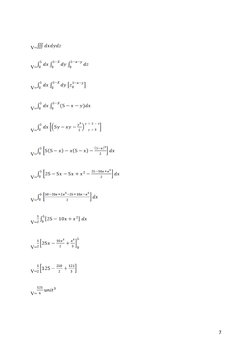1.
Introduction
The multiple integral is a generalization of the definite integral to functions of more than one real
variable, for example, f(x, y) or f(x, y, z). Integrals of a function of two variables over a region
in R2 are called double integrals, and integrals of a function of three variables over a region
of R3 are called triple integrals.
Definition of Double Integral
The definite integral can be extended to functions of more than one variable. Mainly to
determine interval using horizontal and vertical strip which both produce same answer.
Consider, for example, a function of two variables z = f (x,y). The double integral
Where R is the region of integration in the xy-plane. If the definite integral
of a
function of one variablef (x) 0 is the area under the curve f (x) from x = a to x = b, then the
double integral is equal to the volume under the surface z = f (x,y) and above the xy-plane in
the region of integration R .
Definition of the Triple Integral
We have seen that the geometry of a double integral involves cutting the two dimensional
region into tiny rectangles, multiplying the areas of the rectangles by the value of the function
there, adding the areas up, and taking a limit as the size of the rectangles approaches zero.
We have also seen that this is equivalent to finding the double iterated iterated integral. We
will now take this idea to the next dimension. Instead of a region in the xy-plane, we will
consider a solid in xyz-space. Instead of cutting up the region into rectangles, we will cut up
the solid into rectangular solids. And instead of multiplying the function value by the area of
the rectangle, we will multiply the function value by the volume of the rectangular solid. 3
coordinates system which we need to know cartesian coordinate, cylindrical coordinate and
spherical coordinate.
�We can define the triple integral as the limit of the sum of the product of the function times
the volume of the rectangular solids. Instead of the double integral being equivalent to the
double iterated integral, the triple integral is equivalent to the triple iterated integral.
�2.0
Theory
Area by Double Integration
Double Integrals in Polar Form
Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates
Triple Integrals in Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates
�3.0
Question
Find the volume of the tetrahedron bounded by the planes x + y + z = 5, x = 0, y = 0, z = 0
4.0
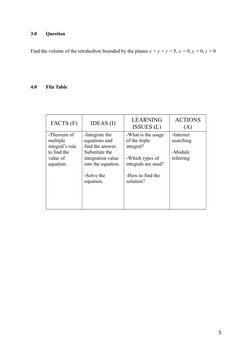
Fila Table
FACTS (F)
-Theorem of
multiple
integrals rule
to find the
value of
equation.
IDEAS (I)
LEARNING
ISSUES (L)
-Integrate the
equations and
find the answer.
Substitute the
integration value
into the equation.
-What is the usage
of the triple
integral?
-Solve the
equation.
-How to find the
solution?
-Which types of
integrals are used?
ACTIONS
(A)
-Internet
searching
-Module
referring
�5.0
Solution
Find the volume of the tetrahedron bounded by the planes x + y + z = 5, x = 0, y = 0, z = 0
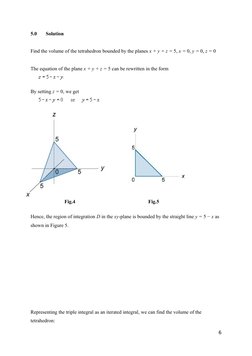
The equation of the plane x + y + z = 5 can be rewritten in the form
By setting z = 0, we get
Fig.4
Fig.5
Hence, the region of integration D in the xy-plane is bounded by the straight line y = 5 x as
shown in Figure 5.
Representing the triple integral as an iterated integral, we can find the volume of the
tetrahedron:
6
�V=
V=
V=
V=
V=
V=
V=
V=
V=
V=
V=
V=
�6.0
Conclusion
In this chapter, we saw that an ''integral of an integral'' is known as an iterated integral,
whereas a double integral is the limit of double sums over ever finer partitions. However, if a
region R is a type I region, then
=
where x = a, x = b, y = p( x) , and y = q( x) are the boundaries of R. Similarly, a double
integral over a type II region can be reduced to a type II iterated integral, and in both cases,
the double integral yields the volume of the solid between z = f( x,y) and the xy-plane over
the region R when f( x,y) 0. Other applications of the double integral include the area of a
region, the mass and center of mass of a laminate, and the computation of probabilities for
joint density functions.
Besides type I and type II regions, double integrals can be reduced to iterated integrals over
regions in other coordinate systems. In that case, the differential is multiplied by the absolute
value of the Jacobian determinant. Among the most important of these coordinate systems are
polar coordinates, and indeed, the calculation of double integrals in polar coordinates is
important in many applications of statistics.
Finally, the double integral concept can be extended to three or more integrals. Triple
integrals often occur in association with densities, where a density is the measure of the
amount of a physical quantity per unit volume of a geometric solid. Triple integrals in
applications also occur frequently in either cylindrical or spherical coordinates, particularly
when those applications involve regular solids such as spheres and right circular cylinders.
8
�7.0
References
1)
2)
3)
4)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiple_integral
http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu/Classes/CalcIII/MultipleIntegralsIntro.aspx
https://www.math.hmc.edu/calculus/tutorials/multipleintegration/
Module Engineering mathematics 3, UTHM.