Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Permanent Upper Canine Notes
Uploaded by
Hayley WelshOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Permanent Upper Canine Notes
Uploaded by
Hayley WelshCopyright:
Available Formats
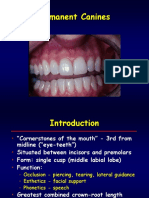
Permanent Upper Canines
Teeth Description Qs must be answered in this order
1. Functions
2. Chronology
3. Number of lobes
4. Geometric Outline of the crown (what is the overall shape of the crown?)
5. Outlines of the crown (trace the borders of the crown and root and describe each border)
6. Outline of the root (see above)
7. Surface anatomy of the crown and root
8. Pulp cavity
Functions
- Cutting and Tearing
- Aethetics: Well-arranged and properly aligned teeth support facial expressions and give a nice
appearance to the face
- Speaking: Clear pronunciation and sound
- Growth of Jaws
Chronology
Upper Cs
Lower Cs
B.O.C
4-5y
4-5y
Crown Completion
6-7y
6-7y
Eruption
9-10y
11-12y
Root Completion
12-13y
14-16y
Number of Lobes
- 4 lobes 3 Lobes (Labially) + 1 Cingulum (Lingually)
o Cingulum: A rounded elevation on the cervical third of the lingual surface of crowns in
anterior teeth representing the maximum convexity on the lingual side.
o Middle labial lobe over-develops (i.e. develops more than the other 2 labial lobes) to form
the labial ridge and the cusp tip
Labial Aspect
Geometric Outline of the crown
- Trapezoid outline with the shorter side cervically and longer side incisally
*The cusp-tip is not included into the trapezoidal outline
Lobe: A primary centre of calcification and growth
formed during crown development. Each tooth is
formed from the union of 4 lobes or more. Pulp horns
in the pulp chamber correspond to each lobe.
Cervical Line: Junction between
cementum and enamel
Outlines of the crown
Mesial Outline
Upper
Cs
Lower
Cs
Convex till the
contact area
(@ the jxn
between
incisal and
middle 1/3)
Straight
Distal Outline
Concave till the
contact area
(@ middle 1/3)
Concave
Mesial
Cusp Slope
Concave
Distal Cusp
Slope
Convex
Cervical
Outline
Convex Root
Wise
Convex
Straight
Convex Root
Wise
Contact
Areas
More
cervically
More
incisally (so
crown
appears
longer and
thinner
than lower)
*Convex/Concave/More convex = All the curvatures are only SLIGHTLY curved, curvature is not very
pronounced
Cusp Slope: A linear elevation on the
*Upper Cs cusp tip is more pointed than lower Cs cusp tip
occlusal surface of posterior teeth.
Outline of the Root
Mesial and Distal
Outline
Upper Cs
Tapered to a pointed distally curved
apex
Lower Cs
Tapered to a sharply pointed distally
curved apex
Cervical Ridge: linear elevation on the cervical 1/3
Surface Anatomy of the Crown
of facial surfaces of all teeth representing the
- Elevations
maximum convexity of the facial surface
o Crown surface is convex with maximum convexity at the cervical ridge
o Prominent ridge that runs from the cusp tip toward the cervical margin representing the
labial ridge
o Middle lobe is well developed giving the cusp
- Depressions
o Shallow longitudinal depression lie mesial and distal to the labial ridge
Labial Developmental Grooves: A narrow, shallow, sharply defined linear depression
on the labial surface of canines representing the fusion between lobes
Surface Anatomy of the Root
- Root shows smooth convex surface
Labial Ridge: A linear elevation on the labial surface of
canines which represents greater development of the
middle labial lobe.
Pulp Cavity
Pulp Chamber: Present in crown
- Outline of pulp chamber follows outline of crown
- In young teeth, pulp chamber has pulp horns related to the cusps
Root Canal: Present in root
- Outline of root canal follows outline of root
- Number of root canal is only one
o Sometimes lower canine has 2 root canines labially and lingually. Canals open in one apical
foramen or separate foramina.
Lingual Aspect
Can skip Geometric outline of the crown, Outlines of the crown, Outline of the root and write The
lingual surface is the reverse outline of the labial surface with lingual convergence
Geometric Outline of the crown: Same as labial aspect
Outlines of the crown: Same as labial aspect
Outline of the Root: Same as labial aspect
Marginal Ridge: A linear elevation on the mesial and distal
margin of the occlusal surface of posterior teeth.
