Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Revised Bloom's Taxonomy Tools
Uploaded by
PrinceCatayloCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Revised Bloom's Taxonomy Tools
Uploaded by
PrinceCatayloCopyright:
Available Formats
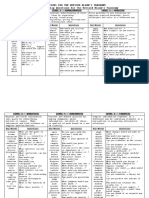
Hierarchical Interpretation of Revised Bloom's Taxonomy
CREATE
Put elements together to form a coherent
whole or functional whole (something new) or
reorganize elements into a new pattern or
structure
EVALUATE
Make judgment based on criteria or standards
APPLY
Carry out or use a procedure in a given situation
ANALYZE
Break material or concept into its constituent
parts and determine how the parts relate to
one another and to the overall structure or
purpose
UNDERSTAND
Construct meaning from instructional messages, including oral, written, and graphic
communication
REMEMBER
Retrieve relevant knowledge and information from long term memory
ADD, SUBTRACT OR MODIFY
FACTS
>Specific details and
elements
>Terminology
CONCEPTS
>Theories, models, and
structure
>Principles and
generalizations
>Classifications and
categories
PROCEDURES or
OPERATIONS
>Criteria for
determining when to
use an appropriate
procedure
>Subject-specific
techniques and
methods
>Subject-specific skills
and algorithms
METACOGNITIVE
KNOWLEDGE
>Self-knowledge
>Knowledge about
cognitive tasks,
including appropriate
contextual and
condition knowledge
>Strategic Knowledge
Hierarchical Interpretation of Revised Bloom's Taxonomy
CREATE
What changes would you make to solve...? How would
you improve...? What would happen if...? Can you
elaborate on the reason...? Can you propose an
alternative...? Can you invent...? How would you
invent...? How would you adapt...to create a
different...? How can you change/modify the
plan/plot...? What could be done to
minimize/maximize...? What way would you design...?
What could be combined to improve/change...? How
would you test...? Can you formulate a theory for...?
Can you predict the outcome if...? How would you
estimate the results for...? What facts can you
compile...? Can you construct a model that would
change...? Can you think and original way for...?
EVALUATE
Do you agree with the actions/outcome...? What is
your opinion...? How would you prove/disprove...? Can
you assess the value or importance of...? Would it be
better if...? Why did they choose...? What would you
recommend...? How would you rate the...? What you
cite to defend...? How would you evaluate...? How
could you determine...? What choice would you have
made...? What would you select...? How would you
prioritize...? What judgment would you make
about...? Based on what you know, how would you
explain...? What information would you use to
support the view...? How would you justify...? What
data was used to make the conclusion...? Why was it
better that...? How would you prioritize the facts...?
How would you compare the ideas/people...?
APPLY
ANALYZE
How would you use...? What examples can you find
What are the parts or features of...? How
to...? How would you solve...using what you have
is...related to...? Why do you think...? What is the
learned...? How would you organize...to show...? How
theme...? What motive is there...? Can you list the
would you show your understanding of...? What
parts...? What inference can you make...? What
approach would you use to...? How would you apply
conclusions can you draw...? How would you
what you have learned to develop...? What other way
classify...? How would you categorize...? Can you
would you plan to...? What would result if...? What
identify the different parts...? What evidence can
elements would you choose to change...? What facts you find...? What is the relationship between...? Can
would you select to show...? What questions would
you make a distinction between...? What is the
you ask in an interview with...?
function of...? What ideas justly...?
UNDERSTAND
How would you classify the type of...? How would you compare/contrast...? Will you state or interpret in
your own words...? How would you rephrase the meaning...? What facts or ideas show...? What is the main
idea...? Which statement supports...? Can you explain what is happening/what is meant...? What can you say
about...? Which is the best answer...? How would you summarize...?
REMEMBER
What is...? Where is...? How did...happen? Why did...? When did...? How would you show...? Who/What were
the main...? Which one...? How is...? When did...happen? How would you explain...? How would you
describe...? Can you recall...? Can you select...? Can you list...? Who was...?
