Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Communication & Networking Practical # 05: Introduction To Packet Tracer What Is Packet Tracer?
Uploaded by
kathirdcn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesOriginal Title
lab05ccn-140307143816-phpapp02
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesComputer Communication & Networking Practical # 05: Introduction To Packet Tracer What Is Packet Tracer?
Uploaded by
kathirdcnCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Computer Communication & Networking
Practical # 05
Object:
Introduction to Packet Tracer
What is Packet Tracer?
Packet Tracer is a protocol simulator
developed by Dennis Frezzo and his team
at Cisco Systems. Packet Tracer (PT) is a
powerful and dynamic tool that displays the
various protocols used in networking, in
either Real Time or Simulation mode. This
includes layer 2 protocols such as Ethernet
and PPP, layer 3 protocols such as IP,
ICMP, and ARP, and layer 4 protocols such
as TCP and UDP. Routing protocols can
also be traced.
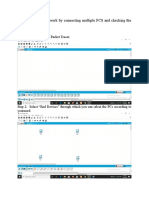
Introduction to the Packet Tracer
Interface using a Hub Topology:
Step 2: Choose Hub and then select
Generic
Step 3: After selecting Generic click on
the main area.
You will see a Hub.
Step 1: Start Packet Tracer
You will see the start screen as shown
below.
Step 4: Select End Devices and then
click at Generic
Choosing Devices and Connections
We will begin building our network topology
by selecting devices and the media in which
to connect them. Several types of devices
and network connections can be used. For
this lab we will keep it simple by using End
Devices, Switches, Hubs, and Connections.
Sorath Asnani 11CS12
Step 5: Click at the workspace to see the
PC.
Repeat the above process to place as many
PCs as you want.
Page 1
Computer Communication & Networking
Practical # 05
Step 8: Double click on a PC, a box will
appear. Click on the Desktop tab.
Step 6: Select Connections from
Power Cycle Devices and click on
Automatically
choose
Connection
Type
Step 9: Then select IP configuration
Step 7: Draw connections from Hub to
PCs
Step 10: Write the IP address of your
network and click at the Subnet mask
filed.
Subnet
Mask
will
appear
automatically.
Sorath Asnani 11CS12
Page 2
Computer Communication & Networking
Practical # 05
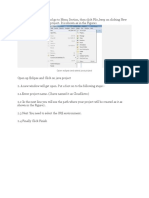
Step 11: Repeat Step 10 to set the IPs for
all the PCs.
Step 12: Select Add simple message
Step 16: Observe the path of the
Message from source to Hub, then to all
devices. And then from Destination to
Hub then back to the source.
Step 13: Drag and Drop the message to
the source device and then to the
Destination device
In this case my source device is PC1 and
destination device is PC4.
Step 14: Select the Simulation Mode at
the bottom right corner
Step 17: Finally observe the marks. If the
source PC is marked correct it means
you have successfully established the
connection.
Step 15: Click at Auto Capture / Play
Conclusion:
Connection
established
successfully
between Source and Destination.
Sorath Asnani 11CS12
Page 3
You might also like
- 8CS5 UNPS Lab Exp. No. 7 PDFDocument3 pages8CS5 UNPS Lab Exp. No. 7 PDFasdNo ratings yet
- CN LAB MANUAL FinalDocument24 pagesCN LAB MANUAL FinalAbdullah ilyasNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With Packet Tracer NDocument45 pagesGetting Started With Packet Tracer Nmedanite ashebirNo ratings yet
- Creating a Topology in Packet TracerDocument18 pagesCreating a Topology in Packet TracerManishNo ratings yet
- How To Connect Between Devices Via Network Wire On Cisco Packet Tracer (Virtual Program) ?Document5 pagesHow To Connect Between Devices Via Network Wire On Cisco Packet Tracer (Virtual Program) ?Anisa NdociNo ratings yet
- Study and Design Internetworking Devices Using Cisco Packet TracerDocument20 pagesStudy and Design Internetworking Devices Using Cisco Packet TracerBrice CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Wa0003.Document44 pagesWa0003.PratiyushNo ratings yet
- CSS NC II - Setup Peer-to-peer Network ConnectionDocument3 pagesCSS NC II - Setup Peer-to-peer Network ConnectionDan AvergonzadoNo ratings yet
- Installation and Introduction of Packet Tracer Objective:: Experiment # 03Document16 pagesInstallation and Introduction of Packet Tracer Objective:: Experiment # 03نیان سیف باٹھNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Creating and Saving TopologiesDocument17 pagesPacket Tracer - Creating and Saving TopologiesSharmarke Shack SamatarNo ratings yet
