Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Full Syllabus
Uploaded by
Santhana BharathiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Full Syllabus
Uploaded by
Santhana BharathiCopyright:
Available Formats
B.E.
(MECHANICAL ENGINEERING)
2011 Regulations, Curriculum & Syllabi
BANNARI AMMAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
(Autonomous Institution Affiliated to Anna University of Technology -Coimbatore
Approved by AICTE - Accredited by NBA and NAAC with A Grade and ISO 9001:2008 Certified)
SATHYAMANGALAM 638 401 Erode District Tamil Nadu
Phone: 04295 226000 Fax: 04295 226666
Web: www.bitsathy.ac.in E-mail:bitsathy@bannari.com
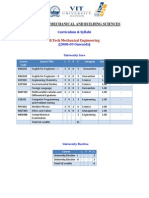
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
CURRICULAM DESIGN & INTERLINKING OF COURSES
360 o
FLEXIBLE
LEARNING
FRAME WORK
XIII
Professional
Ethics
Elective V
Elective VI
Project Phase
II
Total Quality
Management
Computer
Integrated
Manufacturing
Roboticsand
Machine Vision
System
Automotive
Electronics
Elective III
Elective IV
ComputerAided
Design and
ComputerAided
Manufacturing
laboratory
Robotics
Laboratory
Project Work
Phase I
Modelling and
Simulation
Applied
Hydraulics &
Pneumatics
Micro
Controller and
PLC
Design of
Mechatronics
System
Dimensional
Metrology
Elective II
Micro
Controller and
PLC Lab
Hydraulics and
Pneumatics
Lab
Technical
Seminar
Engineering
Metrology &
Quality
Assurance
ElectroMagneti
c Theory
Instrumentatio
n and Control
Systems
CNC
Technology
Sensors and
Signal
Processing
Elective I
Instrumentatio
n & Controls
Laboratory
CNC
Laboratory
Sensors and
Signal
Processing
Laboratory
Numerical
Methods
Microprocessor
s and
Applications
Strength of
Materials
Power
Electronics
Control
Systems
Dynamics of
Machinery
Microprocessor
s Lab
Machine
Dynamics Lab
Power
Electronics
Laboratory
Engineering
Mathematics
III
Engineering
Materials &
Metallurgy
Fluid
Mechanics &
Machineries
Digtal
Electronics
Electrical
Machines and
Drives
Kinematics of
Machinery
Fluid
Mechanics &
Machinery Lab
Electrical
Machines and
Drives Lab
Computer
Aided machine
Drawing
Engineering
Mathematics II
Engineering
Chemistry
Language Elective
Engineering
Mechanics
Applied
Material
Science
Manufacturing
Processes
C
Programming
Engineering
Chemistry
Laboratory
Manufacturing
Technology
Lab I
Engineering
Mathematics I
Engineering
Physics
Communicativ
e English
Basics of Civil
& Mechanical
Engineering
Envrionmental
Science
Basics of
Electrical &
Electronics
Engineering
Engineering
Graphics
Engineering
Phyiscs
Laboratory
Workshop
Practice
S8
S7
S6
S5
S4
S3
S2
S1
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Approved in Sixth Academic Council Meeting
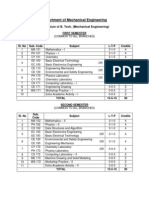
B.E. MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
(Minimum credits to be earned: 193)
First Semester
Code
No.
11O101
11O102
Objectives & Outcomes
PEOs
POs
I
(a)
Course
Engineering Mathematics I*
Engineering Physics
Language Elective I *
11O202
11O105
Environmental Science
Basics of Civil and Mechanical Engineering
**
11O205
Basics of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
11O208
Engineering Graphics$
11O108
Engineering Physics Laboratory
11M209
Workshop Practice
3.5
(a)
3.0
IV
(f)
3.0
(a), (h)
3.0
II
(a)
4.0
II
(a), (g)
4.0
III
(a,) (d)
3.0
(a)
1.0
(a)
1.0
22
25.5
3.5
Total
Second Semester
Code
No.
11O201
11O103
Objectives & Outcomes
PEOs
POs
I
(a)
Course
Engineering Mathematics II*
*
Engineering Chemistry
*
(a)
3.0
11M204
11M106
Language Elective II
Applied Materials Science@
Engineering Mechanics
IV
II
II
(f)
(a,) (c)
(a)
3
3
3
1
0
0
0
0
0
3.5
3.0
3.0
11M206
Manufacturing Processes
II
(c), (g),( i)
3.0
11M207
Manufacturing Technology Laboratory I
II
(c), (g)
1.0
11M107
C Programming
(a), (g)
3.5
(a)
1.0
20
24.5
11O109
Engineering Chemistry Laboratory
Total
Common for all branches of B.E./B.Tech
**
Common to all branches of B.E./B.Tech AE & CE; ECE,EIE,ME,MXE,BT &TT (I Semester) and to CSE,EEE,FT,IT &TT (II
Semester)
+
Common for all branches of B.E./B.Tech except ECE,EEE & EIE; AE,CSE,ME,MXE,IT & FT (I Semester) and to CE,BT&TT (II
Semester)
$
Common for CE,EEE,ME,MXE,BT,IT & TT (I Semester); AE,CSE,ECE,EIE & FT (II Semester)
#
Common for AE,CSE, ECE & EIE , ME & MXE (I Semester); CE,EEE,BT,IT,TT & FT (II Semester)
@
Common for AE, CE, MXE & ME
Common to AE,CE,CSE,ECE & EIE (I Semester); EEE,ME,MXE,BT,IT,TT & FT (II Semester)
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Approved in Sixth Academic Council Meeting
Third Semester
Code No.
Objectives & Outcomes
PEOs
POs
Course
11O301
Engineering Mathematics III*`
(a)
3.5
11M302
Engineering Materials and Metallurgy
II
(c)
3.0
11M303
Electrical Machines and Drives
(a)
3.0
11M304
Engineering Thermodynamics
II
(b), (i)
3.5
11M305
Fluid Mechanics and Machinery
II
(b), (i)
3.5
11M306
Manufacturing Technology
II
(c), (g)
3.0
11M307
Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory
II
(e), (k)
1.5
11M308
Electrical Machines Laboratory
(a), (e)
1.5
11M309
Manufacturing Technology Laboratory II
II
(c), (e), (i), (k)
1.5
18
24.0
Total
Fourth Semester
Code No.
Objectives & Outcomes
PEOs
POs
Course
11M401
Numerical Methods**
(a)
3.5
11M402
Theory of Machines I
II
(d), (k)
3.5
11M403
Computer Aided Design
II
(d)
3.0
11M404
Thermal Engineering
II
(b), (i)
3.5
11M405
Strength of Materials
II
(c)
3.5
III
(d)
3.0
II
(a), (e), (k)
1.5
II
(c), (e), (k)
1.5
II
(a),(e)
2.5
19
25.5
11M406
Engineering Design Concepts
11M407
Thermal Engineering Laboratory I
11M408
11M409
Strength of Materials and Metallurgy
Laboratory
Computer Aided Machine Drawing
Laboratory
Total
*
**
Common to all branches of B.E./B.Tech except BT and CSE
Common to Aero, MXE, ME and CE
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Approved in Sixth Academic Council Meeting
Fifth Semester
Objectives & Outcomes
PEOs
POs
Code No.
Course
11M501
Engineering Metrology and Quality Assurance
II
(a), (c)
3.0
11M502
Theory of Machines II
II
(i),(k)
3.5
11M503
Heat and Mass Transfer
II
(b), (g),(i)
3.5
11M504
Design of Machine Elements
III
(C)
3.5
11M505
Total Quality Management
IV
(e), (h), (k)
3.0
3.0
Elective I
11M507
Instrumentation and Dynamics Laboratory
II
(e)
1.5
11M508
Thermal Engineering Laboratory II
II
(b), (g), (i)
1.5
11M509
Metrology Laboratory
IV
(f)
1.5
11M510
Technical Seminar I
1.0
15
25.01
Total
Sixth Semester
Code No.
Objectives & Outcomes
PEOs
POs
Course
11M601
Automated Manufacturing
II
(h), (k)
3.0
11M602
Hydraulics and Pneumatics
II
(a), (g)
3.0
11M603
Design of Transmission Systems
II
(i), (k)
3.5
11M604
Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion
II
(a), (b), (i)
3.0
11M605
Operations Research
II
(a), (g),(i)
3.0
3.0
Elective II
11M607
Computer Aided Manufacturing Laboratory
II
(c), (g),( j),
(k)
1.5
11M608
Microprocessors and Microcontrollers
Laboratory
(g), (i), (j)
3.0
11M609
Technical Seminar II
IV
(f)
1.0
17
24.01
Total
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Approved in Sixth Academic Council Meeting
Seventh Semester
Code No.
Objectives & Outcomes
PEOs
POs
(a), (b), (g), (i),
IV
(k)
Course
3.0
11O701
Engineering Economics*
11M702
Mechatronics
(g), (i)
3.0
11M703
Finite Element Methods
II
(d), (i), (k)
3.5
11M704
Power Plant Engineering
II
(b)
3.0
Elective III
3.0
Elective IV
3.0
11M707
Computer Aided Engineering Laboratory
II
(d), (i), (k)
1.5
11M708
Mechatronics Laboratory
(g), (i)
1.5
11M709
Project Work Phase I
III
(e)
3.0
12
24.52
2.0
Elective V
3.0
Elective VI
3.0
12.0
20.02
Total
Eighth Semester
Code No.
11O801
11M804
Objectives & Outcomes
PEOs
POs
Course
Professional Ethics*
IV
Project Work Phase II
III
(e), (f), (h)
(e)
Total
11
Minimum credits to be earned. The maximum number of credits as well as the total number of L T P hours may vary depending upon the
elective courses opted
*
Common to all branches of B.E./B.Tech
Minimum credits to be earned. The maximum number of credits as well as the total number of L T P hours
may vary depending upon the elective courses opted
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Approved in Sixth Academic Council Meeting
ELECTIVES
L
LANGUAGE ELECTIVE I
11O10B
Basic English I
3.0
11O10C
Communicative English
3.0
3
3
3
3
3
3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
3.0
3.5
3.5
3.5
3.5
3.5
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.5
3.0
3
3
3
4
3
3
3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
3.0
3.0
3.0
4.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
LANGUAGE ELECTIVE II
11O20B
11O20C
11O20H
11O20G
11O20J
11O20F
Basic English II
Advanced Communicative English
Hindi
German
Japanese
French
DISCIPLINE ELECTIVES
Thermal Engineering
11M001
11M002
11M003
11M004
11M005
11M006
11M007
Internal Combustion Engines
Computational Fluid Dynamics
Direct Energy Conversion Techniques
Cryogenic Engineering
Refrigeration and Air-conditioning
Renewable Energy sources
Automobile Engineering
Design Engineering
11M008
11M009
11M010
11M011
11M012
11M013
11M014
11M015
Instrumentation and Control Engineering
Design of Jigs and Fixtures and Press Tools
Composite Materials and Mechanics
Design of Heat Exchangers
Vibration and Conditions Monitoring
Mechanical Behavior of Materials
Design of Mechanical Drives
Engineering Innovation
Advanced Technology
11M016
11M017
11M018
11M019
11M020
11M021
11M022
Automotive Electronics
Micro-Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS)
Nano-Technology
Design of AirCraft Structures
Flexible Manufacturing Systems
Computer Integrated Manufacturing
Non Traditional Machining Processes
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Approved in Sixth Academic Council Meeting
Production Engineering
11M023
11M024
11M025
11M026
11M027
11M028
11M029
Advanced Casting Processes
Metal Forming
Process Planning and Cost Estimation
Industrial Robotics
Rapid prototyping
Welding Technology
Industrial Engineering
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3
3
3
3
3
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
3.5
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.5
3
3
3
3
3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3
3
3
3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3
3
0
0
0
0
3.0
3.0
General and Management
11M030
11M031
11M032
11M033
11M034
Probability and Statistics
Marketing Management
Organizational Behavior and Management
Principles of Management
Optimization Techniques for Engineering Application
PHYSICS ELECTIVES
11O0PA
11O0PB
11O0PC
11O0PD
11O0PE
Nano Science and Technology
Laser Technology
Electro-Optic Materials
Vacuum Science and Deposition Techniques
Semiconducting Materials and Devices
CHEMISTRY ELECTIVES
11O0YA
11O0YB
11O0YC
11O0YD
Polymer Chemistry and Processing
Energy Storing Devices and Fuel Cells
Chemistry of Nanomaterials
Corrosion Science and Engineering
ENTREPRENEURSHIP ELECTIVES$
11O001
11O002
Entrepreneurship Development I
Entrepreneurship Development II
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Approved in Sixth Academic Council Meeting
ONE CREDIT COURSES*
11M0XA
11M0XB
11M0XC
11M0XD
11M0XE
11M0XF
11M0XG
11M0XH
11M0XI
Condition Monitoring
Design for Manufacture and Assembly
Design of Experiments using Taguchi Approach
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing
Intelligent Optimization Techniques
Lean Manufacturing
Supply Chain Management
Tool Design and Manufacturing
Total Productive Maintenance
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
3.0
SPECIAL COURSES
11M0RA
11M0RB
11M0RC
11M0RD
Design of Automotive Systems
Geometric Modeling of CAD
Design of Experiment
Industrial Safety
Offered during VI and VII semesters only
Pre-requisite for this course is Entrepreneurship Development I
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11O101 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS-I
(Common to all Branches)
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
Acquire knowledge in matrix theory, a part of linear algebra, which has wider application in
engineering problems.
To make the student knowledgeable in the area of infinite series, their convergence and to solve
first and higher order differential equations using Laplace transform.
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects and
thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
Acquire more knowledge in basic concepts of engineering mathematics.
2.
To improve problem evaluation technique.
3.
Choose an appropriate method to solve a practical problem.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
Blooms
Taxonomy
(New Version)
Test I1
Test II1
Remember
20
20
20
20
Understand
40
40
40
40
Apply
30
30
30
30
Analyze/ Evaluate
10
10
10
10
Create
100
100
100
100
Total
Model Examination1
End Semester
Examination
Remember
1
State Cayley Hamilton theorem.
Define eigen value and eigen vector of a matrix.
3. Write the definition of convergence and divergence of a series.
1
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted to 20 and model examination will be converted to 20.
The remaining 10 marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly, internal assessment will be
calculated for 50 marks.
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
4. State the necessary and sufficient condition for the differential equation to be exact.
5. Write the Radius of curvature in cartesian coordinates.
6. Define evolute, centre of curvature and Circle of curvature.
7. Write the Leibneitzs form of linear equation in x and y.
8. Write the general form of Eulers and Legendre linear differential equations.
9. Define Convolution of two functions on Laplace transform.
10. State the existence conditions for Laplace transform.
Understand
1. Find eigen values and eigen vectors of the matrixA = 3
2
5
1
1
3
2. Find the radius of curvature at ( a,0) on the curve xy2 = a3 x3
3. Find the circle of curvature of the parabola y2 = 12x at the point ( 3.6)
4. Solve cos2 x
dy
+ y = tan x
dx
5 Solve y (2xy + ex ) dx = ex dy.
6. Find evolute of the parabola x2 = 4ay.
7. Solve ( D2 + 4 ) y = x2 .
8 Solve ( D 3 ) 2 y = x e-2x.
9. Find the Laplace transform of e2t sin3t.
10. Find the laplace transform of t cos4t.
Apply
3
1
1
1. Diagonalise the matrix A=
1
3
1
1
by means of an orthogonal transformation
1
3
1
2. Find the inverse of the matrix A = 4
3
2
2
3 us ing Cayley Hamilton theorem.
1
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
3 3 .4 3 .4 .5
+
+
+ .....
4 4 .6 4 .6 .8
3. Test the convergence of the series
4. Using Convolution theorem, find inverse Laplace transform of
1
.
( s + 1 )( s + 2 )
5. Use method of variation of parameters , to solve (D2+4)y = tan 2x
6. Use Laplace transform to solve ( D2 + 4D + 13) y = e-t sin t, given y = 0 and Dy = 0 at t = 0.
7. Test for convergence of the series
1+ n
8. Use Bernoullis equation to solve xy ( 1 + xy2 )
9. Use Leibnitzs linear equation to solve
10. Use Laplace Transform to evaluate,
( x + 1)
e t (sin
t
dy
=1
dx
dy
y = e 2 x ( x + 1) 2
dx
3t )
dt
Analyze / Evaluate
2
1. Reduce the quadratic form 8x 1 +7x 2 +3x 3 -12x 1 x 2 -8x 2 x 3 +4x 3 x 1 to canonical form by orthogonal
transformation and find the rank, signature, index and the nature.
2. Reduce 3x + 5y + 3z - 2yz + 2zx - 2xy to its canonical form through an orthogonal transformation
and find the rank, signature, index and the nature.
3. Find the evolute of the cycloid : x = a( +sin ) ; y = a(1 - cos ).
4. Find the circle of curvature of
a a
x + y = at ,
4 4
5. Discuss the convergence of the series
1
2
3
+
+
+ ...
3 .4 .5 4 .5 .6 5 .6 .7
2
6. Verify Cayley-Hamilton theorem for the matrix A=
1
1
1
2
1
1
. Hence find its inverse.
1
2
7. Using the method of variation of parameters, solve (D2 + a 2) y = tan ax.
8. Solve (x2D2 + 4xD + 2) y = x2 +
1
.
x2
10
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
9. Find the envelope of the straight line x + y = 1 , here a and b are connected by the relation a2 + b2 = c2
a
b
10. Find the Laplace transform of the following functions (i) (t + 2t2)2
(ii) sin2 2t
(iii) sin 3t cos 2t
Unit I
Matrices
Characteristic equation - eigen values and eigen vectors of a real matrix - properties of eigen values CayleyHamilton theorem- Reduction of a real matrix to a diagonal form- Orthogonal matrices- Quadratic
form -Reduction of a quadratic form to a canonical form by orthogonal transformation-application to
engineering problems.
9 Hours
Unit II
Series and Differential Calculus
Series- Convergences and divergence- Comparison test Ratio test - Curvature in Cartesian CoordinatesCentre and radius of curvature - Circle of curvature Evolutes Envelopes application to engineering
problems.
9 Hours
Unit III
Differential Equation of First Order
Linear differential equation of first order-exact-integrating factor- Eulers equation-Bernoullis-modelingapplication to engineering problems.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Differential Equations of Higher Order
Linear differential equations of second and higher order with constant and variable coefficients - Cauchys
and Legendres linear differential equations - method of variation of parameters application of engineering
problems.
9 Hours
Unit V
Laplace Transforms
Laplace Transform- conditions for existence(statement only) -Transforms of standard functions properties
(statement only) - Transforms of derivatives and integrals - Initial and Final value theorems (statement
only) - Periodic functions - Inverse transforms - Convolution theorems(statement only) - Applications of
Laplace transforms for solving the ordinary differential equations up to second order with constant
coefficients-application to engineering problems.
9 Hours
Total: 45+15 Hours
Text Books
1. B S Grewal, Higher Engineering Mathematics, Khanna Publications , New Delhi 2000 .
2. K A Lakshminarayanan, K.Megalai, P.Geetha and D.Jayanthi, Mathematics for Engineers,
Volume I, Vikas Publishing House, New Delhi. 2008.
Reference Book
1. P. Kandasamy, K. Gunavathy and K. Thilagavathy, Engineering Mathematics, Volume I, S.
Chand and Co., New Delhi-2009.
2. T. Veerarajan , Engineering Mathematics , Tata McGraw Hill Publications , New Delhi 2008.
3. E. Kreyszig, Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 8th Edition, John Wiley and Sons, Inc,
Singapore, 2008.
C. Ray Wylie and C. Louis Barrett, Advanced Engineering Mathematics, Tata McGrawHill Publishing Company Ltd, 2003
11
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11O102 ENGINEERING PHYSICS
(Common to all branches)
30 0 3
OBJECTIVES
To impart fundamental knowledge in the areas of acoustics, crystallography and new engineering
materials
To apply fundamental knowledge in the area of LASERS and fiber optics
To use the principles of quantum physics in the respective fields
At the end of the course the students are familiar with the basic principles and applications of
physics in various fields
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Making to learn.
Study the working and applications of different types of laser.
Understanding the Schrdinger wave equation and scattering of X-rays.
Utilization of concept of air wedge in determining the thickness of a thin wire.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model Examination*
25
25
20
20
10
100
25
25
20
20
10
100
20
25
20
20
15
100
Semester End
Examination
20
25
20
20
15
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
2*
Give the classifications of sound.
Write a note on loudness.
Define decibel.
What is meant by reverberation time?
Define magnetostriction effect.
Give the classification of crystals.
Define Miller indices.
The marks secured in Test 1 and Test 2 will be converted to 20 and Model examination will be converted to 20. The remaining
10 marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
12
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
Define lattice and unit cells.
Mention the applications of X-ray diffraction.
Write a short note on air wedge.
List the applications of air wedge method.
Give the applications of LASER.
Give the classification of laser based on refractive index.
Write a note on holography.
Draw the block diagram of fiber optic communication system.
Define the term Compton effect.
What is the physical significance of wave function?
What are metallic glasses?
Write a note on shape memory alloys.
Mention the merits of nano materials.
List the advantages of ceramic materials.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
How Weber-Fechner law is formulated?
Explain the characteristics of loudness.
Elucidate the significance of timber.
How the magnetostriction effect is utilized in the production of ultrasonic waves?
What is the importance of reverberation time in the construction of building?
Give the importance of lattice and lattice planes in a crystal.
How do you measure the d-spacing?
How do you calculate the packing factor of BCC structure?
How air wedge is used in determining the flatness of a thin plate?
Give the importance of optical pumping in the production of LASER.
What are the various steps involved in holography?
How can you derive the acceptance angle in fiber?
Why the wave function is called as probability density?
Why the wave function is finite inside the potential well?
Why the particle is not escaping through the walls of the well?
How ceramic materials are prepared by slip casting technique?
What are the advantages of nano materials?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
Discuss the factors affecting the acoustics of buildings.
Ultrasonic waves are electromagnetic waves. Justify.
Sketch the circuit diagram for piezo electric oscillator.
How can you determine the velocity of ultrasonic by acoustic grating?
Explain how Miller indices are used in crystal structures?
How do you calculate the packing factor for FCC structure?
Draw the crystal lattice for (110) plane.
Why does air wedge occur only in the flat glass plates?
Explain the various steps involved in holography techniques.
Discuss the particle in a one dimensional box by considering infinite length of well.
Explain how shape memory alloy change its shape?
How can you prepare the nano materials synthesized by sol gel technique?
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
Compare magnetostriction and piezo-electric method in the production of ultrasonic waves.
Differentiate musical sound and noises.
Compare the packing factor of BCC, FCC and HCP structures.
13
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
4.
5.
Distinguish between photography and holography.
Compare slip casting and isostatic pressing.
Unit I
Acoustics and Ultrasonics
Acoustics: Classification of sound characteristics of musical sound loudness Weber Fechner law
decibel absorption coefficient reverberation reverberation time Sabines formula (growth & decay).
Factors affecting acoustics of buildings and their remedies. Ultrasonics: Ultrasonic production
magnetostriction - piezo electric methods. Applications: Determination of velocity of ultrasonic waves
(acoustic grating) - SONAR.
The phenomenon of cavitation.
9 Hours
Unit II
Crystallography
Crystal Physics: Lattice unit cell Bravais lattices lattice planes Miller indices d spacing in cubic
lattice calculation of number of atoms per unit cell atomic radius coordination number packing
factor for SC, BCC, FCC and HCP structures - X-ray Diffraction: Laues method powder crystal method.
Crystal defects.
9 Hours
Unit III
Waveoptics
Interference: Air wedge theory uses testing of flat surfaces thickness of a thin wire. LASER: Types
of lasers Nd YAG laser CO2 laser semiconductor laser (homojunction). Applications: Holography
construction reconstruction uses.
Fiber Optics: Principle of light transmission through fiber expression for acceptance angle and numerical aperture - types of optical fibers (refractive Index profile,
mode) fiber optic communication system (block diagram only)
Laser gas sensors .
9 Hours
Unit IV
Modern Physics
Quantum Physics: Development of quantum theory de Broglie wavelength Schrdingers wave
equation time dependent time independent wave equations physical significance applications
particle in a box (1d). X-rays: Scattering of X-rays Compton Effect theory and experimental
verification.
Degenerate and non degenerate.
9 Hours
Unit V
New Engineering Materials
Metallic glasses: Manufacturing properties uses. Shape Memory Alloys: Working principle shape
memory effect applications. Nanomaterials: Preparation method sol gel technique mechanical
magnetic characteristics uses. Ceramics: Manufacturing methods slip casting isostatic pressing
thermal and electrical properties - uses.
14
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Carbon nano tubes and applications.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
V. Rajendran, Engineering Physics, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 2011.
P. K. Palanisami, Physics for Engineers, Vol. 1, Scitech Pub. (India) Pvt. Ltd., Chennai, 2002.
References
1. M. N. Avadhanulu and P G Kshirsagar, A Textbook of Engineering Physics, S Chand & Company Ltd.,
New Delhi, 2005
2. S. O. Pillai, Solid State Physics, New Age International Publication, New Delhi, 2006.
3. V. Rajendran and A Marikani, Physics I, TMH, New Delhi, 2004.
4. Arthur Beiser, Concepts of Modern Physics, TMH, 2008.
5. R. K. Gaur and S L Gupta, Engineering Physics, Dhanpat Rai Publishers, New Delhi, 2006
Language Elective I
(Common to all Branches)
3 0 0 3.0
15
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11O202 ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
(Common to all branches)
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
Imparting knowledge on principles of environmental science and engineering
Understanding the concepts of ecosystem, biodiversity and impact of environmental pollution
Awareness on value education, population and social issues
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
h) The graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility and will
display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and upgradation
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Awareness on natural resources and understanding environmental problems.
Realize the benefits of ecology and biodiversity.
Characterize and analyze different levels of pollution and its management techniques.
List human activities that may be responsible for global warming and cooling of earths atmosphere
and pave way for sustainable development.
Classify and understand about the relation between human population and environment.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S.No
1
2
3
4
5
6
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I
Test II
25
25
20
20
10
100
25
25
20
20
10
100
Model
Examination
15
25
20
20
20
100
Semester End
Examination
15
25
20
20
20
100
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10 marks
will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
16
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
Give the scope and importance of environmental studies.
Distinguish between renewable and non- renewable resources.
Explain the impacts of mining on forests.
Explain why fresh water is a precious resource and classification of different water pollutants?
What are the Impacts of modern agriculture?
State the two energy laws and give examples that demonstrate each law.
List the physical, chemical, and biological factors responsible for soil formation.
Give examples of point and nonpoint sources of pollution.
Draw a food web that includes ten or more aquatic organisms.
Distinguish between primary and secondary pollutants.
Identify the four parts of the atmosphere.
Describe secondary and primary succession with suitable examples.
Define the term extinction.
Relate the concept of food web and food chain to trophic levels.
Describe energy flow in a ecosystem.
Define the roles of producers, herbivore, carnivore, omnivore, scavenger, parasite and
decomposer.
List some of the components of an ecosystem.
Distinguish between the biotic and abiotic factors in an ecosystem.
Give some impacts of water pollution.
Explain the source and effects of e waste.
What is the loudest sound possible?
What are the laws regarding noise pollution?
What is rainwater harvesting?
Discuss the concept and reactions of acid rain.
Describe the salient features of Wildlife (protection) Act, 1972.
What is 3R approach?
Give the effects of nuclear fallout.
Differentiate between mortality and natality.
What is exponential growth and zero population growth?
What are the objectives and elements of value education?
Understand
1.
2.
Explain why providing adequate food for all of the world's people is so difficult?
Rank the five major sources of energy used to produce electricity and classify the energy sources
as renewable or nonrenewable.
3. Describe the causes of desertification and its preventive measures.
4. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of the green revolution.
5. Explain the relationship between technology and global warming.
6. Describe any three health effects of air pollution.
7. Identify "greenhouse gases" and explain how they cause the "greenhouse effect".
8. Identify a few plants and animals with the various biomes.
9. Explain the importance of primary species.
10. Explain the five major types of species interactions and give examples of each.
11. Environmental problems involve social, political, and economic issuesJustify.
17
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
What problems does noise pollution cause to animals?
What type of pollution threatens wetlands?
What are the major measures to attain sustainability?
Why is urban energy requirement more than rural requirement?
What are the major limitations to successful implementation of our environmental legislation?
Explain the concept of Malthusian theory.
How age-structure pyramids serve as useful tools for predicting population growth trends of a
nation?
19. Discuss various issues and measures for women and child welfare at international and national level.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
Compare the energy efficiencies of any two inventions.
Name some alternatives to pesticides.
Identify four different habitats found in bodies of water and give examples of organisms that live
in each habitat.
4. Explain how we could reduce air pollution?
5. What are the measures to be taken to reduce your own noise pollution?
6. List the top ten polluted countries in the world?
7. Identify the grants available for rain water harvesting in buildings?
8. What are the major implications of enhanced global warming?
9. Discuss the methods implemented by government to control HIV/AIDS.
10. What is the role of an individual in prevention of pollution?
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
List reasons why it is important that we seek alternatives to fossil fuels.
Explain why fresh water is often in short supply?
Give examples of human-made sources of radiation and explain how human-made sources differ
from natural sources of radiation.
Unit I
Introduction to Environmental Studies and Natural Resources
Environment: Definition- scope - importance need for public awareness. Forest resources: Use over
exploitation- deforestation - case studies- mining - effects on forests and tribal people. Water resources:
Use over utilization of surface and ground water- floods drought - conflicts over water. Mineral
resources: Use exploitation - environmental effects of extracting and using mineral resources - case
studies. Food resources: World food problems - changes caused by agriculture and overgrazing - effects of
modern agriculture- fertilizer-pesticide problems - water logging - salinity -case studies. Energy resources:
Growing energy needs - renewable and non renewable energy sources. Land resources: Land as a resource land degradation - soil erosion. Role of an individual in conservation of natural resources.
Documentation of the effect of degradation of forest resource.
9 Hours
Unit II
Ecosystems and Biodiversity
Concept of an ecosystem: Structure and function of an ecosystem producers - consumers -decomposers
energy flow in the ecosystem ecological succession food chains - food webs and ecological pyramids.
18
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Types of ecosystem: Introduction - characteristic features - forest ecosystem - grassland ecosystem - desert
ecosystem - aquatic ecosystems (ponds, streams, lakes, rivers, oceans, estuaries). Biodiversity:
Introduction definition (genetic - species ecosystem) diversity. Value of biodiversity: Consumptive use productive use social values ethical values - aesthetic values. Biodiversity level: Global - national local levels- India as a mega diversity nation- hotspots of biodiversity. Threats to biodiversity: Habitat loss
- poaching of wildlife man wildlife conflicts endangered and endemic species of India. Conservation of
biodiversity: In-situ and ex-situ conservation of biodiversity - field study.
Documentation of the endangered flora and fauna in your native place.
9 Hours
Unit III
Environmental Pollution
Pollution: Definition air pollution - water pollution - soil pollution - marine pollution - noise pollution thermal pollution - nuclear hazards. Solid waste management: Causes - effects - control measures of urban
and industrial wastes. Role of an individual in prevention of pollution - pollution case studies. Disaster
management: Floods earthquake - cyclone - landslides. Electronic wastes.
Investigation on the pollution status of Bhavani river.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Social Issues and Environment
Sustainable development : Unsustainable to sustainable development urban problems related to energy.
Water conservation - rain water harvesting - watershed management. Resettlement and rehabilitation of
people. Environmental ethics: Issues - possible solutions climate change - global warming and its effects
on flora and fauna - acid rain - ozone layer depletion - nuclear accidents - nuclear holocaust - wasteland
reclamation - consumerism and waste products. Environment protection act: Air (Prevention and Control
of Pollution) act water (Prevention and control of Pollution) act wildlife protection act forest
conservation act issues involved in enforcement of environmental legislation.
Analyze the recent steps taken by government of India to prevent pollution.
9 Hours
Unit V
Human Population and Environment
Human population: Population growth - variation among nations population explosion family welfare
programme and family planning environment and human health Human rights value education HIV
/ AIDS, Swine flu women and child welfare . Role of information technology in environment and human
health.
Population explosion in India, China the present and future scenario.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
T. G. Jr. Miller, Environmental Science, Wadsworth Publishing Co., 2004.
Raman Sivakumar, Introduction to Environmental Science and Engineering, Tata McGraw Hill
Education Private Limited, New Delhi, 2010.
19
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Bharucha Erach, The Biodiversity of India, Mapin Publishing Pvt. Ltd., Ahmedabad India, 2010 .
S. Divan, Environmental Law and Policy in India, Oxford University Press, New Delhi, 2001.
K. D. Wager, Environmental Management, W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, USA, 1998.
W. P. Cunningham, Environmental Encyclopedia, Jaico Publising House, Mumbai, 2004.
S. K. Garg, R. Garg, R. Garg, Ecological & Environmental Studies, Khanna Publishers, Delhi,
2006.
20
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11O105 BASICS OF CIVIL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
4
4.0
OBJECTIVES
To impart basic knowledge in the field of Civil Engineering focusing building materials, surveying,
foundation and transportation Engineering
To impart basic knowledge in the field of Mechanical Engineering focusing on generation of power
from various natural resources and to know about various types of Boilers and Turbines used for
power generation and to understand the working of IC engines and basic manufacturing processes
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Able to understand the fundamental philosophy of Civil engineering and enable them to work
together in a multidisciplinary technical team.
Able to identify the nature of building components, functions, construction practices and material
qualities
Able to demonstrate the manufacturing processes like casting, welding, machining operations
Able to demonstrate the construction and working of IC engines and refrigerators
Able to demonstrate the working principle of boilers, turbines and various power plants utilizing
conventional and non-conventional sources of energy
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze / Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I
Test II
40
30
20
100
40
30
20
100
Model
Examination
40
30
20
100
Semester End
Examination
40
30
20
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
What are the classifications of stones?
What is the frog in a brick?
What is quarrying?
What do you mean by dressing of stones?
What are the systems of bearing?
How the surveying is classified based on purpose?
Define Benchmark and state its effects.
What are the accessories used in chain surveying?
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10 marks
will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated by giving equal weightage (50%) for
both Civil and Mechanical Engineering
21
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
58.
59.
Define bearing of a line.
Define leveling & state its objectives.
State the objectives and requirement of good foundation.
Mention the site improvement techniques.
Define bearing capacity of soil.
How stone masonry is classified?
Define Beam, Column and Lintel.
What are the basic forms of roof?
How floors are classified based on floor finish?
List the materials used for damp proofing.
How roads are classified?
What do you mean by W.B. M. road?
Define Gauge.
What is a permanent way?
How bridges are classified?
What are the advantages of railways?
What are docks?
Classify sleepers.
What are the requirements of a sleeper?
What are the types of traffic signs?
What are the advantages of road signs?
What are the prohibitory signs?
What is the main function of hangars?
What are the sources of Energy Generation?
What are the accessories used in a boiler?
Define Turbine.
Compare and contrast fire tube and water tube boiler?
List the types of steam Turbines?
Classify the I.C engine.
List out the Part of the I.C. Engine.
Define the terms: Top Dead Center, Bottom Dead Center.
Define the term: Compression Ratio.
What are the different sources of energy?
Name four non-renewable sources of energy.
Name some renewable sources of energy.
Name four solid/liquid/gaseous/ fuels.
Name two nuclear fuels.
What are the advantages of wind energy?
State some of the applications of steam boilers.
Classify different steam boilers.
What do you understand by Scavenging
What do you understand by the term IC engine?
What are the operations performed on a Lathe?
What is impulse turbine? Give example.
What is Reaction turbine? Give example.
Define Boiler.
Classify Boilers.
List out the Boiler Mountings and Accessories.
Define Refrigeration.
Define refrigerant. Give some examples of refrigerant.
Define C.O.P.
22
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
What are the qualities of good building stone?
What are the various stages of manufacturing brick?
What is mean by concrete?
State the properties of cement concrete.
What is curing of concrete?
What is water cement ratio?
What is the difference between a plan and a map?
Differentiate between plane surveying and geodetic surveying.
State the principles of surveying.
What is the use of cross staff?
What are the functions of foundation?
Differentiate between shallow foundation & deep foundation
What are the causes of failure of foundation?
Compare stone masonry and brick masonry.
Why bonding in brick wall is necessary?
State the special features of English and Flemish bond.
Define super elevation.
What are the uses of fish plates?
What are the necessities of highway drainage?
What are the three stages of construction of a new railway track?
Define the term visibility.
Define passenger flow.
Differentiate between wharf and jetty.
What are the requirements of a good harbour?
What are the requirements of a good naval port?
How Solar Energy is generated?
How Energy is Generated using steam Turbines?
How power plants are classified?
Compare and contrast reaction and impulse turbines.
How energy is generated from Diesel Power Plants?
What is the difference between renewable and non-renewable sources of energy?
Mention the applications of solar energy.
What is the function of a hydraulic turbine?
What is the function of a surge tank?
What is the function of a moderator?
What are the functions of a control rod?
Name of the important components of diesel power plant.
Name the important parts of gas turbine.
State the function of condenser in steam power plant.
What are the requirements of a good boiler?
What are the specific advantages of water-tube boilers?
What are the aims of pre-heating of air in a boiler?
State the function of economizer.
How does a fusible plug function as a safety device?
What is the function of a steam nozzle?
What is the function of flywheel?
What is the function of a spark plug?
What is the function of a fuel injector in diesel engine?
Why is cooling necessary in an IC engine?
Define compression ratio of an IC engine.
List the ports used in a 2-stroke engine
What are the requirements of a good boiler?
What is the difference between impulse and reaction turbine?
How energy is generated from Nuclear Power Plants?
23
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
55.
56.
57.
58.
59.
60.
How energy is generated from Hydro Power Plants?
Compare and contrast 4 stroke and 2 stroke engine.
What is the Purpose of a fusible Plug?
Differentiate petrol & diesel engines.
How Taper Turning is carried out in Lathes?
Various Mechanical properties of Cast Iron, Steel and HSS.
Apply/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
What is Hardness?
What are the operations to be performed while setting up a plane table at a station?
Explain the steps involved in measuring vertical angle of an object using theodolite
Explain the methods to improve bearing capacity of soil
What are the points to be observed in the construction of brick masonry?
Explain the method of construction of cement concrete flooring.
What are the methods of applying surface dressing in bituminous roads?
Explain the construction steps in bituminous macadam road.
How can you express the hardness number of stones?
Apply the concept of power generation and saving from other energy sources
Apply the concept of Refrigeration in Heat removal and Heat addition
Draw the pressure-velocity diagram for a single stage impulse turbine.
Unit I
Introduction to Civil Engineering
History, development and scope of Civil Engineering - Functions of Civil Engineers. Construction
Materials: Characteristics of good building materials such as stones - Bricks, A.C. sheets - G.I. sheets and
Ceramic tiles - Timber, cement - Aggregates and concrete. Surveying: Definition and purpose
Classification Basic principles Measurement of length by chains and tapes Calculation of area of a
plot Measurement of bearings and angles using a prismatic compass Leveling Contours
Application of contours
10 Hours
Unit II
General Concepts Relating to Buildings
Selection of site Basic functions of buildings Major components of buildings. Foundations: Purpose of
foundation Bearing capacity of soils Types of foundations. Proper methods of construction of: Brick
masonry Stone masonry Hollow Block masonry. Beams Lintels Columns Flooring Doors and
windows Roofing
Damp proof course Surface finishes
10 Hours
Unit III
Transportation Engineering
Classification of Highways Cross sections of water bound macadam - Bituminous and cement concrete
roads Traffic signs and signals. Importance of railways - Gauges Components of a permanent way
Classification of bridges Components of Airport
Examples of Marvelous Structures
10 Hours
24
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Unit IV
Engineering Materials and Manufacturing Processes
Classification of Engineering materials, Mechanical properties and uses of cast iron, steel, and High Speed
Steel.
Introduction to casting process, Green sand moulding - Pattern, Melting furnaces - Cupola and Electric
Furnace. Metal Forming - Forging Process. Introduction to Arc and Gas Welding. Centre Lathe Specifications - Principal parts - Operations - Straight turning, Step turning, Taper turning methods,
Knurling, Thread cutting methods, Facing, Boring, and Chamfering - Lathe tools and Materials. Drilling
Radial drilling machine - Specification and Operation
Milling operation
10 Hours
Unit V
Internal Combustion Engines and Refrigeration
Classification of IC engines, Main components of IC engines, working of a 4 stroke & 2 stroke petrol &
diesel engine, differences between 4 stroke and 2 stroke engine, Lubrication and Cooling systems in IC
Engines. Refrigeration: Working Principle of Vapour Compression & Vapour Absorption System,
Domestic refrigerator
Domestic air conditioning
10 Hours
Unit VI
Alternate Sources of Energy, Power Plants and Boilers
Solar, Wind, Tidal, Geothermal and Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC). Power Plant:
Classification of Power Plants- Steam - Nuclear, Diesel, and Hydro Power Plants. Types of Boilers
Simple Vertical, Babcock and Wilcox and La-Mont Boiler, Differences between fire tube and water tube
boiler. Types of steam turbines- working of a single stage impulse and reaction turbines
Biomass and Biofuels in power generation
10 Hours
Total: 60 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
M. S. Palanichamy, Basic Civil Engineering, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited, New
Delhi, 2009
G. Shanmugam & S Ravindran, Basic Mechanical Engineering, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing
Company Limited, New Delhi, 2010
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
N. Arunachalam, Bascis of Civil Engineering, Pratheeba Publishers, 2000
B. K. Sarkar, Thermal Engineering, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi,
2008
P. N. Rao, Manufacturing Technology: Foundry, Forming and Welding, Tata McGraw-Hill
Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi, 2003.
S. R. J. Shantha Kumar, Basic Mechanical Engineering, Hi-tech Publications, Mayiladuthurai, 2000
http://www.tutorvista.co.in/content/science/science-ii/sources-energy/sources-energyindex.php
25
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11O205 BASICS OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
(Common to all branches except EEE, ECE, EIE)
4 0 0 4.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the basics concepts of electric circuits & magnetic circuits
To learn the operations of electrical machines
To impart knowledge in the concepts of Communication systems
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement in Mechanical, Mechatronics and Electrical Engineering as well as IT companies
g) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Analyze the power in single phase AC systems
Derive an equation for self and mutual inductance
Determine the characteristics of Bipolar junction transistors
Diagnose the operation of half wave and full wave rectifier
Design of an operational amplifier
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Test I
Test II
Model
Examination
Semester End
Examination
Remember
10
10
10
10
Understand
20
20
20
20
Apply
30
30
30
30
Analyze / Evaluate
40
40
40
40
Create
100
100
100
100
Total
Remember
1.
2.
What is an inductor?
State Ohms law.
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10 marks
will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks
26
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
State the operating principle of a transformer.
Draw the circuit symbols of i] step up transformer ii] step down transformer.
What is resistor? Give its symbol.
What are impurities?
Draw the neat-labelled I-V characteristics of zener diode.
Draw circuit symbol of diode and zener diode,
Which process is used to convert the material into extrinsic?
What is junction barrier?
Define the term rectification and efficiency
What is done in the base region of a transistor to improve its operation.
What is BJT?
List the needs for modulation.
Draw symbol of 2-input NOR gate & write its truth table.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
Explain Ohms law relating to (V), (I) and (R).
Explain the working principle of a transformer.
Explain the working principle of an induction motor.
Discuss intrinsic semiconductor are pure semiconductors.
Explain pentavalent impurities with example.
Explain trivalent impurities with example.
Explain in brief, knee voltage of diode.
Explain in brief, breakdown voltage of diode.
Explain the operation of P-N Junction diode when forward and reverse bias.
Explain the formation of depletion region in P-N Junction.
Explain Zener diode as voltage regulator.
With a neat circuit diagram explain the working of a half wave rectifier.
Derive an expression for the efficiency of a half wave rectifier.
With a neat circuit diagram, explain the working of full wave rectifier.
What is Ex-OR gate? Explain its working & tabulate the truth table.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
Why opamp is called as linear amplifier?
Why impurities are used?
Calculate the value of resistance having co lour code sequence Red , Yellow, orange and
Gold.
4. Why do we use transformer in rectifier circuit?
5. Which impurity play important role in formation of P type semiconductor?
6. Calculate the % ripple factior, if the dc output voltage 20 V and ac voltage 2V.
7. Three resistors are connected in series across a 12V battery. The first resistance has a value of 2
, second has a voltage drop of 4V and third has power dissipation of 12 W. Calculate the value
of the circuit current.
8. A 25 resistor is connected in parallel with a 50 resistor. The current in 50 resistor is 8A.
What is the value of third resistance to be added in parallel to make the total line current as 15A.
9. A toroidal air cored coil with 2000 turns has a mean radius of 25cm, diameter of each turn being
6cm. If the current in the coil is 10A, find mmf, flux, reluctance, flux density and magnetizing force.
10. The self inductance of a coil of 500turns is 0.25H.If 60% of the flux is linked with a second coil of
10500 turns. Calculate a) the mutual inductance between the two coils and b) emf induced in the
second coil when current in the first coil changes at the rate of 100A/sec.
27
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11. 2.An air cored toroidal coil has 480 turns, a mean length of 30cm and a cross-sectional area of 5
cm2.Calculate a)the inductance i\of the coil and b) the average induced emf, if a current of 4 A is
reversed in 60 milliseconds
Analyze / Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
Why inductor is referred as a choke?
Why single phase induction motor are not self starting?
How the barrier potential is developed across the P-N Junction, what are the approximate
values this potential for Germenium and Silicon?
4. Trivallent impurity is called as donor impurity, comment.
5. Distinguish with diagram, then solid material on the basis of band diagram.
6. How a zener diode can be used for voltage regulation in power supply?
7. How voltage source is converted into current source and vice versa?
8. Differentiate P type and N type semiconductor
9. Distinguish between metal, semiconductor and insulator. Give examples of each.
10. Distinguish between half wave and full wave rectifier
Create
1.
2.
Design a half wave uncontrolled rectifier and calculate the ripple factor.
Design a full wave uncontrolled rectifier and calculate the efficiency.
Unit I
Electric Circuits
Definition of Voltage, Current, Power & Energy, Ohms law, Kirchoffs Law & its applications simple
problems, division of current in series & parallel circuits, generation of alternating EMF, definition of RMS
value, average value, peak factor, form factor. Power in single phase AC three phase system.
Star to delta and delta to star transformations, R-L and R-C series circuit
12 Hours
Unit II
Magnetic Circuits
Definition of MMF, Flux, Reluctance, Properties of Flux lines, Self & Mutual Inductance, Ampere Turns,
Series & parallel magnetic circuits, Comparison between Electric & magnetic circuits, Law of
Electromagnetic induction, Flemings Right & Left hand rule.
Magnetic impedance, Effective resistance, Magnetic capacitivity
12 Hours
Unit III
Electrical Machines
Construction, Type, Principle of Operation & Working Principle of DC Generator, DC Motor,
Transformer, Induction Motor, Induction type single phase energy meter, Domestic wiring practice, Tube
light circuit, Earthing & earthing methods.
Characteristics of DC generators and DC motors,
12 Hours
28
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Unit IV
Electronics Engineering
PN Junction diode & Zener diode Characteristics Half wave and full wave rectifier Bipolar junction
transistors CB,CE, CC Configurations and characteristics basic concepts of amplifiers and oscillators
Logic gates Inverting, Non inverting amplifiers and Operational amplifiers- Basic Computer organization
Block diagram of Microprocessors (8085).
Semiconductor theory, Diode clippers, op-amp parameters and applications
12 Hours
Unit V
Communication Engineering
Introduction to communication systems Need for modulation Types- Block Diagram representation
only Block diagram of TV system Introduction to cellular & mobile telephony- Block diagram of
Optical and Satellite communication systems.
Analog and digital signals, Transmission medium, Digital communication
12 Hours
Total: 60 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
T. K. Nagsarkar and M S Sukhija, Basic of Electrical Engineering, Oxford Press, 2005
R. Muthusubramaninan, S Salivahanan and K A Muraleedharan, Basic Electrical, Electronics and
Computer Engineering, Tata McGraw Hill, 2004
References
1.
2.
3.
J. A. Edminister, Electric Circuits, Schaums Series, McGraw Hill, 2005
Van Valkenbergm, Electric Circuits and Network Analysis, Prentice Hall (India) Pvt. Ltd., 2005
Smarjith Ghosh, Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Prentice Hall (India)
Pvt. Ltd., 2005
29
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11O208 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS
(Common for CE,EEE,ME,MXE,BT,IT & TT (I Semester); AE,CSE,ECE,EIE & FT (II Semester)
2 0 2 3.0
OBJECTIVES
Upon Successful completion of this course, the student should be able to:
Understand and appreciate the importance of Engineering Graphics in Engineering
Understand the basic principles of Technical/Engineering Drawing
Understand the different steps in producing drawings according to BIS conventions
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
d) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of engineering design. Understanding
theconcept generation, design optimization and evaluation. Knowing the fundamentals of
intellectual property rights. Students will be able to effectively design various engineering
components and make process plan for the production
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Projection of various components according to BIS specifications.
Assembly of datas and information of various components in visualized way
Interpretation of technical graphics assemblies
2D modeling by AutoCAD
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Internal Assessment
Semester End Examination
Preparation
10
15
Observation and Results
15
25
Record
Mini-project/
Model examination/
Viva-voce
10
15
10
50
50
Total
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
Define Graphic communication or Drawing.
List the different drawing instruments.
What is blueprint?
What are the applications of engineering graphics?
What are the two types of drawings?
What are the different types of projections?
Define Orthographic projection.
What do you mean by I angle projection?
What is III angle projection?
Define Plan.
What is Elevation?
List the various types of lines.
What do you mean by a Plane?
Name the five standard sizes of drawing sheets that are specified by BIS.
30
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
Give the BIS codes for Lettering, Dimensioning and lines.
State few important dimensioning rules.
What are the two types of Solids?
What is Representative Fraction (RF)?
What is a Frustum?
Define Truncation.
Define Section Plane and give its types.
What do you mean by development of surfaces?
State the principle of Isometric projection.
What is Isometric View?
Define Isometric scale.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
When an object is said to be in III quadrant?
Why are the projectors perpendicular to the Projection Plane in the Orthographic projection?
What is the Shape of the section obtained when a cone is cut by a plane passing through the apex and
center of the base of the cone?
4. Why II and IV angle projections are not used in industries?
5. What are the differences between I angle and III angle projections?
6. Which method is suitable for developing a truncated prism?
7. Why is a hexagonal headed bolt and nut more common in use as compared to square headed bolt and
nut?
8. Which is the most suitable method for drawing the Perspective Projection?
9. What are the prerequisites for Free hand sketching?
10. What are the two methods used to obtain the Isometric view of a circle?
11. Why CAD is preferred over Conventional drafting?
Apply/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
How will you project a point which is above HP and in front of VP?
How will you project a point which is below HP and behind VP?
What is the method used to determine the True length and inclination of a line inclined to both the
planes?
How will you project a prism whose axis is inclined to HP and parallel to VP by Change of Position
method?
How will you project a cylinder when the axis is inclined to VP and parallel to HP by change of
position method?
How will you project a pyramid whose axis is inclined to HP and parallel to VP by Change of Position
method?
How will you project a cone when the axis is inclined to VP and parallel to HP by change of position
method?
How will you obtain the Sectional view of solids in simple vertical position cut by planes inclined to
any one reference plane?
How will you develop the lateral surfaces of simple and truncated solids?
How will you develop the complete surfaces of Frustums?
Construct an isometric scale.
A cricket ball thrown from the ground level reaches the wicket keepers gloves. Maximum height
reached by the ball is 5m. The ball travels a horizontal distance of 11m from the point of projection.
Trace the path of the ball.
The Pictorial view of an object is shown below. Draw the following views to full size scale.
a) Elevation in the direction of arrow
b) Left end elevation
c) Plan
31
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
14. Read the dimensioned drawing shown below. Redraw the figure to full size and dimension it as per
Indian Standards.
Q. No. 13
Q. No. 14
Unit I
Concepts and Conventions
Use of drafting instruments BIS conventions and specifications Size, layout and folding of drawing
sheets Lettering and dimensioning. General principles of orthographic projection First angle projection
Layout of views Projection of points, located in all quadrant and straight lines located in the first
quadrant Determination of true lengths and true inclinations.
6 Hours
Unit II
Projection of Solids
Projection of simple solids like prisms, pyramids, cylinder and cone when the axis is inclined to one
reference plane by change of position method.
6 Hours
Unit III
Section of Solids and Development of Surfaces
Sectioning of solids like prisms, pyramids, cylinder and cone in simple vertical position by cutting planes
inclined to one Reference: plane Obtaining the true shape of section. Development of lateral surfaces of
simple solids prisms, pyramids, cylinders and cones.
6 Hours
Unit IV
Isometric Projection and Perspective Projection
Principles of isometric projection isometric scale isometric projections of simple solids, pyramids,
cylinders and cones. Orthographic projection - Systems of orthographic projection - First angle
orthographic projection - Conversion of pictorial to orthographic views (Free hand).
6 Hours
Unit V
Introduction to AutoCAD and 2D Modeling
Starting AutoCAD Interfaces Menus Tool bars Coordinates Limits Units 2D commands
Drawing Commands - Creating a Point, Construction of Lines, Polyline, Multiline, Circles, Arcs,
Rectangle, Polygon, Ellipse, Hatch, Text, Mtext, Linetypes Edit and Modify commands - Copy, Move,
Erase, Mirror, Zoom, Pan, Arrays, Trim, Break, Fillet, Chamfer, Redraw, Regen, Dimensioning, Colors,
Layers Exercises
6 Hours
Total: 30+30 Hours
32
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Textbook
1.
K. V. Natarajan, A Textbook: of Engineering Graphics, Dhanalakshmi Publishers, Chennai, 2006
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
S. Julyes Jaisingh, Engineering Graphics, Tri Sea Publishers, 2010
V. Rameshbabu, Engineering Graphics, VRB Publishers Pvt Ltd., 2009
K. Venugopal, Engineering Graphics, New Age International (P) Limited, 2002
N. D. Bhatt, Engineering Drawing, Charotar publishing House 2003
K. L. Narayana and P. Kannaiah, Engineering Graphics, Scitech Publications (Pvt) Limited-2002
List of Experiments
1.
2.
3.
4.
Projection of points located in all quadrants.
Projection of straight lines located in the first quadrant inclined to both the planes.
Determination of true lengths and true inclinations of Straight lines.
Projection of Solids like prisms, pyramids, cylinder and cone when the axis is inclined to one
reference plane by change of position method.
5. Sectioning of solids in simple vertical position by cutting planes inclined to one reference plane
and obtaining true shape of section.
6. Development of lateral surfaces of simple and truncated solids like prisms, pyramids cylinder and
cone.
7. Isometric Projections / Views of Solids like prisms, pyramids and Cylinders.
8. Orthographic Projection of various components from pictorial views.
9. Drawing of front, top and side views from given pictorial views using AutoCAD.
10. Drawing sectional views of prism, pyramid and cylinder using AutoCAD.
Total: 30 Hours
Practical Schedule
Sl. No
1
2
Experiment
Hours
Projection of points located in all quadrants
Projection of straight lines located in the first quadrant inclined to both the
planes.
3
4
Determination of true lengths and true inclinations of Straight lines
Projection of Solids when the axis is inclined to one reference plane by
change of position method.
Sectioning of solids in simple vertical position by cutting planes inclined to
one reference plane and obtaining true shape of section
6
7
8
9
Development of lateral surfaces of simple and truncated solids.
