Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1c Implantation & Placental Development
Uploaded by
Bea SamonteOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.1c Implantation & Placental Development
Uploaded by
Bea SamonteCopyright:
Available Formats
`
OBSTETRICS
1.1C IMPLANTATION & PLACENTAL DEVELOPMENT
DECIDUA
Endometrium of PREGNANCY
- Essential for HEMOCHORIAL PLACENTATION
Decidualization - dependent on : Estrogen, progesterone &
other factors secreted by blastocyst
During the course of pregnancy, decidual transformation is
from thick to thin.
DECIDUAL STRUCTURE
DECIDUAL HISTOLOGY
Zona Spongiosa glands
- Cylindrical -> Cuboidal & flat -> Degenerate & Slough off ->
Disappear
Placental Basal Plate (Decidua Basalis)
1. Spongiosa
- Arteries & dilated veins
- Disappeared glands
2. Cell invasion
- Interstitial trophoblast cells
- Trophoblastic giant cells
Normal Decidual Necrosis: 1st to 2nd trimester
Cell types:
- True decidual cells
- Maternal bone marrow - derived cells
- NK cells
- Trophoblast invasion
- Vasculogenesis
PERIPHERAL NK CELLS
10% Cytokine secretion
90% Cytolytic
3 layers
- Zona Compacta
Zona Functionalis
- Zona Spongiosa
- Zona Basalis - Remains after delivery, gives rise to new
endometrium
DECIDUAL NK CELLS
95 %
Cytokine secretion
50 % Angiogenic
DECIDUAL PROLACTIN
in AMNIOTIC FLUID
Paracrine function between maternal & fetal tissues
Same gene that encodes pituitary PRL
- Alternative Promoter - different regulation
Regulation
- Pituitary regulators do not affect decidual PRL
DECIDUAL BLOOD SUPPLY
Progestins
Cyclic AMP
As a consequence of implantation, blood supply to the decidua
capsularis is lost as the embryo-fetus grows.
Decidua parietalis - spiral arteries
Decidua basalis & intervillous space - invaded by
cytotrophoblasts
Uteroplacental vessels - not responsive to vasoactive agents
Fetal chorionic vessels - transports blood between the placenta
and the fetus
- Contains smooth muscle; doesn't respond to vasoactive
agents
DECIDUAL REACTION
Completed only by blastocyst implantation
Commences mid-luteal phase
Endothelin 1
IL 1
IL 2
EGF
DECIDUAL PROLACTIN ROLES
Amniotic fluid
- Transmembrane solute & water transport
- Fluid volume maintenance
Regulate immunologic functions in pregnancy
- Stimulate T-cells
Protective function
- Repress expression of detrimental genes to pregnancy
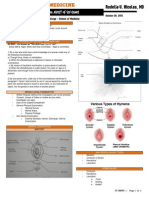
IMPLANTATION & FERTILIZATION
IMPLANTATION
Occurs within 6-7 days post fertilization
Must be on 20-24of the endometrial - ovarian cycle
If it doesn't occur within this period: Failure of implantation
o Placenta Previa or Ectopic pregnancy in the cervical wall
o Apposition is the 1st step of implantation
Page 1 of 5
Obstetrics
1.1C IMPLANTATION & PLACENTAL DEVELOPMENT
FERTILIZATION
With ovulation, the oocyte is engulfed by the fallopian tube
infundibulum. Transport through the tube is by movement of
cilia and tubal peristalsis.
Fertilization, occurs in oviduct in few hours. Spermatozoa must
be present in the tube at the time of oocyte arrival.
Spermatozoa passes between follicular cells; through the zona
pellucida (glycoprotein layer surrounding oocyte Cell
Membrane) and into the oocyte cytoplasm.
Fusion of two nuclei, intermingling of maternal and paternal
chromosomes creates the zygote.
