Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Income Effect and Substitution Effect
Uploaded by
darenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Income Effect and Substitution Effect
Uploaded by
darenCopyright:
Available Formats
Distinguish between the income effect and substitution effect using indifference curve.
Substitution effect
Substitution effect is the change in an items consumptions associated with a change in the price of
the item, with the level of utility held constant. When the price X declines, the substitution effect
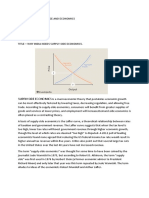
always leads to an increase in the quantity of X demanded. Graphically, the substitution effect is the
movement from point A to D. This point is on the same indifference curve as the original
consumption bundle and it is the point where a budget line that is parallel to the new budget line is
just tangent to initial indifference curve. The point D reflects the consumers choice if faced with the
new prices and the compensated income. The substitution effect is the difference between the
original consumption and the new intermediate consumption as shown on the graph below:
Income effect
The income effect is the change in an items consumption brought about by the increase in
purchasing power, with the price of the item held constant. It is the effect due to the change in real
income, when a persons income increases, the quantity demanded for the product may increase
(normal good) or decrease (inferior good). The income effect can be both positive and negative
depending on whether the product is a normal or inferior good.
You might also like
- National Income Accounting PPT at MBADocument58 pagesNational Income Accounting PPT at MBABabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- Different Complex Multipliers - Government, Expenditure, Tax and Balanced Budget MultiplierDocument15 pagesDifferent Complex Multipliers - Government, Expenditure, Tax and Balanced Budget MultiplierArundhuti RoyNo ratings yet
- Production FunctionDocument29 pagesProduction Functionsinghanshu21100% (2)
- Pricing With Market PowerDocument29 pagesPricing With Market PowerZoey O'BrienNo ratings yet
- Is-LM Open EconomyDocument16 pagesIs-LM Open EconomyAppan Kandala VasudevacharyNo ratings yet
- The Is-Lm Model: ECON 2123: MacroeconomicsDocument56 pagesThe Is-Lm Model: ECON 2123: MacroeconomicskatecwsNo ratings yet
- Relevance of Keynesian Theory To The Current EconomicDocument15 pagesRelevance of Keynesian Theory To The Current EconomicSiva Krishna Reddy NallamilliNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument25 pagesElasticityaljohn anticristoNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand and Supply ExplainedDocument55 pagesAggregate Demand and Supply Explainedcarl jaffersonNo ratings yet
- Investment FunctionDocument23 pagesInvestment FunctionAamir KhanNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4 Demand For MoneyDocument13 pagesCh. 4 Demand For Moneycoldpassion100% (1)
- Money and Inflation: AcroeconomicsDocument67 pagesMoney and Inflation: Acroeconomicsaditya prudhviNo ratings yet
- Income & Substitution EffectDocument4 pagesIncome & Substitution EffectRishabh HajelaNo ratings yet
- Price EffectDocument6 pagesPrice EffectKarpagam MahadevanNo ratings yet
- CH 1 EconometricsDocument49 pagesCH 1 EconometricsGenemo FitalaNo ratings yet
- Free Trade Benefits and DrawbacksDocument21 pagesFree Trade Benefits and Drawbacksrajan2778No ratings yet
- The Modern Theory of Income and EmploymentDocument12 pagesThe Modern Theory of Income and EmploymentShivani Goel100% (1)
- Essay On Consumer's Equilibrium - EconomicsDocument15 pagesEssay On Consumer's Equilibrium - EconomicsUsman KhanNo ratings yet
- Breaking Up Price Effect Into Income and Substitution EffectDocument9 pagesBreaking Up Price Effect Into Income and Substitution Effectanushka KumariNo ratings yet
- Income and substitution effects of a price change explained in 40 charsDocument4 pagesIncome and substitution effects of a price change explained in 40 charsVenkat NarayananNo ratings yet
- Theory of MultiplierDocument9 pagesTheory of MultiplierUday PanditNo ratings yet
- MEI vs MEC - Understanding Investment Elasticity and Expected ReturnsDocument2 pagesMEI vs MEC - Understanding Investment Elasticity and Expected ReturnsshashankNo ratings yet
- The Circular Flow of Income Lesson 1 and 2Document16 pagesThe Circular Flow of Income Lesson 1 and 2api-53255207No ratings yet
