Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Superposition of Electrostatic Forces
Uploaded by
pusa1230 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Superposition of Electrostatic Forces.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesSuperposition of Electrostatic Forces
Uploaded by
pusa123Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Superposition of Electrostatic Forces
COULOMBS LAW
The electrostatic force of interaction between
any two point charges is directly proportional to the
product of the magnitudes of the charges and
inversely proportional to the square of the distance
between the charges.
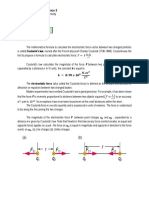
COULOMBS LAW IN VECTOR FORM
Suppose two similar charges q1 and q2 are placed at
points 1 and 2 with the position vectors and . As per
Coulombs law, the force on q2 applied by q1 will be
where is the unit vector in the direction from 1 to 2.
Similarly, force on q1 applied by q2 is
where is unit vector in the direction from 2 to 1.
is equal in magnitude and opposite in the direction of the vector .
Some important points regarding coulombs law
1. Electrostatic force is a conservative force i.e., work done by this force is path
independent and only depends on initial and final positions.
2. Electrostatic force is a central force, in the absence of any other external
force, angular momentum of one particle with respect to the other particle (in
two particle system) is conserved.
3. It follows inverse square law.
4. Electrostatic interaction may be attractive or repulsive.
5. Electrostatic force is medium dependent i.e., this force depends on the nature
of medium in between the two charges.
6. It follows superposition principle.
7. Electrostatic interaction is much stronger than the gravitation force.
You might also like
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 1: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #1From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 1: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #1No ratings yet
- Superposition of Electrostatic ForcesDocument3 pagesSuperposition of Electrostatic Forceseka123No ratings yet
- Superposition of Electrostatic ForcesDocument3 pagesSuperposition of Electrostatic Forceseka123No ratings yet
- Charges: Coulomb'S LawDocument3 pagesCharges: Coulomb'S Lawpusa123No ratings yet
- 1 Coulombs Law and Principle of SuperpositionDocument14 pages1 Coulombs Law and Principle of Superpositionpaulkani-ece100% (11)
- Principles of Physics - Electric Charge and Coulomb's LawDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Physics - Electric Charge and Coulomb's LawTonmoy RoyNo ratings yet
- phys12_c07_7_2Document7 pagesphys12_c07_7_2Andria EspejoNo ratings yet
- Coulomb's LawDocument14 pagesCoulomb's LawEngr Danyal ZahidNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICSDocument50 pagesELECTROSTATICSGladis Grace Restauro NaritNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument8 pagesElectricity and MagnetismAhmed ZarifNo ratings yet
- Coulomb's law electrical force equationDocument2 pagesCoulomb's law electrical force equationLorena Ordoñez BelloNo ratings yet
- What Is Coulomb-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesWhat Is Coulomb-WPS OfficeDesi Steve JobsNo ratings yet
- Coulombs LawDocument1 pageCoulombs LawrodwellheadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document88 pagesLecture 1rafiqshariatpur1200No ratings yet
- PHYSICS PresentationDocument22 pagesPHYSICS PresentationlynkimjoanNo ratings yet
- MasteringPhysics - CH 21 HW #5Document3 pagesMasteringPhysics - CH 21 HW #5Giancarlo Santos100% (2)
- Electric Charge & Field: Gauss' LawDocument25 pagesElectric Charge & Field: Gauss' Lawsuitup100No ratings yet
