Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Multimedia: Interactive Activity Through in Online Learning
Uploaded by
fartien91Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Multimedia: Interactive Activity Through in Online Learning
Uploaded by
fartien91Copyright:
Available Formats
Interactive Activity through Multimedia in Online Learning
Idaho Digital Learning Academy
Kody Stimpson
Contents:
1. Research of the Integration of Interactivity through Multimedia in Online
Learning
2. Resources Used in Research
3. Comparing Before and After with Interactivity
4. IDLA Process for Interactivity Development
Research of the Integration of
Interactive Activity through Multimedia in Online Learning
Kody Stimpson
Research shows that increasing interactive activity through multimedia can benefit students in the
following ways:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Increases Learning
Enables Students with Varying Learning Styles to Learn in a Variety of Ways
Provides Consistent and Continuous Feedback
Increases Retention with a Shorter Learning Time
Empowers and Motivates while Eliciting a Positive Attitude Towards the Course Content.
Offloads Repetitive Teaching Tasks that Allow Teachers to Focus on Specific Issues.
1. Increases Learning
Steven Hick, a Carleton University Professor states that not only does interactive multimedia have a
strong positive effect on learning, but that learners learn faster and have better attitudes towards their
learning experience. Benefits of Interactive Multimedia Courseware.
In a study by Forrester Research, respondents identified the lack of interactivity 56% of the time as
the most common obstacle to a successful elearning strategy. Overcoming human obstacles to Elearning.
A study was done to determine whether the addition of interactivity to a computer-based learning
package enhances the learning process. The result was that interactive systems facilitate deep
learning by actively engaging the learner in the learning process. The Interactivity Effect in
Multimedia Learning.
Studies also show that at-risk students and students with special needs benefit from using interactive
multimedia. Bagui explains that multimedia may make it easier for people to learn because it can
supply stimulating environments that encourage students involvement in the learning process.
Technologies for Education.
In addition to these studies, a major transportation company reported an increase in bottom-line
performance of over 35% which equated to millions in increased revenues and savings when
integrating interactive multimedia to their training. Learners also showed a 40% increased in learning
retention. - ROI with Blended E-learning.
2. Enables Students with Varying Learning Styles to Learn in a Variety of Ways
Interactive multimedia, when used correctly, enables students to learn in a variety of ways addressing
several learning styles and modalities. - Educational Benefits of Interactive Multimedia, - Innovative
Teaching, Cognitive Styles and Computer-aided Learning.
Researchers Mishra & Sharma found that interactive multimedia is also capable of presenting trueto-life situations. Decision tree simulations, video simulations, and simple animations that allow
learners to learn-by-viewing, learn-by-doing, or learn-by-coaching are all effective methods for
developing a practical skill and increase retention. Interactive Multimedia in Education and Training.
3. Provides Consistent and Continuous Feedback
Interactive self assessments provide feedback that help students improve. Blackboard Exemplary
Course Requirement. This feedback encourages students to feel safe and try because they know that
they can fail without humiliation. When they feel free to try, it enables them to learn. - Articulate
Elearning Blog.
4. Increases Retention with a Shorter Learning Time
Over 30 studies have found that interactive technologies reduce learning time requirements by an
average of 50 percent Learning Benefits of Interactive technologies. Interactive multimedia keeps
learners interested in the content while reinforcing the skills. It encourages learners to return again
and again through continual practice.
Research has shown that people remember 20% of what they see, 40% of what they see and hear,
but about 75% of what they see and hear and do simultaneously. Interactive multimedia has been
shown to elicit the highest rate of information retention and results in a shorter learning time.
Innovative Teaching, Benefits of Interactive Multimedia Courseware.
5. Empowers and Motivates while Eliciting a Positive Attitude Towards the Course Content
Interactive multimedia is more likely to be enjoyed by learners than non-interactive content. It elicits
positive attitudes towards the application and students feel empowered and more in control of their
learning. Benefits of Interactive Multimedia.
Students are able to learn better since they use multiple sensory modalities (hearing, seeing, and
doing). They are motivated to pay more attention to the information presented and better retain the
information. Innovative Teaching.
