Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Immunosuppression
Uploaded by
abc007200Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Immunosuppression
Uploaded by
abc007200Copyright:
Available Formats
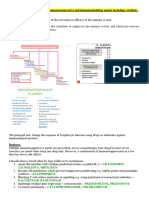
Drugs
Glucocorticoids
Prednisone
Prednisolone
Mechanism
Effects/ Uses
Side effects
GC binds to GC-responsive element, modify the
transcription of genes
Reduce peripheral lymphocytes;
Inhibit T-cell proliferation and immunity;
Downregulate cytokine production
Used in organ transplant/ HSCT (prevent GVHD)
Immunodeficiency
DM (hyperglycaemia)
Osteoporosis (disrupt Ca)
Muscle breakdown
Mood swing
Cushings syndrome
Calcineurin induces different transcription factors
(NFATs) that are important in the transcription of IL-2
genes. IL-2 activates T-helper lymphocytes and induces
the production of other cytokines.
CsA forms a complex with cytophilin
FK506 forms a complex with FKBP
complex inhibits calcineurin
Renal dysfunction
Bone marrow toxicity
Hypertrichosis
Gingival hyperplasia HT, HG, GI
Bind to FKBP and inhibit mTOR, block the progression of
activated T-cells from G1 to S phase of cell cycle
Inhibit mitogenic response to IL-2.
Inhibit B-cell proliferation and antibody production.
Hyperlipidemia
Myelosuppression
Thrombocytopenia
Nephrotoxicity
Prevent clonal expansion of both B and T-cells
Myelosuppression
GI toxicity
Calcineurin inhibitors
Cyclosporine (CsA)
Tacrolimus (FK506)
Proliferation-signal inhibitors
Sirolimus
Everolimus
Antimetabolites and cytotoxic drugs
Azathioprine (AZA)
Inhibit purine synthesis
Inhibit IMPD the enzyme necessary for de novo purine
Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF)
synthesis (lymphocyte has no salvage pathway)
Leflunomide
Inhibit pyrimidine synthesis
Cyclophosphamide
Alkylating agent
Methotrexate
Antifolate agent
Chlorambucil
Alkylating agent
Antibodies (humanised murine Ab)
Polyclonal antibodies bind to T-cells
Antithymocyte globulin (ATG)
cause lysis and mask lymphocyte receptors
Muromonab-CD3
IL-2 antagonists
Basiliximab
Daclizumab
Anti-TNFa agents
Infliximab
Adalimumab
Etanercept
Abatacept
Immunomodulatory agents
Filgrastim (G-CSF)
Sargramostim (GM-CSF)
IFN-g
Aldesleukin
Avoid humoral and CMI response
Directed against CD3 antigen of T cells
Deplete circulating T cells within minutes
Prevent GVHD in HSCT and transplant rejection
Bind to IL-2 receptors on T cells and inactivate IL-2
mediated cell activation and proliferation
Suppress T-cells
Used for prophylaxis in organ transplant
Monoclonal antibodies catch soluble TNF-a, preventing
it from activating TNF receptors
Recombinant form of soluble TNFa receptors, competing
against cell surface TNFa receptors
Bind to CD80 and CD86 on APC, preventing binding to
CD28 on T-cells
(i.e. compete against T-cells for APC cell surface
ligands)
Infliximab: used in Crohns disease
Adalimumab: used in RA
Anaphylaxis
Serum sickness reactions
Fever, vomiting, headache
Pulmonary oedema
Anaphylaxis
Well-tolerated, no side effects
Used in RA
Risk of infections
Used in severe RA
Accelerate bone marrow recovery
Activate phagocytosis by increasing synthesis of TNF
Promote proliferation and differentiation of lymphocytes into cytotoxic cells, activate NK cells
You might also like
- Immunosuppressant Drugs Drug Name Class Function Method/Receptor UseDocument3 pagesImmunosuppressant Drugs Drug Name Class Function Method/Receptor UseKristin DouglasNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOMODULATORS (EDocFind - Com)Document67 pagesIMMUNOMODULATORS (EDocFind - Com)sac00772006No ratings yet
- 1 ImmunopharmDocument63 pages1 ImmunopharmDr.TamilvelanNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressant DrugsDocument87 pagesImmunosuppressant DrugsNagu KopparapuNo ratings yet
- Immunopharmacology: Dr. Hamad AlshabiDocument8 pagesImmunopharmacology: Dr. Hamad AlshabiHamad Alshabi100% (1)
- Immunopharmacology ImmunosupressantsDocument15 pagesImmunopharmacology ImmunosupressantsPraज्ञा GharpankarNo ratings yet
- ExplanationDocument5 pagesExplanationAubrey GadorNo ratings yet