ADD, SUBTRACT OR MODIFY
The basic elements
students must know to
be acquainted with a
discipline or solve
problems in it
>Specific details and
elements
>Terminology
The interrelationship
How to do something, Knowledge of thinking in
among the basic
methods of inquiry, and
general as well as
elements within a larger criteria for using skills,
awareness and
structure that enable
algorithms, techniques, knowledge of ones own
them to function
and methods
thinking in particular
together
>Criteria for determining >Strength and Weakness
>Theories, models, and
when to use an
> Proper and Effective
structure
appropriate procedure
Cognitive Tools that
>Principles and
>Subject-specific
Meet the Context and
generalizations
techniques and methods
Condition
>Classifications and
>Subject-specific skills
>Rehearsal, Elaboration,
categories
and algorithms
Organizational
Strategies, Heuristics,
Algorithms. Etc.
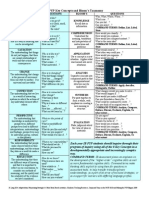
Hierarchical Interpretation of Revised Bloom's Taxonomy
CREATE
EVALUATE
Can you design a to ? Can you see a possible solution to
What fallacies, consistencies, inconsistencies appear?
? If you had access to all resources, how would you deal
Which is more important, moral, better, logical, valid,
with ? Why dont you devise your own way to ? What appropriate? Find the errors. Is there a better solution to
would happen if? How many ways can you ? Can you
? Judge the value of What do you think about ? Can
create new and unusual uses for ? Can you develop a
you defend your position about ? Do you think is a good
proposal which would ? How would you test ? Propose an
or bad thing? How would you have handled ? What
alternative. How else would you ? State a rule.
changes to would you recommend? Do you believe ?
How would you feel if ? How effective are ? What are
the consequences of ? What influence will have on our
lives? What are the pros and cons of ? Why is of
value? What are the alternatives? Who will gain and who
will lose?
APPLY
ANALYZE
Predict what would happen if Choose the best
What is the function of ? Whats fact? Opinion? What
statements that apply. Judge the effects of What
assumptions ? What statement is relevant? What motive
would result ? Tell what would happen if Tell how,
is there? What conclusions? What does the author
when, where, why. Tell how much change there would be if believe? What does the author assume? State the point
Identify the results of Write in your own words
of view of What ideas apply? What ideas justify the
How would you explain ? Write a brief outline What do conclusion? Whats the relationship between? The least
you think could have happened next? Who do you think? essential statements are Whats the main idea/Theme?
What was the main idea ? Clarify why Illustrate the What literary form is used? What persuasive technique is
Does everyone act in the way that
used? Determine the point of view, bias, values, or intent
does? Draw a story map. Explain why a character acted
underlying presented material. Which events could not
in the way that he did. Do you know of another instance
have happened? If happened, what might the ending
where ? Can you group by characteristics such as ?
have been? How is similar to ? What do you see as
Which factors would you change if ? What questions
other possible outcomes? Why did changes occur? Can
would you ask of? From the information given, can you
you explain what must have happened when ? What were
develop a set of instructions about ?
some of the motives behind ? What was the turning
point? What are some of the problems of ? Can you
distinguish between ?
UNDERSTAND
What does this mean? Which are the facts? State in your own words. Is this the same as ? Give an example. Select
the best definition. Condense this paragraph. What would happen if ? Explain why ... What expectations are there?
Read the graph (table). What are they saying? This represents What seems to be ? Is it valid that ? What seems
likely? Show in a graph, table. Which statements support ? What restrictions would you add? Outline What could
have happened next? Can you clarify...? Can you illustrate ...? Does everyone think in the way that does?
REMEMBER
Who? Where? Which one? What? How? Why? How much? How many? When? What does it mean? What happened
after? What is the best one? Can you name all the ? Who spoke to ? Which is true or false?
ADD, SUBTRACT OR MODIFY
The basic elements
students must know to be
acquainted with a discipline
or solve problems in it
>Specific details and
elements
>Terminology
The interrelationship
among the basic elements
within a larger structure
that enable them to
function together
>Theories, models, and
structure
>Principles and
generalizations
>Classifications and
categories
How to do something,
Knowledge of thinking in
methods of inquiry, and
general as well as
criteria for using skills,
awareness and knowledge
algorithms, techniques, and
of ones own thinking in
methods
particular
>Criteria for determining
>Strength and Weakness
when to use an appropriate
> Proper and Effective
procedure
Cognitive Tools that Meet
>Subject-specific
the Context and Condition
techniques and methods
>Rehearsal, Elaboration,
>Subject-specific skills and Organizational Strategies,
algorithms
Heuristics, Algorithms. Etc.