6. Offloads Repetitive Teaching Tasks that Allow Teachers to Focus on Specific Issues.
Interactive multimedia offloads repetitive training tasks and allows facilitators (or teachers in our case)
to focus on other issues. Benefits of Interactive Multimedia Courseware.
A military organization found an increase in the ability to correctly diagnose and repair aircraft
systems the first time by more than 80% when interactive multimedia was integrated into their
training. ROI with Blended E-learning.
Resources:
Benefits of Interactive Multimedia Courseware, by Steven Hick Ph.D. Professor, Carleton University
1997 by Trican Multimedia Solutions Inc.
Cognitive Styles and Computer-Aided Learning (CAL): Exploring designer and user perspectives. Paper
presented at the PATT-11 conference: New media in education, Eidenhoven, the Netherlands. Atkinson,
S. (2001).
Educational Benefits of Multimedia. R.S. Gilliver, B. Randall & Y.M. Pok (1998), learning in cyberspace:
shaping the future, Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, Vol. 14, No 14, 212-222)
Innovative Teaching: Using Multimedia in a Problem-Based Learning Environment Mai Neo and Ken T.
K. Neo, Faculty of Creative Multimedia, Malaysia 2001
Interactive Multimedia in Education and Training, Sanjaya Mishra & Ramesh C. Sharma. 2005
Learning Benefits of Interactive Technologies. Miller, R. L, Multimedia and Videodisc Monitor, February
1990, pg. 14
ROI with Blended E-learning, White Paper Report, 2001
The Interactivity Effect in Multimedia Learning, Centre for Educational Multimedia. Chris Evans & Nicola
J. Gibbons. Brunel University, Uxbridge, Middlesex UB8 3PH, UK.
The Rapid E-learning Blog, Three Things I learned about learning on my deathbed. Tom Kuhlmann
http://www.articulate.com/rapid-elearning/
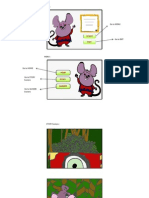
Comparing Before and After with Interactivity
What we have (fairly non interactive)
Read the text
View the presentation slides
View the video
Limited interactive practices,
simulations, and games
Complete the assignment
What we can have (Interactive)
View the presentation Instead of linear locked-step or slide-byslide view, the presentation can be converted to allow students to
view a main topic key at all times so they may quickly view the
areas that they find most relevant or interesting. All the content is
there, it is merely structured in a way that gives them control over
what they are viewing.
View the video Questions pop up as students view the video.
Multiple choice, true/false, or short answer self-assessments with
feedback ensure that students are interacting with the video instead
of merely watching it. Developers decide which questions should
pop up and when to help engage the student as they watch the
video.
Interactive practices, simulations, and games help students
practice what they have studied and be able to quickly identify
which areas they need to study more. They also reinforce the main
concepts while students practice and prepare to complete the
assignments or other assessments.
Complete the assignments - Research indicates students perform
better when interactive components are integrated into their
learning experience.
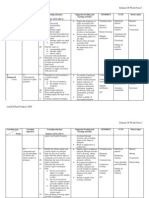
Process for Interactivity Development
1. Academic Specialist integrates requirements into the course development checklist for
interactivities with specifications desired.
Video interactivity
Convert presentations to non-linear format
Practices, simulations, or game interactivities
2. Developers view the samples available at http://idahodigitallearning.org, faculty tab quick links
Interactivity Samples & Templates
3. Developers select the appropriate template for the video, presentation, or practice
interactivity and then complete the template.
4. Developer sends completed template to Multimedia Specialist via email and places all
associated files (graphics, audio, video, slides, etc) in the content collection.
5. Multimedia Specialist uses multimedia tools, audio & graphic repositories, and
templates to develop and publish flash files within specified turn-around time.
6. Multimedia Specialist places .swf flash files in the content collection folder and notifies
developer.
7. Developer links to video/presentation/interactivity files and checks that it works.
Developer links to video / presentation /
interactivity files and checks that it works
Multimedia Specialist places .swf flash files in
appropriate content collection folder and notifies
developer.
Multimedia Specialist uses multimedia tools, audio & graphic
repositories, and templates to develop and publish flash files
within the specified turn-around time.
