Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 KJJK
2 KJJK
Uploaded by
RamiB.AsiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 KJJK
2 KJJK
Uploaded by
RamiB.AsiaCopyright:
Available Formats
An-Najah National
University
Civil Engineering Department
Mechanics Of Materials Lab (61208)
Report Grading Sheet
Instructor Name: Eng. Lama
Asmah & Eng Raya Noor
Academic Year: 2013/2014
Semester:2nd semester
Experiment # 2
: Equilibrium
of Beam
Performed on:
Submitted on:
Students:
1- Anas Qadarh
3- Jehad Kalbonh
Section
2- Ehab Ashor
4-
Projects Outcomes
ILO 1 =15%
ILO 2 =40%
ILO 3 =30%
Evaluation Criterion
ILO 4 =15%
Grade
Objective:
Sufficient, Clear and complete statement of objectives.
Theory
Presents sufficiently the theoretical basis.
Apparatus:
Apparatus
sufficiently
described
to
enable
another
experimenter to identify the equipment needed to conduct the
experiment.
Experimental Results and Calculations (data collected)
Results analyzed correctly. Experimental findings adequately
and specifically summarized, in graphical, tabular, and/or
written form.
Discussion and Conclusions
Crisp explanation of experimental results. Comparison of
theoretical predictions to experimental results, including
discussion of accuracy and error analysis in some cases.
Conclusions summarize the major findings from the
experimental results with adequate specificity.
Recommendations appropriate in light of conclusions. Correct
grammar.
References
Complete and consistent bibliographic information that would
enable the reader to find the reference of interest.
Sources of error:
Appearance
1
1
0.5
2.5
.5
1
0.5
Points
An-Najah National
University
Title page is complete, page numbers applied, content is well
organized, correct spelling, fonts are consistent, good visual
appeal.
Total
10
Objective:To verify the use of condition of
equilibrium to determine the reaction
for simply and supported beam and
cantilever beam.
Introduction:In this experiment we will study about
equilibrium of beam and we want to
calculate the reaction comes from the beam
by using two technique simply support
beam and canteliver under equilibrium
condition and we chose the beam because
it is a most common example of parallel
force in equilibrium . And as we know the
beam support will develop a vertical
reaction to carry the weight on the beam
and the self- weight of beam itself.
An-Najah National
University
Theory :
Here we use equilibrium
equation for simply supported beam
and cantilever beam :
Fx = 0
Fy = 0
Mo = 0
SUPPORT TYPES
The three common types of
connections which join a built
structure to its foundation
are: roller, pinned and fixed supports .
ROLLER SUPPORTS
Roller supports are free to rotate and
translate along the surface upon
which the roller rests. The surface can
An-Najah National
University
be horizontal, vertical, or sloped at any
angle.
PIN SUPPORTS
A pinned support can resist both
vertical and horizontal forces but not a
moment. They will allow the structural
member to rotate, but not to translate
in any direction.
FIXED SUPPORTS
Fixed supports can resist vertical and
horizontal forces as well as a moment.
Type of beam :
1. Simply supported beam
2. Continuos beam
3. Cantilever beam
4. Over hang beam
Apparatus :
1-Beam
An-Najah National
University
2-Weights
3-Mechanical balance.
4-Water balance.
5-Spring.
