Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Furosemide Drug Study
Uploaded by
Crisha Ann Billones Bacuta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views2 pagesFurosemide Drug Study
Uploaded by
Crisha Ann Billones BacutaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
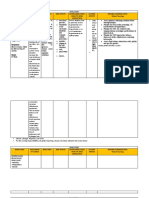
Name of Dosage, Mech.
of Action Indication Adverse Nursing
Drug Route, Reactions Responsibili
Freq., ties
Timing
Generic: Dosage: Acts on the Furosemide is CV: circulatory >Observe 6
furosemid 40 mg ascending loop indicated for collapse rights in
e (Rx) (1 tab ) of Henle in the the treatment giving
kidney, of edema GU: renal failure medication
Brand: inhibiting associated
Lasix Route: with HEMA: >Test if the
reabsorption of
Oral congestive Thrombocytope patient is
electrolytes nia,
heart failure, allergic to
sodium and agranulocytosis,
Edema due to the drug.
Frequen chloride, causing cardiac, leukopenia,
cy: excretion of hepatic & neutropenia. >Monitor
BID sodium, calcium, renal disease, weight,
magnesium, burns; mild to INTEG: Stevens- blood
chloride,water, moderate Johnson pressure,
Timing: and some HTN, syndrome,
and pulse
Every 12 potassium; hypertensive rate
hours crisis, acute SYST: Toxic
decreases routinely
heart failure, epidermal
reabsorption of necrolysis with long
sodium and reduced
term use
urinary
chloride and and during
output due to
increases rapid
gestoses,
excretion of dieresis.
chronic renal
potassium in the failure, Use can
distal tubule of nephrotic lead to
the kidney; syndrome. profound
responsible for water and
slight electrolyte
Classificati antihypertensive Contraindicati Side Effects:
depletion.
on: ons:
effect and
Functional peripheral Anuria, low blood >If oliguria
: hypovolemia, pressure, or azotemia
vasodilatation.
Loop hypokalemia. dehydrati develops or
diuretic Inhibit on and increases,
reabsorption of Contraindicat
electrolyt drug may
sodium and ed in patients e need to be
Chemical: hypersensitive depletion
water in the stopped.
ascending limb to drug and (for
Sulfonami those with example, >Monitor
of the loop of
de anuria. Use sodium, fluid intake
Henle by
derivative cautiously in potassiu and output
interfering with
patients with m). and
the chloride
binding site of hepatic jaundice, electrolyte,
cirrhosis and Loss of BUN, and
the 1Na+, 1K+,
in those hearing,
allergic to ear pain,
sulfonamides. tinnitus,
Use during blurred
pregnancy vision
only if /sensitivi
potential ty to light
(photoph
benefits to
obia),
mother clearly
rash,
outweigh
risks to fetus.
pancreatit
is,
Precautions: nausea,
Pregnancy C, diarrhea,
diabetes abdomina
mellitus, l pain,
dehydration, and
2Cl- cotransport severe renal dizziness. carbon
system. Loop disease, Increased dioxide levels.
diuretics increase cirrhosis, blood >Watch for
the rate of delivery ascites, sugar and signs of
of tubular fluid hypersensitivi uric acid hypokalemia,
and electrolytes to ty to levels such as
the distal sites of sulfonamides, muscle
hydrogen and breastfeeding, weakness and
potassium ion infants, cramps.
secretion, while electrolyte
plasma volume depletion
contraction
increases
aldosterone
production. The
increased delivery
and high
Source:
Skidmore-Roth, Linda. (11th Edition). Mosby's drug guide for nurses. Elsevier publisher.