Developer sends completed template to Kody via email and places all
associated files (graphics, audio, video, slides, etc) in the content collection.
Developer selects the appropriate template for the video, presentation, or practice
interactivity and then completes the template.
Developer views the samples available at view the samples available at http://idahodigitallearning.org,
faculty tab quick links Interactivity Samples & Templates
Academic Specialist integrates requirements into the course development checklist for interactivities with specifications
desired.
Video interactivity
Convert presentations to non-linear format
Practices, simulations, or game interactivities
You might also like
- Quick Hits for Teaching with Technology: Successful Strategies by Award-Winning TeachersFrom EverandQuick Hits for Teaching with Technology: Successful Strategies by Award-Winning TeachersNo ratings yet
- Jurnalinter 3Document5 pagesJurnalinter 3Mutia FatmawatiNo ratings yet
- Learning and Development HemDocument5 pagesLearning and Development HemHemanth KittuNo ratings yet
- Flipped Classroom - Providing Smarter Student Support Through Mobile Learning Tools - V1Document9 pagesFlipped Classroom - Providing Smarter Student Support Through Mobile Learning Tools - V1sreelakshmisamNo ratings yet
- Action Research. 3Document14 pagesAction Research. 3Honey Mae Binarao BuliagNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Roles of Educational TechnologyDocument8 pagesUnit 4 - Roles of Educational TechnologyAVEGAIL SALUDONo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Roles of Educational TechnologyDocument8 pagesUnit 4 - Roles of Educational TechnologyAVEGAIL SALUDONo ratings yet
- Nonlinear MultimediaDocument4 pagesNonlinear Multimediaapi-235241405100% (1)
- Paper SolvingDocument7 pagesPaper Solvingprincikanabar.officeNo ratings yet
- 5.5 Inno-Final (1) - 1Document24 pages5.5 Inno-Final (1) - 1nandanNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Multimedia As An Instructional Tool For Modern TeachingDocument12 pagesThe Effectiveness of Multimedia As An Instructional Tool For Modern TeachingOlive Law DiazNo ratings yet
- Model Digital-Age Work and Learning Teachers Exhibit Knowledge, Skills, and WorkDocument5 pagesModel Digital-Age Work and Learning Teachers Exhibit Knowledge, Skills, and WorkreevajeffersNo ratings yet
- Assessment Strategydocv2Document12 pagesAssessment Strategydocv2api-357627068No ratings yet
- TTL2-Prelim Exam Part 2 and 3Document9 pagesTTL2-Prelim Exam Part 2 and 3denzellvillaverNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document4 pagesUnit 5markperez003398No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Blended Learning DesignDocument8 pagesLesson 6 Blended Learning DesignLou TraveroNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Technology Based TeachingDocument30 pagesUnit 6 Technology Based TeachingerebarenzoeanneNo ratings yet
- Mgt1022-Lean Start-Up Management Assignment:-4 Group-8: Team MembersDocument37 pagesMgt1022-Lean Start-Up Management Assignment:-4 Group-8: Team MembersNagendra babuNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Effectiveness of ComputerDocument5 pagesEvaluating The Effectiveness of ComputerJaeszel PacpacNo ratings yet
- Interaction: Principles and Practice: ELI Summer Session 2005Document9 pagesInteraction: Principles and Practice: ELI Summer Session 2005donadthNo ratings yet
- Objectives: at The End of The Unit, I Am Able ToDocument11 pagesObjectives: at The End of The Unit, I Am Able ToSuga MinNo ratings yet
- Principles of Effective TeachingDocument44 pagesPrinciples of Effective TeachingMrs RehanNo ratings yet
- BP Guide For DL Conversion - 1Document7 pagesBP Guide For DL Conversion - 1Michelle FlamosNo ratings yet
- EDM656 Teacher Training Report Std14505Document11 pagesEDM656 Teacher Training Report Std14505Muhammad Mohsin AltafNo ratings yet