Surface Anatomy of the Crown
- Elevations
Cusp Slope: A linear elevation on the
o Distal and Mesial marginal ridges:
occlusal surface of posterior teeth.
o Cingulum
o In upper canines, prominent lingual ridge extends from cusp tip to the cingulum whereas in
lower canines, the lingual ridge is restricted to the incisal third
o Distal Cusp Slope (also known as distal incisal ridge) and Mesial Cusp Slope (also known as
mesial incisal ridge)
- Depressions
o In upper canines, lingual ridge divides lingual fossa into a mesial and distal lingual fossae (2
fossae) whereas there is only one fossa in lower canines (due to a less developed lingual
ridge)
*Elevations of lower canine are not as well developed as the upper canine
*Lingual surface is smaller in size than the labial surface due to lingual convergence
Surface Anatomy of the Root
- Root shows smooth convex surface
Cingulum: A rounded elevation on the cervical third of the
lingual surface of crowns in anterior teeth representing the
maximum convexity on the lingual side.
Pulp Cavity: Same as labial aspect
Proximal Aspect
Lingual Ridge: A linear elevation that is found on the lingual
surface of canines. Its more developed in the upper canine
than lower canine
Geometric Outline of the crown
Proximal Aspects: Triangular outline with the apex incisally and base cervically
Cusp tip of upper 3 centralized on the long axis or inclined labially from the long axis and is also
shifted mesially from long axis
- Cusp tip of lower 3 inclined lingually from the long axis and is also shifted mesially from long axis
*Long Axis = Line that runs through the crown and root of the tooth in a way that the substance (crown
and root) around the line is symmetrically distributed
Lingual Fossa: A circumscribed depression found on
the lingual surface of anterior teeth.
Outlines of the crown
Labial Outline
Lingual Outline
Cervical outline
Upper Cs
Convex cervically due to
Convex cervically
Concave root-wise
the cervical ridge and
represented by the
however curvature is less
straight in the middle and
cingulum, straight in the
on the distal than mesial
incisal region (straight
middle due to the lingual
side
being labially inclined)
ridge and convex incisally
due to the incisal ridge
Lower Cs
Convex cervically due to
Convex cervically
Concave root-wise
the cervical ridge and
represented by the
however curvature is less
straight in the middle and
cingulum, concave in the
on the distal than mesial
incisal region (straight
middle due to the lingual
side
being lingually inclined)
fossa and convex incisally
due to the lingual fossa
*For upper Cs, in the middle of the lingual outline, you would expect a depression due to the lingual
fossa, however, its straight due to the lingual ridge but in lower Cs, the middle is concave as the lingual
ridge is not as long/prominent.
Incisal Ridge: A linear elevation on the lingual surface at the incisal third of
anterior teeth. Gets worn down by time. Outlines the incisal border of the
lingual fossa.
Outline of the Root
Upper Canine
Labial and Lingual Tapered from cervical line to a pointed
Outline
blunted apex (gradual tapering starting from
cervical 1/3 of root to the end)
Lower Canine
Nearly straight from the cervical line to the
middle third then tapered to a more pointed
apex (tapering only start at the middleincisal 1/3 jxn)
Surface Anatomy of the Crown
- Crown surface is convex and smooth except...
o Area cervical to the contact area shows flattening in the mesial surface
o Area cervical to the contact area shows a concavity on the distal surface
Surface Anatomy of the Root
- Root surface is broad with longitudinal depression
o Longitudinal depression is shallower mesially than distally of same tooth and is shallower in
upper canine than lower canine
*Longitudinal depression in lower canine may be so deep that it may cause bifurcation in the root
(bifurcation apically or extend up to cervical 1/3)
Pulp Cavity: Same as labial aspect
Incisal Aspect
Geometric Outline of the crown
- Diamond shape (thickness>width)
Outlines of the crown
Incisal Aspect (what the diamond outline consist of): Draw PIC!
