Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Circuits Short Notes
Uploaded by
agntx070 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageElectric current is measured in amperes, which represents the flow of electrons in coulombs per second. A coulomb is the charge of approximately 6.242 x 1018 electrons. Current is defined as the charge in coulombs passing through a wire over time in seconds, while voltage is defined as the energy in joules divided by the charge in coulombs. Some example calculations include determining that 10 amperes of current for 1 minute would equal 3.742 x 1021 electrons passing through the wire, and that 360 coulombs passing through a conductor in 20 seconds equals 18 amperes.
Original Description:
random notes
Original Title
Electrical Circuits short notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
ODT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentElectric current is measured in amperes, which represents the flow of electrons in coulombs per second. A coulomb is the charge of approximately 6.242 x 1018 electrons. Current is defined as the charge in coulombs passing through a wire over time in seconds, while voltage is defined as the energy in joules divided by the charge in coulombs. Some example calculations include determining that 10 amperes of current for 1 minute would equal 3.742 x 1021 electrons passing through the wire, and that 360 coulombs passing through a conductor in 20 seconds equals 18 amperes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as ODT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageElectrical Circuits Short Notes
Uploaded by
agntx07Electric current is measured in amperes, which represents the flow of electrons in coulombs per second. A coulomb is the charge of approximately 6.242 x 1018 electrons. Current is defined as the charge in coulombs passing through a wire over time in seconds, while voltage is defined as the energy in joules divided by the charge in coulombs. Some example calculations include determining that 10 amperes of current for 1 minute would equal 3.742 x 1021 electrons passing through the wire, and that 360 coulombs passing through a conductor in 20 seconds equals 18 amperes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as ODT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
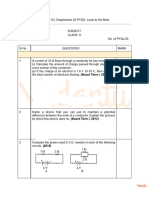
Electric Current measured in Amperes (A) which is flow of electrons in coulombs/ second.
Coulomb = 1C = 1A x 1s = charge of approximately 6.242 x 1018 electrons.
Therefore the charge of 1 electron is 1 / 6.242 x 1018 C = 1.602 x 10-19 C
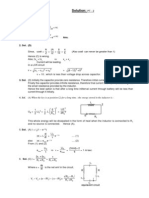
current=i=
dq Coulombs
=
= Ampere
dt
sec
voltage=v=
dw
Joules
=
=Volt
dq Coulombs
How many electrons pass through a wire carrying 10 A of current in 1 minute?
10 x 6.242 x 1018 x 60 = 3.742 x 1021 electrons.
A charge of 360 C pass through a conductor in 20 seconds, how many Amperes is that?
360 C / 20 S = 18 A
1 Joule = 1 N m (work or energy)
1 Watt = 1 J / s = 1 N-m / s (power)
1 Volt = 1 V = 1 J / 1 C = 1 N-m / 1 C = 1 W / 1A
You might also like
- Review Materials NTC LicenseDocument23 pagesReview Materials NTC Licensejoebanpaza194% (18)
- FE Exam Review2011Document53 pagesFE Exam Review2011Juan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 132 KV Aluminium Tube Bus Sizing CalculaDocument12 pages132 KV Aluminium Tube Bus Sizing CalculakamaleshsNo ratings yet
- Bej10303 Electric Circuit I: Dr. Nur Anida Binti JumadiDocument61 pagesBej10303 Electric Circuit I: Dr. Nur Anida Binti JumadiDaneshSathaNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge and CurrentDocument33 pagesElectric Charge and CurrenthasminNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class 10 NotesDocument10 pagesElectricity Class 10 NotesKota SrinadhNo ratings yet
- Numericals HveDocument24 pagesNumericals HveEdward Cullen100% (4)
- Mod. 1 Basic ElectricalDocument21 pagesMod. 1 Basic Electricalderping lemon100% (1)
- Electrical and Eletronic PrinciplesDocument206 pagesElectrical and Eletronic PrinciplesvelisbarNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Linear Circuits Analysis - 2e, DecarloDocument945 pagesSolution Manual Linear Circuits Analysis - 2e, DecarloJorge Silva Velez75% (4)
- ElectricityDocument196 pagesElectricityjingcong liuNo ratings yet
- Electric CurrentDocument4 pagesElectric CurrentMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Cont - . - .ElectricityDocument19 pagesCont - . - .ElectricityLJ ParfanNo ratings yet
- Physics Electricity CBSE 10Document8 pagesPhysics Electricity CBSE 10Ameen AbdullaNo ratings yet
- 4 ElectricityDocument49 pages4 ElectricityKaguya74No ratings yet