- Technology in Teaching and LearningDocument4 pagesTechnology in Teaching and LearningFranz Simeon ChengNo ratings yet
- Symbaloo Web. 2.0 Tool Professional Development Lesson Plan: StandardsDocument2 pagesSymbaloo Web. 2.0 Tool Professional Development Lesson Plan: Standardsapi-256441704No ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document4 pagesLesson 2Efraem CelesteNo ratings yet
- Storyboard - Development - For - Interactive - M20160127 21969 7v3dqc With Cover Page v2Document15 pagesStoryboard - Development - For - Interactive - M20160127 21969 7v3dqc With Cover Page v2s160818035No ratings yet
- Facilitator Training ProgramDocument23 pagesFacilitator Training Programapi-314646401No ratings yet
- Individul Research Chapters 1 To 3Document23 pagesIndividul Research Chapters 1 To 3hilarion bacunoNo ratings yet
- Esbb3 Seagul 2023Document14 pagesEsbb3 Seagul 2023RODEL AZARESNo ratings yet
- Darma 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1233 012042-1 PDFDocument8 pagesDarma 2019 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1233 012042-1 PDFMuhammad Yasnan A1K117082No ratings yet
- Title of The Study: Blended Learning Approach For Less Proficient Students Authors: Sarah Yusoff, Rohana Yusoff, and Nur Hidayah MD Noh AbstractDocument4 pagesTitle of The Study: Blended Learning Approach For Less Proficient Students Authors: Sarah Yusoff, Rohana Yusoff, and Nur Hidayah MD Noh AbstractMariella Alexes Rombaoa EspirituNo ratings yet
- EL - 5 and 7Document27 pagesEL - 5 and 7Krishna KoundinyaNo ratings yet
- text A Virtual Learning Environment (VLE, Tracking, Collaboration and Communication ToolsDocument5 pagestext A Virtual Learning Environment (VLE, Tracking, Collaboration and Communication ToolsHanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.E LearningDocument24 pagesChapter 4.E LearningfelaminaalbertNo ratings yet
- Chapter I - RevisedDocument6 pagesChapter I - RevisedAdzhar S. EsmaliNo ratings yet
- Standard 3 2 Multimedia Design Project ReportDocument8 pagesStandard 3 2 Multimedia Design Project Reportapi-263469306No ratings yet
- Interactive LearningDocument5 pagesInteractive LearningFa Bi EsNo ratings yet
- Modern Trends in EducationDocument18 pagesModern Trends in EducationjeyabairaviNo ratings yet
- Department of Education Region X Division of Bukidnon District of Quezon II Salawagan National High SchoolDocument12 pagesDepartment of Education Region X Division of Bukidnon District of Quezon II Salawagan National High SchoolArchimedes Magsayo CasamaNo ratings yet
- The Innovative Teaching StrategiesDocument23 pagesThe Innovative Teaching Strategiesjunairahali32No ratings yet
- Facilitate and Manage StudentsDocument6 pagesFacilitate and Manage StudentsIrma Estela Marie EstebanNo ratings yet
- Chap 4.e.lean - FrameworkDocument22 pagesChap 4.e.lean - Frameworkbluebird2112No ratings yet
- Action Research in Math 1Document12 pagesAction Research in Math 1Ghraize XanthozNo ratings yet
- Local Media365053542303642825Document9 pagesLocal Media365053542303642825Asnifah DironNo ratings yet
- Computer Assisted LearningDocument15 pagesComputer Assisted Learningmanju talluri100% (3)
- AR ProposalDocument8 pagesAR ProposalKanna ImuiNo ratings yet
- Blended LearningDocument16 pagesBlended LearningKartik KumarNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness, Efficiency and Instruction Appeal of Blended Learning ModelDocument18 pagesEffectiveness, Efficiency and Instruction Appeal of Blended Learning ModelIndra D KristionoNo ratings yet
- Outline in Educ 118Document19 pagesOutline in Educ 118api-262925714No ratings yet
- Module 3 Edtech Blended Learning 2Document10 pagesModule 3 Edtech Blended Learning 2Ma. Vanessa TuanesNo ratings yet
- Ch#3: Role of Instructional & Communication Technology in LearningDocument12 pagesCh#3: Role of Instructional & Communication Technology in LearningAhmad ShahNo ratings yet
