100% found this document useful (2 votes)
220 views3 pagesDesigning Organizations for Competitive Advantage
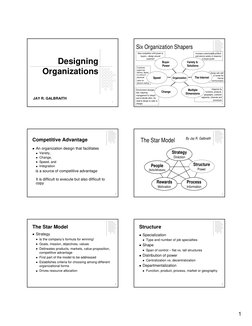
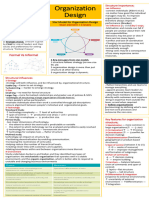
This document discusses six organizational design factors that shape organizations: strategy, structure, processes, rewards, people, and change. It notes that customers expect fast delivery and speed, requiring decentralization. Organizations must be designed to handle communication through the internet and cater to frequent environmental changes. Structure is emphasized but processes, rewards, and developing the right people are also important. The optimal design depends on an organization's strategy, and all aspects must be aligned to create competitive advantage.
Uploaded by
Cyn SyjucoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
220 views3 pagesDesigning Organizations for Competitive Advantage
This document discusses six organizational design factors that shape organizations: strategy, structure, processes, rewards, people, and change. It notes that customers expect fast delivery and speed, requiring decentralization. Organizations must be designed to handle communication through the internet and cater to frequent environmental changes. Structure is emphasized but processes, rewards, and developing the right people are also important. The optimal design depends on an organization's strategy, and all aspects must be aligned to create competitive advantage.
Uploaded by
Cyn SyjucoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- The Star Model
- Six Organization Shapers
- Designing Organizations
- Processes
- Rewards
- People
- Implications
- Departmentalization
- Distribution of Power
- Matching Strategy and Structure