- Labial surface appears convex
- Cingulum forms a short arc
Surface Anatomy of the Crown: Same as labial and lingual aspects
Pulp Cavity: Same as labial aspect
Extra Notes
*Redo defintions and pictures
*Possible Contact Areas: Incisal 1/3, Jxn between incisal (or occlusal) and middle 1/3 and center of
middle 1/3
*Anterior Teeth Contact Areas Mesial side always incisal 1/3, Distal side always jxn between incisal
and middle 1/3
*Majority of Posterior Teeth Contact Areas Mesial side usually Jxn between occlusal 1/3 and middle
1/3 and distal side usually center of middle 1/3
*Most common anterior tooth to have 2 roots is the LOWER CANINE
*3 main differences between mesial/distal surfaces of teeth is the level of contact area, curvature of
cervical line and the depth of the developmental grooves
You might also like
- Internal Medicine NotesDocument54 pagesInternal Medicine NotesHayley Welsh75% (4)
- Tooth Morphology of Permenant Central IncisorsDocument44 pagesTooth Morphology of Permenant Central IncisorsVenkata Ramanan Dasu SubramanianNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormFrom EverandThe Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Gamsat Sample Preview 7Document11 pagesGamsat Sample Preview 7Hayley Welsh100% (1)
- Perio Notes CombinedDocument71 pagesPerio Notes CombinedHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- 8 CaninesDocument51 pages8 CaninesDidar Sadiq KwekhaNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy LectureDocument37 pagesDental Anatomy LectureHitesh Chopra100% (2)
- A Presentation On-: Dr. Nikhil Oza Intern BvdumcDocument43 pagesA Presentation On-: Dr. Nikhil Oza Intern BvdumcMaheboob GanjalNo ratings yet
- RUKUS April 2011Document40 pagesRUKUS April 2011RUKUS Magazine100% (2)
- Igcse Revision BookDocument23 pagesIgcse Revision BookJo Patrick100% (2)
- PharmacologyDocument48 pagesPharmacologyHayley Welsh90% (10)
- Nutrient DeficiencyDocument8 pagesNutrient Deficiencyfeiserl100% (1)
- Maxillary Molars - PadmineeDocument35 pagesMaxillary Molars - PadmineepadmineekrishnanNo ratings yet
- 1.permanent Maxillary PremolarsDocument28 pages1.permanent Maxillary Premolarsdr-ahmedyu67% (3)
- Siemens Internship ReportDocument84 pagesSiemens Internship Reportujjawalbhojawala100% (1)
- Mandibular PremolarsDocument50 pagesMandibular PremolarsShipra SinghNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Physiology Practice QuestionsHayley Welsh100% (1)
- General Medicine ScenarioDocument8 pagesGeneral Medicine ScenarioHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Biomediacal Waste Project FinalDocument43 pagesBiomediacal Waste Project Finalashoknr100% (1)
- 5 Upper CanineDocument26 pages5 Upper Caninemoh.ahm3040No ratings yet
- 4 Lower IncisorsDocument23 pages4 Lower Incisorsmoh.ahm3040No ratings yet
- In The Name of Allah The Most Gracious The Most MercifulDocument118 pagesIn The Name of Allah The Most Gracious The Most Mercifulkhlid21mtz100% (2)
- Mandibular First PremolarDocument5 pagesMandibular First PremolarHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Centeral IncisorDocument22 pagesMaxillary Centeral IncisordrnaglaaNo ratings yet
- Maxillary MolarsDocument46 pagesMaxillary MolarsraminismahelNo ratings yet
- Maxillary First PremolarDocument6 pagesMaxillary First PremolarHayley Welsh100% (1)
- 7 Upper 1st PremolarDocument28 pages7 Upper 1st Premolarmoh.ahm3040No ratings yet
- DR Abhishek SolankiDocument27 pagesDR Abhishek SolankiOdalis CuaspudNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Permanent Lateral IncisorDocument4 pagesMandibular Permanent Lateral IncisorHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Upper CentralDocument27 pagesUpper CentralMarlene CasayuranNo ratings yet
- 3 Dental Anatomy Central Insicor Lec 3Document20 pages3 Dental Anatomy Central Insicor Lec 3Somansh GoyalNo ratings yet
- Permanent Maxillary CanineDocument12 pagesPermanent Maxillary CanineSachin PahariyaNo ratings yet
- 6 Lower CanineDocument19 pages6 Lower Caninemoh.ahm3040No ratings yet
- Mandibular PremolarsDocument28 pagesMandibular PremolarsraminismahelNo ratings yet
- 2-Mandibular IncisorsDocument31 pages2-Mandibular IncisorselctoyasNo ratings yet
- Maxillary and Mandibular Canine 1Document19 pagesMaxillary and Mandibular Canine 1Daynee SuguitanNo ratings yet
- Permanent Max - Central IncisorDocument26 pagesPermanent Max - Central IncisorAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Permanent Central IncisorsDocument68 pagesMaxillary Permanent Central IncisorsAmit Singh100% (1)
- The Permanent Maxillary PremolarsDocument27 pagesThe Permanent Maxillary PremolarsDina YasserNo ratings yet
