Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MIT Environment 10-28-04
Uploaded by
Dr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MIT Environment 10-28-04
Uploaded by
Dr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.Copyright:
Available Formats
1.
89, Environmental Microbiology
Prof. Martin Polz
Lecture 14
Regulation (cont.)
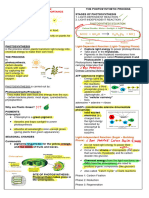
2. Enzyme levels
Transcription:
Promoter Operator Gene 1 Gene 2 Stop codon
RNA Polymerase
binds here Regulatory protein
(activator/repressor)
binds here
mechanisms. Example: attenuation, small RNAs
3. Global control networks
Example:
o Limitation of C, N, P → can’t use carbon if you have no N to grow.
o Damage:
o Oxidation
o Radiation
o Temperature
o Osmosmotic
o Redox reactions: e- transport chains
o Catabolite repression: if preferred carbon source is available, other
substrates often remain untouched
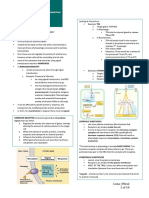
Example:
o Diauxic growth (glucose, lactose used) uses CAP (Catabolite
Activator Protein)
Glucose
- CAP CAP Active CAP
+
Adenylate cyclase
(i.e. inactive when + inducer
glucose is present)
Cyclic AMP binds Alternative
to activate metabolic genes
(turned on when glucose is absent)
1.89, Environmental Microbiology Lecture 14
Prof. Martin Polz Page 1 of 3
o Quorum sensing: signal “density of similar cells”.
Example: uptake of DNA by G+ cells
− Modulated by autoinducer molecules=small diffusible
molecules produced at low but constant levels by the
cell
− Autoinducer molecules induce their own transcription &
other pathways
− Local concentration of autoinducer can reach a critical
level at which point it induces increased production of
itself → strong inducer of other pathways
o Signal transduction & 2-component regulatory systems
− sensory kinases: example: motility
Motility → chemotaxis: attractants
repellants
CCW (Counter Clock Wise) → run, CW → tumble
− Tranducers (MCP protein) binds signal (attractant)
The CW tumble allows the ¤ Che A autophosphorylates
bacterium to explore a
small area where it senses
¤ Che A ~ P has a high tendency of
as attractant
phosphorylation for Che Y
¤ Che Y ~ P binds to flagella are motor → clockwise
rotation
¤ Che Z dephosphorylates Che Y ~ P
Adaptation – signal (attractant) does not change, so
response goes down.
At this point Che A ~ P phosphorylates Che B (but at a
slower rate). Che B ~ P demethylates the transducer
(MCP) (Che are methylated transducer).
Microbial Ecology
• explore how diverse & abundant bacteria are in the environment & their
ecological/biogeochemical function
Individual cells
Populations
(cells of same species)
Communities
Change in our perception of microbial diversity
1. direct cell counts replaced plate counts
1.89, Environmental Microbiology Lecture 14
Prof. Martin Polz Page 2 of 3
2. molecular approaches for estimating diversity
1970’s: “Great plate count anomaly”
• CFU (Colony Forming Units): spread dilution of samples onto culture plates
Count number of colonies
1) Assumption is that a single cell gave rise to each colony
2) Back-calculate for dilutions of environmental concentration
• Direct Counts: Fluorescent dyes (acridine orange, DAPI)
h� Visible light given off when
intercalated into DNA
o Fix the cells with aldehydes
o Mix with dyes
o Observe under fluorescent microscope
Conclusion
Less than 1% of observable cells are easily culturable → direct counts got way higher
numbers than CFU method.
