Professional Documents
Culture Documents
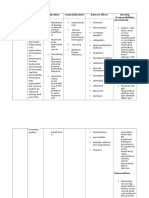
Generic Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing Considerations
Uploaded by
Mary Shine Gonida0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
73 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Furosemide-Lasix
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
73 views2 pagesGeneric Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing Considerations
Uploaded by
Mary Shine GonidaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Generic Mechanism of Indications and Contraindications Common Side Nursing Considerations
Name & Action Drug Rationale Effects
Brand Name
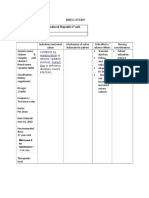
Generic Rapid-acting Treatment of
CV: Postural hypotension, Observe patients receiving
Name: potent edema History of parenteral drug carefully;
hypersensitivity dizziness with excessive
Furosemide sulfonamide associated with closely monitor BP and vital
to furosemide or
Brand Name: "loop" diuretic CHF, cirrhosis of diuresis, acute hypotensive signs. Sudden death from
sulfonamides;
Lasix and liver, and kidney cardiac arrest has been
increasing episodes, circulatory
antihypertensive disease, reported.
Classification: with including oliguria, anuria,
collapse. Metabolic: Hypovol
Electrolyte pharmacologic nephrotic fluid and
electrolyte emia, dehydration, Monitor for S&S of
and water effects and uses syndrome. May hypokalemia (see
balance almost identical be used for depletion states;
hyponatremia hypokalemia, h Appendix F).
agent; loop to those of management of hepatic coma;
pregnancy ypochloremia metabolic Monitor BP during
diuretic ethacrynic acid. hypertension,
(category C), periods of diuresis and
Available Exact mode of alone or in alkalosis, hypomagnesemia,
lactation. through period of
forms: action not combination
hypocalcemia (tetany), dosage adjustment.
20 mg, 40 clearly defined; with other
mg, 80 mg decreases renal antihypertensive hyperglycemia, glycosuria, Observe older adults
tablets; 10 vascular agents, and for closely during period of
elevated BUN, brisk diuresis. Sudden
mg/mL, 40 resistance and treatment of
mg/5 mL oral may increase hypercalcemia. hyperuricemia. GI: Nausea, alteration in fluid and
solution; 10 renal blood Has been used electrolyte balance may
vomiting, oral and gastric
mg/mL flow. concomitantly precipitate significant
injection with mannitol burning, anorexia, diarrhea, adverse reactions.
for treatment of constipation, abdominal Report symptoms to
severe cerebral physician.
edema, cramping, acute pancreatitis, Lab tests: Obtain
particularly in jaundice. Urogenital: Allergi frequent blood count,
meningitis. serum and urine
c interstitial nephritis,
electrolytes, CO2, BUN,
irreversible renal failure, blood sugar, and uric
urinary acid values during first
few months of therapy
frequency. Hematologic: An
and periodically
thereafter.
emia, leukopenia, Monitor I&O ratio and
thrombocytopenic pattern. Report decrease
or unusual increase in
purpura; aplastic anemia,
output. Excessive
agranulocytosis (rare). Speci diuresis can result in
al Senses: Tinnitus, vertigo,
dehydration and
hypovolemia,
feeling of fullness in ears, circulatory collapse,
hearing loss (rarely and hypotension. Weigh
patient daily under
permanent), blurred standard conditions.
vision. Skin: Pruritus, Monitor urine and
urticaria, exfoliative
blood glucose &
HbA1C closely in
dermatitis, purpura, diabetics and patients
photosensitivity, porphyria with decompensated
hepatic cirrhosis. Drug
cutanea tarde, necrotizing may cause
angiitis (vasculitis). Body as hyperglycemia.
a Whole: Increased
Note: Excessive
dehydration is most
perspiration; paresthesias; likely to occur in older
activation of SLE, muscle adults, those with
chronic cardiac disease
spasms, weakness; on prolonged salt
thrombophlebitis, pain at IM restriction, or those
receiving sympatholytic
injection site.
agents.
