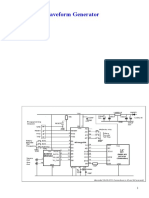
tepper Motor Control using Microcontroller Circuit Principle:
The main principle of this circuit is to rotate the stepper motor step wise at a particular step
angle. The ULN2003 IC is used to drive the stepper motor as the controller cannot provide
current required by the motor.
Also Read the Related Post PWM Based DC Motor Speed Control using Microcontroller
Stepper Motor Control using 8051 Microcontroller Circuit Diagram:
Circuit Diagram of Stepper Motor Control using AT89C51 Microcontroller
Circuit Components:
AT89C51 micro controller
ULN2003A
� Stepper Motor
Crystal
Resistor
Capacitor
Stepper Motor Control using 8051 Microcontroller Circuit Design:
The circuit consists of AT89C51 microcontroller, ULN2003A, Motor. AT89c51 is low power,
high-performance, CMOS 8bit, 8051 family microcontroller. It has 32 programmable I/O lines. It
has 4K bytes of Flash programmable and erasable memory. An external crystal oscillator is
connected at the 18 and 19 pins of the microcontroller. Motor is connected to the port2 of the
microcontroller through a driver IC.
The ULN2003A is a current driver IC. It is used to drive the current of the stepper motor as it
requires more than 60mA of current. It is an array of Darlington pairs. It consists of seven pairs
of Darlington arrays with common emitter. The IC consists of 16 pins in which 7 are input pins,
7 are output pins and remaining are VCC and Ground. The first four input pins are connected to
the microcontroller. In the same way, four output pins are connected to the stepper motor.
Stepper motor has 6 pins. In these six pins, 2 pins are connected to the supply of 12V and the
remaining are connected to the output of the stepper motor. Stepper rotates at a given step angle.
Each step in rotation is a fraction of full cycle. This depends on the mechanical parts and the
driving method.
�Similar to all the motors, stepper motors will have stator and rotor. Rotor has permanent magnet
and stator has coil. The basic stepper motor has 4 coils with 90 degrees rotation step. These four
coils are activated in the cyclic order. The below figure shows you the direction of rotation of the
shaft. There are different methods to drive a stepper motor. Some of these are explained below.
Full Step Drive: In this method two coils are energized at a time. Thus, here two opposite coils
are excited at a time.
Half Step Drive: In this method coils are energized alternatively. Thus it rotates with half step
angle. In this method, two coils can be energized at a time or single coil can be energized. Thus it
increases the number of rotations per cycle. It is shown in the below figure.
How to Operate this Stepper Motor Driver Circuit?
Initially , switch on the circuit.
Microcontroller starts driving the stepper motor.
One can observe the rotation of the stepper motor
The stepper motor has four wires. They are yellow, blue, red and white. These are
energized alternatively as given below.
In full step driving, use the following sequence
� To drive the motor in half step angle, use the following sequence
Stepper Motor Controller Circuit Advantages:
It consumes less power.
It requires low operating voltage
Stepper Motor Control Applications:
� This circuit can be used in the robotic applications.
This can also be used in mechantronics applications.
The stepper motors can be used in disk drives, matrix printers, etc.
Interfacing ADC to 8051
Last Updated on September 6, 2012 by admin in 8051
projects with 5 Comments
ADC (Analog to digital converter) forms a very essential part in many
embedded projects and this article is about interfacing an ADC to
8051 embedded controller. ADC 0804 is the ADC used here and
before going through the interfacing procedure, we must neatly
understand how the ADC 0804 works.
ADC 0804.
ADC0804 is an 8 bit successive approximation analogue to digital
converter from National semiconductors. The features of ADC0804
are differential analogue voltage inputs, 0-5V input voltage range, no
zero adjustment, built in clock generator, reference voltage can be
externally adjusted to convert smaller analogue voltage span to 8 bit
resolution etc. The pin out diagram of ADC0804 is shown in the figure
below.
�ADC0804 pinout
The voltage at Vref/2 (pin9) of ADC0804 can be externally adjusted
to convert smaller input voltage spans to full 8 bit resolution. Vref/2
(pin9) left open means input voltage span is 0-5V and step size is
5/255=19.6V. Have a look at the table below for different Vref/2
voltages and corresponding analogue input voltage spans.