1.89, Environmental Microbiology Lecture 14
Prof. Martin Polz Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- TOPNOTCH DIGITAL HANDOUT - BIOCHEMISTRY Juan Dela CruzDocument2 pagesTOPNOTCH DIGITAL HANDOUT - BIOCHEMISTRY Juan Dela CruzJoy Fucanan100% (1)
- Experiment 4 PCR and Cloning of Alpha-Amylase Gene in E. ColiDocument12 pagesExperiment 4 PCR and Cloning of Alpha-Amylase Gene in E. ColiJiaying ChenNo ratings yet
- Prader Willi Syndrome AAFPDocument4 pagesPrader Willi Syndrome AAFPVeronica Wong Huey ShinNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Heredity NotesDocument63 pagesReproduction and Heredity NotesmceldowneaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Lab-03Document28 pagesAP Biology Lab-03ldlewis0% (2)
- CELL COMMUNICATION: GAP JUNCTIONS PERMIT CLOSE COORDINATIONDocument22 pagesCELL COMMUNICATION: GAP JUNCTIONS PERMIT CLOSE COORDINATIONFidiya Septi Kusma WardaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document40 pagesChapter 3Mutiara KataNo ratings yet
- Multicellular Organisms Have BIG Communication Problems: Hey You - Divide Now!!! Oi! We Need Some Glucose!Document73 pagesMulticellular Organisms Have BIG Communication Problems: Hey You - Divide Now!!! Oi! We Need Some Glucose!kevin andrewNo ratings yet
- Topic 6.2 Proteins (Motifs Ubiquitin) : Cellular and Molecular BiologyDocument26 pagesTopic 6.2 Proteins (Motifs Ubiquitin) : Cellular and Molecular BiologyJorge GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 1P - Physio - Cell Physiology 3&4 - 1BDocument8 pages1P - Physio - Cell Physiology 3&4 - 1Burvashi rao rajputNo ratings yet
- MIT Environtment 9-16-04Document3 pagesMIT Environtment 9-16-04Dr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration 1Document2 pagesCellular Respiration 1Naledi Noxolo BhenguNo ratings yet
- BIOL1040 Lecture NotesDocument50 pagesBIOL1040 Lecture NotesJonathanZhaoNo ratings yet
- 0B1qNKXkQqXldRlRGM2I5VjVDM28 1Document33 pages0B1qNKXkQqXldRlRGM2I5VjVDM28 1Reza WirotamaNo ratings yet
- Structural Components of The Cell MembraneDocument2 pagesStructural Components of The Cell MembraneYumiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cell Biology and Cell CommunicationDocument94 pagesIntroduction To Cell Biology and Cell Communicationjude dwekatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Signal Transduction and Cellular ResponseDocument52 pagesLecture 5 Signal Transduction and Cellular Responseapi-251915360No ratings yet
- MIT Environment 10-21-04Document2 pagesMIT Environment 10-21-04Dr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Cell Communication and Signaling 1: Dr. Ivonne BejaranoDocument29 pagesChapter 7: Cell Communication and Signaling 1: Dr. Ivonne BejaranossaNo ratings yet
- Signal Transduction MechanismsDocument12 pagesSignal Transduction MechanismsAman SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Cell Communication - DADocument66 pagesCell Communication - DAMuhammad Ardiansyah MNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Cellular Physiology: Volume and Composition of Body Fluids, 1Document13 pagesCHAPTER 1 Cellular Physiology: Volume and Composition of Body Fluids, 1mr nice guyNo ratings yet
- Extracellular and Intracellular CommunicationDocument25 pagesExtracellular and Intracellular CommunicationdNo ratings yet
- Cheatt Sheet #2Document2 pagesCheatt Sheet #2layanhaliloNo ratings yet
- Komunikasi Antar SelDocument39 pagesKomunikasi Antar SelMOCHILNo ratings yet
- Cell SignallingDocument7 pagesCell SignallingClaraNo ratings yet
- MIT Environment 9-23-04Document3 pagesMIT Environment 9-23-04Dr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 11Document10 pagesBiology Chapter 11John Michael OsorioNo ratings yet
- Signaling CellDocument45 pagesSignaling Cellsontm1994No ratings yet
