EngineeringDocument10 pagesThermal Engineeringlokeshdhangar842No ratings yet
- A Practical Training Seminar ON: Suratgarh Super Thermal Power StationDocument30 pagesA Practical Training Seminar ON: Suratgarh Super Thermal Power Stationvipul sharmaNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument12 pagesLab ReportFaisal ArslanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Plant Control Instrumentation IDocument41 pagesThermal Plant Control Instrumentation IVishal KhachaneNo ratings yet
- TRNG Proj Rep.Document39 pagesTRNG Proj Rep.sahapinkNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Training ReportDocument26 pagesPower Plant Training ReportAnil YadavNo ratings yet
- NTPC Ltd. - Simhadri Super Thermal Power Station, Visakhapatnam, Andhra PradeshDocument27 pagesNTPC Ltd. - Simhadri Super Thermal Power Station, Visakhapatnam, Andhra PradeshNiharika KolliNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Report NTPCDocument30 pagesIndustrial Training Report NTPCTabish KhanNo ratings yet
- Summer Training in Badarpur NTPCDocument54 pagesSummer Training in Badarpur NTPCRohit VermaNo ratings yet
- T Project ReportDocument63 pagesT Project ReportArif AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Literature Review 2.1 Technical Feasibility StudyDocument20 pagesChapter Two Literature Review 2.1 Technical Feasibility StudymutencoNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument7 pagesSteam Power PlantNav Mehra50% (2)
- محطة شبرا الخيمةDocument15 pagesمحطة شبرا الخيمةعبدالله عبدالمنعم100% (1)
- Thermal Power PlantDocument27 pagesThermal Power Plantvenki249100% (1)
- Power Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineDocument7 pagesPower Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineMonglafru MogNo ratings yet
- Jaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyDocument29 pagesJaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyAnonymous ytZsBOVNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantsDocument24 pagesThermal Power Plantslakshmigsr6610100% (1)
- Training Report at PtpsDocument38 pagesTraining Report at Ptpsrahul93anNo ratings yet
- Jaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyDocument29 pagesJaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyAashish SangwanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument29 pagesThermal Power PlantSiri VenniNo ratings yet
- 0 - STPP Report NNDocument26 pages0 - STPP Report NN045 Devaruppula sairamNo ratings yet
- + Air Fig.1. Production of Electrical Energy by Steam Power Plant Exhaust SteamDocument38 pages+ Air Fig.1. Production of Electrical Energy by Steam Power Plant Exhaust Steamsrihari_bhadabhagniNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Thermal Power PlantDocument27 pagesIntroduction and Thermal Power PlantKshitij AggarwalNo ratings yet
- SIREreport 118ee0297Document13 pagesSIREreport 118ee0297Bhabani sankar KishanNo ratings yet
- Construction and Working of Thermal Power PlantDocument5 pagesConstruction and Working of Thermal Power PlantdibyenindusNo ratings yet
- Steam PlantDocument102 pagesSteam PlantPrakhar Shukla100% (1)
- Project ReportDocument103 pagesProject ReportSeth CamachoNo ratings yet
- Report On "Generation of Thermal Power" AT NTPC DadriDocument17 pagesReport On "Generation of Thermal Power" AT NTPC DadriVaibhav RaoNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training AT: Submitted By: Rishikesh (11-1-6-002) NIT, SilcharDocument26 pagesIndustrial Training AT: Submitted By: Rishikesh (11-1-6-002) NIT, SilcharRakesh Roshan KeshriNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant PresentationDocument37 pagesSteam Power Plant PresentationsharenslaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- SIRCOVERDocument12 pagesSIRCOVERsaumya DuttaNo ratings yet