- EDCK5 Week 12Document11 pagesEDCK5 Week 12Marivic MiradorNo ratings yet
- DocumenthagaDocument4 pagesDocumenthagaGrald Traifalgar Patrick ShawNo ratings yet
- For Teaching and Learning (MC. Allied 2)Document8 pagesFor Teaching and Learning (MC. Allied 2)Jeff Beloso BasNo ratings yet
- Revised-AR-ROMMEL B. OBILLO - MEd - MathDocument25 pagesRevised-AR-ROMMEL B. OBILLO - MEd - MathArtemist FowlNo ratings yet
- The Development of Instructional Media On Physics Subject To Increase The Class EffectivenessDocument5 pagesThe Development of Instructional Media On Physics Subject To Increase The Class EffectivenessHapsari PeniNo ratings yet
- Et 247 Matrix 1Document11 pagesEt 247 Matrix 1api-316948987No ratings yet
- Satori Graphics Free ResourcesDocument1 pageSatori Graphics Free Resourcesfartien91No ratings yet
- Essential Techniques For Military Modeling & SimulationDocument8 pagesEssential Techniques For Military Modeling & Simulationfartien91No ratings yet
- Week 3 CSP600-ArpahDocument42 pagesWeek 3 CSP600-Arpahfartien91No ratings yet
- 471 1260 1 SMDocument28 pages471 1260 1 SMfartien91No ratings yet
- Sinocolor DTG Series T Shirt PrinterDocument3 pagesSinocolor DTG Series T Shirt Printerfartien91No ratings yet
- Presentation TemplateDocument11 pagesPresentation Templatefartien91No ratings yet
- Proposal Table of Content - DetailDocument5 pagesProposal Table of Content - Detailfartien91No ratings yet
- Tien Tien Lee 2012Document5 pagesTien Tien Lee 2012fartien91No ratings yet
- 04 HashDocument34 pages04 Hashfartien91No ratings yet
- Business CardDocument1 pageBusiness Cardfartien91No ratings yet
- Solutions: Cardiff Cardiff University Examination PaperDocument15 pagesSolutions: Cardiff Cardiff University Examination PaperKhan Muhammad ZaidNo ratings yet
- APA Sample PaperDocument10 pagesAPA Sample Paperjeremyreynolds841538No ratings yet
- Maths f3Document66 pagesMaths f3fartien91No ratings yet
- StoryboardDocument6 pagesStoryboardfartien91No ratings yet
- Survival Phrases KoreanDocument2 pagesSurvival Phrases KoreanNila Novita WardaniNo ratings yet
- Matematik Tingkatan 3. Sukatan PelajaranDocument19 pagesMatematik Tingkatan 3. Sukatan Pelajaranb385319No ratings yet
- System Design of Library Management SystemDocument4 pagesSystem Design of Library Management Systemfartien91No ratings yet
- Queen In-Hyun's Man (450p) (01-16 END)Document6 pagesQueen In-Hyun's Man (450p) (01-16 END)fartien91No ratings yet
- Manner of Speaking - HanguladayDocument7 pagesManner of Speaking - Hanguladayfartien91No ratings yet
- SNSD WebDocument5 pagesSNSD Webfartien91No ratings yet
- HangulDocument6 pagesHangulfartien91No ratings yet
- Access Tutorial 1 - Introduction To Microsoft AccessDocument17 pagesAccess Tutorial 1 - Introduction To Microsoft AccessDidier TangaNo ratings yet
- Classroom Debate Rubric Criteria 5 Points 4 Points 3 Points 2 Points 1 Point Total PointsDocument1 pageClassroom Debate Rubric Criteria 5 Points 4 Points 3 Points 2 Points 1 Point Total PointsKael PenalesNo ratings yet
- IVISOR Mentor IVISOR Mentor QVGADocument2 pagesIVISOR Mentor IVISOR Mentor QVGAwoulkanNo ratings yet
- APPSC GROUP 4 RESULTS 2012 - Khammam District Group 4 Merit ListDocument824 pagesAPPSC GROUP 4 RESULTS 2012 - Khammam District Group 4 Merit ListReviewKeys.comNo ratings yet
- Effect of Heater Geometry On The High Temperature Distribution On A MEMS Micro-HotplateDocument6 pagesEffect of Heater Geometry On The High Temperature Distribution On A MEMS Micro-HotplateJorge GuerreroNo ratings yet
- In Search of Begum Akhtar PDFDocument42 pagesIn Search of Begum Akhtar PDFsreyas1273No ratings yet
- Sta404 07Document71 pagesSta404 07Ibnu Iyar0% (1)
- Placa 9 - SHUTTLE A14RV08 - 71R-A14RV4-T840 - REV A0 10ABR2012Document39 pagesPlaca 9 - SHUTTLE A14RV08 - 71R-A14RV4-T840 - REV A0 10ABR2012Sergio GalliNo ratings yet
- Overview of MEMDocument5 pagesOverview of MEMTudor Costin100% (1)