Hierarchical Interpretation of Revised Bloom's Taxonomy
CREATE
EVALUATE
>PRODUCING: Inventing a product
> CRITIQUING: Detecting the appropriateness of a
>PLANNING: Devising a procedure for accomplishing procedure to a given problem; Determining whether
a task
a product has external consistency; Detecting
>GENERATING: Coming up with an alternative
inconsistencies between a product/operation and
hypothesis based on a criteria
external criteria;
>CHECKING: Detecting the effectiveness of a
procedure as implemented; Determining whether a
process/product has internal consistency;
Detecting inconsistencies/fallacies within a process
or product
APPLY
>IMPLEMENTING: Applying knowledge to a nonroutine task
>EXECUTING: Applying knowledge to a routine task
ANALYZE
> ATTRIBUTING: Determining the point of view,
bias, values, or intent underlying the presented
material
>ORGANIZING: Determining how elements fit or
function within a structure
>DIFFERENTIATING: Distinguishing relevant from
irrelevant parts or important from unimportant
parts of presented material
UNDERSTAND
>EXPLAINING: Constructing a cause-and-effect model of a system
>COMPARING: Detecting correspondences between two ideas, objects, and the like
>INFERRING: Drawing a logical conclusion from presented information
>SUMMARIZING: Abstracting a general theme or major point
>CLASSIFYING: Determining that something belongs to a category such as concept or principle
>EXEMPLIFYING: Finding specific example or illustration of a concept or a principle
>INTERPRETING: Changing from one form of representation to another
REMEMBER
>RECALLING: Retrieving relevant knowledge from long term memory
>RECOGNIZING: Locating knowledge in long term memory that is consistent with presented material
ADD, SUBTRACT OR MODIFY
The basic elements
students must know to
be acquainted with a
discipline or solve
problems in it
>Specific details and
elements
>Terminology
The interrelationship
How to do something, Knowledge of thinking in
among the basic
methods of inquiry, and
general as well as
elements within a larger criteria for using skills,
awareness and
structure that enable
algorithms, techniques, knowledge of ones own
them to function
and methods
thinking in particular
together
>Criteria for determining >Strength and Weakness
>Theories, models, and
when to use an
> Proper and Effective
structure
appropriate procedure
Cognitive Tools that
>Principles and
>Subject-specific
Meet the Context and
generalizations
techniques and methods
Condition
>Classifications and
>Subject-specific skills
>Rehearsal, Elaboration,
categories
and algorithms
Organizational
Strategies, Heuristics,
Algorithms. Etc.
Hierarchical Interpretation of Revised Bloom's Taxonomy
CREATE
>PRODUCING: Make, Construct
>PLANNING: Design, Set-Up
>GENERATING: Suggest, Hypothesize, Imagine
EVALUATE
> CRITIQUING: Comment, Appraise, Judge, Assess
>CHECKING: Coordinate, Detect, Verify, Confirm,
Monitor, Test
APPLY
>IMPLEMENTING: Use, Apply
>EXECUTING: Carry out, Perform, Complete
ANALYZE
> ATTRIBUTING: Assign, Deconstruct
>ORGANIZING: Arrange, Find, Structure, Find
Coherence, Integrate, Outline, Parse
>DIFFERENTIATING: Select, Focus, Choose,
Discriminate, Distinguish
UNDERSTAND
>EXPLAINING: Give reasons, Justify, Create Model
>COMPARING: Compare, Contrast, Evaluate, Map
>INFERRING: Predict, Deduce, Extrapolate, Conclude, Interpolate
>SUMMARIZING: Summarize, Review, Abstract, Generalize
>CLASSIFYING: Arrange, Classify, Categorize, Sort, Subsume
>EXEMPLIFYING: Give examples, Illustrate, Demonstrate, Show, Instantiate
>INTERPRETING: Estimate, Convert, Translate, Clarify, Paraphrase, Represent
REMEMBER
>RECALLING: State, Define, Describe
>RECOGNIZING: Identify, Match
ADD, SUBTRACT OR MODIFY
The basic elements
students must know to
be acquainted with a
discipline or solve
problems in it
>Specific details and
elements
>Terminology
The interrelationship
How to do something, Knowledge of thinking in
among the basic
methods of inquiry, and
general as well as
elements within a larger criteria for using skills,
awareness and
structure that enable
algorithms, techniques, knowledge of ones own
them to function
and methods
thinking in particular
together
>Criteria for determining >Strength and Weakness
>Theories, models, and
when to use an
> Proper and Effective
structure
appropriate procedure
Cognitive Tools that
>Principles and
>Subject-specific
Meet the Context and
generalizations
techniques and methods
Condition
>Classifications and
>Subject-specific skills
>Rehearsal, Elaboration,
categories
and algorithms
Organizational
Strategies, Heuristics,
Algorithms. Etc.