- Immunomodulators: Dr. Kaushik Mukhopadhyay Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pharmacology Esi-PgimsrDocument31 pagesImmunomodulators: Dr. Kaushik Mukhopadhyay Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pharmacology Esi-PgimsrsyarintaadeninaNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppression 2008: David LandsbergDocument60 pagesImmunosuppression 2008: David LandsbergTri RachmadijantoNo ratings yet
- Question 21c. Classification of Immunosuppressive and Imunomodulating Agents Including Cytokines and Clinical Uses.Document4 pagesQuestion 21c. Classification of Immunosuppressive and Imunomodulating Agents Including Cytokines and Clinical Uses.wanichysonlyNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppresantmbbs 190608061036Document115 pagesImmunosuppresantmbbs 190608061036syarintaadeninaNo ratings yet
- Addition To MusculoskeletalDocument2 pagesAddition To MusculoskeletalDrSingh1699No ratings yet
- IMMUNOMODULATORSDocument44 pagesIMMUNOMODULATORSMaria khurshidNo ratings yet
- KIT and PDGFRA Mutations in GISTs Guide TreatmentDocument22 pagesKIT and PDGFRA Mutations in GISTs Guide TreatmentCarla CarolineNo ratings yet
- Anticancer and Immunosuppressants - KunjDocument14 pagesAnticancer and Immunosuppressants - KunjDeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- Immuno Modulator SDocument62 pagesImmuno Modulator SAntony Prakash RajNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressive Drugs IK AsDocument25 pagesImmunosuppressive Drugs IK AsAziz KhwajaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology CancerDocument21 pagesPharmacology CancerDương Hà Trúc TâmNo ratings yet
- To Study The Role of T-Regulatory Cells in The Infectious and Non-Infectious UveitisDocument30 pagesTo Study The Role of T-Regulatory Cells in The Infectious and Non-Infectious UveitisRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Veterinary DiseaseDocument21 pagesPathogenesis of Veterinary DiseaseRandy Butternubs67% (6)
- Kaito Et Al. - 2021 - CD155 and CD112 As Possible Therapeutic Targets ofDocument12 pagesKaito Et Al. - 2021 - CD155 and CD112 As Possible Therapeutic Targets ofpablopac2021No ratings yet
- Immunosuppressant DrugsDocument6 pagesImmunosuppressant DrugsShoaib MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- ImmunosuppressantsDocument18 pagesImmunosuppressantsomar khanNo ratings yet
- Immunopharmacology: GlucocorticoidsDocument9 pagesImmunopharmacology: GlucocorticoidsCas BuNo ratings yet
- Lec6 Sem5 HEMWK4 20140207Document9 pagesLec6 Sem5 HEMWK4 20140207Elly ElizaNo ratings yet
- Immunomodulators: Drugs that Regulate the Immune SystemDocument8 pagesImmunomodulators: Drugs that Regulate the Immune Systemfaisalnadeem100% (1)
- FCPS Part1 Q BANK Physiology Flash Cards Very Important For Part 1Document49 pagesFCPS Part1 Q BANK Physiology Flash Cards Very Important For Part 1Sehar IqbalNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 1 NotesDocument5 pagesUSMLE Step 1 NotesvillarexNo ratings yet
- Inhibitors of Immune Response (site of actionDocument39 pagesInhibitors of Immune Response (site of actionGd SuarantaNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressive AgentsDocument36 pagesImmunosuppressive AgentsFlorensa Teolina NdruruNo ratings yet
- Immunodeficiency: Syarifuddin WahidDocument52 pagesImmunodeficiency: Syarifuddin Wahidadzkia-hkNo ratings yet
- PHR 308 - Part 7 - Immunosupressive Agents - Pharmacology-III-1Document9 pagesPHR 308 - Part 7 - Immunosupressive Agents - Pharmacology-III-1Abdur RaquibNo ratings yet
- Gene Therapy Where We Are: and Where To Go?Document60 pagesGene Therapy Where We Are: and Where To Go?Faisal GhairatNo ratings yet
- Table 10-1. Major Properties of Human Interleukins. Interleukin Principal Cell Source Principal EffectsDocument8 pagesTable 10-1. Major Properties of Human Interleukins. Interleukin Principal Cell Source Principal EffectsKhrisnanto NugrohoNo ratings yet
- immunostimulantsimmunosuppressants-201001101027Document23 pagesimmunostimulantsimmunosuppressants-201001101027Suvojit BasakNo ratings yet