- SR# Call Type A-Party B-Party Date & Time Duration Cell ID ImeiDocument12 pagesSR# Call Type A-Party B-Party Date & Time Duration Cell ID ImeiSaifullah BalochNo ratings yet
- An Overview and Framework For PD Backtesting and BenchmarkingDocument16 pagesAn Overview and Framework For PD Backtesting and BenchmarkingCISSE SerigneNo ratings yet
- R67068.0002 2 HB Profibus-Schnittstelle en KueblerDocument42 pagesR67068.0002 2 HB Profibus-Schnittstelle en KueblerSabari StunnerNo ratings yet
- Xii - STD - Iit - B1 - QP (19-12-2022) - 221221 - 102558Document13 pagesXii - STD - Iit - B1 - QP (19-12-2022) - 221221 - 102558Stephen SatwikNo ratings yet
- TOA Project Presentation (GROUP 5)Document22 pagesTOA Project Presentation (GROUP 5)Khadija ShahidNo ratings yet
- Column Buckling TestDocument8 pagesColumn Buckling TestWiy GuomNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: MSBA7003 Quantitative Analysis MethodsDocument29 pagesTutorial: MSBA7003 Quantitative Analysis MethodsAmanda WangNo ratings yet
- Zoom g2 1nu Manual Do Utilizador PDFDocument56 pagesZoom g2 1nu Manual Do Utilizador PDFEliude Gonçalves FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Agenda - Meeting SLC (LT) - 27.06.2014 PDFDocument27 pagesAgenda - Meeting SLC (LT) - 27.06.2014 PDFharshal1223No ratings yet
- SeparexgeneralbrochureDocument4 pagesSeparexgeneralbrochurewwl1981No ratings yet
- Design of AC Chopper Voltage Regulator Based On PIC16F716 MicrocontrollerDocument4 pagesDesign of AC Chopper Voltage Regulator Based On PIC16F716 MicrocontrollerabfstbmsodNo ratings yet
- Relay G30 ManualDocument42 pagesRelay G30 ManualLeon KhiuNo ratings yet
- Motive 27Tmx: Data SheetDocument2 pagesMotive 27Tmx: Data SheetUlisesGómezNo ratings yet
- Jarir IT Flyer Qatar1Document4 pagesJarir IT Flyer Qatar1sebincherianNo ratings yet
- Climatol GuideDocument40 pagesClimatol GuideFressiaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Hydrostatic Force On Curved Surfaces - CE 309-CE22S2 - Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pages4.1 Hydrostatic Force On Curved Surfaces - CE 309-CE22S2 - Fluid MechanicsRUSSELNo ratings yet
- LITERARY THEORY BY TERRY EAGLETON NotesDocument6 pagesLITERARY THEORY BY TERRY EAGLETON NotesPrachi SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Adoption of e Procurement in Tanzani PDFDocument5 pagesThe Adoption of e Procurement in Tanzani PDFDangyi GodSeesNo ratings yet
- Identification of PolymersDocument11 pagesIdentification of PolymersßraiñlĕsšȜĭnšteĭñNo ratings yet
- Hunger Games Mini Socratic Seminar2012Document4 pagesHunger Games Mini Socratic Seminar2012Cary L. TylerNo ratings yet
- Hooke's LawDocument1 pageHooke's LawAnan BarghouthyNo ratings yet
- FhryhfhfhDocument3 pagesFhryhfhfhAffan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Uptime: A Practical Guide to Personal Productivity and WellbeingFrom EverandUptime: A Practical Guide to Personal Productivity and WellbeingNo ratings yet
- Fascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistFrom EverandFascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Truth Detector: An Ex-FBI Agent's Guide for Getting People to Reveal the TruthFrom EverandThe Truth Detector: An Ex-FBI Agent's Guide for Getting People to Reveal the TruthRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (29)
- What's Best Next: How the Gospel Transforms the Way You Get Things DoneFrom EverandWhat's Best Next: How the Gospel Transforms the Way You Get Things DoneRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (33)
- How to Be Better at Almost Everything: Learn Anything Quickly, Stack Your Skills, DominateFrom EverandHow to Be Better at Almost Everything: Learn Anything Quickly, Stack Your Skills, DominateRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (860)