Isometric Projections / Views of Solids like prisms, pyramids and Cylinders.
Orthographic Projection of various components from pictorial views.
3
3
3
Drawing of front, top and side views from given pictorial views using
AutoCAD.
10
Drawing sectional views of prism, pyramid and cylinder using AutoCAD.
33
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
1O108 ENGINEERING PHYSICS LABORATORY
(Common for AE,CSE, ECE & EIE & ME (I Semester); CE,EEE,BT,IT,TT & FT (II Semester)
0 0 2 1.0
OBJECTIVES
To know how to execute experiments properly, presentation of observations and arrival of
conclusions
It is an integral part of any science and technology program
To view and realize the theoretical knowledge acquired by the students through experiments
At the end of the course, the students able to realize the theoretical knowledge acquired through
experiments
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Observation and analytical skills are developed
Various properties of matter can be known
Different optical properties can be analyzed
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Preparation
Execution
Observation and Results
Record
Model Examination
Viva Voce
Total
Internal
Assessment
10
10
10
5
10
Semester End
Examination
15
15
15
-
50
50
List of Experiments (Any 10 Experiments)
1.
Determination of moment of inertia and rigidity modulus of wire using torsion pendulum
(symmetrical masses method).
2. Determination of Youngs modulus by non-uniform bending.
3. Determination of thermal conductivity of a bad conductor using Lees disc.
4. Determination of frequency of vibrating rod using Meldes apparatus.
5. Determination of viscosity of a liquid - Poiseulles method.
6. Determination of thickness of a thin wire - air wedge method.
7. Determination of wavelength of mercury spectrum grating.
8. Determination of refractive index of a liquid and solid using traveling microscope.
9. Determination of energy band gap of a semiconductor diode.
10. Determination of wavelength of LASER and particle size of a given powder.
11. Measurement of numerical aperture and acceptance angle of a optical fiber.
12. Youngs modulus uniform bending (pin and microscope).
34
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
PRACTICAL SCHEDULE
S.No
Total: 30 Hours
Experiment
Hours
1.
Determination of moment of inertia and rigidity modulus of wire using torsion pendulum
(symmetrical masses method).
2.
Determination of Youngs modulus by non-uniform bending.
3.
Determination of thermal conductivity of a bad conductor using Lees disc.
4.
Determination of frequency of vibrating rod using Meldes apparatus.
5.
Determination of viscosity of a liquid - Poiseulles method.
6.
Determination of thickness of a thin wire - air wedge method.
7.
Determination of wavelength of mercury spectrum grating.
8.
9.
Determination of refractive index of a liquid and solid using traveling microscope.
Determination of energy band gap of a semiconductor diode.
3
3
10.
Determination of wavelength of LASER and particle size of a given powder.
35
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11M209 WORKSHOP PRACTICE
0 0 2 1.0
OBJECTIVES
To learn the use of basic hand tools and
To know the need for safety in work place
To gain hands on experience on Carpentry, Fitting, Sheet metal, Plumbing, Arc welding, Foundry
and Basic electrical circuits
To have the basic knowledge on working of domestic appliances
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Perform basic Carpentry work
Perform basic Fitting work
Fabrication of Sheet metal objects
Plumbing work
Arc welding skill
Preparing green sand mould
Soldering skill
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Preparation
Observation and Results
Record
Mini-Project/
Model Examination /
Viva-Voce
Total
Internal Assessment
Semester End Examination
10
10
10
20
10
-
20
20
50
50
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
What are the tools used in sheet metal work?
What are the types of joints in sheet metal work?
What is moulding?
What is green sand mould?
What is gas welding?
List out the types of flames in welding.
What is meant by carpentry?
What is the use of Saw?
What are the types of joints in pipe connection?
What is staircase wiring?
What is the working principle of centrifugal pump?
What are the types of valves in plumbing and where it is used?
List out the cutting tools used in carpentry with specification.
What are the necessary equipments used in Arc Welding?
What are the methods used in sheet metal work?
List out the types and components of Air- Conditioner.
36
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Compare the Refrigeration system with air Condition system.
How the refrigeration system works?
How will you select the suitable welding process for various materials?
How will make a V joint in the given MS flat?
How will you make a green sand mould using solid pattern?
How gadget like chair, sofa, table, cell phone stand by using welding joints?
How metals are manufactured by using casting process?
How cavity is formed by using pattern?
How the wires are joined by soldering?
Apply / Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Sketch the wiring diagram for a room consist of two fans ,three tubelights, and one plug point.
Sketch the line diagram of the plumbing work carried out in your house.
Sketch all the wooden furniture present in your house in three dimensional view.
How will make a connection of basic pipe lines, using PVC pipes, that includes valves and taps?
How will form Staircase and Godown wiring?
Prepare a hexagonal shape pen stand by using power tools.
Prepare a cover with handle by using sheet metal to cover a motor.
Prepare a small trolley to carry wastage by using welding work.
List of Experiments
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
Forming of simple objects using sheet metal.
Preparing a V joint from the given MS flat.
Demonstration of Assembly and Disassembly of centrifugal pump.
Making simple gadget like chair, sofa, table, cell phone stand by using welding joints.
Making simple gadget like pen stand, box, cell phone stand etc., by using power tools.
Making a connection of basic pipe lines, using PVC pipes, that includes valves and taps.
Demonstration of working of domestic appliances: Washing Machine/ Refrigerator and Window
Air-Conditioner.
Preparing a half round joint from the given MS flat.
Preparing a green sand mould using solid pattern.
Staircase and Godown wiring.
Soldering practice.
Assembly and Disassembly of Computer System /Television.
Demonstration of working of domestic appliances: Mixie, Electric Iron/ Heater.
Total: 30 Hours
Practical Schedule
SI. No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
Experiment
Forming of simple objects using sheet metal.
Preparing a V joint from the given MS flat.
Demonstration of Assembly and Disassembly of centrifugal pump.
Making simple gadget like chair, sofa, table, cell phone stand by using
welding joints.
Making simple gadget like pen stand, box, cell phone stand etc., by using
power tools.
Making a connection of basic pipe lines, using PVC pipes, that includes
valves and taps.
Hours
3
3
2
3
2
2
37
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Demonstration of working of domestic appliances: Washing Machine/
Refrigerator and Window Air-Conditioner.
Preparing a half round joint from the given MS flat.
Preparing a green sand mould using solid pattern.
10
Staircase and Godown wiring.
11
Soldering practice.
12
Assembly and Disassembly of Computer System /Television.
13
Demonstration of working of domestic appliances: Mixie, Electric Iron/
Heater.
7
8
9
38
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11O201 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS II
(Common to all branches)
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
Acquire knowledge to use multiple integrals to find area and volume of surfaces and solids
respectively.
Have a good grasp of analytic functions, complex integration and their interesting properties and
applications.
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
Acquire more knowledge in basic concepts of engineering mathematics.
2.
To improve problem evaluation technique.
3.
Choose an appropriate method to solve a practical problem.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
S. No
Test I3
Test II1
Model Examination1
End Semester
Examination
Remember
20
20
20
20
Understand
40
40
40
40
Apply
30
30
30
30
Analyze/ Evaluate
10
10
10
10
Create
100
100
100
100
Total
Remember
1. Define Jacobian in two dimensions.
2. State Greens theorem.
3. Define directional derivative of a vector point function.
4. Define analytic function.
5. What is the formula for finding the residue of a double pole?
6. State Cauchys integral formula.
7. Write the necessary condition for a function f (z) to be analytic.
8. Write the formula for unit normal vector?
9. Write all types of singularities.
10. State the sufficient conditions for a function of two variables to have an extremum at a point.
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted to 20 and model examination will be converted to 20.
The remaining 10 marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly, internal assessment will be
calculated for 50 marks.
39
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Understand
1. If
u = 2 xy, v = x 2 y 2 , x = r cos , y = r sin compute
2.
If
(u , v
..
( x, y )
y x zx
u
u
u
show that x 2
u = f
,
+ y2
+ z2
= 0. .
xz
x
y
z
xy
y
3. Transform the integral
f ( x, y )dxdy to polar coordinates.
0 0
2 x
4.
Change the order of integration in
f (x , y )dydx .
0 0
5.
Find a, such that (3x-2y+z) i + (4x+ay-z)
j + (x-y+2z) k is solenoidal.
6.
What is the greatest rate of increase of
7.
Test the analyticity of the function w = sin z.
8.
Find
9.
Evaluate
= xyz 2 at (1,0,3)?
dw
given w = tan z.
dz
dz
( z 3)
where c is the circle
z = 1.
10. Find the residue of the function
f ( z) =
4
at its simple pole.
z ( z 2)
3
Apply
1.
Examine the function
2.
Check if
u=
between
them.
3.
u = x 4 + y 4 2 x 2 + 4 xy 2 y 2 for extreme values.
x+ y
xy
,v=
are functionally dependent. If so find the relationship
x y
( x y )2
By transforming into cylindrical polar coordinates evaluate
( x
+ y 2 + z 2 )dxdydz taken
over the region of space defined by x
+ y 1 and 0 x 1 .
2
4.
Using Gauss divergence theorem evaluate
F n ds where
is
F = 4 xz i y 2 j + yz k and S
the surface of the cube bounded by x = 0, y = 0, z = 0, x = 1, y = 1, z = 1.
40
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
5.
When the function f(z) = u + iv is analytic, show that u = constant and v = constant are
orthogonal.
1
.
z
6.
Determine the image of 1 < x < 2 under the mapping w =
7.
Find the area of the cardiod r = 4 ( 1+ cos ) using double integral.
8.
Apply Greens theorem in the plane to evaluate
(3x
8 y 2 )dx + (4 y 6 xy )dy
where C is the boundary of the region defined by x = 0, y = 0 and x + y = 1.
If u = log( x + y ) , find v and f (z) such that f (z) = u + iv is analytic.
2
9.
10. Using Cauchys integral formula evaluate
e z dz
where C is the Circle
( z + 2 ) ( z + 1) 2
z = 3.
Analyze / Evaluate
x=
1. Prove that
2. If
u
v
w
,y =
,z =
are functionally dependent.
vw
wu
u v
g ( x, y ) = (u , v) where u = x 2 y 2 , v = 2 xy prove that
2
2g 2g
2
+
= 4 ( x 2 + y 2 )
+
2
2
2
x
y
v 2
u
3. Evaluate the integration
xyzdxdydz
taken throughout the volume for which
x, y, z 0 and
x2 + y 2 + z 2 9 .
4. Evaluate the following integral by changing to spherical coordinates
1
1 x
1 x
dxdydz
1 x
5. Verify Gauss divergence theorem for
F = x 2 i + y 2 j + z 2 k where S is the surface of the cuboid
formed by the planes x= 0, x= a, y = 0, y = b, z = 0 and z = c.
6. Determine the bilinear transformation that maps the points -1, 0, 1 in the z-plane onto the points
0, i, 3i in the w-plane.
7. Evaluate
cos 2
d .
5 4 cos
41
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
8. Using contour integration, evaluate
(
0
9. Expand
f ( z) =
(z 1)(z 3)
x2
dx .
x2 + 9 x2 + 4
)(
as Laurents series valid in the regions:
1 < z < 3 and 0 < z 1 < 2 .
10. Show that
F = (6 xy + z 3 )i + (3x 2 z ) j + (3xz 2 y )k is irrigational vector and find the
scalar potential function
such that F = .
Unit I
Functions of Several Variables
Functions of two variables - Partial derivatives - Total differential - Derivative of implicit functions Maxima and minima - Constrained Maxima and Minima by Lagrangian Multiplier method - Jacobiansapplication to engineering problems.
9 Hours
Unit II
Multiple Integrals
Double integration in cartesian and polar co-ordinates - Change of order of integration - change of
variables- Area and volume by multiple integrals- application to engineering problems.
9 Hours
Unit III
Vector Calculus
Gradient - divergence - curl- line - surface and volume integrals - Greens - Gauss divergence and Stokes
theorems (statement only) - application to engineering problems.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Analytic Functions
Analytic functions- Necessary condition of analytic function-Sufficient condition of analytic
function(statement only)- properties - Determination of analytic function using Milne Thomsons method,
conformal mappings - Mappings of w= z + a, az, 1/z, ez- bilinear transformation - application to
engineering problems.
9 Hours
Unit V
Complex Integration
Cauchys fundamental theorem (statement only)- and application of Cauchys integral formula(statement
only) Taylors and Laurents series- classification of singularities - Cauchys residue theorem (statement
only) Contour integration - circular and semi circular contours (excluding poles on the real axis)application to engineering problems
9 Hours
Total: 45+15 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
B. S. Grewal, Higher Engineering Mathematics, Khanna Publications, New Delhi, 2000.
K. A. Lakshminarayanan, K. Megalai, P. Geetha and D. Jayanthi , Mathematics for Engineers,
Volume II, Vikas Publishing House, New Delhi. 2008.
42
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
P. Kandasamy, K. Gunavathy and K. Thilagavathy, Engineering Mathematics, Volume II, S.
Chand & Co., New Delhi, 2009.
T. Veerarajan, Engineering Mathematics, Tata McGraw Hill Publications, New Delhi, 2008.
E. Kreyszig, Advanced Engineering Mathematics, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, Singapore, 2008.
C. Ray Wylie and Louis. C. Barrett, Advanced Engineering Mathematics, Tata McGraw Hill
Publications, 2003.
43
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11O103 ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY
(Common to all branches)
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
Imparting knowledge on the principles of water characterization, treatment methods and industrial
applications
Understanding the principles and application of electrochemistry and corrosion science
Basic information and application of polymer chemistry, nanotechnology and analytical
techniques
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Understand the chemistry of water and its industrial & domestic application.
Utilization of electrochemistry principle in corrosion control and industrial application.
Understanding the various types of polymers and its industrial application.
Applications of nanotechnology and analytical techniques in day to day life.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S.No
1
2
3
4
5
6
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I
Test II
Model
Examination
Semester End
Examination
20
20
30
20
10
100
20
20
30
20
10
100
10
20
30
20
20
100
10
20
30
20
20
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Distinguish between alkaline and non alkaline hardness.
What is meant by priming? How it is prevented?
What is meant by caustic embrittlement?
What is the role of calgon conditioning in water treatment?
What is break point chlorination?
Write the significances of EMF series.
Define single electrode potential of an electrode.
The marks secured in the Test I and II will be converted to 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks
44
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
Differentiate between electrochemical and electrolytic cells.
What are the advantages of H2-O2 fuel cell?
What are reference electrodes?
Mention the various factors influencing the rate of corrosion.
State Pilling-Bedworth rule.
What are the constituents of water repellant paints?
What is pitting corrosion?
Write any four applications of galvanic series.
Differentiate between nanocluster and nanocrystal.
List the monomers of nylon -6 and nylon-11.
Define functionality of a monomer.
What are the monomers of epoxy resin?
Differentiate between addition and condensation polymers.
What are auxochromes? Give examples.
Give any two applications of IR spectroscopy.
State Beer-Lamberts law.
Write any two applications of flame photometry.
What are the limitations of Beer-Lamberts law?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
Soft water is not demineralized water whereas demineralized water is soft water- Justify.
Why sodium carbonate conditioning is not advisable for high pressure boilers?
Boiling cannot give protection to water for all time Reason out.
What are the significances of RO method of water treatment?
Compare reversible and irreversible cells?
Reason out why do the properties of materials change at nanoscale?
Why calomel electrode is called as secondary reference electrode?
A steel screw in a brass marine hardware corrodes. Why?
What is the action of brine solution on iron rod?
Why magnesium element is coupled with underground pipe line?
Which is the easier way to control corrosion?
Lithium battery is the cell of future- Justify.
Iron corrodes at a faster rate than aluminium- Give reason.
Differentiate between electro and elctroless platting.
How thermoplastics differ from thermosetting plastics?
TEFLON is superior to other addition polymers-Justify.
Write any two advantages of free radical polymerization.
Calculate the degree of freedom of water molecule.
Differentiate between AAS and flame photometry.
What is the role of thiocyanide solution in the estimation of iron by colorimetry?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
A water sample contains 204 mgs of CaSO4 and 73 mgs of Mg(HCO3)2 per litre. Calculate the
total hardness in terms of CaCO3 equivalence.
100 ml of sample water has hardness equivalent to 12.5ml of 0.08N MgSO4. Calculate hardness in
ppm.
What is the single electrode potential of a half cell of zinc electrode dipped in a 0.01M ZnSO4
solution at 250C? E0Zn/Zn2+ = 0.763 V, R=8.314 JK-1Mol-1, F= 96500 Coulombs.
Calculate the reduction potential of Cu2+/Cu=0.5M at 250C. E0Cu2+/ Cu= +0.337V.
Mention the type of corrosion that takes place when a metal area is covered with water.
Bolt and nut made of the same metal is preferred in practice. Why?
Caustic embrittlement is stress corrosion- Justify.
Metals which are nearer in electrochemical series is preferred in practice. Why?
What are the disadvantages of NICAD battery?
45
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
10. What are the requirements of a good paint?
11. What information can you get from DP?
12. What is degree of polymerization? Calculate the degree of polymerization of polypropylene
having molecular weight of 25200.
13. How the functionality of monomer influences the structure of polymer?
14. Mention the commercial applications of epoxy resins.
15. On what basis polyamide is named as NYLON?
16. Why UV spectroscopy is called as electronic spectra?
17. IR spectrum is called as vibrational spectrum- Justify.
18. How absorption spectrum is differing from emission spectrum?
Analyze/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Distinguish between hardness and alkalinity.
Distinguish between battery and cell.
Corrosion phenomenon is known as thousand dollar thief - reason out.
What is the basic difference between polymers and oligomers?
How do you identify an organic molecule using IR spectrum?
Unit I
Chemistry of Water and its Industrial Applications
Hardness of water: Equivalents of calcium carbonate - Units of hardness - Degree of hardness and its
estimation (EDTA method) - Numerical problems on degree of hardness - pH value of water. Use of water
for industrial purposes: Boiler feed water-scale-sludge - caustic embrittlement. Softening of hard water:
External conditioning zeolite - ion exchange methods - internal conditioning calgon - phosphate
methods. Desalination: Reverse osmosis - electrodialysis. Use of water for domestic purposes: Domestic
water treatment - Disinfection of water - break point chlorination.
Characterization of your campus water.
9 Hours
Unit II
Electrochemistry for Materials Processing
Introduction emf - Single electrode potential - Hydrogen electrode - Calomel electrode - Glass electrode
- pH measurement using glass electrode - Electrochemical series. Cells: Electrochemical cells Cell
reactions- Daniel cell Reversible cells and irreversible cells - Difference between electrolytic cells and
electrochemical cells. Concept of electroplating: Electroplating of gold - electroless plating (Nickel).
Batteries: Secondary batteries - lead acid, nickel - cadmium and lithium batteries. Fuel cell: Hydrogen oxygen fuel cell.
Electricity assisted painting.
9 Hours
Unit III
Chemistry of Corrosion and its Control
Corrosion: Mechanism of corrosion- Chemical and electrochemical - Pilling-Bedworth rule - Oxygen
absorption Hydrogen evolution - Galvanic series. Types of corrosion: Galvanic corrosion - Differential
aeration corrosion - Examples - Factors influencing corrosion. Methods of corrosion control: Sacrificial
anodic protection - Impressed current method. Protective coatings: Paints - Constituents and Functions.
Special paints: Fire retardant - Water repellant paints.
Applications of vapour phase inhibitors.
9 Hours
46
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Unit IV
Introduction to Polymer and Nanotechnology
Polymers: Monomer - functionality - Degree of polymerization - Classification based on source applications. Types of polymerization: Addition, condensation and copolymerization. Mechanism of free
radical polymerization. Thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics - Preparation, properties and applications:
Epoxy resins, TEFLON, nylon and bakelite. Compounding of plastics. Moulding methods: Injection and
extrusion. Nanomaterials: Introduction Nanoelectrodes - Carbon nanotubes - Nanopolymers Application.
A detailed survey on application of polymer in day to day life.
9 Hours
Unit V
Instrumental Techniques of Chemical Analysis
Beer Lamberts law - Problems. UV visible and IR spectroscopy: Principle- Instrumentation (block
diagram only) - Applications. Colorimetry: Principle Instrumentation (block diagram only) - Estimation
of iron by colorimetry. Flame photometry: Principle - Instrumentation (block diagram only) - Estimation of
sodium by flame photometry. Atomic absorption spectroscopy: Principle - Instrumentation (block diagram
only) - Estimation of nickel by atomic absorption spectroscopy.
Applications of analytical instruments in medical field.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
3.
P. C. Jain and M. Jain, Engineering Chemistry, Dhanpat Rai Publications., New Delhi, 2009.
R. Sivakumar and N. Sivakumar, Engineering Chemistry, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 2009.
B. R. Puri, L. R. Sharma and Madan S. Pathania, Principles of Physical Chemistry, Shoban Lal
Nagin Chand & Co., 2005.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Sashi Chawla, Text Book of Engineering Chemistry, Dhanpat Rai Publications, New Delhi, 2003.
B. S. Bahl, G. D. Tuli and Arun Bahl, Essentials of Physical Chemistry, S. Chand & Company,
2008.
J. C. Kuriacose and J. Rajaram, Chemistry in Engineering & Technology, Vol. 1&2, Tata
McGraw-Hill, 2009.
C. P. Poole Jr., J. F. Owens, Introduction to Nanotechnology, Wiley India Private Limited, 2007.
Andre Arsenault and Geoffrey A. Ozin, Nanochemistry: A Chemical Approach to Nanomaterials,
Royal Society of Chemistry, London, 2005.
Language elective II
(Common to all branches)
3 1 0 3.5
47
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11A204/11C204/11M204 - APPLIED MATERIALS SCIENCE
(Common to AE, CE, and ME)
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To make students familiar in the properties of conducting, semiconducting, magnetic and
dielectric materials
To acquire knowledge in thermal properties of materials used in construction and non-destructive
techniques
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
a.
c.
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in
various materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting,
fabrication, machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of
the course, students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable
component in industry
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Understanding the electrical properties of metals.
Able to differentiate intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors.
Realize the frequency and temperature dependence of various polarization mechanisms.
The importance of good and bad conductors and their practical applications in their respective
fields.
Acquiring knowledge about the non-destructive technology.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S.No
1
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Test 1
25
Test 2
25
Model
Examination
20
Semester End
Examination
20
Understand
25
25
25
25
3
4
Apply
Analyze
20
20
20
20
20
20
20
20
5
6
Evaluate
Create
10
-
10
-
15
-
15
-
100
100
100
100
Total
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted to 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10 marks
will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
48
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
Mention the postulates of classical free electron theory.
State Wiedemann-Franz law.
Define the term Fermi energy and mention its importance.
Define drift velocity. How is it different from thermal velocity of an electron?
Explain the Fermi-Dirac distribution function of electrons. Illustrate graphically the effect of
temperature on the distribution.
Define mean free path.
Distinguish between the p-type and n-type semiconductors.
What are donors and acceptors?
What is the meaning of band gap of a semiconductor?
Discuss the variation of Fermi level with temperature in the case of p-type and n-type
semiconductors.
Explain the different types of polarization mechanisms in dielectrics and sketch their dependence
on the
frequency of applied electric field.
What is dielectric breakdown? Summarize the various factors contributing to breakdown in
dielectrics.
Discuss the different modes of heat transfer and mention their special features.
Write a note on X-ray fluoroscopy.
Describe the construction and working of ultrasonic flaw detector. Also write the merits and
demerits.
What is the basic principle of liquid penetrant method?
Briefly discuss the different stages involved in LP testing.
What are the characteristics of the LP testing materials?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
Mention the salient features of the free electron gas model. Obtain the Ohms law based on it.
Mention the limitations of classical free electron theory.
Define density of states and also mention its uses.
Explain thermal conductivity and derive an expression for thermal conductivity of metals.
Derive an expression for density of states in a metal and hence obtain the Fermi energy in terms of
density of free electrons.
Distinguish between relaxation time and collision time.
Why do you prefer extrinsic semiconductor over intrinsic semiconductor?
What is Hall effect? What is its use in semiconductors?
Deduce the relation for the local field of a dielectric material which is in cubic structure.
Deduce Clausius-Mosotti relation and explain its use in predicting dielectric constants of solids.
Distinguish between thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity.
Explain the heat flow through compound media in series and parallel.
Explain the principle behind radiography.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
Assuming the electron-lattice interaction to be responsible for scattering of conduction electrons in
a metal, obtain an expression for conductivity in terms of relaxation time and explain any three
drawbacks of classical free electron theory of metals.
Explain any two practical applications of conduction and convection.
Explain the thermal conductivity of rubber.
Elaborate how you will explore the defects in automotive parts?
49
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Analyze/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
State the relation between thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. Does it hold good for
all types of materials?
Calculate the Fermi energy of copper at 0K. Atomic weight and density of copper are 63.54 and
8950 kg/m3 respectively.
By how many orders of magnitude is the mean free path reduced in a certain metal when
temperature increases from 0C to 340C? The temperature coefficient of resistivity = 5x10-3.
Why do you prefer silicon for transistors and GaAs for laser diodes?
Sketch the variation of conductivity with temperature in the case of intrinsic and extrinsic
semiconductors.
How will you determine the type of charge carriers present in a semiconductor?
Mention the limitations of LP testing.
Unit I
Electrical Properties of Metals
Introduction- Derivation of microscopic form of Ohms law- postulates of classical free electron theoryderivation of electrical conductivity of metals (Drude- Lorentz theory)- merits and demerits. Derivation of
thermal conductivity Wiedemann-Franz law- verification. Electron energies in metal and Fermi energyFermi-Dirac distribution function and its variation with temperature- density of energy states- calculation of
density of electron and fermi energy at 0K- average energy of free electron at 0K- Importance of fermi
energy- problems.
Quantum free electron theory and Band theory of solids.
9 Hours
Unit II
Semiconducting Materials & Devices
Introduction - elemental and compound semiconductors - Intrinsic semiconductors: density of electrons density of holes- determination of carrier concentration and position of Fermi energy- band gap energy
determination (quantitative treatment). Extrinsic semiconductors: carrier concentration in p-type and n-type
semiconductors. Hall effect- theory of Hall effect- experimental determination of Hall voltageapplications. Semi conducting devices: solar cells (Photovoltaic effect) uses. Photo detectors: pin photo
diodes applications.
Variation of Fermi level with temperature and doping concentration in extrinsic semiconductors.
9 Hours
Unit III
Dielectrics
Introduction- fundamental definitions in dielectrics- expressions for electronic, ionic and orientation
polarization mechanisms- space charge polarization- Langevin- Debye equation- frequency and
temperature effects on polarization- dielectric loss- internal field- expression for internal field (cubic
structure)- derivation of Clausius-Mosotti equation importance. Dielectric breakdown- various
breakdown mechanisms with characteristics- applications of dielectric materials and insulating materials problems.
Charging and discharging of capacitors.
9 Hours
50
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Unit IV
Thermal Physics
Mode of heat transfer-thermal conductivity-thermal diffusivity-thermal conduction through compound
media (bodies in series and parallel) - thermal conductivity of good conductor - Forbes method-thermal
conductivity of bad conductor- Lees disc-radial flow of heat-expression for thermal conductivity of
rubber-experimental determination-practical applications of conduction-problems.
Thermal and ventilation design of buildings .
9 Hours
Unit V
Non-Destructive Testing
Introduction - various steps involved in NDT process-X-ray radiographic technique -displacement method
merits, demerits and applications of X-ray radiography - X-ray fluoroscopy liquid penetrant methodadvantages, disadvantages and applications ultrasonic flaw detector - block diagram - construction and
working - merits and demerits. Thermography: types-block diagram - recording of thermal images - merits,
demerits and applications.
Fluoroscopy or Real-time Radiography.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
V. Rajendran, Engineering Physics, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 2011.
M. Arumugam, Physics II, Anuradha Publications, Kumbakonam, 2005.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
S. O. Pillai, Solid State Physics, New Age International Publications, New Delhi, 2006.
M.N. Avadhanulu and P.G. Kshirsagar, A Text Book of Engineering Physics, S. Chand &
Company Ltd., New Delhi, 2005.
V. Raghavan, Materials Science and Engineering, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2009.
D.S Mathur, Elements of properties of matter, S.Chand Publications, New Delhi, Reprints 2010.
P.K. Palanisami, Physics For Engineers, Scitech Publications (India)Pvt. Ltd, Chennai, 2002
51
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11M106 ENGINEERING MECHANICS
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To comprehend the static equilibrium of particles and rigid bodies, effect of friction on
equilibrium, laws of motion, kinematics of motion and the interrelationship
To gain knowledge on properties of surfaces and solids, learn the behaviour of particles and rigid
bodies under motion
To be able to write the equation for dynamic equilibrium
All these should be achieved both conceptually and through solved examples
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Analysis of state of equilibrium of a particle or rigid body
Resolving the support reactions under 2D and 3D analysis
Basic knowledge in analyzing forces and prediction of rigid body motion
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
Remember
20
20
10
10
Understand
30
20
20
20
Apply
30
20
30
30
Analyze
20
20
20
20
Evaluate
--
20
20
20
Create
--
--
--
--
100
100
100
100
Total
4
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10 marks
will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated by giving equal weightage (50%) for
both Civil and Mechanical Engineering
52
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
What is rigid body?
Name the system of units.
Mention the two systems of dimensions.
Give the dimension of acceleration under MLT system.
What is a force?
Define system of forces.
How the force system is classified?
Which is known as resultant force?
State Newtons three laws.
Name three graphical methods used to find the resultant of a system of forces.
Which are known as laws of mechanics?
What is dimensional homogeneity?
State parallelogram law of forces.
State Lamis theorem.
Define equilibrium.
Define equilibrant.
What is a moment?
Define couple.
What are the types of supports used in beams?
Name the types of loads applied onto a beam.
Give an example for coplanar concurrent system of forces.
What is a truss?
How the forces in a truss are analyzed?
Give the equations of equilibrium for particle in 2D and in space.
Write down the equations of equilibrium of a rigid body under 2D and 3D.
What is called as resolving a force?
Define friction.
How the friction is classified?
What is motion impending?
State the nature of friction force.
What is angle of friction?
What is cone of friction?
State the usage of wedge.
Give the condition for self-locking of screw jack.
What is polar moment of inertia?
State parallel axis theorem.
State perpendicular axis theorem.
Give the relation between area MOI and mass MOI.
Write down the formula to find centroid of right angled triangle.
State the law of conservation of momentum.
State the work-energy principle.
What is general plane motion?
Give the expression for Newtons laws of motion.
What is angular velocity?
What is angular acceleration?
Define displacement.
Define velocity.
Define acceleration.
What is linear motion?
Classify the motions of a rigid body.
53
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
Differentiate unit and dimension.
How to get the net effect of forces acting simultaneously on a particle?
What does the principle of transmissibility imply?
State the difference between mass and weight.
At what situation Lamis theorem can be used.
When to apply parallelogram law or triangular law of forces.
Mention the relation between resultant force and an equilibrant.
Give two practical examples for application of moment.
Give two practical examples for application of couple.
How to convert a force into force couple system?
Which kind of support has maximum reactions and what are they?
Which law is applicable to analyze supports and reactions?
Which theorem helps to determine resultant of a parallel coplanar system of forces?
Differentiate moment from couple.
How will you identify whether the given system is under equilibrium or not?
Why force is called as a vector?
In problems involving three dimensions, which kind of approach is used to determine the resultant
force? Why?
Give two practical situations where friction is considered as good.
Why friction force is not liked at some situations?
F = N is applied only during motion impending condition. State the reason.
How to decide whether a body is in motion or not?
When to include friction forces?
What is the difference between applied force and friction force?
When does centroid and centre of gravity will be same?
A jet is used to irrigate the plants in a lawn. How to get the maximum length of the jet?
A bobber plane is dropping a bomb on the enemys target. Under which category the analysis can
be carried out inorder to find the correct position of dropping?
A droplet of water is dropping from the tap. To find the distance between the drops, which laws
could be used?
What is the use of radius of gyration?
How principal MOI differs from MOI?
At what situation conservation of momentum principle can be applied?
Differentiate distance from displacement.
Write the difference between moment and momentum.
Apply / Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
A boat is towed by two ropes making certain inclination from the boat axis. How to determine the
resulting direction of boat movement?
A load is hanging through rope and a pulley fixed to the ceiling. Knowing the friction coefficient
between rope and pulley and the magnitude of weight compute the effort and its direction required
to hold the weight in equilibrium position.
Given the applied forces, frictional coefficient and weight of a block resting on a rough plane how
to check the equilibrium condition of the block?
A non-coplanar parallel system of forces is acting on a structure. How to reduce it to a forcecouple system?
In a 3D analysis of forces a ball and socket support is used. Give the procedure to determine the
value of support reactions.
Knowing the friction co-efficients and position of the ladder compute the distance through which a
man can climb on the ladder before the ladder starts slipping.
What is understood by calculating the effort applied to a screw jack to lift up and lower down the
given amount of load? Justify the phenomenon.
54
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
8.
In positioning a beam in a structure, always the depth portion is chosen greater than its width
portion. Analyze and write down the reason.
9. Two trains are starting at different time from the same station. Assume that first train always
moves with velocity less than that of second train and the acceleration pattern for both trains is
different during start, motion and stop of the trains. Enumerate the approach of finding the
distance at which second train overtake the first train
10. How to determine the velocity and direction of two bodies having an oblique central impact after
the impact is over?
11.
The girl has a mass of 17kg and mass center at Gg, and the tricycle has a mass of 10kg and mass center
at Gt. Determine the normal reactions at each wheel for equilibrium. [NA = 128.8 N, NB = NC =
68.0 N]
12.
The crane provides a long-reach capacity by using the telescopic boom segment DE. The entire
boom is supported by a pin at A and by the telescopic hydraulic cylinder BC, which can be considered as a
two-force
member. The rated load capacity of the crane is measured by a maximum force
developed in the hydraulic cylinder. If this maximum force is developed when the boom supports a mass m
55
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
= 6 Mg and its length is l =
40 and = 60, determine the greatest mass that can be supported when
the boom length is extended to l = 50
m and = 45. Neglect the weight of the boom and the size of
the pulley at E. Assume the crane does not overturn. Note: when = 60 BC is vertical; however, when
= 45 this is not the case. [m = 3.26 Mg]
13.
The boy at D has a mass of 50 kg, a center of mass at G, and stands on a plank at the position shown.
The plank is pin-supported at A and rests on a post at B. Neglecting the weight of the plank and post,
determine the magnitude of force P his friend (?) at E must exert in order to pull out the post. Take =
0.3 and C = 0.8. [P = 264 N]
14.
The mine car is being pulled up to the inclined plane using the motor M and the rope-and-pulley
arrangement shown. Determine the speed vp at which a point P on the cable must be traveling
toward the motor to move the car up the plane with a constant speed of v = 5 m/s. [VP = 15.00
m/s]
15.
.
56
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Each of the three barges has a mass of 30 Mg, whereas the tugboat has a mass of 12 Mg. As the
barges are being pulled forward with a constant velocity of 4 m/s, the tugboat must overcome the frictional
resistance of the water, which is 2 kN for each barge and 1.5 kN for the tugboat. If the cable between A and
B breaks, determine the acceleration of the tugboat. [a = 0.0278 m/s2 ]
Unit I
Basics and Equilibrium of Particles
Introduction - Units and Dimensions - Laws of Mechanics Parallelogram Law of forces Vectors
Vectorial representation of forces -Coplanar Forces Resolution and Composition of forces Equilibrium
of a particle under coplanar forces Forces in space - Equilibrium of a particle in space
Equivalent force systems
9 Hours
Unit II
Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies
Free body diagram Types of supports and their reactions Moments and Couples Vectorial
representation of moments and couples Scalar components of a moment Varignons theorem
resolution of a given force into a force acting at a given point and a couple reduction of a system of
coplanar forces acting on a rigid body into a single force and a single couple - Equilibrium of Rigid bodies
in two dimensions Equilibrium of Rigid bodies in three dimensions Problems involving ball and socket
joint only
Internal forces in a member
9 Hours
Unit III
Friction
Frictional force Laws of Coulomb friction Angle of friction cone of friction Equilibrium of bodies
on inclined plane Ladder friction - Wedge Friction Belt friction Band brakes - Screw Jack - Self
locking - Rolling Resistance
Friction in journal bearing
8 Hours
Unit IV
Properties of Surfaces and Solids
Determination of Areas and Volumes First moment of area and the Centroid of sections Rectangle,
circle, triangle from integration T section, I section, Angle section, Hollow section by using standard
formula second and product moments of plane area Rectangle, triangle, circle from integration T
section, I section, Angle section, Hollow section by using standard formula Parallel axis theorem and
perpendicular axis theorem Polar moment of inertia Principal moments of inertia of plane areas Mass
moment of inertia Relation with area MOI
Mohrs circle to determine principal MOI
9 Hours
Unit V
Dynamics of Particles
Displacements, Velocity and acceleration, their relationship Linear motion Curvilinear motion (no
derivations) Newtons law Work Energy Equation of particles Principle of Impulse and Momentum
Impact of elastic bodies
Dependent motion between particles
10 Hours
Total: 45 + 15 Hours
57
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Textbook
1.
F.P. Beer, and Jr. E.R Johnston, Vector Mechanics for Engineers Statics and Dynamics, Tata
McGraw-Hill Publishing Company, New Delhi, 2007
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Irving H. Shames, Engineering Mechanics - Statics and Dynamics, Pearson Education Asia Pvt.
Ltd., 2006
R.C.Hibbeller, Engineering Mechanics: Combined Statics & Dynamics, Prentice Hall, 2009
D. P. Sharma, Engineering Mechanics, Dorling Kindersley (India) Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 2010
S. Rajasekaran and G. Sankarasubramanian, Fundamentals of Engineering Mechanics, Vikas
Publishing House Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 2005
Robert W. Soutas-Little, Daniel J. Inman and Daniel S. Balint, Engineering Mechanics - Statics
and Dynamics, Cengage LearningIndia Private Limited, New Delhi, 2009
58
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11M206 MANUFACTURING PROCESSES
3
0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To make the students learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in various
Materials
To make students understand requirements and methodologies to be followed in casting,
fabrication and forming of engineering materials
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
c.
g.
i.
The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in
various materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting,
fabrication, machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of
the course, students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable
component in industry.
The graduates can become job-givers rather than just job-seekers
The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement in Mechanical, Mechatronics and Electrical Engineering as well as IT companies
SKILL SET
1.
Manufacturing a desirable component in industry
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
6
Blooms Taxonomy
(New version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
create
Total
Test I*
Test II*
25
25
20
10
20
100
25
25
20
10
20
100
Model
Examinations*
25
25
20
10
20
100
Semester End
Examination
25
25
20
10
20
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Define casting
What is meant by pattern?
List out various types of patterns
Define solidification.
Define core print.
List out various types of patterns allowances.
What are the various methods of special casting process?
Define centrifugal casting
What do you mean by lost wax process?
What are the defects of casting?
Define welding.
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10 marks
will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
59
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
List out various types welding process
What are the different types of electrodes in arc welding?
What are the different flames available in gas welding?
Define brazing and soldering.
Define recrystalization
What do you mean by hot working and cold working?
What is meant by plastic deformation?
Define metal forming.
Define blanking and piercing.
What is meant by trimming and nibbling?
Define embossing and coining?
What is meant by stretch forming?
What is meant by high energy rate forming?
Give some application of metal spinning process and explosive forming.
List out various types of plastics
What is meant by thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic?
Give some application of Blow molding process.
What is meant by rotational molding?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
What are the functions of a binder in moulding sand?
Why the cores are reinforced?
What are the special features of resistance projection welding?
What effect does carbon content of steel have on weldability?
What is arc Stability? How is it achieved?
What is press forging? How does it differ from drop forging?
What is purpose of heat treatment of forgings?
Write down the significance of parison.
Apply / Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Can the ferrous metals be cast by die-casting method? If yes, then how?
Why permanent moulds are preheated before operations?
How the dies for die casting are manufactured?
Why the cleaning of a joint is important before welding?
Why is tungsten the preferred material for non-consumable electrodes?
Why a cold worked metal is annealed?
Why for cold rolling done, a four high rolling mill is usually used?
How the moulds for plastic parts are manufactured?
How are the injection moulding machines rated?
What are the applications of investment casting?
Unit I
Metal Casting Processes
Different terminologies used in production processes - Sand casting Sand moulds - Type of patterns
Pattern materials Pattern allowances Types of Moulding sand Properties Core making Methods of
Sand testing Moulding machines Types of moulding machines - Melting furnaces Cupola Electric
furnaces Sand Casting defects Inspections methods - Importance of Special casting processes Shell,
investment casting Pressure die casting Centrifugal casting
To find the coarse grain fineness number for the sand particles.
9 Hours
60
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Unit II
Fabrication Processes
Fusion welding processes Types of Gas welding Equipments used Flame characteristics Filler and
Flux materials - Arc welding equipments - Electrodes Principles of Resistance welding Spot/butt, seam
stud welding Percusion welding - Gas metal arc welding Submerged arc welding TIG welding
Principle and application of Plasma arc welding, Thermit welding, Electron beam welding and Friction
welding Weld defects Brazing and soldering - Process adhesivebonding Gluing
Laser welding techniques
9 Hours
Unit III
Bulk Deformation Processes
Hot working and cold working of metals Forging processes Open and close die forging
Characteristics of the process Types of Forging Machines Typical forging operations Rolling of
metals Flat strip rolling Types of Rolling mills Shape rolling operations Tube piercing Defects in
rolled parts Principles of Extrusion Types of Extrusion Principle of rod and wire drawing
Equipments used
Orbital forging and Isothermal forging process
9 Hours
Unit IV
Sheet Metal Forming Processes
Sheet metal characteristics - Typical shearing operations, bending and drawing operations clinching
operation - Stretch forming operations Working principle and application of special forming processes Hydro forming Rubber pad forming Metal spinning Explosive forming Magnetic pulse forming
Peen forming Super plastic formingProcess characteristics
Formability of sheet metal Test methods
9 Hours
Unit V
Forming and Shaping of Plastics
Types of plastics - Characteristics of the forming and shaping processes Moulding of Thermoplastics
Working principles and typical applications of - Injection moulding Plunger and screw machines Blow
moulding Rotational moulding Extrusion - Typical industrial applications Thermoforming
Processing of Thermosets Working principles and typical applications - Compression moulding
Transfer moulding Bonding of Thermoplastics Fusion and solvent methods
Film blowing
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
P. N. Rao, Manufacturing Technology vol I, Tata-McGraw-Hill Publishing Limited, 2010
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Serope Kalpakjian and Steven R. Schmid, Manufacturing Engineering and Technology, Pearson
Education, Inc. 2009 (Second Indian Reprint).
Begman, Manufacturing Process, John Wilely & Sons, VIII Edition, 1999
Radhakrishnan, Manufacturing Technology I, Scitech Publications Pvt Ltd, 2010
Hajra Choudhury, Elements of Workshop Technology, Vol. I & II, Media Promotors Pvt Ltd.,
2009
Thirupathy Reddy, Production Technology, Scitech Publications Pvt Ltd, 2010
61
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11M207 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LABORATORY I
0
1.0
OBJECTIVES
Manufacturing processes used for converting raw materials into finished products. Various
processes,machinery, and operations will be examined with emphasis placed on understanding
engineering materials and processing parameters that influence design considerations, product
quality, and production costs
The program also helps students develop basic machinability concepts and improve to your
teamwork and entrepreneurial skills
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
c)
The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in
various materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting,
fabrication, machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of
the course, students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable
component in industry.
i)
The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes
g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement in Mechanical, Mechatronics and Electrical Engineering as well as IT companies
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Mention the various directions of cutting tool movement.
Role of chip breakers in machining process
Increased complexity in manufacturing requires an awareness of new manufacturing processes and
materials
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Internal Assessment
Semester end examination
Preparation
Remember
Understand
Apply
30
30
20
50
20
--
30
20
Observation and results
Analyze
Evaluate
Record
Mini project /
Model Examination /
Viva-Voce
62
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
Lathe specification
What are the parts present in lathe
Write down the names of any four lathe accessories
lathe bed material
Difference between 3 jaw and 4 jaw chuck?
What are the operations performed in lathe machine
Purpose of dead centre
Purpose of tail stock
What is meant by orthogonal cutting?
Give two examples for orthogonal cutting
What are the four important characteristics of materials used for cutting tools?
What is the purpose of chamfering and boring?
Types of knurling
Types of threads with suitable angles
Define the term Thread cutting
Give the HSS composition
Define feed and depth of cut.
What is meant by tool signature?
What is side rake angle? And mention its effects?
What is clearance angle? And mention its types?
What is meant by nose radius?
What is function of chip breakers?
Name the factors that contributes to poor surface finish in cutting
What are the functions of cutting fluids?
What is meant by milling?
purpose of end milling cutter
Purpose of flute in drill tool
Drill tool point angle________
Name the taper turning methods used in lathe
Purpose of swivel base in lathe machine
Define tolerance
Difference between unilateral and bilateral tolerance
Define pitch
Define clearance
List out some quality symbols
Types of jigs and fixtures used in lathe machine
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Name the various cutting tool materials.
List out various type of feed mechanisms
Name the various tool parts of a single point cutting tool
What are the standard angles of cutting tool?
What is the application of air operated chuck?
Write down the formula for calculating taper turning angle by compound rest method.
Merits on automatic machine.
What are the advantages of automatic lathes?
How surface finish obtain in lathe machine.
How quality component acquire in lathe machine?
63
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Apply/ Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
To find cutting forces are calculated?
How taper angle are calculated?
Write the formula for tail stock set over method
Write the formula for tolerance
List of Experiments
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Exercise on Simple Facing & Turning
Exercise on Step Turning using four jaw chuck
Exercise on Taper turning Model
Exercise on Knurling & Grooving
Exercise on Boring & Chamfering
Exercise on External thread cutting.
Exercise on Drilling using lathe
Study on semiautomatic & automatic lathes
Design experiment
Application oriented experiment
Total: 30 Hours
Practical schedule
Sl.No
Experiment
Hours
Exercise on Simple Facing & Turning
Exercise on Step Turning using four jaw chuck
Exercise on Taper turning Model
Exercise on Knurling & Grooving
Exercise on Boring & Chamfering
Exercise on External thread cutting
Exercise on Drilling using lathe
Study on semiautomatic & automatic lathes
Design experiment
10
Application oriented experiment
64
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11M107 C PROGRAMMING
2 0 3 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To know the basic concepts problem solving.
To understand the basic concepts of C.
To develop the programming skills of students in C.
Program Outcomes
a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement in Mechanical, Mechatronics and Electrical Engineering as well as IT companies
SKILL SET
a. Programming ability.
b. Developing applications for real world problems.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S.No
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Blooms Category
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
TOTAL
Test I
Test II
20
20
50
10
0
100
10
20
40
20
10
100
Model
Examination
10
10
40
20
20
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
What is the general structure of a C program?
List the rules for defining a variable.
What are the I/O functions in C?
What is a header file?
State the associativity property of an operator.
Define a ternary operator. Give example
What is an array and a pointer?
What is the significance of function?
Define a structure.
What are bit-wise operators?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Compare while loop with do while Loop.
What are the advantages of using Macro?
Explain how recursive functions affect the run time efficiency.
Differentiate between Structure and Union in C.
How is memory managed in C?
How garbage collection is done in C?
End-semester
Examination
10
10
40
20
20
100
65
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Write a recursive function to calculate the factorial of number.
Write a C program to check whether the given number is palindrome or not
Write a program to check whether the given number is prime or not.
Write a C program to find the roots of quadratic equation ax2+bx+c=0.
Write a C program to find average of n numbers.
Write a program to generate the pay slip of an employee using Structure.
Write a C program to search for a specified element in an array.
Write a program to compute Matrix Multiplication.
Analysis
1.
2.
3.
4.
Explain the difference between while and do-while statements
Why are pointers so powerful? Analyze their efficiency giving an example?
Is there any advantage of using recursion over looping control structures? Give a suitable example.
Illustrate the Limitation of array of pointers to strings using a sample example.
Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
Differentiate the keywords BREAK and CONTINUE.
Justify the need for Type Casting over Type Conversion.
Compare and contrast I/O mapped I/O with Memory mapped I/O.
Summarize the various built in String functions.
Create
1.
Create a structure to store the following details: Rollno, Name, Mark1, Mark2, Mark3, Total,
Average, Result and Class. Write a program to read Rollno, name and 3 subject marks. Find out the
total, result
and class as follows:
a) Total is the addition of 3 subject marks.
b) Result is "Pass" if all subject marks are greater than or equal to 50 else "Fail".
c) Class will be awarded for students who have cleared 3 subjects
i. Class "Distinction" if average >=75
ii. Class "First" if average lies between 60 to 74 (both inclusive)
iii. Class "Second" if average lies between 50 & 59 (both inclusive)
d) Repeat the above program to manipulate 10 students' details and sort the structures as per rank
obtained by them.
2 0 3 3.5
Unit I
Fundamentals of C
History of C-Importance of C-Basic structure of C programs-Programming style-Executing a C programCharacter set-C tokens-Keywords and identifiers-Constants (Declaration, Definition)-Variables
(Declaration)-Data types.
6 Hours
66
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
Unit II
Operators and Expressions
Arithmetic operators-Relational operators-Logical operators-Assignment operator-Increment and
decrement operator-Conditional operator-Bitwise operator-Arithmetic expressions-Evaluation of
expressions-operator precedence-Managing I/O operations.
6 Hours
Unit III
Branching and Looping
Decision making - IF statement-IF-ELSE-Nested IF-ELSE, ELSE-IF Ladder-Switch statement-GOTO
statement-?: operator-While statement-DO statement-FOR statement-Jumps in loops.
6 Hours
Unit IV
Arrays and Strings
One dimensional, two dimensional, multi dimensional arrays-Initialization and declaration-Dynamic
arrays-Strings-Declaring-Initializing-Reading-Writing strings-Arithmetic operations on characters-string
comparison-string handling functions.
6 Hours
Unit V
Functions, Structures and Pointers
User defined function-Declaration-Definition of function-function calls-category of functions-Nesting of
functions-Recursion-Structures-Definition, Declaration, Accessing structure members-PointersDeclaration, Initialization, Accessing.
6 Hours
List of Exercises
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Simple C programs.
Program using operators and expressions.
Programs to implement Looping and decision statements.
Write a C program to copy the content of one array into another array in reverse order.
Write a C program to reverse a string and check whether the string is a palindrome or not.
Write a C program to illustrate the concept of Call by Value and Call by Reference.
Write a C Program to find factorial of given N numbers with recursion function.
Simple programs using structures and pointers
Total: 30+45 Hours
Textbook
1.
E.Balagurusamy, Programming in ANSI C, Fourth Edition, Tata McGraw Hill,2007
References
1.
2.
Behrouz A.Forouzan and Richard F. Gilberg, Computer Science: A Structure program approach
using C, Cengage learning India edition. 2008
Ritchie D.M, Kernighan B.W, C Programming Language, PHI, 2000.
67
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
11O109 ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY LABORATORY
(Common to all branches)
0 0 2 1.0
OBJECTIVES
Imparting knowledge on basic concepts and its applications of chemical analysis
Training in chemical and instrumental methods
Develop skills in estimation of a given sample by chemical and instrumental methods
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Estimate the strength of solution by chemical and instrumental methods.
Analyze the water quality parameters of given water samples.
Measurement of corrosion rate of a given sample.
Knowledge of various components used in analytical instruments.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Internal Assessment
Semester
End Examination
Preparation
10
15
Execution
10
15
Observation & Results
Record
Model Examination
Viva Voce
10
5
10
5
15
5
Total
50
50
List of Experiments (Any ten experiments)
1.
Preparation of molar and normal solutions of the following substances oxalic acid, sodium
carbonate, sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid.
2. Determination of alkalinity in a water sample.
3. Determination of molecular weight of a polymer by viscometry method.
4. Determination of total, temporary and permanent hardness of water by EDTA method.
5. Conductometric titration of mixture of acids.
6. Determination of strength of iron by potentiometric method using potassium dichromate.
7. Estimation of iron (thiocyanate method) in the given solution by spectrophotometric method.
8. Determination of strength of hydrochloric acid by sodium hydroxide using pH meter.
9. Determination of sodium and potassium ions in water sample by flame photometric method.
10. Determination of corrosion rate by weight loss measurements.
11. Comparison of alkalinities of the given water samples.
12. Comparison of total dissolved solids (TDS) and hardness of water in Bhavani river and Bannari
Amman Institute of Technology campus.
Total: 30 Hours
68
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Inst. of Tech. | Regulation 2011
69
Practical Schedule
S.No
Experiment
Hours
Preparation of molar and normal solutions of the following substances
oxalic acid, sodium carbonate, sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid.
Determination of molecular weight of a polymer by viscometry method.
Conductometric titration of mixture of acids.
Determination of strength of iron by potentiometric method using
potassium dichromate.
Estimation of iron (thiocyanate method) in the given solution by spectrophotometric
method.
Determination of strength of hydrochloric acid by sodium hydroxide using pH meter.
Determination of sodium and potassium ions in water sample by flame photometric method.
Determination of corrosion rate by weight loss measurements.
Comparison of alkalinities of the given water samples.
10
Comparison of total dissolved solids (TDS) and hardness of water in Bhavani river and
Bannari Amman Institute of Technology campus.
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11O301
ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS III
(Common to all branches Except CSE and Bio-Tech)
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To obtain the knowledge of expressing periodic functions as Fourier series, Fourier transform and
Z transform which is used to analyze signals in signal processing.
Ability to solve boundary value problems in heat and wave equation using partial differential
equations.
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects and
thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1. Acquire more knowledge in basic concepts of engineering mathematics.
2. To improve problem evaluation technique.
3. Choose an appropriate method to solve a practical problem.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Test I1
Test II1
Model Examination1
End Semester
Examination
Remember
20
20
20
20
Understand
40
40
40
40
Apply
30
30
30
30
Analyze/ Evaluate
10
10
10
10
Create
--
100
100
100
100
Total
Remember
1. State the Dirichlets Conditions.
2. Define even and odd function graphically.
3. Write down the complex Fourier transform pair.
4. State convolution theorem in Fourier transform.
5. Define unilateral and bilateral Z-transform of {f(n)}.
6. State initial value theorem in Z-transform.
7. Define complete solution of a partial differential equation.
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted to 20 and model examination will be converted to 20.
The remaining 10 marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly, internal assessment will be
calculated for 50 marks.
70
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
8. Write the complementary function of non homogeneous second order equations of distinct and repeated
roots.
9. What does a2 represent in the equation ytt = a2yxx ?
10. Write any two solutions of the Laplace equation obtained by the method of separation of variables.
Understand
1. Find the general solution of x z y
2. Solve
(D
) p + y (x
+ 2 DD + D 2 z = x 2 y + e x y .
3. Find the half-range cosine series for the function
z2 q = z y2 x2 .
f (x ) = x, 0 < x < and hence deduce the sum of
the
series
(2n + 1)
n =0
4. Find the Fourier series of period 2 for the function
x
f ( x) =
(2 x )
0 x 1
1 x 2
Deduce the sum of
1
.
2
n =1, 3, 5,.. n
5. Find the Fourier transform of
Hence evaluate
1 x
f (x ) =
0
sin x
0 x dx and
for x 1
sin x
x dx .
0
6. Solve the integral equation
for | x | > 1
f ( x ) cos x dx
4z3
7. Find inverse transform
(2 z 1)2 (z 1)
8. Find Z transform of
2n + 3
.