- Wa0000 1Document12 pagesWa0000 1varunr751No ratings yet
- Trinidad, John Rabbi (Electro Static Force) - Electricity and MagnitismDocument10 pagesTrinidad, John Rabbi (Electro Static Force) - Electricity and MagnitismJohn Ry-Mhel GatacilloNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument44 pagesElectrostaticsEbun EgbewunmiNo ratings yet
- The WTF A Level Package Physics Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesThe WTF A Level Package Physics Cheat Sheet7063673nasNo ratings yet
- Electrical ChargeDocument18 pagesElectrical ChargeSamrat100% (1)
- Electric ChargeDocument14 pagesElectric Chargefrancis solivenNo ratings yet
- Coulomb's Law and Electric Fields ExplainedDocument2 pagesCoulomb's Law and Electric Fields ExplainedJhon Cusme (jhoncusme)No ratings yet
- Applied Physics L-1Document27 pagesApplied Physics L-1Åñäs Prïñçē MäqbóòlNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument35 pagesChapter Onedavididosa40No ratings yet
- CCC Yenching College CKNGDocument12 pagesCCC Yenching College CKNGEmily LukNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument11 pagesDocumentArnnav MarwahNo ratings yet
- thiele_LE18Document18 pagesthiele_LE18amayaruiz55No ratings yet
- Ass. in Physics Q3Document1 pageAss. in Physics Q3joannapiezaNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 PDFDocument23 pagesPhysics 2 PDFFranchezca ChavezNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldsDocument9 pagesElectric Charges and FieldsSrushti ChouguleNo ratings yet
- 2 ElectrostaticsDocument83 pages2 ElectrostaticsNooh hereNo ratings yet
- Physics 42 Electricity & Magnetism: Instructor: Unofre B. Pili References: Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7Document28 pagesPhysics 42 Electricity & Magnetism: Instructor: Unofre B. Pili References: Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7Jerjer KingNo ratings yet
- Snell's Law: Force As A Vector QuantityDocument2 pagesSnell's Law: Force As A Vector QuantityMegan CabahugNo ratings yet
- How Charges Interact: Calculating Forces with Coulomb's LawDocument16 pagesHow Charges Interact: Calculating Forces with Coulomb's LawEduard Nonato IINo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Electricity and ElectronsDocument40 pagesLesson 1: Electricity and ElectronsBarakat IsmailNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics PDFDocument51 pagesElectrostatics PDFDanish JunejaNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism: Electric Charges and ForcesDocument56 pagesElectricity and Magnetism: Electric Charges and ForcesPortia A. EgkenNo ratings yet
- Electric charges and fields explainedDocument55 pagesElectric charges and fields explainedHitesh Bhatia100% (2)
- Physics Pro 12Document17 pagesPhysics Pro 12roshan rojerNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2 - Coulomb's LawDocument14 pagesLECTURE 2 - Coulomb's LawEngr Grace DT PNo ratings yet
- Reading Resource-1 (Electrostatics)Document40 pagesReading Resource-1 (Electrostatics)sambit1912No ratings yet
- Lecture 8 (1)Document26 pagesLecture 8 (1)ansat5.ansatNo ratings yet
- Electric Field: University of Zakho Faculty of Science Department of Physic 1 Stage MorningDocument7 pagesElectric Field: University of Zakho Faculty of Science Department of Physic 1 Stage MorningRayan KestayNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Electric Forces and FieldDocument39 pagesPhysics 2 Electric Forces and FieldMae MejaresNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge FundamentalsDocument10 pagesElectric Charge FundamentalsMuhammad HasanNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Electric FieldDocument15 pagesCh1 Electric FieldAkash tech. videoNo ratings yet
