0% found this document useful (0 votes)
526 views16 pagesAtom Structure and Chemical Reactions Guide
This document provides information on the structure of atoms, chemical formulae and equations, the periodic table, chemical bonding, rates of reaction, carbon compounds, redox reactions, acids and bases, salts, alloys, carbon compounds, and chemicals for consumers. It discusses topics such as the electronic structure of atoms, writing chemical equations, periodic trends, ionic and covalent bonding, factors affecting reaction rates, hydrocarbon functional groups and reactions, oxidation-reduction reactions, acid-base theories, salt properties and analyses, alloy uses and glass types, and functions of soap, detergents, food additives, and medicines.
Uploaded by
Cherry T CYCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
526 views16 pagesAtom Structure and Chemical Reactions Guide
This document provides information on the structure of atoms, chemical formulae and equations, the periodic table, chemical bonding, rates of reaction, carbon compounds, redox reactions, acids and bases, salts, alloys, carbon compounds, and chemicals for consumers. It discusses topics such as the electronic structure of atoms, writing chemical equations, periodic trends, ionic and covalent bonding, factors affecting reaction rates, hydrocarbon functional groups and reactions, oxidation-reduction reactions, acid-base theories, salt properties and analyses, alloy uses and glass types, and functions of soap, detergents, food additives, and medicines.
Uploaded by
Cherry T CYCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
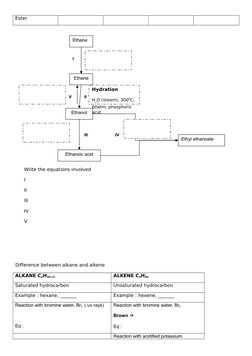
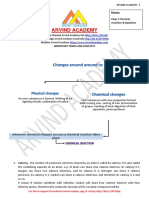
- The Structure of an Atom: Discusses the fundamental structure of atoms, isotopes, and electronic structure.
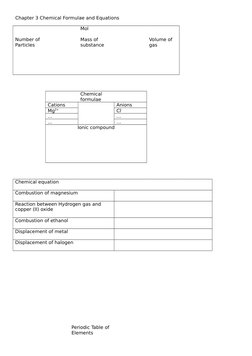
- Chemical Formulae and Equations: Explains the chemical formulae, equations, and reactions, with focus on ionic and covalent bonds.
- Acids and Bases: Covers the properties and reaction behaviors of acids and bases, including pH considerations.
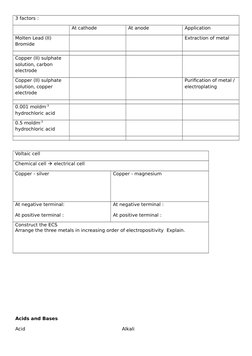
- Industry and Chemical Applications: Details industrial uses of chemicals, including synthesis processes and effects on materials.
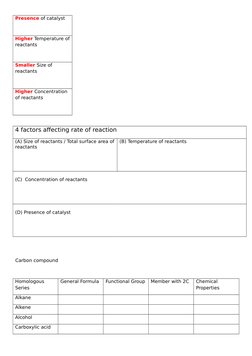
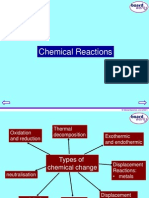
- Rate of Reaction: Examines factors affecting chemical reaction rates and introduces Collision Theory.
- Redox Reactions: Explores oxidation-reduction reactions and their balancing with detailed examples.
- Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions: Explains energy changes in reactions, including the concepts of endothermic and exothermic processes.
- Chemical Effects and Consumers: Discusses practical applications of chemical reactions for consumers, including soap and detergents.