Hierarchical Interpretation of Revised Bloom's Taxonomy
CREATE
Abstract, Animate, Arrange, Assemble, Budget,
Categorize, Code, Combine, Compile, Compose,
Construct, Cope, Correspond, Create, Cultivate,
Debug, Depict, Design, Develop, Devise, Dictate,
Enhance, Explain, Facilitate, Format, Formulate,
Generalize, Generate, Handle, Import, Improve,
Incorporate, Integrate, Interface, Join, Lecture,
Model, Modify, Network, Organize, Outline,
Overhaul, Plan, Portray, Prepare, Prescribe, Produce,
Program, Rearrange, Reconstruct, Relate,
Reorganize, Revise, Rewrite, Specify, Summarize,
Write
EVALUATE
Appraise, Assess, Compare, Conclude, Contrast,
Counsel, Criticize, Critique, Defend, Determine,
Discriminate, Estimate, Evaluate, Explain, Grade,
Hire, Interpret, Judge, Justify, Measure, Predict,
Prescribe, Rank, Rate, Recommend, Release, Select,
Summarize, Support, Test, Validate, Verify
APPLY
ANALYZE
Acquire, Adapt, Allocate, Alphabetize, Apply,
Analyze, Audit, Blueprint, Breadboard, Break down,
Ascertain, Assign, Attain, Avoid, Back up, Calculate, Characterize, Classify, Compare, Confirm, Contrast,
Capture, Change, Classify, Complete, Compute,
Correlate, Detect, Diagnose, Diagram, Differentiate,
Construct, Customize, Demonstrate, Depreciate,
Discriminate, Dissect, Distinguish, Document,
Derive, Determine, Diminish, Discover, Draw,
Ensure, Examine, Explain, Explore, Figure out, File,
Employ, Examine, Exercise, Explore, Expose,
Group, Identify, Illustrate, Infer, Interrupt,
Express, Factor, Figure, Graph, Handle, Illustrate,
Inventory, Investigate, Layout, Manage, Maximize,
Interconvert, Investigate, Manipulate, Modify,
Minimize, Optimize, Order, Outline, Point out,
Operate, Personalize, Plot, Practice, Predict,
Prioritize, Proofread, Query, Relate, Select,
Prepare, Price, Process, Produce, Project, Provide,
Separate, Size up, Subdivide, Train, Transform
Relate, Round off, Sequence, Show, Simulate,
Sketch, Solve, Subscribe, Tabulate, Transcribe,
Translate, Use
UNDERSTAND
Add, Approximate, Articulate, Associate, Characterize, Clarify, Classify, Compare, Compute, Contrast,
Convert, Defend, Describe, Detail, Differentiate, Discuss, Distinguish, Elaborate, Estimate, Example,
Explain, Express, Extend, Extrapolate, Factor, Generalize, Give, Infer, Interact, Interpolate, Interpret,
Observe, Paraphrase, Picture Graphically, Predict, Review, Rewrite, Subtract, Summarize, Translate,
Visualize
REMEMBER
Cite, Define, Describe, Draw, Enumerate, Identify, Index, Indicate, Label, List, Match, Meet, Name,
Outline, Point, Quote, Read, Recall, Recite, Recognize, Record, Repeat, Reproduce, Review, Select, State,
Study, Tabulate, Trace, Write
ADD, SUBTRACT OR MODIFY
The basic elements
students must know to
be acquainted with a
discipline or solve
problems in it
>Specific details and
elements
>Terminology
The interrelationship
How to do something, Knowledge of thinking in
among the basic
methods of inquiry, and
general as well as
elements within a larger criteria for using skills,
awareness and
structure that enable
algorithms, techniques, knowledge of ones own
them to function
and methods
thinking in particular
together
>Criteria for determining >Strength and Weakness
>Theories, models, and
when to use an
> Proper and Effective
structure
appropriate procedure
Cognitive Tools that
>Principles and
>Subject-specific
Meet the Context and
generalizations
techniques and methods
Condition
>Classifications and
>Subject-specific skills
>Rehearsal, Elaboration,
categories
and algorithms
Organizational
Strategies, Heuristics,
Algorithms. Etc.