(n + 1)(n + 2)
9. Use convolution theorem to find the inverse Z transform of
8z 2
(2 z 1)(4 z + 1)
10. Give a function which is self reciprocal under Fourier sine and cosine transform.
Apply
1. Find the PDE of all planes having equal intercepts on the x and y axis.
2. Form the PDE of all planes passing through the origin.
3. Expand the function
f ( x ) = cos x in ( , ) as a Fourier series of periodicity 2.
4. A function y=f(x) is given by the following table of values. Make the harmonic analysis
of the function in (0,T) up to the second harmonic.
x
0
T/6
T/3
T/2
2T/3
5T/6
T
y
0
9.2
14.4
17.8
17.3
11.7
0
5. Obtain the constant term and the first harmonic in the Fourier series expansion in (0,12) for the function
y = f(x) defined by the table below
71
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
x
f (x)
0
1.8
1
1.1
2
0.3
3
0.16
4
0.5
5
1.5
6
2.16
7
1.88
8
1.25
9
1.30
10
1.76
11
2.00
6. A taut string of length L is fastened at both ends. The midpoint of the string is taken to a height of b and
then released from rest in this position. Find the displacement of the string at any time t.
7. A string is stretched between two fixed points at a distance 2L apart and the points of the string are
given initial velocities v where
v = cx /L
0 < x <L
= c ( 2L - x) /L
L < x < 2L . x being the distance from an end
point. Find the displacement of the string at any subsequent time.
8. A rod 30 cm long, has its ends A and B at 20C and 80C respectively, until steady state conditions
prevail.
The temperature at the end B is then suddenly reduced to 60 C and at the end A is raised to 40 C and
maintained so. Find the resulting temperature u (x,t).
9. A rectangular plate with insulated surface is 10 cm wide so long compared to its width that it may be
considered infinite length .If the temperature along the short edge y=0 is given by 8 sin(
x
10
) , while the
two long edges x= 0 and x=10 as well as the other short edge are kept at 00c . Find the steady state
temperature.
10. Solve the equation y n + 2 7 y n +1 + 12 y n = 2 , given that y 0 = y1 = 0 .
n
Analyze/ Evaluate
1. Solve (D2-5DD+6D2) z= y sinx.
2. Solve (4D2-4DD+D2)z = 16 log(x+2y).
3. Solve z = p x + q y + p2 q2 .
4. Evaluate
(x
5. Evaluate
(x
0
dx
using transform method.
+ a x 2 + b2
2
dx
2
+ a2
)(
and
(x
0
6. Find Fourier sine transform of
x 2 dx
2
+ a2
e ax
, a >0.
x
7. Find Fourier sine and cosine transform of e-ax , a > 0 and hence find Fourier sine and cosine transform of
x e-ax.
8. Find Fourier transform of e
a2 x2
, a > 0 and hence find Fourier transform of
x2
2
9. Find Fourier sine and cosine transform of x n-1.
10 Find inverse
transform
4z3
.
(2 z 1)2 (z 1)
Unit -I
Fourier Series
Dirichlets conditions General Fourier series Odd and even functions Half range cosine and sine series
Parsevals Identity - Harmonic Analysis- Application to engineering problems.
9 Hours
72
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Unit II
Fourier Transform
Fourier transform pair Sine and Cosine transforms Properties Transforms of simple functions
Convolution theorem - Parsevals Identity-Finite Fourier Transform- Application to engineering
problems.
9 Hours
Unit III
Z -Transform and Difference Equations
Z-transform - Elementary properties Inverse Z-transform Convolution theorem -Formation of difference
equations Solution of difference equations using Z- transform - Application to engineering problems.
9 Hours
Unit-Iv
Partial Differential Equations
Formation of partial differential equations by elimination of arbitrary constants and arbitrary functions
Solution of standard types of first order partial differential equations (excluding reducible to standard forms
Lagranges linear equation Linear partial differential equations of second and higher order with constant
coefficients.
9 Hours
UNIT V
Boundary value problems
Classification of second order quasi linear partial differential equations Fourier series solutions of one
dimensional wave equation One dimensional heat equation (Insulated ends excluded ) Steady state
solution of two-dimensional heat equation (Insulated edges excluded ) Fourier series solutions in
Cartesian coordinates .
9 Hours
Total: 45+15Hours
Textbooks
1 B. S .Grewal , Higher Engineering Mathematics , Khanna Publications , New Delhi ,2000.
2 K. Megalai, P. Geetha and D. Jayanthi , Mathematics for Engineers, Volume III, Vikas Publishing
House, New Delhi,2008.
References
1. P. Kandasamy, K. Gunavathy and K. Thilagavathy, Engineering Mathematics ,Volume III , S. Chand &
Co., New Delhi, 2008.
2. E. Kreyszig. Advanced Engineering Mathematics , 8th Edition , John Wiley & Sons, Inc,Singapore
(2008).
3. T. Veerarajan , Engineering Mathematics ,Tata McGraw Hill
73
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M302 ENGINEERING MATERIALS AND METALLURGY
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge on the structure, properties, treatment, testing and applications of metals and nonmetallic materials
To acquire overall sound knowledge in metallurgy and materials engineering
To predict and control material properties through an understanding of atomic, molecular, crystalline,
and microscopic structures of engineering materials
PROGRAM OUTCOME
(c) The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in various
materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting, fabrication, machining,
materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of the course, students will be able
to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable component in industry.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Adequate to ensure the desired product life in complex environments.
Analysis the various crystal structures and bonding processes.
Identify the materials based on micro structures.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Test 1*
Test 2*
40
30
30
100
40
30
30
100
Model
Examination*
40
30
30
100
Semester End
Examination
40
30
30
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
*
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Define alloy and steel.
What are cooling curves?
What is an equilibrium phase diagram?
How the materials are classified?
Define the term heat treatment.
List the various stages of heat treatment processes.
List some quenching medium generally used in industries.
What is TTT and CCT diagram?
How can you classify iron and steel?
List the bearing materials that commonly used.
What are HSLA and maraging steels?
Define the term degree of polymerization
Name any four thermosetting and thermoplastics.
Define engineering ceramics and composites.
List the various matrix materials used.
What are the factors affecting mechanical properties.
The marks secured in Test 1 and Test 2 will be converted to 20 and Model examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
74
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
Define the term slip and twinning
What is meant by fatigue and creep fracture?
What are the properties that can be determined by tensile test.
How the Brinell hardness number is calculated?
Write down the various formulas to determine the various properties by tensile test.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
When the materials attain their required properties.
How cast iron differ from steel in carbon content?
What are the types of testing carried out to test the mechanical properties
How the deformation of materials taken place?
How the ceramics are manufactured by various processes.
How the ceramics and composites are manufactured?
How the hardness is achieved by various heat treatment processes?
Unit I
Constitution of Alloys and Phase Diagrams
Phase diagram Solid solutions Substitutional and interstitial intermetallic compound cooling curves,
phase rule, lever rule, equilibrium diagrams Isomorphous, and eutectic, peritectic, and eutectoid reactions
with examples Iron Iron carbide equilibrium diagram
Study on microstructure of iron in various transformation phase
9 Hours
Unit II
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment of steel, annealing stress relief, recrystallisation and spheroidizing normalizing,
hardening and Tempering of steel TTT Diagram - Isothermal transformation diagrams cooling curves
superimposed on I.T. diagram, CCR Austempering, martempering, ausforming Hardenability, Jominy
end quench test, Case hardening processes Carburising, Nitriding, Cyaniding, Carbonitriding Flame
and Induction hardening
Testing of salt content in bath, sub zero treatment, Cryogenic treatment
9 Hours
Unit III
Metals and Alloys
Classification of steel and cast iron -- properties and application. Gray, White, Malleable, Spheroidal
Graphite alloy cast irons Effect of alloy additions on steel (Mn, Si, Cr, Mo, V Ti & W) Stainless and
tool steels, HSLA, Maraging steels Alloys of copper, aluminum, magnesium, nickel and zinc composition
and their uses Bearing materials precipitation treatment Alloys for brazing and soldering
Extraction of copper by Smelting process and aluminum by bayers process
9 Hours
Unit IV
Non Metallic Materials
Polymers types, Properties and applications of PE, PP, PS, PVC, PMMA, PET, PC, PA, ABS, PI, PAI,
PPO, PPS, PEEK, PTFE Polymers Rubber and its types- Metal matrix composites manufacturing,
properties and applications - Ceramics Properties and applications of Al2O3, SiC, SiN3, PSZ and Sialon,
ceramic composites
Smart materials such as shape memory alloys
9 Hours
Unit V
Mechanical Properties and Testing
Mechanism of elastic and plastic deformation, slip and twinning tensile test, stress strain curves for
ductile and brittle materials, Types of fracture compression test Hardness tests Impact test Creep
test. fatigue test, endurance limit fatigue limit, S N Curve, Fracture ideal fracture stress, Fracture
toughness, ductile failure - cup and cone type fracture
75
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Metallurgical testing-spectrometer, Strolin apparatus - NDT - Dye Penetrant Test
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
William D Callister, Material Science and Engineering, John Wiley and Sons, Singapore, 2007
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Kenneth G Budinski and Michael K Budinski, Engineering Materials, Prentice-Hall of India, New
Delhi ,2002
V. Raghavan, Materials Science and Engineering, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi 2009
Sydney H Avner, Introduction to Physical Metallurgy, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company
Pvt Ltd., New Delhi 1994
P. Khanna, Text Book of Material Science and Metallurgy, Dhanpat Rai Publication (P) Ltd., New
Delhi, 2007
G. E. Dieter, Mechanical Metallurgy, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi
2007
76
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M303 ELECTRICAL MACHINES AND DRIVES
3 0 0 3
OBJECTIVES
To understand the working principle, performance characteristics of DC Generator and DC Motor
To understand the working principle, operation of 3-phase and 1-phase Induction motor and
synchronous motor
To provide knowledge in the area of electrical dives and their control techniques.
To impart knowledge on
o Basics of electric drives and their characteristics
o Different speed control methods
o Various motor starters
o Applications of electrical machines
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects and
thus acquire the capability to applying them.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Determine the generated EMF, Speed of DC Generator.
Determine the back EMF and Torque of DC Motor.
Construction of DC machines and AC machines.
Determine the voltage regulation of Synchronous Motor.
Demonstrate the different speed control methods of DC and AC drives.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze / Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
20
30
20
30
100
20
30
20
30
100
Model
Examination*
20
30
20
30
100
Semester End
Examination
20
30
20
30
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
What is the function of carbon brush and commutator used in DC generator?
Write the number of parallel paths in a lap and wave connected windings
Name the types of DC generators.
What is meant by self excited and separately excited dc generator?
What is the basic difference between dc generator and dc motor?
What are open circuit characteristics of DC shunt generator?
How can one differentiate between long shunt compound generator and short shunt compound
generator?
8. Why is the emf not zero when the field current is reduced to zero in a dc generator?
9. On what occasions dc generators may not have residual flux?
10. Define the term armature reaction in dc machines.
11. What is the basic principle of operation of DC motor?
12. How does a DC motor differ from DC generator in construction?
13. How will you change the direction of rotation of a DC motor?
14. What is back emf in DC motors?
15. Write down the equation for back emf of DC motor.
*
The marks secured in Test 1 and Test 2 will be converted to 20 and Model examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks
77
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
Write down the equation for torque developed in DC motor.
Why is the starting current high in a DC motor?
What is the need for starter in a DC motor?
What is the function of over-load release coil provided in a DC motor starter?
What is the function of a no-voltage release coil provided in a DC motor starter?
How does 4 point starter differ from 3 point starter?
Enumerate the factors on which the speed of a DC motor depends.
Write the two extra features of slip ring induction motors.
What are slip rings?
State the difference between slip ring rotor and cage rotor of an induction motor?
Write an expression for the slip of an induction motor
Define slip of induction motor?
What are the advantages of cage motor?
What is Rotating magnetic field?
Write down the equation for frequency of emf induced in an alternator
List the different methods of speed control employed for DC motors.
List the different methods of speed control employed for AC motors.
What is meant by solid state speed control?
What is meant by dc chopper?
Write down the main feature of v/f control?
What is stator voltage control?
Write the output voltage equation for single phase full converter and half converter.
Define slip power.
What are the slip power recovery schemes?
Define power factor.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
Draw the performance characteristics curve of DC shunt, series, and compound generator.
Derive the EMF equation of DC generator.
Explain the different types of DC generators.
Derive the equation for torque developed in DC motor
Describe the working of three point starter and four point starter
How will you control the speed of DC shunt and series motor?
What are the various method used for selection of drives?
Draw the slip-torque characteristics curve of three phase induction motor
Explain the different types of induction motor.
Derive the equation for torque developed in induction motor
Explain the operation of synchronous motor.
Describe the working of alternator
What are the different types of speed control of three phase induction motor? Explain
Describe the operation of Kramers system & Scherbius system
Explain in details about single phase half full converter drive speed control for DC drive
Explain in detail about V/F control?
Explain in detail about Ward Leonard drives.
What are the different power factor correction methods?
Explain chopper control DC drives.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Why are carbon brushes preferred for dc machines?
Why DC motors are not operated to develop maximum power in practice?
Why starter is necessary for DC motors?
Why a differentially compound motor is not used in practice?
Why an induction motor is called rotating transformer?
Why an induction motor will never run at its synchronous speed?
Why starter is necessary for the induction motor?
Why the Chopper controlled DC drives are used?
Why the static Rotor resistance control is used?
Why the slip power recovery schemes are used?
78
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Analyze / Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
Formulate the relation between speed and torque of DC motor.
For a given DC machine, evaluate the drop across the armature and field.
Construct the equivalent circuit diagram of Induction motor.
Analyze the Control of DC drives using controlled rectifiers and chopper.
Unit I
DC Machines
Constructional details of DC Generator Emf equation Types of DC Generators Characteristics of DC
generators Principle of operation of DC motor Back emf and torque equation Characteristics of DC
motors - Starting of D.C. motors Types of starters.
9 Hours
Unit II
AC Machines and Transformers
Construction of AC machines Types Principle of operation of three phase induction motor Equivalent
circuit Speed torque characteristics Single phase induction motors Principle of operation Starters for
induction motor Construction of synchronous machines types Induced emf Voltage regulation
Principle of operation of synchronous motor Starting of synchronous motor Three phase Transformer,
construction, principle of operation.
9 Hours
Unit III
Drive Characteristics
Types of electrical drives Advantages of electrical drives- Factors influencing the choice of electrical
drives, heating and cooling curves Loading conditions and classes of duty Braking Types of braking
Braking characteristics for DC drive and AC drive.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Conventional and Solid State Speed Control of DC Drives
Speed control of DC series and shunt motor using armature control, field control and Ward - Leonard
control system Speed control characteristics Control of DC drives using controlled rectifiers and
choppers Applications.
9 Hours
Unit V
Conventional and Solid State Speed Control of AC Drives
Control of three phase induction motors using stator voltage and frequency control static rotor resistance
control Slip power recovery schemes Static Kramer control method Static Scherbius control method
Power Factor correction-Applications.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
G. K. Dubey, Fundamentals of Electrical Drives, Wiley Eastern Ltd., New Delhi, 2007.
D. P. Kothari and I. J. Nagrath, Basic Electrical Engineering, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company
Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2007.
References
1.
2.
3.
S. K. Pillai, A First Course on Electrical Drives, Wiley Eastern Ltd., New Delhi, 2008
M. D. Singh and K. B. Khanchandani, Power Electronics, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt
Ltd., New Delhi, 2007
Vedam Subrahmaniam, Electric Drives (concepts and applications), Tata McGraw Hill Publishing
Company Pvt Ltd, New Delhi, 2007
79
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M304 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To acquire knowledge about the fundamentals of thermodynamic laws, concepts, principles and
mechanism in accounting for the macroscopic physical systems
To study and understand the concepts and working of power generating equipments
To apply the thermodynamic concepts in various applications like IC engines and Air conditioning
systems
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(b) The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge, capability of analyzing and solving any concept
or problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students will be able to understand
the working concepts of thermal engineering.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Evaluate the heat transfer and work transfer with in a actual or ideal system.
An ability to identify and suggest the thermodynamic process and corelations for particular application.
Selection of equipment for thermal application
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze / Evaluate
Create
Total
20
20
30
30
100
20
20
30
30
100
20
20
30
30
100
20
20
30
30
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
Define entropy.
Define enthalpy.
Define refrigerator.
Define heat engine.
Define internal energy.
Define property and state.
Define path, process, cycle.
Define Coefficient of Performance.
State Clausius statement of second law of thermodynamics
State Kelvin-plank statement of second law of thermodynamics.
Define volumetric efficiency and clearance ratio
Define Avagadros law.
Define Daltons law of partial pressure
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
*
Identify a steady flow system and indicate the expressions.
Give examples for open system and closed system
Justify the limitations for first law of thermodynamics?
Name the various gas power cycles.
The marks secured in Test 1 and Test 2 will be converted to 20 and Model examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks
80
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
How is vapour power cycle suited for three phase flow? Give some examples.
Sketch the p-V and T-s diagram for Carnot cycle.
Why we apply Maxwell relations?
Indicate the importance of work ratio in vapour cycles?
What is the effect of Cut-off ratio in the efficiency of a Diesel cycle?
Sketch the P-V diagram of dual cycle and mark the processes
Differentiate 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines based on construction.
Apply/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
What do you mean by reversible process? Brief with examples.
Write down the continuity equation for the flow process. Explain for various applications.
Give the limitations of critical point for pure substances.
With suitable examples explain the term wet, dry and saturated and super heat.
Mention the relation between heat and work transfer for a flow and non flow process.
Relate the terms enthaphy, entropy, internal energy for a thermodynamic system.
Prove that the difference in specific heat capacities equal to Cp-Cv = R and
Cp-Cv = TV2 / kT
8. Evaluate clausius inequality with its p-V diagram.
9. How will you differentiate dual cycle with diesel cycle in IC engines?
10. How the ignition takes place in C.I.Engine?
Unit I
Concepts and First Law of Thermodynamics
Basic Concepts concept of continuum Macroscopic approach Thermodynamic systems Closed Open
Control volume Thermodynamic properties and equilibrium state of a system Path and process
Quasi Static process Modes of work Zeroth law of thermodynamics Concept of temperature and heat
Concept of ideal and real gases. First law of thermodynamics Applied to closed and open systems
Internal energy Specific heat capacities Cv and Cp Enthalpy.
Study on Perpetual motion machine of the first kind
9 Hours
Unit II
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Second law of thermodynamics Kelvin Planck and Clausius statements Reversibility and Irreversibility
Clausius inequality Entropy concept efficiency COP Principle of increase of entropy Carnot
theorem Absolute entropy Availability.
Third law of Thermodynamics and Postulatory Thermodynamics
9 Hours
Unit III
Properties of Pure Substances
Thermodynamic properties of pure substances in solid , liquid and vapour phases, P-V, P-T, T-V, T-S, H-S
diagrams Thermodynamic properties of steam Calculations of work done and heat transfer in non flow
and flow process.
Measurements of steam quality
9 Hours
Unit IV
Properties of Gases, Thermodynamic Relations
Properties of ideal and real gases - equation of state - Avagadros law - Vander Waals equation of states Daltons law of partial pressure - Properties of mixture of Gases - Maxwell relations - T- dS equation Clausius Clayperon equations - Joule Thomson Coefficient.
Conditions of stability
9 Hours
81
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Unit V
Air Standard Cycles and Psychrometry
Air standard cycles Otto, Diesel and Dual Calculation of mean effective pressure and Air standard
efficiency - Concepts of Stirling cycle and Ericsson cycle - Psychrometric properties and processes Psychrometric chart.
Adiabatic flame Temperature
9 Hours
Total: 45 + 15 Hours
Textbook
1.
Y. Cengel and Boles, Thermodynamics - An Engineering Approach, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing
Company Pvt Ltd, New Delhi, 2003.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
R. S. Khurmi, Steam table with Psychometric chart, S. Chand Publications, New Delhi 2009
J. P. Holman, Thermodynamics, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi 2002
Vanwylen and Sontag, Classical Thermodynamics, Wiley Eastern, 1987
C. P. Arora, Thermodynamics, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2003
C. Merala, Pother, W. Craig and Somerton, Thermodynamics for Engineers, Schaum Outline Series,
Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2004
82
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M305 FLUID MECHANICS AND MACHINERY
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To understand the application of fluid in various engineering requirements
To make familiar with calculation of forces in fluid structure interaction
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects and
thus acquire the capability to applying them.
g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry- level.
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Measurement of fluid properties.
Design of components interacting with fluid flow.
Selection of pumps and turbines for suitable application.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
6
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
30
20
25
25
-
30
20
25
25
-
30
20
25
25
-
30
20
25
25
-
100
100
100
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
*
What are all the properties of fluid?
What are all the types of fluid?
Write Pascal Law.
What are all the methods of measuring pressure?
Write an equation to measure pressure using Manometer.
What are all the types of fluid flow?
Write two and three dimensional continuity equation.
State Euler and Bernoullis equation.
State momentum principle.
Write the methods of measurement of flow of fluid.
Write equation to find loss of pressure due to friction.
Write various minor Losses.
Write equations to find loss of pressure due to minor losses.
State the concepts of branched pipe flow.
Write the dimensions of physical quantities used in fluid mechanics in terms of fundamental
dimensions.
What is dimensional homogeneity?
State Buckinghams pi theorem.
What are all dimensionless numbers?
State model laws.
Write the concepts of boundary layer.
The marks secured in Test 1 and Test 2 will be converted to 20 and Model examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks
83
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
What are boundary layer thicknesses?
Define boundary layer separation.
Write equations to find drag and lift.
What are all the types of turbo machineries?
Write the concept of velocity triangle.
Write equations to find work done on turbine.
Write equations to find efficiency of various turbines.
What are all types of positive displacement pumps?
What are all the types of draft tubes?
What are unit quantities?
Write equation to calculate work done by the centrifugal pump.
What is Cavitations in pumps?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
How importance is the various fluid properties in engineering application?
What is all the application of different types of fluid?
Why Concepts of measuring pressure is important?
How manometers work?
Why types of flow important in engineering application?
How Continuity equations are applied in real world application?
How Bernoullis equation is useful to fluid mechanics?
How important is knowledge on fluid forces and momentum principle for an engineer?
How Important is fluid flow losses in designing fluid circuits?
How to form governing equations using dimensionless analysis?
How important are dimensionless numbers?
Why concept on boundary layer is important?
How to differentiate turbines based on the working principle?
How pumps are selected with respect to their working principle?
Apply/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
Find various properties of given fluid
Create various types of flow using given fluid and pump
Designing manometers for various applications
Applying Bernoullis equation and finding flow of given fluid flow
Calculation and verification of losses of fluid flow in given pipe system
Writing governing equation for a pipe system using dimensional analysis
Designing a model for a real world prototype using dimensionless numbers
Finding the significance of boundary layer in a fluid structure interaction
Suggesting a suitable turbine for the given environment
Designing of turbine for given environment
Suggest suitable pump for given application
Designing a pump for given application
Unit I
Introduction to Fluid and Fluid Motions
Units & Dimensions. Properties of fluids Specific gravity, specific weight, viscosity, compressibility,
vapour pressure and gas laws. Three dimensional Continuity equation in Cartesian and polar coordinates,
Bernoulli equation, energy equation, momentum equation and moment of momentum equation,
Measurement of Pressure using Manometers
Capillarity and surface tension
9 Hours
84
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Unit II
Internal and External Flow
Laminar flow in pipe, between parallel plates - Turbulent Flow in a pipe Flow Separation, Lift and Drag
on Airfoils Boundary layer thickness and boundary layer Theory - Losses in pipe system, Darcy
Weisbach equation - Friction factor - Flow through pipes in series and in parallel, Moody diagram
Minor Losses
9 Hours
Unit III
Dimensional Analysis and Similitude
Dimension and Units: Buckinghams theorem. Discussion on dimensionless parameters. - Dimensionless
parameters Reynolds Number, Froudes Number, Eulers Number, Webers Number, Machs Number Laws of Models and similitude Reynolds model law Froude Model Law
Classification of Models
9 Hours
Unit IV
Hydraulic Turbine
Fluid machines: definition and classification - exchange of energy - Euler's equation for turbo machines Construction of velocity vector diagram's - head and specific work - degree of reaction.
Hydro turbines: definition and classifications - Pelton turbine - Francis turbine - propeller turbine - Kaplan
turbine - working principles - velocity triangles - work done - specific speed efficiencies
Performance Curves for Turbine
9 Hours
Unit V
Hydraulic Pump
Pumps: definition and classifications - Centrifugal pump: classifications, working principles, velocity
triangles, specific speed, efficiency and performance curves - Reciprocating pump: classification, working
principles, indicator diagram, work saved by air vessels - cavitations in pumps - rotary pumps: working
principles of gear and vane pumps
Characteristics curve for centrifugal pump
9 Hours
Total: 45 + 15 Hours
Textbook
1.
R.K.Bansal, Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery, Laxmi Publications, NewDelhi, Ninth Edition
2010.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Streeter and L. Victor, Fluid Mechanics, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New York,
1975
Bruce R Munson , Donald F Young, Theodore H Okiishi and Wade W. Huebsch, Fundamentals of
Fluid Mechanics, John Wiley & Sons, 2009
Pijush K Kundu and Ira M Cohen, Fluid Machines, Academic Press, Burlington, USA, 2010
Yunus Cengel and John Cimbala, Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals and Application, Tata McGraw Hill
Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi 2009
Robert and W Fox, Introduction to Fluid Machines, 6th ed., John Wiley Eastern Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi
2006
85
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M306 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To acquire knowledge about the mechanism of chip formation in machining, cutting tool materials, tool
life, cutting fluids
To understand the working of machine tools such as semi automatic & automatic lathes shaping and
allied machines, milling, drilling and allied machines, grinding and allied machines and broaching
To understand the basic concepts of Non Traditional Machining, & computer numerical control (CNC)
machine tool
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
c)
The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in various
materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting, fabrication,
machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of the course,
students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable component in
industry.
g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level placement
in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Selection of correct tool depends on machining process and material to be machined.
An ability to identify and suggest correct manufacturing process for practical application.
Selection of nontraditional machining process for suitable application.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
30
40
30
100
30
40
30
100
Model
Examination*
30
40
30
100
Semester End
Examination
30
40
30
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
*
State Taylors tool life equation.
List various cutting tool materials
List various cutting tool characteristics.
What is the purpose of cutting fluids?
What is tool life?
List various types of cutting fluids.
List the basic parts of turret lathe.
What are the machining operations performed on a capstan lathe?
Define drilling
Define reaming
Define boring
Define tapping
What types of operations can be performed in planer?
List out various milling operations
List out different types of milling cutters
Define milling
The marks secured in Test 1 and Test 2 will be converted to 20 and Model examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks
86
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
List out the basic parts of plain milling machine.
What is indexing?
Define grinding process
What is meant by grain size, grade, and structure of grinding wheel?
Define broaching.
Define honing, lapping, and polishing.
What prompted the development of unconventional machining process?
List out the main criteria for selecting the electrolyte in electro chemical machining
Name the abrasive materials used in abrasive water jet machining.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
Differentiate between orthogonal and oblique cutting.
Why tool fails during cutting?
What are the factors that affect tool life?
List the reasons for tool wear.
How the milling machine is specified?
Where rough and finish turning are used?
How the size of drilling machine is specified?
How the size of lathe is specified?
Name the machining process which uses single point cutting tool
Compare drilling and reaming operation.
What is the difference between planer and shaper?
How the milling differs from turning in lathe?
How gear hobbing differ from gear shaping process?
What is the difference between a fixed and swiveling head vertical milling machine?
What is the difference between rough and precision grinding?
How the size of grinding machine is specified?
Why a grinding wheel is to be balanced?
How the jobs are held during surface grinding operation?
List out the difference between capstan , turret , and centre lathe
What are the different methods of production of gears?
Why surface finish is an important in manufacturing process?
Why surface finish is an important in manufacturing process?
State the advantages of CNC machines over conventional machines
What are the advantages of rapid prototyping?
Unit I
Metal Cutting Theory
Introduction Orthogonal & Oblique Cutting chip formation Mechanisms of metal cutting: Shear
plane, Stress, Strain and cutting forces Merchants Circle cutting tool materials, tool wear, tool life,
cutting fluids Single point cutting tool nomenclature - Machinability Problems in Merchants Circle
and tool life
Metal Cutting Economics
9 Hours
Unit II
Automatic Turning and Milling
Introduction to Capstan and turret lathes Indexing mechanism Bar feeding mechanism - Automats
single spindle automates & its types - multi spindle automates & its types. Milling Introduction types
up milling & down milling, various operations Milling cutter and its nomenclature Indexing - types
simple, compound & differential Accuracy and repeatability of a positioning system in conventional
machine tools.
Machining Time Calculation for Milling Machine
9 Hours
87
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Unit III
Reciprocating Machine Tools and Hole Making
Shaper Introduction, types, specification & Quick return Mechanisms. Planer - Introduction, types,
specification & Quick return Mechanisms Slotter - Introduction, types, specification & Quick return
Mechanisms.
Introduction to hole making operations drilling, reaming, boring & tapping. Broaching -Introduction,
types of broaching methods nomenclature of broach tool.
Drill Size Calculation for Tapping Operation
9 Hours
Unit IV
Gear Cutting and Finishing Processes
Gear cutting Introduction forming, generation, shaping, and hobbing. Grinding Introduction, types of
grinding process Grinding wheel selection honing, lapping, super finishing, polishing and buffing
Gear finishing operations
9 Hours
Unit V
Advanced Machining Processes
Introduction to Unconventional Machining process overview of all techniques working principle of
abrasive jet machining & water jet cutting process Introduction to Electric Discharge Machining,
Chemical & Electro Chemical Machining processes Introduction to Laser Beam Machining Introduction
to CNC Machine Tool Turning centre Vertical turning centre - Milling centre
Overview of Rapid Prototyping Processes
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
J P Kaushish, Manufacturing Processes, PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 2010
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Richerd R Kibbe, John E Neely, Roland O Merges and Warren J White, Machine Tool Practices,
Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2003
Serope Kalpakjian and Steven R Schmid, Manufacturing Engineering and Technology, Pearson
Education, New Delhi, 2002
S. K. Hajra Choudhury, Elements of Workshop Technology Vol. II, Media Promoters & Publishers
Pvt Ltd., Mumbai,2003
P. C. Sharma, A Text Book of Production Engineering, S. Chand and Co. Ltd, New Delhi,2005
P. N. Rao, Manufacturing Technology- Metal Cutting and Machine Tools, Tata McGraw Hill
Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2006
88
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M307 FLUID MECHANICS AND MACHINERY LABORATORY
0 0 3 1.5
OBJECTIVES
To reinforce and enhance the understanding of the fundamentals of Fluid mechanics and Hydraulic
machines
To introduce a variety of classical experimental and diagnostic techniques, and the principles behind
these techniques
To provide practice in making engineering judgments, estimates and assessing the reliability of your
measurements, skills which are very important in all engineering disciplines
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
e) The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team.
k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Measurement of fluid properties.
Design of components interacting with fluid flow.
Selection of pumps and turbines for suitable application.
Ability of reducing the various losses in the pipe connections.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Internal Assessment
Preparation
Remember
Understand
Apply
Observation and Results
Analyze
Evaluate
Record
Mini-Project/Model
Examination/Viva-Voce
Total
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
Define fluid statics.
What is fluid mechanics?
What is fluid kinetics?
Define Viscosity.
What are Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids?
Define Surface Tension
What is meant by transition state
Define Pascals law
What is meant by energy lines
Define the term drag
What is boundary layer?
Define energy thickness.
State the methods of dimensional analysis
Define density.
Define Specific volume.
List the types of fluid
Define Pascal Law
Semester End Examination
15
15
15
25
15
10
50
50
89
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
Mention the methods of measuring pressure
Write equation to measure pressure using Manometer
Mention Types of fluid flow
Mention Two and three dimensional continuity equation
Write Euler and Bernoullis equation
Define Momentum principle
Write Equation to find loss of pressure due to friction
Mention Various minor Losses
Equations to find loss of pressure due to minor losses
Write the Concepts of branched pipe flow
Define Dimensional homogeneity
Define Buckinghams pi theorem
Define Dimensionless numbers
Define Model laws
Write the Concepts of boundary layer
Define Boundary layer thicknesses
What is meant Boundary layer separation
Write Equations to find drag and lift
Mention the types of turbo machineries
Define Velocity triangle
Write the Equations to find work done on turbine
Write the Equations to find efficiency of various turbines
Mention Types of positive displacement pumps
Mention Types of draft tubes
Mentions Unit quantities
Write Equation to calculate work done by the centrifugal pump
Define Cavitation in pumps
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
What are the similarities between model and prototype?
When will you select a reciprocating pump?
Compare the viscosity of the different fluid.
Difference between the laminar and turbulent flow.
How can Apply of Continuity equations
How to apply Bernoullis equation for incompressible fluid.
Difference between Fluid forces and momentum principle
Why fluid flow losses in designing fluid circuits
At what conditions, the laminar flow becomes turbulent flow?
Difference between pump and turbine.
Apply/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
Calculation and verification of losses of fluid flow in given pipe system.
Writing governing equation for a pipe system using dimensional analysis.
Designing a model for a real world prototype using dimensionless numbers.
Finding the significance of boundary layer in a fluid structure interaction.
Suggesting a suitable turbine for the given environment.
Designing of turbine for given environment.
Suggestion of pump for given application.
Designing a pump for given application.
Find various properties of given fluid.
Create various types of flow using given fluid and pump.
Designing manometers for various applications.
Applying Bernoullis equation and finding flow of given fluid flow.
90
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
List of Experiments
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
Determination of the Coefficient of discharge of given Orifice meter.
Determination of the Coefficient of discharge of given Venturi meter.
Calculation of the rate of flow using Rota meter.
Determination of friction factor for a given set of pipes.
Conducting experiments and drawing the characteristic curves of centrifugal pump/Submergible pump
Conducting experiments and drawing the characteristic curves of reciprocating pump.
Conducting experiments and drawing the characteristic curves of Gear pump.
Conducting experiments and drawing the characteristic curves of Pelton wheel.
Conducting experiments and drawing the characteristics curves of Francis turbine.
Conducting experiments and drawing the characteristic curves of Kaplan turbine.+
Conducting experiments to find the Lift and Drag of a given Aerofoil using wind tunnel.
Demonstrating and measuring the boundary layer formation using various cross sectional objects in a
open channel flow.
Design Experiments
Application oriented experiments
Mini Project
Total: 45 Hours
Practical Schedule
Sl.
No.
1
Determination of the Coefficient of discharge of given Orifice meter.
Determination of the Coefficient of discharge of given Venturi meter.
Calculation of the rate of flow using Rota meter.
Determination of friction factor for a given set of pipes.
Experiment
Conducting experiments and drawing the characteristic curves of centrifugal
pump/Submergible pump
Conducting experiments and drawing the characteristic curves of reciprocating
pump.
Conducting experiments and drawing the characteristic curves of Gear pump.
Conducting experiments and drawing the characteristic curves of Pelton wheel.
5
6
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Conducting experiments and drawing the characteristics curves of Francis
turbine.
Conducting experiments and drawing the characteristic curves of Kaplan
turbine
Conducting experiments to find the Lift and Drag of a given Aerofoil using
wind tunnel.
Demonstrating and measuring the boundary layer formation using various
cross sectional objects in an open channel flow.
Design Experiments
Application oriented experiments
Mini Project
Hours
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
91
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M308 ELECTRICAL MACHINES LABORATORY
0
1.5
OBJECTIVES
To understand the working principle, performance characteristics of DC Generator and DC Motor
To understand the different types of Transformers, working principle and their performance
To estimate the various losses taking place in DC machines and Transformers and apply the different
testing methods to arrive their performance
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
a)
e)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects and
thus acquire the capability to applying them.
The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Determine the generated EMF, Speed, Field flux and Flux density.
Determine the back EMF and Torque.
Construction of DC generator and transformer.
Diagnose the cause of failure of voltage built up in dc generator.
Design of starters.
Determine the voltage regulation and efficiency of transformer.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Internal Assessment
Preparation
Remember
Understand
Apply
Observation and Results
Analyze
Evaluate
Record
Mini-Project/Model
Examination/Viva-Voce
Total
Semester End Examination
10
15
15
20
10
15
15
50
50
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
What is the function of carbon brush used in DC generator?
Distinguish between lap winding and wave winding used in dc machine.
Write the number of parallel paths in a lap and wave connected windings
Name the three things required for the generation of emf.
What is meant by self excited and separately excited dc generator?
What is the basic difference between dc generator and dc motor?
Write down the emf equation of dc generator. Give the meaning of each symbol
What is pole pitch?
How can the voltage in a DC generator be increased?
What is critical resistance of a DC shunt generator?
What are the conditions to be fulfilled for a shunt generator to build up voltage?
What do you mean by residual flux in DC generator?
A DC generator fails to self excite. List the cause for the failure for the failure.
What are open circuit characteristics of DC shunt generator?
How can one differentiate between long shunt compound generator and short shunt compound
generator?
16. Why is the emf not zero when the field current is reduced to zero in a dc generator?
92
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
58.
59.
60.
61.
62.
63.
64.
65.
66.
67.
68.
69.
70.
71.
72.
73.
74.
75.
76.
Define the term critical speed in dc shunt generator.
On what occasions dc generators may not have residual flux?
How the critical field resistance of a dc shunt generator is estimated from its OCC?
Define the term armature reaction in dc machines.
What are the two unwanted effects of armature reaction?
Differentiate between geometric neutral axis (GNA) and magnetic neutral axis (MNA).
In which part of the dc machine is the compensating winding situated?
What are the various types of commutation?
Name the two methods of improving commutation.
What is reactance emf in dc machine?
Define the term commutation in dc machines.
How and why the compensating winding in dc machine excited?
How is the interpole winding in dc machine excited?
To what polarity are the interpoles excited in dc generators?
What is the basic difference between DC generator and DC motor?
What is the basic principle of operation of DC motor?
What is torque proportional to?
Distinguish between shunt and series field coil constructions.
How does a DC motor differ from DC generator in construction?
How will you change the direction of rotation of a DC motor?
What is back emf in DC motors?
Write down the equation for back emf of DC motor.
Write down the equation for torque developed in DC motor.
Under what condition the mechanical power developed in a DC motor will be maximum?
Why shaft torque is always less than that developed inside the armature in a DC motor?
Why is the starting current high in a DC motor?
What is the need for starter in a DC motor?
What is the function of over-load release coil provided in a DC motor starter?
What is the function of a no-voltage release coil provided in a DC motor starter?
How does 4 point starter differ from 3 point starter?
Enumerate the factors on which the speed of a DC motor depends.
List the different methods of speed control employed for DC series motor.
Draw the N Vs Eb characteristics of a dc motor for two different field currents.
What is the relation between electrical degree and mechanical degree?
What is the meaning of electrical degree?
List out some examples of prime movers.
Give some applications of DC motor.
State one advantage and disadvantage in the application of each of the three basic types of DC motors.
List all the important information on name plate of a DC motor.
Why field control is considered superior than armature control method of DC shunt motor?
State the principle of operation of a transformer.
What are the main parts of a transformer?
What type of material is used for the core?
What is an ideal transformer?
Mention two types of constructions used in transformer.
What is the purpose of laminating the core in transformers?
Why do we use iron core in a transformer?
Where is core type and shell type construction suitable for a transformer?
What is meant by turns ratio in transformer?
List four applications of a transformer.
Give the emf equation of a transformer and define each term.
Name two important electrical performances of transformers?
What will happen if the primary of a transformer is connected to a DC supply?
How does flux leakage occur in transformer?
How do you reduce hysteresis loss in a transformer?
The efficiency of a transformer is always higher than that of rotating electrical machines. Why?
List the advantages of stepped core arrangement in a transformer.
Why are breathers used in transformers?
When will a Bucholz relay operate in a transformer?
What is the function of transformer oil in a transformer?
93
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
77. What are the applications of step-up and step-down transformers?
78. State the condition for maximum efficiency.
79. State the advantages of Swinburnes test.
80. Is it possible to conduct Swinburnes test on DC series motor? Justify.
81. Does the transformer draw any current when secondary is open? Why?
82. What do you mean by no-load current of a transformer?
83. What are the functions of no-load current in a transformer?
84. How does change in frequency affect the operation of a given transformer?
85. How will you transfer the quantities from one circuit to another circuit in a transformer?
86. Define voltage regulation of a transformer
87. Can the voltage regulation of a transformer go to negative? If so under what condition?
88. Full load copper loss in a transformer is 1600 watts. What will be the loss at half load?
89. What is the angle by which no-load current will lag the ideal applied voltage?
90. Distinguish between power transformer and distribution transformer.
91. What is the purpose of providing taps in transformer and where these are provided?
92. What are the advantages of 3-phase transformers over 3 numbers of single phase transformers?
93. State the conditions under which OC and SC tests are conducted in a transformer.
94. What is the purpose of conducting OC test on a transformer?
95. What is the purpose of conducting SC test on a transformer?
96. What are the advantages of OC and SC tests of a transformer over the load test?
97. What is the condition for obtaining maximum efficiency of a transformer?
98. What do you understand by all-day efficiency?
99. List the merits of an autotransformer.
100. What are the components of magnetic losses in transformer and on what factors they depend?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
Draw the performance characteristics curve of DC shunt, series, and compound generator.
Derive the EMF equation of DC generator.
Explain the different types of DC generators.
Derive the equation for torque developed in DC motor
Draw the mechanical and electrical characteristics of DC shunt, series, compound motors.
What are the effects caused by armature reaction?
Explain the different methods of commutation.
Explain the parallel operation of two DC generators.
Describe the working of three point starter and four point starter
How will you control the speed of DC shunt and series motor?
Derive an expression for EMF induced in single phase transformer.
What are the differences between two winding transformer and auto transformer?
Explain the different types of instrumentation transformers?
Derive the equivalent circuit of single phase transformer.
What are the various losses that occur in DC machines?
Give the conditions for maximum efficiency in DC machines.
What are the various losses that occur in transformer?
Explain the different ways of connecting the three phase transformer.
Apply / Analyze / Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Why are carbon brushes preferred for dc machines?
Why DC motors are not operated to develop maximum power in practice?
Why a differentially compound motor is not used in practice?
Why the iron losses in a transformer are independent of the load current?
Why is the rating of a transformer given in kVA?
Why OC test is generally performed on LV side of a transformer?
Why SC test is generally performed on HV side of a transformer?
Why are iron losses considered as constant losses in transformer?
Why the range of efficiency of transformers higher than those of other electrical machines?
A d.c series motor having a resistance of 1 ohm drives a fan for which the torque varies as the square of
the speed. At 220 V the set runs at 350 rpm and takes 25 A. The speed is to be raised to rpm by
94
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
increasing the voltage. Determine the necessary voltage and the corresponding current assuming the
field to be unsaturated.
Two series motors run at the speed of 500 rpm and 550 rpm respectively when taking 50 A at 500 V.
The terminal resistance of each motor is 0.5 ohm. Calculate the speed of the combination when
connected in series and coupled mechanically. The combination is taking 50A on 500V supply.
A 4 pole 240 V, wave connected shunt motor given 1119 kW when running at 1000 rpm and drawing
armature and field current of 50 A and 0.1 A respectively. It has 540 conductors. Its resistance is 0.1
ohm. Assuming a drop of 1 volt/brush, find (a) Total torque. (b) Useful Torque. (c) Useful flux/pole.
(d) Rotational Losses. (e) Efficiency
A 45 kW, 250 V, 4 pole, lap connected dc shunt motor has 32 slots with 10 conductors/slot. The
armature and shunt field resistance are 0.05 ohm and 125 ohm respectively. The flux/pole is 0.03 Wb.
If the full load efficiency is 85% find at full load. (a) Useful torque at shaft. (b)The speed
A 1500 kW, 550 V,16 pole generator run at 1500 rpm.What must be the useful flux per pole if there are
2500 conductor in the armature of the winding is lap connected and full load armature copper loss in 25
kW? Calculate the area of the pole shoe if the gap flex density has a uniform value of 0.9Wb/m2, Also
find the no load terminal voltage. Neglect change in speed.
Formulate the relation between losses and efficiency of DC machines.
For a given DC machine, how to evaluate the constant and variable losses.
Analyze the performance of given transformer and evaluate the core loss and cu loss occurring in it.
List of Experiments
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Load test on DC Shut & DC Series motor
O.C.C & Load characteristics of DC Shunt and DC Series generator
Speed control of DC shunt ,motor (Armature, Field control)
Load test on single phase transformer
O.C & S.C Test on a single phase transformer
Regulation of an alternator by EMF & MMF methods.
Load test on single phase alternator
Load test on three phase squirrel cage Induction motor
Speed control of three phase slip ring Induction Motor
Load test on single phase induction Motor.
Study of DC & AC Starters
Design experiment
Application oriented experiment
Total: 45 Hours
Practical Schedule
Sl. No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Experiment
Load test on DC Shut & DC Series motor
O.C.C & Load characteristics of DC Shunt and DC Series generator
Speed control of DC shunt ,motor (Armature, Field control)
Load test on single phase transformer
O.C & S.C Test on a single phase transformer
Regulation of an alternator by EMF & MMF methods.
Load test on single phase alternator
Load test on three phase squirrel cage Induction motor
Speed control of three phase slip ring Induction Motor
Load test on single phase induction Motor.
Study of DC & AC Starters
Design experiment
Application oriented experiment
Hours
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
6
3
95
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M309 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LABORATORY II
0 0 3 1.5
OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge and skill in the field of conventional machine tools used in the industries
To supplement the theory course on Machining Processes
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
c)
The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in various
materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting, fabrication,
machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of the course,
students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable component in
industry.
e) The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team.
i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Identification of manufacturability.
Machine setting like Stroke length adjustment.
Selection of suitable cutting tool.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Internal Assessment
Preparation
Remember
Understand
Apply
Observation and Results
Analyze
Evaluate
15
15
10
25
Record
10
Mini-Project/Model
Examination/Viva-Voce
15
10
50
50
Total
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
Semester End Examination
How the surface roughness is designated?
What is meant by up-milling and down milling?
What is multi point cutting tool?
How the quick return mechanism works?
What is the principal of working of slotting machine?
Designate the milling cutter.
List the different operations performed in slotting machine.
List out different operations performed in milling machine.
How the gear hobber works?
How the speed of hob/work piece is calculated?
List the types of abrasives used in grinding wheel.
Name the types of grinding wheel used for finishing.
Specify the applications of cylindrical grinding.
Name the coolants used for grinding of different materials.
Designate the drill bits.
List the types of drill bits.
96
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
17.
18.
19.
20.
Write the equation for finding tool life?
How chips are coming out during drilling?
Write the gear cutting calculation formulae.
Write the formula to calculate indexing rotation.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
How to select speed for drilling different materials?
How the return speed is controlled in shaping machine?
Why down milling is most preferred than up-milling?
Why conventional grinding wheels not suitable for aluminium and its alloys?
Why tolerances are allocated for parts?
Why V- belt is preferred for transmission?
How indexing carried out during face milling?
Why universal milling machine is preferred in many cases?
How the helical gear is formed in gear hobber?
Which machine is suitable for surface milling?
Apply/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
How will you calculate depth of cut for octagonal face milling?
How the stroke of slider is controlled?
How the proper tap is selected for making an internal thread?
How will you relate surface roughness and abrasive grades?
List solution for avoiding over heating of tool during machining.
For mass production of surface milling parts which type of milling process is preferred?
List of Experiments
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Preparation of spur gear from cylindrical work piece using gear hobbing machine.
Machining of Pentagonal/Hexagonal/octagonal sides from cylindrical work piece using Milling
machine.
Machining Metal flat using surface grinding machine.
Machining a shaft using cylindrical grinding machine.
Preparation of dovetail groove using Shaping Machine.
Machining an internal keyway using Slotter.
Preparing an internal thread in metal flat using Drilling & Tapping.
Cut a simple shape like circle, rectangle from OHNS using Wire cut-EDM.
Selection and allocation of proper fit and tolerances Example and Simple problems
Design experiment
Application oriented experiment
Mini project.
Total: 45 Hours
97
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Practical Schedule
Sl. No.
Experiment
Preparation of spur gear from cylindrical work piece using gear
hobbing machine.
Machining of Pentagonal/Hexagonal/octagonal sides from
cylindrical work piece using Milling machine.
Machining Metal flat using surface grinding machine.
Machining a shaft using cylindrical grinding machine.
Preparation of dovetail groove using Shaping Machine.
Machining an internal keyway using Slotter.
1
2
10
Preparing an internal thread in metal flat using Drilling &
Tapping.
Cut a simple shape like circle, rectangle from OHNS using Wire
cut-EDM.
Selection and allocation of proper fit and tolerances Example
and Simple problems
Design experiment
11
Application oriented experiment
7
8
9
Hours
3
3
3
6
3
3
3
6
3
6
6
98
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M401 / 11C401 / 11A401 NUMERICAL METHODS
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
Acquire the knowledge of finding approximate solutions of algebraic, transcendental, differential
and integral equations by numerical methods and interpolating the values of a function using
Lagranges and Newtons polynomial approximations.
Ability to find solution of initial and boundary value problems using multi step approximations
and ability to solve boundary value problems using finite difference methods.
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES
b) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects and
thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Acquire more knowledge in basic concepts of engineering mathematics.
To improve problem evaluation technique.
Choose an appropriate method to solve a practical problem.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Test I7
Test II1
Model Examination1
End Semester
Examination
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
20
40
30
10
100
20
40
30
10
100
20
40
30
10
100
20
40
30
10
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
State the Fundamental theorem of algebra.
Define Algebraic and Transcendental equations.
Write the formula for Regula Falsi method .
What do you mean by Interpolation?
State the derivatives of Newtons Forward and Backward Interpolation formula.
Write the conditions for applying Trapezoidal and Simpsons rules.
Write the formula for two point and three point Gaussian quadrature.
Mention the multistep methods available for solving ordinary differential equation.
Write the Bender schmidt Scheme for solving one dimensional heat equation.
Write the explicit formula for one dimensional wave equation.
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted to 20 and model examination will be converted to 20.
The remaining 10 marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly, internal assessment will be
calculated for 50 marks.
99
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Give an example of a transcendental equation?
Write the condition of convergence of Iteration method.
What is the order of convergence of Newton - Raphson method?
Write the differences between Direct and Iterative method.
State the sufficient condition for solving Gauss Jacobi and Gauss Seidel method.
Using Lagranges interpolation, find the polynomial through (0,0), (1,1) and (2,2).
What do you mean by power method.
State the way in which you can find the solution for Laplace equation.
Write Milnes & Adams Predictor and Corrector formula.
What are the methods for solving simultaneous algebraic equations.
Apply
1. Obtain by power method, the numerically largest eigen value of the matrix
15 4 3
1
(0 )
A = 10 12 6 with the starting vector x = 1 . Perform only 4 iterations.
20 4 2
1
2.
Explain briefly Gauss Elimination Iteration to solve simultaneous equations.
3.
If
4.
What is the relation between divided differences and forward differences ?
5.
Find the value of
6.
The following data gives the velocity of a particle for 20- secs at an interval of 5-secs.
f ( x) =
1
, find the divided difference f (a, b).
x2
f ' (8) from the table given below
Find the acceleration for the following data
7.
8.
9.
10.
x:
12
f ( x ) : 1.556 1.690 1.908 2.158
time(sec) :
0 5 10 15 20
velocity (m / s ) : 0 3 14 69 228
1
3
If y = xy , y (1) = 1, find y (1.1) using Taylors method.
If y= x2 + y2, y (0 ) =1 find y (0.1) by Eulers method.
For which points of x and y, the equation x fxx + y fyy = 0, x > 0, y > 0 is elliptic.
Name at least two numerical methods that are used to solve one dimensional diffusion equation.
Analyze / Evaluate
1. Using Newtons method, find the positive root of cos x = 3x 1.
2. Solve by Gauss-Elimination method : 6x + 3y +12z = 36 ; 8x -3y +2z = 20 ; 4x +11y z =33 .
5 0 1
3. Using Power method, find all the Eigen values of A = 0 2 0 .
1 0 5
4. Use Lagranges interpolation formula to find the value of x when y = 20 for the following
data . X : 1 2
3
4
Y: 1
8
27
64
100
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
5. Given 5 x
y + y 2 2 = 0 ;
y (4 )= 1;
i)y ( 4.2 ) by Eulers method
iii) y ( 4.4 ) by Adams method.
y (4.1) = 1.0049
find
ii) y (4.3) by Runge-kutta method
6. Using Taylor series method, find the value of y(0.1) , given dy /dx = x + y and y (0) =1 and correct
to 3 decimal places.
7. Using Bender-Schmitt formula, solve
2u u
, u (0,t ) =0, u (5,t) = 0 , u (x,0) = x2 (25 - x2).
=
x 2 t
Assume x =1. Find u(x, t) up to t=5.
2u 2u
=
, 0 < x < 1, t >0; u (x,0) = 100 (x-x2) , ut (x,0) = 0, u (0,t) = 0, u (1,t) = 0.
t 2 x 2
9. Solve u xx + u yy = 0 over the square mesh of side 4 units, satisfying the following conditions
8. Solve
u (x,0) = 3x for 0 x 4 ; u (x,4) = x2 for 0 x 4 ; u (0,y )= 0 for 0 y 4 ; u (4,y) =12 +
y
for 0 y 4.
2. 2 2.6
10. Evaluate
dydx
using Trapezoidal formula.
x2 + y 2
Unit I
Solution of Equations and Eigen Value Problems
Solution of Algebraic and Transcendental equations by the method of False position Newton- Raphson
method- Solution of system of linear equations : Gauss- elimination method and Gauss-Jordan method Iterative method: Gauss Seidel method- Inverse of a matrix by Gauss-Jordan method. Eigen value of a
matrix by power method.
9 Hours
Unit II
Interpolation and Curve Fitting
Newton s Forward and Backward interpolation. Newtons Divided difference interpolation formula
Lagranges interpolation formula Fitting of curves by the method of Least squares: Straight line,Parabolic
curves and the conversion of equations of the curves in the form of straight lines.
9 Hours
Unit III
Numerical Differentiation and Integration
Derivatives from difference table Numerical differentiation using Newton s
forward and backward
interpolation formulae - Numerical integration by Trapezoidal and Simpsons 1/3 and 3/8 rules - Rombergs
method - Two and three point Gaussian quadrature formulae - Double integrals using Trapezoidal and
Simpsons rules.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Initial Value Problems for Ordinary Differential Equations
Single step Methods : Taylor Series method for solving first and second order equations - Eulers and
Modified Eulers methods - Fourth order Runge-Kutta method for solving first order equations Multistep methods Milnes and Adams predictor and corrector methods.
9 Hours
101
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Unit V
Boundary Value Problems
Finite difference solution for the second order ordinary differential equations- Finite difference solution for
one dimensional heat equation by implicit and explicit methods - one dimensional wave equation and two
dimensional Laplaces and Poissons equations.
9 Hours
Total: 45+15 Hours
MAT LAB: Invited Lectures on Mat lab and its applications on Numerical methods.
Text books
1.
2.
P. Kandasamy, K. Gunavathy and K. Thilagavathy, Numerical Methods, S.Chand and Co. New
Delhi, 2009.
B.K. Moorthy, P.Geetha, Numerical Methods ,Tata McGraw-Hill Publication company Ltd, New
Delhi 2010, First Edition
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
R. L Burden, and T.D Faries, Numerical Analysis, Seventh Edition, Thomson Asia Pvt. Ltd.,
Singapore, 2002.
K. Sankara Rao , Numerical Methods for Scientists and Engineers, Third Ed.Prentice Hall of India,
2007.
C.F Gerald., and P.OWheatley, Applied Numerical Analysis, Sixth Edition, Pearson Education
Asia, New Delhi.2006.