- 1, Maxillary Permanent Central IDocument39 pages1, Maxillary Permanent Central Icelestina dawn peterNo ratings yet
- الرابعةDocument35 pagesالرابعةzainb1990355No ratings yet
- CaninesDocument15 pagesCaninesSuresh BabburiNo ratings yet
- Lower CentralDocument1 pageLower CentralHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Mand. IncisoresDocument25 pagesMand. IncisoreselctoyasNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatom12014Document48 pagesDental Anatom12014Sweet manNo ratings yet
- The Permanent Mandibular PremolarsDocument67 pagesThe Permanent Mandibular PremolarsSushmitKoju100% (1)
- Mandibular First PremolarDocument36 pagesMandibular First PremolarmaeenalmathaniNo ratings yet
- Maxillary First PremolarDocument8 pagesMaxillary First PremolarmaeenalmathaniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Permanent TeethDocument76 pagesAnatomy of Permanent TeethSinchita MahataNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy Lec.6Document48 pagesDental Anatomy Lec.6zainb1990355No ratings yet
- Anterior Teeth 09Document6 pagesAnterior Teeth 09DrSumaiya SayyedNo ratings yet
- CaninesDocument42 pagesCaninesKeerthikaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Landmarks of The CrownDocument3 pagesAnatomical Landmarks of The CrownHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Permanent Anterior Teeth06Document5 pagesPermanent Anterior Teeth06Tram BuiNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Second PremolarDocument6 pagesMaxillary Second PremolarmaeenalmathaniNo ratings yet
- Terminoligies of Tooth MorphologyDocument33 pagesTerminoligies of Tooth MorphologyAyeshaNo ratings yet
- PDF - 2 PDFDocument29 pagesPDF - 2 PDFDina YasserNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy: The Permanent Canines .Document7 pagesDental Anatomy: The Permanent Canines .S:M:ENo ratings yet
- Permanent Mandibular IncisorsDocument22 pagesPermanent Mandibular IncisorsManar AlmousawiNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy: Lec-The Permanent Mandibular 1st PremolarDocument8 pagesDental Anatomy: Lec-The Permanent Mandibular 1st Premolarعبدالرحمن عدي عبدالفتاحNo ratings yet
- Permanent Maxillary PremolarsDocument33 pagesPermanent Maxillary PremolarspnnavyaaNo ratings yet
- Maxillary 2nd Premolar: Smaller Less Seldom SeenDocument16 pagesMaxillary 2nd Premolar: Smaller Less Seldom SeenAbdallah Essam Al-ZireeniNo ratings yet
- MolarsDocument8 pagesMolarsJoubert ViannaNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy - Lecture-5Document27 pagesDental Anatomy - Lecture-5zainb1990355No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - MORPHOLOGY OF PERMANENT CANINESDocument22 pagesLecture 5 - MORPHOLOGY OF PERMANENT CANINESSara Al-Fuqaha'No ratings yet
- Maxillary & Mandibular CaninesDocument35 pagesMaxillary & Mandibular CaninesNarayana Sarma MarthiNo ratings yet
- Permanent Mandibular MolarsDocument78 pagesPermanent Mandibular Molarsmarydent101No ratings yet
- Morphology of Permanent CaninesDocument14 pagesMorphology of Permanent CaninesPrince AhmedNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Permanent CaninesDocument15 pagesMorphology of Permanent Caninesamanita238No ratings yet
- Prostho Sheet 8 LatestDocument17 pagesProstho Sheet 8 LatestDaniel AtiehNo ratings yet
- A New Order of Fishlike Amphibia From the Pennsylvanian of KansasFrom EverandA New Order of Fishlike Amphibia From the Pennsylvanian of KansasNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum ExamDocument2 pagesCerebellum ExamHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Ankle & Foot ExamDocument2 pagesAnkle & Foot ExamHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Scenario - Colicky PainDocument6 pagesPaediatric Scenario - Colicky PainHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- You Are A Paediatric Registrar at GCUH and Judy, Has Brought Her Son Dylan, Age 3, To See You With Concerns of Delayed DevelopmentDocument2 pagesYou Are A Paediatric Registrar at GCUH and Judy, Has Brought Her Son Dylan, Age 3, To See You With Concerns of Delayed DevelopmentHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument2 pagesBasic Life SupportHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Headache History TakingDocument1 pageHeadache History TakingHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Year 1 OsceDocument1 pageYear 1 OsceHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine Exam HintsDocument2 pagesOral Medicine Exam HintsHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- General Medical ScenarioDocument5 pagesGeneral Medical ScenarioHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- New Questions Oral Med in 2014Document3 pagesNew Questions Oral Med in 2014Hayley WelshNo ratings yet
