Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atomic Structure: Proton: Charge (+ve) Mass Element Neutron: Mass Electron: Charge (-Ve)
Atomic Structure: Proton: Charge (+ve) Mass Element Neutron: Mass Electron: Charge (-Ve)
Uploaded by
TiaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atomic Structure: Proton: Charge (+ve) Mass Element Neutron: Mass Electron: Charge (-Ve)
Atomic Structure: Proton: Charge (+ve) Mass Element Neutron: Mass Electron: Charge (-Ve)
Uploaded by
TiaCopyright:
Available Formats
Green House Gases:
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
Water Vapour
Carbon dioxide
Methane
Nitrous Oxide
Ozone
CFCs
My favourite gases:
1) Methane
2) Ethane
3) Propane
4) Butane
Name Gases:
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
Laughing gas: N2O
Water gas: H2 + CO
Coal gas: Mixture of many hydrocarbons
Tear gas: Chloropicrin, CN, CR, CS, Pepper-spray etc.
Acid rain: Oxides of Sulfur or Nitrogen + Water = HNO3 + H2SO4
Gobar gas (bio gas): CH4 + CO + H2 + CO2 + SO2
Bhopal Gas Tragedy : Methyl Isocynate
Atomic Structure
Proton:
Charge (+ve)
Mass
Element
Neutron: Mass
Electron: Charge (-ve)
Isotopes:
C-14 is radioactive
Half-life = 5730 years
Used in radioactive dating (carbon dating)
Undergoes Beta decay
C-12
C-13
C-14
N-14
Atomic
Number (p)
6
6
6
7
Isotopes
Isotopes of Hydrogen
1) Protium
2) Deuterium
3) Tritium
Mass Number
(p+n)
12
13
14
14
Isobars
Neutron
Number (n)
6
7
8
7
Isotones
Atomic number Mass number
radioactivity
-2
-4
radioactivity
+1
0
radioactivity
0
0
H2O
D 2O
T2O
Light Water
Heavy Water
Tritiated Water
Heavy water is used in nuclear reactors as moderator and coolant. India is the largest
producer of Heavy Water in the world.
Metals lose electrons
Non-metals either gain electrons, or exist as noble gases
Every atom has tendency to fill its outermost orbit with 8 electrons
Metalloids are between metals and non-metals. Examples: Si and Ge
Property
pH
Physical nature
Acid
Less than 7.0.
Taste sour.
depends on concentration of
Strength
H+ ions
Phenolphthalein
remains colorless
Other
Electrolytes, conduct
Properties
electricity
Acids free hydrogen ions (H+)
Dissociation
when mixed with water.
Made of
Oxides of non-metals
Examples
Acetic acid, Sulfuric acid
Acids change litmus paper
Litmus test
red.
pH + pOH = 14
Acids + Base = Salt + Water
Base
Greater than 7.0
Bases feel slippery. Taste bitter.
depends on concentration of OHMakes it pink
Electrolytes, conduct electricity
Bases free hydroxide ions (OH-) when mixed with
water.
Oxides of metals
Sodium Hydroxide, Ammonia
Bases change litmus paper blue.
Oxydation: Loss of electrons
Reduction: Gain of electrons
Nuclear reactions:
1) Fission
2) Fusion
Fission (Top)
Fusion (Left)
You might also like
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- Student Pocket HandbookDocument64 pagesStudent Pocket Handbookadarsh_mrNo ratings yet
- Bod and CodDocument66 pagesBod and CodKamlesh Kamlesh EtwaroNo ratings yet
- Olympiad Model Paper 2018Document9 pagesOlympiad Model Paper 2018deeyamullaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument13 pagesChemistryas2182No ratings yet
- Hydrogen Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Chlorine Hydrogen Chloride GasDocument4 pagesHydrogen Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Chlorine Hydrogen Chloride GashamsterraymandsNo ratings yet
- SNC2D - ReviewDocument4 pagesSNC2D - ReviewZeenat ShahidullahNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Life: Atoms and MoleculesDocument50 pagesThe Chemistry of Life: Atoms and MoleculesZaman RaiNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Life: Atoms and MoleculesDocument50 pagesThe Chemistry of Life: Atoms and MoleculesZaman RaiNo ratings yet
- Covalent BondingDocument4 pagesCovalent Bondingbooksale SiNo ratings yet
- 1.6B Solutions For Molecular Compounds, Extra ExercisesDocument2 pages1.6B Solutions For Molecular Compounds, Extra ExercisesDaniel StandringNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument37 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Atoms, Molecules and IonsSeth CapellanNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Nomenclature: AnionsDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistry Nomenclature: Anions65yyssNo ratings yet
- P Block Elements in PPT FormDocument138 pagesP Block Elements in PPT FormharshadNo ratings yet
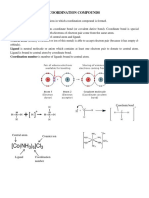
