Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Furosemide Drug Study
Uploaded by
milkvCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Furosemide Drug Study
Uploaded by
milkvCopyright:
Available Formats
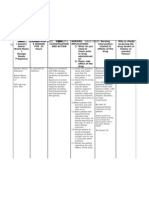
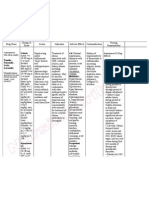
Name of Patient
B. V.
Age
20 y.o
Height
52
Diagnosis
G1P1 PU 31 wks. AOG/LMP cephalic, IPTL, severe
preeclampsia with pulmonary congestion
M. M. Olmillo
Sex
Female
Weight
60 kg
Website
milkv.co.vu
A/N
youre welcome J
Author
DRUG DATA
Generic name:
Furosemide
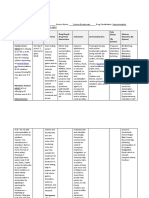
CLASSIFICATION
Pharmacologic:
Loop diuretic
Trade name/s:
Lasix
Patients dose:
20mg qo 12 hrs
Maximum dose:
40mg (may
increase dose in
increments of
20mg in 2 hr)
Minimum dose:
1 mg/kg
Therapeutic:
Loop diuretic
Pregnancy Category
Risk: C
Availability:
Tablets 20, 40,
80mg; oral
solution
10mg/ml,
40mg/ml;
injection
10mg/ml
Inhibits reabsorption
of sodium and
chloride from the
proximal and distal
tubules and
ascending limb of the
loop of Henle, leading
to a sodium-rich
dieresis
Onset: 5 min
Peak: 30 min
Duration: 2 hr
Metabolism: hepatic;
30-60 min
INDICATIONS
General:
> Oral, IV: Edema
associated with
heart failure,
cirrhosis, renal
disease
> IV: acute
pulmonary edema
> oral:
hypertension
Patients actual
indication:
Furosemide is
given to patient to
treat acute
pulmonary
congestion and
hypertension
Distribution: crosses
placenta; enters
breast milk
Route:
IVTT
Source: 2011
Lippincotts NDG
MECHANISM OF
ACTION
Excretion: feces, urine
Source: 2011
Lippincotts NDG
Source: 2011
Lippincotts NDG
Source: 2011
Lippincotts NDG
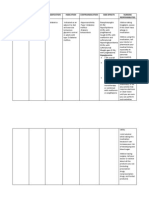
CONTRAINDICATI
ON
Contraindicated with
allergy to furosemide,
sulphonamides; allergy
to tartrazine; anuria,
severe renal failure;
hepatic coma;
pregnancy; lactation
Precaution:
Use cautiously with SLE,
gout, diabetes mellitus
Interactions:
> drug-drug: increased
risk of cardia arrhythmias
with cardiac glycosides;
increased risk of
ototoxicity with
aminoglycoside
antibiotics, cisplatin;
decreased absorption of
furosemide with
phenytoin; decreased GI
absorption with charcoal;
may reduce effect of
insulin or oral
antidiabetics because
blood glucose levels can
become elevated
Source: 2011
Lippincotts NDG
ADVERSE
EFFECTS
CNS: dizziness,
vertigo,
paresthesias,
xanthopsia,
weakness
CV: orthostatic
hypertension,
thrombophlebitis
Dermatologic:
photosensitivity,
pruritus, urticaria,
purpura
GI: nausea,
anorexia, vomiting,
oral and gastric
irritation
GU: nocturia,
glycosuria, urinary
bladder spasm
Hematologic:
leukopenia,
anemia,
thrombocytopenia,
Other: muscle
cramps and muscle
spasms
Source: 2011
Lippincotts NDG
NURSING
RESPONSIBILITIE
S
Before:
> check doctors order
> assess allergy to furosemide,
sulfonamides, tartrazine
> do not mix parenteral solution with
highly acidic solutions with ph below
3.5
> do not expose to light, which may
discolour tablets or solution
> educate the patient about the
purpose and importance of the drug
During:
> check the patency of the IV site and
IV line
> Give early in the day so that
increased urination will not disturb
sleep
> administer the right dose at the
right time
> measure and record weight to
monitor fluid changes
After:
> monitor blood glucose levels
> arrange to monitor serum
electrolytes, hydration, liver and renal
function
> arrange for potassium-rich diet or
supplemental potassium as needed
> report loss or gain of more than
1.5kg in 1 day, swelling in your ankles
or fingers, unusual bleeding or
bruising
> document and record.