CHORION & DECIDUA DEVELOPMENT
FATE OF TROPHOBLAST
During implantation into the uterine wall at 8th day the
trophoblast differentiates itself into two layers:
o
Syncytiotrophoblast (ST)
outer multinucleated syncytium
has an amorphous cytoplasm without cell borders
has nuclei that are multiple and diverse in size and
shape
has a continuous syncytial lining
o
Cytotrophoblast (CT)
inner layer of primitive mononuclear cells
germinal cells for the syncytium
has a well-demarcated cell border
has a single nucleus
has the ability to undergo DNA synthesis and mitosis
1 Syncytiotrophoblast (ST)
2 Cytotrophoblast (CT)
3 Epiblast
4 Hypoblast
5 Blastocyst cavity
6 Maternal blood capillary
7 Amniotic cavity
1.
2.
3.
4.
During Early Pregnancy
Villi in the entire periphery (chorionic membrane)
Blastocysts expand to form DECIDUA (endometrial cavity)
Villous trophoblast & anchoring cytotrophoblast, PLACENTA
Chorionic villi (Decidua Basalis) form Chorion Frondosum
Fetal Development of Placenta
5. Avascular fetal membrane abuts Decidua Parietalis -> Chorion
laeve
End Of 3rd Month
1. Chorion laeve separated from amnion by EXOCOELOMIC
CAVITY
2. Intimate contact to form AVASCULAR AMNIOCHORION
10th day, - the blastocyst becomes
totally encased within the
endometrium
Embryo enlarges - more maternal
decidua basalis is invaded by syncytiotrophoblast
Trophoblastic Lacunae- a system of intercommunicating
channels that permeates syncytiotrophoblast
Lacunae - become filled with maternal blood
FETAL & MATERNAL BLOOD CIRCULATION IN MATURE PLACENTA
MATERNAL CIRCULATION
TROPHOBLAST
The peripheral cells of the Blastocyst, which attach the zygote
(fertilized ovum) to the uterine wall and become the placenta
and the membranes that nourish and protect the developing
organism.
Physiologic maternal-placental circulation
- Maternal blood thru the basal plate and driven high up to the
chorionic plate
- Blood flows back down as it baths the microvillous surface
- Maternal blood drains back to the venous orifices
Page 2 of 5
Obstetrics
1.1C IMPLANTATION & PLACENTAL DEVELOPMENT
> Produce PGE2 and fetal fibronectin
> Site of prostaglandin production
> Synthesis of vasoactive peptides
FETAL CIRCULATION
Deoxygenated blood flows through 2 umbilical arteries
Umbilical vessels branch repeatedly beneath the amnion and
diving villi
Blood with a higher 02 content passes thru the umbilical vein
Placental Surface / Chorionic vessels
- Umbilical vessels along the fetal surface of the chorionic plate
- Responsive to vasoactive substances
- Arteries always cross over the veins
Truncal arteries
- Perforating branches of the surface arteries
- Each supply one cotyledon
- Decrease amount of smooth muscle but has increase in
caliber
AMNION MESENCHYMAL CELLS
Synthesis of interstitial collagens that compose the compact
layer of the amnion.
Synthesize cytokines that include IL-6, IL-8 and monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1.
Greater source of PGE2 compared to epithelial cells
AMNION TENSILE STRENGTH
Resides almost exclusively in the compact layer
Regulated in part by fibrillar collagen interacting with
proteoglycans such as decorin.
Decorin - promotes tissue strength.
Compact layer:
> Cross linked interstitial collagens I and III
> Lesser amounts of collagens V and VI
Collagen I is the major interstitial collagen in tissues
characterized by great tensile strength, such as bone and
tendon.
Collegen III is believed to contribute to tissue integrity and
provides both tissue extensibility and tensile strength.