You might also like
- RememberDocument6 pagesRememberStella Marie ParanNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Comprehension Application Analysis Synthesis EvaluationDocument3 pagesKnowledge Comprehension Application Analysis Synthesis EvaluationAileen PoLyNo ratings yet
- 6blooms Question StemsDocument2 pages6blooms Question Stemsapi-278656540No ratings yet
- Bloom Question StemsDocument3 pagesBloom Question Stemsapi-266088524No ratings yet
- Higher Order Thinking Question Stems for MathDocument5 pagesHigher Order Thinking Question Stems for MathVikrant SwamiNo ratings yet
- Bloom Taxonomyename: BloomTaxonomy PDFDocument10 pagesBloom Taxonomyename: BloomTaxonomy PDFAzrul AkmarNo ratings yet
- Level Level Attributes Keywords QuestionsDocument2 pagesLevel Level Attributes Keywords QuestionsbitbknNo ratings yet
- Bloom S Taxonomy Questions: KnowledgeDocument2 pagesBloom S Taxonomy Questions: KnowledgeCentro De Desarrollo Espiritual MultidisciplinarioNo ratings yet
- Blooms Sentence StartersDocument2 pagesBlooms Sentence Startersapi-224303452No ratings yet
- Use Old Ideas To CreateDocument3 pagesUse Old Ideas To CreateMarmhar Lumancas QuiñoNo ratings yet
- Writing Lesson ObjectivesDocument16 pagesWriting Lesson ObjectivesRosel Gonzalo-AquinoNo ratings yet
- Marzano's Levels of Thinking Question StemsDocument1 pageMarzano's Levels of Thinking Question StemsNathan LeeNo ratings yet
- Level 1: Remembering QuestionsDocument2 pagesLevel 1: Remembering QuestionsKriss HeiNo ratings yet
- Up0 Level 1: Remembering QuestionsDocument2 pagesUp0 Level 1: Remembering QuestionsKriss HeiNo ratings yet
- 2016 - RBT HandoutDocument2 pages2016 - RBT Handoutapi-325580763No ratings yet
- Types of Questions Based On BloomDocument2 pagesTypes of Questions Based On BloomElijah Loh Keng Soon100% (1)
- Higher Order Thinking Skill Question StemsDocument4 pagesHigher Order Thinking Skill Question Stemsm79pk2tkmyNo ratings yet
- Assessment Criteria ThesisDocument3 pagesAssessment Criteria ThesisJoseph JohnNo ratings yet
- Questions Aligned With Levels of BloomsDocument2 pagesQuestions Aligned With Levels of BloomscindymandalsumalinogNo ratings yet
- Bloom-Question Cues-ChartDocument1 pageBloom-Question Cues-Chartapi-317429889No ratings yet
- Bloom WRITING ObjectivesDocument3 pagesBloom WRITING Objectivesozypics6858No ratings yet
- Ela Question StemsDocument2 pagesEla Question Stemsapi-260890993No ratings yet
- Blooms Higher Order Thinking Questions 2Document2 pagesBlooms Higher Order Thinking Questions 28headNo ratings yet
- How to Write a Critical AnalysisDocument11 pagesHow to Write a Critical AnalysisSandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Bloom S Taxonomy of QuestionsDocument20 pagesBloom S Taxonomy of QuestionsDivina Gracia Barrion Cuya100% (1)
- During or After Reading/Teaching - Asking Questions: Adapted From Center For Resource Management Materials, © 2006Document3 pagesDuring or After Reading/Teaching - Asking Questions: Adapted From Center For Resource Management Materials, © 2006Jo MarchNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy Guide To Writing QuestionsDocument2 pagesBlooms Taxonomy Guide To Writing QuestionsAileen BaguhinNo ratings yet
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument32 pagesBloom's TaxonomyothmaneNo ratings yet
- Bloom Critical ThinkingDocument3 pagesBloom Critical ThinkingThan Rey SihombingNo ratings yet
- Writing Objectives Using Bloom's TaxonomyDocument4 pagesWriting Objectives Using Bloom's Taxonomyannie100% (1)