You might also like
- Drug Study of FurosemideDocument5 pagesDrug Study of FurosemideAntonette Lei100% (1)
- Disaster Nursing ReviewerDocument60 pagesDisaster Nursing ReviewerGienelle Susana San Juan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Elsevier - Anaesthesiology Clinics - Vol.26, Issues 1 - Obstetric Anesthesia (2008) PDFDocument230 pagesElsevier - Anaesthesiology Clinics - Vol.26, Issues 1 - Obstetric Anesthesia (2008) PDFMila KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate)Document13 pagesDrug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate)Flauros Ryu Jabien50% (2)
- AtorvastatinDocument2 pagesAtorvastatinJasmin T LarizaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationDocument1 pageNursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationOmar Izzo100% (1)
- DR Amaefula, E. Temple MBBS, Fwacs, Faoi,: Inflamation, Infection, and Use of Antibiotics in SurgeryDocument40 pagesDR Amaefula, E. Temple MBBS, Fwacs, Faoi,: Inflamation, Infection, and Use of Antibiotics in SurgeryPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Maxillectomy A ReviewDocument17 pagesMaxillectomy A ReviewDr. T. Balasubramanian100% (3)
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyPamela DomingoNo ratings yet
- Clonidine Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Document2 pagesClonidine Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse688875% (4)
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Clopidogrel Drug StudyDocument2 pagesClopidogrel Drug StudyEdelweiss Marie CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Drug study on HydrochlorothiazideDocument2 pagesDrug study on Hydrochlorothiazidekuro hanabusa100% (1)
- Drug Study AtorvastatinDocument1 pageDrug Study AtorvastatinEzron Kendrick DuranNo ratings yet
- Drug Study IbuprofenDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ibuprofendawnscribd80% (5)
- All-On-4, For PatientsDocument28 pagesAll-On-4, For PatientsmmsbabakNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyIsagani Socrates Loreto100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studywarlocke100% (2)
- Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesPotassium ChlorideRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment, Interventions and Evaluation of Mood and Mental StateDocument8 pagesNursing Assessment, Interventions and Evaluation of Mood and Mental StateCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment, Interventions and Evaluation of Mood and Mental StateDocument8 pagesNursing Assessment, Interventions and Evaluation of Mood and Mental StateCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Fondaparinux and Clopidogrel Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesFondaparinux and Clopidogrel Nursing ConsiderationsShayneAngelMarieMatubangNo ratings yet
- 2019 Afk ProtocolDocument10 pages2019 Afk Protocoldrsunny159840% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJonica CamposNo ratings yet
- Paranoid SchizophreniaDocument26 pagesParanoid SchizophreniaCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study on Furosemide, Carvedilol and RanitidineDocument14 pagesDrug Study on Furosemide, Carvedilol and RanitidineJenniferValmocenaNo ratings yet
- Clonidine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageClonidine HydrochlorideLovelyn Joy Abubo CortezNo ratings yet
- MCQs Ch07-45651100rdzDocument27 pagesMCQs Ch07-45651100rdzKhalifa AL-Wishahi100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY - Furosemide (Lasix)Document1 pageDRUG STUDY - Furosemide (Lasix)julesubayubay542876% (25)
- 7 Drug StudyDocument17 pages7 Drug StudyMa. Mechile MartinezNo ratings yet
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- 2022ABFM ITEMultChoiceDocument71 pages2022ABFM ITEMultChoiceMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyRamon Carlo Almiranez100% (2)
- Humalog Drug StudyDocument3 pagesHumalog Drug StudyKristinelou Marie ReynaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1Document3 pagesDrug Study 1G4 AMOYO ANGELICA NICOLENo ratings yet
- 1 Drug Study - DexamethasoneDocument6 pages1 Drug Study - DexamethasoneJohn100% (1)
- Atorvastatin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAtorvastatin Drug StudyJustine May Gervacio0% (1)
- Sodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyDocument5 pagesSodium Bicarbonate Drug Studyvan0% (1)
- PRILOSEC 20 MG: Drug study for patient with anemia and uterine bleedingDocument3 pagesPRILOSEC 20 MG: Drug study for patient with anemia and uterine bleedingMarvie CadenaNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University: Institute of Nursing S.Y. 2018-2019Document1 pageFar Eastern University: Institute of Nursing S.Y. 2018-2019shendae cosmianoNo ratings yet
- Arixtra Drug StudyDocument2 pagesArixtra Drug StudyEdelweiss Marie Cayetano100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAnn Therese C. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Copd Drug StudyDocument9 pagesCopd Drug StudyJoegie Ario100% (1)
- Drug Study NorepinephrineDocument2 pagesDrug Study NorepinephrinePearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- DuaventDocument2 pagesDuaventKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Aii Mhit Script 1 - Anxiety EngDocument3 pagesAii Mhit Script 1 - Anxiety EngCheska Feleciano100% (1)
- 3 Drugs Study Updates Issues HemodialysisDocument7 pages3 Drugs Study Updates Issues HemodialysisKim GalamgamNo ratings yet
- Dr's Consultation GuideDocument13 pagesDr's Consultation GuideMaria Wabas100% (8)
- Drug Study ClonidineDocument2 pagesDrug Study ClonidineCezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug SyudyDocument1 pageFurosemide Drug SyudyallenininiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Cimetidine (Tagamet)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Cimetidine (Tagamet)mikErlh100% (3)
- K PotaDocument2 pagesK PotaJustine May GervacioNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyYanna N. Cuaki100% (2)
- CaptoprilDocument2 pagesCaptoprilVina Jane P Laurel100% (2)
- Subcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More CommonDocument2 pagesSubcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More Commonahmad ryanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument3 pagesClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENo ratings yet
- Digoxin DrugstudyDocument1 pageDigoxin DrugstudyJustine GarciaNo ratings yet
- RanitidineDocument1 pageRanitidineMcmac YangoNo ratings yet
- AmilorideDocument1 pageAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- Drug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheryhan Tahir BayleNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony's College Nursing Department Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSt. Anthony's College Nursing Department Drug StudyMariella Saavedra Aranda CercadoNo ratings yet
- Mycophenolate MofetilDocument1 pageMycophenolate MofetilAndyPua100% (1)
- Dopamine HCLDocument2 pagesDopamine HCLianecunarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CISPLATINDocument1 pageDrug Study CISPLATINIrish Jane Gallo100% (1)
- TelmisartanDocument2 pagesTelmisartanRea LynNo ratings yet
- Ramipril Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRamipril Drug StudyCheezy Bread0% (1)
- Drug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN EtcDocument6 pagesDrug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN Etc'jmark FranciaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study LosartanDocument3 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Losartanhahahahaaaaaaa100% (1)
- Drug Study: SaluronDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Saluronunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: SaluronDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Saluronunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument8 pagesDrug Study FinalWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Furosemide LasixDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Furosemide LasixG4 AMOYO ANGELICA NICOLENo ratings yet
- Generic Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMary Shine GonidaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Prepareness EssayDocument3 pagesEmergency Prepareness EssayCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- NLM Hand Outs ReviewerDocument5 pagesNLM Hand Outs ReviewerCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Activity 10 Day 2Document7 pagesActivity 10 Day 2Crisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Activity 11 Day 2Document6 pagesActivity 11 Day 2Crisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Revised Drug StudyDocument7 pagesRevised Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- COLLEGE OF ST. JOHN - ROXAS Member: Association ofDocument6 pagesCOLLEGE OF ST. JOHN - ROXAS Member: Association ofCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Assessing Musculoskeletal Function and Care ModalitiesDocument7 pagesAssessing Musculoskeletal Function and Care ModalitiesCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Midterm ResearchDocument87 pagesMidterm ResearchCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- E KardexDocument3 pagesE KardexCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- COLLEGE OF ST. JOHN - ROXAS Member: Association ofDocument5 pagesCOLLEGE OF ST. JOHN - ROXAS Member: Association ofCrisha Ann Billones Bacuta0% (1)
- Week 6 QuizDocument6 pagesWeek 6 QuizCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Activity 9 Day 1 & 2Document10 pagesActivity 9 Day 1 & 2Crisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Reflection - Comfort RoomDocument1 pageReflection - Comfort RoomCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Hip Answer SheetDocument19 pagesPostoperative Hip Answer SheetCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- BPD ReportDocument1 pageBPD ReportCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Professional RNDocument2 pagesProfessional RNapi-121454402No ratings yet
- Endopore Insert eDocument20 pagesEndopore Insert eMery MerryNo ratings yet
- BeneHeart D6 Defibrillator Product BrochureDocument6 pagesBeneHeart D6 Defibrillator Product BrochureAdel KadyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Mind Maps Chapter 1: March 2020Document12 pagesPharmacology Mind Maps Chapter 1: March 2020Muntather HameedNo ratings yet
- Ezzat PaperDocument15 pagesEzzat PaperMohamedAbdelmonaemNo ratings yet
- I-Choose The Correct Answer of The Following Sentences:: Palestine College of NursingDocument9 pagesI-Choose The Correct Answer of The Following Sentences:: Palestine College of NursingHasan A AsFourNo ratings yet
- Candesartan CDocument8 pagesCandesartan CLeyte ProvinceNo ratings yet
- Template Article UpdateDocument11 pagesTemplate Article UpdateAnggun SasmitaNo ratings yet
- Certificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsDocument1 pageCertificate For COVID-19 Vaccination: Beneficiary DetailsSanchita KunwerNo ratings yet
- Non Sterile Dressing ChangeDocument2 pagesNon Sterile Dressing ChangePam West0% (1)
- Week 5 Hematology 2 Laboratory Tests For Primary HemostasisDocument15 pagesWeek 5 Hematology 2 Laboratory Tests For Primary HemostasisKelvssNo ratings yet
- 3 - Evaluation and Management of Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument56 pages3 - Evaluation and Management of Rheumatoid ArthritisDwi Astika SariNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Certain DrugsDocument10 pagesDrug Study On Certain DrugsMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Patient SafetyDocument352 pagesGlossary of Patient SafetyEman ShalabyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for HyperthermiaJhensczy Hazel Maye AlbaNo ratings yet
- NNVJHDocument94 pagesNNVJHAnda AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Essay For The Atlantis ProjectDocument2 pagesEssay For The Atlantis ProjectDaniela BocaNo ratings yet
- Dramatically Lower Blood Pressure in Just 17 Days NaturallyDocument29 pagesDramatically Lower Blood Pressure in Just 17 Days NaturallyRamon Alberto Portillo MedinaNo ratings yet
- Asepsis 1Document52 pagesAsepsis 1严子明 Renz Ryan SevillenoNo ratings yet
- BioXtrim 3 Page ESDocument4 pagesBioXtrim 3 Page ESEyal GeronNo ratings yet
- ABSLI Life Shield Plan Term InsuranceDocument12 pagesABSLI Life Shield Plan Term InsuranceRitesh AgrawalNo ratings yet