THE UMBILICAL CORD
DEVELOPMENT
AMNION
Provides almost all tensile strength of the fetal membranes
Preterm rupture of fetal membrane - major cause of preterm
delivery
5 separate amnion layers:
> Inner surface - bathed by amnionic fluid, uninterrupted single
layer of cuboidal epithelium
> Basement membrane
> Acellular compact layer - composed primarily of interstitial
collagens
> Outer side of the compact layer - row of fibroblast-like
mesenchymal cells
> Outermost amnion layer - acellular zona spongiosa contiguous with the second fetal membrane, the chorion laeve.
DEVELOPMENT
Amniogenic cells - precursor of amnionic epithelium
Growth of amnion eventually engulfs the embryo & prolapses
into the cavity
End of the 1st trimester - apposition of the mesoblast of the
chorion and mnion
AMNION EPITHELIAL CELLS
May respond to signals derived from the fetus of the mother
Responsive to various endocrine or paracrine modulators
Metabolically active:
> Inhibits metalloprotinase-1 synthesis
By middle of the 3rd month, the exocoelom (primitive yolk sac)
is obliterated due to expanding amnion
The amnion fuses with the chorion laeve (non-placental part of
the chorion), and covers the bulging placental disc and the
lateral surface of the body stalk.
This covered body stalk becomes the Umbilical Cord or funis
STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
Dull white in color, is a part of the fetal membranes
Extends from the fetal surface of the placenta to the fetal
umbilicus
Contains three vessels within
Two Arteries and One Vein
Flow into the umbilical vein passes two routes through the
ductus venosus into the inferior vena cava as well as hepatic
circulation
The flow then leaves through the two umbilical arteries
Page 3 of 5
Obstetrics
1.1C IMPLANTATION & PLACENTAL DEVELOPMENT
These vessels twist within cord, dextral (Right) or sinistral (left)
> It is theorized that crimping of the cord is prevented by
twisting
dayis by far the greatest of any known hormone in humans.
The half-life of hPL in maternal plasma is between 10 and 30
minutes. In late pregnancy, maternal serum concentrations
reach levels of 5 to 15 g/mL.
hPL concentration is proportional to placental mass, because
the levels of mRNA for hPL is relatively constant throughout the
pregnancy
Energy source for maternal metabolism and fetal nutrition
OTHER PLACENTAL HORMONES
Protein/peptide hormones, analogous to hypothalamic or pituitary
hormone, differ in terms of feedback inhibition.
1.
2.
PLACENTAL HORMONES
BIOLOGIC FUNCTIONS OF hCG
Rescue and maintenance of the corpus luteum
Stimulation of fetal testosterone secretion
Stimulation of the maternal thyroid gland
Relaxin secretion of the corpus luteum
Promotion of uterine vascular vasodilation
Myometrial smooth muscle relaxation
Regulation of expansion of uterine natural killer cell numbers
3.
4.
5.
Glycoprotein with a biological activity same to LH
Produced almost exclusively by the placenta, however low
levels are also synthesized in the kidney
METABOLIC ACTIONS
Promotes maternal lipolysis
Inhibits leptin secretion
Maternal adaptation to fetal energy requirements
Increase maternal beta cell proliferation to augment insulin
secretion (with prolactin)
Angiogenic -> function in fetal vasculature
Lactogenic
Growth-hormone like
Immunochemical
Concentrated in the syncitiotrophoblast
Detected as early as 2-3 weeks after fertilization
Secreted in the maternal circulation
And has low concentrations in the urine
Similar with hGH
There are five genes in the growth hormoneplacental lactogen gene cluster that are linked and located on chromosome
17. Two of thesehPL2 and hPL3encode hPL, and the
amount of mRNA in the term placenta is similar for each.
Within 5 to 10 days after conception, hPL is demonstrable in
the placenta and can be detected in maternal serum as early
as 3 weeks. Maternal plasma concentrations are linked to placental mass, and they rise steadily until 34 to 36 weeks gestation. The hPL production rate near termapproximately 1 g/
6.
7.
8.
9.
Chorionic Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH):
Product of Pro-opiomenanocortin.