- Critical Thinking PromptsDocument1 pageCritical Thinking PromptskszonyiNo ratings yet
- Bentuk-Bentuk Pertanyaan Berdasarkan Taxonomy BloomDocument16 pagesBentuk-Bentuk Pertanyaan Berdasarkan Taxonomy BloomyoyokNo ratings yet
- Blooms Question StartersDocument4 pagesBlooms Question StartersAlex prhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts - AlexanderCh01finalR1 - V2 - Oct 19Document64 pagesChapter 1 - Basic Concepts - AlexanderCh01finalR1 - V2 - Oct 19Hammad Qazi HRNo ratings yet
- Questions For The Revised Bloom TaxonomyDocument2 pagesQuestions For The Revised Bloom Taxonomyapi-360025326No ratings yet
- Noelle Combs Inquiry LessonDocument6 pagesNoelle Combs Inquiry LessonBrandi Hughes CaldwellNo ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy Thinking SkillsDocument2 pagesBloom's Taxonomy Thinking SkillsFabio DelanoNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy Question Stem Cards RevisedDocument4 pagesBlooms Taxonomy Question Stem Cards Revisedangela3112No ratings yet
- Questions For The Revised BloomDocument2 pagesQuestions For The Revised BloomvempadareddyNo ratings yet
- Learning ObjectivesDocument21 pagesLearning ObjectivesLara ÖzerNo ratings yet
- Writing Objectives Using BloomDocument5 pagesWriting Objectives Using BloomEdher QuintanarNo ratings yet
- Blooms ConceptsDocument1 pageBlooms Conceptsapi-253971991No ratings yet
- Bloom's Posters ElementaryDocument7 pagesBloom's Posters Elementaryjrmitche100% (1)
- Questions for Effective LearningDocument26 pagesQuestions for Effective LearningHamidi HamidNo ratings yet
- BLOOM'S TAXONOMY: Sample Questions: KnowledgeDocument2 pagesBLOOM'S TAXONOMY: Sample Questions: KnowledgeSarah SaritaNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy Guide LinesDocument3 pagesBlooms Taxonomy Guide LinesSatish BojjawarNo ratings yet
- Blooms Question StemsDocument1 pageBlooms Question Stemsapi-263656720No ratings yet
- Bloom's Taxonomy (1)Document1 pageBloom's Taxonomy (1)mazvitamunopo05No ratings yet
- Types of Questions Based On Bloom'S TaxonomyDocument4 pagesTypes of Questions Based On Bloom'S Taxonomytan234567No ratings yet
- SixlevelsDocument6 pagesSixlevelsapi-281597833No ratings yet
- Socratic Questioning Techniques: Questions of ClarificationDocument6 pagesSocratic Questioning Techniques: Questions of Clarificationsunilmba2004No ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy and TOSDocument58 pagesBlooms Taxonomy and TOSNyora Donald100% (4)
- The Art of Effective Questioning: Asking The Right Question For The Desired ResultDocument25 pagesThe Art of Effective Questioning: Asking The Right Question For The Desired ResultAnaliza Yanoc RabanesNo ratings yet
- Mi Matrix Inquiry ProjectsDocument2 pagesMi Matrix Inquiry Projectsapi-279426599No ratings yet
- Math StemsDocument2 pagesMath StemsCornelia TwilleyNo ratings yet
- Types of Questions Based On Bloom'S Taxonomy: KnowledgeDocument5 pagesTypes of Questions Based On Bloom'S Taxonomy: KnowledgeMarjorie De Vera - PileNo ratings yet
- Blooms TaxonomyDocument3 pagesBlooms Taxonomysample sampleNo ratings yet
- Four Levels of Questions Level 1. Summarizing/Definition/Fact Questions Level 3. Hypothesis/Prediction QuestionsDocument1 pageFour Levels of Questions Level 1. Summarizing/Definition/Fact Questions Level 3. Hypothesis/Prediction QuestionsihavenoaddressNo ratings yet