T.Veerarajan, Numerical Methods with programs in C,
Second Edition, Tata McGraw-Hill
Publication,co.Ltd, New Delhi ,2008.
102
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M402 THEORY OF MACHINES I
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To impart students with the knowledge about the basics of Mechanisms and understand the geometry
of motion at any point in a link of a mechanism
To facilitate students to understand the types of cam and follower, motion and profile drawing of cam
To give awareness to students on the phenomenon of direction of rotation, speed and torque
determination for simple, compound and planetary gear systems
To understand the effects of friction in motion transmission and in machine components
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(d) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of engineering design. Understanding the
concept generation, design optimization and evaluation. Knowing the fundamentals of intellectual
property rights. Students will be able to effectively design various engineering components and make
process plan for the production.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Interpret interrelationship between components of various mechanisms like bicycle, Geneva
mechanism, steering gear mechanism etc.
Determine velocity and acceleration of links in a given mechanism and drawing of cam profiles from a
given data.
Compare the various power transmission devices and friction elements.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
25
20
10
10
Remember
Understand
30
30
20
20
Apply
30
30
30
30
Analyze / Evaluate
15
20
40
40
Create
Total
100
100
100
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
8 *
Define kinematic link, pair and chain.
Define Inversion of Mechanism.
What is lower and higher pair?
What are the types of Constrained Motion?
What is locked chain?
What are the types of Joints in a Chain?
Define Kutzbach Criterian to Plane Mechanism.
State Grashofs law for four bar mechanism.
Give an example of straight line generators.
Define Velocity and acceleration of a link
Define Radial component of an acceleration
Define Tangential component of an acceleration
What is the direction of radial and tangential component of acceleration of a link?
The marks secured in Test 1 and Test 2 will be converted to 20 and Model examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks
103
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
Define Rubbing Velocity at a pin joint.
Write the formula to calculate the angular velocity () of a link when speed (N) is given in rpm.
What is Coriolis component of Acceleration?
Define Cam and Follower.
How to classify cams?
Give the applications of cam and follower mechanism.
Define Pressure angle of the cam
What is meant by lift and stroke of the follower?
Discuss the term of dwell period in the Cams and Follower?
What is meant by Undercutting in Cams?
State the advantages and disadvantages of gear drives.
Define module
What is spiral gearing?
Define Law of gearing
Which materials are used to make gears?
Define gear train.
What are the types of gear trains?
Write the applications of flat, V belt and rope drive of belt.
Which are the materials used for belts?
Define Slip and Creep of the belt
What is the use of idler pulley in the belt drive?
Define Initial tension in the belt drive
Define static and dynamic friction
What is the use of friction clutches in automobiles?
List out the materials used for brake lining
What is the use of the collar bearing?
Define Journal bearing.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
What are the differences between a Machine and a Structure?
What is a Sliding Pair, and how it differs from turning and rolling pair?
Which is all the kinematic chain in the following arrangement?
(a) Three links
(b) Four links
(c) Five links
(d) Six links
How to find the Length of Stroke of the Crank and Slotted Lever Quick Return Motion Mechanism?
How to draw the velocity and acceleration diagram for a slider link?
How to draw the velocity and acceleration diagram for a fixed link?
How to calculate the radial and tangential component of acceleration of a link?
What is the condition to draw the tangential component for an input link?
What is the difference between Prime Circle and Pitch Circle of Cam?
Differentiate Pitch and Trace point of a cam.
How the follower is classified according to the surface in contact and path of motion?
Compare the different types of motion used in cam and follower motion?
Draw the displacement, Velocity and acceleration diagram for the follower moves with simple
harmonic motion.
What is helical gearing, and how it differs from heringbone gearing?
How the power is transmitted in bevel and worm gear drive?
Which type of profile generally used in gear? Give reason
Discuss length of path of contact and length of arc of contact in gear systems.
How to find the velocity ratio of epicyclic gear train?
What are the factors affecting the amount of power transmission?
State the disadvantages of the V belt drive over flat belt drive.
What type of belt drive is selected for rotating the opposite direction of rotation of driver and driven
pulley?
What are the factors considering the selection of the belt drive?
Compare Sliding friction and Rolling friction
List the various factors depends on the capacity of the brake.
104
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Apply/Evaluate
1.
2.
Sketch & describe working of bicycle free wheel sprocket mechanism
A local toy shop has asked you to design a model to encourage parents to buy their young children
mechanical toys. The partially made model is seen below Figure 1. Add a suitable cam that controls
two followers so that they rise and fall.
Fig. 1
3.
4.
Design with suitable drive to transmit the power of 12 kW.
What happens to friction when we use wheels to roll an object instead of sliding it?
Unit I
Basics of Mechanisms
Basic concepts of Link, Pair, Chain, Mechanism, Machine and Structure, Degree of freedom, Mobility of
mechanism Kutzbach Criterian, Grashoffs Law Inversions of mechanisms Four bar and Slider Crank
Mechanical advantage Transmission Angle Description of some common mechanisms Straight line
generators, Dwell mechanisms, Ratchets and Escapements, Universal Joint Basic structures of Robot
Manipulators (serial & parallel)
Davis and Ackermanns steering mechanisms, Hookes joint and Pantograph
9 Hours
Unit II
Friction
Laws Static, Dynamic and Rolling friction Dry and Viscous friction Friction in inclined plane and
screw threads Friction in Journal bearings Friction in clutches Single plate and multi plate clutches,
Cone clutches Friction in Flat and V-belt drives - Friction aspects in brakes
Band brake, block brakes, Internal and external shoe brakes, braking of vehicles
9 Hours
Unit III
Kinematics
Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration - Graphical Method of Velocity (Relative Velocity Method) and
Acceleration diagrams for Simple Mechanisms - Kliens construction for Single Slider Crank Mechanism
Coriolis component of Acceleration
Instantaneous method of velocity and acceleration diagram
9 Hours
Unit IV
Kinematics of Cam
Classifications of Cam and Follower Radial cam nomenclature Analysis of follower motion Uniform
Velocity Motion, Simple Harmonic Motion, Uniform Acceleration and Retardation Motion and Cycloidal
Motion Construction of Cam Profile for a Radial Cam Pressure angle and undercutting
Cams with specified contours, tangent and circular are cams
9 Hours
105
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Unit V
Gears and Gear Trains
Law of toothed gearing Involutes and cycloidal tooth profiles Spur Gear terminology and definitions
Gear tooth action Interference and undercutting Problems Helical, Bevel, Worm, Rack and Pinion
gears [Basics only] Introduction to gear correction
Gear trains Speed ratio, train value Parallel axis gear trains Epicyclic Gear Trains Determination of
gear speeds using tabular method; torque calculations in simple, compound and Epicyclic gear trains
Differentials Automobile gear box
9 Hours
Total: 45 + 15 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
S. S. Rattan, Theory of Machines, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company pvt Ltd, New Delhi, 2009
R. L. Norton, Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt
Ltd., New Delhi, 2005
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Ashok G. Ambekar, Mehanism and Machine Theory, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi,2009.
John J. Uichker and Joesph E. shigley, Theory of Machines and Mechanism, Tata McGraw Hall
Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2005.
Jack T. Kimbrell, Kinematics Analysis and Synthesis, Tata McGraw Hall Publishing Company Pvt
Ltd., New Delhi, 1991.
Sadhu Singh, Theory of Machines, Pearson Education, New Delhi, 2007.
Syad and R. L. Singal, Kinematics of Machinery, Tech Mac Publishers,Chennai, 2007.
106
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M403 COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To make the students understand the computer graphics fundamentals, various data exchange formats
that is used in design software
To know the geometric modeling concepts and mating conditions of the different solids
To build the students to identify with the various file types used in the CAD software
PROGRAM OUTCOME
(d) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of engineering design. Understanding the
concept generation, design optimization and evaluation. Knowing the fundamentals of intellectual
property rights. Students will be able to effectively design various engineering components and make
process plan for the production.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Basic concepts of Geometric Modeling.
Computer Animation concepts and software operations.
Coloring and rendering concepts.
Database Management System.
Parametric representation of various Geometric Shapes.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
40
30
30
100
40
30
30
100
Model
Examination*
40
30
30
100
Semester End
Examination
40
30
30
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
9 *
List out the scope of CAD
What is Database Management System?
Mention the CAD tools required to support various phases of the design.
What do you mean by data structure?
What is viewing transformation and windowing transformation?
Define Scaling
Name the various approaches used in hidden line elimination algorithm.
What are the entities of wire frame modeling?
Give some characteristics of Bezier curves.
List out the various principles of geometric based software.
What is hidden line removal algorithm?
Define Segmentation.
Write the various applications of modeling.
Give the expansion for IGES.
List out the various files for data exchange.
What are the important sources of errors in FEA solution?
Define Design of product
What is Rotation?
What are the types of an animation?
What are all the softwares used for Animation?
The marks secured in Test 1 and Test 2 will be converted to 20 and Model examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks
107
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
21.
22.
Give the equation of Bezier curve?
Give the equation of B-spline curve?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
Some design applications would be better with CAD than others? Why? What characteristics make an
application a good candidate for CAD?
Can a light pen be used with a storage tube display? Why? How can a locating or pointing function be
performed on this type of display?
What is product cycle and explain the various steps involved in product cycle?
What is the difference between Bezier surface and B-spline surface?
Unit 1
Fundamentals of CAD
Product design and life cycle, Role of CAD in engineering , Definitions of CAD tools, Input and Output
devices, Data structure- Database, DBMS Coordinate systems, Mechanical Applications and benefits of
CAD
Industrial look at CAD/CAM
9 Hours
Unit II
Computer Graphics Fundamentals
Introduction- Transformation of Geometric Models- Translation, scaling, reflection, rotation, Windowing,
view port clipping, view port transformation
Mappings of Geometric models
9 Hours
Unit III
Visual Realism
Hidden -line, surface, solid removal algorithms, shading and coloring. Introduction to parametric and
variation geometry based softwares and their principles - User Interface for Shading and Coloring
9 Hours
Unit IV
Geometric Modeling
Introduction to modeling and viewing- geometric modeling of solids, surface, wire frame, Assembly
modeling- mating conditions. Computer Animation Types
Parametric Representation of Synthetic Curves
9 Hours
Unit V
Data Exchange and CAD in FEM
Exchange of CAD data between software packages, File types- IGES, PDES, PARASOLID, ACIS, DXF
Files. Applications of CAD in FEM- Finite element Modeling- Interfaces
Mesh Generation in FEM
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1. Ibrahim Zied, CAD/CAM-Theory and Practice, Tata McGraw Hall Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New
Delhi, 2007
References
1. P. Radhakrishnan, CAD-CAM-CIM, New Age International Publishers, New Delhi 2000
2. Donald Hearn and M. Pauline Baker, Computer Graphics, Prentice Hall of India., New Delhi 2005
3. Richard M. Lueptow, Graphics Concepts for Computer-Aided Design, Pearson ESL Publishers, New
Delhi 2006
4. William M. Neumann and Robert F. Sproul, Principles of Computer Graphics, Tata McGraw Hall
Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2005
5. Mikell P. Groover and Emory W. Zimmers Jr., CAD/CAM Computer-Aided Design and Manufacturing,
Prentice Hall of India., New Delhi, 2007
108
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M404 THERMAL ENGINEERING
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To integrate the concepts, laws and methodologies from the first course in thermodynamics
To analyze different cyclic processes involved in the power plant and IC Engines
To apply the thermodynamic concepts into various thermal application like IC engines, Steam
Turbines, Compressors and Refrigeration and Air conditioning systems
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(b)
The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge, capability of analyzing and solving any concept
or problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students will be able to understand
the working concepts of thermal engineering.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Power Generation Calculation.
Performance calculation of IC Engine.
Performance analysis of Nozzle, Turbine.
Performance analysis of compressor and refrigeration system.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
20
20
20
40
100
20
20
20
40
100
Model
Examination*
20
20
20
40
100
Semester End
Examination
20
20
20
40
100
10
Remember
1. What is thermodynamic cycle?
2. List out the assumptions made for the analysis of thermodynamic air cycles.
3. What is meant by compression ratio?
4. Sketch the schematic arrangement of open cycle gas turbine plant and name the components.
5. What is meant by highest useful compression ratio
6. What are the limitations of simple carburettor?
7. What are the various types of nozzles and their function?
8. Define nozzle efficiency.
9. Write down the expression for velocity at exit from steam nozzle.
10. What is supersaturated flow?
11. What is meant by compounding of turbines?
12. Classify the various types of air-compressors.
13. What is meant by free air delivered?
14. Define: COP
15. What is the function of throttling valve
16. What is meant by sub-cooling?
17. Define Degree of saturation.
The marks secured in Test 1 and Test 2 will be converted to 20 and Model examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
109
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Understand
1. What are the effects of reheating process in Rankine cycle?
2. When will be the gas turbine cycle efficiency reaches maximum?
3. It is always useful to have a regenerator in gas turbine power cycle. Why?
4. Write down the effect of pressure ratio on the net output and efficiency of Brayton cycle
5. Compare two stroke and four stroke engines.
6. Why diesel engines are more efficient than petrol engines?
7. Which is efficient two stroke or four stroke engines? Why?
8. Why the actual cycle efficiency is much lower than the air-standard cycle efficiency?
9. Why a choke is used in carburetor and what is meant by automatic chocking?
10. What are the effects of super saturation in a steam nozzle?
11. Why clearance is necessary in reciprocating compressor?
12. Compare reciprocating and rotary compressor.
13. What is the effect of clearance volume on the power required and work done in a reciprocating air
compressor?
14. How does the actual vapour compression cycle differ from that of the ideal cycle?
15. Which thermodynamic cycle is used in air conditioning of air planes using air as refrigerant?
16. High compression ratios not used in spark-ignition engines, why?
Apply/Evaluate
1. Air enters the compressor of an air-standard Brayton cycle at 100kPa, 300K with a volumetric flow ratio
of 5m3/s. The compressor pressure ratio is 10. The turbine inlet temperature is 1400K. Determine (a)
thermal efficiency of the cycle, (b) back work ratio, (c) net power developed in kW.
2. A nozzle is to be designed to expand steam at the rate of 0.10 kg/s from 500kPa, 210C to 100kPa.
Neglect inlet velocity of steam. For a nozzle efficiency of 0.9, determine the exit area of the nozzle.
3. In a single-stage, single-row impulse turbine, the steam is entering at a velocity of 1200m/s with a
nozzle angle of 20 and leaving the blade in the axial direction. The ratio of blade velocity to whirl
velocity of steam is 0.6. Sketch the velocity diagram and calculate (a) Blade velocity (b) Work done per
kg of steam.
4. Find the percentage saving in work input by compressing air in two stages from 1 bar to 7 bar instead of
one stage. Assume a compression index of 1.35 in both the cases and optimum pressure and complete
intercooling in a two-stage compressor.
Unit I
Power Plant Cycles
Gas Turbine power plant cycle Joule cycle - Expression for efficiency, work ratio Modifications of
Joule cycle with Intercooler, Reheater and Regenerator. Steam Power Plant cycle Rankine cycle
Modifications with Reheater and Regenerator. Problems solving using Mollier chart
Rocket engines, co-generation steam power plant
9 Hours
Unit II
Internal Combustion Engines
Classification of IC engine- IC engine components and functions. Valve timing diagram and port timing
diagram -Comparison of two stroke and four stroke engines. Comparison of petrol & diesel engine, Fuel
supply systems - Ignition Systems Lubrication system and cooling system. Performance calculation Heat
balance sheet preparation- Air-fuel ratio calculation - Knocking and Detonation. Exhaust gas analysis,
pollution control norms
Advanced fuel injection system-CRDi, Electronic fuel injection
9 Hours
Unit III
Steam Nozzles and Turbines
Flow of steam through nozzles-shapes of nozzles- Effect of friction- Critical pressure ratio, supersaturated
flow. Impulse and reaction principles- Compounding of Turbines - velocity diagrams for simple and
multistage turbines- Speed regulations- Governors
Aircraft - nozzle and turbine
9 Hours
110
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Unit IV
Air Compressor
Classification and working principle- Work of compression with and without clearance. Volumetric
efficiency- Isothermal efficiency and isentropic efficiency of reciprocating air compressors. Multistage air
compressor and inter cooling work of multistage air compressor. Working principle of various Rotary
compressors - Centrifugal, vane and roots blower (Descriptive treatment only)
Screw compressor-working, comparison with reciprocating compressor
9 Hours
Unit V
Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning
Vapour compression Refrigeration cycle Effect of superheat, subcooling of refrigerant - performance
calculations. Working principle of vapour absorption system. Ammonia water, Lithium bromide water
systems (Description only), Comparison between vapour compression and absorption systems.
Psychrometry- Psychometric chart, Cooling load calculations. Concept of RSHF, GSHF, ESHF, Air
conditioning systems
Automobile air-conditioning system-working
9 Hours
Total: 45 + 15 Hours
Textbook
1.
Mahesh M. Rathore, Thermal Engineering, Tata McGraw - Hill Education Private Limited, New Delhi,
2011
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
C. P. Kothandaraman, Steam Tables, New Age International Private limited, 2007
R. S. Khurmi & J. K. Gupta, Refrigeration Tables with Chart, S Chand & Company Limited, New
Delhi, 2008
Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach, Tata McGraw Hill
Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2008
J. P. Holman, Thermodynamics, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2007
C. P. Kothandaraman, S. Domkundwar and A. V. Domkundwar, A course in Thermal Engineering,
Dhanpat Rai & Sons, 2002
111
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M405 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To develop the theoretical basis about the stress, strain and elastic modulus concepts in various
components with sound mathematical principles and to enable students to systematically solve
engineering problems regardless of difficulty
To familiarize about finding shear force, bending moment, deflection and slopes in various types of
beams with different load conditions
To develop confidence and competence in solving problems related to the machine components like
shafts, columns, springs and purposes
PROGRAM OUTCOME
(c) The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in various
materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting, fabrication,
machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of the course,
students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable component in
industry.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Identify the dimensional specifications of the regular and composite structures by analyzing its
Stress and strains values.
Problems relevant to various beam structures can be analyzed.
Finding the mechanical properties of machine components.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
25
30
30
15
100
20
30
30
20
100
Model
Examination*
10
20
30
40
100
Semester End
Examination
10
20
30
40
100
11
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
Define Stress and strain.
What are the types of stress?
State Hooks law.
Define Poissons ratio.
Write the equations which relate E and C and K.
Define factor of safety.
State the range of Poissons ratio value for ductile material.
What do you mean by bulk modulus?
Define resilience.
Define proof resilience.
Define principle stress and principle strain.
Define hoop and longitudinal stress.
List out the types of beams.
What are the types of supports used in beams?
Name the types of loads applied onto a beam.
* The marks secured in Test 1 and Test 2 will be converted to 20 and Model examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
112
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
Define slenderness ratio.
State the assumptions made in simple bending.
Write the simple bending equation of beam.
Define stiffness of the spring.
Define crippling load.
List the assumptions made in simple torsion.
Write the torsional equation of the shaft.
Name the theories of failure.
Define section Modulus.
Define fluctural rigidity.
Define polar moment of inertia.
Name the methods available to find the slope and deflection of beams.
Define shear stress.
Define bending stress.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
State the role of factor of safety in the design of product?
Differentiate true stress and engineering stress.
How do you find the value of E using stress strain diagram.
Differentiate shear stress and shear strain.
Give some practical examples where bending stress stresses may occur.
What is the difference between limit of proportionality and elastic limit?
Write the significance of elastic constants in product design.
Distinguish pressure and stress.
Differentiate Ultimate and Yield strength of material with respect to applied load.
How do you reduce the induced stress value in cylindrical shells?
How do you differentiate thin and thick cylinders?
Why do cylindrical pressure vessels have hemispherical ends?
Differentiate simple and compound stress.
At what situation thin cylinders can be used?
State the use of Mohrs circle.
What do you mean by composite beam?
Draw the schematic representation of hinged, continuous and over hanging beams.
What do you mean by radius of curvature of the beam?
Compare the strength beams which have rectangular and I shape cross sections.
How do you reduce the stress induced in the cantilever beam where the load value remains same?
What do you mean by point of contra flexure of the beam?
Differentiate open coil and closed coil helical springs.
Give some real time applications for open coil and closed coil helical springs.
What conditions must be met for neutral axis to pass through the centroid of a beam.
Differentiate Resilience and Proof resilience.
Apply/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
For axially loaded members, what is the maximum normal stress and in which plane does this stress
act? What is the value of shear stress in this plane?
State how normal stress varies with the orientation of the section in a long slender member under axial
load.
Which shaft will you recommend for design purposes when maximum shear stress due to torsion is
same in both solid and hollow shaft?
What is the difference between plane stress and plane strain situations? Give practical examples.
If axial force F is fixed, then find a relation of geometrical parameters of a cylindrical pressure vessel
for attainment of equal axial and hoop stress.
How to find the maximum shear force and bending moment from shear force and bending moment
diagrams? Explain with an example.
What is understood by calculating the effort applied to a screw jack to lift up and lower down the given
amount of load? Justify the phenomenon.
In positioning a beam in a structure, always the depth portion is chosen greater than its width portion.
Analyze and write down the reason.
113
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Unit I
Stress, Strain and Deformation of Solids
Mechanical properties of materials - Simple stress and strain Stresses and strains due to axial force Stress-strain curve for ductile and brittle materials Hookes law - Factor of safety Poissons ratio Elastic constants and their relationship- Stresses in Stepped shafts and Uniformly varying sections
Stresses in Composite sections - Temperature stresses. Strain energy Stresses due to different loadings
Strain energy in bending and torsion
Viscoelastic Materials, Fatigue, Strain Gages
10 Hours
Unit II
Analysis of Stresses in Two Dimensions
State of stresses at a point Normal and tangential stresses on inclined planes - Principal planes and
stresses Plane of maximum shear stress - Mohrs circle for biaxial stresses. Hoop and longitudinal stresses
in thin cylindrical and spherical shells Changes in dimensions and volume
Behavior of thick wall pressure vessels
8 Hours
Unit III
Beams - Loads and Stresses
Types of beams: Supports and Loads Shear force and Bending Moment in beams Cantilever Simply
supported and overhanging beams - Point of contra flexure. Theory of simple bending - Stresses in beams:
bending and shear stress - Stress variation along the length and section of the beam Section modulus
Shear flow and Shear centre
9 Hours
Unit IV
Deflection of Beams
Slope and Deflection of beams: Double integration method, Macaulays method and Moment-area method,
for Cantilever, Simply supported and overhanging beams. Columns Buckling of long columns due to
axial load - Equivalent length of a column Eulers and Rankines formulae for columns of different end
conditions Slenderness ratio
Inelastic column buckling, Case studies related to column buckling
9 Hours
Unit V
Torsion in Shafts and Springs
Analysis of torsion of circular bars Shear stress distribution Bars of Solid and hollow circular section
Stepped shaft Twist and torsion stiffness Compound shafts Fixed and simply supported shafts
Closed coil helical springs: Maximum shear stress in spring section including Wahl Factor Deflection of
helical coil springs under axial loads Introduction to the design of helical coil springs stresses in helical
coil springs under torsion loads, applications
Theories of Failures, Stress concentrations
9 Hours
Total: 45 +15 Hours
Textbook
1. R. K. Bansal, A text book of Strength of Materials, Lakshmi Publications (P) Limited, New Delhi, 2007
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Egor P. Popov, Engineering Mechanics of Solids, PHI Learning Pvt Ltd, New Delhi, 2010.
D. K. Singh, Mechanics of Solids, Pearson Education New Delhi ,2006.
R.K. Rajput, Strength of Materials, S Chand & Co., New Delhi, 2006.
F. P. Beer and R. Johnston, Mechanics of Materials, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd.,
New Delhi, 2002.
B. K. Sarkar, Strength of Materials, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd, New Delhi, 2006.
114
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M406 ENGINEERING DESIGN CONCEPTS
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the concept generation, concept selection, design process, planning for manufacture
To know the various techniques used in designing a product
PROGRAMME OUTCOME
(d) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of engineering design. Understanding the
concept generation, design optimization and evaluation. Knowing the fundamentals of intellectual
property rights. Students will be able to effectively design various engineering components and make
process plan for the production.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
PDS development.
Brainstorming.
Morphological analysis.
Patent drafting
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
30
40
30
100
30
40
30
100
Model
Examination*
30
40
30
100
Semester End
Examination
30
40
30
100
12
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
What is engineering design?
What are the principles of engineering design?
What are the six elements of design process?
List the content of a PDS?
What is meant by Brainstorming?
List out the five creativity methods.
List out the five concept selection methods.
What are the five basic patterns of decision making?
List the principles of engineering design.
What are the steps follwed in industrial design?
What is Ergonomics in Engineering Design?
Define factor of safety?
What are the elements of cost?
What is meant by BOM?
What is meant by QFD?
List the content of a design report?
Name the three types of patents?
Understand
1.
2.
How does engineering design interfaces are made within and outside the design department?
How will you identify a problem?
* The marks secured in Test 1 and Test 2 will be converted to 20 and Model examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
115
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
Why we go for computer aided decision making?
How will you identify customer needs?
Differentiate between criteria weighting and datum method of concept selection?
How will you make decision based on knowledge?
How will you estimate a manufacturing cost?
For what break even analysis is carried out in a company?
Differentiate between final and intermediate design review.
Differentiate between Patent and copyright?
Differentiate between concept sketches and scheme drawing
What are the steps followed in drafting a patent application?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Write PDS for a car?
Write the concept generation for a under seat suspension system of an excavator.
Write the methods of selection of material for aircraft.
Write the material selection procedure for bought out components
Write a design report for a new product?
Write a patent draft for any one product you know.
Unit I
Principles and Problem Identification
Engineering design introduction and definition, Considerations of a good design, Engineering design
interfaces, Principles of engineering design, Problem identification, Design process, Product Design
Specification (PDS) criteria, Content of a PDS, specification Principles, Exercises
Sample PDS
9 Hours
Unit II
Concept Generation and Selection
Identifying customer needs, bench marking,
Societal considerations in engineering, Creativity and
problem solving, creativity methods - Brainstorming, Morphological analysis, Exercises. Concept selection
- Subjective decision-making, Criteria ranking, Criteria weighting, Datum method, Computer aided
decision making, Exercises
Product and process cycle of a simple product
9 Hours
Unit III
Design Process
Detailed description of design process, five basic patterns of decision making , decision making based on
state of knowledge, Design for manufacturing (DFM), Design for Assembly (DFA), Industrial design,
Human factors design - ergonomics, Design for environment, engineering design principles
Design for X
9 Hours
Unit IV
Planning for Manufacture
Quality function deployment (QFD), Design review, Value analysis/engineering, Detail design, Factor of
safety, Materials selection, break even analysis - problem, cost evaluation, Elements of cost, ISO concepts
in brief
Impact of Computer Aided Engineering in design
9 Hours
Unit
116
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Unit V
Report Preparation and Intellectual Property Rights
Presentation Techniques - Introduction, Concept sketches, Scheme drawing, Design Validation Design
report. Intellectual Property Rights Introduction, Patent, Trademark, copyright, Patentability, patenting
process
Patenting for a simple product - a case study
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
Ken Hurst, Engineering Design Principles, Elsevier Science and Technology Books, 2004
George E Dieter, Engineering Design, Tata McGraw Hill publishing Company Pvt Ltd, New Delhi,
2008
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Danlel E. Whitney, Mechanical Assembles: Design Manufacture and Role in Product Development,
Oxford University, Press, 2008
K. Otto, Product Design, Pearson Publications, 2005
Richard Birmingham, Graham Cleland, Robert Driver and David Maffin, Understanding Engineering
Design, Prentice Hall of India, 1997
www.patentoffice.nic.in
ep.espacenet.com/advanced Search
117
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M407 THERMAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I
0 0 3 1.5
OBJECTIVES
Expertise in the various thermodynamic concepts and principles
Conduct performance tests on petrol engine and diesel engine, heat balance test, energy balance test on
4 stroke diesel engine
Retardation test to find frictional power of a diesel engine, determination of oil viscosity, flash and fire
point
Comparative justification on conventional fuel with alternative fuel
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects and
thus acquire the capability to applying them.
(e) The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
An Idea about Valve timing and port timing.
Familiarization in various IC engines and its components.
Experience in Performance maintenance of conventional fuel engines.
Knowledge about lubrication and its necessity.
Preparation of heat balance test report.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Preparation
Remember
Understand
Apply
Observation and Results
Analyze
Evaluate
Record
Mini-project
/
Model
Examination / Viva-voce
Total
Internal Assessment
Semester end Examination
10
15
25
25
10
10
50
50
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
What is valve timing and port timing?
Define cetane number and octane number?
List some factors that affect performance of the engine?
Is the heat balancing is necessary?
Give the firing order based on number of cylinder?
What is Frictional power?
Define Specific Fuel Consumption?
What is Brake power?
What roll the viscosity of oil plays in engine?
Is the steam engine in practice? Why not?
What is flash point and fire point?
What is data acquisition system?
118
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Real-time application of various cycles.
Thermodynamic Laws and application..
Concepts of various thermal applications.
Efficiency of different type engines.
Energy balancing of thermal power.
Industrial engine performance testing set-up.
Apply/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
How to tune up the engine performance?
How to avoid the heat loss in engine?
How to differentiate diesel and petrol engine?
How to best suit the right engine for the various application?
How to avoid the engine breakdown?
How the perfect energy utilization can be done?
How the revolution can be done on conventional fuels?
How to overcome the fossil fuel usage?
List of Experiments
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Valve Timing and Port Timing Diagrams.
Performance Test on 4-stroke Diesel Engine.
Heat Balance Test on 4-stroke Diesel Engine.
Morse Test on Multicylinder Petrol Engine.
Retardation Test to find Frictional Power of a Diesel Engine.
Performance Test on 4-stroke Diesel engine hydraulic loading with data acquisition system.
Comparative study on conventional fuel with alternative fuel.
Determination of Viscosity Red Wood Viscometer.
Determination of Flash Point and Fire Point.
Study of Steam Generators and Turbines.
Performance of Cooling Tower.
Design experiment
Application oriented experiment
Practical Schedule
Total: 45 Hours
Sl.
No.
1
2
Valve Timing and Port Timing Diagrams.
Performance Test on 4-stroke Diesel Engine.
3
3
Heat Balance Test on 4-stroke Diesel Engine.
Morse Test on Multicylinder Petrol Engine.
Retardation Test to find Frictional Power of a Diesel Engine.
Performance Test on 4-stroke Diesel engine hydraulic loading with
data acquisition system.
Comparative study on conventional fuel with alternative fuel.
Determination of Viscosity Red Wood Viscometer.
Determination of Flash Point and Fire Point.
10
Study of Steam Generators and Turbines.
11
Performance of Cooling Tower.
12
Design experiment
13
Application oriented experiment
Experiment
Hours
119
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M408 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS AND METALLURGY LABORATORY
0 0 3 1.5
OBJECTIVES
To understand the procedure of doing different tests like hardness, compression, tension, shear and
impact etc in various materials and automobile components.
To inject the knowledge about the testing of springs and composites materials subjected to compressive
and tensile loads
To explain the concept of testing the mechanical properties of materials under untreated and heat
treated conditions.
The study would provide knowledge to the students for use in the designing of engineering components
The student should acquire enough knowledge to understand:
a) Basic elements of materials microstructures.
b) Metals deformation and microstructures.
c) Metal alloys and heat treatments
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(c) The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in various
materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting, fabrication,
machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of the course,
students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable component in
industry.
(e) The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Choosing the Material for Air plane components, Heavy vehicle application.
Understand Material Microstructure.
Material Hardness.
Choosing the Material for Industry application.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Internal Assessment
Preparation
Remember
Understand
Apply
Observation and Results
Analyze
Evaluate
Record
Mini-project
/
Model
Examination / Viva-voce
Total
10
15
25
25
10
10
50
50
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Semester end Examination
Define stress.
Define strain.
What is Youngs modulus?
What is shear modulus?
What is bulk modulus?
State Hookes law.
What do you mean by limit of proportionality of elastic constants?
What do you mean by the term necking?
120
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
What do you mean by strain hardening?
List out the various types of support.
List the various types of loading conditions
What are the various assumptions made in the theory of simple bending?
What do you mean by torsion?
List out the various types of spring.
Define stiffness of a spring.
What do you mean by flexural rigidity?
Define Maxwells theorem.
Define alloy and steel?
What are cooling curves?
What is an equilibrium phase diagram?
Define the term heat treatment.
List the various stages of heat treatment processes.
List some quenching medium generally used in industries.
What is TTT and CCT diagram?
Write the governing equation for torsion of circular shaft.
How the materials are classified?
Write the formula to find the modulus of rigidity of springs
Write the formula to calculate the stiffness of a spring
How the Brinells hardness number is calculated?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
When a material is said to be of perfectly elastic?
What is the type of stress induced in a structural member subjected to torsional loading?
Why the shear stress is maximum at the outer surface of the shaft than the inner core?
Why hollow circular shafts are preferred when compared to solid circular shafts?
What are the differences between closed coil & open coil helical springs?
What are the various stresses induced in the open coil helical spring?
What is surge in springs?
When the materials attain their required properties.
How the deformation of materials taken place?
How the ceramics and composites are manufactured?
How the hardness is achieved by various heat treatment processes?
Apply/Analyze/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
How will you calculate yield stress?
How will you calculate ultimate stress?
How the ultimate shear stress is estimated?
How will you calculate the value of shear stress at a particular distance from the neutral axis?
How the pitch of helical springs is calculated?
How will you evaluate the torsional stress of a shaft?
How will you choose the material for industrial application?
On what basis the cycle time is finalized in heat treatment process?
How will you estimate the hardness number in various testing methods?
How the ceramics are manufactured by various processes.
How you evaluate the fatigue strength of a shaft?
List of Experiments
Standards to be referred:
For cast iron:
Grey cast iron
- IS-210
Spheroidal cast iron - IS-1865
For alloy steels:
Low carbon, Medium carbon & High carbon - IS -1570
121
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Strength of Materials
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Test involving axial compression and tension to obtain the stress strain curve and the strength
Test involving torsion and flexure to obtain the torque vs. angle of twist and load deflection curve
respectively and hence the stiffness
Tests on springs
Hardness tests and shear test on metal specimen
Test for impact resistance
Bending tests on metal beam
Verification of Maxwells reciprocal theorem
Tests on thin cylinders
Study on the variation of shear force and bending moment in a beam
Design Experiments
Application oriented experiments
Mini Project
Metallurgy
1.
2.
3.
4.
Study of microstructure of low carbon, medium carbon, high carbon steels, tool steel and stainless
steels.
Study of microstructure of various cast irons
Heat treatment annealing, normalizing, hardening and tempering of plain carbon steels, Measurement
of their hardness and study of their microstructure.
Performance study of specimen preparation with different polishing time.
Design experiment
Application oriented experiment
Total: 45 Hours
Practical Schedule
Sl. No.
Experiment
Test involving axial compression and tension to obtain the stress
strain curve and the strength
Test involving torsion and flexure to obtain the torque vs. angle of
twist and load deflection curve respectively and hence the
stiffness
Tests on springs
Hardness tests and shear test on metal specimen
Test for impact resistance
Bending tests on metal beam
Verification of Maxwells reciprocal theorem
Tests on thin cylinders
Study on the variation of shear force and bending moment in a
beam
Design experiment
Application oriented experiment
Study of microstructure of low carbon, medium carbon, high
carbon steels, tool steel and stainless steels.
Study of microstructure of various cast irons
1
2
3
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Heat treatment annealing, normalizing, hardening and tempering
of plain carbon steels, Measurement of their hardness and study of
their microstructure
Performance study of specimen preparation with different
polishing time.
Design experiment
Application oriented experiment
Hours
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
6
122
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
11M409 COMPUTER AIDED MACHINE DRAWING LABORATORY
1 0 3 2.5
OBJECTIVES
To know the specifications and symbols of standard machine components used in machine drawing
To understand the concept of various tolerances and fits used for component design
To understand and practice the drawings of machine components and simple assemblies using standard
CAD packages
At the end of the course the students will able to understand and create drawings manually or using any
one CAD packages for standard machine components and assemblies with tolerance
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement
in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes
(j) The graduates can become job-givers rather than just job-seekers
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
T o create a 2D drawings by converting orthographic to isometric views and vice versa
To analyze the tolerance and limits in the given drawings.
To create a rough drawing by viewing the real component.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Internal Assessment
Semester
Examination
End
Preparation
Remember
Understand
10
15
15
20
10
15
15
50
50
Apply
Observation and Results
Analyze
Evaluate
Record
Mini-Project/Model
Examination/Viva-Voce
Total
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
State the role of CAD in product design.
Draw the symbols for first angle and third angle projections.
Name the input and output devices used in CAD.
What are the methods of dimensioning used in CAD?
Draw the symbols used for surface finish in machine drawing.
List out the types of tolerances used in machine drawing.
Name the types of fits.
Define tolerance.
Draw the symbol used in machine drawing for welding.
What do you meant by BIS specifications?
Name the different types of fasteners used in machine components.
123
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
Highlight the main advantages of CAD system in design and drafting.
What do you meant by designing of a component?
Differentiate Orthographic and isometric views.
Give two practical applications of reduced scale and enlarged scale drafting.
Differentiate first angle and third angle projection.
What is the use of Modeling in product life cycle?
State the use of windowing and clipping in drafting.
Differentiate CAD, CAM and CAE.
State the applications for different types of fits.
Differentiate limits and tolerances.
State the use of tolerances in product design.
Differentiate tolerance and allowance.
Name the methods used for tolerance analysis.
Apply / Evaluate
1.
Solving exercises for tolerance analysis
List of Experiments
1
2
3
Orthographic views of brackets and V- blocks
Screw threads and threaded fasteners
BIS specifications Welding symbols, riveted joints, keys
Referring to hand book for the selection of standard components like bolts,
4
nuts, screws, keys etc
5
Introduction to Modeling software simple exercises using any one CAD package
6
Preparation of Assembly drawings Piston and cylinder
7
Assembly of plummer block bearing
8
Assembly of flange Couplings
9
Assembly of universal Joint
10
Assembly of eccentric cam
Design Experiment
Application oriented experiment
Total: 45 Hours
Practical Schedule
Sl. No.
Name of the Experiment
Hours
Orthographic views of brackets and V- blocks
Screw threads and threaded fasteners
BIS specifications Welding symbols, riveted joints, keys
Referring to hand book for the selection of standard components
like bolts, nuts, screws, keys etc
Introduction to Modeling software simple exercises using any one
CAD package
Preparation of Assembly drawings Piston and cylinder
7
8
9
10
Assembly of plummer block bearing
Assembly of flange Couplings
Assembly of universal Joint
Assembly of eccentric cam
4
5
6
6
3
3
3
3
3
124
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology| Regulation 2011
Unit I
Drawing Standards
Code of practice for Engineering Drawing, BIS specifications Welding symbols, riveted joints, keys, and
fasteners Reference to hand book for the selection of standard components like bolts, nuts, screws, keys
etc.
3 Hours
Unit II
Introduction to Machine Drawing
Fundamentals of machine drawing: Geometric Dimensioning - Limits, fits, Tolerances Types - Tolerance
Analysis.
Isometric to Orthographic conversion of Part drawings and vice versa, Assembly Drawings - Manual
drawing.
6 Hours
Unit III
Preparation of Part Models using Modeling Software
Preparing isometric view of various industrial oriented machine components - Selection of machine
components from software library - Conversion of part drawing into orthographic views. (Drafting)
3 Hours
Unit IV
Preparation of Assembly Models using Modeling Software
Preparing the assembly views (with minimum four components) of various industrial oriented
equipments.(E.g. Piston and connection rod, Coupling and shafts, Plummer block etc)
3 Hours
Total: 45 + 15 Hours
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
N. D. Bhatt and V. M. Panchal, Machine Drawing, Charotar Publishing House, Anand, Gujarat,
388001, India. 2004.
K R Gopalakrishnan, Machine drawing, Subhas Stores, Bangalore. 2007
www.ptc.com
www.solidworks.com
125
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M501 ENGINEERING METROLOGY AND QUALITY ASSURANCE
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the concept of various measuring instruments like linear, angular, form, and Surface
finish measurements
To introduced the fundamental concept of statistical quality control
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
c) The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in
various materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting,
fabrication, machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of
the course, students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable
component in industry.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Checking the angle of a piece tapered on one side using sine bar, angle dekkor and
bevel
protractor.
Measuring the parameters of screw thread (Pitch, thread angle, and major and minor diameter) by
using tool makers microscope.
Maintain the tolerances for a manufacturing component by using comparator.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I*
Test II*
30
40
30
--100
30
40
30
--100
Model
Examinations*
30
40
30
--100
Semester End
Examination
30
40
30
--100
Remember
1. Define metrology.
2. What is meant by measurements?
3. List out various types of measurements.
4. Define range and span..
5. Define sensitivity.
6. What is meant by repeatability and reproducibility?
7. Define precision and accuracy
8. List out various types of linear instrument.
9. What do you mean by least count?
10. What is meant by comparator?
11. Define angular measurement?
12. List out various types angular measurement
13. What are all the parameters obtained screw thread terminology?
14. State Taylors principle
15. Define eccentricity and circularity.
16. What are all the parameters obtained gear measurement?
17. Define RMS.
1
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
126
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
18. List out various methods for surface finish measurement.
19. Define LASER.
20. What are different types of geometric tolerance?
21. What is meant by CMM?
22. Define machine vision.
23. What is meant by CAI?
24. Define sample and population
25. What is meant by alternative and null hypothesis?
26. Define ANOVA
27. What is meant by acceptance sampling?
28. Define producers risk.
29. What is meant by LQL and AQL?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Difference between accuracy and precision
What are the different bases used for selection of measuring instrument?
What are salient features of a comparator?
What are the necessary conditions for interference of light waves?
State the essential requirements for accuracy in the construction of a sine bar.
Difference between the length and flatness interferometers?
What are the essential characteristics of an autocollimator?
What is the difference between primary texture and secondary texture?
What is meant by Best size wire?
What do you understand about the Alignment test of a machine tool?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
At what angle to the optical flat, the fringe pattern should be observed and why?
How the accuracy of a straight edged is specified, and how it can be checked?
Why surface finish is important in engineering applications?
How you would check the accuracy of pitch of a plug screw gauge?
How the quality of products can be improved?
How would you check the flatness and squareness with the axis of the spindle end of a 25-50mm
external micrometer?
7. Discuss the need for precision measurement in an engineering industry.
8. Design a plug gauge for checking the hole of 70H8.
9. Calculate the dimension of the maximum chord over four teeth when the gear under inspection has
the following specifications.
No. of teeth=32; module=4; Pressure angle =20
10. Calculate the diameter of the best wire for an M20 x 25 screws.
Unit I
Linear and Angular Measurement
Concept of Measurement Definition of metrology Levels of Measurement - Fits and Tolerances
Linear measuring instruments Vernier, micrometer, Slip gauges and classification interferometer,
optical flats, limit gauges. Comparators mechanical, optical, pneumatic and electrical types,
applications Angular measurements Sine bar, optical bevel protractor, angle Decker Taper
measurements
Bore micrometer
9 Hours
Unit II
Form Measurement
Measurement of screw threads Thread gauges, floating carriage micrometer Measurement of gears
tooth thickness constant chord and base tangent method radius measurements surface finish,
straightness, flatness and roundness measurements
Parkinsons gear testing machine
9 Hours
127
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit III
Laser and Advances in Metrology
Precision instruments based on laser Principles - laser interferometer application in linear angular
measurements and machine tool metrology. Coordinate measuring machine (CMM) Constructional
features, types, and applications Digital devices Computer aided inspection 3D Scanning, Machine
Vision Systems
Nanometrology.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Statistical Testing
Sampling theory and testing of Hypothesis Population and Sample influence of sample size
Random sampling Confidence intervals choice of sample size for estimation Testing of
hypothesis for large and small samples, testing of hypothesis for mean, difference between means F
distribution C-distribution Goodness of fit
Design of experiments
9 Hours
Unit V
Acceptance Sampling
Sampling plans need, types probability of acceptance in single, double, multiple sampling
techniques OC curves, Producers risk and Consumer's risk AQL, LTPD, AOQL concepts standard
sampling plans for AQL and LTPD uses of standard sampling plans
General inspection levels
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
Bewoor and Vinay Kulkarni, Metrology & Measurement, Tata Mc Graw Hill Publishing Company
Pvt Ltd, New Delhi,2009.
Douglas C. Montgomery, Introduction to Statistical Quality Control, John Wiley and Sons Inc,
2008.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Alan S. Morris, The Essence of Measurement, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi ,1996
R. K. Jain, Engineering Metrology, Khanna Publishers, New Delhi, 1994.
A. K. Jayal, Instrumentation and Mechanical Measurements, Galgotia Publications, New Delhi
2000.
T. G. Beckwith and N. Lewis Buck, Mechanical Measurements, Addison Wesley, New Delhi
2008.
Monohar Mahajan, Statistical Quality Control, Dhanpat Rai & Sons, 2001.
128
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M502 THEORY OF MACHINES II
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To impart with the knowledge about the static and dynamic force analysis on various parts of
reciprocating engine
To understand the function of flywheel and to construct the various turning moment diagram
To impart the knowledge about balancing of various parts for different engine
To understand the effects of vibration in various beams under different load conditions and the
basic concepts of governor and gyroscopes
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(i)
(k)
The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes
The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern
practices.
SKILL SET
1. Interpret interrelationship between forces of various members and mechanisms
2. Construction of turning movement diagram for a single and multi cylinder double acting Steam
Engine
3. Analyze various balancing forces acting on the reciprocating engine parts.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
25
30
30
15
-100
20
30
30
20
-100
Model
Examination*
10
20
30
40
-100
Semester End
Examination
10
20
30
40
-100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
State D Alemberts principle
Define inertia force and inertia torque.
Write an expression for the inertia force due to reciprocating mass in reciprocating engine,
neglecting the mass of the connecting rod.
What are the methods of finding the crank effort in a reciprocating single acting, single cylinder
petrol engine?
What is the acceleration of the piston in a reciprocating steam engine?
In an engine, what is the work done by inertia forces in a cycle?
What is turning moment diagram?
What is crank effort diagram?
Write the formula to calculate the turning moment on the crankshaft
Define : Fluctuation of energy
Define : Maximum fluctuation of energy
Define : Coefficient of fluctuation of energy
In turning moment diagram, write the formula to calculate the workdone per cycle
In turning moment diagram, write the formula to calculate the mean torque
In turning moment diagram, Write the formula to calculate the workdone per cycle when number
of working strokes per minute
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
129
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
51.
52.
Define : Maximum fluctuation of speed
Define : Coefficient of fluctuation of speed
Define : Coefficient of steadiness
Define : Static balancing
Write the expression for primary unbalanced forces of reciprocating masses
Write the expression for secondary unbalanced forces of reciprocating masses
Write the formula to calculate the magnitude of the resultant centrifugal force
What is tractive force in balancing?
What is swaying couple in balancing?
What is hammer blow in balancing?
Define : Vibratory motion
Define : Period of vibration
Define : Time period
Define : Cycle in vibration
Define : Frequency in vibration
Define : Free vibration
Define : Natural vibration
Define : Free frequency
Define : Forced vibration
Define : Damped vibration
Define : Longitudinal vibrations
Define : Transverse vibration
What is critical speed of a shaft?
Define the term Vibration Isolation
What is the function of the governor?
State the different types of governor
State the difference types of centrifugal governor
What is the controlling force in centrifugal governor?
What is the function of a simple Watt governor?
Define sensitivity of governor
What is hunting of governor?
What is the condition of isochronisms in governor?
What is the stability of the governor?
Write the formula for gyroscopic couples magnitude.
Name the effect of gyroscopic couple acting on it, when the pitching of a ship is upward?
What are the different cases of balancing?
State the necessary conditions of dynamic balancing
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
What is the difference between piston effort, crank effort and crank-pin effort?
The inertia of the connecting rod can be replaced by two masses concentrated at two points and
connected rigidly together. How to determine the two masses so that it is dynamically equivalent
to the connecting rod? Show this
Given acceleration image of a link. Explain how dynamical equivalent system can be used to
determine the direction of inertia force on it.
What is the function of flywheel?
Draw the turning moment diagram for a single cylinder, double acting steam engine.
Draw the turning moment diagram for a four stroke cycle internal combustion engine
State the functional difference between the governor and flywheel?
What is the effect of friction on the functioning of a Porter governor?
State the limitations of the Watt governor
How does a Porter governor differ from that of Watt governor?
In what type of governors can isochronisms be achieved?
What do you understand by gyroscopic couple?
What is isochronous governor?
Define sensitive of governor
State the application of gyroscopic principles to aircrafts.
In an automobile, what is the gyroscopic torque when the vehicle makes a left turn?
What is the gyroscopic effect on sea going vessels?
130
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
18. What is the effect of the gyroscopic couple on the reaction of the four wheels of a vehicle
negotiating a curve?
19. What is the effect of the gyroscopic couple on a two wheeled vehicle when taking a turn?
20. What will be the effect of the gyroscopic couple on a disc fixed at a certain angle to a rotating
shaft?
21. What is the couple applied to the disc causing precession when a disc is spinning with an angular
velocity rad/s about the axis of spin?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
How are velocity and acceleration of the slider of a single slider crank chain determined
analytically?
What is the velocity of the piston, When the crank is at the inner dead centre, in a horizontal
reciprocating steam engine?
Write the essential condition of placing the two masses, so that the system becomes dynamically
equivalent
A horizontal steam engine running at 240 r.p.m. has a bore of 300 mm and stroke 600 mm. The
connecting rod is 1.05 m long and the mass of reciprocating parts is 60 kg. When the crank is 600
past its inner dead centre, the steam pressure on the cover side of the piston is 1.125 N/mm2 while
that on the crank side is 0.125 N/mm2. Neglecting the area of the piston rod, determine:
1. The force in the piston rod ; and
2. The turning moment on the crankshaft.
A machine has to carry out punching operation at the rate of 10 holes per minute. It does
6
kN-m of work per mm2 of the sheared area in cutting 25 mm diameter holes in 20 mm thick plates.
A flywheel is fitted to the machine shaft which is driven by a constant torque. The fluctuation of
speed is between 180 and 200 r.p.m. The actual punching takes 1.5 seconds. The frictional losses
are equivalent to 1/6 of the work done during punching. Find:
1. Power required driving the punching machine, and
2. Mass of the flywheel, if the radius of gyration of the wheel is 0.5 m.
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
A rotating shaft carries four masses A, B, C and D which are radially attached to it. The mass
centres are 30 mm, 38 mm, 40 mm and 35 mm respectively from the axis of rotation. The masses
A, C and D are 7.5 kg, 5 kg and 4 kg respectively. The axial distances between the planes of
rotation of A and B is 400 mm and between B and C is 500 mm. The masses A and C are at right
angles to each other. Find for a complete balance,
1. The angles between the masses B and D from mass A
2. The axial distance between the planes of rotation of C and D,
3. The magnitude of mass B.
A shaft 1.5 m long is supported in flexible bearings at the ends and carries two wheels each of 50
kg mass. One wheel is situated at the centre of the shaft and the other at a distance of 0.4 m from
the centre towards right. The shaft is hollow of external diameter 75 mm and inner diameter 37.5
mm. The density of the shaft material is 8000 kg/m3. The Youngs modulus for the shaft material
is 200 GN/m2. Find the frequency of transverse vibration.
A Porter governor has all four arms 200 mm long. The upper arms are pivoted on the axis of
rotation and the lower arms are attached to a sleeve at a distance of 25 mm from the axis. Each ball
has a mass of 2 kg and the mass of the load on the sleeve is 20 kg. If the radius of rotation of the
balls at a speed of 250 r.p.m. is 100 mm, find the speed of the governor after the sleeve has lifted
50 mm. Also determine the effort and power of the governor.
Unit I
Force Analysis
Applied and constraint forces Free body diagrams Static equilibrium conditions Two, three &
four members Static force analysis of simple mechanisms Dynamic force analysis Inertia force
and Inertia torque D Alemberts principle The principle of superposition Dynamic Analysis in
reciprocating engines Gas forces Equivalent masses Bearing loads Crank shaft torque
Inertia forces in a reciprocating engine considering the weight of the connecting rod
9 Hours
131
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit II
Turning Moment Diagram and Flywheel
Turning Movement Diagram for a Single Cylinder Double acting Steam Engine and Multi Cylinder
Engine. Fluctuation of Energy. Flywheel and Flywheel in Punching Press. Balancing of masses
Basics only
Flywheel in printing and cutting machines
9 Hours
Unit III
Balancing
Single Rotating mass by a Single mass rotating in the Same plane and Two masses rotating in Different
planes. Several masses rotating in the Same plane and Different planes. Partial Balancing of
Unbalanced primary force in a Reciprocating Engine. Partial balancing of Locomotives. Variation of
Tractive force. Swaying Couples. Hammer Blow. Coupled Locomotives. Primary and Secondary forces
of Multi Cylinder In-line Engine. Radial and V Engines
Effect of Partial Balancing of Reciprocating Parts of TwoCylinder Locomotives
9 Hours
Unit IV
Vibration
Free Vibration. Natural Frequency of free transverse vibration due to a point load, Uniformly
distributed load acting over a Simply Supported beam and Shaft fixed at both ends carrying a
Uniformly distributed load and a shaft subjected to a number of point loads. Critical speed at a shaft.
Viscous Damping. Damping and Magnification Factor. Randam vibrations. Resonance migration from
one point to another. Isolation and Transmissibility. Free Torsional Vibrations of a Single, Two and
Three Rotor System. Torsionally Equivalant Shaft.
Logarithmic Decrement and Free torsional vibration of a geared system
9 Hours
Unit V
Mechanism for Control
Governors Types Centrifugal governors Gravity controlled and spring controlled centrifugal
governors Characteristics Effect of friction Controlling force Other Governor mechanisms.
Gyroscopes Gyroscopic forces and torques Gyroscopic stabilization Gyroscopic effects in
Automobiles, ships and airplanes.
Sensitiveness and Hunting of governor
9 Hours
Total: 45 + 15 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
S. S. Rattan, Theory of Machines, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi,
2011.
John J Uichker and Joesph E. Shigley, Theory of Machines and Mechanism, Tata McGraw Hill
Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2005.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Ashok G Ambekar, Mechanism and Machine Theory, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2009.
R. L. Norton, Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company
Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2005.
Sadhu Singh, Theory of Machines, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2007.
Syad and R. L. Singal, Kinematics of Machinery, Tech Mac Publishers, Chennai, 2007.
R. L. Norton, Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company
Pvt Ltd,, New Delhi, 2005.
132
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M503 HEATS AND MASS TRANSFER
(Use of standard heat and mass transfer data book is permitted)
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
The course is intended to build up necessary background for understanding the physical behavior
of various modes of heat transfer, like, conduction, convection, and radiation, incompressible and
compressible flow
To understand the application of various experimental heat transfer correlations in engineering
calculations
To learn the thermal analysis and sizing of heat exchangers
To understand the basic concepts of mass transfer
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(b) The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge, capability of analyzing and solving any
concept or problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students will be able to
understand the working concepts of thermal engineering.
(g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Heat transfer rate for different modes
Analysis of different modes of heat transfer
Performance analysis of heat exchanger
Analysis of different modes of mass transfer
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
20
20
20
40
-100
20
20
20
40
-100
Model
Examination3*
20
20
20
40
-100
Semester End
Examination
20
20
20
40
-100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
3
What is Fouriers law and write the equation?
What is conduction?
State Newtons law of cooling or convection law
Write down the equation for heat transfer through a composite plane wall.