Source: 2011 Lippincotts Nursing
Drug Guide
You might also like
- CaptoprilDocument2 pagesCaptoprilJohn Louie EscardaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of FurosemideDocument5 pagesDrug Study of FurosemideAntonette Lei100% (1)
- Drug Study FurosemideDocument3 pagesDrug Study FurosemideLouie Danielle Segarra100% (1)
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Zosyn Drug StudyDocument2 pagesZosyn Drug StudyAnalyn SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Clonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyDocument3 pagesClonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDrug Study - FurosemideKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - FurosemideKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Puerto Princesa City: Palawan State UniversityDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Puerto Princesa City: Palawan State UniversityRosemarie EustaquioNo ratings yet
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- AmilorideDocument1 pageAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- NebivololDocument2 pagesNebivololSophia MarieNo ratings yet
- GENERIC NAME: Clonazepam BRAND NAME: RivotrilDocument2 pagesGENERIC NAME: Clonazepam BRAND NAME: RivotrildanaNo ratings yet
- DilantinDocument1 pageDilantinitsmeayaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyBobot Julius Oropeza100% (2)
- Furosemide (Diumide-K) Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide (Diumide-K) Drug StudyMariella Saavedra Aranda CercadoNo ratings yet
- Atorvastatin Calcium Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAtorvastatin Calcium Drug StudyFranz.thenurse6888100% (7)
- Albumin Drug StudyDocument1 pageAlbumin Drug StudyMaine Concepcion100% (1)
- Amiodarone (Cordarone)Document1 pageAmiodarone (Cordarone)jaybamanNo ratings yet
- Calcium Carbonate (Calci-Aid)Document1 pageCalcium Carbonate (Calci-Aid)Chelsy Muriel100% (2)
- Montelukast Levoceterizine (ZYKAST)Document2 pagesMontelukast Levoceterizine (ZYKAST)Kristine Young100% (2)
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmlodipine Drug StudyRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- 10 DRUG-STUDY-Atropine-SulfateDocument2 pages10 DRUG-STUDY-Atropine-SulfateamitNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug SyudyDocument1 pageFurosemide Drug SyudyallenininiNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmlodipine Drug StudyJoseph Dann Enero Jr.100% (3)
- Irbesartan-North DistrictDocument2 pagesIrbesartan-North DistrictSergi100% (1)
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisJenina Kaye Mostoles Gravides0% (1)
- NebivololDocument1 pageNebivololshaeNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Budesonide (Drug Study)Document3 pagesBudesonide (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesSodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- Clomid Drug StudyDocument3 pagesClomid Drug StudySheen Ivashkov-BelikovNo ratings yet
- Isosorbide DinitrateDocument2 pagesIsosorbide DinitrateMavy CantonNo ratings yet
- Carvedilol Drug Name Classifications Indications Contraindications Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesCarvedilol Drug Name Classifications Indications Contraindications Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsClaudette Sanvictores0% (1)
- EnalaprilDocument4 pagesEnalaprilGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- CaptoprilDocument2 pagesCaptoprilVina Jane P Laurel100% (2)
- Drug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideMark ToxNo ratings yet
- Amiodarone (PACERONE)Document1 pageAmiodarone (PACERONE)Amanda CoadNo ratings yet
- Warfarin SodiumDocument3 pagesWarfarin SodiumAndrea Huecas TriaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Furosemide (Lasix)Document1 pageDRUG STUDY - Furosemide (Lasix)julesubayubay542876% (25)
- Drug Study VALSARTANDocument1 pageDrug Study VALSARTANThrizia Salas100% (1)
- Drug Study AtorvastatinDocument2 pagesDrug Study AtorvastatinNicole Anne TungolNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- LosartanDocument2 pagesLosartanVina Jane P Laurel89% (9)
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyYou know whoNo ratings yet
- Hydrocortisone - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHydrocortisone - Drug StudyKevin H. Milanes100% (2)
- Pantoprazole DrugDocument1 pagePantoprazole Drugman12No ratings yet
- EpinephrineDocument3 pagesEpinephrinealexjerimiahNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesKarl Lourenz DeysolongNo ratings yet
- Tobramycin + Dexamethasone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesTobramycin + Dexamethasone Drug StudySheen Ivashkov-BelikovNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ClopidogrelDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Clopidogrelryan100% (1)
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument2 pagesSodium BicarbonateHera Pamela Buelis Batoy100% (1)
- Drug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Document2 pagesDrug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Melinda Cariño Ballon100% (1)
- Arixtra & Plavix Drug StudyDocument3 pagesArixtra & Plavix Drug StudyShayneAngelMarieMatubangNo ratings yet