- MMG 301 Exam 3 Study GuideDocument14 pagesMMG 301 Exam 3 Study GuideRamin RajaeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Receptor ActivationDocument44 pagesLecture 4 Receptor Activationapi-251915360No ratings yet
- Midterm Biochem ReviewerDocument19 pagesMidterm Biochem ReviewerNATALIE NICOLE GABASNo ratings yet
- Signal Transduction, Cell Bio - 2023Document91 pagesSignal Transduction, Cell Bio - 2023ayushrajgupta831No ratings yet
- Sekolah Pelita Harapan Year 10 MYP ScienceDocument12 pagesSekolah Pelita Harapan Year 10 MYP Sciencejovanka kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms: All Eukaryotic Macro & Micro Organisms (Plants, Animals, Algae, Fungi, Protozoa) Microbial & ProkaryoticDocument4 pagesMicroorganisms: All Eukaryotic Macro & Micro Organisms (Plants, Animals, Algae, Fungi, Protozoa) Microbial & ProkaryoticDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- 7 - Receptor FamiliesDocument15 pages7 - Receptor FamiliesTeshale TekleNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument25 pagesBiologyIce BearNo ratings yet
- Promo 2015 Medical Physiology A 2Document29 pagesPromo 2015 Medical Physiology A 2Lemuel ValerioNo ratings yet
- B373 Unit 1Document38 pagesB373 Unit 1tamaraamhaNo ratings yet
- Adverbial Clauses Adverb of Time Adverb of Place Adverb of Manner Adverb of Degree of Comparison Adverb of ReasonDocument16 pagesAdverbial Clauses Adverb of Time Adverb of Place Adverb of Manner Adverb of Degree of Comparison Adverb of ReasonDormian SianturiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cell Communications - 20234Document35 pagesChapter 3 - Cell Communications - 20234afeeqrashidNo ratings yet
- 6 Cell Membrane-Sv22Document41 pages6 Cell Membrane-Sv22ThiệnÂnDươngNo ratings yet
- Bio Phto and CellularDocument4 pagesBio Phto and Cellulargbs040479No ratings yet
- Module 1C - Ch. 5 (Cell Signaling) 2023Document19 pagesModule 1C - Ch. 5 (Cell Signaling) 2023futurebiologist00pNo ratings yet
- Plant ResponseDocument61 pagesPlant ResponseGia HoàngNo ratings yet
- Saqs - (Very Important)Document67 pagesSaqs - (Very Important)BRIGHTON JOSHUANo ratings yet
- Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction-L3: Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PHDDocument30 pagesReceptors Functions and Signal Transduction-L3: Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PHDLaura RossiNo ratings yet
- Communication 27feb24Document67 pagesCommunication 27feb24Bano aliNo ratings yet
- 2 2update PDFDocument41 pages2 2update PDFJohnnyNo ratings yet
- Chapt09 Lecture 2019-SDocument45 pagesChapt09 Lecture 2019-SPaulNo ratings yet
- CC-LEC-NOTES-1Document4 pagesCC-LEC-NOTES-1CDNo ratings yet
- TMP AF40Document4 pagesTMP AF40FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Importance of Signal Amplification in PhototransductionDocument7 pagesImportance of Signal Amplification in PhototransductionRuby M. FajardoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Signal TransductionDocument10 pagesCellular Signal TransductionNica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- Theme1Module1and2ReviewLecture BIO1A03Fall2022Document22 pagesTheme1Module1and2ReviewLecture BIO1A03Fall2022proplayer910No ratings yet
- Cellular CommunicationDocument51 pagesCellular CommunicationBerslan ArslanNo ratings yet
- Cell-Cell Signaling - Masika 2021Document50 pagesCell-Cell Signaling - Masika 2021omarswaleh490No ratings yet
- Biology Glossary Terms 1Document15 pagesBiology Glossary Terms 1Tim PopeNo ratings yet
- Physiology - Cellular PhysiologyDocument58 pagesPhysiology - Cellular PhysiologyИринаNo ratings yet
- Lecturio: QuizDocument6 pagesLecturio: QuizHazel FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- RevalidaDocument5 pagesRevalidaHawkins FletcherNo ratings yet