Define overall heat transfer co-efficient.
Define fins or extended surface.
State the application of fins.
Define Fin efficiency.
Define Fin effectiveness.
What is meant by steady state heat conduction?
What is periodical flow?
What is meant by Lumped heat analysis?
Define Biot number.
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks
133
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
58.
What is meant by semi-infinite solids?
What is meant by infinite solids?
What are the factors affecting the thermal conductivity?
Define Radiation
Define Emmissive power.
Define monochromatic emissive power.
What is meant by absorptivity, reflectivity, and transmissivity?
State Planks distribution law.
State Wiens displacement law.
State Stefan-Boltzmann law.
What is meant by gray body?
Define intensity of radiation.
What is the purpose of radiation shield?
Define irradiation, radiosity.
What are the assumptions made to calculate radiation exchange between the surfaces?
What is meant by shape factor?
What is dimensional analysis?
State Buckingham theorem.
What are all the advantages of dimensional analysis?
Define Reynolds number, Prandtl number, Nusselt number, Grashof number, Stanton number.
What is meant by Newtonion and non-newtonion fluid?
What is meant by laminar flow and turbulent flow?
What is hydrodynamic boundary layer and thermal boundary layer?
What are the dimensionless parameters used in forced convection?
Define boundary layer thickness.
Define Boiling.
Give application of boiling and condensation.
What is meant by filmwise condensation and dropwise condensation?
Draw different regions of boiling and what is Nucleate boiling?
What is Heat Exchanger?
What are the types of heat exchanger?
What is meant by direct and indirect contact heat exchanger?
What is meant by Regenerators and Recuperators?
What is meant by parallel flow and counter flow?
What is meant by shell and tube heat exchanger and compact heat exchanger?
What is meant by LMTD?
What is meant by Fouling factor and effectiveness of heat exchanger?
What is mass transfer?
Give the examples of mass transfer.
What are the modes of mass transfer?
What is molecular diffusion and eddy diffusion?
What is convective mass transfer?
State Ficks law of diffusion.
What is meant by free and forced convective mass transfer?
Define Schmidt number, Scherwood number.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
What is different between thermodynamics and heat transfer?
What is the significance of heat transfer?
What is conduction heat transfer? How does it differ from convection heat transfer?
What is the difference between the natural and forced convection?
How is the conduction resistance of solids affected by its thermal conductivity?
How is the convection resistance at a surface affected by the convection co-efficient? How is the
radiation resistance affected by the surface emissivity?
What is the physical basis for existence of a critical insulation radius? How do the thermal
conductivity and the convection coefficient affect its value?
Heat is transferred from hot water flowing through a tube to air flowing over the tube. To enhance
the rate of heat transfer, should fins be installed on the tube interior or exterior surface?
134
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
Under what condition the lumped capacitance method may be used to predict the transient
response of a solid to a change in its thermal environment?
Why is the semi-infinite solution applicable to any geometry at early times?
Can snow be thought of as a good absorber or reflector of incident radiation?
How is the thermal energy of material affected by the absorption of incident radiation? By
reflection of incident radiation?
Can the view factor of a surface with respect to itself be nonzero? If so, what kind of surface
exhibits such behavior?
What is the difference between local and average convection coefficient for species transfer? What
are their units?
Do we expect heat transfer to change with transition from a laminar to a turbulent boundary layer?
If so, How?
What quantities change with location in a velocity boundary layer? A thermal boundary layer?
What important boundary layer parameters are linked by the Reynolds analogy?
In what way Boiling & Condensation differs from other types of heat exchange?
What physical features distinguish a turbulent flow from a laminar flow?
How does the velocity boundary layer thickness vary with distance from the leading edge for
laminar flow? For turbulent flow?
How does the local convection heat transfer coefficient vary with distance from the leading edge
for laminar flow over a flat plate?
How is local heat transfer from the surface of a flat plate affected by the existence of an unheated
starting length?
How does the average convection coefficient of a tube vary with its location in a tube bank?
Why are baffles used in a shell-and-tube heat exchanger?
What effect does fouling have on the overall heat transfer coefficient and hence the performance of
a heat exchanger?
What effect does finned surfaces have on the overall heat transfer coefficient and hence the
performance of a heat exchanger? When is the use of fins most appropriate?
Will the fluid having the minimum or the maximum heat capacity rate experience the largest
temperature change in a heat exchanger?
Why is the maximum possible heat rate for a heat exchanger not equal to Cmax(Thi Tci)?
Can the outlet temperature of the cold fluid ever exceed the inlet temperature of the hot fluid? If
so, why? If not why not?
In using Ficks law to determine the mass or molar flux of a species in a mixture, what specifically
is being determined?
Under what conditions does the species diffusion flux equal the absolute flux associated with
transport of the species?
In a transient diffusion process, what can be said about the mass transfer Biot number?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
How would you approximate the total irradiation of a small surface in a large isothermal
enclosure?
How does the directional emissivity of a material change as the zenith angle associated with
emission approaches 90
If the spectral emissivity of material increases with increasing wavelength, how does its total
emissivity vary with temperature?
If a cube of sugar is placed in a cup of coffee, what is the driving potential for dispersion of the
sugar in the coffee? What is the physical mechanism responsible for dispersion if the coffee is
stagnant? What is the physical mechanism if the coffee is stirred?
An aluminium alloy fin of 7mm thick and 50mm long protrudes from a wall which is maintained at
120C. The ambient air temperature is 22C. The heat transfer coefficient and conductivity of the
fin material are 140 W/m2K and 55 W/mK respectively. Determine (a) Temperature at the end of
the fin. (b) Temperature at the middle of the fin. (c) Total heat dissipated by the fin.
A long cylindrical heater 30mm in diameter is maintained at 700C. It has surface emissivity of
0.8. The heater is located in a large room whose wall are 35C. Find the radiant heat transfer. Find
the percentage of reduction in heat transfer if the heater is completely covered by radiation shield
(=0.05) and diameter 40mm.
In a double pipe heat exchanger, hot fluid with a specific heat of 2300J/kgK enters at 380C and
leaves at 300C. Cold fluid enters at 25C and leaves at 210C. Calculate the heat exchanger area
135
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
7.
required for (a) Parallel flow (b) Counter flow. Take over all heat exchanger is 750W/m2K and
mass flow rate of hot fluid is 1kg/s.
CO2 and air experience equimolar counter diffusion in a circular tube whose length and diameter
are 1.2m and 60mm respectively. The system is at a total pressure of 1atm and a temperature of
273K. The ends of the tube are connected to large chambers. Partial pressure of CO2 at one end is
200 mm of Hg while at the other end is 90 mm of Hg. Calculate the following (a) Mass transfer
rate of CO2 and (b) Mass transfer rate of air.
Analyze/ Evaluate
Design a Heat exchanger that meets the following specification:
m(kg/s)
Tm,i (C)
Hot water
28
90
Cold water
27
34
Tm,o (C)
60
Unit I
Conduction
Fourier law of conduction in simple and composite geometrics, types of boundary and initial
conditions, contact resistance, conduction with heat generation, extended surface heat transfer, transient
and periodic heat conduction
Application of numerical methods
11 Hours
Unit II
Radiation
Basic laws of radiation - radiation in ideal and real surfaces - view factor algebra - radiation shields electrical analog using radiosity and irradiation - gaseous emission and absorption.
Concept of reradiating surface
7 Hours
Unit III
Convection Heat Transfer
Dimensional analysis - boundary layer concept - basic governing equations - laminar and turbulent
external and internal flows - forced and free convections - integral methods - semi empirical
correlations flow over bank of tubes
Concept of companied free and forced convection
9 Hours
Unit IV
Phase Change Heat Transfer and Heat Exchangers
Modes of boiling - Nusselt theory of condensation - correlations in boiling and condensation - types of
heat exchangers - methods of analysis - fouling factor and simple design problems
Working principle of cooling tower
9 Hours
Unit V
Diffusion Mass Transfer
Introduction Concentrations, Velocities and fluxes Ficks Law of Diffusion The Diffusion
Coefficient Species Conservation Equation Initial and Boundary Conditions Steady-State
Molecular Diffusion Mass Transfer with Chemical Reactions Transient Diffusion.
Convective Mass Transfer
Introduction The Convective Mass Transfer Coefficient The Concentration Boundary Layer
Governing Equations Momentum, Heat and Mass Transfer Analogies Turbulence Effects on Mass
Transfer Convective Mass Transfer Correlations The Evaporation of Water into Air
Concept of sublimation
9 Hours
Total: 45 + 15 Hours
136
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Textbooks
1. R. C. Sachdeva, Fundamentals of Engineering Heat and Mass Transfer, New Age International
Private limited, New Delhi, 2009.
2. C. P. Kothandaraman and S. Subramanyan, Heat and Mass Transfer Data Book, New Age
International Private limited, New Delhi, 2008.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Iacropera, DeWitt, Bergmann and Lavine, Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, Wiley India
Edition Private limited, 2011.
Yunus A Cengel, Heat and Mass Transfer an Practical Approach, Tata McGraw Hill publishing
Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2007.
J. P. Holman, Heat Transfer, Tata McGraw Hill publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2009.
C. P. Kothandaraman and S. Subramanyan, , Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, New Age
International Private limited, New Delhi, 2008.
R. K. Rajput, Heat and Mass Transfer, S Chand and Company, New Delhi, 2003.
137
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M504 DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To understand the basic geometrical specifications of various machine component with their
functional and strength requirements
To understand the procedures and standards for designing various machine components with
maximum economy and efficiency
To inject the knowledge to evaluate the design parameters of machine components.
PROGRAM OUTCOME
c)
The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in
various materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting,
fabrication, machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of
the course, students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable
component in industry.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Selecting the proper dimensions for the machine component for specific applications.
Checking the failure modes in machine component and identify the solution.
Designing the machine component for particular applications.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
25
30
30
15
-100
20
30
30
20
-100
Model
Examination*
10
20
30
40
-100
Semester End
Examination
10
20
30
40
-100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
4
Define standardization.
List out the factors influencing machine design.
Define principal stress.
What do you meant by curved beams?
Name some of the failure theories.
Define factor of safety.
Define torsional rigidity of the shaft.
Define critical speed of the shaft.
What do you meant by flexible shafts?
What is coupling? Where do you use it?
Define lead of screw threads.
Define pitch of the thread.
Name the types of threads used in fasteners.
List out types of joints used in welding.
Define stiffness of the spring.
Define spring index.
What is solid length of the helical compression springs?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
138
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
Name the types of bearings used in machine components.
What are the functions of bearings?
State some of the applications of ball and roller bearings.
What is coefficient of fluctuation of speed?
What is the difference between the function of flywheel and governor?
Define fatigue failure.
Define mechanical advantage.
What is leverage?
How will you classify bearings?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
State the significance of factor of safety in machine design.
What are the causes for stress concentration?
What are the effects of stress concentration on machine component?
What are the methods of reducing stress concentration?
Why hollow shaft is stronger than solid shaft?
How resonance will be avoided in shafts?
Why maximum principal stress theory is not applicable for shafts?
What is the difference between coupling and clutch?
State the difference between rigid and flexible coupling.
In What situation flexible coupling is used?
Why taper is provided in the key?
If a coupling is assembled to the shaft by key which should be stronger?
What are the advantages of threaded joints?
What are the advantages of V threads?
What is the function of plain washer in bolted joints?
State the difference between course and fine threads.
List out the name of stresses induced in threaded joints.
What are the advantages of welded joints compared to riveted joints?
What are the causes of residual stress in welded joint? How they are relieved?
How do you differentiate open and closed coil helical spring?
Name the types of stresses induced in the springs.
What is the use of Wahl?
Name the types of springs.
What do you meant by nip of leaf spring?
What do you meant by active coils of the spring?
Why ball and roller bearings are called antifriction bearings/
Why taper roller bearings are used in pairs?
What is the function of flywheel?
What do you understand by fluctuation of energy and maximum fluctuation of energy?
What types of stresses are induced in the spokes of a rimmed flywheel?
What is the effect of keyway on the torsional rigidity of the shaft?
Why steps are provided in the shaft? How it affects the shaft strength?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
What is approximate friction power loss in a single radial ball bearing having a bore diameter of
55mm and subjected to a radial load of 225KN? The shaft rotates at 600RPM.
Determine the approximate friction torque expected in single deep groove ball bearing under a
radial load of 30KN. The bore of the bearing is 50mm.
A shaft is subjected to the varying load cycle as follows; 3KN for 1 Sec, 1 KN for 1s and 0.5KN
for 3s. If the shaft rotates at the constant speed of 500RPM, What basic load rating for each
fraction of cycle should be used in selecting the ball bearing with a life of 15000 hours?
Analyze / Evaluate
1.
Taking stress concentration into account find the maximum stress induced when a tensile load of
20kN is applied to i) A rectangular plate 80mm wide and 12mm thick with a transverse hole of
16mm diameter ii) A stepped shaft of 60mm and 30mm diameter with 6 mm fillet radius.
139
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
2.
A factory line shaft is 4m long and is to transmit 75KW at 200rpm. The allowable stress in shear is
40Mpa and maximum allowable twist is 10 in a length of 20mm diameter. Determine the required shaft
diameter.
3.
Design a journal bearing for a centrifugal pump with the following data.
Diameter of the journal = 150mm
Load on bearing = 40KN
Speed of journal = 900Rpm
Unit 1
Steady Stresses and Variable Stresses in Machine Members
Introduction to the design process - factor influencing machine design, selection of materials based on
mechanical properties Direct, Bending and Torsional stress equations Impact loading Calculation
of principle stresses for various load combinations Design of curved beams Crane hook and C
frame - Factor of safety - The theories of failure Introduction to fracture mechanics-Stress
concentration Design for variable loading Soderberg, Goodman and Gerber relations
Stress intensity factor
9 Hours
Unit II
Design of Shafts and Couplings
Design of solid and hollow shafts based on strength, rigidity and critical speed Design of keys and
key ways - Design of rigid and flexible couplings Muff, Clamp, Rigid Flange, Bushed-pin flexible
couplings Design of knuckle joints
Introduction to gear and shock absorbing couplings
9Hours
Unit III
Design of Joints and levers
Threaded fasteners - Design of bolted joints Eccentrically loaded bolted joint in shear Eccentric
load perpendicular to axis of bolt Eccentric load on Circular base Design of welded joints for
pressure vessels and structures Butt, Fillet welded Joints Strength of Parallel, Traverse fillet
Welded Joints - Theory of bonded joints Failures in pressure vessel joints - Design of levers
Metal stir welding Process
9 Hours
Unit IV
Design of Springs and Flywheel
Design of helical, multi- leaf and torsional springs under constant loads and varying loads - End
conditions and length of springs - Stresses in Helical springs of circular wire Wahl stress factor
Concentric torsion springs Belleville springs Special springs - Design of flywheels involving
stresses in rim and arm
Flywheel energy storage
9 Hours
Unit V
Design of Bearings
Design of bearings Sliding contact and rolling contact types Cubic mean load Design of journal
bearings Mckees equation Lubrication in journal bearings Calculation of bearing dimensions
Fundamentals of engineering Tribology
Advance Bearings
9 Hours
Total: 45 + 15 Hours
Textbook
1.
V. B. Bhandari, Design of Machine Elements, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd,
New Delhi, 2010.
140
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, PSG College of Technology, Design Data Book,
M/s.Kalaikathir Achchagam, 2009.
J. E. Shigley and C. R. Mischke, Mechanical Engineering Design, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing
Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2003.
R. C. Juvinall and K. M. Marshek, Fundamentals of Machine Component Design, John Wiley &
Sons, New Delhi, 2002.
R. L. Norton, Design of Machinery, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi,
2004.
W. Orthwein, Machine Component Design, Jaico Publishing Co, 2003.
141
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M505 TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the Total Quality Management concept and principles and the various tools
available to achieve Total Quality Management
To understand the application of statistical approach for quality control
To create an awareness about the ISO and QS certification process and its need for the industries
To apply the quality concepts in product design, manufacturing etc in order to maximize customer
satisfaction
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(e) The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team
(h) The graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility and
will display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and upgradation
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Understanding the management philosophies
Able to demonstrate the uses of SPC and its application in the shop floor
Knowing the tools available for converting the customers need into usable product
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
40
40
20
--100
40
40
20
--100
40
40
20
--100
Semester End
Examination
40
40
20
--100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
*
Define the term Total Quality Management.
Enlist the basic concepts of Total Quality Management.
Write the names of any four gurus of Total Quality Management.
Define the term Quality.
How the quality can be quantified?
List the obstacles for TQM implementation
Mention few benefits of TQM.
Define the term leadership.
List the characteristics of quality leaders.
Mention some concepts of leadership.
Write the functions of quality council.
What is meant by quality policy?
What meaning is conveyed through vision statement?
What is meant by mission statement?
Draw customer satisfaction organization diagram.
Who is a customer?
What is the customer perception to quality?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
142
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
58.
59.
60.
61.
62.
63.
64.
65.
66.
67.
68.
69.
70.
71.
72.
73.
74.
75.
76.
77.
Name the elements of customer service.
What is the meaning of customer retention?
What is meant by motivation?
What are the concepts used to achieve motivated workforce?
What is meant by empowerment?
Mention few benefits of empowerment.
What is a team?
What are the different types of teams?
Give one example' for cross functional team and natural work team.
List any four characteristics of successful team.
What is meant by gain sharing? " .
What is meant by profit sharing?
State the meaning of performance appraisal.
What is meant by employee involvement?
Write few benefits of employee involvement
What is continuous process Improvement?
State Juran's Trilogy.
List the objectives of performance measures.
Write the meaning of quality cost.
Write the meaning of vital few and useful many with respect to Pareto diagram.
What are the functions of a check sheet?
What is a histogram?
What is the difference between histogram and check sheet?
How the central tendency is calculated?
What is the objective of measuring central tendency?
Write an equation for sample standard deviation.
What is a non conforming unit?
What is meant by nonconformity?
State the meaning of attributes related to quality.
How the subgroup is sized?
What is a scatter diagram?
What is an np chart?
Name the benefits of quality management tools
What is an affinity diagram?
What is a tree diagram?
What is a matrix diagram?
State the benefits of matrix diagram.
What is meant by PDPC?
What is an activity network diagram?
What are the reasons for benchmarking?
Mention few benefits of benchmarking.
Mention the pitfalls of benchmarking.
Initiated the quality function deployment.
What is quality function deployment?
List the benefits of QFD.
Draw the structure of the house of quality.
What is meant by house of quality?
List the steps for building house of quality.
What are the technical descriptors?
What is the need for competitive assessment?
How QFD is carried out?
What is the value of Cp and Cpk?
State the meaning of Total Productive Maintenance.
List the goals of TPM.
Mention the planned downtimes in an organization.
List the unplanned downtimes in an organization.
How the down time loss is measured?
How the loss of reduced speed is measured?
Name the losses due to poor quality as per Taguchi.
What is average loss? How it is estimated?
143
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
78. Write Taguchi's quadratic loss function.
79. What is meant by FMEA?
80. Enlist the important types of FMEA.
81. What is meant by reliability?
82. How the failure rate is predicted?
83. State the benefits of FMEA.
84. Name the stages of FMEA.
85. How RPN is calculated?
86. How the central tendency is calculated?
87. What is the objective of measuring central tendency?
88. Write an equation for sample standard deviation
89. What is meant by population?
90. What is a sample?
91. What is a control chart?
92. What is the meaning of upper and lower control limits?
93. Mention the control charts used for variables.
94. What is meant by process capability?
95. Define process capability index.
96. What is the significance of Cp and Cpk?
97. What is the difference between mean and median?
98. What is meant by mode?
99. Abbreviate ISO and ASQ.
100. List the benefits of ISO certification.
101. What is ISO 9000 standard and series?
102. Write the applications of ISO/TSI 16949.
103. List out the ISO 9000 requirements.
104. What are the customer related processes in ISO.
105. What are the important steps required to implement a quality management system?
106. List the objectives of internal quality audits.
107. Mention the environmental management systems.
108. What are the requirements of ISO 140001?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
How the suppliers are rated?
How a process flow diagram can be used as a quality improvement tool?
How an interrelationship diagram can be used for the quality improvement?
How the loss of poor quality is measured?
What is the difference between a document and a record?
Differentiate between the chance causes and assignable causes of variations giving suitable
examples
When a process is in control or stable? What type of variations is present in the process?
Compare X Bar & R charts.
How do recognition and reward affect employee involvement?
When do you use the scatter diagram?
Why poission distribution curve is used for preparing c-chart?
How the service quality affects companys performance?
Why the implementation of TQM is necessary?
How control charts helps in finding poor quality?
Why do we invest more on prevention cost than appraisal cost?
How the dispersion of the data is measured?
Why motivation is necessary?
Why team works?
How the benchmarking is done?
How customer requirements are converted into product specifications?
How environmental management systems are benefit to industries?
What is the difference between histogram and check sheet?
Differentiate defect and defective.
When are c-charts used?
144
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
Is customer complaint necessary for an organization? If yes, list the various tools used for
collecting customer complaints.
Differentiate control limit and specification limit
Why np chart is not recommended when the sub group size is variable?
Under what situation, one can use cause and effect diagram.
How should control charts be used by shop-floor personnel?
Differentiate discrete and variable data, with suitable example?
When do you use the affinity diagrams?
Under what situation, one can use matrix diagram?
Differentiate the term failure mode and failure effect
Why aero diagrams are called PERT diagrams?
Differentiate recognition and reward.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
Assuming that the life in hours of an electric bulb is a random variable following normal
distribution with a mean of 2000 hrs and standard deviation of 840 hrs. Find the expected number
of bulbs from a random sample of 2000 bulbs having life
i)
More than 3000 hrs
ii)
Between 2600 and 2800 hrs.
Consider a company involved in testing the strengths of components. Currently 50
engineers are working in the company. Explain briefly the steps that the company should take to
implement ISO 9000:2000 based quality system and obtain the certificate from a certifying
agency.
The inspection results of copper bushes in a machine shop based on samples size 50 are as given
below. Construct a suitable control chart and offer r inference about the process.
Sample no
No
of
rejections
Sample no
No
of
rejections
4.
10
11
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
10
16
14
A machine shop produces steel pins. The width of 100 pins was checked after machining and data
was recorded as follows
Width
9.509.509.509.509.509.509.509.50in mm
9.51
9.51
9.51
9.51
9.51
9.51
9.51
9.51
Frequency
(1) Find the arithmetic mean, standard deviation and variance.
(2) What percentage of the pins manufactured has width of 9.52 to 9.63?
5.
A certain product has been statistically controlled al a process average of 36.0 and a S:D. of 1.00.
The product IS presently being sold to two users who have different specification requirements.
User A has established a specification of 38.0 4.0 for the product, and user R has specification of
36.04.0.
(i) Based on the present process set up, what percent of the product produced will not meet the
specifications set up by user A?
(ii) What percent of the product will not match the specifications of user B?
(iii) Assuming that the two users needs are equal, a suggestion is made to shift the process target
to 37.0. At this suggested value, what percent of the product will not meet the specifications of
user A?
(iv) At the suggested process target, what percent or the product will not meet the specifications of
user B?
(v) Do you think .that this shift to a process target of 37.0 would be desirable? Explain your
answer.
145
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
6.
In the manufacture of connecting rod assemble; the numbers of defectives found in the inspection
of 15 samples of 50 Items in each sample are given in the following table
Sample
no:
No
of
defectives:
7.
8.
9.
10
11
12
13
14
15
21
12
10
16
15
17
(i) Determine the trial control limits, construct the np chart and state whether the process is in
control.
(ii) If any point goes outside the control limits, determine the revised control limits eliminating that
point.
(i) An industrial product was subjected to inspection with a batch size of 500 for consecutive days
The number of defective pieces found are 33, 42, 44, 56, 60, 43, 55, 42, 28 and 70. Draw a p-chart
and discuss.
(ii) How is process Decision Program Chart (PDPC) used? Give an example.
The mean weight of 500 male students at a certain college is 65.6 kg and tile standard deviation is
10 kg.
Assuming tl1at the weights are normally distributed, find how many students, weigh (i) more than
75.5 kg, and (ii) between 55.5 and 75.5 kg
At a certain examination 10% of the students who appeared for the paper in statistics got less than
30 marks and 97% of the students got less than 62 marks. Assuming tire distribution is normal,
find the mean and tile standard deviation of the distribution
Unit I
Introduction
Definition of Quality Dimensions of Quality Quality Planning Quality costs Analysis
Techniques for Quality Costs Basic concepts of Total Quality Management Historical Review
Quality Statements Strategic Planning, Deming Philosophy Crosby philosophy Continuous
Process Improvement Juran Trilogy, PDSA Cycle, 5S, Kaizen Obstacles to TQM Implementation OSHA standards
9 Hours
Unit II
TQM Principles
Principles of TQM, Leadership Concepts Role of Senior Management Quality Council, Customer
satisfaction Customer Perception of Quality, Customer Complaints, Service Quality, Customer
Retention, Employee Involvement Motivation, Empowerment, Teams, Recognition and Reward,
Performance Appraisal, Benefits Supplier Partnership Partnering, sourcing, Supplier Selection,
Supplier Rating, Relationship Development, Performance Measures Basic Concepts, Strategy,
Performance Measure
Supplier certification
9 Hours
Unit III
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
The seven tools of quality Statistical Fundamentals Measures of central Tendency and Dispersion,
Population and Sample, Normal Curve, Control Charts for variables X bar and R chart and attributes P,
nP, C, and u charts, Industrial Examples, Process capability, Concept of six sigma New seven
Management tools
Application of Poissons distribution
9 Hours
146
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit IV
TQM Tools
Benchmarking Reasons to Benchmark Benchmarking Process, Quality Function Deployment
(QFD) House of Quality, QFD Process, and Benefits Taguchi Quality Loss Function Total
Productive Maintenance (TPM) Concept, Improvement Needs, and FMEA Stages of FMEA- Case
studies
Failure rate
9 Hours
Unit V
Quality Systems
Need for ISO 9000 and Other Quality Systems ISO 9000:2000 Quality System Elements,
Implementation of Quality System, Documentation, Quality Auditing, ISO 9000:2005 (definitions),
ISO 9001:2008 (requirements) and ISO 9004:2009 (continuous improvement), TS 16949, ISO 14000,
AS9100 Concept, Requirements and Benefits- Case studies
Benefits of EMS
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
Dale H. Besterfiled, Total Quality Management, Pearson Education Inc, New Delhi, 2003.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
N. Gupta and B. Valarmathi, Total Quality Management, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company
Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2009.
James R. Evans and William M. Lidsay, The Management and Control of Quality, South-Western
2002.
Dr S. Kumar, Total Quality Management, Laxmi Publications Ltd., New Delhi 2006.
P. N. Muherjee, Total Quality Management, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi,2006.
http://nptel.iitm.ac.in/courses/Webcourse-contents/IIT-roorkee/industrial enginerring/index.htm
147
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M507 DYNAMICS LABORATORY
0 0 3 1.5
OBJECTIVES
To explain the various practical aspects of Instrumentation with emphasis on Mechanical domain
To introduce the various types of Governor, cam, balancing of rotating masses and to determine
the M.I. of various systems
To explain the concept of Mechanical measurement and various methods used for measuring the
variables
At the end of the course, students will be able to handle various instruments to measure mechanical
parameters and get inference out of it for further action
PROGRAMS OUTCOME
(e) The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
To check the profile of cam.
To find out the MOI for different apparatus.
To determine the gyroscopic couple effect.
To maintain the constant speed by using governor.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Preparation
Remember
Understand
Apply
Observation and Results
Analyze
Evaluate
Record
Mini-Project/Model
Examination/Viva-Voce
Total
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
Define equilibrium speed.
Define height of a governor.
Define the effect of governor
Define hunting of a governor
Define stability of governors
Define sensitivity of governors
Define axis of precession
Define period of vibration or time period
Define a cycle
Define simple harmonic motion
Define degree of freedom
Define the pressure angle of cam
Define whirling or critical speed of a shaft
Define logarithmic decrement
Define variation in tractive effect
Define damping
Define damping factor or damping ratio
Internal Assessment
Semester End
Examination
10
15
15
20
10
15
15
50
50
148
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
What are the function of the governor?
What are the centrifugal governor?
What are the types of governors?
Write down the expression for finding the speed of the balls of porter governor.
What is the porter governor?
Write down the expression for governor effort and power of a porter governor
Write down the expression for finding the speed of a proell governor
What is active force?
What is centripetal acceleration and its magnitude?
What is reactive force?
What is frequency?
What is the function of flywheel?
What is the crank pin effect?
What is the crank effect?
Difference between free and forced vibration.
What is viscous damping?
What are the types of damping?
Apply / Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
When the load sleeve moves up and down along the spindle, the frictional force acts on it in a
direction______ to that of the motion of sleeve.
A governor is said to be unstable if the radius of the rotation __________ as the speed
___________
Centrifugal force is ___________ to centripetal force but __________
How cams are classified?
How followers are classified according to motion of follower?
How followers are classified according to surfacing contact?
What are cams and its purpose?
What is the maximum fluctuation of speed?
The factors affecting the critical speed of a shaft is ________
What are the methods for finding out natural frequency of free longitudinal vibration?
Application of torsional vibration
What is the transmissibility at resonance and no damper condition?
What is the need for balancing?
What is the static, dynamic and complete balancing?
What is the limiting condition in order that the wheel will not lift from the rails?
List of Experiments
1. Determination of sensitivity and effort using Watt and Proell Governors.
2. Study of jump phenomenon and drawing profile of the cam.
3. Determination of gyroscopic couple using Gyroscope and verify its laws.
4. Determination of critical speed of shaft with concentrated loads by Whirling of shaft apparatus.
5. Exercise on Balancing of reciprocating masses.
6. Exercise on Balancing of rotating masses.
7. Determination of moment of inertia by oscillation method for connecting rod and Flywheel.
8. Determination of damping co-efficient of Single degree of freedom system using spring mass
system.
9. Determination of torsional frequencies for compound pendulum and flywheel system with lumped
Moment of inertia.
10. Exercise on Epicyclic gear train model differential & worm wheel reducers.
11. Determination of moment of inertia by bifilar suspension system
12. Exercise on measuring the displacement using LVDT (Linear variable displacement Transducer)
13. Exercise on measuring the torque using Torque indicator.
14. Determine the load using load cell apparatus.
149
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
15. Study of sound measurement.
Design experiment
Application oriented experiment
Mini project
Total: 45 Hours
Practical Schedule
S.No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Experiment
Determination of sensitivity and effort using Watt and Proell
Governors.
Study of jump phenomenon and drawing profile of the cam.
Determination of gyroscopic couple using Gyroscope and verify its
laws.
Determination of critical speed of shaft with concentrated loads by
Whirling of shaft apparatus.
Exercise on Balancing of reciprocating masses.
Exercise on Balancing of rotating masses.
Determination of moment of inertia by oscillation method for
connecting rod and Flywheel.
Determination of damping co-efficient of Single degree of freedom
system using spring mass system.
Determination of torsional frequencies for compound pendulum and
flywheel system with lumped Moment of inertia.
Exercise on Epicyclic gear train model differential & worm wheel
reducers.
Determination of moment of inertia by bifilar suspension system
Exercise on measuring the displacement using LVDT (Linear variable
displacement transducer)
Exercise on measuring the torque using Torque indicator.
Determine the load using load cell apparatus.
Study of sound measurement
Design experiment
Application oriented experiment
Mini project
Hours
3
2
2
2
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
15
150
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M508 THERMAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY II
0 0 3 1.5
OBJECTIVES
To integrate the various basic thermodynamic concepts
To apply the concept into various thermal applications like Heat exchanger, Heat transfer,
conduction, convection, radiation, compressors, refrigeration and air conditioning
To get the experimental skill
PROGRAMS OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge, capability of analyzing and solving any
concept or problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students will be able to
understand the working concepts of thermal engineerings.
(g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Analysis of different modes of heat transfer
Heat Transfer rate for different modes
Performance of heat exchanger
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Internal Assessment
Preparation
Remember
Understand
Apply
Observation and Results
Analyze
Evaluate
Record
Mini-Project/Model
Examination/Viva-Voce
Total
Semester End Examination
10
15
15
20
10
15
15
50
50
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
What is Fouriers law and write the equation?
What is conduction?
State Newtons law of cooling or convection law
Write down the equation for heat transfer through a composite plane wall.
Define overall heat transfer co-efficient.
What are the factors affecting the thermal conductivity?
Define Radiation
Define Emmissive power.
Define monochromatic emissive power.
What is meant by absorptivity, reflectivity,transmissivity?
State Planks distribution law.
State Wiens displacement law.
State Stefan-Boltzmann law.
What is meant by gray body?
Define intensity of radiation.
What are the assumptions made to calculate radiation exchange between the surfaces?
What are all the advantages of dimensional analysis?
151
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
Define Reynolds number, Prandtl number, Nusselt number, Grashof number, Stanton number.
What is meant by Newtonion and non-newtonion fluid?
What is meant by laminar flow and turbulent flow?
What is hydrodynamic boundary layer and thermal boundary layer?
What are the dimensionless parameters used in forced convection?
Define boundary layer thickness.
What is Heat Exchanger?
What are the types of heat exchanger?
What is meant by direct and indirect contact heat exchanger?
What is meant by Regenerators and Recuperators?
What is meant by parallel flow and counter flow?
What is meant by shell and tube heat exchanger and compact heat exchanger?
What is meant by LMTD?
What is meant by Fouling factor and effectiveness of heat exchanger?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
How is the conduction resistance of solids affected by their thermal conductivity?
How is the convection resistance at a surface affected by the convection co-efficient?
How is the radiation resistance affected by the surface emissivity?
If heat is transferred from a surface by convection and radiation, how are the corresponding
thermal resistance represented in a circuit?
Can a material experiencing heat generation be represented by a thermal resistance and included in
a circuit analysis? If so, why? If not, why not?
What is the physical basis for existence of a critical insulation radius? How do the thermal
conductivity and the convection coefficient affect its value?
Heat is transferred from hot water flowing through a tube to air flowing over the tube. To enhance
the rate of heat transfer, should fins be installed on the tube interior or exterior surface?
Can snow be thought of as a good absorber or reflector of incident radiation?why?
How is the thermal energy of material affected by the absorption of incident radiation?
How is the thermal energy of material affected by reflection of incident radiation?
Can the view factor of a surface with respect to itself be nonzero? If so, what kind of surface
exhibits such behavior?
What is the difference between local and average convection coefficient for species transfer? What
are their units?
Do we expect heat transfer to change with transition from a laminar to a turbulent boundary layer?
If so, How?
What quantities change with location in a velocity boundary layer? A thermal boundary layer?
Under what conditions velocity, thermal and concentration boundary layers may be termed
analogous? What is the physical basis of analogous behavior?
What important boundary layer parameters are linked by the Reynolds analogy?
What physical features distinguish a turbulent flow from a laminar flow?
Why are baffles used in a shell-and-tube heat exchanger?
What effect does fouling have on the overall heat transfer coefficient and hence the performance of
a heat exchanger?
Will the fluid having the minimum or the maximum heat capacity rate experience the largest
temperature change in a heat exchanger?
Why is the maximum possible heat rate for a heat exchanger not equals to Cmax(Thi Tci)?
Can the outlet temperature of the cold fluid ever exceed the inlet temperature of the hot fluid in
Heat Exchanger? Justify?
Apply / Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
How would you approximate the total irradiation of a small surface in a large isothermal
enclosure?
How does the directional emissivity of a material change as the zenith angle associated with
emission approaches 90 ?
If the spectral emissivity of material increases with increasing wavelength, how does its total
emissivity vary with temperature?
152
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
If a cube of sugar is placed in a cup of coffee, what is the driving potential for dispersion of the
sugar in the coffee? What is the physical mechanism responsible for dispersion if the coffee is
stagnant? What is the physical mechanism if the coffee is stirred?
How does the velocity boundary layer thickness vary with distance from the leading edge for
laminar flow? For turbulent flow?
How does the local convection heat transfer coefficient vary with distance from the leading edge
for laminar flow over a flat plate?
How is local heat transfer from the surface of a flat plate affected by the existence of an unheated
starting length?
How does the average convection coefficient of a tube vary with its location in a tube bank?
List of Experiments
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Thermal conductivity of lagged pipe
Thermal conductivity of metal rod
Heat transfer by natural convection
Heat transfer by forced convection
Heat exchanger test-parallel and counter flow
Emissivity measurement
Stefan Boltzmann constant
Refrigeration test
Air conditioning test
Reciprocating compressor testing
Design experiment
Application oriented experiment
Mini Project
Practical Schedule
Total: 45 Hours
Sl. No.
1
Experiment
Introduction about laboratory
Hours
3
Thermal Conductivity of lagged pipe
Thermal Conductivity of Metal Rod
Heat transfer by natural convection
Heat transfer by forced convection
Heat exchanger test-parallel and counter flow
Emissivity measurement
Stefan Boltzmann constant
Refrigeration test
10
Air conditioning test
11
Reciprocating compressor testing
12
Design experiment
13
Application oriented experiment
153
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M509 METROLOGY LABORATORY
0 0 3 1.5
OBJECTIVES
To understand the concept Students will be able to measure various parameters by using standard
measuring instruments
To enable the students to use dimensional measuring instruments and SPC tools for manufacturing
process analysis
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(j) The graduates can become job-givers rather than just job-seekers
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Check the angle of a tapered hole.
Determine the straightness and flatness on the surface plate.
Maintain the tolerances for a manufacturing component by using comparator.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Internal Assessment
Preparation
Remember
Understand
Apply
Observation and Results
Analyze
Evaluate
Record
Mini-Project/Model
Examination/Viva-Voce
Total
10
15
15
20
10
15
15
50
50
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
Semester End
Examination
Define metrology.
What is meant by precision and non-precision instrument?
List out various methods of measurement.
What is meant by direct and indirect methods of measurement?
Define line and end measurement.
What are the different types of errors.
Define sensitivity.
What is meant by repeatability and reproducibility?
Write down the characteristics of precision measuring instrument.
What is the purpose of surface and angle plate?
Define least count.
Define fits and tolerance.
What is the least count for vernier and micrometer?
What is the usage of vernier and micrometer?
What is the purpose of gear tooth vernier?
Define comparator.
List out various types of comparators
Mention any two advantages of comparators.
Stat the working principle of electrical comparator.
What are the advantages of electrical comparator?
Classify the pneumatic comparator.
154
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
Name the various types of pitch errors found in screw thread.
Name the various method of measuring the minor diameter of the thread.
Name the various method of measuring the major diameter of the thread.
Name the various method of measuring the major effective diameter of the thread.
Define drunken error.
What is the best wire size?
Name the various methods for measuring pitch diameter.
What are the applications of tool makers microscope?
What are the commonly used forms of gear teeth?
What are the types of gear.
Name any four gear errors.
What is meant by straightness measurement?
Name the device used for measurement of roundness?
What is interferometer?
Name the different types of interferometer.
List out various geometrical checks made on machine tools.
What is the stylus probe instrument?
What is CMM?
Define machine vision.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
What are the different bases used for selection of measuring instruments?
Differentiate between systematic and random error.
Distinguish between primary, secondary and working standards.
How the mechanical comparator is used? Sate with any one example.
How the displacement are measured using laser interferometer.
How an autocollimator is calibrated?
State the limitations of sine bar
Why surface finish is important in engineering applications?
What is the difference between primary texture and secondary texture?
What is meant by best size wire?
Apply / Evaluate
1.
In which instrument you will use for measuring
a) Diameter of a hole of up to 50mm
b) Diameter of holes greater than 50mm
c) Diameter of hole less than 5 mm
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Aluminum though light, is not used for micrometer frames, why?
What are the important design considerations in design of metrological instrument?
How slip gauges are manufactured?
What do you understand by geometrical tolerances?
How the standard tolerance grades are designated?
Why hole-basis system of fit is generally employed?
Why is it that the use of a sine bar is not recommended for angles larger than 45 with the reference
plane.
9. A 20mm diameter hole is drilled and reamed at an angle of 75 to a flat surface. How the angle
could be checked by using two unequal rollers and calculate the values of the measurement which
must be made, using suitable size of rollers.
10. Calculate the chord length and its distance below the tooth tip for a gear of module 2.5mm and
14.5pressure angle.
List of Experiments
1.
2.
3.
Use of precision measuring instruments like micrometer, vernier, height and depth gauge and
surface plate etc.,
Calibration of Vernier / Micrometer / Dial Gauge
Measurement of angles between centre lines of holes drilled radially on a shaft.
155
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
4.
5.
6.
7.
Taper and bore measurement using spheres.
Measurements of Gear Tooth Dimensions using Gear Tooth vernier / Optical profile projector
Measurement of thread parameters using Tool Makers Microscope / Floating Carriage Micrometer
Checking the limits of dimensional tolerances using Comparators (Mechanical / Pneumatic /
Electrical / Optical comparators) and construction of SQC chart.
8. Checking straightness of a surface plate using Autocollimator / Spirit Level.
9. Checking alignment of radial drilling machine using dial gauge.
10. To check the dimensions of a machine component using CMM
11. Measurement of the Surface roughness.
Design experiment
Application oriented experiment
Mini Project
Total: 45 Hours
Practical Schedule
Sl. No.
Experiment
Hours
Introduction about laboratory
Use of precision measuring instruments like micrometer, vernier, height
and depth gauge and surface plate
Calibration of Vernier / Micrometer / Dial Gauge
Measurement of angles between centre lines of holes drilled radially on a
shaft
Taper and bore measurement using spheres
6
7
8
Measurements of Gear Tooth Dimensions using Gear Tooth vernier /
Optical profile projector
Measurement of thread parameters using Tool Makers Microscope /
Floating Carriage Micrometer
Checking the limits of dimensional tolerances using Comparators
(Mechanical / Pneumatic / Electrical / Optical comparators) and
construction of SQC chart
3
3
3
Checking straightness of a surface plate using Autocollimator / Spirit Level
10
Checking alignment of radial drilling machine using dial gauge.
11
Checking the dimensions of a machine component using CMM
12
Measurement of the Surface roughness.
13
Design experiment
14
Application oriented experiment
156
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M601 AUTOMATED MANUFACTURING
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To set up, program, maintain and troubleshoot the automated machines during manufacturing
process
To give a broad exposure to Engineering graduates in the field of automated machines like CNC
and robotics
To understand the concept of Computer aided manufacturing systems, automated material
handling systems and group technology
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(h) The graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility
will display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and up gradation.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern
Practices.
and
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Analysis of various manufacturing systems in automation industry.
Able to perform automated and representative production requirements.
Integration in linking the manufacturing and design functions using Computers.
Take a lead role at a highly automated industry.
Analysis of various transducer and sensor in a robot.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
35
35
30
--100
30
40
30
--100
Model
Examination*
30
40
30
--100
Semester End
Examination
30
40
30
--100
Remember
1. What are the ten strategies for Automation and process improvement?
2. Give examples for automated manufacturing system.
3. What is flexible automation?
4. What is lean production?
5. What is just-in-time delivery of parts?
6. What is mean time between failures (MTBF) and mean time to repair (MTTR?)
7. What are the basic elements of an automated system?
8. What is mean by CNC?
9. What are the advantages and disadvantages of CNC machine over conventional machines?
10. Name the four feed drives that are used in CNC machine tools.
11. Name the typical positional sensors used in the CNC machine tools.
12. What are the different types of EDM?
13. What is mean by basic load capacity?
14. What are the requirements of a good slide way system?
15. What is mean by flaking and how will you determine the nominal life of a linear motor bearing?
6
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
157
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
16. Name the three types of Spindle Heads.
17. What is the significance of touch trigger?
18. What are the various types of DC motors used in a CNC machine tools?
19. What are the advantages of AC servo motors over DC servomotors for axes feed drivers?
20. What is a machining center? How it differs from conventional CNC milling?
21. What are the advantages of digital feed-back devices over analog feedback.
22. What is a rotary type encoder?
23. State the principle of Moir-fringes.
24. What are the advantages of circular interpolation technique.
25. What is APT system?
26. What do you understand by modal and non-modal G CODES?
27. What is meant by canned cycle? List any 4 types of canned cycle
28. Name the commonly available fixed cycles for Lathe Operations.
29. What is mean by Tool change cycle?
30. What are the features of custom macros?
31. What is Rapid Traverse Function?
32. When a Dwell function is to be used in the part programming?
33. What is Tool nose radius compensation and what is Cutter diameter compensation.
34. List out the functions of a post-processor in a CNC system.
35. What do you understand by the term machine zero, work zero and Zero Shift?
36. What is meant by the term contact and noncontact inspection?
37. What is a visual inspection method?
38. What is an industrial robot?
39. What do you understood by the term Dead reckoning?
40. What are the various components of an Industrial Robot?
41. What does a manipulator consists of in an industrial robot?
42. What is degree-of-freedom?
43. What are the common robot configurations?
44. Name the five types of joints commonly used in industrial robot
45. The operations that can be performed using the limited sequence control in a robot are?
46. What is a play back robot with point-to-point control?
47. What is a gripper? What are the various types of grippers used in industrial robot applications?
48. Name the types of sensor used in robots.
49. Write down the applications of industrial robot.
50. Write down the material handling applications of industrial robot.
51. Name some processing operation that a robot can perform?
52. What is mean by Repeatability and accuracy of a robot?
53. What is a robot program?
54. What is material handling?
55. What do you mean by External and internal logistics?
56. What are the commonly used material transport equipments?
57. What is the use of palletizer and depalletizer?
58. What are the design considerations to be considered during the design of a material handling
equipment?
59. Name the principal types of powered trucks?
60. What are nonpowered material transport equipments?
61. Mention some typical applications of automated guided vehicle system?
62. What is an automated guided vehicle system (AGVS)?
63. What are the different types of automated guided vehicles?
64. What are the roles of material transport equipments inside an industry?
65. Mention the applications of AGVS.
66. What is vehicle guidance technology?
67. State the purpose of traffic control in an automated guided vehicle system.
68. What is frequency select method and path switch select method?
69. What are the advantages of Self-guided vehicle technology over fixed path ways?
70. What are the two aspects of vehicle management?
71. Name the two methods of traffic control used in a commercial AGV system.
72. What is forward sensing?
73. What is the use of obstacle detection sensor?
74. What is on-machine inspection system?
158
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
75. What do you understand by the term uniting equipment?
76. The methods used in AGV system to dispatch vehicles are_______________.
77. What is vehicle acquisition distance?
78. What is the use of emergency bumper in AGV system?
79. What are mono rails?
80. What is the function of material storage system?
81. What is storage capacity and storage density?
82. What is system throughput?
83. Name some advantages and applications of automated storage systems?
84. What is an automated storage/retrieval system (AS/RS)?
85. What is Work-in-process (WIP) storage technology?
86. What are the applications of carousel storage system?
87. What are the four basic components of nearly all automated storage/retrieval system?
88. What is a manufacturing support system?
89. Define CAD and CAM.
90. What is the role of CAD/CAM in design and manufacturing firms?
91. What are the features of CIM in the manufacturing process?
92. What are the elements of a CIM system?
93. What are the benefits of CAD system?
94. What is Lean product development?
95. What is Rapid prototyping?
96. What is shop floor control and inventory control?
97. W hat is ERP?
98. What is a retrieval CAPP system?
99. What is a generative CAPP system?
100. What is a Flexible manufacturing system?
101. What are the various types of workstation of a flexible manufacturing system?
102. The basic components of a flexible manufacturing system are__________________.
103. The four reasonable tests of flexibility in an automated manufacturing systems are __________.
104. What is a flexible manufacturing cell?
105. What is group technology?
106. What is a route sheet and what does it contains?
107. What is a part family?
108. What are the benefits of group technology and part family in a manufacturing sector?
109. What is cellular manufacturing?
Understand
1. How will you classify the manufacturing costs?
2. How manufacturers can successfully compete by employing modern manufacturing approaches and
technologies.
3. Before starting programming what are the various items one must check in a CNC machine.
4. The four factors that govern the selection of tooling for CNC machines are?
5. Why linear tooling is preferred in some CNC Chuckers?
6. State the significance of preparatory function.
7. What are the significance of Subroutines and Do loops.
8. Differentiate between point-to-point control and continuous path control.
9. How do you pre-load a ball screw nut?
10. How canned cycle works?
11. What are the importances of feedback devices in a CNC Machine tool?
12. State the importance of sensors in a robot.
13. What are the advantages of dual grippers over a single gripper?
14. What is a robot control systems?
15. How are robot controllers classified?
16. What is the role of Machine vision in robotics?
17. What do you understand by the term control resolution in a robot?
18. When a vehicle is said to be a Self-guided vehicle (SGV)?
19. How SGV differs from other guidance methods?
20. How forklift rider trucks are distinguished from walkie trucks?
21. What are the various capabilities that a manufacturing system must possess in order to be flexible?
159
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
Whats the main feature of cranes and hoists over other material transport equipments?
What is flexibility in a manufacturing system?
When a system is referred to as flexible manufacturing system?
Whats the importance for automating a companys storage operations?
Compare the advantages of automated system over manual work system and worker-machine
system.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
On what attributes similar parts can be distinguished?
How a Hierarchical structure differs from Chain type structure?
How a firm can automate the task of process planning using computers?
Importance and necessity for making the manufacturing system automated?
Justify the need to automate the manufacturing process.
How a machining center differs from conventional CNC milling machine?
Using the list of sensor devices used in robot work cells, describe several methods for determining
the presence or absence of a nonmetallic part in a fixture. Assume the dimensions of the part are:
length = 127.0 mm, width = 36.0 mm and thickness = 20.0 mm. The fixture is a mechanical vise
with two jaws for holding the part. For each alternative make a sketch of how the sensor would be
positioned relative to the part.
Unit I
Introduction and Structure of CNC Machine Tools
Introduction to Automation, definition, types, reasons for automating, and types of production.
Development of CNC Technology, principles, features, advantages, economic benefits, applications,
CNC,DNC concept, classification of CNC Machine, types of control, CNC Machine building, guide
ways and its types, ball Screws and recalculating ball screw, working of 3 axis and 5 axis CNC
machines
CNC controllers, characteristics, interpolators
9 Hours
Unit II
CNC Programming and Tooling
Coordinate system, structure of a part program, G & M Codes, Manual part programming for Fanuc,
APT part programming using CAD/CAM, and simple Examples. Selection of CNC cutting tools
Cutting tool materials, carbide inserts classification, tooling system for Machining centre and Turning
centre;(work holding devices), Tool magazines - ATC, APC
Maintenance of CNC Machines
9 Hours
Unit III
Industrial Robotics
Introduction, robot anatomy, robot control systems, and other specifications, end effectors, sensors,
drive system, safety monitoring. Robot applications- Characteristics of robot applications, work cell
layout
Robot applications in material handling, processing, Fettling, assembly, welding and inspection
9 Hours
Unit IV
Automated Material Handling and Inspection
Introduction to Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) Systems and Automated Storage and retrieval
system (AS/RS) - basic components, types and its application. Automated inspection principles- Off
line & on line inspection, distributed inspection & final inspection
Sensor technologies for automated inspection and Shop floor control
9 Hours
160
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit V
Computer Aided Manufacturing and Group Technology
Introduction to CAM- Manufacturing planning, manufacturing control- Computer integrated
manufacturing, Flexible manufacturing systems -Components, Types of systems, FMS layout and FMS
benefits. Computer aided process planning: Retrieval CAPP systems and generative CAPP systems,
benefits of CAPP. Group Technology
Part families, parts classification and coding- Benefits of group technology
9 Hours
Total 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
Mikell P. Groover, Automation, Production System and Computer Integrated Manufacturing,
Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2008.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
P. Radhakrishnan, S. Subramanyan and V. Raja , CAD/CAM/CIM, New Age International
Private Ltd, NewDelhi, 2008.
Mikell P. Groover, Mitchell Weiss and Roger N. Nagel G Odrey, Industrial Robotics, Tata
McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd. New Delhi, 2007.
M. M. M . Sarcar, Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing, Prentice Hall of India, New
Delhi, 2008.
P. Radhakrishnan, Computer Numerical Control Machines, New Central Book Agency, 2004.
HMT, Mechatronics, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd, New Delhi, 2010.
161
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M602 HYDRAULICS AND PNEUMATICS
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To learn hydraulic fluid / Pneumatic air fundamentals including generation and distribution
To understand working principles, operation of hydraulic and pneumatic components
To expose to various techniques of circuit building in pneumatics
Have exposure to diagnose / troubleshoot Hydraulic pneumatic, electro pneumatic circuits
To know about the ladder logic diagram to programmable logic control of fluid power system
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for
entry-level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Ability to demonstrate the basic principles of hydraulics and pneumatics.
Identify proper control valves and cylinder for a specific application.
Ability to interpret any given hydraulic / pneumatic circuits.
Knowledge on troubleshooting in hydraulic/pneumatic circuits.
Design the circuits using pneumatic / hydraulic components for a small scale industrial application.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
S. No.
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
Remember
30
30
30
30
Understand
40
40
40
40
Apply
30
30
30
30
Analyze/Evaluate
--
--
--
--
Create
--
--
--
--
100
100
100
100
Total
7
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
7
Define the term fluid power.
Name three basic methods of transmitting power?
Define the term mass density.
Define the term absolute viscosity and kinematic viscosity.
Define surface tension, capillarity.
What is oxidation stability?
What are fluid power symbols?
State Pascals law.
State the continuity equation.
What are the various energy losses occur when liquid flows through a pipe?
What is the function of pump?
What is the function of hydraulic actuator?
What are the types of hydraulic cylinder?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
162
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
What is the function of a Hydraulic motor?
Name the basic types of rotary actuators?
What is the function of direction control valve?
What is check valve? What are its functions?
What is pressure control valve?
What is flow control valve?
What is sequence valve?
What is the function of an accumulator?
Define the term intensifier ratio.
What is the use of pressure switch?
List the various types of accumulator.
What are limit switches?
What do you meant by electrical relay?
What is the purpose of a timer?
Define pneumatics.
State Boyles law, Charles law.
What is the function of air filter?
What do you mean by FRL unit?
What is the function of pneumatic actuator?
What do you meant by sequencing of cylinders?
What is hydro pneumatic circuit?
What is servo system?
What is the function of servo amplifier?
What is fluidics?
State the coanda effect.
What is PLC?
What are the fluid sensors?
What is meant by contact sensing?
What do you meant by SRT-Flip flop?
List three major units of a PLC.
What does the term trouble shooting refer?
List four basic requirements on which the life of the fluid power system depend.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
What is the fundamental difference between Hydraulics and pneumatics?
State the effect of temperature and pressure on viscosity of liquids?
What is the difference between the force and pressure?
Differentiate between the laminar and turbulent flow?
Where the hydrodynamic displacements pumps are employed? Why?
Which pump-external gear, internal gear, screw vane and piston generates the least noise? Why?
Why are centrifugal pumps not preferred for fliud power application?
Why are double acting cylinders known as differential cylinders?
Which hydraulic motor is generally the most efficient? Why?
State the difference between the hydraulic motor and hydraulic pump?
When do you prefer poppet type hydraulic valves?
Distinguish between a pressure control valve and pressure relief valve?
Why is pressure measurement considered as a crucial process in the hydraulic system?
For what type of application, you would prefer to use pneumatic systems rather than hydraulic
system?
Why are mufflers used in pneumatic system?
Why is extension stroke faster than the retraction stroke in a regenerative circuit?
What is the difference between an OR Gate and an EXCLUSIVE OR Gate?
Where the fluidics control system preferred than other control system?
If a pump is delivering insufficient oil what are the possible causes and also give remedies for
them?
What will you do to reduce /prevent excessive heating of oil in a hydraulic system?
163
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Apply
1. To investigate a hydraulic and pneumatic system
Requirements: Two syringes of equal size.