- Micardis PlusDocument2 pagesMicardis PlusKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- For Drug Recitation 1Document33 pagesFor Drug Recitation 1Abigail LonoganNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEDocument12 pagesDiuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEJR BetonioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyRizzi DeveraNo ratings yet
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone Drug StudyDocument1 pageCeftriaxone Drug Studymilkv71% (7)
- MV + FeSO4 Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMV + FeSO4 Drug Studymilkv71% (7)
- Azithromycin Drug StudyDocument1 pageAzithromycin Drug Studymilkv100% (6)
- Tranexamic Acid Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTranexamic Acid Drug Studymilkv93% (28)
- Spirinolactone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSpirinolactone Drug StudymilkvNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument1 pageTramadol Drug Studymilkv82% (11)
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetoprolol Drug Studymilkv100% (1)
- Hydralazine Drug StudyDocument1 pageHydralazine Drug Studymilkv71% (7)
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCefuroxime Drug Studymilkv93% (15)
- Methyldopa Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMethyldopa Drug Studymilkv100% (14)
- Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCefuroxime Drug Studymilkv93% (15)
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocument1 pageMefenamic Acid Drug Studymilkv70% (10)
- Clindamycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesClindamycin Drug Studymilkv100% (4)
- Ferrous Sulfate Drug StudyDocument1 pageFerrous Sulfate Drug Studymilkv82% (11)
- Celecoxib Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCelecoxib Drug Studymilkv100% (2)
- Ampicillin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmpicillin Drug Studymilkv92% (12)
- Clozapine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesClozapine Drug Studymilkv100% (8)
- Assignment 1: Renal Treatment: InstructionsDocument16 pagesAssignment 1: Renal Treatment: InstructionsAJ BayNo ratings yet
- Mata Drug Study FurosemideDocument14 pagesMata Drug Study FurosemideNicole Keesha MataNo ratings yet
- CHF-Diuretics v2.1 Apr-2017Document1 pageCHF-Diuretics v2.1 Apr-2017Robbie WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Drug Information Worksheet: Hypertension - 40 Twice DailyDocument57 pagesDrug Information Worksheet: Hypertension - 40 Twice DailyMichelle Davis-JacksonNo ratings yet
- Nclex DietDocument109 pagesNclex DietDanica Chiara Motia100% (4)
- Drug Study FUROSEMIDE (Eugene San)Document2 pagesDrug Study FUROSEMIDE (Eugene San)Ana LanticseNo ratings yet
- Calvin Damanik, DR, SPPD: Departement Penyakit Dalam Fak Kedokteran Umi MedDocument37 pagesCalvin Damanik, DR, SPPD: Departement Penyakit Dalam Fak Kedokteran Umi MedMaria lestari harianjaNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document18 pagesGroup 1TrishaRaquepoNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanNo ratings yet
- Drug ListDocument18 pagesDrug ListMinh PhungNo ratings yet
- Ralph's ProposalDocument15 pagesRalph's ProposalHeilene Ethel AngcayaNo ratings yet
- Drug Chart 7 - Hee InternetDocument19 pagesDrug Chart 7 - Hee InternetAhmzzdNo ratings yet
- Study Questions-Medical Pharmacology - MED 301 - Drugs Used in Coardiovascular Disorders - Prof. Nedret AltıokDocument16 pagesStudy Questions-Medical Pharmacology - MED 301 - Drugs Used in Coardiovascular Disorders - Prof. Nedret Altıokفاعل خيرNo ratings yet
- Furosemide 1Document1 pageFurosemide 1Marck A. AlcedoNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Cardiogenic ShockDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Cardiogenic ShockShyla Manguiat100% (1)
- نسخة Pharma1 diuretics and anti HTN. Manar.BQDocument6 pagesنسخة Pharma1 diuretics and anti HTN. Manar.BQAblah Hamdan ThaherNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, VecuroniumDocument12 pagesDrug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, Vecuroniumpaupaulala100% (4)
- Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument37 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Imbalancesapi-3797941100% (4)
- Pharmacology - Drug Cards (Index Cards)Document272 pagesPharmacology - Drug Cards (Index Cards)Henrietta100% (9)
- Drug study+NCPDocument24 pagesDrug study+NCPchelsea_ishk12100% (2)
- FurosemideDocument1 pageFurosemideCassie100% (1)
- S 061 LBLDocument9 pagesS 061 LBLJORGE IRAM BARRAZA ROMERONo ratings yet
- Terapi Cairain Dan ElektrolitDocument39 pagesTerapi Cairain Dan ElektrolityulyaNo ratings yet
- Top 200 Drugs in OrderDocument7 pagesTop 200 Drugs in OrderEamon BarkhordarianNo ratings yet
- "Natural Healing With Herbs For A Healthier You": DandelionDocument5 pages"Natural Healing With Herbs For A Healthier You": Dandelionak09100% (1)
- Pastel Watercolor Painted PowerPoint TemplateDocument44 pagesPastel Watercolor Painted PowerPoint TemplateFatimah AlzahraNo ratings yet
- Drug TabulationDocument13 pagesDrug TabulationKristian Dave DivaNo ratings yet
- Acquired Heart DiseasesDocument41 pagesAcquired Heart DiseasesSaman SarKoNo ratings yet
- HNN215 Drug DiaryDocument10 pagesHNN215 Drug DiaryMaddison MitchellNo ratings yet