- Kinds of SummaryDocument1 pageKinds of SummaryPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- QuotesDocument8 pagesQuotesPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Republica de Filipinas Ciudad de Zamboanga Officina Del Consejo Local Khymer Adan T. Olaso District I, City CouncilorDocument1 pageRepublica de Filipinas Ciudad de Zamboanga Officina Del Consejo Local Khymer Adan T. Olaso District I, City CouncilorPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- HonestyDocument1 pageHonestyPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- 2016 RemediallawquestionsDocument6 pages2016 RemediallawquestionsPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- HonestyDocument1 pageHonestyPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Fox and HedgehogDocument1 pageFox and HedgehogPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Capital PunishmentDocument1 pageCapital PunishmentPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Baguio Anti TruancyDocument8 pagesBaguio Anti TruancyPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Position Paper GuideDocument2 pagesPosition Paper GuidePrinceCataylo100% (1)
- FAQ - Teaching Proof and CertificateDocument2 pagesFAQ - Teaching Proof and CertificateNokki SabalboroNo ratings yet
- AccurateDocument1 pageAccuratePrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- List of Possible Themes in Literary WorksDocument2 pagesList of Possible Themes in Literary WorksPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Fox and HedgehogDocument1 pageFox and HedgehogPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Human Tragedy and MeaningDocument40 pagesHuman Tragedy and MeaningPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Man-Christianity's PerspectiveDocument14 pagesPhilosophy of Man-Christianity's PerspectivePrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- L1 Character AccurateDocument1 pageL1 Character AccuratePrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Explore Elements of Art in a Multi-Module CourseDocument350 pagesExplore Elements of Art in a Multi-Module CoursePrinceCataylo100% (2)
- Issue StatementDocument20 pagesIssue StatementPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Man Christianity Human Spirit Spirituality MysticismDocument14 pagesPhilosophy of Man Christianity Human Spirit Spirituality MysticismPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Position Paper GuideDocument2 pagesPosition Paper GuidePrinceCataylo100% (1)
- A Brain Fart On The Inconvenient TruthDocument3 pagesA Brain Fart On The Inconvenient TruthPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Paragraph ReasoningDocument29 pagesParagraph ReasoningPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Hi Cement vs. Insular Bank DigestDocument2 pagesHi Cement vs. Insular Bank DigestPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Paat vs. CADocument2 pagesPaat vs. CAPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- CapCo Vs Macasaet DigestDocument1 pageCapCo Vs Macasaet DigestPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- GSIS Vs CA Case DigestDocument1 pageGSIS Vs CA Case DigestPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Brain Fart On Wildlife and Forest ConservationDocument4 pagesBrain Fart On Wildlife and Forest ConservationPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- Brain Fart On The IPRA LawDocument2 pagesBrain Fart On The IPRA LawPrinceCatayloNo ratings yet
- BPI Vs Roxas DigestDocument1 pageBPI Vs Roxas DigestPrinceCataylo100% (1)
- English WordsDocument136 pagesEnglish Wordshhavijian1970No ratings yet