A plastic tube of about 10 cm that will fit tightly over the opening of both syringes
Draw out the plunger (piston) of one syringe and push in the plunger of the other syringe.
Connect the two syringes by means of the plastic tube.
Push in the plunger of one syringe.
Draw that plunger out again.
2. For the Hydraulic System shown, following data are given:
Pump is adding 5 hp (3730 W) to fluid
Pump flow is 0.001896 m3/s
Pipe has 0.0254 m inside dia
Sp. Gravity of oil = 0.9
Kinematic viscosity of oil is 100 CS
Elevation difference between station 1 & 2 is 6.096 m
Pipe lengths: 1 ft = 0.305 m, 4 ft = 1.22 m, 16 ft = 4.88 m
Find pressure available at inlet to hydraulic motor. The pressure at the oil top surface level in the
hydraulic tank is atmospheric (01 MPa).
Unit I
Fluid Power Systems and Fundamentals
Introduction to fluid power, Advantages of fluid power, Application of fluid power system. Types of
fluid power systems, Properties of hydraulic fluids General types of fluids Fluid power symbols
164
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
.Basics of Hydraulics-Applications of Pascals Law- Laminar and Turbulent flow Reynolds number
Darcys equation Losses in pipe, valves and fittings.-Problems
Bernoullis equation, Hydraulic circuit analysis
9 Hours
Unit II
Hydraulic System and Components
Sources of Hydraulic Power: Pumping theory Pump classification Gear pump, Vane Pump, piston
pump, construction and working of pumps pump performance Variable displacement pumps. Fluid
Power Actuators: Linear hydraulic actuators Types of hydraulic cylinders Single acting, Double
acting special cylinders like tandem, Rodless, Telescopic, Cushioning mechanism, Construction of
double acting cylinder, Rotary actuators Fluid motors, Gear, Vane and Piston motors.
Pump characteristics
9 Hours
Unit III
Control Components
Construction of Control Components : Direction control valve 3/2 way valve 4/2 way valve
Shuttle valve check valve pressure control valve pressure reducing valve, sequence valve, Flow
control valve Fixed and adjustable, electrical control solenoid valves, Relays. Accumulators and
Intensifiers: Types of accumulators Accumulators circuits, sizing of accumulators, Intensifier
Applications of Intensifier
Intensifier circuit.-Cylinder Sequencing circuits
9 Hours
Unit IV
Pneumatic System Components and Servo Systems
Pneumatic Components: Properties of air Compressors Filter, Regulator, and Lubricator Unit Air
control valves, Quick exhaust valves, and pneumatic actuators. Servo systems Hydro Mechanical
servo systems, Electro hydraulic servo systems and proportional valves. Fluidics Introduction
Simple circuits in fluidics devices
9 Hours
Unit V
Design of Hydraulic and Pneumatic Circuits
Introduction to PLC - ladder diagrams, PLC applications in fluid power control. Fluid Power Circuit
Design, Speed control circuits, synchronizing circuit, Pneumo hydraulic circuit, Sequential circuit
design for simple applications using cascade method.
Fluid power circuits -failure and troubleshooting.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
Anthony Esposito, Fluid Power with Applications, Pearson Education New Delhi, 2011.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
S. R. Majumdar, Oil Hydraulics, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd. New Delhi,
2004.
James L. Johnson, Introduction to Fluid Power, Delmar Thomson Learning, 2003.
S. R. Majumdar, Pneumatic systems Principles and maintenance, Tata McGraw Hill
Publishing Company Pvt Ltd. New Delhi, 2008.
Andrew Parr, Hydraulics and Pneumatics, Jaico Publishing House, 2006.
Illangov Soundarrajan, Introduction to Hydraulics and Pneumatics, Prentice hall of India,
New Delhi, 2007.
165
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M603 DESIGN OF TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS
(Use of PSG design data book is permitted)
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To gain knowledge on the principles and procedure for the design of power transmission
components
To understand the standard procedure available for the Design of Transmission systems
To learn to use standard data and catalogues
To familiarize the students with the different mechanisms like cam, geneva and ratchet and pawl
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes
k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
Interpret interrelationship between components of various flexible elements like belt, chain, rope
drives
Able to select the various power transmission drives based on the applications
Strengthen the analytical skills of the students.
Able to draw the ray diagram for the single, multi stage and overlapping type of gear boxes and
also to calculate the output speed
2.
3.
4.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
S.No.
1
2
3
4
5
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
25
30
25
15
05
100
20
30
25
20
05
100
20
20
30
25
05
100
20
20
30
25
05
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
Mention the types of power drive.
State the Law of Belting
What are the types of belts?
State the materials for belts.
What factors should be considered during the selection of a belt drive?
What is meant by the ply of belt?
Mention the different types of joints employed for joining flat belts.
What are the various stresses induced in wire ropes?
How is a wire rope specified?
What is meant by chordal action in chain drives?
What is a gear drive?
State the Law of gearing
Mention some applications of gear drives.
What is meant by spur gear?
How are gears classified?
What factors influence backlash?
What is meant by a corrected gear?
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
166
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
What stresses are induced in gear tooth?
What is a helical gear?
What are the advantages of helical gears?
Specify the types of gears failures.
Define the following terms.
a) Tip circle b) Root circle c) Pitch circle
What is a herringbone gears?
State the advantages of Herringbone gear.
What is a bevel gear?
What is a crown gear?
Define the following terms: (a) Cone distance, (b) Face angle.
In which gear drive, self locking is available?
Write some applications of worm gear drive.
Specify the machine tools used for producing spur gears.
What are the components of gear box?
Give the applications of gear box?
What is a speed diagram?
What is preferred number?
What is step ratio?
What does the ray diagram of gear-box indicate?
What are the requirements of a speed gear box?
State the types of cam.
Define the term undercutting of cam profile
What are the advantages of knife edge follower?
What are the different types of follower motions?
What is bearing?
What are the functions of bearing?
How bearings are classified?
How do you classify cams?
What is sliding contact bearing?
What are the applications of sliding contact bearing?
What is an antifriction bearing?
Give two applications of hydrodynamic journal bearing.
What is the range of number slots in Geneva mechanism?
Give the applications of Geneva mechanism.
What is the purpose of pawl used in ratchet mechanism?
Write the common materials used for ratchet and pawl mechanism.
In general what type of load acting on pawl pin?
Give the applications of ratchet & pawl mechanism.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
What conditions should be followed when flat belt drive is installed?
Why tight-side of the belt should be at the bottom side of the pulley?
In what ways, timing belts are superior to ordinary V belts?
In what ways wire ropes are superior to fibre ropes?
Find the difference between chain sprocket and gear.
What are the possible ways by which a chain drive may fail?
In what way silent chain is better than ordinary driving chain?
At what occasions non-metallic gears are employed.
What is interference in gears? How can you overcome it?
Compare simplex, duplex and triplex chain type
What preliminary design considerations should be, adopted, when selecting gear drive?
Why dedendum value is more than addendum value?
Differentiate axial pitch and normal pitch of the helical gear.
Why pinion is made harder than gear?
Why are gear drives superior to belt drives or chain drives? The advantages of gear drives?
In what ways helical gears are differed from spur gears.
Why is multistart worm more efficient than the single start one?
The efficiency of worm gear drive comparatively lower than other drive. Why?
167
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
19. When the number start of a worm is increased in worm gear drive, how it affects the other
parameters and action of the drive?
20. What is the specific feature of mitre gear?
21. What is kinematic arrangement, as applied to gear boxes?
22. What purpose does the housing of gear box serve?
23. List out the possible arrangement to achieve 16 speed gear box.
24. When do we use bevel gears?
25. For what purpose we are using gear box?
26. What is the purpose of cam drive?
27. What is pressure angle? What is the effect of increase in pressure angle?
28. Why ball and roller bearings are called antifriction bearing?
29. Why hydrodynamic journal bearing is called self acting bearing?
30. State advantages of hydrodynamic bearings over hydrostatic bearings.
Apply
1.
A motor shaft rotating at 1500 rpm has to transmit 15kW to a low speed shaft with a speed
reduction of 3:1. Assume starting torque to be 25% higher than the running torque. The teeth are
200 involutes with 25 teeth on the pinion. Assume both the gears are made of same material and
life of gear is 10000 hours. Design a spur gear drive to suit the above conditions and check for
compressive and bending stresses and plastic deformations. Also sketch the spur gear drive
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
The pulley system is used to lift small loads from a ground floor to an upper floor (Figure 1).
The load being lifted is 200N.
a.
What is the mechanical advantage of this pulley
system?
b. What is the velocity ratio of the system?
c. What effort is required to lift the load?
d. If the system moves the load 5metes upwards, how far
must
the effort move?
Figure 1
2.
A small hillside village has discovered a fresh water spring and wishes to pump the water up to
the surface, into a bottling plant. A local engineer has developed a simple pump. Refer Figure 2
The motor has broken down and the pulley mechanism has been removed. Draw in the box an
alternative mechanism, powered by hand, that could be used as a short term alternative to the
motorised system. Refer Figure 3
List four advantages / disadvantages of your design
168
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Figure 2
Figure 3
Create
1.
2.
Design a crushing machine is to be run at 560 rpm. Design a suitable drive to transmit 15 kW from
a motor at 1200 rpm. Minimum centre distance is 1.5 m.
Design a layout of a 9 speed gear box for a machine tool. The minimum and maximum speeds are
100 and 900 rpm. Power is 5 kW from 1200 rpm induction motor
Unit I
Design of Transmission Systems for Flexible Elements
Need for power transmission - type and classifications of transmission systems - applications limitations Belt and wire rope drives: Design of belt drives - Flat and V-belt drives - Condition for
Transmission of maximum power - Selection of belt and pulleys - Design of wire rope and pulleysDesign of chain drives with sprockets
9 Hours
Unit II
Spur Gears and Helical Gears
Gear Terminology - Speed ratios and number of teeth - Force analysis - Tooth stresses - Dynamic
effects - Basics of gear design - Gear tooth failure modes Design of Helical Gears - Pressure angle in
the normal and transverse plane - Equivalent number of teeth - Forces and stresses
Gear lubrication - selection of materials for gears
9 Hours
Unit III
Bevel Gears and Worm Gears
Types of bevel gears - Straight bevel gear - Tooth terminology - tooth forces and stresses. Estimating
the dimensions of pair of straight bevel gears - Applications of gear drives Worm gears drives terminology - Applications strength and wear rating of worm gears - thermal considerations - Forces
and stresses, estimating the size of the worm gear pair
Design of spiral bevel gears - beam and wear strength for bevel and worm gears
9 Hours
Unit IV
Design of Gear Boxes and Cam Design
Gear boxes - applications to spur, helical, bevel and worm gear drives - Standard step ratio - Ray
diagram, kinematics layout - Design of single stage, single speed gear boxes - Design of multistage,
multi speed gear boxes Cam Design: Types - pressure angle and under cutting base circle
determination - relative advantages and disadvantages - forces and surface stresses.
Design of gear boxes - application in machine tool
9 Hours
169
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit V
Design of Power Screws and Mechanisms
Power screws - Introduction, Forms and Terminology - Efficiency - Stress in screws - Calculation of
wear and strength - design of power screws. Design of Ratchet & pawl mechanism and Geneva
mechanism
Introduction to Snap Latches
9 Hours
Total: 45 + 15 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
T. J. Prabhu, Design of Transmission Elements, Mani Offset, Chennai, 2008.
V. B. Bhandari, Design of Machine Elements, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd.,
New Delhi, 2007.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
R. C. Juvinall and K. M. Marshek, Fundamentals of Machine component Design, John Wiley &
Sons, New Delhi 2002.
R. L. Norton, Design of Machinery, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi
2004.
B. J. Hamrock, B. Jacobson and S. R. Schmid, Fundamentals of Machine Elements, Tata McGraw
Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2007.
J. E. Shigley and C. R. Mischke, Mechanical Engineering Design, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing
Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2004.
S. G. Kulkarni, Machine Design, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi,
2010.
170
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M604 GAS DYNAMICS AND JET PROPULSION
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the basics of incompressible and compressible flow
To study the phenomenon of shock waves and its effect on flow
To gain basic knowledge about jet propulsion and Rocket Propulsion
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology
Subjects and thus acquire the capability to applying them
(b) The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge, capability of analyzing and solving any
concept or problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students will be able to
understand the working concepts of thermal engineering.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education
programmes
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Analysis capability with Enriched Fluid flow fundamentals
Will easily select the best suit nozzle and diffuser for any application
Will apply the jet and rocket propulsion principles in any of his project
Capable for producing the mini rocket or jet set-up with minimum deviation in the design aspect
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
20
20
20
40
--
20
20
20
40
--
20
20
20
40
--
20
20
20
40
--
100
100
100
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
What is energy and momentum equation?
What are the various regimes of fluid flow?
Define Stagnation state and Critical state.
What is Mach number, mach angle, mach cone?
Define nozzle and diffuser.
What is fanno flow and Raleigh flow?
What is mean by shock wave in fluid flow?
What is the difference between normal shock and oblique shock?
Define nozzle efficiency.
Tell the types of jet engines.
What is propulsive and overall efficiency?
What is thrust augmentation?
What is air breathing and non-air breathing engines?
Classify the rocket engines.
What are the applications of rocket?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
171
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Be aware of fundamentals of compressible and incompressible flow and where to apply that flows?
How Flow phenomena works?
How to make the fluid passage with hot fluid content?
How to avoid void the heat loss and to achieve maximum heat transfer?
Realize the shock wave principles how it happen?
Comprehend Aircraft engine working principles and various aircraft engines
Recognize Rocket engine performance and its application
Apply
1.
2.
3.
A supersonic nozzle expands air from p o = 25 bar and To = 1050 K to an exit pressure of 4.35 bar ;
the exit area of the nozzle is 100 cm 2. Determine
a. Throat area
b. Pressure and temperature at the throat
c. Temperature at exit
d. Exit velocity as fraction of the maximum attainable velocity and
e. Mass flow rate.
Ambient air ( p o = 1.013 bar and To = 288 K ) is sucked by a blower through a convergent
nozzle ( throat diameter = 10 cm ) . If the air velocity at the throat reaches the sonic value,
determine
a. Pressure and temperature at the throat,
b. Mass flow rate through the nozzle, and
c. Maximum mass flow rate.
A turbojet engine is being used to propel an aero plane. The drag is 3900 N. The coefficient of
drag is 0.01835. The wing area is 21.25 m2. The air consumption per second of the engine is 14.5
kg / sec and the thrust developed is 8900 N. Calculate the flight speed and effective jet velocity.
Also calculate the specific thrust. What is the density ratio at this altitude of 10000 m? Take =
0.5 kg / m3 at this altitude.
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
Will Best suggestion and decide the best suit fluid transfer in industrial applications.
Will try to adopt the aircraft and jet propulsion principles in real time applications
Will construct the best fluid transfer system with optimum heat transfer options.
Unit I
Compressible Flow Fundamentals
Energy and momentum equations for compressible fluid flows- various regions of flows - reference
velocities - stagnation state - Wave propagation in elastic medium propagation of sound waves and
derivation for velocity of sound - critical states, Mach number, critical Mach number - types of waves Mach cone - Mach angle - effect of Mach number on compressibility
Fluid flow fundamentals11 Hours
Unit II
Flow Through Variable Area and Constant Area Ducts
Isentropic flow through variable area ducts - T-s and h-s diagrams for nozzle and diffuser flows - area
ratio as a function of Mach number - mass flow rate through nozzles and diffusers - effect of friction in
flow through nozzles. Flow in constant area ducts with friction (Fanno flow) Fanno curves and
Fanno flow equation - variation of flow properties and variation of Mach number with duct length in
Fanno flow- Flow in constant area ducts with heat transfer (Rayleigh flow) - Rayleigh line and
Rayleigh flow equation - variation of flow properties and maximum heat transfer in Rayleigh flow.Wind potential possibilities in and around somanur11 Hours
172
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit III
Compressible Flow with Normal Shock
Governing equations - variation of flow parameters like static pressure, static temperature, density,
stagnation pressure and entropy across the normal shock Prandtl-Meyer equation - impossibility of
shock in subsonic flows - flow in convergent and divergent nozzle with shock - normal shock in Fanno
and Rayleigh flows - flow with oblique shock (elementary treatment only).
Shock waves advantage and disadvantage
6 Hours
Unit IV
Air Craft Propulsion Systems
Aircraft propulsion types of jet engines energy flow through jet engines - study of turbojet engine
components diffuser, compressor, combustion chamber, turbine and exhaust systems - performance
of turbo jet engines thrust, thrust power, propulsive and overall efficiencies - thrust augmentation in
turbo jet engine - ram jet and pulse jet engines.
Modern aircraft propulsion systems9 Hours
Unit V
Rocket Propulsion Systems
Rocket propulsion Classification of rocket engines Propellants: solid and liquid propellants, rocket
engines thrust equation effective jet velocity specific impulse rocket engine performance - Flow
through rocket nozzles mass ratio and propellant mass fraction Vertical flight of a rocket: powered
flight and coasting flight Rocket applications
Rocket propulsion case studies8 Hours
Total: 45+15 Hours
Textbook
1.
P. Balachandran, Fundamental of Compressible Fluid Dynamics, Prentice Hall of India, New
Delhi, 2009.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
S. M. Yahya., Gas Tables for Compressible Flow, New Age International Pvt Ltd., New Delhi,
S. M. Yahya., Fundamental of Compressible Flow, New Age International Pvt Ltd. New Delhi,
E. Rathakrishnan, Gas Dynamics, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2008.
Patrich.H. Oosthvizen, William E. Carscallen, Compressible fluid flow, Tata McGraw Hill
Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi,2004
Cohen. H., R. E. C Rogers and Sravanamutoo, Gas Turbine Theory, Addison Wesley Ltd.,
173
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M605 OPERATIONS RESEARCH
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To understand the various techniques of optimization in utilization of resources, operations
research techniques for industrial applications
To Develop analytical skills for solving industrial and real world problems (Identify, Formulate
and solve industrial Engineering Problems)
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and
technology
subjects and thus acquire the capability to applying them
g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry- level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies
i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes
SKILL SET
1.
2.
Understand the various linear optimization techniques and algorithms and its implementation for
solving industrial problems.
Select and perform suitable optimization technique to solve the industrial problem.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
15
15
25
45
-100
15
15
25
45
-100
Model
Examination*
15
15
25
45
-100
Semester End
Examination
15
15
25
45
-100
10
Remember
1. Define the term operations research.
2. What are the main characteristics of OR
3. Define feasible solution.
4. Name any two methods to solve artificial variable technique.
5. What do you mean by unbounded solution?
6. What do you mean by transportation problem?
7. List any three approaches used with T. P for determining the starting solution (or) IBFS.
8. Define a project.
9. Define a dummy activity.
10. What are the three common errors in the constructing of network?
11. What is meant by critical path?
12. Name the three types of float.
13. List out some basic characteristics of queuing system
14. What do you mean by FCFS?
15. Define sequencing.
16. Write down the formula used to find average weighted cost in replacement.
17. Give any two methods to solve the individual replacement.
18. Classify the replacement model.
19. The concept of obtaining a degenerate basic feasible solution in a LPP is known as ______.
10
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
174
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
State limitation of the Graphical method
In what aspect the slack variable differs from surplus variable.
How do you check the degeneracy in transportation?
How do you solve the unbalanced assignment problem?
Compare the transportation with assignment.
Distinguish between PERT and CPM.
When do you use dummy activity in the network?
A waiting customer leaves the queue due to impatience is _________.
How do you solve the three machine problem?
Why the replacement is necessary?
Mention some application areas of queuing model.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
How the OR technique is used in defense field?
How do you evaluate the optimality in transportation?
How do you convert the maximization A.P into a minimization one?
State the application of travelling salesman problem.
Which type of network model is applied in construction industry?
Which type of queuing model is applied in petrol bunk?
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
Select the appropriate optimization techniques for solving the transportation problem and justify it.
Unit I
Linear Models
Origin of Operations Research - The phases of O.R Applications - Linear Programming: Formulation
- Graphical method - Simplex method Artificial Variable techniques: Big M Method, two phase
method.
Dual simplex method simple problems only- shadowing pricing
9 Hours
Unit II
Transportation and Assignment Model
Transportation Problems: Optimal solution by North West corner method VAM Least cost method
MODI method. Assignment Problems: Formulation - Unbalanced Assignment Problem Hungarian
algorithm Traveling Salesman Problem.
Introduction to Inventory models - theory only
9 Hours
Unit III
Network Models
Network models - Shortest route - Minimal spanning tree - Maximum flow models - Project network CPM and PERT networks - Critical path scheduling
Introduction to crashing- theory only
9 Hours
Unit IV
Queuing Theory
Queuing models - Queuing systems and structures - Notation - parameter - Single Server and multi
server models - Poisson input - Exponential service - Constant rate service - Infinite population.
Introduction to game theory theory only
9 Hours
175
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit V
Sequencing and Replacement Model
Sequencing Problem: Models with n jobs with 2 machines Models with n jobs with 3 machines.
Replacement Models: Replacement of items that deteriorate with time Value of money changing with
time & not changing with time Optimum replacement policy: Individual & Group replacement.
Models with n jobs with n machines simple problems only
9 Hours
Total: 45 + 15 Hours
Textbook
1. Prem Kumar Gupta and D. S. Hira, Introduction to Operations Research, S.Chand and Co., New
Delhi, 2004
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Handy A. Taha, , Operation Research - An Introduction, Pearson Publications., New Delhi, 2008
R. Panneerselvam, Operations Research, Prentice Hall of India., New Delhi, 2010.
S . Dharani Venkatakrishnan, Operations Research, Kirthi Publishing House (P) Ltd., Coimbatore
1991.
Wagner, Operations Research, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2000.
Frederick S. Hiller and Gerald J. Liberman, Operations Research Concepts and Cases, Tata
McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2010.
176
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M607 COMPUTER AIDED MANUFACTURING LABORATORY
0 0 3 1.5
OBJECTIVES
To impart hands on training on CNC Machine tools
To acquire practical knowledge through intensive practice on CNC Machines & related software
To develop part programs for various components
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(c) The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in
various materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting, fabrication,
machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of the course,
students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable component in
industry.
.
(g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for
entry-level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies
(j) The graduates can become job-givers rather than just job-seekers
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
CNC programming
Tool path simulation
Tool and machine setting and
Maintenance of CNC lathe and milling machine
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Internal Assessment
Preparation
Remember
Understand
Apply
Observation and Results
Analyze
Evaluate
Record
Mini-Project/Model
Examination/Viva-Voce
Total
Semester End Examination
15
15
10
25
10
15
10
50
50
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
Define CNC programming
Designate the CNC cutting tools.
List the types of tool changers.
What is meant by modal and non-modal codes?
List the code with syntax used for feed rate in different unit system.
Name the codes used for units setting in CNC program.
Mention the M codes used for Spindle ON, OFF and START and STOP.
What are the advantages of canned cycles?
What is meant by peck drilling?
List G codes used for setting feed rate.
What is the use of Macro programming?
What is use of dwell? Name the G code.
177
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
Write syntax for end face peck drilling.
What is the use of G73 cycle in CNC lathe programming?
Write the syntax for G76 - taper threading cycle.
What is meant by sub-routine?
Name the M code used for coolant ON and OFF.
Write M code meant for tool changing.
Name the codes used for work clamping and unclamping.
What is meant by single block execution?
Depict the axis convention used in CNC lathe and Milling.
Which G code helps for enabling absolute coordinate system?
What are the benefits of using G 76 for internal threading?
What is the use of offsetting a tool?
Name the codes used for mirror imaging in CNC mill programming.
What is machine zero and tool zero?
List the advantages of using online programming.
Define each word in the following block of information. N 20 G90 X1.5 Z -3 M03
List the different modes for verifying CNC program.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
How to select speed for drilling different materials?
How CNC machine works?
How the tool changer works?
Why CNC turning is preferred than conventional lathe?
Differentiate turning centre and machining centre?
How the tools are held in the CNC milling?
Is G01 modal? How?
How to activate metric units in CNC program?
What is the need of cutter compensation?
Differentiate absolute and incremental programming with example.
How the right hand thread can be made?
How the canned cycle works?
How multiple threads are formed? Name the G code
How macros are called inside the programming?
Differentiate the uses of G00 and G28.
How CNC mill cutter works on different planes? List the G Codes used.
How circular interpolation is enabled?
When to use sub routines?
Differentiate offline programming and on-line programming.
What is purpose of dry run with air cutting?
Compare modal and non-modal code
Why axis convention is required in CNC machines?
How nose radius compensation is done?
How cutter length compensation is done?
How cutter compensation is done?
Why simulation is necessary before actual manufacturing?
How offsetting is done?
Why canned cycles are preferred than single line programming?
How to stop the CNC machine in case of emergency condition?
List out the functions of part programming.
What is the purpose of spindle encoder?
Differentiate DNC and CNC.
In which order the following functions are executed?
Speed, Feed rate, Dwell, G code and M code
34. What is used of speed and feed override?
178
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Apply/Evaluate
1.
Mention the applications of the following tools.
2.
Write the part program, simulate and fabricate the following components using XLTURN CNC
Lathe.
179
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
3.
Write the part program, simulate and fabricate the following components using STAR MILL
CNC Milling.
List of Experiments
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Exercise on linear and circular interpolation CNC Lathe
Exercise on facing and step turning
Exercise on taper turning
Exercise on thread cutting
Exercise on grooving cycle
Exercise on drilling and boring cycle
Exercise on linear and circular interpolation CNC Milling
Exercise on contour milling
Exercise on drilling
180
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
10. Exercise on peck drilling
11. Tool path simulation of various programs using anyone of CAM packages like CADEM/ProManufacturing/CATIA Software
12. Exercise on robot programming Pick and place, Palletizing
Design experiment
Application oriented experiment
Total: 45 Hours
Practical Schedule
S.No.
Experiment
Hours
Study and Practice on CNC Tool setting and Work setting
Linear and circular interpolation lathe and milling
Facing and step turning
Taper turning
Thread cutting
Grooving Cycle
Drilling and boring cycle
Contour milling
Drilling and Peck drilling using Milling
10
Tool path simulation using CAM packages
11
Robot Programming Pick and Place, Palletizing
12
Application Design experiments and oriented experiments Fabrication
of lettering and logo
181
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M608 MICROPROCESSORS AND MICRO CONTROLLERS LABORATORY
2 0 2 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To acquire basic knowledge about Microprocessors
To study the Architectures of 8, 16, 32-bit Microprocessors
To understand the concept of Assembly language and C language programming
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
(e) The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Identify the various types of microprocessors.
Enhancement of programming skills.
Computation of assembly language programs.
Interfacing with peripherals.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Internal Assessment
Preparation
Remember
Understand
Apply
Observation and Results
Analyze
Evaluate
Record
Mini-project
/
Model
Examination / Viva-voce
Total
Semester end Examination
10
15
25
25
10
10
50
50
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
Define microprocessor
.
List out various addressing modes of 8085 and 8086 microprocessors.
Recall classifications of 8086 instruction set.
Name the different types of memories used in microprocessor and Cold Fire processors.
Recall registers organization of 8085.
Recall the number and names of various peripherals of 8086 microprocessor.
Define T state, machine cycle and instruction cycle.
What are the difference between Compiler and Interpreter?
Name the three buses of a microprocessor.
Recall the register organization of 8086.
Recall the pins on the chip 8085 which can be grouped into 6 groups.
Recall the pins of 8086.
List the various arithmetic instructions of 8085.
Name the assembly directives of 8086.
Define maskable and non maskable interrupts.
Name various condition and non conditional branch instructions.
Define interrupt.
Recall various constituents in Interrupt vector table.
182
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
Explain the concepts of assembly language programming.
Discuss the flags of 8085 and their utility.
Distinguish memory mapped I/O devices and I/O mapped memory devices.
Discuss the function of instruction queue in 8086.
Explain the predefined interrupts of 8086.
Discuss the conditional and unconditional flags of 8086
State the significance of LOCK signal in 8086.
Explain Interrupt service routine of 8086.
Distinguish addressing modes of 805 and 8086.
Describe the process control instructions of microprocessor.
Explain various pin attributes of 8085
Distinguish the POP and PUSH, Wait and Halt instructions.
Explain ALIGN & ASSUME.
Discuss the need of debugging in ALP.
Discuss MACROS in 8086.
Explain various pin attributes of 8086
Recognize the formation of physical address
Differences between microprocessors and controllers.
Apply/Analyze/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
Apply timing diagram to calculate the time required to execute MOV A, B.
Use rotate instruction for multiplication operation.
Illustrate the timing states of SIM and RIM instructions.
Demonstrate the position SP after the pop instruction.
Illustrate the 2 K memory construction with flip flops.
Illustrate the block diagrams of microprocessors.
Apply the read and write cycles to any given instruction.
Illustrates various types of interrupts.
Demonstrate I/O read and I/O write cylices for a given instruction
Practice the conditional jump instructions of 8086.
Use various addressing modes a write program for addition of two numbers.
Multiply two given numbers without using MUL instruction.
Demonstrate the utility of external memory in microprocessors.
Illustrate various types of DMA transfer.
Use the processor to convert hex code to decimal code.
Illustrate the timing diagram for minimum and maximum modes of operation for 8086.
Demonstrate the memory read and memory write cycles for a given instruction.
Illustrate the timing diagram in minimum and maximum modes of operation.
Distinguish Clock generation, Reset generation & synchronization,
Test the wait state computation & generation, Ready synchronization.
Inspect interfacing of RAM and EPROM memories.
Distinguish the performance of 8085 and 8086 processors with respect to their instructions
Analyze the Modes of I/O data transfer.
Calculate the physical address from the segment address 6055H and offset address as 3000H.
How do we select minimum versus maximum modes.
Inspect PSW of 8085 and 8086.
Analyze NEAR and FAR Call.
Inspect the stack operations in 8086.
Distinguish NOP and HALT instructions
Inspect on rotate instruction.
Analyze various types of interrupts in 8085.
Distinguish between inter and intra segment jumps.
Evaluate the contents of BX by 4 using shift instructions.
Judge which arithmetic instruction should be used with carry.
Compare the addressing modes of 8085 with 8086.
Compare memory mapped and I/O mapped memories.
Judge the contents of carry and Auxiliary carry flags when carry occurs.
183
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
38. Assess the prerequisite for a conditional jump.
39. Evaluate LIFO, LILO, FIFO and FILO
40. Determine the memory address accessed by each of the following instructions in real mode
operations, if DS = 1000H ,SS = 2000H, BP = 1000H and DI = 0100H.
41. Compare DMA and eDMA in ColdFire.
Unit I
8085 CPU
8085 Architecture Instruction set Addressing modes Timing diagrams Assembly language
programming Counters Time Delays Interrupts Memory interfacing Interfacing, I/O devices
6 Hours
Unit II
Peripherals Interfacing
Interfacing Serial I/O (8251)- parallel I/O (8255) Keyboard and Display controller (8279)
ADC/DAC interfacing Inter Integrated Circuits interfacing (I2C Standard)- Bus: RS232C-RS485GPIB
6 Hours
Unit III
8086 CPU
Intel 8086 Internal Architecture 8086 Addressing modes- Instruction set- 8086 Assembly language
ProgrammingInterrupts.
6 Hours
Unit IV
8051 Microcontroller
8051 Micro Controller Hardware- I/O Pins, Ports And Circuits- External Memory Counters And
Timers-Serial Data I/O- Interrupts-Interfacing to External Memory And 8255.
6 Hours
Unit V
8051 Programming and Applications
8051 Instruction Set Addressing Modes Assembly Language Programming I/O Port
Programming -Timer And Counter Programming Serial Communication Interrupt Programming
8051 Interfacing: Lcd, Adc, Sensors, Stepper Motors, Keyboard And Dac.
6 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
3.
Ramesh S. Gaonkar, Microprocessor Architecture, Programming and application with 8085,
Penram International Publishing, New Delhi, 2000.
John Uffenbeck, The 80x86 Family, Design, Programming and Interfacing, Pearson Education,
New Delhi, 2002.
Mohammed Ali Mazidi and Janice Gillispie Mazidi, The 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded
Systems, Pearson Education Asia, New Delhi, 2003.
References
1.
2.
3.
A. K. Ray and K. M. Burchandi, Intel Microprocessors Architecture Programming and
Interfacing, McGraw Hill International Edition, New Delhi ,2000
Kenneth J. Ayala, The 8051 Microcontroller Architecture Programming and Application, Penram
International Publishers (India), New Delhi, 1996.
M. Rafi Quazzaman, Microprocessors Theory and Applications, Intel and Motorola, Prentice Hall
of India, New Delhi, 2003.
List of Experiments
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Programs for 8/16 bit Arithmetic operations (Using 8085).
Programs for Sorting and Searching (Using 8085, 8086).
Programs for String manipulation operations (Using 8086).
Programs for Digital clock and Stop watch (Using 8086).
Interfacing ADC and DAC.
Parallel Communication between two MP Kits using Mode 1 and Mode 2 of 8255.
184
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
7.
8.
9.
10.
Interfacing and Programming 8279, 8259, and 8253.
Serial Communication between two MP Kits using 8251.
Interfacing and Programming of Stepper Motor and DC Motor Speed control.
Programming using Arithmetic, Logical and Bit Manipulation instructions of
8051microcontroller.
11. Programming and verifying Timer, Interrupts and UART operations in 8031 microcontroller.
12. Communication between 8051 Microcontroller kit and PC.
Design oriented experiment
Application oriented experiment
Total: 30 + 30 Hours
Practical Schedule
Sl.
No.
1
Experiment
Hours
Programs for 8/16 bit Arithmetic operations (Using 8085).
Programs for Sorting and Searching (Using 8085, 8086).
Programs for String manipulation operations (Using 8086).
Programs for Digital clock and Stop watch (Using 8086).
Interfacing ADC and DAC.
Parallel Communication between two MP Kits using Mode 1
and Mode 2 of 8255.
Interfacing and Programming 8279, 8259, and 8253.
Serial Communication between two MP Kits using 8251.
Interfacing and Programming of Stepper Motor and DC Motor
Speed control.
Programming using Arithmetic, Logical and Bit Manipulation
instructions of 8051microcontroller.
Programming and verifying Timer, Interrupts and UART
operations in 8031 microcontroller.
9
10
11
3
3
3
12
Communication between 8051 Microcontroller kit and PC.
13
Design oriented experiment
14
Application oriented experiment
6
Total
45
185
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
011O701 ENGINEERING ECONOMICS
(Common to all branches)
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the basics of Micro and Macro Economics
To understand the methods by which Demand Forecasting, Cost Analysis, Pricing and Financial Accounting are
done in the Industry
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
a.
b.
g.
i.
k.
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects and thus
acquire the capability to applying them.
The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge, capability of analyzing and solving any concept or
problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students will be able to understand the working
concepts of thermal engineering.
Graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level placement in the
industry.
The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
Costing of products and services.
Market Analysis.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
2
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I
20
30
30
20
100
Test II1
20
30
30
20
100
Model
Examination1
20
30
30
20
100
Semester End
Examination
20
30
30
20
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Define Economics
Define Managerial Economics
What are the branches of Economics?
What are the two methodologies used for Investigation in Economics?
Name the other disciplines which are linked to Managerial Economics.
List the theories that explain the basic objectives of a firm.
What are the basic concepts in Decision making?
What are the types of decisions a manager is expected to make?
What are the techniques used in the process of decision making?
What is opportunity cost?
What is Demand?
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10 marks will be
calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
186
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
What are the types of Demand?
What are the variations in the nature of Demand?
State the law of Demand.
What are the factors determining Demand?
Define Elasticity of Demand.
State the different degrees of elasticity of Demand?
What are the factors determining Elasticity of Demand?
State the Law Of Diminishing Marginal Utility.
What is Consumer Equilibrium?
List the factors effecting Demand Forecasting.
What methods will you use for forecasting demand for a new product?
Define Cost.
What is a semi variable cost.
What are fixed costs?
Define Short Run and Long Run costs.
Define Optimum Size of a Firm.
Define Replacement Cost and Historic Cost.
What is a Monopoly?
What is an Oligopoly?
What is Price Discrimination?
What are the reasons for Price Discrimination?
What are the advantages of Price Discrimination?
Define Oligopoly in terms of market share.
Name the two types of Oligopoly.
What are the objectives of Pricing?
What are the two basic methods of Pricing?
What is Market Skimming?
What is sealed bid pricing?
Define Accounting.
What are the uses of accounting?
What is a Balance Sheet?
Definitions of key words used in Financial Statements.
What is inflation?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
Explain the nature and scope of Economics.
Differentiate between Macro and Micro economics
List and explain the focus areas of Managerial economics.
Give reasons why Mangers aim to Maximize Sales even at the cost of a lower profit.
Explain the steps in the decision making process.
Differentiate between Mechanistic and Analytical Decision making with xamples.
Explain Giffens Paradox.
Explain with examples, exceptions to the Law of Demand.
Explain the nature of Demand.
Differentiate between Extension and Increase in Demand.
What is the significance of Elasticity of Demand?
Differentiate between Point and Arc Elasticity of Demand.
What are the assumptions made when talking about the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility?
Explain the characteristics of the Indifference Curve with examples.
Explain the concepts of consumers equilibrium and consumers surplus with examples.
Can Demand Forecasting principles be applied to Services? Substantiate your answer with an example.
What is the difference between Accounting Cost and Economic Cost? Explain with an example.
Match the following type of question between Cost Concepts and their Basis of Distinction
Why is a study of Cost-Output Relationship necessary for a good Manager?
How is Incremental cost different from Sunk Cost?
187
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
Differentiate between Monopoly and Monopolistic Competition.
Explain the concept of a Perfect Market and its features.
Explain Total Revenue, Average Revenue and Marginal Revenue.
Distinguish between Cost and Price.
Explain with an appropriate diagram, the mechanism of pricing in a Perfectly Competitive Market.
Explain the role of Time in price determination.
Under what conditions can a firm charge different prices for the same products?
What are the characteristic features of an oligopoly industry ?
What causes Oligopoly?
Why does a firm need to have a Pricing Policy?
Explain the types and features of Cost Based Pricing.
Explain the types and features of Demand Based Pricing.
Explain the types and features of Strategy Based Pricing.
Under what conditions does a company go in for Cross Subsidization pricing?
Explain the Business Entity concept.
What are the advantages of Double-entry Book-keeping?
What is the role of the Central bank in controlling inflation?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Compare the merits and demerits of the Deductive Method and the Inductive Method of Investigation.
Explain decisions based on the degree of certainty of the outcome with examples.
Problems involving Marginal and Incremental Costs.
Problems concerning Elasticity of Demand.
Problems using statistical methods for Demand Forecasting.
Problem Calculate and plot Average Variable Cost, Average Total Cost, and Marginal Cost and find the
optimal production volume.
7. Give examples of products falling under the various kinds of Competition, and the reasons they are able to
survive in the market.
8. Give six examples of products that fall under Monopolistic Competitive pricing.
9. Give six examples of products that fall under Oligopolistic pricing.
10. Pick any six Consumer Items and based on your knowledge of the markets, explain the pricing method that you
think is most likely to have been followed for each of these items.
11. Compare the types of information that one can derive from a Balance Sheet and a P&L Statement.
Analyze/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
The per-capita income of farmers in the country has to be raised by 20% this year to prevent their migration to
cities. Analyze this statement from the point of view of Positive and Normative Economics.
Decision making improves with age and experience. Discuss.
Do a survey of the automotive (only cars) industry and analyze the reasons and timing for discounts offered
from the point of view of elasticity of demand.
What are the methods you would adopt to forecast demand for an industrial product? Assuming that the actual
demand versus forecast is very high, what would the most likely reason be for failure of the forecast?
Most of the cost concepts are overlapping and repetitive. Yes or No? Substantiate your answer with reasons.
How would you modify a sealed bid pricing system to take care of different technical approaches by different
bidders for a project for which bids are called for, given that the cost varies depending on the technical
approach?
What are the steps you would take to control inflation?
188
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit I
Introduction
Introduction to Economics, Kinds of Economic Systems, Production Possibility Frontier, Opportunity Cost,
Objective of Organizations, Kinds of Organizations, Business Decision Making,
Legal rights and responsibilities of types of Organizations.
8 Hours
Unit II
Demand and Supply
Functions of Demand & Supply, Law of Demand and Supply, Elasticity of Demand, Demand Forecasting Methods,
Price Equilibrium.
Role of logistics in managing supply and demand.
8 Hours
Unit III
Production and Cost
Production Function, Returns to Scale, Economies & Diseconomies of scale, Fixed Cost, Variable Cost, Average
Costs, Cost Curves, Break Even point, Law of diminishing Marginal Utility.
Costing of a product during the stages of its life cycle
10 Hours
Unit IV
Pricing & Market Structure
Components of Pricing, Methods of Pricing, Return on Investment, Payback Period, Market Structure and Pricing,
Perfect Competition, Monopoly, Oligopoly, Monopolistic, Non price competition, E-commerce.
The secure payment process in e-commerce.
12 Hours
Unit V
Introduction to Macro Economics & Financial Accounting,
National Income GDP, Per Capita Income, Inflation, Stagflation, Deflation, Business Cycle, Stabilization
Policies, Direct Taxes, Indirect Taxes, Balance of Payment. Accounting - Terminology, Book Keeping, P&L,
Balance Sheet.
Role of Central Excise and Customs
12 Hours
Total: 50 Hours
Textbook
1.
A. Ramachandra Aryasri and V V Ramana Murthy, Engineering Economics and Financial Accounting, Tata
McGraw Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi, 2006.
References
1.
2.
3.
V. L. Samuel Paul and G S Gupta Managerial Economics Concepts and Cases Tata McGraw Hill Publishing
Company Limited , New Delhi, 1981.
S N Maheswari, Financial and Management Accounting, Sultan Chand.
R Kesavan, C Elanchezhian and T Sunder Selwyn, Engineering Economics and Financial Accounting Laxmi
Publication (P) Ltd , New Delhi, 2005.
189
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M702 MECHATRONICS
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To provide a basic background to mechatronics and link to more specialized skills
To develop the mix of skills in mechanical engineering, electronics and computing
To familiarize about sensors and control system used in mechatronics
To develop confidence and competence in designing mechatronics systems
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Identifying sensors used for various applications.
Interpret system drawings and design simple systems for sequential control systems involving valves and
cylinders.
Devising the mathematical models for mechanical, electrical and thermal systems.
Predicting the behavior of systems with proportional, integral, derivative, proportional plus derivative and PID
control.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
35
35
30
100
30
40
30
100
30
40
30
100
30
40
30
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
3
What are the basic elements of a measurement system?
Define sensor.
Define the terms accuracy & precision.
What is hysteresis?
State the dynamic characteristics of simplified measuring system.
Define mechatronics.
What is meant by cylinder sequencing?
List the factors to be considered when selecting the belt drives.
What is MOSFET?
State the objectives of DCVs.
What are the factors to be considered for selecting solenoids?
What is the purpose of Air receiver?
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10 marks will be
calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
190
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
What are the types of field effect transistor?
List down the features of JFET.
State the function of Bipolar Transistor.
List down the features of synchronous motor.
What is a stepper motor?
What is meant by adaptive control?
What is damper?
Define electromechanical system.
Define thermal capacitance.
What is meant by program scan?
List down the different types of timers?
What are shift registers?
State two methods of Input / Output processing.
List down PLC programming methods.
What are counters?
What is a Latch circuit?
What are the factors to be considered for selecting PLC?
Where the shift registers are used?
What is an engine management? List out the various sensors involved in engine management system?
What are the uses of sensors? List the various sensors contained in automatic camera?
What are the various movements of robots?
Mention the stages in designing a mechatronic system.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
State the difference between primary and secondary transducer.
How the mechatronics used in industries?
State, in general, the principle of operation of transducers and highlight their difference with sensors.
Distinguish between accuracy and sensitivity of a transducer.
Compare the touch & proximity sensor.
Discuss how velocity is measured by using electromagnetic transducers.
Differentiate inductive sensors and capacitive sensors.
What are the configurations in operating stepper motor?
Why sequential valves are necessary in pneumatic system?
Distinguish between pressure relief valve and pressure reducing valve.
Where the timing belts are used?
How do you compare the operation of brushless DC motor with the operation of a stepper motor?
Why brushless D.C motor has been designed?
What is the difference between field- controlled and armature-controlled motors?
Why differential controllers are combined with other modes of controllers for practical application?
Differentiate between DIAC and TRIAC.
Why derivative controller is never used alone?
Compare the PLC and a general-purpose computer.
Distinguish between traditional design approach and mechatronics approach.
How does a simple weighing scale work using traditional mechanical system?
How a traditional design of temperature control of domestic central heating system is improved by
mechatronic design?
191
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Apply / Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Identify and explain the various elements that might be present in a control system involving a thermostatically
controlled electric heater.
Compare and contrast the control system for the domestic central heating system involving a bimetallic
thermostat and that involving a microprocessor.
You are offered a choice of an incremental shaft encoder or an absolute shaft encoder for the measurement of an
angular displacement. What is the principal difference between the results that can be obtained by these
methods?
Suggest a sensor that could be used, as part of a control system, to determine the difference in levels
between liquids in two containers. The output is to provide an electrical signal for the control system.
Derive differential equations for a permanent magnet d.c. motor.
Derive an expression for a Hydraulic mechanical systems.
Devise a timing circuit that will switch an output ON for 1 s then OFF for 20 s, then ON for 1 s, then OFF for
20 s and so on.
Device a circuit by using Ladder logic format and Mnemonics that could be used with a domestic Washing
machine to switch on pump to pump water for 100sec into the machine, then switch off and switch on the heater
for 50sec to heat the water. The heater is then switched off and another pump is to empty the water from the
machine for 100sec.
Case studies
o Engine Management System
o Automatic Camera
o Automatic Car park system
Unit I
Mechatronics, Sensors and Transducers
Introduction to Mechatronics Systems Measurement Monitoring Systems Automation Control Systems
Microprocessor based Controllers. Sensors and Transducers Performance Terminology Sensors for
Displacement, Position and Proximity; Velocity, Motion, Force, Fluid Pressure, Liquid Flow, Liquid Level,
Temperature, Light Sensors Selection of Sensors.
Smart sensors
9 Hours
Unit II
Actuation Systems
Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems Directional Control Valves Rotary
Actuators. Mechanical Actuation
Systems Cams Gear Trains Ratchet and pawl Belt and Chain Drives Bearings. Electrical Actuation
Systems Mechanical Switches Solid State Switches Solenoids D.C Motors A.C Motors Stepper Motors
Servomotors.
Hybrid motor
9 Hours
Unit III
System Models and Controllers
Building blocks of Mechanical, Electrical, Fluid and Thermal Systems, Rotational Translational Systems,
Electromechanical Systems Hydraulic Mechanical Systems. Continuous and discrete process Controllers
Control Mode Two Step mode Proportional Mode Derivative Mode Integral Mode PID Controllers
Digital Controllers Velocity Control Adaptive Control Digital Logic Control Micro Processors Control.
Advanced Controllers.
9 Hours
192
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit IV
Programmable Logic Controllers
Programmable Logic Controllers Basic Structure Input / Output Processing Programming Mnemonics
Timers, Internal relays and counters Shift Registers Master and Jump Controls Data Handling Analogue
Input / Output Selection of PLC.
PLC in Mechatronics.
9 Hours
Unit V
Design of Mechatronics System
Stages in designing Mechatronics Systems Traditional and Mechatronic Design - Possible Design Solutions Case
Studies of Mechatronics Systems, Automatic washing Machine Automatic Camera - Pick and place robot
Automatic Car Park Systems Engine Management Systems.
Fault finding
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
W. Bolton, Mechatronics: Electronic control systems in Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Pearson
Education, New Delhi,2008.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
David G. Alciature and Michael B. Histand, Introduction to Mechatronics and Measurement Systems, Tata
McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi,2007.
Nitaigour Premchand Mahalik, Mechatronics : Principles, Concepts and Applications, Tata McGraw Hill
Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi,2008
M. D. Singh, and J. G. Joshi, Mechatronics, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi,2009.
K. P. Ramachandran, G. K. Vijayaraghavan, and M. S. Bala-Sundram, Mechatronics : Integrated Mechanical
Electronic Systems, Wiley India Pvt. Ltd.,New Delhi 2008.
Newton C. Braga, Mechatronic Source Book, Delmar Cengage Learning, 2009.
193
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M703 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To impart basic knowledge in the area of finite element method focusing on design of mechanical components
To make one to ensure the design by FEM is correct and can go for real time testing
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(d) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of engineering design. Understanding the concept
generation, design optimization and evaluation. Knowing the fundamentals of intellectual property rights.
Students will be able to effectively design various engineering components and make process plan for the
production.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
Understand the fundamental philosophy of finite element analysis and enable them to carry out a
multidisciplinary projects.
Convert a physical model into a finite element model and applying this to simple structural and heat transfer
problem.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
30
30
30
10
100
20
30
30
20
100
20
20
40
20
100
20
20
40
20
100
Remember
1.
What is the basic concept of finite element method?
2.
List the applications of FEM.
3.
What are the types of analysis that can be performed in fem?
4.
What is weighted residual method?
5.
What are the different types of boundary conditions?
6.
What is an Eigen value problem?
7.
What are the methods for solving equilibrium problem?
8.
What are the types of analysis that can be performed in FEM?
9.
State the principle of minimum potential energy.
10. What is meant by Discretisation of the domain?
11. What are the properties of stiffness matrix?
12. What are the methods for solving propagation problem?
13. What are the three major categories of problem in FEM?
14. What is natural coordinate system?
15. What is global Coordinate system?
_______________________________________________________________________________
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10 marks will be
calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
194
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
What is local Coordinate system?
What are the advantages of natural Coordinate system
What is aspect ratio?
Draw one 2 D element and one 3-D element and name it.
What is stiffness matrix?
Define CST element with diagram.
Define LST element with diagram.
What is a truss element?
Define beam element,
What is meant by plane stress?
What is meant by plane strain?
What is field variable?
Define simplex element.
What is meant by Multiplex elements?
What are the advantages of polynomial type of interpolation function?
Write down the finite element equation for one dimensional heat conduction.
What are the three convergence requirement that is to be satisfied for attaining an exact solution?
What are higher order elements?
Define serendipity element.
Write down the finite element equation for two dimensional heat transfer problem.
Write down the finite element equation for one dimensional heat conduction.
Define shape function.
What are the types of error in FEA?
What are the types of mesh refinement?
What are the types of non linearity?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
Name any 4 commercial FEA packages
What is meant by CAD and CAE?
What is the difference between Propagation and Steady state problem?
Compare FEM with other methods
Differentiate between static and dynamic analysis
How do you make a node numbering scheme for a fem model?
What do you understand by element connectivity?
How do you built a finite element model?
Differentiate Beam element and Truss element
Differentiate between plane stress and plane strain?
Differentiate between Multiplex and Complex element.
For what the Numerical integration is used in FEM?
Is beam element an isoparametric element? Give reason for your answer.
Differentiate between Sub and Super parametric element with diagram.
How will you select the order of the polynomial
How will you draw a Pascals triangle and tetrahedron for arranging 2-D and 3-D polynomial
Function.
17. Differentiate h-method and p-method of mesh refinement?
18. In Steady state and Propagation there exist ______solution but in Eigen value problem there is no _________
solution.
19. If the interpolation polynomial is of the order two or more
the element is known as
a____________________element
195
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Apply/Evaluate
1.
2.
Elucidate the step by step procedure for solving a static structural problem in FEM for the axially loaded
stepped bar.
Find the approximate deflection of a simply supported beam under a uniformly distributed load p as shown
below using Rayleigh-Ritz method.
p per unit length
x
3.
4.
5.
When you will apply the Pascals triangle and tetrahedron and for what?
In a CST element the nodal coordinates are given by (1,1) (4,1) and (1,4), the temperature distribution has been
computed as T1 is 100C, T2 is 60C and T3 is 50C respectively. Calculate the temperature at a point P.
Whose coordinates are given by (2,3).
Calculate the displacement at a point P. whose co-ordinates are given by (2,3), if the nodal displacement of a
triangular element are given by
Ui = 3mm
Uj = 4mm
Uk = 2mm
Vi = 2mm
Vj = 3mm
Vk = 4mm
and the nodal co-ordinates
are given
by (1,1) (4,1) and (1,5)
6.
Calculate the element stresses and strain for the element shown below
(15,10)
(15,5)
(10,7.5)
The nodal displacements are
U1 = 2.0mm,
V 1 = 1.0mm,
U2 =0.5mm,
V2 = 0.0mm,
U3 = 3.0mm,
V3 = 1.0mm.
Take E = 2.1 x105 N/mm2 and = 0.25. Assume plane stress condition
7.
Find the shape function at a point P (6,9) located inside a triangular element and its coordinates are
x1 = 4mm, y1 = 8mm,
x2 =10mm, y2 = 5mm,
x3 = 8mm, y3 = 12mm.
196
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Analyze/Evaluate
1.
Find the stresses distribution in the tapered bar shown in fig. below using two finite element under an axial
load of P=10N.Cross section areas at root = 200mm2, at the end = 100mm2 and Youngs modulus
E = 2x105 N/mm2.
2.
For the two bar truss shown in fig. below determine the displacement at node 1 and stress in element 2.
Take A= 200mm2E = 70x 103 N/mm2
3.
Find the temperature distribution in the stepped fin shown in fig. below using two finite element.
4.
Evaluate the integral I = (2+x+x2 ) dx and compare with exact solution.
-1
197
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit I
Introduction-Calculus of Variations
Basic concepts of Finite Element Method(FEM) - step by step procedure. Stresses and equilibrium boundary
conditions. strain Vs displacement relations potential energy and equilibrium - general procedure of FEM-solution
of equilibrium problems- Gaussian elimination method- Rayleigh Ritz method- Galerkin method. FEA applications
Comparison of FEM with finite difference method and finite volume method
9 Hours
Unit II
One-Dimensional Problems
Discretisation of domain-element shapes, types, size, location & numbers. Coordinate types, 1 D bar element shape function using natural coordinates and generalized coordinates, stiffness matrix of a 1-D bar element, finite
element formulation of stiffness matrix, load vector and assembly of global equations example problems.
Stiffness matrix and finite element equation for a two noded Truss element example problems.
Types of Non linearity
9Hours
Unit III
Two-Dimensional Problems
Finite element modeling shape function for the Constant Strain Triangular element using natural coordinates and
generalized coordinates , strain displacement matrix of CST element, stress- strain relationship matrix for 2-D
element under plane stress and plane strain condition example problems.
Linear Strain Triangular and Quadratic Strain Triangular elements.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Heat Transfer
Basic equations of heat transfer - Shape function of 1-D heat conduction, stiffness matrix for 1-D heat conduction,
with free end convection, with internal heat generation- assembly of global equations and load vector, Finite element
formulation-Example problems. Higher order elements. Selection of the order of the polynomial, Convergence
requirements, Linear, simplex, complex, Multiplex
Serendipity and Degenerate element
9 Hours
Unit V
Isoparametric Element Formulation
Errors in FEA, Mesh refinement methods, Iso , Sub & Super parametric element, shape functions for a 2-D four
noded and eight noded Isoparametric rectangular element using natural coordinate system example problems.
Gaussian quadrature example problems.
Grid sensitivity test
9 Hours
Total 45 + 15 Hours
Textbook
1.
Chennakesava R. Alavala Finite Element Methods: Basic Concepts and Applications,
Prentice Hall of India Learning, New Delhi,2008
References
1.
2.
3.
S. S. Rao, Finite Element Method in Engineering, Elsevier India, 2005
David V. Hutton, Fundamentals of Finite Element Analysis, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd.,
New Delhi,2005.