- 02 CB Membrane 2019Document34 pages02 CB Membrane 2019Мөнхгэрэл ГанбатNo ratings yet
- l1 NotesDocument53 pagesl1 NotesRaju BhaiyaNo ratings yet
- Research in ProtozoologyFrom EverandResearch in ProtozoologyTze-Tuan ChenRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Relatório SternDocument613 pagesRelatório SternANDI Agencia de Noticias do Direito da Infancia100% (2)
- Transport Generation Modeling For Tasikmalaya Regency - 1Document12 pagesTransport Generation Modeling For Tasikmalaya Regency - 1Dr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Transportation Planning Arround Conservation Forest Area at Supiori As A New Expanding Regency at Biak IslandDocument8 pagesTransportation Planning Arround Conservation Forest Area at Supiori As A New Expanding Regency at Biak IslandDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Rotary Wing Transportation System For Steep Mountain Range at Papua - Revised For - Full - Papers - APTE - 2010Document9 pagesRotary Wing Transportation System For Steep Mountain Range at Papua - Revised For - Full - Papers - APTE - 2010Dr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Report of Recruitment 2012Document3 pagesReport of Recruitment 2012Dr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Highway MeteorologyDocument216 pagesHighway MeteorologyaldokrenaNo ratings yet
- Investigasi Numerik Pada Sistem Interaksi Aktif Terintegrasi Antara Smart Material-Solid-Fluid - Transportasi Maritim - Bucchi - ADocument1 pageInvestigasi Numerik Pada Sistem Interaksi Aktif Terintegrasi Antara Smart Material-Solid-Fluid - Transportasi Maritim - Bucchi - ADr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Investigasi Tentang Perilaku Dinamik Alami Dari Struktur Kurva Akibat Perubahan Bentuk Kurva - Transportasi Maritim - Hu - BoDocument1 pageInvestigasi Tentang Perilaku Dinamik Alami Dari Struktur Kurva Akibat Perubahan Bentuk Kurva - Transportasi Maritim - Hu - BoDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Reivision - Kalimantan River Transportation SustainabilityDocument10 pagesReivision - Kalimantan River Transportation SustainabilityDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Karakteristik Emisi Suara Pada Kerusakan Komposit - Marine Transport - VenturiniAutieriPosterDocument1 pageKarakteristik Emisi Suara Pada Kerusakan Komposit - Marine Transport - VenturiniAutieriPosterDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Investigasi Numerik Pada Interaksi Struktur Keairan Menggunakan Metoda Berbasis Partikel Untuk Aplikasi Maritim - Marine Transport - Sun - FanfanDocument1 pageInvestigasi Numerik Pada Interaksi Struktur Keairan Menggunakan Metoda Berbasis Partikel Untuk Aplikasi Maritim - Marine Transport - Sun - FanfanDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Karakteristik Struktur Textile Dan Woven Menggunakan Digital Image Correlation - Marine Transport - Williams - Helen - FSI Away Day Poster 2009Document1 pageKarakteristik Struktur Textile Dan Woven Menggunakan Digital Image Correlation - Marine Transport - Williams - Helen - FSI Away Day Poster 2009Dr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Interaksi Tempat Duduk Penumpang Pada Kapal Cepat - Transportasi Maritim - Coe - TomDocument1 pageInteraksi Tempat Duduk Penumpang Pada Kapal Cepat - Transportasi Maritim - Coe - TomDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Investigasi Dan Aplikasi Dalam Analisis Power Flow Pada Sistem Dinamik Non Linier - Marine Transport - Yang - JianDocument1 pageInvestigasi Dan Aplikasi Dalam Analisis Power Flow Pada Sistem Dinamik Non Linier - Marine Transport - Yang - JianDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Investigasi Dalam As Leleh Fatigue Dari Struktur