Vref/2 (pin9) (volts)
Input voltage span (volts)
Left open
05
04
1.5
03
1.28
0 2.56
1.0
02
0.5
01
�Steps for converting the analogue input and reading
the output from ADC0804.
Make CS=0 and send a low to high pulse to WR pin to start the
conversion.
Now keep checking the INTR pin. INTR will be 1 if conversion is
not finished and INTR will be 0 if conversion is finished.
If conversion is not finished (INTR=1) , poll until it is finished.
If conversion is finished (INTR=0), go to the next step.
Make CS=0 and send a high to low pulse to RD pin to read the
data from the ADC.
Circuit diagram.
�Interfacing ADC to 8051
The figure above shows the schematic for interfacing ADC0804 to
8051. The circuit initiates the ADC to convert a given analogue input ,
then accepts the corresponding digital data and displays it on the LED
array connected at P0. For example, if the analogue input voltage Vin
is 5V then all LEDs will glow indicating 11111111 in binary which is
the equivalent of 255 in decimal. AT89s51 is the microcontroller used
here. Data out pins (D0 to D7) of the ADC0804 are connected to the
port pins P1.0 to P1.7 respectively. LEDs D1 to D8 are connected to
the port pins P0.0 to P0.7 respectively. Resistors R1 to R8 are current
limiting resistors. In simple words P1 of the microcontroller is the input
�port and P0 is the output port. Control signals for the ADC (INTR, WR,
RD and CS) are available at port pins P3.4 to P3.7 respectively.
Resistor R9 and capacitor C1 are associated with the internal clock
circuitry of the ADC. Preset resistor R10 forms a voltage divider which
can be used to apply a particular input analogue voltage to the ADC.
Push button S1, resistor R11 and capacitor C4 forms a debouncing
reset mechanism. Crystal X1 and capacitors C2,C3 are associated
with the clock circuitry of the microcontroller.
Program.
ORG 00H
MOV P1,#11111111B // initiates P1 as the input port
MAIN: CLR P3.7 // makes CS=0
SETB P3.6 // makes RD high
CLR P3.5 // makes WR low
SETB P3.5 // low to high pulse to WR for starting
conversion
WAIT: JB P3.4,WAIT // polls until INTR=0
CLR P3.7 // ensures CS=0
�CLR P3.6 // high to low pulse to RD for reading the data
from ADC
MOV A,P1 // moves the digital data to accumulator
CPL A // complements the digital data (*see the notes)
MOV P0,A // outputs the data to P0 for the LEDs
SJMP MAIN // jumps back to the MAIN program
END
Notes.
The entire circuit can be powered from 5V DC.
ADC 0804 has active low outputs and the instruction CPL A
complements it t0 have a straight forward display. For example, if
input is 5V then the output will be 11111111 and if CPL A was not
used it would have been 00000000 which is rather awkward to
see.
interface Humidity Sensor with 8051 Microcontroller
Himanshu Choudhary
Physical quantities like Humidity, temperature, pressure etc. are monitored to get
information about the environmental conditions. Various sensors are being used
to measure these quantities in analog form.
This article demonstrates the
�principle
and
operation
of
interfacing
the
humidity
sensor
with 8051
microcontroller (AT89C51). The humidity sensor is widely used in applications
like weather forecast, air conditioner, Hygrometers etc.Click to read more
about humidity sensor and its working.
Humidity sensor works on the principle of relative humidity and gives the output
in the form of voltage. This analog voltage provides the information about the
percentage relative humidity present in the environment.
The relative humidity is defined as:
The analog output of sensor is connected to ADC to get its corresponding digital
value. For calibration of digital values, the reference voltage of ADC is set to 1.5
volts. The digital values are received at port P0 of microcontroller. These digital
values are used to calculate percentage relative humidity of environment. The
calculated data is sent to LCD to display the percentage relative humidity. The
connections of ADC0804 and LCD with the 8051 microcontroller (AT89C51) are
shown in circuit diagram.
Algorithm
{C.
Define the input and output port of microcontroller.
{2.
Initialize LCD.
{C}. Monitor the value of ADC 0804.
{C}{ Calculate the relative humidity
{C5. Convert the calculated value in their corresponding ASCII codes.
6.
Display the converted value on the LCD.
{C}{7.
Repeat steps 4 to 7 in an infinite loop.