- Macro Economics 11e Arnold CH 7 Homework No4Document5 pagesMacro Economics 11e Arnold CH 7 Homework No4PatNo ratings yet
- National Income AccountsDocument13 pagesNational Income AccountsPlatonicNo ratings yet
- Income and Substitution Effects ExplainedDocument3 pagesIncome and Substitution Effects ExplainedMatthew MulleyNo ratings yet
- 9.6 Keynesian MultiplierDocument23 pages9.6 Keynesian MultiplierkimmoNo ratings yet
- National Income DeterminationDocument27 pagesNational Income Determinationsachinrema100% (1)
- National IncomeDocument4 pagesNational Incomesubbu2raj3372No ratings yet
- MultiplierDocument47 pagesMultiplierShruti Saxena100% (3)
- Theory of Marginal Utility AnalysisDocument4 pagesTheory of Marginal Utility AnalysisBalasingam Prahalathan100% (3)
- Income and Substitution Effects of A Wage ChangeDocument24 pagesIncome and Substitution Effects of A Wage ChangemanashchoudhuryNo ratings yet
- The IS-LM Model: Equilibrium: Goods and Money Markets Understanding Public PolicyDocument37 pagesThe IS-LM Model: Equilibrium: Goods and Money Markets Understanding Public PolicyShashank Shekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- What is the difference between economic growth and developmentDocument19 pagesWhat is the difference between economic growth and developmentsdsdawoodNo ratings yet
- The Simple Keynesian Model of Income Determination ExplainedDocument60 pagesThe Simple Keynesian Model of Income Determination ExplainedRakesh Seela100% (2)
- Consumer Theory of Demand (Indifference Curve Analysis)Document32 pagesConsumer Theory of Demand (Indifference Curve Analysis)Breanna CampbellNo ratings yet
- Hec Ohlin TheoryDocument13 pagesHec Ohlin TheoryPavithra PRabhuNo ratings yet
- Production Analysis PPT at BEC DOMSDocument26 pagesProduction Analysis PPT at BEC DOMSBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- Price and Output Determination Under Different Market StructuresDocument19 pagesPrice and Output Determination Under Different Market StructuresAnkush Bhoria43% (7)
- Harrod Model of Growth Explained in DepthDocument6 pagesHarrod Model of Growth Explained in Depthvikram inamdarNo ratings yet
- National Income As An Index of DevelopmentDocument7 pagesNational Income As An Index of DevelopmentNguyễn Tùng SơnNo ratings yet
- Income Elasticity of Demand: InterpretationDocument10 pagesIncome Elasticity of Demand: Interpretationabhijeet9981No ratings yet
- Explain The Functions of Price in A Market EconomyDocument6 pagesExplain The Functions of Price in A Market Economyhthomas_100% (5)
- Managerial Economics Lecture NotesDocument21 pagesManagerial Economics Lecture NotescprabhakaranNo ratings yet
- THEORY Cost of ProductionDocument16 pagesTHEORY Cost of ProductionKum Rene EbuaNo ratings yet
- U II: T K T D N I: NIT HE Eynesian Heory of Etermination of Ational NcomeDocument56 pagesU II: T K T D N I: NIT HE Eynesian Heory of Etermination of Ational NcomePrateek GoyalNo ratings yet
- Partial Equilibrium: EconomicsDocument5 pagesPartial Equilibrium: EconomicsSamantha SamdayNo ratings yet
- Revealed Preference TheoremDocument10 pagesRevealed Preference TheoremelinexaxaNo ratings yet
- Consumption and SavingDocument6 pagesConsumption and Savingmah rukhNo ratings yet
- 4Document445 pages4lilylikesturtle75% (4)
- Intermediate Macro Economics - Assignment 1 PDFDocument12 pagesIntermediate Macro Economics - Assignment 1 PDFTriple HNo ratings yet
- Static and Dynamic Effects of Customs Union - Part2Document24 pagesStatic and Dynamic Effects of Customs Union - Part2djvapidNo ratings yet
- Consumer Surplus Explains Water-Diamond ParadoxDocument13 pagesConsumer Surplus Explains Water-Diamond ParadoxAnushriAdarshRathiNo ratings yet
- Business Economics Why India Needs Supply Side EconomicsDocument7 pagesBusiness Economics Why India Needs Supply Side Economicsrishi jainNo ratings yet
- Ricardian or Classical Theory of Income DistributionDocument15 pagesRicardian or Classical Theory of Income DistributionketanNo ratings yet
- Welfare EconomicsDocument4 pagesWelfare EconomicsManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Relative Income HypothesisDocument8 pagesRelative Income Hypothesisthafsira100% (2)
- SEO-Optimized Title for Document on Substitution and Income EffectsDocument14 pagesSEO-Optimized Title for Document on Substitution and Income EffectsPAUL TIMMYNo ratings yet
- Econ Task A1 (1) Anglia Ruskin UniversityDocument4 pagesEcon Task A1 (1) Anglia Ruskin Universitytowshield50% (4)
- MICRO ECONOMICSDocument63 pagesMICRO ECONOMICStimepass22551No ratings yet