Placental CRH Chorionic ACTH, important in fetal
lung maturation and parturition timing.
Promotes glucocorticoid production.
Growth Hormone Variant (hGH-V)
GH, synthesized in the syncytium by 21- 26 weeks
of gestation but not expressed in Pituitary.
Growth Promoting and antilipogenic function similar
to hGH but has reduced diabetogenic and lactogenic
actions. Mediates Pregnancy Insulin Resistance.
Hypothalamic Releasing Hormones
Analogous of Hypothalamic releasing or inhibiting
hormones.
GnRH
Found in cytotrophoblast but not in
cyncytiotrophoblast
Regulates trophoblast hCG production.
CRH Related Peotides:
CRH, Ucoroctin, Ucoroctin II and III
CRH level surges (upto 100pmol/L) in third trimester.
Increases trophoblast ACTH secretion. In maternal
plasma CRH binds to CRH-binding protein and
remains inactive.
Induces smooth muscle relaxation in vascular and
myometrial tissues and immunosuppression.
Glucocorticoids stimulates CRH production.
GHRH (Grhelin)
Regulator of hGH secretion produced by placental
tissue.
Peaks at midpregnancy and plays role in regulating
hGH-V
Relaxin:
Similar to Insulin and IGF-, expressed in Corpus
luteum, decidua and placenta.
Act on myometrium with progesterone to promote
relaxation and quiescence of early pregnancy.
Also plays role in postpartum. extracellular
degradation
Parathyroid Hormone Related Hormone (PTH-rP)
Regulate transfer of calcium and other solutes and
fetal mineral homeostasis in bone, amnionic fluid and
circulation.
Leptin :
Plays role in birthweights, fetal development and
growth, inhbitis apotosis and promotes trophoblast
proliferation.
Page 4 of 5
Obstetrics
1.1C IMPLANTATION & PLACENTAL DEVELOPMENT
10. Neuropeptide Y
Expressed in cytotrophoblast, plays role in CRH
release.
11. Inhibin and Activin.
Inhibin produced by trophoblast inhibit pituitary FSH
release thereby inhibiting ovulation during pregnancy
also regulates placental hCG synthesis via GnRH
Activin is expressed in placenta and amnion.
FETAL ADRENAL GLANDS
At term, it weigh the same as those of the adult.
More than 85 percent of the fetal gland is composed of a
unique fetal zone
Daily steroid production of fetal adrenal glands near term is 100
to 200 mg/day.
The fetal zone is lost in the first year of life and is not present in
the adult.
In addition to ACTH, fetal adrenal gland growth is influenced by
factors secreted by the placenta.
The principal secretory
products of the fetal adrenal
glands are pregnenolone
sulfate and DHEA-S.
Cortisol arises primarily in the
neocortex and transitional
zone of the fetal adrenal
glands
stimulatory activity.
Fetal adrenal glands are
highly dependent on
circulating LDL as a source
of cholesterol for optimum
steroidogenesis
The low level of LDL
cholesterol in fetal plasma
results from the rapid use of
LDL by the fetal adrenal
glands for steroidogenesis
FETAL ADRENAL HORMONES
PLACENTAL ESTRIOL
SYNTHESIS
Estradiol- primary placental
estrogen secretory product at
term.
High levels of fetal hepatic 16hydroxylase act on adrenal
derived steroids.
16-OHDHEA, were converted
to estriol by placental tissue.
Most placental estrogens are
released into the maternal
circulation.
Maternal estriol and estetrol
are produced by fetal steroid
precursors.
There is a severe deficiency
in the expression of 3HSD in
adrenal fetal zone cells
But there is a very active
steroid sulfotransferase
activity in the fetal adrenal
glands.
FETAL ADRENAL STEROID
PRECURSOR
The precursor for fetal
adrenal steroidogenesis is
cholesterol.
Fetal adrenal glands
synthesize cholesterol from
acetate.