- PHYSICS 4th QuarterDocument86 pagesPHYSICS 4th QuarterJ i nNo ratings yet
- Tumangan Mod1 Act2Document8 pagesTumangan Mod1 Act2Mela TumanganNo ratings yet
- Electricity 1Document20 pagesElectricity 1api-255043845No ratings yet
- Electricity BasicsDocument47 pagesElectricity Basicspinev96397No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Electricity - Mabborang, Mary Kristelle UDocument4 pagesChapter 11 - Electricity - Mabborang, Mary Kristelle Uyram LetsirkNo ratings yet
- Mark Z. Jacobson Stanford UniversityDocument45 pagesMark Z. Jacobson Stanford Universityanmn123No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument40 pagesDocumentHaseeb AhemdaniNo ratings yet
- Basic in CircuitsDocument9 pagesBasic in CircuitsEllimacOdnumrebNo ratings yet
- HC Verma Solutions Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 Electric Current in ConductorsDocument22 pagesHC Verma Solutions Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 Electric Current in ConductorsAiraNo ratings yet
- Module Template 1.1Document23 pagesModule Template 1.1Allenzkie CuesoNo ratings yet
- Electricity 1Document22 pagesElectricity 1leena ronyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Basic Concepts: Today's ObjectivesDocument16 pagesChapter 1: Basic Concepts: Today's ObjectivesWan RodieNo ratings yet
- 2 - Current ElectricityDocument40 pages2 - Current ElectricityRamJiPandeyNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity NotesDocument26 pagesCurrent Electricity NotesSourav SahaNo ratings yet
- Circuitry Ch01 Basic ConceptsDocument19 pagesCircuitry Ch01 Basic ConceptsWasim MagsiNo ratings yet
- Electricity ProblemsDocument8 pagesElectricity ProblemsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Ec1semi2223 Chapter1 NurmizapdfDocument61 pagesEc1semi2223 Chapter1 NurmizapdfYathavan A/l KalaichlvanNo ratings yet
- Electricity Fundamental EquationsDocument5 pagesElectricity Fundamental EquationsKristian ForestNo ratings yet
- Eectricity C 10Document62 pagesEectricity C 10Gursharan SinghNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits Sample Problems and AnswersDocument5 pagesElectric Circuits Sample Problems and AnswerskakiksNo ratings yet
- Chapter1Document12 pagesChapter1consuelomorgadoNo ratings yet
- EEEB113 Chap 1 NotesDocument28 pagesEEEB113 Chap 1 NotesNabilahJasmiNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Class Notes 2024-25Document9 pagesElectricity - Class Notes 2024-25samasama.gldNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision On Electric (Calculation)Document1 pagePhysics Revision On Electric (Calculation)Lim JingNo ratings yet
- Solucionario 17Document28 pagesSolucionario 17web SoftNert ChileNo ratings yet
- ProblemDocument6 pagesProblemkatriellearnaultNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument91 pagesCurrent Electricityfriged spinnerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 IntroductionDocument33 pagesLesson 1 IntroductionEVITH BERNALDEZ. ALMONIANo ratings yet
- CH21 Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves PDFDocument32 pagesCH21 Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves PDFKristineNo ratings yet
- Bjte2023 WK02Document36 pagesBjte2023 WK02Hafiz khalidNo ratings yet
- Units of ElectricityDocument36 pagesUnits of ElectricityMSM7865No ratings yet
- As Unit1 Electricity 01 Electric CurrentDocument27 pagesAs Unit1 Electricity 01 Electric CurrentAvinash BoodhooNo ratings yet
- Electric CurrentDocument40 pagesElectric CurrentPankaj KumarNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument11 pagesElectricityskluckyskashifNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument4 pagesProblem SetPaul KellyNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Solution: SolutionDocument62 pagesElectricity: Solution: SolutionJatin PathakNo ratings yet
- Physics Cl10 Assign16Document2 pagesPhysics Cl10 Assign16Tapas Banerjee100% (1)
- Chapter 1 BNJ 10903 E&ETECHDocument45 pagesChapter 1 BNJ 10903 E&ETECHMuhammad NaufalNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions Electrical Engineering PDFDocument150 pagesObjective Questions Electrical Engineering PDFzahidqur2003100% (3)
- Solutions Exam 2001Document17 pagesSolutions Exam 2001bmmostefaNo ratings yet
- Solution:: DT DQ e RC C V BDocument5 pagesSolution:: DT DQ e RC C V BAritra LahiriNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electric Circuit: Ee1CpeDocument106 pagesFundamentals of Electric Circuit: Ee1CpeDark AngelNo ratings yet
- Electric CurrentDocument6 pagesElectric CurrentTakahiroTsubasaNo ratings yet
- Physics Lesson 1Document7 pagesPhysics Lesson 1nathanpiper10No ratings yet