- Nomenclature of Coordination Complexes With KeyDocument7 pagesNomenclature of Coordination Complexes With KeyUmendra KhokharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 CHDocument11 pagesChapter 4 CHPuneet AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 10 Important Questions For CbseDocument69 pagesChemistry Class 10 Important Questions For CbseRam LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Chemical NomenclatureDocument23 pagesChemical NomenclatureDương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Topic: General Organic Chemistry-IDocument21 pagesTopic: General Organic Chemistry-IWTF GammerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 10Document2 pagesChemistry 10Talha AzizNo ratings yet
- Chemistry McqsDocument3 pagesChemistry McqsSHeHzAdA MALiK EHtiShAm AzAmNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PDFDocument13 pagesChemistry PDFTiaNo ratings yet
- Memorization List: Ions-Names and ChargeDocument4 pagesMemorization List: Ions-Names and ChargepringlekNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument22 pagesCarbon and Its Compoundsrameshchinnala123No ratings yet
- SPM Form 4 Terminology and Concepts Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument7 pagesSPM Form 4 Terminology and Concepts Chemical Formulae and EquationsJedidah JongNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesOrganic ChemistryKhin Mg WinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Reference TablesDocument8 pagesChemistry Reference Tablescauten2100% (1)
- SAT Subject Chemistry SummaryDocument25 pagesSAT Subject Chemistry SummaryYoonho LeeNo ratings yet
- Struct 4c2Document2 pagesStruct 4c2mariesonguilao92No ratings yet
- Chem 301: 2004MT1Document2 pagesChem 301: 2004MT1AmirKazemianNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Reference SheetDocument12 pagesChemistry Reference SheetJaneFreeNo ratings yet
- 04 Chem Review 3Document36 pages04 Chem Review 3Khizra Abdul shakoorNo ratings yet
- Faculty Selection Test Chemistry: Pre-Foundation Sample PaperDocument7 pagesFaculty Selection Test Chemistry: Pre-Foundation Sample PaperRam Ji PandeyNo ratings yet
- Ternary CompoundsDocument27 pagesTernary CompoundsIam PaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument15 pagesChapter 4 - Carbon and Its Compoundsnorthamericaffid31No ratings yet
- Hots 7Document3 pagesHots 7rahulNo ratings yet
- 6a. Naming Covalent CompoundsDocument5 pages6a. Naming Covalent CompoundsSahar HakimiNo ratings yet
- (L1) - Coordinate Compounds - 28th NovDocument32 pages(L1) - Coordinate Compounds - 28th NovKhushi RathoreNo ratings yet
- AirDocument29 pagesAirdefiantnxds9No ratings yet
- Types of Chem ReactionsDocument32 pagesTypes of Chem ReactionsKarlyn C. AngNo ratings yet
- (a) mixture of oо and pоbromotoluenesDocument19 pages(a) mixture of oо and pоbromotoluenesmotikaviNo ratings yet
- CARBON COMPOUND (Asid Carboxylic)Document24 pagesCARBON COMPOUND (Asid Carboxylic)Shirley SimonNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument30 pagesGreenhouse EffectFernan SibugNo ratings yet
- 10.5. Chemical Nomenclature - Molecular Compounds and AcidsDocument17 pages10.5. Chemical Nomenclature - Molecular Compounds and AcidsNina Anne Marie PascualNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds NotesDocument27 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds NotesBALAJI VARA PRASAD100% (1)
- CU-2020 B.Sc. (General) Chemistry Semester-III Paper-CC3-GE3 QPDocument4 pagesCU-2020 B.Sc. (General) Chemistry Semester-III Paper-CC3-GE3 QPSatyajitDeyNo ratings yet
- Pollution: Elisabeth Deta Lustiyati, M.Si / 0856.281.2724Document10 pagesPollution: Elisabeth Deta Lustiyati, M.Si / 0856.281.2724prilly melaniNo ratings yet
- Week 1 For Students BDocument15 pagesWeek 1 For Students BNazym TurkebayNo ratings yet
- اختصاراتDocument2 pagesاختصاراتMaha ZNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 4 - Learn CBSEDocument1 pageCarbon and Its Compounds Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 4 - Learn CBSEArnav KumarNo ratings yet
- AIPMT 2015 Sample PaperDocument26 pagesAIPMT 2015 Sample PaperFirdosh Khan100% (3)
- Term I Chemistry Practical Examination: Salt Analysis-McqsDocument9 pagesTerm I Chemistry Practical Examination: Salt Analysis-McqsHarishankar SNo ratings yet
- 2007 Aus. Chem OlympiadDocument31 pages2007 Aus. Chem OlympiadRunpeng LiuNo ratings yet
- Carbonyls, Phosphine Complexes and Substitution ReactionsDocument66 pagesCarbonyls, Phosphine Complexes and Substitution ReactionsFitriani SariNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument4 pagesCoordination Compoundskatarina sladeckovaNo ratings yet
- 1.1.0.1.5 Data Tables For Periodic TableDocument1 page1.1.0.1.5 Data Tables For Periodic TablebashanabilNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972From EverandCoordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972A. B. P. LeverNo ratings yet