You might also like
- Drug study on chemotherapeutic alkylating agentsDocument16 pagesDrug study on chemotherapeutic alkylating agentsPrincess CruzNo ratings yet
- Methyldopa nursing management for hypertensionDocument4 pagesMethyldopa nursing management for hypertensionRico Mae ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study on CelecoxibDocument11 pagesDrug Study on CelecoxibPrincess Brigitte R. PATE�ANo ratings yet
- Vii. Drug Study Drug Mechanism of ActionDocument7 pagesVii. Drug Study Drug Mechanism of ActionRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Setraline Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSetraline Drug StudyOtaku MiyoNo ratings yet
- Chn-Herbal MedicineDocument5 pagesChn-Herbal MedicineBSN 1-N CASTRO, RicciNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbigail BascoNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayDocument4 pagesMetronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayCrisyl LipawenNo ratings yet
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- FluconazoleDocument3 pagesFluconazoleMary Kate ClarosNo ratings yet
- Chloral Hydrate (Drug Study)Document3 pagesChloral Hydrate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Drug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Andrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- Miglitol (Glyset)Document1 pageMiglitol (Glyset)ENo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument10 pagesDrugsRebecca JolieNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Purpose: 9. Check Blood For Presence of BubblesDocument2 pagesBlood Transfusion Purpose: 9. Check Blood For Presence of BubblesMabes100% (1)
- Drug Study OrthoDocument4 pagesDrug Study OrthoJhessa Curie Pitagan100% (1)
- Discharge PlanDocument9 pagesDischarge PlanRheynel NietesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyNikki RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyHerwincayeNo ratings yet
- Insulin Mechanism of Action and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument7 pagesInsulin Mechanism of Action and Nursing ResponsibilitiesGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Manage uterine contractions and bleeding with MetherginDocument2 pagesManage uterine contractions and bleeding with MetherginOtan Cuison100% (1)
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- Simethicone Relieves Gas and BloatingDocument1 pageSimethicone Relieves Gas and BloatingDivine Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Ertapenem (Invanz)Document1 pageErtapenem (Invanz)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Urokinase Dosage WheelDocument2 pagesUrokinase Dosage WheelNidhiNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CDocument6 pagesDRUG-STUDY - BALLON, Karlo CMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Alprazolam BiperidinDocument6 pagesAlprazolam BiperidinFionah RetuyaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyhsiriaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MetoprololDocument2 pagesDrug Study MetoprololHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Detrol (Tolterodine)Document1 pageDetrol (Tolterodine)ENo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Case Pre Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCase Pre Drug StudyJoule PeirreNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug Studyjho_26100% (2)
- Drug Study SummaryDocument7 pagesDrug Study SummaryKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for PreeclampsiaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for PreeclampsiaTsu Wei Chua0% (1)
- NCP Episiotomy WoundDocument3 pagesNCP Episiotomy WoundJP2001No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Document11 pagesDRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationNicole CalpoturaNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Obat ObgynDocument8 pagesObat ObgynMuhammad Naqiuddin JalaluddinNo ratings yet
- NCP DM and HCVDDocument3 pagesNCP DM and HCVDMAYBELINE OBAOB100% (1)
- Assess Vital Signs For Baseline Data. Assess Vital Signs For Baseline Data. Directl y Affects NeuroreDocument14 pagesAssess Vital Signs For Baseline Data. Assess Vital Signs For Baseline Data. Directl y Affects NeuroreBianca Marithè RejanoNo ratings yet
- AtroventDocument2 pagesAtroventKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Ceftriaxone IM Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCeftriaxone IM Drug StudyCastillo MikaellaNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesAmoxicillin Nursing ConsiderationsNico DonatoNo ratings yet
- Quinine anti-malarial drugDocument3 pagesQuinine anti-malarial drugDoubleHeartedNo ratings yet
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- Fansidar Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFansidar Drug StudyjangzieNo ratings yet
- MG Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMG Drug StudySandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument4 pagesDischarge PlanVillanueva NiñaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDrug Study (Acetaminophen)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- NCP & Drug Study (Tondo Med)Document5 pagesNCP & Drug Study (Tondo Med)Kevin_Remollo_2431No ratings yet