Di Las Pada Badan Kereta API Kecepatan Tinggi - Marine Transport - Song - ZhanxunDocument1 pageInvestigasi Dalam As Leleh Fatigue Dari Struktur Di Las Pada Badan Kereta API Kecepatan Tinggi - Marine Transport - Song - ZhanxunDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Interaksi Fluida-Struktur Pada Kapal Layar Balap Yacht - Marine Transport - Trimarch - DanieleiDocument1 pageInteraksi Fluida-Struktur Pada Kapal Layar Balap Yacht - Marine Transport - Trimarch - DanieleiDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- As Struktur Balok Berlapis Tipis - Marine Transport - Miao - ShihuaDocument1 pageAs Struktur Balok Berlapis Tipis - Marine Transport - Miao - ShihuaDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Investigasi Dan Aplikasi Dalam Analisis Power Flow Pada Sistem Dinamik Non Linier - Marine Transport - Yang - JianDocument1 pageInvestigasi Dan Aplikasi Dalam Analisis Power Flow Pada Sistem Dinamik Non Linier - Marine Transport - Yang - JianDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Hydroelastisitas Kapal Menggunakan RANS CFD - Marine Transport - Querard - AymericDocument1 pageHydroelastisitas Kapal Menggunakan RANS CFD - Marine Transport - Querard - AymericDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- As # Dimensi Non Linier - Transportasi Maritim - Chapchap - AlbertoDocument1 pageAs # Dimensi Non Linier - Transportasi Maritim - Chapchap - AlbertoDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Interaksi Fluida-Struktur Pada Kapal Layar Balap Yacht - Marine Transport - Trimarch - DanieleiDocument1 pageInteraksi Fluida-Struktur Pada Kapal Layar Balap Yacht - Marine Transport - Trimarch - DanieleiDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Disain Kapal Layar Balap Yach - Marine Transport - Scarponi - MatteoDocument1 pageDisain Kapal Layar Balap Yach - Marine Transport - Scarponi - MatteoDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Efek Ketaksempurnaan Geometrik Pada Renspon Kompresif Dari Panel Komposit - Transportasi Maritim - de - Verdiere - MathieuDocument1 pageEfek Ketaksempurnaan Geometrik Pada Renspon Kompresif Dari Panel Komposit - Transportasi Maritim - de - Verdiere - MathieuDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Disain Peningkatan Kendali Dan Keamanan Kapal Rigid Inflatable Boats (RIBs) - Marine Transport - Townsend - TDocument1 pageDisain Peningkatan Kendali Dan Keamanan Kapal Rigid Inflatable Boats (RIBs) - Marine Transport - Townsend - TDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Dinamika Perahu Layar Balap Yacht - Marine Transport - Spenkuch - ThomasDocument1 pageDinamika Perahu Layar Balap Yacht - Marine Transport - Spenkuch - ThomasDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Efek Kebakaran Pada Struktur Komposit - Transportasi Maritim - Cutter - PhilipDocument1 pageEfek Kebakaran Pada Struktur Komposit - Transportasi Maritim - Cutter - PhilipDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Efisiensi Reparasi Resin Infused Scarf Struktur Komposit - Marine Transport - Palaniappan - JayanthiDocument1 pageEfisiensi Reparasi Resin Infused Scarf Struktur Komposit - Marine Transport - Palaniappan - JayanthiDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Disain Dan An Turbin Air Berbiaya Efektif Yang Ditempel Di Permukaan Air Untuk Produksi Listrik Di Pedesaan - Transportasi Maritim - Ahmed - TauseefDocument1 pageDisain Dan An Turbin Air Berbiaya Efektif Yang Ditempel Di Permukaan Air Untuk Produksi Listrik Di Pedesaan - Transportasi Maritim - Ahmed - TauseefDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Disain Craft Kecepatan Tinggi Suatu Persepektif Faktor Manusia Suatu Tes Model - Marine Transport - Taunton - DominicDocument1 pageDisain Craft Kecepatan Tinggi Suatu Persepektif Faktor Manusia Suatu Tes Model - Marine Transport - Taunton - DominicDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Degradasi Thermal Pada Sandwich Struktur - Marine Transport - Zhang - ShufengDocument1 pageDegradasi Thermal Pada Sandwich Struktur - Marine Transport - Zhang - ShufengDr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.No ratings yet