- Microb Seminar Group 3 (LATEST)Document21 pagesMicrob Seminar Group 3 (LATEST)HasifNo ratings yet
- Artigo OncoDocument14 pagesArtigo OncoCatarina LuísNo ratings yet
- Gout DrugsDocument1 pageGout DrugsMichael BrownNo ratings yet
- Cytokine Role Source IL-3 IL-5 IL-7 C-Kit Ligand G-CSF M-CSF GM-CSF IFN-GammaDocument2 pagesCytokine Role Source IL-3 IL-5 IL-7 C-Kit Ligand G-CSF M-CSF GM-CSF IFN-Gammamliou0417No ratings yet
- MedSurg Medications & TablesDocument71 pagesMedSurg Medications & TablesSarah PlunkettNo ratings yet
- T Cell Dysregulation in SLEDocument7 pagesT Cell Dysregulation in SLEVasincu AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Cancer BiologyDocument7 pagesCancer BiologyemanNo ratings yet
- Question 38b. Summarize Drugs That Modulate Immune Function (Mechanism of Action, Clinical Applications, Pharmacokinetics and ToxicitiesDocument2 pagesQuestion 38b. Summarize Drugs That Modulate Immune Function (Mechanism of Action, Clinical Applications, Pharmacokinetics and ToxicitieswanichysonlyNo ratings yet
- Systemic Response To Injury and Metabolic Support, Chapter 2 of Schwartz by Anas MK HindawiDocument99 pagesSystemic Response To Injury and Metabolic Support, Chapter 2 of Schwartz by Anas MK HindawiAnas Mk Hindawi81% (16)
- Med Chem Tutoring Session 2Document34 pagesMed Chem Tutoring Session 2Morrigan DearmanNo ratings yet
- Terapia BiologicaDocument34 pagesTerapia BiologicaBianca Postolache100% (1)
- Meyer 2010Document24 pagesMeyer 2010deltanueveNo ratings yet
- BRM NotesDocument4 pagesBRM NotesforminskoNo ratings yet
- Transglutaminase 2 in The Balance of Cell Death and SurvivalDocument6 pagesTransglutaminase 2 in The Balance of Cell Death and SurvivalOsman FrankNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic InflammationDocument6 pagesAcute and Chronic Inflammationarif shahNo ratings yet
- Intracellular Signaling Pathway in T-Cell ActivationDocument45 pagesIntracellular Signaling Pathway in T-Cell Activationatapour100% (1)
- Hematopoietic Growth Factors and Treatments for Leukocyte DisordersDocument11 pagesHematopoietic Growth Factors and Treatments for Leukocyte DisordersKimberlyRobelinNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type I Insulin Secretions and Genetic DefectsDocument2 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Type I Insulin Secretions and Genetic Defectsabc007200No ratings yet
- S 25 Staud ImmunomodulatorsDocument41 pagesS 25 Staud ImmunomodulatorsCarlo MaxiaNo ratings yet
- Biomedicine & PharmacotherapyDocument18 pagesBiomedicine & PharmacotherapyMiriam Sanchez moralesNo ratings yet
- Jak Stat InhibitorsDocument64 pagesJak Stat InhibitorsSupratim KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Cancer Chemo TableDocument4 pagesCancer Chemo TableChristine NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy - DR RatihDocument7 pagesChemotherapy - DR RatihKenneth TanNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Treatment-Free Remission in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: From concept to practice and beyondFrom EverandFast Facts: Treatment-Free Remission in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: From concept to practice and beyondNo ratings yet
- Nikon: Instruction ManualDocument58 pagesNikon: Instruction Manualabc007200No ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type I Insulin Secretions and Genetic DefectsDocument2 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Type I Insulin Secretions and Genetic Defectsabc007200No ratings yet
- Cytotoxic Drugs in The Treatment of CancerDocument2 pagesCytotoxic Drugs in The Treatment of Cancerabc007200No ratings yet
- Blood Coagulation System Overview & Key FactorsDocument4 pagesBlood Coagulation System Overview & Key Factorsabc007200100% (1)
- Yashica FX 3 FX 7Document16 pagesYashica FX 3 FX 7Amrina RosadaNo ratings yet
- Work of BreathingDocument32 pagesWork of Breathingabc007200No ratings yet