Enzymes involved in
cholesterol synthesis are
elevated compared with
adult.
It is still insufficient to
account for the steroids
produced by these glands.
Fetal glands take up
lipoproteins as a source of
cholesterol for
steroidogenesis.
LDL was most effective,
HDL was much less, and
VLDL was devoid of
Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- The Black Emperor's Grand Grimoire - by Frank GenghisDocument144 pagesThe Black Emperor's Grand Grimoire - by Frank GenghisFrank Genghis0% (2)
- COMPLETE Medical Disease in PregnancyDocument210 pagesCOMPLETE Medical Disease in PregnancyCHANDREN ARUMUGAMNo ratings yet
- Nephroblastoma FinalDocument24 pagesNephroblastoma FinalKrissy_Singh_211No ratings yet
- Identification and Management of Ambiguous GenitaliaDocument31 pagesIdentification and Management of Ambiguous Genitaliateslimolakunleraji100% (1)
- Genetics For MrcogDocument4 pagesGenetics For MrcogsriniNo ratings yet
- Choose the Right Low Boy Trailer ModelDocument42 pagesChoose the Right Low Boy Trailer ModelOdlnayer AllebramNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument26 pagesEctopic PregnancysandhyakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Fetal MonitoringDocument6 pagesFetal MonitoringRraouzmaaliNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument36 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingPranshu Prajyot 67100% (1)
- Adnexal MassDocument28 pagesAdnexal MassJuan P. RuedaNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Pregnancy LossDocument61 pagesRecurrent Pregnancy LossHerman FiraNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning Assignment - TescoDocument16 pagesStrategic Planning Assignment - TescoKayode Trinity Omosebi100% (1)
- AUBDocument45 pagesAUBJBNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdomen During Pregnancy BelaynehDocument47 pagesAcute Abdomen During Pregnancy BelaynehYohannis AsefaNo ratings yet
- MOH Pocket Manual in Obstetrics and GynaecologyDocument194 pagesMOH Pocket Manual in Obstetrics and GynaecologyBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sharda Jain: Director: Secretary GeneralDocument91 pagesDr. Sharda Jain: Director: Secretary GeneraljijaniNo ratings yet
- 1.3b Medico-Legal Aspect of Sex CrimesDocument2 pages1.3b Medico-Legal Aspect of Sex CrimesJaybee SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Antepartum HaemorrhageDocument65 pagesAntepartum HaemorrhageAmit RamrattanNo ratings yet
- Investigating Primary Amenorrhea CaseDocument23 pagesInvestigating Primary Amenorrhea CaseMohammed AbdulNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Benign Gynecologic TumorsDocument9 pagesModule 6 - Benign Gynecologic TumorsRenz Francis SasaNo ratings yet
- OB Williams Chap 2 Maternal PhysiologyDocument9 pagesOB Williams Chap 2 Maternal PhysiologyRem Alfelor100% (2)
- OB MustKnowsDocument90 pagesOB MustKnowsHarlyn MagsinoNo ratings yet
- GYNE 4.08 Benign and Malignant Lesions of The CervixDocument9 pagesGYNE 4.08 Benign and Malignant Lesions of The CervixGray SnellNo ratings yet
- Daniel J. Wood - Realm of The Vampire - History and The Undead-Galde Press (2013)Document156 pagesDaniel J. Wood - Realm of The Vampire - History and The Undead-Galde Press (2013)Jerry KanneNo ratings yet
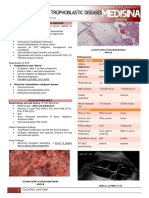
- 02 Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument8 pages02 Gestational Trophoblastic Diseasemisakichan FrandoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Labor and Infertility 2016 PDFDocument12 pagesAbnormal Labor and Infertility 2016 PDFLarissa TacalanNo ratings yet
- Ovarian TumoursDocument24 pagesOvarian TumoursBinta BaptisteNo ratings yet
- ART Methods Guide Infertility TreatmentDocument8 pagesART Methods Guide Infertility Treatmentsagi muNo ratings yet
