Fabrication and Joining Section
Universiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysia France Institute (UniKL-MFI)
UNIVERSITI KUALA LUMPUR
Malaysia France Institute
LAB SHEET
HARDNESS TEST
Fabrication and Joining Section
Universiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysia France Institute
Seksyen 14, Jalan Teras Jernang,
43650 Bandar Baru Bangi, Selangor.
�Fabrication and Joining Section
Universiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysia France Institute (UniKL-MFI)
LAB SHEET
HARDNESS TEST
1. INTRODUCTION
Hardness is the resistance of a material to localized deformation. Hardness
measurements are widely used for the quality control of materials because they are
quick and considered to be non destructive tests when the marks or indentations
produced by the test are in low stress areas.
The manual contains some fundamental theory for understanding the experiment,
description of the apparatus and experimental procedure for hardness.
2. OBJECTIVE
1. To determine the hardness of various engineering materials using Vickers
Hardness test.
2. To develop an understanding of suitable scale for hardness test specimens.
3. THEORY
General
Hardness is a measure of the resistance of a metal to permanent (plastic) deformation.
The hardness of the metal is measured by loading an indenter into its surface. The
indenter material which is usually a ball, pyramid, or cone, is made of a material much
harder than the material being tested. For most standard hardness test a known load is
applied slowly by pressing the indenter at 90 degrees into the metal surface being
tested. After the indentation has been made, the indenter is withdrawn from the surface.
An empirical hardness is then calculated or read off a dial (or digital display). Which is
based on the cross-sectional area of depth of the indentation.
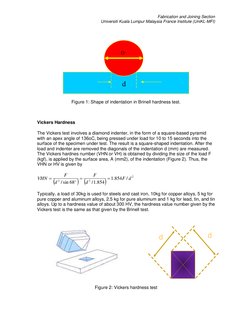
Brinell hardness Test
With the Brinell test, a hardened steel ball or tungsten carbide ball is pressed for a time
of 10 to 30 seconds into the surface of specimen by a standard load F (kgf) (Figure 1).
After the load and the ball have been removed, the diameter of the indentation d (mm) is
measured. The Brinell hardness number (BHN or HB), is obtained by dividing the size of
the load applied by the surface area of the spherical indentation A (mm2).
HB
F
F
F
A Db D
D D2 d 2
Where b (mm) is the depth of indentation, D (mm) is the diameter of the ball. The Brinell
test cannot be used with very soft or very hard materials with hardnesses up to 450HB
with a hardened steel ball and 600 HB with a tungsten carbide ball.
�Fabrication and Joining Section
Universiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysia France Institute (UniKL-MFI)
d
Figure 1: Shape of indentation in Brinell hardness test.
Vickers Hardness
The Vickers test involves a diamond indenter, in the form of a square-based pyramid
with an apex angle of 136oC, being pressed under load for 10 to 15 seconds into the
surface of the specimen under test. The result is a square-shaped indentation. After the
load and indenter are removed the diagonals of the indentation d (mm) are measured.
The Vickers hardnes number (VHN or VH) is obtained by dividing the size of the load F
(kgf), is applied by the surface area, A (mm2), of the indentation (Figure 2). Thus, the
VHN or HV is given by
VHN
F
F
2
1.854 F / d 2
o
d / sin 68
d / 1.854
Typically, a load of 30kg is used for steels and cast iron, 10kg for copper alloys, 5 kg for
pure copper and aluminum alloys, 2.5 kg for pure aluminum and 1 kg for lead, tin, and tin
alloys. Up to a hardness value of about 300 HV, the hardness value number given by the
Vickers test is the same as that given by the Brinell test.
Figure 2: Vickers hardness test
�Fabrication and Joining Section
Universiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysia France Institute (UniKL-MFI)
Rockwell Hardness Test
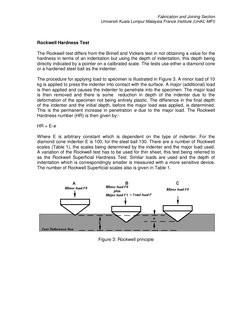
The Rockwell test differs from the Brinell and Vickers test in not obtaining a value for the
hardness in terms of an indentation but using the depth of indentation, this depth being
directly indicated by a pointer on a calibrated scale. The tests use either a diamond cone
or a hardened steel ball as the indenter.