- Basic Pascal Syntax: in This ChapterDocument54 pagesBasic Pascal Syntax: in This ChapterEldar ČokićNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation: Molecular Biochemistry IDocument47 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation: Molecular Biochemistry Iabc007200No ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument17 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesChrystele Ann Ramilo100% (1)
- Textbook of Medical Parasitology Protozoology HelmDocument2 pagesTextbook of Medical Parasitology Protozoology HelmRomelu MartialNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Pediatric Infectious Disease 3rdDocument330 pagesHandbook of Pediatric Infectious Disease 3rdPedro Jose Ramos Cabrera100% (2)
- Moraxella: The Bacteria That Causes Ear Infections and MoreDocument20 pagesMoraxella: The Bacteria That Causes Ear Infections and Moreshinwar benyamenNo ratings yet
- Immunization Seminar BenefitsDocument42 pagesImmunization Seminar BenefitsRionaMarieMagbutay67% (3)
- Fuo, Sepsis and Septic Shock: Clinical Clerk Mary Christine S. IlangaDocument62 pagesFuo, Sepsis and Septic Shock: Clinical Clerk Mary Christine S. IlangaPraise BechaydaNo ratings yet
- Typhoid fever: A deadly bacterial infectionDocument8 pagesTyphoid fever: A deadly bacterial infectionMARIANTO PUTRA SUHARDINo ratings yet
- Student Health Clearance Certificate ChecklistDocument2 pagesStudent Health Clearance Certificate Checklistimdaking123No ratings yet
- Clinical Parasitology: 1. Direct Fecal Smear (DFS)Document3 pagesClinical Parasitology: 1. Direct Fecal Smear (DFS)Monique Eloise GualizaNo ratings yet
- Verorab Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVerorab Drug StudyHanna SeNo ratings yet
- Flt3 signaling required for murine B cell IgG1 class switchingDocument10 pagesFlt3 signaling required for murine B cell IgG1 class switchingAycaNo ratings yet
- Kidney NewDocument4 pagesKidney NewParth BhayanaNo ratings yet
- BULLY DISEASESDocument60 pagesBULLY DISEASESIbrahim Sidahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Parvo BacteriaDocument2 pagesParvo BacteriaErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDNo ratings yet
- SSJ TenDocument5 pagesSSJ TenSelviana SudarmanNo ratings yet
- Congenital SyphilisDocument22 pagesCongenital SyphilisJuliana MariaNo ratings yet
- Surat Keterangan Vaksinasi COVID-19 CertificateDocument1 pageSurat Keterangan Vaksinasi COVID-19 CertificateRidwanNo ratings yet
- Correspondence: Morphea masquerading as leprosyDocument3 pagesCorrespondence: Morphea masquerading as leprosyPriyanka JajuNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ON Upper Respiratory Tract Infections: Presented by Saranya.K Lecturer IconDocument26 pagesLesson Plan ON Upper Respiratory Tract Infections: Presented by Saranya.K Lecturer IconKumar BijayNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument69 pagesImmunologyburhaninho100% (5)
- SepsisDocument19 pagesSepsisapi-308355800No ratings yet
- 4.05 Virtual Blood Typing / Transfusion Lab Simulation LabDocument3 pages4.05 Virtual Blood Typing / Transfusion Lab Simulation LabMichael TownsendNo ratings yet
- Ear Discharge HandoutDocument9 pagesEar Discharge HandoutPorori BookshopNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need To Know About AllergiesDocument26 pagesEverything You Need To Know About AllergiesGiuliana FloresNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Infections of The Oral CavityDocument212 pagesBacterial Infections of The Oral CavitydrrakbdsNo ratings yet
- Pemphigus Vulgaris Case Report: Occlusal Splint and Topical Steroid TreatmentDocument4 pagesPemphigus Vulgaris Case Report: Occlusal Splint and Topical Steroid TreatmentLidwina ApyakaNo ratings yet
- Fluconazole Versus Nystatin in The Prevention of CandidaDocument25 pagesFluconazole Versus Nystatin in The Prevention of CandidaMutia SesunanNo ratings yet
- PCR 1 - Nashita Nawal Dzikra. NNDocument1 pagePCR 1 - Nashita Nawal Dzikra. NNDesy Ariza Eka PutriNo ratings yet
- Dr Cabrera's Contributions to ParasitologyDocument11 pagesDr Cabrera's Contributions to ParasitologyElle CruzNo ratings yet
- Create PDFDocument88 pagesCreate PDFSisnawaty SabatinyNo ratings yet