- Legal Med Identification & Death AspectsDocument4 pagesLegal Med Identification & Death AspectsBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Anaemia During PregnancyDocument21 pagesAnaemia During Pregnancybotet_2306100% (2)
- High Risk PregnancyDocument42 pagesHigh Risk PregnancyLisa KriestantoNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Cases For MS-IIIDocument13 pagesObstetric Cases For MS-IIIkukadiyaNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Obstructed LabourDocument98 pagesSeminar On Obstructed Labourtesfahuntekletilahun80% (5)
- Breast Abcess PDFDocument4 pagesBreast Abcess PDFponekNo ratings yet
- Adoption: Legal DefinitionDocument8 pagesAdoption: Legal Definitionsharon victoria mendezNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument23 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingTakeru Ferry100% (1)
- Normal & Abnormal LabourDocument5 pagesNormal & Abnormal Labourra100% (1)
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyDocument33 pagesBleeding in Early PregnancyFirdaus ShaharNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Menstrual Cycle 1Document22 pagesPhysiology of The Menstrual Cycle 1annonymousNo ratings yet
- InfertilityDocument14 pagesInfertilityDrChauhanNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Hemorrhage GuideDocument27 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhage GuideSahil Chadgal100% (2)
- Antepartum HemorrhageDocument105 pagesAntepartum HemorrhageBablablo LolaleNo ratings yet
- Gynecology & Obstetrics NotesDocument58 pagesGynecology & Obstetrics Notessrhmd100% (2)
- Infertilityseminarppt 190718134710Document77 pagesInfertilityseminarppt 190718134710subiNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Morning SessionDocument20 pagesWelcome To The Morning SessionGENERAL sharpNo ratings yet
- Pte Academic Test Practice Repeat SentenceDocument3 pagesPte Academic Test Practice Repeat SentenceJackAziz100% (7)
- 10 - PlacentaDocument21 pages10 - Placentaalejosshht100% (1)
- Instrumental Vaginal Delivery: Professor Roshan Ara QaziDocument27 pagesInstrumental Vaginal Delivery: Professor Roshan Ara Qazikaram008No ratings yet
- Surgical Treatment of Traumatic PPHDocument23 pagesSurgical Treatment of Traumatic PPHAyushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Hemorrhage PDFDocument23 pagesAntepartum Hemorrhage PDFfrizkapfNo ratings yet
- Williams 03 - Implantation, Embryogenesis, Placental DevelopmentDocument14 pagesWilliams 03 - Implantation, Embryogenesis, Placental DevelopmentAhmed Abou SeifNo ratings yet
- Puerperal Sepsis Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument36 pagesPuerperal Sepsis Diagnosis and TreatmentRufai Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Disease and Pregnancy RCOG GuidelineDocument18 pagesCardiac Disease and Pregnancy RCOG GuidelinedanielsusenoNo ratings yet
- Operative ObstetricsDocument4 pagesOperative Obstetricssarguss14100% (3)
- Gynecology Topics: Uterine Prolapse, Amenorrhea, Dysfunctional Bleeding, PCOS, Infertility, Menopause (39Document101 pagesGynecology Topics: Uterine Prolapse, Amenorrhea, Dysfunctional Bleeding, PCOS, Infertility, Menopause (39jojolilimomo100% (1)
- Abnormal Uterin ActionDocument65 pagesAbnormal Uterin Actionshweta raiNo ratings yet
- 19 - LSCSDocument16 pages19 - LSCSTrishenth FonsekaNo ratings yet
- OSCE Revision OBG DocumentDocument60 pagesOSCE Revision OBG DocumentshreyaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Diagnosis and ManagementDocument128 pagesCervical Cancer Diagnosis and Managementnicewan0% (1)
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) : Ahmed Refaat Abd ElzaherDocument41 pagesGestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) : Ahmed Refaat Abd ElzaherJessica NadiaNo ratings yet
- Case 10: Placenta Previa: ST ND RDDocument6 pagesCase 10: Placenta Previa: ST ND RDMengda ZhangNo ratings yet
