Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 03 - Data Set
Uploaded by
bella_dsCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 03 - Data Set
Uploaded by
bella_dsCopyright:
Available Formats
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 03 Data Set
Data Set used in the Petrel
The Gullfaks data set has been released for commercial use by
the Norwegian oil company Statoil. Gullfaks is one of the major
oil fields in the North Sea and one of the largest oil producing
fields on the Norwegian continental shelf, Fig. 3.1 Gullfaks is an oil
and gas field in the Norwegian sector of the North Sea operated
by Statoil Hydro. It was discovered in 1979, in block 34/10, at a
water depth of 135 meters (442.913 foot). The initial recoverable
reserve is 2.1 billion barrels, and the remaining recoverable
reserve in 2004 is 234 million barrels. This oil field reached peak
production in 2001 at 180,000 barrels per day.
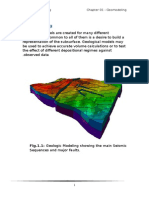
Fig. 3.1: Gullfaks Oil Field
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 03 Data Set
Fig3.2: Infrastructure on the Gullfacks field
Development
The sea depth in the area is 130 - 220 meters (426.509 - 721.784
foot). The field has been developed with three integrated
processing, drilling and accommodation facilities with concrete
bases and steel topsides, Gullfaks A, B and C. Gullfaks B has a
simplified processing plant with only first-stage separation.
Gullfaks A and C receive and process oil and gas from Gullfaks
Sr and Gimle. The facilities are also involved in production and
transport from Tordis, Vigdis and Visund. The Tordis production is
processed in a separate facility on Gullfaks C.
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 03 Data Set
Reservoir
The Gullfaks reservoirs consist of Middle Jurassic sandstones of
the Brent Group, and Lower Jurassic and Upper Triassic
sandstones of the Cook, Statfjord and Lunde formations. The
reservoirs are 1700 - 2000 meters (5577.427- 6561.679 foot)
below the sea level.
The Gullfaks reservoirs are located in rotated fault blocks in
the west and a structural horst in the east, with an intermediate
highly faulted area.
Fig3.3: Structural setting of the Gulfacks main field showing
3 main areas
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 03 Data Set
Fig3.4: Lithostratigraphy of the Gulfacks main field
Recovery strategy
4
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 03 Data Set
The drive mechanisms are water injection, gas injection or
water/alternating gas injection (WAG). The drive mechanism
varies between the drainage areas in the field, but water injection
constitutes the main strategy.
Fig3.5: Gullfaks offshore
Transport
Oil is exported from Gullfaks A and Gullfaks C via loading buoys to
shuttle tankers. The part of the rich gas that is not reinjected is
sent through the export pipeline to Stat pipe for further
processing at Krst and export to the Continent as dry gas.
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 03 Data Set
Fig3.6: Transportation of Gullfaks
Status
Production from Gullfaks is in the decline phase. Efforts are being
made to increase recovery, partly by locating and draining
pockets of remaining oil in water flooded areas, and partly
through continued massive water circulation.
Implementation of a chemical flooding pilot will be considered in
2010. A new project has also been initiated to evaluate necessary
facility upgrades for lifetime extension of the field towards 2030.
Facts about Gullfaks
Operations:
Operator:
Location:
Discovery year:
Production
start:
In Norway.
Statoil Hydro ASA
34/10 in the northern part of the North Sea
1978
Gullfaks A December 1986
Gullfaks B February 1988
Production:
API:
S.G.:
Sulphur:
Pour Point:
Exploration
wells:
Development
wells:
Licensees:
Gullfaks C November 1989
Oil and Gas
37.5
0.8372
0.22 mass%
-15 C
Den norske stats oljeselskap a.s: 25 wells
Statoil ASA: 6 wells
Den norske stats oljeselskap a.s: 169 wells
Statoil ASA: 52 wells
Statoil Hydro ASA: 4 wells
Petro AS (30.0 %)
6
3D Geological Modeling
Recoverable
reserves:
Chapter 03 Data Set
Statoil Hydro ASA (61.0 %)
Statoil Hydro Petroleum AS (9.0 %)
357 million Sm3 oil 24 billion Sm3 gas 3 million tonns
ngl
Remaining 2008-02-01:
27 million Sm3 oil 2 billion Sm3 gas 0 million tonns
ngl
3D Geological Modeling
Chapter 03 Data Set
The Supplied Reservoir Data
The following wells, along with their well headers (well location
map), well deviations (well paths), well logs, and well tops
(formation tops), are supplied: A10, A15, A16, B1, B2, B4, B8, B9,
C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, and C7. The stratigraphic succession of
the reservoir under study is given in the following table:
Succession
1 (top)
Horizon
Cretaceous
Tarbert
Ness
4 (bottom)
Ettive
Zone
Tarbert-3
Tarbert-2
Tarbert-1
Ness-2
Ness-1
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Program of WorksDocument53 pagesProgram of Worksrhea gayoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Management Systems (EMS) : Components of An EMSDocument7 pagesEnvironmental Management Systems (EMS) : Components of An EMSBhaskar RoychoudhuriNo ratings yet
