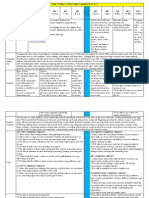
Kindergarten Quarter 4 Standards
st
2nd column-code of standard
1 column- if used this week
meaning of code
I=Reading for
Lit.
Language Arts
IIIB Phonological
Awareness
III.A.= Print
Concepts
IIB = Craft/
Structure
II= Reading for
Information
IIC-Integration of
Knowledge/Ideas
I.B.=Craft/Structure
VB=Presentation
of
Knowledge/Ideas
IIIC= Phonics/
Word Recognition
II.A.=Key Ideas/Details
VIA= Conventions
of Standard English
VIC=Vocabulary
Acquisition/Use
IVA 2
IVB 5
IVB 6
IVC 7
IVC 8
VB 4
VB 5
IIC 8
IIIC 3d
VIA 1e
VIA 1f
VIA 2
VIC 4b
VIC 5
VIC 5d
3rd columnIII= Reading; Found.
Skills
IC= Integration of
knowledge/Ideas
ID= Range of
Reading/
Level of Text
Complexity
IV = Writing Strand
VA=Comprehensi
on/
Collaboration
IV A= Text Types/
Purpose
VI=Language
Strand
Use a combination of drawing, dictating, and writing to compose
informative/explanatory texts in which they name what they are writing about and
supply some information about the topic
WG&S, respond to questions and suggestions from peers and add details to strengthen
writing as needed
WG&S, explore a variety of digital tools to produce and publish writing, including in a
collaboration with peers
Participate in shared research and writing projects
WG&S, recall information from experiences or gather information from provided
sources to answer a question
Describe familiar people, places, things, and events wp&s, provide additional detail
Add drawings or other visual displays to descriptions as desired to provide additional
details
WP&S, identify the reasons an author gives to support points in a text
Distinguish between similarly spelled words by identifying sounds of the letters that
differ
Use the most frequently occurring propositions (e.g to, from,, in, out, on, off, for, of, by,
with)
Produce and expand complete sentences in shared language activities
Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English capitalization,
punctuation and spelling when writing
Use the most frequently occurring inflections and affixes (e.g. ed, -s, re-, un-, pre-,
-ful, -less) as clue to the meaning of an unknown word
WG&S, explore word relationships and nuances in word meanings
Distinguish shades of meaning among verbs describing the same general action (walk,
march, strut, prance) by acting out the meanings
�Social Studies
S 11
PC 12
S=Scarcity
PC= Production and
Consumption
People have many wants and make decisions to satisfy those wants. These decisions
impact others
Goods are objects that can satisfy peoples wants. Services are actions that can satisfy
peoples wants
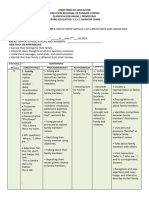
Kindergarten Quarter 4 Standards
st
1 column- if used this week
meaning of code
Math
Science
2nd column-code of standard
3rd column-
NOBT=Numbers
CC=Countin OAT=Operations/
LS
1
&
LS
2Life
Science:
Physical
and Behavioral
of Living Things
Algebraic
and
Operations
in Traits
M=Measurem
Geo=Geom
g/
Cardinality
Thinking
Base Ten
ent & Data
etry
LS11
are different from nonliving things
CC
countLiving
to 100 things
by ones/tens
Elaboratio
Understand
what
it means
be living,
not
to distinguish
living
and nonliving
CC 2
Count forward beginning
from a to
given
number
within
the known
sequence
(instead of 1)
ns:3
CC
Write numbers from 0 to 20; represent a number of objects with a written numeral 0-20
Living things
include anything
that
is aliveand
or has
ever been
alive counting to
CC 4
Understand
the relationship
between
numbers
quantities;
connect
Observe
and
learn
that
living
things
respond
to
stimuli,
grow,
reproduce, and require
cardinality (a,&b)
energy
CC 4a
When counting objects, say the number names in the standard order, pairing each object
Animals
require
for energy;
plants
make
theirname
own food
with one
and only
onefood
number
name and
each
number
with one and only one
LS 2
Living things have physical traits and behaviors, which influence their
object.
CC 5
Countsurvival
to answer how many questions about as many as 20 things arranged in a variety
Elaboratio
Explore and investigate the local environment
of ways
ns:6
CC
Identify whether the number of objects in one group is greater than, less than, or equal to
Interact and observe with a large variety of living things
the number of objects in another groups (e.g. by using matching and counting strategies)
Observe that organisms are made of parts; and because this they can do specific
OAT 1
Represent addition/subtraction with objects, fingers, mental images, drawings, sounds
things
(etc)
OAT 2
Solve addition and subtraction word problems, and add and subtract within 10
OAT 3
Decompose numbers less than or equal to 10 into pairs in more than one way
OAT 4
For any number from 1 to 9, find the number that makes 10 when added to the given
number
OAT 5
Fluently add/ subtract within 5
NOBT
Compose and decompose numbers from 11 to 19 into ten ones and some further ones,
1
e.g, by using objects or drawings, and record each composition or decomposition by a
drawing or equation (18- 10 +8); understand that these numbers are composed of ten ones and one, two,
three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine ones.
M/D 1
M/D
Describe measurable attributes of objects, such as length or weight.
Directly compare two objects with a measurable attribute in common to see which object
has more of/ less of the attribute, and describe the difference. For example, two children and
describe as being taller/shorter
M/D 3
Geo 2
Geo 3
Geo 4
Geo 5
Geo 6
Classify objects into given categories; count the numbers of objects in each category
Correctly name shapes
Identify shapes as 2-d or 3-d
Analyze/ compare 2D and 3D shapes
Model shapes in the world by building shapes from components and drawing shapes
Compose simple shapes to form larger shapes