- Building DNASEDocument3 pagesBuilding DNASEadhrit.mahatoNo ratings yet
- 2018 H3 Mol Bio Exam Paper MARK SCHEMEDocument5 pages2018 H3 Mol Bio Exam Paper MARK SCHEMEughNo ratings yet
- Finkeldey - Tropical Forest Genetics PDFDocument318 pagesFinkeldey - Tropical Forest Genetics PDFLewisKarl100% (1)
- Avida-ED Sample Model Lessons ExplainedDocument44 pagesAvida-ED Sample Model Lessons ExplainedLara Patricia Causo0% (1)
- Assignment On Animal Cloning Edexcel Igcse Biology 9-1Document8 pagesAssignment On Animal Cloning Edexcel Igcse Biology 9-1Rawdatul JannahNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based Prerequisites and Precursors of Athletic Talent: A ReviewDocument18 pagesEvidence Based Prerequisites and Precursors of Athletic Talent: A ReviewruiNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Phoneutria Nigriventer Spider VenomDocument29 pagesAn Overview of Phoneutria Nigriventer Spider VenomFerenc TörökNo ratings yet
- Addison Wesly Biology PDFDocument662 pagesAddison Wesly Biology PDFRicaasdfghjkNo ratings yet
- The Covid-19 Fraud & War On Humanity: DR Mark Bailey and DR John Bevan-SmithDocument46 pagesThe Covid-19 Fraud & War On Humanity: DR Mark Bailey and DR John Bevan-SmithAditya Ikhsan Prasiddha100% (2)
- ReflectionDocument1 pageReflectionapi-255450912No ratings yet
- Developing Explanation Mouse Fur Color Teacher ADADocument9 pagesDeveloping Explanation Mouse Fur Color Teacher ADABella kolbNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 DLL ScienceDocument30 pagesGrade 9 DLL ScienceSpencer GudinNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Cancer - Clinical Management-Intech (2012)Document324 pagesPancreatic Cancer - Clinical Management-Intech (2012)María Reynel TarazonaNo ratings yet
- Prader-Willi SyndromeDocument2 pagesPrader-Willi SyndromeadamNo ratings yet
- PCR OlaDocument7 pagesPCR OlaBeena KakranNo ratings yet
- Mitosis in Onion Root Tips LabDocument4 pagesMitosis in Onion Root Tips LabJohn Osborne40% (5)
- Project Camelot DR - Pete Peterson, Part 2 - David Wilcock TranscriptDocument22 pagesProject Camelot DR - Pete Peterson, Part 2 - David Wilcock TranscriptChristian UFO Illuminati100% (1)
- Next GenerationDocument5 pagesNext GenerationWajiha FatimaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Bee BreedingDocument38 pagesAdvanced Bee BreedingAlexander GintingNo ratings yet
- DNA Methylation MarkerDocument16 pagesDNA Methylation MarkerMAIKOL OLARTENo ratings yet
- Incomplete DominanceDocument53 pagesIncomplete Dominancemarian buenafeNo ratings yet
- Whale Formal Lab ReportDocument4 pagesWhale Formal Lab ReportMohamed AdnanNo ratings yet
- Potential Use of A Weak Ethylene Receptor Mutant, Sletr1 2, As Breeding Material To Extend Fruit Shelf Life of TomatoDocument13 pagesPotential Use of A Weak Ethylene Receptor Mutant, Sletr1 2, As Breeding Material To Extend Fruit Shelf Life of TomatoGugun GunawanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Genomics Laboratory: Test ResultDocument1 pageClinical Genomics Laboratory: Test ResultMigz OrtiagaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis With Discordant Drug Resistance Patterns - A Diagnostic DilemmaDocument4 pagesTuberculosis With Discordant Drug Resistance Patterns - A Diagnostic DilemmaKevinNo ratings yet
- 7-12th Bio Chap 22 Genetics (A)Document2 pages7-12th Bio Chap 22 Genetics (A)Raees Ali KhanNo ratings yet