- HDFC Credit CardDocument2 pagesHDFC Credit CardraviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 - Seismic InterpretationDocument11 pagesChapter 06 - Seismic Interpretationbella_ds0% (1)
- Chapter 1 PetrelDocument5 pagesChapter 1 PetrelmydealiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Fault ModelingDocument52 pagesChapter 11 - Fault Modelingbella_ds100% (1)
- An Interpreters Guide To Understanding and Working With Seismic-Derived Acoustic Impedance DataDocument8 pagesAn Interpreters Guide To Understanding and Working With Seismic-Derived Acoustic Impedance Databella_dsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 - Input Data EditingDocument34 pagesChapter 09 - Input Data Editingbella_dsNo ratings yet
- Petrel 2011 - Data ImportDocument41 pagesPetrel 2011 - Data ImportBangsawan Arief100% (1)
- Chapter 05 - 3D Seismic DataDocument8 pagesChapter 05 - 3D Seismic Databella_dsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - Petrel InterfaceDocument12 pagesChapter 02 - Petrel Interfacebella_ds100% (1)
- Gartner IT Key Metrics Data: 2011 Summary ReportDocument12 pagesGartner IT Key Metrics Data: 2011 Summary ReportVincent BoixNo ratings yet
- The Total Environment of The FirmDocument27 pagesThe Total Environment of The FirmNikko Albano100% (2)
- Chapter 10 - Well CorrelationDocument33 pagesChapter 10 - Well Correlationbella_ds50% (2)
- Chapter 01 - GeomodelingDocument10 pagesChapter 01 - Geomodelingbella_dsNo ratings yet
- Nautilus Full Course List: Nautilus Is Part of The RPS GroupDocument23 pagesNautilus Full Course List: Nautilus Is Part of The RPS Groupbella_dsNo ratings yet
- Aapg08 Chimney PosterDocument6 pagesAapg08 Chimney Posterbella_dsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Vertical LayeringDocument30 pagesChapter 13 - Vertical Layeringbella_dsNo ratings yet
- Activity Report - Mas KowiDocument5 pagesActivity Report - Mas Kowibella_dsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07 - Fault DataDocument8 pagesChapter 07 - Fault Databella_dsNo ratings yet
- Greatest Prophet, Muhammad SAW, His Family, His Friends, and All of His Followers. Amin!Document1 pageGreatest Prophet, Muhammad SAW, His Family, His Friends, and All of His Followers. Amin!bella_dsNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 1Document12 pagesJurnal 1bella_dsNo ratings yet
- Laporan Workshop FixDocument16 pagesLaporan Workshop Fixbella_dsNo ratings yet
- Fulbright Ref LetterDocument2 pagesFulbright Ref Letterbella_dsNo ratings yet
- 320 - 33 - Powerpoint-Slides - Chapter-10-Monopolistic-Competition-Oligopoly (Autosaved)Document37 pages320 - 33 - Powerpoint-Slides - Chapter-10-Monopolistic-Competition-Oligopoly (Autosaved)Ayush KumarNo ratings yet
- Featurs of Marketing Strategy - Meaning and Its ImportanceDocument2 pagesFeaturs of Marketing Strategy - Meaning and Its ImportanceChetan ChanneNo ratings yet
- Alternative Centres of PowerDocument40 pagesAlternative Centres of PowerJigyasa Atreya0% (2)
- Ecl Annual Report 2018-19Document208 pagesEcl Annual Report 2018-19Rohit VishwasNo ratings yet
- Cityam 2012-06-29Document39 pagesCityam 2012-06-29City A.M.No ratings yet
- NDT and Tpi Control1Document87 pagesNDT and Tpi Control1KyNo ratings yet
- 6 Ch14 - Central BanksDocument63 pages6 Ch14 - Central BanksNgọc Ngô Thị MinhNo ratings yet
- Pending Home SalesDocument2 pagesPending Home SalesAmber TaufenNo ratings yet
- MCQ Dcs 3Document7 pagesMCQ Dcs 3Christopher JakeNo ratings yet
- Synopsis of Bharti AirtelDocument16 pagesSynopsis of Bharti AirtelAnnie JosephNo ratings yet
- Cera Sanitaryware Limited: Annual Report 2007-08Document40 pagesCera Sanitaryware Limited: Annual Report 2007-08Rakhi183No ratings yet
- Sixth Avenue Business District Association Board Meeting NotesDocument4 pagesSixth Avenue Business District Association Board Meeting NoteschelsealevyNo ratings yet
- AFST Sample TestDocument1 pageAFST Sample Testsad gurlNo ratings yet
- Industrialization WebquestDocument4 pagesIndustrialization WebquestmrsorleckNo ratings yet
- 1923 Baragwanath The Ballarat Goldfield, Memoir 14 - pt-2Document143 pages1923 Baragwanath The Ballarat Goldfield, Memoir 14 - pt-2Yuri Vladimir Ordonez LamaNo ratings yet
- NTPCDocument26 pagesNTPCShradha LakhmaniNo ratings yet
- Historicizing Precarious Work Forty Years of Research in The Social Sciences and HumanitiesDocument47 pagesHistoricizing Precarious Work Forty Years of Research in The Social Sciences and HumanitiesBren Mmtz100% (1)
- Chronological Order of EconomistsDocument6 pagesChronological Order of EconomistsPrince PotterNo ratings yet
- AhlanDocument10 pagesAhlanNur FayzaNo ratings yet
- City A.M.'S Polo Team Wins at Hurlingham: Diary SportDocument32 pagesCity A.M.'S Polo Team Wins at Hurlingham: Diary SportCity A.M.No ratings yet
- Stringing IRDocument10 pagesStringing IRRohit Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- India Map in Tamil HDDocument5 pagesIndia Map in Tamil HDGopinathan M0% (1)
- Tech Mahindra Integrated Report 2018 19 PDFDocument153 pagesTech Mahindra Integrated Report 2018 19 PDFfilmcer100% (1)
- Cap RootDocument11 pagesCap Rootrobokrish6No ratings yet
- FNCCI Executive Committe (2020-2023)Document14 pagesFNCCI Executive Committe (2020-2023)Rosha Maharjan0% (1)