- Hypercharger 225 Hypercharger 300: Key FeaturesDocument5 pagesHypercharger 225 Hypercharger 300: Key FeaturesVlad BuracNo ratings yet
- Cableado Radio Nissan SentraDocument1 pageCableado Radio Nissan SentraLuis FernandoNo ratings yet
- Olman CB100 Capacitance and Power Factor Test SetDocument3 pagesOlman CB100 Capacitance and Power Factor Test SetReginald D. De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 75 kVA Specification SheetDocument2 pages75 kVA Specification SheetAlex MohanNo ratings yet
- Enphase Micro-Inverter Models M175 and M200: Installation and Operations ManualDocument24 pagesEnphase Micro-Inverter Models M175 and M200: Installation and Operations ManualfudgemonsterNo ratings yet
- Sfu HandleDocument82 pagesSfu HandlenalasekaranNo ratings yet
- Delta Boost Module DatasheetDocument1 pageDelta Boost Module DatasheetJhunieby GarciaNo ratings yet
- DC Poweer Distribution Switch BoardDocument9 pagesDC Poweer Distribution Switch BoardpvenkyNo ratings yet
- BX1S-KV-BT212M80 P40 P52 P52 LP52N BT212M81 BT212N40 BT212N50Document11 pagesBX1S-KV-BT212M80 P40 P52 P52 LP52N BT212M81 BT212N40 BT212N50Jomasando10No ratings yet
- Canadian Solar HiKu6 Mono - CS6W MS - 525 545 Vico Export Solar EnergyDocument2 pagesCanadian Solar HiKu6 Mono - CS6W MS - 525 545 Vico Export Solar EnergyasadiqbalditechNo ratings yet
- ENG DS PCF Series Relay Data Sheet E 0411 PDFDocument3 pagesENG DS PCF Series Relay Data Sheet E 0411 PDFJOSE JESUS ARCIA VILLAMININo ratings yet
- CO PO1 PO2 PO3 PO4 PO5 PO6 PO7 PO8 PO9 PO10 PO11 PO12 Pso1 Pso2 Pso3 CO1 3 2 3 3 CO2 3 3 3 1 CO3 3 2 3 3 1 CO4 3 2 3 3 CO5 3 2 3 3 1Document2 pagesCO PO1 PO2 PO3 PO4 PO5 PO6 PO7 PO8 PO9 PO10 PO11 PO12 Pso1 Pso2 Pso3 CO1 3 2 3 3 CO2 3 3 3 1 CO3 3 2 3 3 1 CO4 3 2 3 3 CO5 3 2 3 3 1KK100% (1)
- Precision 10 12 To 10 54 European Test DataDocument19 pagesPrecision 10 12 To 10 54 European Test DataDaniel PeluffoNo ratings yet
- Option-1 ICAR AHF FA34 SeriesDocument14 pagesOption-1 ICAR AHF FA34 Seriessureshbabum85No ratings yet
- Electrical Plan - Clarence HernandezDocument47 pagesElectrical Plan - Clarence HernandezClarence Hernandez100% (1)
- Tara Pharmacology PDF Medicalstudyzone - Com - CompressedDocument572 pagesTara Pharmacology PDF Medicalstudyzone - Com - Compressedunbridled.instinct.218No ratings yet
- Aircraft Electrical Systems (Pallett)Document192 pagesAircraft Electrical Systems (Pallett)Abolfazl Mazloomi100% (2)
- B767 L3 ATA 24 Electrical PowerDocument232 pagesB767 L3 ATA 24 Electrical PowerOliver IrrazabalNo ratings yet
- Applied Directly To The Stator WindingsDocument53 pagesApplied Directly To The Stator WindingsSew HunNo ratings yet
- Different Bus-Bar Schemes in Electrical SubstationsDocument28 pagesDifferent Bus-Bar Schemes in Electrical SubstationsdivaNo ratings yet
- Foster Seeley DiscriminatorDocument2 pagesFoster Seeley DiscriminatorDebesh Bar100% (1)
- Inverter 12v 3kv PDFDocument13 pagesInverter 12v 3kv PDFirfz44No ratings yet
- Impedansi Loop Aturan IEEEDocument2 pagesImpedansi Loop Aturan IEEEIkmalNo ratings yet
- Meg MegtDocument13 pagesMeg MegtvietnhuNo ratings yet
- Ölflex® Solar XLWP: Product InformationDocument4 pagesÖlflex® Solar XLWP: Product InformationHendra BudimanNo ratings yet
- 3X240 - AL - XLPE - STA - PVC - 12 - 20 (24) KV - DistributionDocument1 page3X240 - AL - XLPE - STA - PVC - 12 - 20 (24) KV - DistributionMohamed AliNo ratings yet
- UENR8264UENR8264-01 - SIS Manual Deif m1 MarinoDocument2 pagesUENR8264UENR8264-01 - SIS Manual Deif m1 MarinoJOHAN DAVID RODRIGUEZ100% (1)
- Excerpt From: Electricity InformationDocument7 pagesExcerpt From: Electricity InformationCarlosNo ratings yet
- Fuji TK26 016TN 22ADocument13 pagesFuji TK26 016TN 22AtokusanNo ratings yet