- Eat That Frog!: 21 Great Ways to Stop Procrastinating and Get More Done in Less TimeFrom EverandEat That Frog!: 21 Great Ways to Stop Procrastinating and Get More Done in Less TimeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3226)
- Summary of Dan Martell's Buy Back Your TimeFrom EverandSummary of Dan Martell's Buy Back Your TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mastering Productivity: Everything You Need to Know About Habit FormationFrom EverandMastering Productivity: Everything You Need to Know About Habit FormationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- The Ultimate Rich Dad Library: To Elevate the Financial Well-Being Of HumanityFrom EverandThe Ultimate Rich Dad Library: To Elevate the Financial Well-Being Of HumanityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (21)
- Powered by Storytelling: Excavate, Craft, and Present Stories to Transform Business CommunicationFrom EverandPowered by Storytelling: Excavate, Craft, and Present Stories to Transform Business CommunicationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- The Like Switch: An Ex-FBI Agent's Guide to Influencing, Attracting, and Winning People OverFrom EverandThe Like Switch: An Ex-FBI Agent's Guide to Influencing, Attracting, and Winning People OverRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Becoming Bulletproof: Protect Yourself, Read People, Influence Situations, and Live FearlesslyFrom EverandBecoming Bulletproof: Protect Yourself, Read People, Influence Situations, and Live FearlesslyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (355)
- The 12 Week Year: Get More Done in 12 Weeks than Others Do in 12 MonthsFrom EverandThe 12 Week Year: Get More Done in 12 Weeks than Others Do in 12 MonthsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Writing Without Bullshit: Boost Your Career by Saying What You MeanFrom EverandWriting Without Bullshit: Boost Your Career by Saying What You MeanRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Get it Done Now! (2nd Edition): Own Your Time, Take Back Your LifeFrom EverandGet it Done Now! (2nd Edition): Own Your Time, Take Back Your LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (28)
- You've Got 8 Seconds: Communication Secrets for a Distracted WorldFrom EverandYou've Got 8 Seconds: Communication Secrets for a Distracted WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- The Leader Habit: Master the Skills You Need to Lead--in Just Minutes a DayFrom EverandThe Leader Habit: Master the Skills You Need to Lead--in Just Minutes a DayRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- The First 90 Days: Proven Strategies for Getting Up to Speed Faster and SmarterFrom EverandThe First 90 Days: Proven Strategies for Getting Up to Speed Faster and SmarterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The 80/20 Principle and 92 Other Powerful Laws Nature: The Science of SuccessFrom EverandThe 80/20 Principle and 92 Other Powerful Laws Nature: The Science of SuccessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (220)
- Negotiating the Impossible: How to Break Deadlocks and Resolve Ugly Conflicts Without Money or MuscleFrom EverandNegotiating the Impossible: How to Break Deadlocks and Resolve Ugly Conflicts Without Money or MuscleRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (25)
- Rich Dad Secrets: to Money, Business and Investing… and How YOU can Profit from ThemFrom EverandRich Dad Secrets: to Money, Business and Investing… and How YOU can Profit from ThemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (19)
- The Five Temptations of A CEO: A Leadership FableFrom EverandThe Five Temptations of A CEO: A Leadership FableRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (215)
- Social Media Success for Every Brand: The Five StoryBrand Pillars That Turn Posts Into ProfitsFrom EverandSocial Media Success for Every Brand: The Five StoryBrand Pillars That Turn Posts Into ProfitsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)