Robert D. Cook, s. David , Malkucs Michael E. Plesha, Concepts and Applications of Finite Element Analysis,
Wiley, New Delhi,2007.
198
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
4.
5.
T. R. Chandrupatla and A. D. Belegundu, Introduction to Finite Elements Engineering, Pearson Education,
New Delhi,2002,
S. S. Bhavikati, Finite Element Analysis, New Age International Publishers, 2005
199
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M704 POWER PLANT ENGINEERING
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To expose the fundamental power generation principles
To use this principle for the engineering applications of power generation
To integrate the basic concepts into various thermal applications like gas turbines, boilers, steam turbines,
diesel engines, nuclear, hydel power plant and other power plant applications
PROGRAM OUTCOME
(b) The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge, capability of analyzing and solving any concept or
problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students will be able to understand the working
concepts of thermal engineering.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
Design of boilers and various equipments in steam power plant.
To occur knowledge in Diesel and gas turbine components selection.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I*
Test II*
35
35
30
100
35
35
30
100
Model
Examinations*
35
35
30
100
Semester End
Examination
35
35
30
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
4
List out the factors to be considered in the selection of power plant.
What is meant by super critical boilers?
Mention the advantages of modern high pressure boilers.
State the advantages of regenerative feed heating in steam power cycle.
What is meant by run- off river plant?
What is the function of surge tank and draft tube in hydroelectric power plant?
Mention the application for diesel engine power plant.
What are the factors to be considered for the selection of diesel engine?
Name some of the mills used for pulverizing the fuel.
Mention the different types of burners used to burn pulverized fuel.
State the pollution caused by the power plant.
Name the different types of cooling towers available
State the advantages of pulverized fuel firing system
Mention the different firing system available
Name the various methods of ash handling.
Name the various draught systems
What is the cause of smoke?
Name the different types of chimney used.
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10 marks will be
calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
200
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
Define the term demand factor and diversity factor.
What is meant by power plant economics? What are the fixed and operating costs?
Define - nuclear chain reaction.
Name some of the fissionable and fertile materials.
State the functions of control rod, moderator, coolant and reflector.
Mention the application of MHD power plant.
Mention some of the shielding material for reactors.
What is meant by nuclear binding energy?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
Compare the diesel engine power plant with steam power plant.
Compare base load plant and peak load plant.
Compare the gas turbine power plant with steam power plant.
Compare the performance of the combined cycle operation with the other cycles.
Compare the forced draught fan and induced draught fan.
Differentiate hand firing and mechanized firing of fuel.
Compare the performance of bag house collector and cyclone separator.
Name the methods used for calculating the depreciation of the power plant.
Compare the Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion process.
Explain load factor, load curve, load duration curve.
Describe plant capacity factor, utilization factor.
What do mean by connected load and maximum demand?
How the reactors are classified?
Compare the advantages of pressurized water reactor with boiling water reactor.
Classify the different types of MHD.
Apply
1.
A base load plant power station and standby power station share a common load as follows:
Base load station annual output = 200 x 103 MWh
Base load station capacity = 48MW
Maximum demand on basew load station =45 MW
Standby station capacity = 25MW
Standby station annual output = 200 x 103MWh
Maximum demand on standby station = 15MW
Determine the following for the both power stations: a) Load factor, b) Capacity factor.
2.
The peak load on a thermal power plant is 75MW. The loads having maximum demands of 35MW, 20MW,
15MW and 18MW are connected to the power plant. The capacity of the power plant is 90MW and the annual
load factor is 0.53. Calculate
a) The average load on the power plant
b) The energy supplied per year
c) The demand factor
d) The diversity factor.
3.
It is required to supply a load with a maximum demand of 500MW and load factor of 0.74. Choice is to be
made from a steam power plant, a nuclear power plant and hydro electric power plant. Calculate the overall cost
per kWh in case of each scheme given below
:
201
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
S.No
Cost
1
2
3
4
5
Capital cost / MW installed
Interest
Depreciation
Operating cost / kWh
Transmission & Distribution
cost / kWh
Steam power
plant
Nuclear power
plant
Hydro electric
power plant
Rs 3.8 crore
5%
6%
50paise
Rs 5.2crore
6%
4%
30paise
6 crore
5%
5%
15paise
2paise
2.5paise
4paise
Unit I
Introduction to Power Plants and Boilers
Layout of Steam, Components, Selection - Steam Boilers and Cycles High Pressure and Super Critical Boilers
Fluidized Bed Boilers. Combined Power Cycles - Load Duration Curves Comparison and Selection.
Efficiency calculation methods for Boilers
9 Hours
Unit II
Steam Power Plant
Fuel and Ash Handling, Combustion Equipment for burning coal, Mechanical Stokers, Pulveriser, Electrostatic
Precipitator, Mechanical Collectors, Draught different types, Surface Condenser Types, Cooling Towers, Pollution
controls
Pollution control Methods
9 Hours
Unit III
Nuclear and Hydel Power Plants
Nuclear Energy Fission, Fusion Reaction, Layout - Types of Reactors, pressurized water reactor, Boiling Water
Reactor, Waste Disposal and safety. Hydel Power Plant Layout - Essential Elements, pumped storage - Selection
of Turbines, Governing of Turbines
Micro Hydel developments.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Diesel and Gas Turbine Power Plants
Layout and types of Diesel Plant, Components, Selection of Engine Type, applications. Gas Turbine Power Plant
Layout - Fuels - Gas Turbine Material Open and Closed Cycles Reheating Regeneration and Intercooling
Combined Cycle.
9 Hours
Unit V
Other Power Plants and Economics of Power Plants
Geo thermal OTEC Tidal - Solar thermal Wind energy - Wind turbines- MHD Plants. Cost of Electric Energy
Fixed and operating Costs Economics of load sharing,
comparison of economics of various power plants.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
S. C. Arora and S. Domkundwar, A course in Power Plant Engineering, Dhanpatrai & Sons, New Delhi, 2008.
202
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
M. M. EI-Wakil, Power Plant Technology, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi,1985.
P. K. Nag, Power plant Engineering, Tata McGraw Hill Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi,2007.
G. R. Nagpal, Power Plant Engineering, Khanna Publishers, New Delhi,2002.
G. D. Rai, Introduction to Power Plant Technology, Khanna Publishers, New Delhi,1995.
R. K. Rajput, Power Plant Engineering, Laxmi Publications, New Delhi,1995.
203
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M707 COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING LABORATORY
0 0 3 1.5
OBJECTIVES
To understand the types of element used, type of analysis done, interpretation of results, method of solving and
analyzing a given problem
To have better knowledge in finite element analysis software , applied to structural and heat transfer
components at various loading conditions
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(d) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of engineering design. Understanding the concept
generation, design optimization and evaluation. Knowing the fundamentals of intellectual property rights.
Students will be able to effectively design various engineering components and make process plan for the
production.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
Able to Select the method, meshing, analysis and optimize the given problem for structural and thermal
applications.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Preparation
Remember
Understand
Apply
Observation and Results
Analyze
Evaluate
Record
Mini-Project/Model
Examination/Viva-Voce
Total
Internal Assessment
Semester End Examination
10
15
15
20
10
15
15
50
50
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
What are the types of co-ordinate systems in 2 dimension drawing?
What are the types of co-ordinate systems in 3 D / GUI / goemetric modeling?
What are the types of goemetric modeling?
Name any five 2D packages.
Name any ten 3D packages.
Name any ten CAM packages.
Name any ten finite element analysis packages.
What is 2 D?
What are the types of non linearity?
What are three general modules of FEA software?
What are the methods of analysis?
What is an exact solution?
204
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
58.
59.
60.
61.
62.
63.
64.
65.
66.
67.
68.
What is an approximate solution?
What is meant by discretisation?
What is plane stress?
What is plane strain?
What is meant by CAD and CAE?
What is aspect ratio?
What is stiffness matrix?
What is an axisymmetric problem?
What is bottom up modeling?
What is top down modeling?
What is structural analysis?
What is thermal analysis?
What is node?
What is an element?
What is general post processor?
What is nodal solution?
What is pre processor?
What is pro processor?
What type of options we use in preferences?
What is h-method and p-method of mesh refinement?
What is DOF?
What is steady state analysis?
What is unsteady state analysis?
What are the types of Thermal analysis?
What are the types of structural analysis?
What are the types of elements used in ANSYS?
What are the types of loads?
What is truss?
What are the theories of failure?
What is von mises stress?
What is material non linearity?
What is geometric non linearity?
What is boundary non linearity?
What are the types of coupled field analysis?
What are the types of meshing involved in ANSYS?
Name any three thermal elements in ANSYS?
What is transient thermal analysis?
Define modal analysis.
APDL is an acronym for _______________________
What is a quadratic element?
What is a real constant?
Expand CFD.
Name few applications of FEA.
What is an element solution?
What are higher order elements?
Define beam element?
Define Truss element?
What is r- refinement method?
What are the numerical errors? Name them?
Define band width?
What is load step in ANSYS?
What are the steps involved in pre processor?
What are the steps involved in pro processor or solution?
What are the steps involved in post processor?
What all are the ways that a result can be plotted?
What is various symmetry encountered in practice?
205
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
69.
70.
71.
72.
73.
74.
Name the solver methods used in ANSYS to solve non linear problem.
What is error estimation?
What are basic primitives? Name any ten.
What is meant by screen coordinate system?
Nonlinear structural behavior arises from a number of causes, name them.
In What way Boolean operations are useful.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
What is the difference between FDM and FEM?
How do you identify data loss in ANSYS?
Differentiate between material and geometric non-linearity.
Why the grid sensitivity test is made in FEA?
When you will go for coupled field analysis?
What is the difference between animation and modeling?
What is the difference between structural analysis & thermal analysis?
What is the difference between node & element?
Differentiate between h-method and p-method of mesh refinement?
What is the difference between static and dynamic analysis?
What is the difference between global/ world/ model coordinate system and working/user coordinate system?
How to apply loads in thermal analysis?
How to apply loads in structural analysis?
How to create a node?
How to create an element?
Is it possible to apply load on key point and solve?
How will you print the ansys display?
How will you decide on which element to be meshed in ANSYS?
How do you animate a result and capture it?
How will you decide on the solution you obtain is right?
Apply / Analyze / Evaluate
1.
Determine the maximum deformation that occur when a truss is loaded as shown below. The truss is fully
constrained at the one end; while the other end is constrained in y-direction. Load of 150 N act at each point as
shown in sketch. The truss is made of A36 steel with a Youngs modulus of 2e5 and Poissons ratio of 0.33.
Take section of the link as 10 x 30 mm.
206
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
2.
Determine the maximum deformation, shear force and bending moment that occur when a simply supported
beam of 100 x 5 x 5 mm is used. The beam with a point load of 100N is acting downward at mid point of the
span. Take Youngs modulus as 2E5 N/ mm2 and Poissons ratio as 0.3.
Determine the mode shapes and frequencies of a
steel fixed beam of circular section having 100 x 8 mm.
Take Youngs modulus as 183 GPa Poissons ratio as 0.25 and density of 7750 kg/m3
Using ANSYS find out the temperature distribution of a rectangular fin when the heat transfer is steady and
convective. The fin size is 10 x 2 x 1 m. A temperature of 5000 C is admitted on the left side of the fin, while
the remaining three sides are subject to convection with film coefficient of 10 W/m2 0C at 800C and the
conductivity of the fin material is 80 W/m 0C
3.
4.
5.
Find out the maximum deformation that occurs in a pressure vessel with a thickness of 25mm as shown below.
The vessel is subjected to a pressure of 20 bar at the inner side of the walls. Take Youngs modulus as 20e4 and
Poissons ratio of 0.3.
All dimesions in mm
6.
Using ANSYS find out the temperature distribution of a 3 D circular fin when the heat transfer is steady and
convective.. A temperature of 150 0 C is admitted on the left surface of the fin, while the remaining surfaces are
subject to convection.
207
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit I
Introduction to FEA Software
Basics of FEA, software available for FEA, Geometric modeling co-ordinate systems, types of elements, preferences
available, types of problem, pre processor, pro processor, post processor.
1hour
Unit II
Geometric Modeling
Creation of keypoints,lines,areas and volumes. Modeling using basic primitives, Types of modeling top down and
bottom up, Modeling of 2D components & Modeling of 3D components. Operations Boolean addition,
subtraction, division, extrude. Creation, edition and deletion of entities.
5 hours
Unit III
Meshing
Choosing the element type, assigning - real constants, material properties, size of element or division of element,
Free meshing of 2D & 3D components, Mapped meshing of 2D & 3D components. Optimizing element size.
5 hours
Unit IV
Pro Processor and Post Processor
Choosing the type of analysis, constraining the object, loading on node, line, area, volume and distribution of
loading and Solving of the problem.
Reading of results, Listing the results, Plotting of results stress, deformation, temperature, vectors etc., animation
of results. Saving results and printing. Importing and exporting of files.
1 hour
List of Experiments
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Analysis of Trusses
Stress analysis of a plate with a circular hole.
Stress analysis of Rectangular L bracket
Static analysis of simple Mechanical elements.
Stress analysis of beams (Cantilever, Simply supported, fixed end
Analysis of a composite system
Conduction and Convection heat transfer analysis of a 2D component
Convective heat transfer analysis of a 3D component
Modal analysis of beams (Cantilever, Simply supported, Fixed ends)
Dynamic analysis of a structure
Coupled field analysis
Design experiment
Application Oriented experiment
Total: 45 Hours
208
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Practical Schedule
S. No.
Experiment
Hours
Analysis of Trusses
Stress analysis of a plate with a circular hole.
Stress analysis of Rectangular L bracket
Static analysis of simple Mechanical elements.
Stress analysis of beams (Cantilever, Simply supported, fixed
ends)
Analysis of a composite system
Conduction and Convection heat transfer analysis of a 2D
component
Convective heat transfer analysis of a 3D component
Modal analysis of beams (Cantilever, Simply supported, Fixed
ends)
10
Dynamic analysis of a structure
11
Coupled field analysis
12
Design experiment
13
Application oriented experiment
209
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M708 MECHATRONICS LABORATORY
0 0 3 1.5
OBJECTIVES
To understand the concepts and applications of pneumatic / electro - pneumatic based automation system for
industries
To develop the Capability of design and implementation of pneumatic / electro - pneumatic circuits for
industrial automation
To learn the virtual instrumentation software and its applications for automated measurement / monitoring
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for
entry-level placement in
both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Identifying various methods to create automation.
Designing simple circuits systems for sequential control systems involving valves and cylinders.
Monitoring and controlling of temperature, pressure, flow, level by using virtual instrumentation.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Internal Assessment
Preparation
Remember
Understand
Apply
Observation and Results
Analyze
Evaluate
Record
Mini-Project/Model
Examination/Viva-Voce
Total
10
15
15
20
10
15
15
50
50
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
Semester End Examination
What is air receiver?
What is a FRL unit?
Define actuator.
What are the types of actuator?
What is semi rotary actuator?
What are the different types of control valves?
What is pneumatic direction control valve?
State the use of Time Delay Valves.
What is a Quick exhaust valve?
What is meant by sequencing circuit?
What are the conditions for the two cylinders to be synchronized?
List the factors to be considered while designing a fluid power circuit.
Sate the purpose of regenerative circuit.
210
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
What is automatic sequencing circuit?
Define PLC.
What is ladder programming?
State the function of a LATCH circuit.
What is an up counter?
What is meant by on-delay timer?
What is meant by off-delay timer?
List the function of counter.
What is a system? Give an example.
What is a measurement system?
List the two basic forms of the control system.
State the purpose of a sensor.
Define Relay.
State the use of DAQ.
What is meant by front panel?
What is meant by PID?
List the different types of temperature sensors.
What is meant by stepper motor?
State the function of encoder.
What is level sensor?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
Compare hydraulic and pneumatic circuit with respect to their characteristics.
What are the reasons for pressure drop in pneumatic lines?
Why pneumatic systems are not used for heavy application?
How the cylinder velocity is controlled?
How the cylinder position is controlled?
What is the need of lubricator unit in the pneumatic system?
Draw the Meter-in circuit.
What is the effect of pneumatic circuit using quick exhaust valve?
Why are mufflers used in pneumatic system?
Differentiate between single acting and double acting cylinders.
Compare open loop control system and closed loop control system.
Why differential controllers are combined with other modes of controllers for practical application?
Apply/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Verify and test the automatic sequence of Double acting cylinder using Fluidsim software and Pneumatic
Trainer kit.
Using Fluidsim verify and test the simulation of the A+B+C+A-B-CWrite a PLC program for the automatic forward and reverse stroke of a double acting cylinder.
Using Fluidsim software verify and test the simulation of the following stroke of the cylinder A, B and C. A + ,
B +, A --, B -- , A + , B +, A --, B -- C + , C
Write a Lab VIEW program to interface with the DIO line to the control the pneumatic cylinder.
Write a Lab View program for maintaining the temperature of air to 30C using DAQ interface module.
Write a Lab View program for maintaining the pressure of the vessel to 50 bar using DAQ interface module.
Write a Lab View program for maintaining the flow of the liquid to 25 m3/s using DAQ interface module.
Write a Lab View program for maintaining the level of the liquid in a tank to 20 cm using DAQ interface
module.
211
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
List of Experiments
Standards to be reffered
ANSI Y32.10 Graphic symbols
BS ISO 1219:1995 for electrical circuit diagrams
1.
Design and testing of fluid power circuits to control
(i) Velocity (ii) direction and (iii) force of single and double acting actuators
2. Design of circuits with logic sequence using Electro pneumatic trainer kits.
3. Simulation of basic Hydraulic, Pneumatic and Electric circuits using software.
4. Circuits with multiple cylinder sequences in Electro pneumatic using PLC.
5. PID controller interfacing.
6. Stepper motor interfacing using Lab VIEW
7. Modeling and analysis of basic electrical, hydraulic and pneumatic systems and temperature.
8. Fluid level, flow control using Lab VIEW / PLC.
9. Fluid pressure control using Lab VIEW / PLC.
10. Fluid temperature control using Lab VIEW / PLC.
Design experiment
Application oriented experiment
Total: 45 Hours
Practical Schedule
Sl. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Experiment
Introduction about laboratory
Design and testing of fluid power circuits to control
(i) Velocity (ii) direction and (iii) force of single and double
acting actuators
Design of circuits with logic sequence using Electro pneumatic
trainer kits
Simulation of basic Hydraulic, Pneumatic and Electric circuits
using software
Circuits with multiple cylinder sequences in Electro pneumatic
using PLC
Hours
6
3
3
3
3
PID controller interfacing.
Stepper motor interfacing using LabVIEW
Modeling and analysis of basic electrical, hydraulic and
pneumatic systems and temperature
Fluid level, flow control using LabVIEW / PLC
10
Fluid pressure control using LabVIEW / PLC
11
Fluid temperature control using LabVIEW / PLC
12
Design experiment
13
Application oriented experiment
212
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O801 PROFESSIONAL ETHICS
(Common to all branches)
2 0 0 2.0
OBJECTIVES
To study the basic issues in Professional Ethics
To appreciate the rights of others and to instill moral, social values and loyalty
To enable the student in their engineering profession who explore the ethical issues in technological society
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(e) The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team.
(f) The graduates will demonstrate effective English-language communication skills.
(h) The graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility and will
display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and up gradation.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Ability to propose possible solutions using articulated ethical theories.
Ability to form opinions based on reasoned ethical positions, supported with facts and evidence.
Increase in awareness of the ethical component of daily engineering decisions.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I
Test II
30
40
30
100
30
40
30
100
Model
Examination
30
40
30
100
Semester End
Examination
30
40
30
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
Define Human Values.
What are Morals and Values?
What do you mean by Civic virtue and Respect for others?
Write the various meanings of Spirituality?
List four different types of Virtues.
Mention different Human values.
What is meant by moral autonomy?
Classify the types of inquiry.
What are the steps needed in confronting moral dilemmas?
List the levels of moral development suggested by Kohlberg.
What do you understand by self-interest and ethical egoism?
What are the steps needed in confronting moral dilemmas?
What are the three virtues of religion?.
What are the professional responsibilities?
What is meant by Informed consent when bringing an engineering product to market?
What is engineering experimentation?
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10 marks will be
calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
213
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
17.
18.
19.
20.
What are the different roles and functions of Code of Ethics?
What are the Limitations of Code of Ethics?
Name some of the engineering societies which published codes of ethics.
What is meant by a disaster?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Which are the practical skills that will help to produce effective independent thought about moral issues?
Why does engineering have to be viewed as an experimental process?
Why isnt engineering possible to follow a random selection in product design?
Why is the code of ethics important for engineers in their profession?
What does the Balanced Outlook on Law stress in directing engineering practice?
Are the engineers responsible to educate the public for safe operation of the equipment? How?
What kind of responsibility should the engineer have to avoid mistakes that may lead to accident due to the
design of their product?
8. What is the use of knowledge of risk acceptance to engineers?
9. Why is Environmental Ethics so important to create environmental awareness to the general public?
10. Why do the engineers refuse to do war works sometimes?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
How does the consideration of engineering as a social experimentation help to keep a sense of autonomous
participation is a persons work?
How does the code of ethics provide discipline among the engineers?
How would you classify the space shuttle Challenger case accident?
How does the manufacturer understand the risk in a product catalog or manual?
How does the knowledge of uncertainties in design help the engineers to access the risk of a product?
How can the quantifiable losses in social welfare resulting from a fatality be estimated? Give some examples.
How does the engineer act to safeguard the public from risk?
Unit I
Human Values
Morals, Values and Ethics Integrity Work Ethic Service Learning Civic Virtue Respect for Others Living
Peacefully Caring Sharing Honesty Courage Valuing Time Co-operation Commitment Empathy
Self-Confidence
Character Spirituality in business..
6 Hours
Unit II
Engineering Ethics
Senses of 'Engineering Ethics' Variety of moral issues Types of inquiry Moral autonomy Kohlberg's theory
Gilligan's theory Consensus and controversy Models of Professional Roles Theories about right action
Self-interest Uses of ethical theories.
6 Hours
Unit III
Engineering as Social Experimentation
Engineering as experimentation Engineers as responsible experimenters Codes of ethics A balanced outlook on
law The Challenger case study Bhopal Gas Tragedy The Three Mile Island and Chernobyl case studies
Safety aspects in Nuclear Power plants
6 Hours
214
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit IV
Responsibilities and Rights
Fundamental Rights, Responsibilities and Duties of Indian Citizens Collegiality and loyalty Respect for
authority Collective bargaining Confidentiality Conflicts of interest Occupational crime Professional rights
Employee rights Discrimination
Right to Information Act.
6 Hours
Unit V
Global Issues
Multinational corporations Environmental ethics and Environmental Protection Act Computer ethics Engineers
as managers Consulting engineers Engineers as expert witnesses and advisors Moral leadership Sample code
of ethics like IETE, ASME, ASCE, IEEE, Institution of Engineers (India), Indian Institute of Materials Management
Weapons development.
6 Hours
Total: 30 Hours
Textbook
1.
M. Govindarajan, S. Natarajan and V. S. Senthil Kumar, Engineering Ethics, PHI Learning Private Ltd, New
Delhi, 2012.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Charles D. Fleddermann, Engineering Ethics, Pearson Education/ Prentice Hall of India , New Jersey, 2004.
Mike W. Martin and Roland Schinzinger, Ethics in Engineering, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt
Ltd, New Delhi, 2003.
Charles E. Harris, Michael S. Protchard and Michael J. Rabins, Engineering Ethics Concepts and Cases,
Wadsworth Thompson Learning, United States, 2005.
http://www.slideworld.org/slidestag.aspx/human-values-and- Professional-ethics
www.mne.psu.edu/lamancusa/ProdDiss/Misc/ethics.ppt
215
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O10B BASIC ENGLISH I *
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To offer students the basics of the English Language in a graded manner.
To promote efficiency in English Language by offering extensive opportunities for the
development of four language skills (LSRW) within the classroom.
To give an intense focus on improving and increasing vocabulary.
To improve Spelling and Pronunciation by offering students rigorous practice and exercises.
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES
f) The graduates will demonstrate effective English-language communication skills
h) The graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility and
will display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and upgradation
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Listening
Speaking
Reading
Writing
Unit I
Vocabulary/ Grammar
Skills Sets
Skill Sets
Basic words- 12 most used words in
English, usage and pronunciation
Starting a conversation and
talking about what one does
Sentence construction
bolstered by mother
tongue
Basic words- 20 oft used words, usage
and pronunciation
Analysing an action plan
Creating and presenting
ones own action plan
Basic words with a focus on spelling
Discriminative listening
Informal conversation
Basic words- 10 oft used words, usage
and pronunciation
Content listening and
Intonation
Reading comprehension
Tutorial
Module
216
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit II
Module
Vocabulary/ Grammar
Skills Sets
Skill Sets
Basic words + greetings to be used at
different times of the day
Formal conversation
Intonation to be used in
formal address
Last 28 of the 100 most used words
Informal conversation
between equals
Reading practice and peer
learning
Using the 14 target words to form
bigger words
Informal dialogues using
contracted forms
Guided speaking- talking to
peers using contracted forms
Palindromes, greetings- good luck,
festivals
Placing a word within its
context- culling out meaning
Offering congratulations
10
Tutorial
Vocabulary/ Grammar
Skills Sets
Skill Sets
11
Homophones
Formal and informal methods
of self-introduction
Lets Talk is a group
activity that gives them
some important pointers of
speech
12
Homophone partners, matching words
with their meanings
Contracted forms of the be
verbs, ve and s
Translating English
sentences to Tamil
13
Briefcase words- finding smaller words
from a big word
Formal and informal ways of
introducing others
Team work- speaking
activity involving group
work, soft skills
14
Compound words and pronunciation
pointers
Giving personal details about
oneself
Using the lexicon
15
Tutorial
*Subject to continuous assessment
Unit III
Module
217
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit IV
Module
Vocabulary/ Grammar
Skills Sets
Skill Sets
16
Proper and common nouns
Asking for personal
information and details
Pronunciation pointers- an
informal introduction to the
IPA
17
Pronouns
Telephone skills and etiquette
Reading aloud and
comprehension
18
Abstract and common nouns
Dealing with a wrong number
Reading practice and
comprehension
19
Group names of animals, adjectives
Taking and leaving messages
on the telephone
Pronunciation pointers
20
Tutorial
Unit V
Module
Vocabulary/ Grammar
Skills Sets
Skill Sets
21
Determiners
Interrupting a conversation
politely- formal and informal
Pair work reading
comprehension
22
Conjugation of the verb to be- positive
and negative forms
Thanking and responding to
thanks
Comprehension questions
that test scanning,
skimming and deep
reading
23
Am/is/are questions
Giving instructions and
seeking clarifications
Small group activity that
develops dialogue writing
24
Present continuous tense-form and usage
Making inquiries on the
telephone
Finishing sentences with
appropriate verbs
25
Tutorial
Skills Sets
Skill Sets
Calling for help in an
emergency
Dialogue writing
Making requests and
responding to them politely
Identifying elements of
grammar in text extract
Unit VI
Module
26
Vocabulary/ Grammar
Words with silent b
Present continuous questions
27
Words with silent c
Simple present tense- form and usage
218
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
28
Simple present tense- rules
Describing people
Guided writing
29
Words with silent g
Describing places
Filling in the blanks with
correct markers of tense
Questions in the simple present tense
30
Tutorial
Total: 45 Hours
Resources
1. Basic English Module, L&L Education Resources, Chennai, 2011.
219
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O10C COMMUNICATIVE ENGLISH *
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To equip students with effective speaking and listening skills in English
To help the students develop speaking skills in Business English
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES
f) The graduates will demonstrate effective English-language communication skills
h) The graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility and
will display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and upgradation
SKILL SET
1. Students will develop the fluency and language competence of learners of Business English at
the lower intermediate level
Unit I
Grammar and Vocabulary
Vocabulary for describing different company structures and company hierarchy Practice using wh
questions; there is / there are, Definitions of Quality, Vocabulary of quality management Using
nouns and adjectives to form group nouns Phrases for offering and accepting help and invitations
Telephone terms Verb tenses Questions and responses Conditionals Gap Filling Exercises.
9 Hours
Unit II
Listening
Business Presentation Conversation between old friends; introducing a stranger A Quality Manager
talks about his work Conversation between acquaintances Sales talk at a sports equipment stand
Small talk among colleagues A tour of a factory in Italy Lunch in the factory canteen A meeting
to improve the efficiency of internal communication A phone conversation arranging to meet A
credit card salesman talks to the bank A conversation between business acquaintances - A
management meeting about a recent merger A conversation about a town, a country and its people.
9 Hours
Unit III
Speaking
Pronunciation Practice Describing organizations - A company presentation Practicing of
conversation starters and closers with friends and strangers Practice of simple language and step by
step procedures to describe complex ideas Explaining visual information The language of
increase and decrease applied to graphs and bar charts - Presenting a work related graph Making a
telephone call A sports equipment buyer and a manufacturers sales representative talk business
Entertaining a visitor in your country A short marketing meeting Negotiating to meet around a busy
schedule Pairs or small groups discuss the implications of problems at an electronics factory
Finding out all you can about a partner Chairing and holding meetings Pairwork on questions and
answers about places and people.
9 Hours
* Subject to continuous assessment
220
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit IV
Reading
Signalling the structure of a presentation introducing, sequencing and concluding a talk - Explaining
concepts and ideas The pattern of phone call conversations Giving, getting and checking
information Common Business phrases Giving encouragement: phrases for positive feedback; more
emphatic adjectives and adverbs Giving facts and explaining functions and processes Asking for
and clarifying information How to state your point, agree and disagree Practice of frequency,
quantity and number - A short marketing meeting Suggesting and agreeing times and places
Phrases for the Chairperson People at work: their emotions, skills and attitudes.
9 Hours
Unit V
Writing
Making conditions using the present and future conditional Phrases for stalling for time - Common
telephone phrases and responses - Business Communication Calling for Quotation Letter asking for
Clarification Transcoding Rearranging the sentences Cloze Explaining visual information
Explaining concepts and ideas Giving, getting and checking information Business description
Informal negotiations.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
Jeremy Comfort, Pamela Rogerson, Trish Stott, and Derek Utley, Speaking Effectively
Developing Speaking Skills for Business English, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge,
2002.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
Brook-Hart Guy, BEC VANTAGE: BUSINESS BENCHMARK Upper-Intermediate Students
Book, Cambridge University Press, New Delhi, 2006.
Aruna Koneru, Professional Communication, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company
Limited, New Delhi, 2008.
P. Kiranmai Dutt, Geetha Rajeevan and CLN Prakash, A Course in Communication Skills,
Cambridge University Press, New Delhi, 2008.
Krishna Mohan Balaji, Advanced Communicative English, Tata McGraw-hill Education
Private Limited, New Delhi, 2009.
221
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O20B BASIC ENGLISH II *
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To promote fluency even downplaying accuracy
To give room for a tacit acquisition of Basic English Grammar through ample listening,
reading and writing inputs with direct theory wherever relevant
To specifically focus on speaking and conversation skills with an aim to increase speaking
confidence
To nurture in students the capacity to express themselves lucidly and articulate their thoughts
and impressions on a wide gamut of topics both through speech and writing
To improve Spelling and Pronunciation by offering rigorous practice and exercises
To correct common mistakes and to teach self-assessment techniques
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES
f) The graduates will demonstrate effective English-language communication skills
h) The graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility and
will display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and upgradation
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Unit I
Listening
Speaking
Reading
Writing
Vocabulary/ Grammar
Skills Sets
Skill Sets
Difference between present
continuous and simple present
tense.
Calling for help in an
emergency
Reporting an eventjournalistic style
Verbs have and have got
Describing animals
Asking for and giving
directions
Simple past tense
Inviting people,
accepting and declining
invitations
Self- enquiry and offering
ones opinion on a given topic.
Spelling rules & table of irregular
verbs
Refusing an invitation
Reading and practicing prewritten dialogues
Module
31
32
33
34
Tutorial
35
222
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
* Subject to continuous assessment
Unit II
36
Questions and the negative form
of the simple past tense
Apologizing and
responding to an
apology
(Reading) conversation
practice
Asking questions in the simple
past tense
Reading comprehension
37
Seeking, granting and refusing
permission
Past continuous tense
Paying compliments and
responding to them
Pair work: writing dialogues
and presenting them
Difference between simple past
and past continuous- when and
where to use each
Describing daily
routines
Reading and comprehension
skills
Simple future tense
Talking about the
weather
Making plans- applying
grammar theory to written
work
Simple future tense- more aspects,
possessive pronouns
Talking about
possessions
Opening up and expressing
ones emotions
Future continuous
Talking about current
activities
Listening comprehension
Revision of future tense- simple
and continuous forms,
prepositions used with time and
date
Asking for the time and
date
Discussion- analyzing and
debating a given topic
38
39
Tutorial
40
Unit III
41
42
43
44
Tutorial
45
223
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit IV
46
Articles a/an
Writing, speaking and
presentation skills
Transcribing dictation
47
Singular- Plural (usage of a/an)
Reading practiceindependent and shared
reading
Comprehension logical
analysis, process analysis and
subjective expression
48
Countable and uncountable
nouns- a/an and some
Listening
comprehension
Vocabulary: using context
tools to decipher meaning
49
Articles- the
Sequencing sentences in
a paragraph
Listening to a poem being
recited, answer questions on
it and practice reciting the
same
50
Tutorial
Articles- the: usage and avoidance
Speaking: sharing
stories about family,
village/town, childhood,
etc. 10 students
Listening: comprehend and
follow multiple step
instructions read out by the
teacher
52
Articles- the: usage and avoidance
with like and hate
Speaking: sharing
stories about family,
village/town, childhood,
etc.- 10 students
Reading: make inferences
from the story about the plot,
setting and characters
Articles- the: usage and avoidance
with names of places
Speaking: sharing
stories about family,
village/town, childhood,
etc.- 10 students
Comprehension passage
53
This/ that/ these and those
Writing a noticeannouncement
Speaking: Debate
Unit V
51
54
Tutorial
55
224
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit VI
56
One and ones
Collaborative learningproblem solving
Writing short answers to
questions based on reading
57
Capitalization and punctuation
Controlled writing
Listen to a story and respond
to its main elements
58
Syntax and sentence constructionrearrange jumbled sentences
Guided writing
Listen to a poem and discuss
its elements
59
Cloze
Free writing
Frame simple yet purposeful
questions about a given
passage
60
Tutorial
Total:45+15
Hours
Resources
1. Basic English Module, L&L Education Resources, Chennai, 2011.
225
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O20C ADVANCED COMMUNICATIVE ENGLISH *
OBJECTIVES
To take part in a discussion in an effective manner
To listen to an explanation and respond
To write a formal communication
To read company literature or any document
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES
f) The graduates will demonstrate effective English-language communication skills
h) The graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility and
will display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and upgradation
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Read graphs and charts
Skim and scan texts like job adverts
Read business articles for specific information
Understand the structure of a text
Unit I
Grammar and Vocabulary
Comparison of adjectives and adverbs tenses simple and complex questions countable/
uncountable nouns, -ing forms and infinitives conditionals comparing and contrasting ideas
modal verbs while and whereas for contrasting ideas passives used to, articles, reported speech,
relative pronouns and expressing cause and result workplace-related vocabulary.
9 Hours
Unit II
Listening
Prediction - the ability to identify information ability to spell and write numbers correctly ability to
infer, understand gist, topic, context, and function, and recognize communicative functions (
complaining, greeting, apologizing, etc.) ability to follow a longer listening task and interpret what
the speakers say.
9 Hours
Unit III
Speaking
The ability to talk about oneself and perform functions such as agreeing and disagreeing ability to
express opinions, agree, disagree, compare and contrast ideas and reach a decision in a discussion
appropriate use of stress, rhythm, intonation and clear individual speech sounds - take an active part in
the development of the discourse - turn-taking and sustain the interaction by initiating and responding
appropriately.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Reading
The ability to skim and scan business articles for specific details and information To understand the
meaning and the structure of the text at word, phrase, sentence, and paragraph level ability to read in
detail and interpret opinions and ideas to develop ones understanding and knowledge of collocations
ability to identify and correct errors in texts.
9 Hours
* Subject to continuous assessment
226
3 1 0 3.5
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit V
Writing
The ability to write concisely, communicate the correct content and write using the correct register
ability to write requests, instructions, explanations, and ask for information by using the correct format
in business correspondences like charts, memo, note, email, letter, fax, report, proposal understanding
formal and informal styles responding to written or graphic input.
9 Hours
Total: 45+15 Hours
Text Book
1.
Brook-Hart, Guy, Business Benchmark: Upper Intermediate Students Book, Cambridge
University Press, New Delhi, 2006.
References
1.
2.
Whitby, Norman, Bulats Edition: Business Benchmark, Pre-Intermediate to Intermediate
Students Book, Cambridge University Press, New Delhi, 2006.
Cambridge Examinations Publishing, Cambridge BEC Vantage Self-study Edition,
Cambridge University Press, UK, 2005.
227
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O20H HINDI *
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To help students acquire the basics of Hindi
To teach them how to converse in Hindi in various occasions
To help learners acquire the ability to understand a simple technical text in Hindi
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES
f) The graduates will demonstrate effective English-language communication skills
h) The graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility and
will display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and upgradation
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Listening
Speaking
Reading
Writing
Unit I
Hindi Alphabet
Introduction - Vowels - Consonants - Plosives - Fricatives - Nasal sounds - Vowel Signs - Chandra
Bindu & Visarg -Table of Alphabet -Vocabulary.
9 Hours
Unit II
Nouns
Genders (Masculine & Feminine Nouns ending in ,,, u, )- Masculine & Feminine Reading
Exercises.
9 Hours
Unit III
Pronouns and Tenses
Categories of Pronouns - Personal Pronouns - Second person (you & honorific) - Definite & Indefinite
pronouns - Relative pronouns - Present tense - Past tense - Future tense - Assertive & Negative
Sentences - Interrogative Sentences.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Classified Vocabulary
Parts of body Relatives Spices Eatables Fruit & Vegetables - Clothes - Directions Seasons Professions.
9 Hours
Unit V
Speaking
Model Sentences Speaking practice for various occasions.
9 Hours
Total: 45+15 Hours
Textbook
1.
B. R. Kishore, Self Hindi Teacher for Non-Hindi Speaking People, Vee Kumar Publications
(P) Ltd., New Delhi, 2009.
228
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
References
1. Syed, Prayojan Mulak Hindi, Rahamathullah Vani Prakasan, New Delhi, 2002.
2. Ramdev, Vyakaran Pradeep, Saraswathi Prakasan, Varanasi, 2004.
* Subject to continuous assessment
229
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O20G GERMAN *
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To help students acquire the basics of German language
To teach them how to converse in German in various occasions
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES
f) The graduates will demonstrate effective English-language communication skills
h) The graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility and
will display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and upgradation
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Listening
Speaking
Reading
Writing
Unit I
Grammar & Vocabulary
Introduction to German language: Alphabets, Numbers Nouns - Pronouns Verbs and Conjugations definite and indefinite article - Negation - Working with Dictionary Nominative - Accusative and
dative case propositions - adjectives - modal auxiliaries - Imperative case - Possessive articles.
9 Hours
Unit II
Listening
Listening to CD supplied with the books, paying special attention to pronunciation: Includes all lessons
in the book Greetings - talking about name country studies nationalities - ordering in restaurants
- travel office - Interaction with correction of pronunciation.
9 Hours
Unit III
Speaking
Speaking about oneself - about family studies - questions and answers - dialogue and group
conversation on topics in textbooks - talks on chosen topics.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Reading
Reading lessons and exercises in the class - pronunciation exercises: Alphabet name country
people profession family shopping travel numbers friends restaurant studies - festivals
9 Hours
Unit V
Writing
Alphabets numbers - words and sentences - Exercises in the books - control exercises - writing on
chosen topics such as one self family studies - country.
9 Hours
Total: 45+15 Hours
230
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
* Subject to continuous assessment
Textbooks
1.
2.
Grundkurs DEUTSCH A Short Modern German Grammar Workbook and Glossary, VERLAG
FUR DEUTSCH, Munichen, 2007.
Grundkurs, DEUTSCH Lehrbuch Hueber Munichen, 2007.
References
1.
2.
3.
Cassel Language Guides German: Christine Eckhard Black & Ruth Whittle, Continuum,
London / New York, 1992.
Kursbuch and Arbeitsbuch, TANGRAM AKTUELL 1 DEUTSCH ALS FREMDSPRACHE,
NIVEAUSTUFE AI/1, Deutschland, Goyal Publishers & Distributers Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi,
2005.
Langenscheidt Eurodictionary German English / English German, Goyal Publishers &
Distributers Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 2009.
231
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O20J JAPANESE *
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To help students acquire the basics of Japanese language
To teach them how to converse in Japanese in various occasions
To teach the students the Japanese cultural facets and social etiquettes
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES
f) The graduates will demonstrate effective English-language communication skills
h) The graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility and
will display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and upgradation
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Listening
Speaking
Reading
Writing
Unit I
Introduction to Japanese - Japanese script - Pronunciation of Japanese(Hiragana) - Long vowels Pronunciation of in,tsu,ga - Letters combined with ya,yu,yo - Daily Greetings and Expressions Numerals. N1 wa N2 des - N1 wa N2 ja arimasen - S ka - N1mo - N1 no N2 - .san - Kanji Technical Japanese Vocabulary (25 Numbers)
9 Hours
Unit II
Introduction - Kore - Sore - are - Kono N1 - Sono N1 - ano N1 - so des - so ja arimasen - S1 ka - S2 ka
- N1 no N1 - so des ka koko - soko - asoko - kochira - sochira - achira - N1 wa N2 (Place) des
dhoko-N1 no N2 - Kanji-10 - ima.jifun des - Introduction of verb - V mas - V masen - V mashitha
- V masen deshitha - N1(Time) ne V - N1 kara N2 des - N1 tho N2 / S ne Kanji-10 - Technical
Japanese Vocabulary (25 Numbers) Dictionary Usage.
9 Hours
Unit III
- N1(Place) ye ikimas - ki mas - kayerimasu - Dhoko ye mo ikimasen - ikimasendheshitha N1(vehicle) de ikimasu - kimasu - kayerimasu - N1(Personal or Animal) tho V ithsu - S yo. - N1 wo
V (Transitive) - N1 wo shimus - Nani wo shimasu ka - Nan & Nani - N1(Place) de V - V masen ka - V
masho - Oo. Kanji-10 , N1( tool - means ) de V - Word / Sentence wa go nan des ka - N1(
Person ) ne agemus - N1( Person ) ne moraimus - mo V shimashitha - , Kanji-10 Japanese
Typewriting using JWPCE Software, Technical Japanese Vocabulary (25 Numbers)
9 Hours
Unit IV
Introduction to Adjectives - N1 wa na adj des. N1 wa ii adj des - na adj na N1 - ii adj ii N1 - Thothemo
- amari - N1 wa dho des ka - N1 wa dhonna N2 des ka - S1 ka S2 dhore - N1 ga arimasu wakarimasu - N1 ga suki masu - N1 ga kiraimasu - jozu des - hetha des - dhonna N1 - Usages of yoku dhaithai - thakusan - sukoshi - amari - zenzen - S1 kara S2 - dhoshithe, N1 ga arimasu - imasu N1(Place) ne N2 ga arimasu - iimasu - N1 wa N2(Place) ne arimasu - iimasu - N1(Person,Place,or
232
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Thing ) no N2 (Position) - N1 ya N2, Kanji-10 - Japanese Dictionary usage using JWPCE Software,
Technical Japanese Vocabulary (25 Numbers)
9 Hours
* Subject to continuous assessment
Unit V
Saying Numbers , Counter Suffixes , Usages of Quantifiers -Interrogatives - Dhono kurai - gurai
Quantifier-(Period ) ne .kai V - Quantifier dhake / N1 dhake Kanji - Past tense of Noun sentences
and na Adjective sentences - Past tense of ii-adj sentences - N1 wa N2 yori adj des - N1 tho N2 tho
Dhochira ga adj des ka and its answering method - N1 [ no naka ] de {nani/dhoko/dhare/ithsu} ga
ichiban adj des ka - answering -N1 ga hoshi des - V1 mas form dhake mas - N1 (Place ) ye V masu
form ne iki masu/ki masu/kayeri masu - N1 ne V/N1 wo V - Dhoko ka - Nani ka gojumo - Technical
Japanese Vocabulary (25 Numbers)
9Hours
Total: 45+15 Hours
Textbooks
1. Japanese for Everyone: Elementary Main Textbook 1-1, Goyal Publishers and Distributors Pvt.
Ltd., Delhi, 2007.
2. Japanese for Everyone: Elementary Main Textbook 1-2, Goyal Publishers and Distributors Pvt.
Ltd., Delhi, 2007.
References
Software
1. Nihongo Shogo-1
2. Nihongo Shogo-2
3. JWPCE Software
Websites
1. www.japaneselifestyle.com
2. www.learn-japanese.info/
3. www.kanjisite.com/
4. www.learn-hiragana-katakana.com/typing-hiragana-characters/
233
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O20F FRENCH *
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVE
To help students acquire the basics of French language
To teach them how to converse in French in various occasions
PROGRAMME OUTCOMES
f) The graduates will demonstrate effective English-language communication skills
h) The graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility and
will display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and upgradation
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Listening
Speaking
Reading
Writing
Unit I
Alphabet Franais (alphabets) - Les accents franais (the accents in French) aigu grave
circonflexe trma - cdille - crire son nom dans le franais (spelling ones name in French)
9 Hours
Unit II
Les noms de jours de la semaine (Days of the week) - Les noms de mois de l'anne (Months) - numro
1 100 (numbers 1 to 100)
9 Hours
Unit III
Moyens de transport (transport) - noms de professions (professions) - noms d'endroits communs
(places) - nationalits (nationalities)
9 Hours
Unit IV
Pronoms (pronouns) - Noms communs masculins et de femme (common masculine and feminine
nouns) - Verbes communs (common verbs)
9 Hours
Unit V
Prsentation - mme (Introducing Oneself) - narration de son nom - l'endroit o on vit - son ge - date
de naissance - sa profession - numro de tlphone - adresse (name - where one lives age - date of
birth profession - telephone number and address) - Narration du temps (tellling the time)
9 Hours
Total: 45+15 Hours
Textbook
1. Angela Wilkes, French for Beginners, Usborne Language Guides, Usborne Publishing Ltd.,
Ohio, 1987.
References
1. Ann Topping, Beginners French Reader, Natl Textbook Co, 1975.
2. Stanley Applebaum, First French Reader, Dover Publications, 1998.
3. Max Bellancourt, Cours de Franais, London: Linguaphone, 2000.
234
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Software
1. Franais Linguaphone, Linguaphone Institute Ltd., London, 2000.
2. Franais I. Harrisonburg: The Rosetta Stone: Fairfield Language Technologies, 2001.
* Subject to continuous assessment
235
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M001 INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To introduce the advanced topics in combustion phenomenon in engines
To make the students familiar with the effects of knocking
To make the awareness of pollutants emitted through the use of I C engines
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(b) The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge, capability of analyzing and solving any
concept or problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students will be able to
understand the working concepts of thermal engineering.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1
2
Evaluate the heat transfer and work transfer with in an actual or ideal system.
An ability to identify and suggest the thermodynamic process and corelations for particular
application.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
30
40
30
--100
30
40
30
--100
Model
Examination*
30
40
30
--100
Semester End
Examination
30
40
30
--100
Remember
1. Define the terms i. Octane number and Cetane number.
2. Define volumetric efficiency and clearance ratio.
3. Define the term knocking in SI engine.
4. Define the term SAC volume
5. What are the major pollutants from SI Engine exhaust?
6. What is meant by homogenous charge compression ignition?
7. Name the types of combustion chambers used in CI engine.
Understand
1. Compare LPG and petrol as fuel for SI engine.
2. Mention the advantages of using natural gas as alternate fuel..
3. List any two salient features of gasoline direct injection engine.
4. State the factors affecting the delay period.
1 *
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
236
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
5. What is the effect of Cut-off ratio in the efficiency of a Diesel cycle?
6. Differentiate 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines based on construction.
7. Write short notes on particulate trap
8. Discuss the properties of alcohol as engine fuel.
9. Compare direct and indirect injection systems.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Evaluate the relationship between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixture.
How will you differentiate dual cycle with diesel cycle in IC engines?
How the ignition takes place in C.I. Engine?
For the same compression ratio and heat rejection, which cycle is most efficient: Otto or Diesel?
Mention the advantages of turbo charging
Indicate the various factors that influence the flame speeds
State the modifications to be made to the engine to make it lean burn engine.
Indicate the features of mono point and multi point injection systems
Unit I
Spark Ignition Engines
Spark ignition engine- Mixture requirements - Feedback control - Carburetors -Fuel injection systemsMonopoint and Multipoint injection -Stages of combustion - Normal and Abnormal combustionFactors affecting knock-Combustion chambers- Introduction to Thermodynamic analysis of S.I. engine
combustion.
Combustion stoichiometry
9 Hours
Unit II
Compression Ignition Engines
States of combustion in C.I. Engine Combustion knock in CI engines Knock comparison in SI and
CI Engines-Methods of controlling knock- Direct and indirect injection systems - Combustion
chambers - Fuel spray behavior-spray structure, spray penetration and evaporation-Air motion-Turbo
charging-Introduction to Thermodynamic analysis of C.I. Engine combustion.
Physical factors affecting ignition delay.
9 Hours
Unit III
Pollutant Formation and Control
Pollutant - Sources and types - formation of NOx - Hydrocarbon emission mechanism - Carbon
monoxide formation - Particulate emissions Measurement of exhaust emissions-Methods of
controlling emissions- Catalytic converters and Particulate traps.
Euro and BS norms
9 Hours
Unit IV
Alternative Fuels
Bio-fuels: Alcohol, Hydrogen, Natural Gas and Liquefied Petroleum Gas Properties Suitability Engine Modifications - Merits and Demerits as fuels.
Biodiesel production process
9 Hours
237
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit V
Recent Trends
Lean Burn Engines - Stratified Charge Engines Gasoline: Direct Injection Engine Common rail
Diesel injection system (CDRI)- Homogeneous charge compression ignition - Plasma Ignition
Ignition Measurement techniques.
Exhaust gas recirculation
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
V. Ganesan, Internal Combustion Engines, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New
Delhi, 2007.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
John B. Heywood, Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing
Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi,2008
S. Rowland Benson and N. D. Whitehouse., Internal combustion Engines, Vol.I and II, Pergamon
Press.
H. N. Gupta Fundamentals of Internal Combustion Engineering, Prentice Hall of India Pvt Ltd,
New Delhi, 2006.
R. B. Mathur and R. P. Sharmal Internal Combustion Engines, Dhanpat Rai Publications, 2008.
http://www.gtmresearch.com/report/third-and- fourth generation- bio fuels.
238
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M002 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To acquire knowledge about the fundamentals and analysis techniques used in computational
solutions of fluid mechanics and heat transfer problems
To study the interaction of physical processes and numerical techniques and understand the
contemporary methods for boundary layers, incompressible viscous flows, and in viscid
compressible flows
PROGRAM OUTCOME
(b) The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge, capability of analyzing and solving any
concept or problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students will be able to
understand the working concepts of thermal engineering.
SKILL SET
1
2
Evaluate the heat transfer and work transfer with in an actual or ideal system.
An ability to identify and suggest the thermodynamic process and corelations for particular
application.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
20
20
20
40
-100
20
20
20
40
-100
Model
Examination*
20
20
20
40
-100
Semester End
Examination
20
20
20
40
-100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Define the terms i. Continuum, ii. Stability
Define Reynolds transport theorem.
Write the continuity equation.
What is known as thermal diffusivity?
Explain the terms i. Strokes equation, ii. Euler equations.
List out the different types of error?
What is Courant number?
What is known as Peclet number?
Understand
1.
2.
2 *
Differentiate between compressible and incompressible flow.
Compare Implicit and Explicit methods.
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
239
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
3.
4.
Write the significance of Von Neumann stability analysis.
Give the advantages of staggered grid.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
Develop a Navier-Strokes equation for a Newtonian fluid.
Construct the advection-diffusion equation for thermal energy in Cartesian, cylindrical and
spherical coordinate systems.
Generalize the formulation of first order wave equation.
With a suitable example, indicate the significance of upwind differencing scheme.
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
Starting with the three dimensional incompressible Strokes equations, derive the depth- averaged
pressure equation.
Develop the transient heat equation T / t = Txx + Tyy +1 with the initial condition T ( x,y,0 ) =
0 and the boundary conditions T ( 0, y, t ) = T ( 1,y, t ) = T ( x,0,T ) = T ( x,1,t ) = 0 using finite
difference method.
Establish the truncation error for a uniform mesh using a finite difference approximation.
Unit I
Introduction
Impact and applications of CFD in diverse fields - governing equations of fluid dynamics- continuity
momentum and energy - generic integral form for governing equations - Initial and Boundary
conditions - Classification of partial differential equations- Hyperbolic, Parabolic, Elliptic and Mixed
types - Applications and Relevance.
Linear algebraic equations
9 Hours
Unit II
Basic Aspects of Discretization
Discretization techniques- Finite difference, Finite volume and Finite element method- Comparison of
discretization by the three methods. Introduction to Finite differences, Difference equations, Uniform
and non-uniform grids, numerical errors, Grid independence test and Optimum step size.
Axisymmetric geometry
9 Hours
Unit III
Grid Generation
Transformation of non-uniform grids to uniform grids, General transformation of the equations - Form
of the governing equations suitable for CFD - Compressed grids, Boundary fitted co-ordinate systemsElliptic grid generation - Adaptive grids - Modern developments in grid generation.
Automatic grid refinement generation
9 Hours
Unit IV
Conduction and Convection
Steady One dimensional conduction- two and three-dimensional conduction- Steady one-dimensional
convection and Diffusion -Transient one-dimensional and two-dimensional conduction- Explicit,
Implicit, Crank-Nicolson, ADI scheme-Stability criterion.
SIMPLE algorithm for1D heat flow
9 Hours
240
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit V
Incompressible Fluid Flow and Applications of CFD
Gradient term and continuity equation- Staggered grid- Momentum equations-Pressure and velocity
corrections- Pressure Correction equation - Numerical procedure for SIMPLE algorithm - Boundary
conditions for the pressure correction method - Stream function- Vorticity method, Discussion of case
studies. Applications of CFD fluent software - Drying, Sterilization, Mixing, Refrigeration. Other
applications Heat exchanger, Clean room condition, Future of CFD in food industry
Inviscid simulation of real flows
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
J. D. Anderson., Jr. Computational Fluid Dynamics- The Basic with Applications, Tata McGraw
Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi,2004
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
P. Ghosdastidar, Computational Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing
Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2003
K. A. Hoffman, Computational Fluid Dynamics for Engineering, Engineering Education System,
Austin, Texas 1989.
Muralidhar and T. Sundarajan, Computational Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer, Narosa Publishing
House, New Delhi, 2002.
S. V. Patankar, Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow, Hemisphere, New York, 1994.
T. J. Chung, Computational Fluid Dynamics, Cambridge University Press, Chennai 2003.
241
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M003 DIRECT ENERGY CONVERSION TECHNIQUES
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To study the various forms of energy and conversion techniques
To know the methodologies of producing electrical energy thus fulfilling the energy crisis
To introduce knowledge about future energy producing/storage devices like fuel cells
At the end of this course the student is expected to understand what are the precious resources in
the environment are available for the future generations
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(b) The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge, capability of analyzing and solving any
concept or problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students will be able to
understand the working concepts of thermal engineering.