6-Hangers
An-Najah National
University
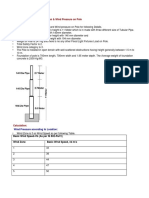
Experimental Results and Calculations (data
collected)
Simply Support
M A=0
( By * L ) ( P * a ) = 0
By =
Pa
L
F y=0
Ay + By P = 0
Ay = P By
Ay = P
F x=0
Pa
L
An-Najah National
University
Ax = 0
Table (1)
Reaction for a simply supported beam
Beam span =1
Right
Reactio
n Exp
(gm)
Left
Reactio
n
Theory
(N)
Left
Reaction
Exp (N)
Left
Reactio
n Exp
(gm)
758*9.81/1
00
=7.43598
9.49608
8.4366
5.01291
6.66099
758
968
860
511
679
17.60895
1795
Right
Reaction
Theory (N)
Right
Reaction
Exp (N)
10*250/100
0
=2.5
6
8.5
15
23.4
248*9.81/10
00
=2.43288
5.86638
8.3385
14.80329
23.09274
248
598
850
1509
2354
10-2.5
=7.5
9
8.5
5
6.6
24.25
23.87754
2434
17.75
Positio
n (mm)
Load
(N)
250
400
500
750
780
250,80
0
10
15
17
20
30
17,25
An-Najah National
University
%error Right Reaction
%error Left Reaction
2.4328-2.5/2.5 x 100%
= %2.6848
7.43589-7.5/7.5 x 100%
= % 0.8536
%2.227
%5.512
%1.9
%0.745
%1.311
%0.2582
%1.313
%0.924
%1.5
%0.794
% Avg error Left Reaction
= 1.5%
% Avg error Right Reaction =
1.82%
Shear Digram & Moment Digram :
Cantilever
An-Najah National
University
An-Najah National
University
M spring=0
R supp * a
R supp =
+
PL
a
P*L = 0
,L=1m
F y=0
R supp P R . spring = 0
R spring =
PL
a
-P
An-Najah National
University
Table (2)
Reaction for a cantilever supported beam
Beam span =1
% error
spring
Reaction
6.5-5/5
x100%
= %1.118
%2
%0.66
%error
support
Reactio
n
%1.118
%3.617
%0.04
Fixing
Momen
t = P*L
(N.M)
Distance
Between
Reactaion
(mm)
5
10
15
500
500
500
% Avg error Support Reaction =
% Avg error Spring Reaction =
Spring
Reactio
n
Theory
(N)
Spring
Reactio
n Exp
(N)
10-5
=5
10
15
1.59%
10.88%
Discussion and Conclusions :
6.5
9.8
14.9
Support
Reactio
n
Theory (
N)
5*1/0.5
=10
20
30
Support
Support
Reactio
Reaction
n Exp
Exp ( N )
( gm )
1009*9.81
/1000
= 9.8882
1009
19.2766
1967
29.988
3060
An-Najah National
University
In this experiment , we determine the
reaction and we have learned about the
different types of beams and their
supporters (simply and cantilever) . we
have studied beam in static equilibrium
condition . we calculated the reactions
and compared them with experiment
results . we found that the percentage of
errors
were
relatively
law
andThe
averages percentage of errors in the
experiment is a low. This mean that the
experiment was successful and the
devices are good and can be used we can
reduce these errors by different ways.
and we can find the error in the balance
readings by measuring a known weights
and then we can correct the measured
results . and be more careful in
calculations.
Standard specification :% of error 5%
acceptable.
5 % %of error 15%
needs calibration
% of error > 15%
defected .
error is
the device
the device is
An-Najah National
University
References :
The reference in these experiment : Eng.
Raya and Manual book
And information within website .
Sources of error :
1)
2)
Some mistakes in calculations .
The nature and device can be
produce errors
3) Water balance might not be in
the horizontal exactly.
4) The errors in tools such as:
The reading of the spring might
have some errors.
5) Human error (not accuracy in
balancing the beam)and make it
horizontal , and reading results in
spring.
6) Mechanical error (balance).