- Gynecological History Taking and ExaminationDocument17 pagesGynecological History Taking and Examinationnmsiswaridewi100% (1)
- ObstetricsDocument23 pagesObstetricsSundar MuneesNo ratings yet
- Threatened AbortionDocument1 pageThreatened AbortionKEn PilapilNo ratings yet
- University of Gondar College of Medicine and Health ScienceDocument100 pagesUniversity of Gondar College of Medicine and Health ScienceCHALIE MEQUNo ratings yet
- AUBDocument26 pagesAUByayaslaras96No ratings yet
- Primary Amenorrhea Causes and EvaluationDocument15 pagesPrimary Amenorrhea Causes and EvaluationbobNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Disorders & Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDocument5 pagesBleeding Disorders & Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: N. GonorrhoeaeDocument2 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease: N. GonorrhoeaeBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- 1.1k Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument6 pages1.1k Coronary Artery DiseaseBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- 1.1e Sudden Cardiac ArrestDocument4 pages1.1e Sudden Cardiac ArrestBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- 1.1b AutopsyDocument3 pages1.1b AutopsyBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow Failure Diseases & TreatmentsDocument2 pagesBone Marrow Failure Diseases & TreatmentsBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Collection of Biological Sample For Dna-Oct 9Document84 pagesCollection of Biological Sample For Dna-Oct 9Bea SamonteNo ratings yet
- 3rd Year Clinical Nephrology Preceptorial-1Document1 page3rd Year Clinical Nephrology Preceptorial-1Bea SamonteNo ratings yet
- 1.3G Forensic Path PDFDocument17 pages1.3G Forensic Path PDFBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Clinpharm SGD Bronchial AsthmaDocument9 pagesClinpharm SGD Bronchial AsthmaBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- 1.1d EvidenceDocument2 pages1.1d EvidenceBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Clinpharm SGD Organophosphayte PoisoningDocument2 pagesClinpharm SGD Organophosphayte PoisoningBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- 1.1a Prescription WritingDocument4 pages1.1a Prescription WritingBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- 1.6e CopdDocument6 pages1.6e CopdBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- 1.4A Intro To HemaDocument4 pages1.4A Intro To HemaBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- 1.1c Rdu ProcessDocument3 pages1.1c Rdu ProcessBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- 1.1b Clinical PharmacologyDocument1 page1.1b Clinical PharmacologyBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacology SGD 3 - HypertensionDocument2 pagesClinical Pharmacology SGD 3 - HypertensionBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- 1.2a PhlebotomyDocument7 pages1.2a PhlebotomyBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- History PEDocument6 pagesHistory PEBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Semen AnalysisDocument8 pagesSemen AnalysisBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Thyroid CA Case Pres EditDocument42 pagesThyroid CA Case Pres EditBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Small Group DiscussionDocument3 pagesSmall Group DiscussionBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- CPC-Patho Version 6Document20 pagesCPC-Patho Version 6Bea SamonteNo ratings yet
- 1.1A Total Quality Management in Health Care: Hospital ErrorsDocument3 pages1.1A Total Quality Management in Health Care: Hospital ErrorsBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Dilatation Clock Time Hour of Labor: Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PartographDocument1 pageDilatation Clock Time Hour of Labor: Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PartographBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- EN3: Introduction To Engineering and Statics: 3. Resultant of Systems of ForcesDocument6 pagesEN3: Introduction To Engineering and Statics: 3. Resultant of Systems of ForceskarthikaNo ratings yet