The procedure for applying load to specimen is illustrated in Figure 3. A minor load of 10
kg is applied to press the indenter into contact with the surface. A major (additional) load
is then applied and causes the indenter to penetrate into the specimen. The major load
is then removed and there is some reduction in depth of the indenter due to the
deformation of the specimen not being entirely plastic. The difference in the final depth
of the indenter and the initial depth, before the major load was applied, is determined.
This is the permanent increase in penetration e due to the major load. The Rockwell
Hardness number (HR) is then given by:HR = E-e
Where E is arbitrary constant which is dependent on the type of indenter. For the
diamond cone indenter E is 100, for the steel ball 130. There are a number of Rockwell
scales (Table 1), the scales being determined by the indenter and the major load used.
A variation of the Rockwell test has to be used for thin sheet, this test being referred to
as the Rockwell Superficial Hardness Test. Similar loads are used and the depth of
indentation which is correspondingly smaller is measured with a more sensitive device.
The number of Rockwell Superficial scales also is given in Table 1.
Figure 3: Rockwell principle
�Fabrication and Joining Section
Universiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysia France Institute (UniKL-MFI)
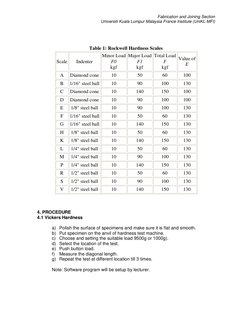
Scale
Table 1: Rockwell Hardness Scales
Minor Load Major Load Total Load
Value of
Indenter
F0
F1
F
E
kgf
kgf
kgf
Diamond cone
10
50
60
100
1/16" steel ball
10
90
100
130
Diamond cone
10
140
150
100
Diamond cone
10
90
100
100
1/8" steel ball
10
90
100
130
1/16" steel ball
10
50
60
130
1/16" steel ball
10
140
150
130
1/8" steel ball
10
50
60
130
1/8" steel ball
10
140
150
130
1/4" steel ball
10
50
60
130
1/4" steel ball
10
90
100
130
1/4" steel ball
10
140
150
130
1/2" steel ball
10
50
60
130
1/2" steel ball
10
90
100
130
1/2" steel ball
10
140
150
130
4. PROCEDURE
4.1 Vickers Hardness
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
f)
g)
Polish the surface of specimens and make sure it is flat and smooth.
Put specimen on the anvil of hardness test machine.
Choose and setting the suitable load 9500g or 1000g).
Select the location of the test.
Push button load.
Measure the diagonal length.
Repeat the test at different location till 3 times.
Note: Software program will be setup by lecturer.
�Fabrication and Joining Section
Universiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysia France Institute (UniKL-MFI)
5. ANALYSIS
a) Determine the average hardness value by used the formula.
b) Convert to Rockwell by used the hardness conversion table.
c) Compare the result for different materials.
6. REFERENCES
a)
b)
c)
d)
ASM Metals Handbook
Mechancial Testing of Materials, A.J. Fenner, Philosophical Library Inc., 1965.
Pollack, H. W., Materials Science and Metallurgy, Reston Pub. Co., Reston:1981.
Van Vlack, L.H., Materials Science for Engineers, Addison Wesly Pub. Co.,
Mass: 1970.
e) Standards:
Conversion : ASTM E 140: 1956
Brinell : DIN 50351, ASTM E 10-73, BS 240: Parti: 1961, TS 189.
Vickers : DIN 50133, ASTM E 92-72, BS 427 : Part 1: 1961, TS 207
Rockwell : DIN 50103, ASTM E 18-74, BS 4175: Part 1: 1967, TS 140.
�Fabrication and Joining Section
Universiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysia France Institute (UniKL-MFI)
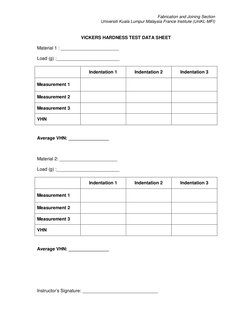
VICKERS HARDNESS TEST DATA SHEET
Material 1 : _______________________
Load (g) :_________________________
Indentation 1
Indentation 2
Indentation 3
Indentation 2
Indentation 3
Measurement 1
Measurement 2
Measurement 3
VHN
Average VHN: ________________
Material 2: _______________________
Load (g) :_________________________
Indentation 1
Measurement 1
Measurement 2
Measurement 3
VHN
Average VHN: ________________
Instructors Signature: ______________________________
�Fabrication and Joining Section
Universiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysia France Institute (UniKL-MFI)
Prepared by,
____________________
Endorsed by,
_______________________