- Iot3X Module 1 Activity - Networking in Packet Tracer: Open The Activity Starting Point FileDocument13 pagesIot3X Module 1 Activity - Networking in Packet Tracer: Open The Activity Starting Point FileThắng TrầnNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Computer NetworkDocument44 pagesLab Manual Computer NetworkMayank PantNo ratings yet
- Akku 75Document7 pagesAkku 75sonupawar8883No ratings yet
- Tcp/IpDocument3 pagesTcp/IpSatishNo ratings yet
- IT31012_First Semester Lab ManualDocument48 pagesIT31012_First Semester Lab ManualpadaukzunNo ratings yet
- CN FilesDocument64 pagesCN FilesAdityaNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument82 pagesLab ManualSafa MNo ratings yet
- Packet Sniffing and Spoofing Lab - FinalDocument26 pagesPacket Sniffing and Spoofing Lab - FinalKhalil Ullah67% (3)
- Experiment 3Document34 pagesExperiment 3dundundunzNo ratings yet
- Reading 3 - How Does The Internet WorkDocument1 pageReading 3 - How Does The Internet WorkVarenya KumarNo ratings yet
- DCN Manual 2019Document73 pagesDCN Manual 2019Suhani SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- DC Rec RemainingDocument25 pagesDC Rec Remainingbilnot9No ratings yet
- DCN Manual 2019Document74 pagesDCN Manual 2019Suhani SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 1network LabDocument35 pages1network LabBharani DharanNo ratings yet
- 2: Create A Local Network by Connecting Multiple PCS and Checking The ReachabilityDocument5 pages2: Create A Local Network by Connecting Multiple PCS and Checking The ReachabilityShivani DhakalNo ratings yet
- How the Internet Works: A Concise Guide to Internet Infrastructure and TechnologiesDocument25 pagesHow the Internet Works: A Concise Guide to Internet Infrastructure and TechnologiesJaiRathoreNo ratings yet
- How Does Internet WorksDocument12 pagesHow Does Internet WorksVinay J KatNo ratings yet
- Information and Network Security Lab: Lab Mannual FOR VII SEMESTER Computer Science & EngineeringDocument30 pagesInformation and Network Security Lab: Lab Mannual FOR VII SEMESTER Computer Science & EngineeringAnitha McNo ratings yet
- CL307 Spring 2018 02Document11 pagesCL307 Spring 2018 02Awais AhmedNo ratings yet
- CN 8-10 WeekDocument28 pagesCN 8-10 WeekMmi IndabettuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Packet TracerDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Packet TracerKevinz KerrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document32 pagesChapter 2Lemuel GallegoNo ratings yet
- Network Security LabDocument22 pagesNetwork Security Labsangee20039No ratings yet
- Rus Shuler How Does The Internet WorkDocument12 pagesRus Shuler How Does The Internet WorkLiviu AndreiNo ratings yet
- 1 Configuring SLIP Under Windows XPDocument6 pages1 Configuring SLIP Under Windows XPrezamdNo ratings yet
- Statement Purpose:: CCSXXX Lab ManualDocument19 pagesStatement Purpose:: CCSXXX Lab ManualSaleem IqbalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Packet TracerDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Packet TracerRJ GieNo ratings yet
- To Install and Configure NIC, HUB, Switch and RouterDocument1 pageTo Install and Configure NIC, HUB, Switch and RouterPodadai VadaNo ratings yet
- How Internet WorksDocument13 pagesHow Internet Worksnidee_nishokNo ratings yet
- PACKET TRACER. GithubDocument6 pagesPACKET TRACER. GithubMeduzagyzaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1packet SniffingDocument5 pagesAssignment 1packet Sniffingcecohav455No ratings yet
- Introduction to Packet Tracer Lab TasksDocument6 pagesIntroduction to Packet Tracer Lab TasksAkira MannahelNo ratings yet
- Lab - Mapping The Internet: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesLab - Mapping The Internet: ObjectivesDelaida MuminovicNo ratings yet
- K2NetworkConnectionDocument1 pageK2NetworkConnectionNathalis CortexNo ratings yet
- CN 11 WeekDocument18 pagesCN 11 WeekMmi IndabettuNo ratings yet
- 7.3.2.8 Lab - Mapping The InternetDocument8 pages7.3.2.8 Lab - Mapping The InternetParthPatel0% (5)
- 6cse10 NP Lab Final ManualDocument110 pages6cse10 NP Lab Final ManualvyshuNo ratings yet
- Network DebugDocument5 pagesNetwork DebugFERNANDONo ratings yet
- Tcp&Udp ExplainingDocument17 pagesTcp&Udp ExplainingG TugstuguldurNo ratings yet