- Conversion Cycle (Process Cost) : Rizal Technological UniversityDocument25 pagesConversion Cycle (Process Cost) : Rizal Technological UniversityHatdogNo ratings yet
- Regina Downtown Community Support Team ReportDocument28 pagesRegina Downtown Community Support Team ReportJeremy SimesNo ratings yet
- CaracterizacióndeSalpicadurasSMAW Molleda 2007Document5 pagesCaracterizacióndeSalpicadurasSMAW Molleda 2007Tamara Maria Ortiz MendezNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support Checklist CSLLFIDocument1 pageBasic Life Support Checklist CSLLFIShane Frances SaborridoNo ratings yet
- Myths of Membership The Politics of Legitimation in UN Security Council ReformDocument20 pagesMyths of Membership The Politics of Legitimation in UN Security Council ReformCaroline GassiatNo ratings yet
- Template PharmaconDocument4 pagesTemplate PharmaconDanang RaharjoNo ratings yet
- Medical Services Recruitment Board (MRB)Document20 pagesMedical Services Recruitment Board (MRB)durai PandiNo ratings yet
- AET Aetna 2017 Investor Day Presentation - Final (For Website) PDFDocument73 pagesAET Aetna 2017 Investor Day Presentation - Final (For Website) PDFAla BasterNo ratings yet
- Quotation SS20230308 100KVAR APFC PANEL VIDHYA WIRESDocument4 pagesQuotation SS20230308 100KVAR APFC PANEL VIDHYA WIRESsunil halvadiyaNo ratings yet
- Queen'S University Midterm Examination Department of EconomicsDocument7 pagesQueen'S University Midterm Examination Department of EconomicsAsif Ahmed NeloyNo ratings yet
- تركيب وتشغيل وحدات تكييف الهواءDocument49 pagesتركيب وتشغيل وحدات تكييف الهواءOmar NabilNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Shimadzu Analytical BalanceDocument169 pagesInstruction Manual: Shimadzu Analytical BalanceChanthar SoeNo ratings yet
- Journal of Materials Processing Technology: Jun Cao, Michael A. Gharghouri, Philip NashDocument11 pagesJournal of Materials Processing Technology: Jun Cao, Michael A. Gharghouri, Philip NashJesus Ismael Jimenez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Enquiries: 1. Enquiry From A Retailer To A Foreign ManufacturerDocument7 pagesEnquiries: 1. Enquiry From A Retailer To A Foreign ManufacturerNhi Hoàng Lê NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Farrukh QAMAR - Assessment 2 Student Practical Demonstration of Tasks AURAMA006 V2Document19 pagesMuhammad Farrukh QAMAR - Assessment 2 Student Practical Demonstration of Tasks AURAMA006 V2Rana Muhammad Ashfaq Khan0% (1)
- Outline of The Gospel of John: Book of Signs: Jesus Reveals His Glory To The World (Israel) (1:19-12:50)Document4 pagesOutline of The Gospel of John: Book of Signs: Jesus Reveals His Glory To The World (Israel) (1:19-12:50)Aamer JavedNo ratings yet
- ZISCO Installs World LongestDocument11 pagesZISCO Installs World LongestJoshua GrahitaNo ratings yet
- Group L2 Nitish at Solutions UnlimitedDocument10 pagesGroup L2 Nitish at Solutions UnlimitedMani ThomasNo ratings yet
- Transcricao How To Be Happy (Before Success) - by Earl NightingaleDocument62 pagesTranscricao How To Be Happy (Before Success) - by Earl NightingalepauloalaraNo ratings yet
- Case3: What's in A Car 1. What Kind of Research Study Should Shridhar Undertake? Define TheDocument2 pagesCase3: What's in A Car 1. What Kind of Research Study Should Shridhar Undertake? Define TheRoshan kumar Rauniyar0% (3)
- Small BusinessDocument22 pagesSmall BusinessAngelie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Impromtu Speech Covid 19Document7 pagesImpromtu Speech Covid 19ESWARY A/P VASUDEVAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Taeka HaileleulDocument167 pagesTaeka HaileleulBini100% (1)