- O&G StationDocument4 pagesO&G StationHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Questions PerioDocument9 pagesQuestions PerioHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- List of DentinDocument1 pageList of DentinHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- PBL Case 3 - Felipe and GarciaDocument25 pagesPBL Case 3 - Felipe and GarciaHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Local Anaesthetic CourseDocument123 pagesLocal Anaesthetic CourseHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Geometric Outlines of Permanent TeethDocument1 pageGeometric Outlines of Permanent TeethHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Prepoll TimesDocument68 pagesPrepoll TimesHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Maturational Changes in The Jaw and TeethDocument4 pagesMaturational Changes in The Jaw and TeethHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 SummaryDocument6 pagesLab 2 SummaryHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Neural Crest Cell: As The Groove Gets Deeper, Neural Crest. After The Neural Fold Meet andDocument4 pagesNeural Crest Cell: As The Groove Gets Deeper, Neural Crest. After The Neural Fold Meet andHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Microscope Slides - Decalcified Sections Tooth DevelopmentDocument3 pagesMicroscope Slides - Decalcified Sections Tooth DevelopmentHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Permanent Lateral IncisorDocument4 pagesMandibular Permanent Lateral IncisorHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Direct Factors Affecting The PeriodontiumDocument4 pagesDirect Factors Affecting The PeriodontiumHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Communication Models in Internet of Things: A SurveyDocument5 pagesCommunication Models in Internet of Things: A SurveyIJSTENo ratings yet
- DEEP ECOLOGY - An Intro - McLaughlinDocument5 pagesDEEP ECOLOGY - An Intro - McLaughlinCarlo MagcamitNo ratings yet
- TS SR Chemistry Imp Questions PDFDocument5 pagesTS SR Chemistry Imp Questions PDFUnknown Khan100% (3)
- Trawl Master Present A TieDocument19 pagesTrawl Master Present A Tieapi-3719203No ratings yet
- Generalized Anxiety DisorderDocument24 pagesGeneralized Anxiety DisorderEula Angelica OcoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds WorksheetDocument2 pagesChemical Bonds WorksheetJewel Mae MercadoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 English As Grade 4Document28 pagesQuarter 4 English As Grade 4rubyneil cabuangNo ratings yet
- MiscanthusDocument27 pagesMiscanthusJacob GuerraNo ratings yet
- Furuno CA 400Document345 pagesFuruno CA 400Димон100% (3)
- Case StudyDocument61 pagesCase StudyA GNo ratings yet
- ODA X9 2SL DatasheetDocument8 pagesODA X9 2SL DatasheetYudy UtamaNo ratings yet
- A Tired BrainDocument3 pagesA Tired BrainSivasonNo ratings yet
- A Textual Introduction To Acarya Vasuvan PDFDocument3 pagesA Textual Introduction To Acarya Vasuvan PDFJim LeeNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: B.E Ece (5Th Semester)Document17 pagesDigital Signal Processing: B.E Ece (5Th Semester)Saatwat CoolNo ratings yet
- 10th ORLIAC Scientific Program As of 26 Jan 2018Document6 pages10th ORLIAC Scientific Program As of 26 Jan 2018AyuAnatrieraNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure, Function Practice Test With AnswersDocument16 pagesCell Structure, Function Practice Test With AnswersDJ ISAACSNo ratings yet
- Fret Position Calculator - StewmacDocument1 pageFret Position Calculator - StewmacJuan Pablo Sepulveda SierraNo ratings yet
- Relationsh Between EM and Young S ModuliDocument7 pagesRelationsh Between EM and Young S ModuliDwight AndersonNo ratings yet
- Project Title Discipline Project Stage Client Attendance CirculationDocument4 pagesProject Title Discipline Project Stage Client Attendance CirculationgregNo ratings yet
- YogaDocument116 pagesYogawefWE100% (2)
- Germania Agenturinfo enDocument4 pagesGermania Agenturinfo enДушан СтепановићNo ratings yet
- Physics 101Document21 pagesPhysics 101Kuna KunavathiNo ratings yet
- 1ST SUMMATIVE TEST FOR G10finalDocument2 pages1ST SUMMATIVE TEST FOR G10finalcherish austriaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Internet of Things: Presented To-Presented byDocument18 pagesIndustrial Internet of Things: Presented To-Presented byGaurav RaturiNo ratings yet