- Creating a LAN and Testing Network ConnectivityDocument8 pagesCreating a LAN and Testing Network ConnectivityQaisarayub QasNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Devices On Windows XP SP2 With 7.5v5 / 4.0v5Document4 pagesTCP/IP Devices On Windows XP SP2 With 7.5v5 / 4.0v5alfonso manosalvaNo ratings yet
- 5 Ways To Connect Two Computers - WikiHowDocument6 pages5 Ways To Connect Two Computers - WikiHowAnjith AkNo ratings yet
- LAN 2 .VNBDocument21 pagesLAN 2 .VNBLê NghĩaNo ratings yet
- 9 NetworkDocument43 pages9 Networkapi-371092170No ratings yet
- Internet Technologies Practicals Documentation: AuthorDocument42 pagesInternet Technologies Practicals Documentation: Authorrama.narayanareddy963No ratings yet
- 113 - CN Lab Manual - 2022Document76 pages113 - CN Lab Manual - 2022Dharmisha panjriNo ratings yet
- CCN Lab ManualDocument28 pagesCCN Lab ManualMuhammad Usman NasirNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- A Topical Start-Up Guide Series On Emerging Topics On Educational Media and TechnologyDocument12 pagesA Topical Start-Up Guide Series On Emerging Topics On Educational Media and TechnologykathirdcnNo ratings yet
- Co Ma PRDocument32 pagesCo Ma PRShalu KumariNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper: Employee Employee Name, Employee ID Getdata, PutdataDocument7 pagesSample Question Paper: Employee Employee Name, Employee ID Getdata, PutdataAshutosh PatilNo ratings yet
- Final Best Practices in Aicte Approved InstitutuionsDocument44 pagesFinal Best Practices in Aicte Approved InstitutuionsamitsagaNo ratings yet
- PSG SWING COURSE REPORTDocument17 pagesPSG SWING COURSE REPORTkathirdcnNo ratings yet
- Diploma Computer Networking Exam - Cryptography and Network SecurityDocument2 pagesDiploma Computer Networking Exam - Cryptography and Network SecuritykathirdcnNo ratings yet
- Cadl PDFDocument67 pagesCadl PDFjeevan prasadNo ratings yet
- It Sem7 It2406lmDocument28 pagesIt Sem7 It2406lmSenthil RNo ratings yet
- Web Lab SyllabusDocument7 pagesWeb Lab SyllabuskathirdcnNo ratings yet
- OIT552-Cloud ComputingDocument10 pagesOIT552-Cloud Computingkathirdcn50% (2)
- Lab Manual: ISC 440 (Web Programming 2)Document44 pagesLab Manual: ISC 440 (Web Programming 2)kathirdcnNo ratings yet
- Diploma Computer Networking Exam - Cryptography and Network SecurityDocument2 pagesDiploma Computer Networking Exam - Cryptography and Network SecuritykathirdcnNo ratings yet
- Activities To Be Undertaken During The Fitness Week CelebrationDocument1 pageActivities To Be Undertaken During The Fitness Week CelebrationkathirdcnNo ratings yet
- Index: SL No Experiment NameDocument23 pagesIndex: SL No Experiment NamekathirdcnNo ratings yet
- Security Challenges in Cloud Computing: January 2010Document16 pagesSecurity Challenges in Cloud Computing: January 2010kathirdcnNo ratings yet
- Cloud Security Architecture Framework for IaaS and PaaSDocument15 pagesCloud Security Architecture Framework for IaaS and PaaSkathirdcnNo ratings yet
- A Classification and Characterization of Security Threats in Cloud ComputingDocument28 pagesA Classification and Characterization of Security Threats in Cloud ComputingkathirdcnNo ratings yet
- PSG Alumni WebinarDocument1 pagePSG Alumni WebinarkathirdcnNo ratings yet
- CLOUD COMPUTING CA TEST - 1 (Responses)Document10 pagesCLOUD COMPUTING CA TEST - 1 (Responses)kathirdcnNo ratings yet
- Proud To Be Indian: Happy Independence DAYDocument2 pagesProud To Be Indian: Happy Independence DAYkathirdcnNo ratings yet
- 74TH Independence Day of IndiaDocument1 page74TH Independence Day of IndiakathirdcnNo ratings yet
- Rtosss 130720123442 Phpapp01 PDFDocument38 pagesRtosss 130720123442 Phpapp01 PDFkathirdcnNo ratings yet
- Open Up Eclipse and Go To Menu SectionDocument5 pagesOpen Up Eclipse and Go To Menu SectionkathirdcnNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Task States and SchedulingDocument3 pages5.3 Task States and SchedulingkathirdcnNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document84 pagesUnit 2mjayaprakashphdNo ratings yet
- Web Programming Lab Manual 5th Sem CS PDFDocument54 pagesWeb Programming Lab Manual 5th Sem CS PDFPramodh ShettyNo ratings yet
- RTOS Basics SemaphoreDocument3 pagesRTOS Basics SemaphorekathirdcnNo ratings yet
- Electronics Communication Sample Question PaperDocument6 pagesElectronics Communication Sample Question PaperAkhlad Alqurash100% (1)
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument81 pagesChapter 2 PDFkathirdcnNo ratings yet
- RTOS Basics SemaphoreDocument3 pagesRTOS Basics SemaphorekathirdcnNo ratings yet