- Columbs LawDocument16 pagesColumbs Lawronil luzanoNo ratings yet
- Electric FieldDocument47 pagesElectric FieldUtkarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Understanding of How Electrostatic Works Using PhET Colorado Experimental Laboratory SimulatorDocument12 pagesUnderstanding of How Electrostatic Works Using PhET Colorado Experimental Laboratory Simulator48MUHAMMAD ARIEF MULYANANo ratings yet
- Class 12 ElectrostaticsDocument8 pagesClass 12 ElectrostaticsMathew AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics FundamentalsDocument36 pagesElectrostatics FundamentalsHadiya Deepak Hadiya DeepakNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic ForcesDocument3 pagesElectrostatic ForcesPrincess Roan RobertoNo ratings yet
- 2 ElectrostaticsDocument44 pages2 ElectrostaticsNooh hereNo ratings yet
- 2nd WeekDocument6 pages2nd WeekNanzkie Andrei SamanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23Document76 pagesChapter 23Sami HassounNo ratings yet
- Malabanan-Matthew Gt2 Phyla1Document6 pagesMalabanan-Matthew Gt2 Phyla1Matt MalabananNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge and Coulomb's LawDocument30 pagesElectric Charge and Coulomb's LawIsraat PorshiNo ratings yet
- January2012 Part2 PDFDocument7 pagesJanuary2012 Part2 PDFpusa123No ratings yet
- January2014 Part1 PDFDocument7 pagesJanuary2014 Part1 PDFpusa123No ratings yet
- Spring2002 PDFDocument14 pagesSpring2002 PDFpusa123No ratings yet
- January2012 Part1p PDFDocument7 pagesJanuary2012 Part1p PDFpusa123No ratings yet
- January2014 Part2 PDFDocument7 pagesJanuary2014 Part2 PDFpusa123No ratings yet
- January2012 Part2 PDFDocument7 pagesJanuary2012 Part2 PDFpusa123No ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics Ph.D. Qualifying ExaminationDocument6 pagesClassical Mechanics Ph.D. Qualifying Examinationpusa123No ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics Qualifier ExamDocument4 pagesClassical Mechanics Qualifier Exampusa123No ratings yet
- Ph.D. Qualifying Examination Department of Physics and Astronomy Wayne State UniversityDocument7 pagesPh.D. Qualifying Examination Department of Physics and Astronomy Wayne State Universitypusa123No ratings yet
- Physics exam solutions for classical mechanics, electromagnetism problemsDocument55 pagesPhysics exam solutions for classical mechanics, electromagnetism problemspusa123No ratings yet
- CM Qualifier2012fallDocument4 pagesCM Qualifier2012fallpusa123No ratings yet
- January2012 Part1p PDFDocument7 pagesJanuary2012 Part1p PDFpusa123No ratings yet
- Quals 2011 Sec 4Document13 pagesQuals 2011 Sec 4pusa123No ratings yet
- CM Qualifier2013fallDocument5 pagesCM Qualifier2013fallpusa123No ratings yet
- Qual CM Aug 2011Document3 pagesQual CM Aug 2011pusa123No ratings yet
- 2009 SpringDocument70 pages2009 Springpusa123No ratings yet
- 2008 FallDocument60 pages2008 Fallpusa123No ratings yet
- Algebra 1, April 2009Document1 pageAlgebra 1, April 2009pusa123No ratings yet
- Quals 2013 Sec 6Document16 pagesQuals 2013 Sec 6pusa123No ratings yet
- Analysis 1, April 2009Document1 pageAnalysis 1, April 2009pusa123No ratings yet
- CM 2014 SolnDocument11 pagesCM 2014 Solnpusa123No ratings yet
- TopologyQE, Jan 2010Document1 pageTopologyQE, Jan 2010pusa123No ratings yet
- Quals 2008 Sec 3Document16 pagesQuals 2008 Sec 3pusa123No ratings yet
- QF 09Document6 pagesQF 09pusa123No ratings yet
- QEProbability, January 2010Document1 pageQEProbability, January 2010pusa123No ratings yet
- Probability QE 0Document1 pageProbability QE 0pusa123No ratings yet
- The Klein Bottle Is Obtained From The Square I ( (X, Y) : 0 X, y 1) R by The Equivalence Relation (0, Y) (1, Y) and (X, 0) (1 X, 1)Document5 pagesThe Klein Bottle Is Obtained From The Square I ( (X, Y) : 0 X, y 1) R by The Equivalence Relation (0, Y) (1, Y) and (X, 0) (1 X, 1)Jonel PagalilauanNo ratings yet