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5811)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Calculate Size of Pole FoundationDocument3 pagesCalculate Size of Pole Foundationsomjitsahani100% (4)
- Kozyrev Aether Time and TorsionDocument8 pagesKozyrev Aether Time and Torsionjjuulliisseess100% (2)
- Matlab Laboratory (ELEC 323) Session II: Convolution 1. OverviewDocument4 pagesMatlab Laboratory (ELEC 323) Session II: Convolution 1. OverviewFranch Maverick Arellano LorillaNo ratings yet
- Pages From WRC Bulletin 368 (1991) - 2 PDFDocument1 pagePages From WRC Bulletin 368 (1991) - 2 PDFabhisheks5987No ratings yet
- Quantum Artificial Life in An IBM Quantum ComputerDocument9 pagesQuantum Artificial Life in An IBM Quantum Computerlexleo1000No ratings yet
- Fr. Daneil McNamara PDFDocument6 pagesFr. Daneil McNamara PDFJanice BangonanNo ratings yet
- Ashrae DL Seminar by Wei Sun On 2nd March 2011flierDocument2 pagesAshrae DL Seminar by Wei Sun On 2nd March 2011flierMohd HerzallahNo ratings yet
- Catalogo ServcampDocument96 pagesCatalogo ServcampMegan PierceNo ratings yet
- Nandani Medical Laboratories Pvt. LTD.: Industrial Training in Nandani Laboratory: Special Reference To Parentral SectionDocument24 pagesNandani Medical Laboratories Pvt. LTD.: Industrial Training in Nandani Laboratory: Special Reference To Parentral SectionSandeep DarwaiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 (Kinematics)Document5 pagesAssignment 3 (Kinematics)ankit gandhi33% (3)
- Improving Productivity With Instrument Calibration: ScheduleDocument2 pagesImproving Productivity With Instrument Calibration: SchedulenuroniNo ratings yet
- Fast-Processing Modulation Strategy For The Neutral-Point-Clamped Converter With Total Elimination of The Low-Frequency Voltage Oscillations in The Neutral PointDocument6 pagesFast-Processing Modulation Strategy For The Neutral-Point-Clamped Converter With Total Elimination of The Low-Frequency Voltage Oscillations in The Neutral PointMaikPortnoyNo ratings yet
- Oscillations QuestionsOscillations QuestionsDocument61 pagesOscillations QuestionsOscillations QuestionsAli SajjadNo ratings yet
- Benzalkonium ChlorideDocument1 pageBenzalkonium ChlorideVaibhav SankheNo ratings yet
- Technical Science Notes Students VersionDocument22 pagesTechnical Science Notes Students VersionAriff AziziNo ratings yet
- 1 Surfactant Chemistry and General Phase BehaviourDocument10 pages1 Surfactant Chemistry and General Phase BehaviourAnonymous cgKtuWzNo ratings yet
- (XLS SVY 20) Solver TraverseDocument9 pages(XLS SVY 20) Solver TraverseAlif algifariNo ratings yet
- RetrofitOfSteelStructuresUsing FiberwReinforcedPloymers Shaat Schnerch Amir TRB-Nov-03-Revised-PaperDocument15 pagesRetrofitOfSteelStructuresUsing FiberwReinforcedPloymers Shaat Schnerch Amir TRB-Nov-03-Revised-Paperisha patelNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Study of The Recrystallization Mechanism During Hot Deformation of AluminiumDocument15 pagesAn Experimental Study of The Recrystallization Mechanism During Hot Deformation of AluminiumManolo GipielaNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis of Wing Fuselage Lug Attachment of A Transport A/cDocument8 pagesStress Analysis of Wing Fuselage Lug Attachment of A Transport A/cAbrahamJPulickalNo ratings yet
- Response To Harmonic and Periodic ExcitationDocument102 pagesResponse To Harmonic and Periodic ExcitationAhmet TükenNo ratings yet
- Sample Amf K40 - Thermatex Acoustic DB 41Document1 pageSample Amf K40 - Thermatex Acoustic DB 41mpwasaNo ratings yet
- Geo 2 - CompressibilityDocument8 pagesGeo 2 - CompressibilityKristan Rae GaetosNo ratings yet
- Sep 2016 Assign-1 Mec 465 ProbDocument3 pagesSep 2016 Assign-1 Mec 465 ProbMohammad TahirNo ratings yet
- Manual Turbidimetro HANNA-HI98703 PDFDocument40 pagesManual Turbidimetro HANNA-HI98703 PDFluis_1024No ratings yet
- George GreenDocument11 pagesGeorge GreenLoizosNo ratings yet
- Surveying IIDocument92 pagesSurveying IIrahul landgeNo ratings yet
- API Engine Oil Classifications 2010Document6 pagesAPI Engine Oil Classifications 2010amsoilromaniaNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness Evaluation of 314L Stainless Steel Vibratory Stress Relief by Dynamic StressDocument5 pagesThe Effectiveness Evaluation of 314L Stainless Steel Vibratory Stress Relief by Dynamic StressHarshada DhekaleNo ratings yet
- Plastic Analysis 3rd Year Structural EngineeringDocument117 pagesPlastic Analysis 3rd Year Structural EngineeringArjun RajNo ratings yet