- 20+ EOS Terms Your EmployeesDocument6 pages20+ EOS Terms Your Employeesjosh pocock100% (1)
- Oracle DBADocument569 pagesOracle DBASraVanKuMarThadakamalla100% (2)
- FAQ HEPAs and ULPAs Technical Bulletin - Parte2Document1 pageFAQ HEPAs and ULPAs Technical Bulletin - Parte2Nicolás VargasNo ratings yet
- Rate of Respiration in Small InvertebratesDocument2 pagesRate of Respiration in Small InvertebratestahjsalmonNo ratings yet
- SAS Universal Viewer 1.2: User's GuideDocument32 pagesSAS Universal Viewer 1.2: User's GuideSmita AgrawalNo ratings yet
- The Qualities of A Good Businessman-Syed Muhammad JubairDocument8 pagesThe Qualities of A Good Businessman-Syed Muhammad JubairAdeel AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Participles & Participial Phrases: - A Verb Form That Is Used As AnDocument13 pagesParticiples & Participial Phrases: - A Verb Form That Is Used As AnRoy SihombingNo ratings yet
- Kreiger Set Volume BibleDocument21 pagesKreiger Set Volume Biblechris_blair_1No ratings yet
- 8 - HEURTEY PETROCHEM Flux Distribution in Fired Heaters A Case StudyDocument27 pages8 - HEURTEY PETROCHEM Flux Distribution in Fired Heaters A Case Studyfawmer61No ratings yet
- Analisis Perancangan Struktur Organisasi Penyelenggaraan Proyek Pembangunan Pelabuhan PatimbanDocument12 pagesAnalisis Perancangan Struktur Organisasi Penyelenggaraan Proyek Pembangunan Pelabuhan PatimbanAthanasius Kurniawan Prasetyo AdiNo ratings yet
- Econometrics I: Professor William Greene Stern School of Business Department of EconomicsDocument47 pagesEconometrics I: Professor William Greene Stern School of Business Department of EconomicsAnonymous 1tv9MspNo ratings yet
- Big Car Small Car Big Car IiDocument6 pagesBig Car Small Car Big Car IierwinssNo ratings yet
- Isi Mtech Qror 05Document20 pagesIsi Mtech Qror 05api-26401608No ratings yet
- Module 8Document7 pagesModule 8Maiden UretaNo ratings yet
- Ananga Rang ADocument17 pagesAnanga Rang Aonlinemoney4uNo ratings yet
- 2 Math Review Q1 (Value of a 3 digit number)Document3 pages2 Math Review Q1 (Value of a 3 digit number)N Plai PlaiNo ratings yet
- Management 1Document6 pagesManagement 1Mardi UmarNo ratings yet
- 10 Meaningful Pros and Cons of Mandatory Military ServiceDocument4 pages10 Meaningful Pros and Cons of Mandatory Military ServiceJoseph LopezNo ratings yet
- The Oak Island Money Pit: Remote Viewing Summary Sheet © Daz Smith - Do Not Distribute Without PermissionDocument49 pagesThe Oak Island Money Pit: Remote Viewing Summary Sheet © Daz Smith - Do Not Distribute Without PermissionJosh RNo ratings yet
- Sarsi Cola Life CycleDocument3 pagesSarsi Cola Life CycleMary Joy Credo LangamanNo ratings yet
- For Serving Railway Employees of East Coast RailwayDocument11 pagesFor Serving Railway Employees of East Coast Railwaypunithrgowda22No ratings yet
- Unit - 4 - Key AnswersDocument22 pagesUnit - 4 - Key Answerskurd gamerNo ratings yet
- Spatial Manager User Guide v4.0Document172 pagesSpatial Manager User Guide v4.0MuhamadYogieSyahbandarNo ratings yet
- AmazonDocument30 pagesAmazonMunishArora100% (1)
- International Rice Research Newsletter Vol.3 No.3Document24 pagesInternational Rice Research Newsletter Vol.3 No.3ccquintosNo ratings yet
- How To Motivate YourselfDocument4 pagesHow To Motivate YourselfAbialbon PaulNo ratings yet
- MBO as a tool for performance in Nigerian banksDocument11 pagesMBO as a tool for performance in Nigerian banksMiguelNo ratings yet
- Roland XP-60 PDFDocument36 pagesRoland XP-60 PDFeliasNo ratings yet