- 9 Ketamine Drug StudyDocument7 pages9 Ketamine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- GanciclovirDocument3 pagesGanciclovirRosher Deliman JanoyanNo ratings yet
- PrimaquineDocument3 pagesPrimaquineVijayakumar NsNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyBella Cy LopezNo ratings yet
- Drug LordsDocument25 pagesDrug LordsGlen DaleNo ratings yet
- Furosemide: Agranulocytosis, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopen Ia, Anemia, Aplastic AnemiaDocument9 pagesFurosemide: Agranulocytosis, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopen Ia, Anemia, Aplastic AnemiaRanee Diane AnanayoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, VecuroniumDocument12 pagesDrug Study Amphotericin B, Meropenem, Furosemide, Ciprofloxacin, Pentoxifylline, Pip-Tazo, Midazolam, Vecuroniumpaupaulala100% (4)
- Dialysis: Edna Co RN ManDocument37 pagesDialysis: Edna Co RN ManMary Shine GonidaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Epidemiology and Control A Global PerspectiveDocument329 pagesCommunicable Disease Epidemiology and Control A Global PerspectiveMarisela FuentesNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Case StudyDocument29 pagesChronic Renal Failure Case StudyMary Shine GonidaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Epidemiology and Control A Global PerspectiveDocument329 pagesCommunicable Disease Epidemiology and Control A Global PerspectiveMarisela FuentesNo ratings yet
- Articles - Math Invented or DiscoveredDocument35 pagesArticles - Math Invented or DiscoveredRonibeMalinginNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive UrgencyDocument8 pagesHypertensive UrgencyTony A.No ratings yet
- UM-DP12-25R UM-DP20-25R: The World's First Ultrasonic Probes With Dual-Plane Reconstruction Scanning CapabilityDocument3 pagesUM-DP12-25R UM-DP20-25R: The World's First Ultrasonic Probes With Dual-Plane Reconstruction Scanning CapabilityRicardo PaterninaNo ratings yet
- Child Growth. Growth Disorders UpdateDocument57 pagesChild Growth. Growth Disorders UpdateShahpoor Ahmad ShirzadaNo ratings yet
- The Human Excretory System: A 40-Character GuideDocument3 pagesThe Human Excretory System: A 40-Character GuideMelvel John Nobleza AmarilloNo ratings yet
- LD Implant FailuresDocument152 pagesLD Implant Failureswasim hussainNo ratings yet
- Meda QantasDocument12 pagesMeda QantasAviasiNo ratings yet
- TEACHING PLAN FOR Varicose VeinsDocument5 pagesTEACHING PLAN FOR Varicose Veinscertified_maharot_ako2828No ratings yet
- Simulation in Health Care Education: Perspectives in Biology and Medicine February 2008Document6 pagesSimulation in Health Care Education: Perspectives in Biology and Medicine February 2008Birendra MahatNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Respirology ASPRDocument55 pagesJurnal Respirology ASPRyosukexxNo ratings yet
- Koenig Pastoral Counseling With The AgedDocument11 pagesKoenig Pastoral Counseling With The AgedDavid Danao Franco MendezNo ratings yet
- Three Treasures Correspondences BrochureDocument4 pagesThree Treasures Correspondences Brochure292293709No ratings yet
- Cram Reviewer MusculoskeletalDocument32 pagesCram Reviewer MusculoskeletalGwynthselle SalazarNo ratings yet
- Gonadal Hormones and Their Pharmacological InhibitorsDocument7 pagesGonadal Hormones and Their Pharmacological InhibitorsHydieNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Acute Gastroenteritis and Acid Peptic-2Document15 pagesCase Study On Acute Gastroenteritis and Acid Peptic-2FHAMITHANo ratings yet
- Physiologic Changes in Pregnancy: 1. UterusDocument14 pagesPhysiologic Changes in Pregnancy: 1. UterusNiña Ricci MtflcoNo ratings yet
- Intro To HematologyDocument9 pagesIntro To HematologyDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Odds Ratio Calculations for Disease ExposureDocument4 pagesOdds Ratio Calculations for Disease ExposureJoshMatthewsNo ratings yet
- Histologi KelinciDocument7 pagesHistologi Kelinciummu0% (2)
- 2021 - СРРРРРРС - 3 Course - GM - EnglDocument17 pages2021 - СРРРРРРС - 3 Course - GM - EnglAiganym AmanovaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory MedicationsDocument18 pagesRespiratory Medicationsapi-338095748No ratings yet
- Cna Practice ExamDocument4 pagesCna Practice ExamJennifer Venfield83% (12)
- Medical Data Base Bahrain 2018Document122 pagesMedical Data Base Bahrain 2018Shibu KavullathilNo ratings yet
- J Clinic Periodontology - 2023 - RattuDocument19 pagesJ Clinic Periodontology - 2023 - RattutzulinNo ratings yet
- Goldman-Cecil Medicine 25th 2015Document39 pagesGoldman-Cecil Medicine 25th 2015Dumitru HarsenieNo ratings yet
- BBBFDocument3 pagesBBBFSkAliHassanNo ratings yet
- Forensic PathologyDocument3 pagesForensic PathologyjmosserNo ratings yet
- Books PhysiotherapyDocument22 pagesBooks Physiotherapyroyalviren100% (1)
- Ulator REV2 USA EXAMPLEDocument35 pagesUlator REV2 USA EXAMPLEMilton UrrozNo ratings yet
- 2-Shortness of Breath by Dr.hananDocument49 pages2-Shortness of Breath by Dr.hananSoon SheedNo ratings yet
- Sample: Pediatric Hernia Inguinal and Femoral RepairDocument8 pagesSample: Pediatric Hernia Inguinal and Femoral RepairSamuel Sebastian SirapanjiNo ratings yet