- Analysis (Specialization)Document1 pageAnalysis (Specialization)pusa123No ratings yet
- Analysis1, QE, Jan 2010Document1 pageAnalysis1, QE, Jan 2010pusa123No ratings yet
- QF 05Document4 pagesQF 05pusa123No ratings yet
- Kuruk Etra:: Dharma-K Etra Śalya-ParvaDocument1 pageKuruk Etra:: Dharma-K Etra Śalya-ParvaRavinder Khullar100% (1)
- Analyzing Historical DocumentDocument4 pagesAnalyzing Historical DocumentChristine Joy VillasisNo ratings yet
- Combustion ChemistryDocument17 pagesCombustion Chemistryrajeev50588No ratings yet
- How To Make Lampblack - AllDocument6 pagesHow To Make Lampblack - AllclaudjiuNo ratings yet
- Problem29 40Document1 pageProblem29 40IENCSNo ratings yet
- Text 1 Is For No 1 - 4 The Rabbit Revenge: I. Pilihlah Salah Satu Jawaban Yang Benar!Document4 pagesText 1 Is For No 1 - 4 The Rabbit Revenge: I. Pilihlah Salah Satu Jawaban Yang Benar!Diandra MomentNo ratings yet
- Kwame Ture InterviewDocument8 pagesKwame Ture InterviewSumayya K AliNo ratings yet
- 2narrative Essay - My Favorite TeacherDocument9 pages2narrative Essay - My Favorite TeacherHerbertKoh100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Stability The Science and RegulationsDocument32 pagesPharmaceutical Stability The Science and RegulationsMostofa Rubal100% (1)
- Medical Services Recruitment Board (MRB)Document20 pagesMedical Services Recruitment Board (MRB)durai PandiNo ratings yet
- Sales Target Planning ToolkitDocument7 pagesSales Target Planning ToolkitCarmenLarisaNo ratings yet
- CaracterizacióndeSalpicadurasSMAW Molleda 2007Document5 pagesCaracterizacióndeSalpicadurasSMAW Molleda 2007Tamara Maria Ortiz MendezNo ratings yet
- CXO 7050 Rev 14.3.13 PDFDocument1 pageCXO 7050 Rev 14.3.13 PDFrajaramghoshNo ratings yet
- Midcheek Lift Using Facial Soft-Tissue Spaces of The MidcheekDocument11 pagesMidcheek Lift Using Facial Soft-Tissue Spaces of The MidcheekЩербакова ЛенаNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - Shock - Diagnosis and ManagementDocument10 pagesChapter 21 - Shock - Diagnosis and ManagementNeily Maulida UlfaNo ratings yet
- Social Engineering For Pentester PenTest - 02 - 2013Document81 pagesSocial Engineering For Pentester PenTest - 02 - 2013Black RainNo ratings yet
- Otr Product CatalogDocument116 pagesOtr Product CatalogIwan KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Vedic Healing Through Gems4Document3 pagesVedic Healing Through Gems4gesNo ratings yet
- Hindustani Music HistoryDocument28 pagesHindustani Music HistoryChamod ArunaluNo ratings yet
- Carlo Gavazzi EM26-96Document4 pagesCarlo Gavazzi EM26-96dimis trumpasNo ratings yet
- 286129Document23 pages286129Cristian WalkerNo ratings yet
- Power Over Ethernet - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesPower Over Ethernet - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaManitNo ratings yet
- Resume Masroor 3Document3 pagesResume Masroor 3mohammad masroor zahid ullahNo ratings yet
- 14 Ways To Acquire KnowledgeDocument4 pages14 Ways To Acquire KnowledgeRenato MiguelNo ratings yet
- ECMT1020 - Week 06 WorkshopDocument4 pagesECMT1020 - Week 06 Workshopperthwashington.j9t23No ratings yet
- Strategic Planning Assignment - TescoDocument16 pagesStrategic Planning Assignment - TescoKayode Trinity Omosebi100% (1)
- PreceptronDocument17 pagesPreceptroneng_kmmNo ratings yet
- Gabriel MarcelDocument6 pagesGabriel MarcelCeciBohoNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Appendix-Iii: Colligative PropertiesDocument3 pagesClass Xii Appendix-Iii: Colligative PropertiesSrijan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Taeka HaileleulDocument167 pagesTaeka HaileleulBini100% (1)