(g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
SKILL SET
1
2
3
4
5
Able to use the basic principles of direct energy conversion techniques.
Can select the proper energy conversion technique for a industrial application.
Identify proper energy storage system for a particular application.
Identify importance of understanding system and component principles to troubleshooting.
Able to design the comparative analysis of fuel cell in industrial application.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
S. No.
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
1
2
Remember
Understand
35
30
35
30
35
30
35
30
3
4
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
35
--
35
--
35
--
35
--
Create
--
--
--
--
100
100
100
100
Total
3
Test 1*
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
3*
What is energy conservation? What are its advantages?
What are the methods of energy conservation?
What are the methods used to improve the efficiency in thermal power plants.
List out the different energy management techniques used in practice.
List out the different sources of geothermal energy?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
242
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
What are the specific environmental effects if the geothermal source of energy is used for power
generation?
What is the function of Ferro Electric Converter?
What are the types of Energy Storage Systems?
What is the function of a Thermo Magnetic Converter?
What is the function of Battery?
What is the function of Solar Cells?
Define fuel cell.
What is the use of Alkali fuel cell?
List the various types of fuel cell.
What do you meant by electrical storage system?
Define Thermoelectric Generator.
Define Nernst Effect.
What is the purpose of a fuel cell?
State various subsystems in a solar thermal energy conversion system.
State the functions of the following:
1. Solar thermal collector.
2. Central receiver
3. Thermal storage system in a solar thermal plant.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
What is the trend of power development in India in future?
What is the fundamental difference between Otto and Diesel cycle?
What are the advantages of Stirling cycle over Ericsson cycle?
Differentiate between the Brayton and Rankine cycle?
Where the Thermoelectric Generator is employed? Why?
Why is Thermo Magnetic Converter preferred for thermo electric conversion?
Which is the best for energy storage system? Why?
Difference between the mechanical and electrical storage system?
When do you prefer thermal energy storage system?
For what type of application, you would prefer to use methanol fuel in fuel cell.
What are the advantages of Alkali electrolyte over molten carbonate electrolyte?
What do you understand by distribution of energy consumption?
Energy conservation will help to reduce the energy growth in India. Discuss.
Use of non-conventional sources is considered a proper and logical method to meet the energy
demand in India. Discuss.
What is meant by energy management?
How to the efficiencies of the ideal Otto cycle and Carnot cycle compare for the same temperature
limits?
How is the rpm of an actual four stroke gasoline engine related to the number of thermodynamic
cycles? What would your answer be for a two stroke engine?
How does the thermal efficiency of an ideal Otto cycle change with the compression ratio of the
engine and specific heat ratio of the working fluid?
Why is high compression ratios not used in spark ignition engines?
How does a diesel engine differ from a gasoline engine?
How does the ideal Diesel cycle differ from the ideal Otto cycle?
Do diesel or gasoline engines operate at higher compression ratios? Why?
What is the cut off ratio? How does it affect the thermal efficiency of a Diesel cycle?
243
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
For fixed maximum and minimum temperatures, what are the effect of the pressure ratio on (a) the
thermal efficiency and (b) the net work output of a simple ideal Bray ton cycle?
Why thermal energy storage is not of much use in storing electrical energy for peak load
application.
What is the need of Energy Storage for Electrical Power Systems with the help of a Daily Load
Curve?
Under what modifications will the ideal simple gas turbine cycle approach the Ericsson cycle?
For a specified pressure ratio, why does multistage compression with inter cooling decrease the
compressor work, and multistage expansion with reheating increase the turbine work?
Compare the following types of collectors to be used for a solar thermal power plant with respect
to 1. Temperature 2. Concentration ratio 3. Suitability 4. Cost
Unit I
Introduction
Energy Conversion Conventional Techniques Reversible & Irreversible Cycles Carnot, Stirling &
Ericsson Otto, Diesel, Dual, Lenior, Atkinson, Brayton and Rankine.Application of Brayton and
Rankine cycle.
Cogeneration rankine cycle
9 Hours
Unit II
Direct Conversion of Thermal to Electrical Energy
Thermoelectric Converters Thermoelectric refrigerator Thermoelectric Generator Thermionic
Converters Ferro Electric Converter Nernst Effect Generator
Thermo magnetic converter
9 Hours
Unit III
Chemical and Electromagnetic Energy to Electrical Energy
Batteries Types Working Performance - Governing Parameters Hydrogen Energy Solar Cells.
Advance Batteries - Lithium chloride
Hybrid vehicles
9 Hours
Unit IV
Energy Storage Systems
Introduction Storage of Mechanical Energy, Electrical Energy, Chemical Energy, Thermal Energy.
Nuclear energy storage system
9 Hours
Unit V
Fuel Cells
Basics Working Advantages & Drawbacks Types Comparative Analysis Thermodynamics &
Kinetics of fuel cell process Performance of fuel cell
Fuel cell for portable and power plant applications
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
244
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Textbook
1.
B. K. Hogde, Analysis and Design of Energy Systems, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi,1998.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Archie W. Culp, Principles of Energy Conversion, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt
Ltd., Singapore,
Rakosh das Begamudre, Energy conversion systems, New age international Publishers, New Delhi,
2000.
K. Kordesch and G. Simader, Fuel Cell and Their Applications, Wiley-Vch, Germany M. A.
Kettari, Direct Energy Conversion, Addision Wesley Pub.Co
A. B. Hart and G. J. Womack, Fuel Cells: Theory and Application, Prentice Hall, London
http://www.personal.utulsa.edu/~kenneth-weston/
245
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M004 CRYOGENIC ENGINEERING
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
This course provides students with a practical prospective on the cryogenic world
It imparts knowledge on properties of cryogenic fluid, cycles, cryogenic refrigerators and
Applications
At the end one can able to apply this to practical problems
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(b) The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge, capability of analyzing and solving any
concept or problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students will be able to
understand the working concepts of thermal engineering.
(g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement
in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Able to use the basic principles of cryogenic engineering.
Can select the proper Cryo-coolers and Cryo-refrigerators for an industrial application.
Identify proper Cryogens Handling system for a particular application.
Identify importance of understanding system and component principles to troubleshooting.
Able to design the comparative analysis of Cryogens in industrial application.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
Remember
25
25
25
25
Understand
30
30
30
30
Apply
20
20
20
20
Analyze/ Evaluate
25
25
25
25
Create
--
--
--
--
100
100
100
100
Total
4
Test 1*
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
4*
What is cryogenic engineering?
What are the Properties of Cryogenic fluids?
Define Inversion Curve.
Define Joule Thomson Effect.
Draw T-s diagram of Precooled Linde Hampson Cycle
Define Sulzer Helium Liquefaction process.
What is the function of Separation plant?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
246
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
8. What are the types of separation plant?
9. What is the function of a Gas purifier?
10. What are the configurations for heat exchanger?
11. Define surface effectiveness factor.
12. Define multi layer super insulation.
13. What is the use of cryogenic regenerators?
14. List the various types of insulation systems for space propulsion.
15. What do you meant by Aerogel Beads?
16. Define cryogenic propellants.
17. Define specific impulse.
18. What is the purpose of storage tank in rocket propulsion?
19. What is the function of Metallic Resistance thermometer?
20. Define thermocouple.
Understand
1.
2.
What is the trend of cryogenic engineering in India in future?
What is the fundamental difference between simple Lindle hampson and precooled Lindle
hampson process?
3. What are the advantages of simple Claude process over kapitza process?
4. Differentiate between the Dual pressure Claude and Heylandt process?
5. Where the Philips helium liquefaction process is employed? Why?
6. Why Simon helium liquefaction process is preferred for liquefaction process for Helium?
7. Which is the best for Helium liquefaction process? Why?
8. Difference between the Linde Brown and L Air Liquide process of Hydrogen seperation?
9. When do you prefer cryogenic separator of Helium?
10. For what type of application, you would prefer to use propellant feed system in rocket propulsion?
11. What are the advantages of Alkali electrolyte over molten carbonate electrolyte?
12. What do you understand by sub atmospheric pressure?
13. Cryogenic engineering will help to reduce the energy growth in India. Discuss.
14. What is meant by magnetic Thermometer?
15. What is the purpose of Optical liquid level indicator?
16. What do you understand by Thermal shields and insulation?
17. Which is the best method for transportation of Cryogenic fluids?
18. Differentiate between the fatigue and impact strength.
19. What are the advantages of pressure swing adsorption over vacuum swing adsorption?
20. Why do you prepare pressure swing adsorption for separation of air?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
Evaluate the liquid yield, the work per unit mass compressed, the work per unit mass liquefied, and
the figure of merit for a simple Linde Hampson system using nitrogen as the working fluid. The
system operates between 1 atm and 300K at point 1 and 200atm and point 2. The compressor may
be assumed to be 75% reversible and the temperature of approach is 10C.
An ideal gas mixture of 30% methane and 70% hydrogen by volume is to be separated at 300K.
Determine the minimum power requirement to produce 1 kg/s of hydrogen.
Determine the inside heat transfer coefficient and friction factor for flow of nitrogen gas at 150K
and 1 atm inside a 12 mm inside diameter smooth tube that is coiled in a 600 mm diameter helix.
The tube wall has a temperature of 160K, and the mass flow rate of the nitrogen gas is 30 kg/s.
Determine the threshold field strength for indium at 3 K, assuming that the parabolic rule for the
transition curve is valid for indium.
247
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
5.
6.
When an external magnetic field of 0.0150 tesla is applied to an indium wire, the material changes
from the superconducting state to the normal state. Determine the temperature of the wire.
Determine the ratio of the electronic contribution to the specific heat to the lattice specific heat for
copper at (a) 20K, (b) 2K, and (c) 0.2K.
Analyze/Evaluate
1.
2.
To develop cryogenic fluids for medical applications.
To develop new cryogenic fluids for space programme.
Unit I
Fundamentals of Cryogenics
Insight on Cryogenics - Properties of Cryogenic fluids - Material properties at Cryogenic Temperatures
- Carnot Liquefaction Cycle - F.O.M. and Yield of Liquefaction Cycle - Inversion Curve Joule
Thomson Effect - Linde Hampson Cycle - Precooled Linde Hampson Cycle - Claudes Cycle Dual
Cycle
Helium refrigerated hydrogen liquefaction systems
9 Hours
Unit II
Separation of Cryogenic Gases
Binary Mixtures - T-C and H-C Diagrams - Principle of Rectification - Rectification Column Analysis
McCabe Thiele Method - Adsorption Systems for purification
Cryogenic gas plants
9 Hours
Unit III
Cryo-coolers and Cryo-refrigerators
J. T. Cryocoolers - Stirling Cycle Refrigerators - G. M. Cryocoolers - Pulse Tube Refrigerators
Regenerators used in Cryogenic Refrigerators
Magnetic refrigerators
9 Hours
Unit IV
Cryogens Handling
Cryogenic Dewar Constructive and Design, Cryogenic Transfer Lines - Different Types of Vacuum
Pumps - Instrumentation to measure Flow - Level and Temperature.
Insulations used in cryogenic systems
9 Hours
Unit V
Cryogens Handling Applications
Applications of Cryogenics in Space Programs Superconductivity - Cryo Metallurgy - Medical
applications
Cryo electronics - cryogenic detectors - cryonics
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
248
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Textbook
1.
Mamata Mukhopadhyay, Fundamentals of Cryogenic Engineering, Prentice Hall of India, 2010.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Thomas M. Flynn, Cryogenic Engineering, Marcel Dekker, New York 2005.
J. G. Weisend, The Handbook of Cryogenic Engineering, CRC Press, 1998.
K. D. Timmerhaus and T. M. Flynn, Cryogenic Process Engineering, Plenum Press, New York,
1989.
R. B Scott., Cryogenic Engineering, Van Nostrand and Company Inc., 1985.
Randall F. Barron, Cryogenic Systems, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd.,
New Delhi, 1985.
249
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M005 REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITIONING
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To understand the underlying principles of operation in different Refrigeration & Air conditioning
systems and components
To study the air-conditioning cycles and their applications
To provide knowledge on design aspects of Refrigeration & Air conditioning Systems
To study the refrigeration and air conditioning components
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(a) The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge capability of analyzing and solving any
concept or problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. To teach and train the
students about the heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students can able to understand the
working concepts of Thermal Engineering.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
Performance analysis of refrigeration system.
Performance calculation of cooling load calculation for air-conditioning system Duct design.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
20
20
20
40
-100
20
20
20
40
-100
Model
Examination*
20
20
20
40
-100
Semester End
Examination
20
20
20
40
-100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Write any five applications of refrigeration
Define RSHF and Bypass factor.
State merits of an air refrigeration system
Define tons of refrigeration
How are the fans classified?
List the components of cooling load estimate.
Define COP.
What is the function of throttling valve?
What is meant by cascade system?
Define specific humidity.
State the function of rectifier in vapour absorption refrigeration systems.
5 *
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
250
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
12. Define by-pass factor for cooling coil.
13. Mention the function of each fluid in a three-fluid vapour absorption system.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
What do you mean by the term infiltration in heat load calculations?
Compare the vapour compression and vapour absorption refrigeration systems?
What is the refrigeration effect of the refrigerant?
Represent the following psychrometric process using skeleton psychrometric chart? a) Cooling and
dehumidification, b) Evaporative cooling.
5. How does the actual vapour compression cycle differ from that of the ideal cycle?
6. Which thermodynamic cycle is used in air conditioning of air planes using air as refrigerant?
7. Differentiate absolute humidity and relative humidity?
8. why reciprocating compressor cannot be used as a vaccum pump for producing high vacuum.
9. What are the specific problems concerned to factory air conditioning?
10. Why a throttle valve is used in vapour compressor refrigerator.
11. What are the different factors which must be considered in evaluating cooling load?
12. What are the different means by which this cooling load can be reduced?
13. Compare the use of two position valve with the use of a modulating valve.
14. Differentiate between comfort air-conditioning and industrial airconditioning.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
Air enters the compressor of an air-standard Brayton cycle at 100kPa, 300K with a volumetric
flow ratio of 5m3/s. The compressor pressure ratio is 10. The turbine inlet temperature is 1400K.
Determine (a) thermal efficiency of the cycle, (b) back work ratio, (c) net power developed in kW.
Dew point temperature of above air is 10.08. How cooling tower should be designed for
refrigeration systems?
A one tonne refrigerator on vapour compression cycle works within the temperature limits of 268
K and 313 K. Refrigerant leaves the compressor dry and saturated. Calculate the COP (i) if there
is no sub-cooling and (ii) If the refrigerant is sub-cooled by 20oC. Also calculate the power
required to run the refrigerator in both the cases. The properties of the refrigerant is
Temp
K
4.
Enthalpy (kJ/kg)
hf
hg
Entropy (kJ/kg K)
hfg
sf
sg
Sp. heat
sfg
Cpl
268
31.5
---
154
0.125
---
0.574
1.03
313
74.59
203.2
---
-5
0.6825
---
---
The atmospheric air at 760 mm of Hg, dry bulb temperature 15oC and wet bulb temperature 11oC
enters a heating coil whose temperature is 41oC. Assuming by-pass factor of heating coil as 0.5,
determine dry bulb temperature, wet bulb temperatre and relative humidity of the air leaving the
coil. Also determine the sensible heat added to the air per kg of dry air.
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
2.
Design a vapour compression refrigeration system that will maintain the refrigerated space at 15C while operating in an environment at 20C using refrigerant 134a as a working fluid.
A multi-storied shopping mall has installed 5 x 110 TR reciprocating compressors of which
fourcompressors are in use for 16 hours per day. Due to higher energy cost shopping mall chief
engineerhas decided to replace reciprocating compressors with screw compressors. Chief engineer
needfollowing input from energy consultant.i. Comparison of power consumption of both
251
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
reciprocating and screw compressors?ii. Annual cost savings (for 350 days operation). Present unit
cost Rs 6.50 per kWh, investmentfor 220 TR machine Rs 30 lakh.iii. What should be the size of
cooling tower required for proposed screw compressors?
Unit I
Refrigeration Systems
Multistage and multiple vapour compression refrigeration systems - Cascade system - Vapour
absorption refrigeration system- Single Effect / Double Effect Systems Types Analysis Advanced
cycles .Simulation of Refrigeration cycles, Flowcharting and programming
Solar vapour absorption system
9 Hours
Unit II
Refrigeration System Components
Refrigeration Compressors, Different Types, Performance, Capacity Control Evaporators,
Evaporators Circuitry, Applications and Different Types Condensers, Types, Evaporative Condenser,
Optimum Cooling Water Rate and Velocity, Cooling Towers, Range and Approach, Air Washers,
Spray Ponds, Natural and Induced Draught System Expansion Devices
Solenoid valve and Shutoff valve
9 Hours
Unit III
Refrigerants Refrigeration Controls and Applications
Refrigerants - properties - selection of refrigerants, Alternate Refrigerants, Refrigeration plant controls
- testing and charging of refrigeration Units. Balancing of system components. Control system of
temperature, Pressure, Oil Flow. Applications to refrigeration systems - ice plant - food storage plants milk -chilling plants refrigerated cargo ships
Defrost control concept
9 Hours
Unit IV
Air Conditioning Systems and Components
Characteristics of Human metabolic activities with changing climate-sensation of heat and comfort
zone- Design of solar shading devices and Mechanical Ventilation systems- Construction Details of
Room Air Conditioner Window Type, Package Type, Split Type Central Units Air Distribution
Devices Air Circuits Air Supply System air cleaning and air filters - humidifiers - dehumidifiers air washers - elementary treatment of duct design - air distribution system
Automotive air conditioning system
9 Hours
Unit V
Cooling Load Calculations
Types of loads considered for Air Conditioning - Design of space cooling load - heat transmission
through building-Solar radiation - infiltration - internal heat sources (sensible and latent) - outside air
and fresh air load - estimation of total load - Domestic, commercial and industrial systems - central air
conditioning systems. Computerized cooling load calculations Packages - Simulation of
psychometric processes - Simulation of air flow in AC systems - EER value assessment Environmental issues in simulation - Computerized energy calculation
Radiant time series cooling load calculation.
9 Hours
Total: 45 + 15 Hours
252
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Textbook
1.
C. P. Arora, Refrigeration and Air Conditioning, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd.,
New Delhi, 2008.
References
1. Langley and C. Billy, Refrigeration and Air conditioning, Ed. 3, Engle wood Cliffs (NJ), Prentice
Hall of India ,New Delhi, 2006.
2. Roy J. Dossat, Principles of Refrigeration, Pearson Education , New Delhi, 2007
3. N. F Stoecker and Jones, Refrigeration and Air Conditioning, TMH, New Delhi, 2008
4. Manohar Prasad, Refrigeration and Air Conditioning, Wiley Eastern Ltd., 2007
5. J. B Hains, Automatic Control of Heating & Air conditioning ,Tata McGraw Hill Publishing
Company Pvt Ltd., 2005
253
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M006 RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the importance of renewable energy and its utilization for the thermal and electrical
energy needs and also the environmental aspects of these resources
The students are expected to do understand and analyze the pattern of renewable energy resources
and suggest methodologies / technologies for its utilization
PROGRAMME OUTCOME
(b) The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge, capability of analyzing and solving any
concept or problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students will be able to
understand the working concepts of thermal engineering.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
Design of solar thermal and solar Photovoltaic system.
Ability to develop wind turbine and biogas plant.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
35
35
30
--100
35
35
30
--100
Model
Examination*
35
35
30
--100
Semester End
Examination
35
35
30
--100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
6
State various subsystems in a solar thermal energy conversion system.
State the principle of solar thermo electric convertors.
What are the applications of solar PV system?
Which are the types of geothermal fluids? What is the temperature range?
What is geothermal gradient?
What is geothermal deposit?
State the various forms of Ocean Thermal Resources.
State the merits and limitations of Ocean Energy Conversion Plants.
What are the limitations of ocean wave energy?
Write the principle of oscillating air column ocean wave machine.
State the essential features of a probable site for a wind farm.
Define yaw control and pitch control.
What is ethanol?
What is methanol?
State the various principal routes of Biomass energy conversion to useful energy.
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
254
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
16.
17.
18.
19.
What are the types of fuel cells?
Define hydrogen energy.
What is nuclear fusion?
State the various main equipments and main auxiliaries in a Municipal Waste to Energy
Incineration plant. State the typical ratings.
20. What is Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells (MCFC)?
21. What is Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC)?
Understand
1.
Compare the following types of collectors to be used for a solar thermal power plant with respect
to temperature, Concentration ratio, Suitability
i.
Flat plate collector
ii.
Evacuated tube collector
2. Difference between the distributed collector system and central receiver system in solar thermal
applications.
3. Why thermal storage is preferred in solar power plants?
4. What is hot dry rock geothermal source? How is it used?
5. Compare a geothermal power plant and a thermal power plant.
6. Describe a binary cycle geothermal power plant.
7. Differentiate between ocean wave energy and ocean tidal energy
8. Compare ocean waves and ocean tides with references to the period, energy density and energy
conversion plants.
9. How a wind farm is controlled? Which are the hierarchical control levels?
10. Describe the construction of a typical three blade horizontal shaft wind turbine generator unit.
11. What is the difference between fuel cell and battery?
12. Derive an expression for emf of a fuel cell.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Calculate the angle made by beam radiation with the normal to a flat collector on December 1, at
9.00 AM., solar time for a location at 28o 35 N. The collector is tilted at an angle of latitude plus
10o, with the horizontal and is pointing due south.
Wind at 1 standard atmospheric pressure and 15oC temperature has a velocity of 10 m/s.
The turbine has diameter of 120 m and its operating speed in 40 r.p.m at maximum efficiency.
Calculate
i.
The total power density in the wind stream
ii.
The maximum obtainable power density assuming efficiency is 40%
iii.
The total power produced in kW
iv.
The torque and axial thrust
Why geothermal energy has not been in commercial use in India?
For a parabolic collector of length 2 m, the angle of acceptance is 15o. Find the concentration ratio
of the collector.
What are the main four fusion reactions, which are considered for use in fusion reactors? Which
one is most favorable reaction?
Unit I
Solar Energy
The sun as a perennial source of energy; flow of energy in the universe and the cycle of matter in the
human ecosystem; direct solar energy utilization - solar thermal applications water heating systems,
255
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
space heating and cooling of buildings, solar cooking, solar ponds, solar green houses, solar thermal
electric systems;
Solar photovoltaic power generation; solar production of hydrogen
9 Hours
Unit II
Ocean Energy and Geothermal Energy
Wave energy Energy from waves; energy potential, Conversion devices; Tidal Energy Basic
principle, energy potential, Conversion systems, Ocean thermal energy conversion Methodology,
Applications. Geothermal energy - classification of geothermal resources; schematic of geothermal
power plants, operational and environmental problems
Estimation of energy and power in simple single basin and double cycle tidal system
9 Hours
Unit III
Wind Energy
Basic principles of wind energy conversion classification of wind turbines - Types of rotors ; Design
of windmills wind turbine rotor, regulating system for rotor, wind power generation curves - wind
data and energy estimation; site selection considerations Merits and demerits of wind energy systems
Selection of optimum wind energy generators
9 Hours
Unit IV
Bio-Energy
Bio mass resources Conversion technologies Biochemical conversion Biomass gasification;
Biogas production, Factors affecting bio gas production Biogas plants; Energy recovery from
Urban waste, power generation from liquid waste Biomass cogeneration - Bio-fuels
Power generation from land fill gas
9 Hours
Unit V
Emerging Technologies
Fuel cell types AFCs, PEMFC, PAFC, MCFCs, SOFC Comparison of Electrolysis and the Fuel
cell process; Hydrogen energy hydrogen production - hydrogen storage types, using nanocrystalline magnesium based nickel hydride; alcohol energy; nuclear fusion; cold fusion; application
Merits and demerits
Power from satellite stations
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
D. P. Kothari, K. C. Singal and Rakesh Ranjan, Renewable Energy Sources and Emerging
Technologies, Prentice Hall of India , New Delhi, 2009.
References
1.
2.
Godfrey Boyle, Renewable energy power for sustainable future, Oxford University Press in
association with the Open University, New Delhi,2004.
S. A. Abbasi and Naseema Abbasi, Renewable energy sources and their environmental impact
Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi,2001.
256
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
3.
4.
5.
John W. Twidell and Anthony D. Weir, Renewable energy resources, English Language Book
Society (ELBS), 2006.
G. D. Rai, Renewable Energy Sources, Khanna Publishers, New Delhi 2000.
Harsh K. Gupta, Sukanta Roy, Geothermal energy: an alternative resource for the 21st century,
Elsevier Publication, Netherlands, 2007.
257
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M007 AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge to the students in the principles of operation and constructional details of
various Automobile components and subsystems
To impart knowledge to students in various systems of Automobile Engineering and to have the
practice for Assembling and Dismantling of Engine Parts
At the end of the course, the students will be able to have a sound knowledge of the vehicles and
the mechanisms involved in the starting systems, ignition systems and an engine control systems
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
(j) The graduates can become job-givers rather than just job-seekers.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and Modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
Graduates can able to diagnose, if any malfunction occurs in automobiles.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I*
Test II*
30
40
30
--100
30
40
30
--100
Model
Examinations*
30
40
30
--100
Semester End
Examination
30
40
30
--100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
7 *
Name the parts that are attached to the engine block.
What is the function of camshaft?
What is a circlip? Where it is used?
State the advantages of synthetic lubricating oils.
Name a few materials used for oil filter elements.
What is a dip stick?
What is known as common rail fuel injection system?
What are the functions of a carburettor?
What is the voltage of the batteries generally used in the automotive ignition systems?
What are the two basic approaches to decrease pollution from automobiles?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The
remaining 10 marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated
for 50 marks.
258
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
Define light-off temperature of a catalytic converter.
Name the electrolyte used in a lambda probe.
State the functions of automobile transmission system.
What is an over drive? What are its advantages?
Define whirling of shafts.
What are the objectives of vehicle suspension?
Define offset with reference to automobile wheels.
What are primary and secondary brakes?
Name any two brake shoe adjusters.
List main parts of an ABS.
What is a radial engine?
Name various type of fuel cells.
Enlist main components of a hybrid electric car.
Give some application of metal spinning process and explosive forming.
List out various types of plastics.
What is meant by thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic?
Give some application of Blow molding process.
What is meant by rotational molding?
Name any two brake shoe adjusters.
Name any Indian vehicle using common rail
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
How are the materials choosen for chassis frames and body?
Which types of engines generally employ air cooling system?
How does the feed pump gets drive?
How is the seizing of piston caused?
Why are the baffle plates provided in the fuel tank?
Which type of final drives is used most commonly?
Why is an automobile tyre usually black in colour?
State the advantages of hydraulic brakes over mechanical brakes?
Which material is generally used for brake drums? why?
Out of the camber and the castor , which is measured first and why?
Why do we provide gear box in a vehicle?
Where is the contact breaker located on the engine?
Why asbestos being phased out as material for clutch facings?
Compare plug-in-hybrids with conventional hybrids.
Out of the diesel and petrol engines , which involves less risk of catching fire ? why ?
Give the basic difference between a fluid flywheel and a torque converter.
Apply
1.
2.
An automobile clutch has a clutch plate of 160mm inside and 240mm outside diameters. Six
springs in the clutch provide a total force of 4.8 kN , when the clutch is new and each spring is
compressed 5mm. The maximum torque developed by the automobile engine is 250Nm .
Determine (i) factor of safety for the new clutch and (ii) the amount of wear of the clutch facing
that will take place before the clutch starts slipping . Assume coefficient of friction for the facing is
0.3.
Two shafts, Whose axes are inclined at 20 are connected by means of a Hookes joint at 20 . The
driving shaft rotates uniformly at 500 r.p.m .What are the maximum and the minimum velocities of
the driven shaft?
259
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit I
Vehicle Structure and Engines
Types of Automobiles - Vehicle Construction Chassis Frame and Body aerodynamics.
Components of Engine Their forms, Functions and Materials - Review of Cooling and Lubrication
systems in Engine Turbo Chargers Engine Emission Control by 3Way Catalytic Controller .
Alternative Energy Resources - LPG Bio Diesel Electric vehicles.
Hybrid vehicles fuel cells
9 Hours
Unit II
Engine Auxiliary Systems
Carburetorworking principle- Electronic fuel injection system Mono-point and Multi - Point
Injection Systems Construction, Operation and Maintenance of Lead Acid Battery - Electrical
systems Battery generator Starting Motor and Drives Lighting and Ignition (Battery, Magneto
Coil and Electronic Type)-Regulators-cut outs. CRDI
Variable geometry technology
9 Hours
Unit III
Transmission Systems
Clutch Types and Construction Gear Boxes, Manual and Automatic Simple Floor Mounted Shift
Mechanism Fluid flywheel-Torque convertors Propeller shaft Slip Joint Universal Joints
Differential and Rear Axle Hotchkiss Drive and Torque Tube Drive.
Over drives transfer box
9 Hours
Unit IV
Steering, Brakes and Suspension
Wheels and Tyres Wheel Alignment Parameters - Steering Geometry and Types of steering gear
box Power Steering Types of Front Axle Suspension systems Braking Systems Types and
Construction Diagonal Braking System Antilock Braking System
Tubeless tire, wire drive steering mechanism
9 Hours
Unit V
Engine Control Systems
Control modes for fuel control-engine control subsystems ignition control methodologies different
ECUs used in the engine management block diagram of the engine management system. In vehicle
networks: CAN standard, format of CAN standard diagnostics systems in modern automobiles.
Safety system: air bags, parking sensor, cruise control
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
Kirpal Singh, Automobile Engineering Vol. 1& 2, Standard Publishers, New Delhi. 2009.
References
1.
2.
Crouse and Anglin, Automotive Mechanism, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd.,
New Delhi, 2003.
Newton, Steeds and Garet, Motor vehicles, Butterworth Publishers, 2000
260
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
3.
4.
5.
S. Srinivasan, Automotive Mechanics, 2003, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd.,
New Delhi,2003
Joseph Heitner, Automotive Mechanics, East-West Press, 2006.
H. M. Sethi, Automobile Technology, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New
Delhi, 2007
261
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M008 INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL ENGINEERING
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To provide sound knowledge about various techniques used for the measurement of industrial
parameters
To have an adequate knowledge about Transducers and various elements and components of Control
system
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
(g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
Ability to contribute to process automation and instrumentation.
Ability to increase plant efficiency, profitability and productivity by devising and implementing
better control systems.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination$
Semester End
Examination**
40
35
25
--100
35
45
20
--100
30
40
30
--100
30
35
35
--100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
8
Define Measurement.
What is Calibration?
Define Sensitivity.
Define Precision.
What is Systematic Error?
Mention the types of Errors.
What is piezoelectric effect?
What is meant by moral autonomy?
Name any two devices used for acceleration measurement.
Name any two devices used for vibration measurement.
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
262
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
Define Photo cell.
Define Solar cell.
State the principle used in Bimetallic thermometer.
Define Thermocouple.
Define Thermistor.
Name the parameters used for measurement of temperature.
What is the significance of Pressure measurement?
What is Absolute Pressure?
Define Gauge Pressure.
Give the value for standard Atmospheric pressure.
Define Sensitivity of a control system.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
How electrical amplifications are superior to mechanical amplifications?
Distinguish between Vibration and Shock.
What is the advantage of using Multi Lever system in Force measurement?
How do the static and dynamic characteristics of instruments affect measurement?
Compare the static and dynamic characteristics of Measuring Instruments.
Distinguish between Recording and Indicating instruments.
Why Emissivity is important in radiation temperature measurement?
Give the expression for calculating conduction error in temperature measurement of flowing fluids.
Why is reference temperature necessary when using thermocouples?
What are the difficulties associated with measurement of low resistance?
Compare RTD with Thermistor.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
In a NC machine, the displacement of the tool is to be measured accurately. Suggest any one
instrument for this.
In a mechanical industry, the floor vibrations surrounding a high-speed compressor are to be
measured. Discuss any two methods suitable for this condition.
How is low pressure measured?
A Thermistor of resistance 1000 ohms at 50C temp is connected in a bridge circuit having all
arms of resistance 1000 ohms. The supply voltage to the bridge is 40V. The resistance of the
Thermistor increases by 5 ohms for a decrease of temp of 1C. Find the temp if the open circuit
voltage of the bridge is 50mv.
An automobile driver uses a control system to maintain the speed of the car at a prescribed level.
Sketch a block diagram to illustrate this feedback system.
Unit I
General Concepts of Measurement
The three stages of Generalized Measurement System Performance Characteristics Static and Dynamic
characteristics - Factors considered in Selection of instruments Error analysis and classification, Sources
of error Transducers, Classification - Displacement and Velocity transducers, Tachometer. Types of
Electric Strain Gauges Strain gauge bridges
Calibration of strain gauges, gauging techniques and other factors
9 Hours
263
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit II
Acceleration, Vibration and Level Measurement
Elementary Accelerometers and Vibrometers - the Seismic instrument as Accelerometer, Piezoelectric and
Bonded Strain gauge Accelerometers Calibration of Accelerometers and Vibrometers Level
measurement Float and Electrical conductivity methods
Introduction to fast fourier transform (FFT) analyzer
9 Hours
Unit III
Temperature and Pressure Measurement
Glass thermometers, Platinum resistance thermometers, Thermistors, Thermocouples, Total Radiation
Pyrometers, Temperature measuring problems in flowing fluid - Manometers, Pressure cells, Elastic
transducers - Bulk modulus pressure gauge, McLeod gauge, Thermal Conductivity gauge
Calibration of pressure gauge using dead weight tester
9 Hours
Unit IV
Signal Conditioning and Data Acquisition
Instrumentation Amplifier characteristics Wheatstone bridge Integration, Differentiation and Sampling,
A / D and D / A conversion Elements and Types of Data Acquisition system Data logging. Recording
instruments Chart recorder, X-Y recorder and UV recorder
Introduction to indicating instruments
9 Hours
Unit V
Control Systems
Open loop and Closed loop controls, Elements of Closed loop control system - Introduction to Sampled
data, Digital control and Multivariable control system, Mathematical models for Mechanical and Electrical
systems, Transfer function, Block diagram representation,. Applications of Control systems Machine Tool
control, Position Control system using Servo motor, Feed water control, Speed control of drives,
Temperature control system
Signal flow graphs and control system components.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
Thomas G. Beckwith, Roy D. Marangoni and V.John H. Lienhard, Mechanical Measurements,
Pearson Education, New Delhi, 2006.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
I. J. Nagrath and Madan Gopal, Control Systems Engineering, New Age International, New Delhi,
2007.
Ernest O. Doebelin, Measurement Systems - Application and Design, Tata McGraw Hill
Publishing Company Pvt Ltd.,, New Delhi, 2005.
D.V.S. Murty, Transducers and Instrumentation, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2010.
Richard S. Figliola, Donald E Beasley, Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements, Wiley
India Pvt Ltd, New Delhi, 2010.
D. Patranabis, Principles of Industrial Instrumentation, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company
Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2009.
264
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M009 DESIGN OF JIGS, FIXTURES AND PRESS TOOLS
(Use of approved design data book is permitted)
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To learn various design considerations in designing jigs and fixtures for industrial application
To impart knowledge on press work technology and to learn the various design considerations for
making press work dies
Able to design the jigs and fixtures and press work dies for the real world applications
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(g) Graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement in Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
(j) The graduates can become job-givers rather than just job-seekers.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
Able to design jigs, fixtures and press work dies for machine tool application.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I*
Test II*
30
30
25
15
-100
20
30
20
30
-100
Model
Examinations*
20
30
20
30
-100
Semester End
Examination
20
20
20
40
-100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11
12
**
What is meant by tooling?
Define jigs and fixtures.
List the objectives of tool design.
What is the difference between production and inspection devices?
List some important tool materials.
What is clamping?
Define tolerance.
Define drill bush.
List different types of jigs.
List different types of fixtures,
List the advantages of modular fixtures.
List the uses of inspection fixtures.
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
265
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
13 What is meant by die clearance?
14 What are the major advantages of compound dies?
15 What is purpose of stop?
16 List out various types of tooling
17 What are the advantages of jigs and fixtures?
18 What are the important properties of tool materials?
19 List different types of drill bushes.
20 What are the different types of error considered in jigs and fixtures design?
Understand
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
What is the difference between jigs and fixtures?
Where will you select hydraulic clamping?
What is the use of tolerances in jigs and fixtures design?
What are the general rules to be applied for designing jigs and fixtures?
Why clearance required between work piece and bush?
What is milling fixture? Name any two.
List the steps to be followed in fixture designing.
What are the functions of broaching fixture?
Where will you prefer press work over metal cutting process?
What is the difference between progressive and combination dies?
what is meant by press tonnage?
What is the standard method of holding job in surface grinding?
What is the minimum wall thickness of drilling bushes?
How the jigs are classified?
Why angular clearance is necessary?
Apply
1 How to select the clamping type?
2 How to identify the deviation in V block locator?
3 How to decide drilling bush material, length, wall thickness and clearances?
4 How the turning fixtures differ from milling fixture?
5 Select the jig type for drilling holes in outer periphery of cylindrical Component and state the
reason.
6 Select the die type and state the reason for selection to produce M20 plain washer.
Analyze/ Evaluate
1
2
3
Design drilling jig for engine cylinder head.
Design lathe fixture for I.C.Engine crank case machining
Design die for Induction motor cooling fan cover
Unit I
Purpose Types and Functions of Jigs and Fixtures
Tool design objectives - Production devices - Inspection devices - Materials used in Jigs and Fixtures
Types of Jigs - Types of Fixtures-Mechanical actuation-pneumatic and hydraulic actuation-Analysis of
clamping force-Tolerance and error analysis
Locating and supporting methods.
9 Hours
266
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit II
Jigs
Drill bushes different types of jigs-plate latch, channel, box, post, angle plate, angular post, turnover,
pot jigs-Automatic drill jigs-Rack and pinion operated - Air operated Jigs components - Design of Jigs
for given components
Clearance between work piece and bushing
9 Hours
Unit III
Fixtures
General principles of boring, lathe, milling and broaching fixtures- Grinding, planning and shaping
fixtures, assembly, Inspection and welding fixtures- Modular fixtures. Design of fixtures for given
component.
Errors in design and use of fixtures
9 Hours
Unit IV
Press Working Terminologies and Elements of Dies and Strip Lay Out
Press working terminology-Presses and press accessories-Computation of capacities and tonnage
requirements - Elements of progressive combination and compound dies: Die block-die shoe - Bolster
plate-punch holder-guide pins and bushes strippers knockouts-stops pilots
Bending springback & bend radius
9 Hours
Unit V
Design and Development of Dies
Design and development of progressive and compound dies for Blanking and piercing operations.
Bending dies development of bending dies-forming and drawing dies-Development of drawing dies.
Design considerations in forging, extrusion, casting and plastic dies
Design a die for a given simple cup shaped component
9Hours
Total: 45 hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
Edward G. Hoffman, Jigs & Fixture Design, Thomson Delmar Learning, Singapore, 2004
C. Elanchezhian, Design of Jigs, Fixtures and Press Tools, Eswar Press, 2007
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
David Spitler, Jeff Lantrip, Fundamentals of Tool Design, Society of Manufacturing Engineers,
2003
Fred Herbert Colvin, Jigs and Fixtures: A Reference Book Showing Many Types of Jigs and
Fixtures in Actual Use, and Suggestions for Various Cases, Nabu Press, 2010
P. H. Joshi, Jigs & Fixtures,Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi 2004
Hiram E Grant, Jigs and Fixture, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi,
2003
Fundamentals of Tool Design, CEEE Edition, ASTME, 1983
267
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M010 COMPOSITE MATERIALS AND MECHANICS
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the need of composite in structural and non-stuctural applications
To know the manufacturing, properties and application of different types of reinforcement and
matrix
To understand the fabrication techniques involved in the polymer, metal, and ceramic matrix
composites
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
To use the composite materials in various applications.
Able to select the proper fabrication technique required to manufacture the composite products.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
10
S.
No
Blooms Taxonomy
(New version)
Test I*
Test II*
Model
Examinations*
1
2
3
4
5
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
40
40
20
--100
35
40
25
--100
30
40
30
--100
Semester
End
Examination
30
40
30
--100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
What is mean by composites?
Explain the need for composites.
List out the advantages of composite.
What are all the types composite based on matrix?
Draw neat sketches for (i) fiber (ii) particulate and (iii) laminar composites and mark the different
constituents.
6. Mention various forms of fibers used for composite materials.
7. State any two functions of matrix in composite materials.
8. State any two functions of reinforcement in composite materials.
9. What is mean by Whiskers?
10. What is mean by Thermoset Matrix Materials?
11. State the benefits of polymer matrix composites.
10
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
268
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
Give two applications for composites in biomedical applications.
What is mean by lamina?
Define laminate.
What is meant by hybrid composites?
Write some of the application of filament winding method.
State any four advantages of RTM.
List any four defects in compression molded SMC part.
What is mean by Nonautoclave curing?
Define the term Metal Matrix Composite.
Write down applications of Metal Matrix Composites.
List out the advantages of aluminium matrix composite.
What is mean by Rule of Mixture?
Define the term squeeze casting
What is the liquid state processes used for manufacturing MMCs?
What is mean by powder metallurgy?
State the benefits of powder metallurgy.
What are monolithic ceramics?
Explain the Chemical Vapor Infiltration processes.
Write the salient properties of ceramic materials.
State any two methods used for manufacturing Carbon/Carbon composites.
State any two applications of Carbon/ Carbon composites.
What is mean by oxidative etching?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
How the composite differs from alloy?
What is the need of composite?
Why the composite is an orthotropic material?
What is use of fillers in composites?
Why small diameter fiber is preferred in composite?
What are the advantages of ceramics over metals as fibers?
Why Sol-gel technique is used for manufacturing glass fiber?
Why the polymer matrix composite used in large proportion in aerospace?
Why the hand lay-up process mostly preferred?
How composite is manufactured by RTM process?
What is the use of hardener in polymer matrix composite?
How the liquid state processes used for manufacturing of MMCs?
What is the use of control systems in an autoclave molding process?
How the volume fractions effect the overall performance of the composites?
What are all the various process involved in the recycling of PMCs
Where the ceramic matrix composite are mostly used?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
How many elastic constants are required to describe stress to strain relation for an isotropic
material, an orthotropic material and an anisotropic material?
What is ratio to be required for mixing the hardener in epoxy for curing purpose?
How the fiber angle can be changed in filament winding machine?
Find out the youngs modulus of composite having 60% volume fraction of fiber. Ef = 68.9 GPa
and
Em = 3.45GPa
Evaluate the effect of fiber volume fraction in composite.
Give the solution to avoid improper mixing of reinforcement in MMC.
269
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit I
Introduction to Composites
Fundamentals of composites, characteristics, need for composites, Enhancement of properties,
Reinforcements - glass fibers, boron fibers, carbon fibers, organic fibers, aramid fibers, ceramic fibers,
oxide and nonoxide fibers, Forms of reinforcements - Roving , Woven fabrics Non woven, random
mats, whiskers, Matrix materials Polymers - Thermosetting resins, thermoplastic resins , Metals,
Ceramic materials
Fiber surface treatment, sol-gel technique
9 Hours
Unit II
Polymer Matrix Composites
Processing of polymer matrix composites- hand lay-up, Spray lay-up processes, Compression moldingSMC Reinforced reaction injection molding, Resin transfer molding, Pultrusion, Filament winding,
Applications of polymer matrix composites
Auto clave method, Bulk molding compound, vaccum assisted resin transfer molding,
9 Hours
Unit III
Metal Matrix Composites
Characteristics of MMCs, Various types of Metal matrix composites, Advantages and limitations of
MMCs, Effect of reinforcements on properties Volume fraction Rule of mixtures, Processing of
MMCs - Liquid state processing- stir casting, squeeze casting, infiltration, solid state processing Powder metallurgy, diffusion bonding, In situ processes, applications of MMCs
Selection of reinforcement and matrix for MMC
9 Hours
Unit IV
Ceramic Matrix Composites
Need for CMCs, Processing of CMCs- cold pressing and sintering, hot pressing, infiltration, chemical
vapor deposition and chemical vapor impregnation, sol-gel and polymer pyrolysis, high temperature
synthesis properties and applications of CMC.
Quality inspection methods for composites
9 Hours
Unit V
Advances in Composites
Carbon fiber composites properties, chemical vapor deposition oxidative etching, liquid phase
oxidation carbon/carbon composites - properties and applications of C/C Composites, multifilament
superconducting composites
Applications smart composites
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
K. K. Chawla, Composite Materials Science and Engineering, Springer, New York, 2008.
P. K. Mallick, Fiber-Reinforced Composites: Materials Manufacturing and Design, CRC Press,
New Delhi,2007.
270
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
References
1. A. K. Kaw, Mechanics of Composite Materials, CRC Press, New Delhi 2005
2. S. C. Sharma, Composite materials, Narosa Publications, New Delhi, 2000.
3. www.netcomposites.com
4. http://www.ae.iitkgp.ernet.in/ebooks/index.html
271
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M011 DESIGN OF HEAT EXCHANGERS
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the basic types of heat exchangers to fabricate the heat exchanger
To study the stress and flow analysis and failures in heat exchanger
To study the performance and application of heat exchanger
To study the types of condensers and cooling towers
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(b) The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge, capability of analyzing and solving any
concept or problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students will be able to
understand the working concepts of thermal engineering.
(c) The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in
various materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting,
fabrication, machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of
the course, students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable
component in industry.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Performance analysis of condensers.
Performance calculation of cooling towers.
Temperature Distribution in the heat exchanger and its effects.
Stress analysis in tubes, pressure vessels.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
11
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
20
30
20
30
-100
20
30
20
30
-100
Model
Examination*
20
30
20
30
-100
Semester End
Examination
20
30
20
30
-100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
11
What is a heat exchanger?
How the heat exchangers are classified?
Define heat exchanger effectiveness.
What do you meant by fouling in heat exchanger?
Give four industrial application of heat exchanger
What are the effects of turbulence?
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining
10 marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
272
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
Define the term thermal stress
List out the limitation of plate heat exchanger
What are the modes of condensation?
Write down the importance of friction factor.
Mention the applications of the heat exchanger.
What is meant by film boiling?
Write the Weins displacement law.
Write the relationship between effectiveness and number of transfer units for a parallel flow heat
exchanger.
15. Define Reynolds number.
16. Identify industries where the cooling tower is used.
17. What are the salient features of multiple effect evaporators?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
Differentiate regenerator and recuperator.
Why are baffles used in shell-and-tube used in heat exchanger?
What characterizes a unit as compact?
Differentiate evaporator and condenser.
Classify tubular heat exchanger based on operating range?
In what way the extended surfaces are helpful in heat exchangers?
Differentiate effectiveness and number of transfer units method.
compare film wise and drop wise condensation.
Why Reynolds number is important?
What is the effect of liquid pressure on boiling?
Find the various factors which have an effect on heat transfer capacity of an Evaporator.
How the local and average convection coefficients for flow past a flat plate are related?
Characterize the effect of non-condensable gases on rate of condensation.
Apply
1.
2.
Oil is cooled to 375K in concurrent heat exchanger by transferring its heat to the cooling
water that leaves the cooler at 300K. However, it is required that oil must be cooled down
to 350K by lengthening the cooler while the oil and water flow rates, their inlet
temperatures and other dimensions of the cooler remaining.
Air at 1 atm and 400K and with a velocity of U=10 m/s flows across a compact heat exchanger
matrix having the configuration of circular tube continuous fin heat exchanger. Surface 8.0-3/8T:
tube OD=1.02cm; fin pitch=3.15/cm; fin thickness=0.033cm; fin area/total area=0.839; air-passage
hydraulic diameter=0.3633 cm; free area/frontal area, =0.534; heat transfer area/total
volume=587m2/m3. Calculate the heat transfer coefficient, and frictional pressure drop for the air
side. The length of the matrix is 0.6 m.
A gas-to-air single pass cross-flow plate-fin heat exchanger has overall dimensions of
0.300m X 0.600m X 0.900m and employs strip fins on the air side. The following
information is provided for the air side:
Geometrical properties
operating conditions
Fin density = 0.615mm-1
Volumetric airflow rate = 0.6m3 /s Plate spacing
= 6.35mm
Reynolds number = 786
Fin offset length = 3.18mm; Fanning friction factor = 0.0683
Air flow length = 0.6m;
Inlet pressure = 110kPa
Hydraulic diameter = 0.002383m; Inlet temperature = 4C
Fin metal thickness = 0.15mm; Outlet temperature = 194.5C
Minimum free-flow area =0.1177m2; Gas constant forair = 287.04J/kgK;
273
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Free-flow area / frontal area = 0.437. Determine the air-side pressure drop.
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
Distilled water with a flow rate of 50kg/s enters a baffled shell-and-tube heat exchanger at 32C
and leaves at 25C. Heat will be transferred to 150kg/s of raw water coming from a supply at
20C. Design a heat exchanger for this purpose. A single shell and tube pass is preferable. The
tube diameter is 19mm OD with 16mm ID and tubes are laid out on a 6.25cm2pitch. A maximum
length of the heat exchanger of 8m is required because of space limitations. The tube material
thermal conductivity is 42.3W/mK. Assume a total fouling resistance of 0.000176m2K/W. Note
that surface over design should not exceed 30%. The maximum flow velocity through the tube is
also suggested to be 2m/s to prevent erosion. Perform a thermal and hydraulic analysis of the heat
exchanger.
2.
A heat exchanger is required to heat treated cooling water with a flow rate of 60 kg/s from 10C to
50C using the waste heat from water, cooling from 60C to 20C with the same flow rate as the
cold water. The maximum allowable pressure drop for both streams is 120 kPa. A gasketed plate
heat exchanger with 301 plates having a channel width of 50 cm and a vertical distance between
ports of 1.5 m is proposed and the plate pitch is 0.0035 m with an enlargement factor 1.25. The
spacing between the plates is 6 mm. Plates are made of stainless steel (16.5W/mK). For a two-pass
arrangement, analyze the problem to see if the proposed design is feasible. Could this heat
exchanger be smaller or larger?
Unit I
Heat Exchanger Types and Fabrication
Heat exchanger types fluid flow arrangement, types of application Heat exchanger fabrication
tubular versus flat plate construction, tubes-to-header and joints, Header-sheet mounting,finned
surfaces,tube bending and joining -Regenerators and Recuperators Industrial Applications
Temperature Distribution and its Implications
Types of regenerators and recuperators
9 Hours
Unit II
Flow and Stress Analysis
Regenerators heat transfer analysis - Governing equation influences of longitudinal wall heat
conduction and transverse wall heat conduction - Effect of Turbulence Friction Factor Pressure
Loss Extended surface, tubular, plate heat exchanger - Stress in Tubes Header sheets and Pressure
Vessels Thermal Stresses, Shear Stresses, Types of Failures
Stress analysis of pulsed flow in plate type heat exchanger
9 Hours
Unit III
Design Aspects
Basic concepts LMTD method, inverse relationships, the effectiveness method Design process Effect of temperature-dependent fluid properties, fin efficiency and surface effectiveness, layer
stacking and banking factor, entry and exit losses, header and distributors, effect of longitudinal
conduction - Baffles Effect of Deviations from Ideality
Pinch design
9 Hours
274
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit IV
Industrial Compact Heat Exchangers
Types and performance of heat exchanger - Tube-fin, Diffusion bonded, welded plate, plate and shell,
spiral, compact shell and tubes heat exchanger reactors with reactant injection, catalytic reactor
exchanger surface selection process exchangers, refrigeration exchangers
Fouling in heat exchangers
9 Hours
Unit V
Condensers and Cooling Towers
Condenser types Design of Surface and Evaporative Condensers Cooling Tower
Performance characteristics.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
Ramesh K. Shah, Fundamentals of Heat Exchanger Design, Wiley, 2003
Sadik Kakac and Hongton Lu, Heat Exchangers: Selection, Rating and Thermal Design, CRC
Press, 2002.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
John E. Hesselgreaves, J.E Hesselgreaves, Hesselgreaves, Compact Heat Exchangers: Selection,
Design and operation, Pergamon Pub 2001.
Bernd Becher, Hilla Becher, Cooling Towers Mit Press 2005.
Detlev G Kroger, Air cooled Heat Exchanger and Cooling Towers:Thermal Flower
Performance Evaluation and Design Vol-2, Pennwell Books Pub 2004.
L. Wang, B. Sunden and R. M Manglik, Plate Heat Exchangers Design, Application and
Performance - Computational Mechanics 2007.
D. Q. Kern, Process Heat Transfer, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi,
2004.
275
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M012 VIBRATION AND CONDITIONS MONITORING
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the basics of vibration and condition monitoring of mechanical systems
At the end of the course students will be able to apply this to practical problems
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology
subjects and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern
practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
To understand the different types of vibrations and degrees of freedom of a system.
Able to find out the defects due to vibration in different tools.
Strengthen the machine condition monitoring techniques of the systems.
Able to control the vibration of the machine.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S.No.
1
2
3
4
5
12
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
25
30
30
15
-100
20
30
30
20
-100
Model
Examination*
10
20
30
40
-100
Semester End
Examination
10
20
30
40
-100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
12
Define vibration.
Define forced vibration
Define free vibration.
Define resonance.
Define frequency
Define simple harmonic motion
Define critical speed of the shaft
What is transmissibility ratio?
Define normal mode
Define principle coordinates
Define influence Co-efficient
List the types of vibration
What are types of damping?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
276
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
List out the different methods of vibration
State degrees of freedom
What is the eigen value and eigen vectors?
What is vibration isolation?
What is vibration absorber?
Differentiate between linear and non-linear vibration.
Define coulomb damping.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
What is the need for vibration analysis test?
Mention the parts of vibration systems
What is the marginal density function?
What is the application of Duhamel's integral?
What is an exciter? Name different types.
State the condition for stable and unstable node
State Lagranges equations
What are vibration sensitivity criteria?
Why vibration monitoring techniques is needed?
What is the choice of monitoring parameters?
What is the function of artificial damping?
What are the condition monitoring methods?
How to reduce the vibration at the source?
Sate the mathematical modeling of vibrating system
What is orthogonality principle?
Apply
1.
Consider two pendulums of length L as shown in the fig. Determine the natural frequency of each
pendulum. If k=100 N/m, m1=2 kg, m2=5kg, L=0.20m, a=0.10m.
2.
A spring-mass system is shown in the fig. If the system is initially relaxed and a step-function is
applied to the mass, find the response of the system.
3.
Find the natural frequency and amplitude ratio of the system shown in the fig.
277
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
2.
A gun barrel weighing W kg has a recoil spring whose stiffness is k kg/m. If W = 450kg, k =
36000kg/cm and the barrel recoils 1m on firing determine.
(a) The initial recoil velocity of the barrel.
(b) The critical damping co-efficient of a dashpot which is engaged at the end of the recoil stroke.
(c) The time required for the barrel to return to a position 5cm from its initial position.
An air compressor, running at a constant speed of 1200 rpm, is having large amplitude of
vibration. A vibration absorber is added. The weight of the compressor is 500 lb and the
compressor has an unbalance of 1.00 in-lb. Calculate the weight and the spring constant of the
absorber if the natural frequencies of the system should be at least 10% from the impressed
frequency.
Unit I
Introduction
Relevance of and need for vibration analysis - Mathematical modeling of vibrating systems - Discrete
and continuous systems - review of single-degree of freedom systems - free and forced vibrations,
Various damping models
Ground vibration testing
9 Hours
Unit II
Two Degree-of-Freedom Systems
General solution to free vibration problem - damped free vibration - Forced vibration of undamped
system -dynamic vibration absorbers - Technical applications
Vibration test on torsion pendulum
9 Hours
Unit III
Multi Degree-of-Freedom Systems
Free and forced vibrations of multi-degree of freedom systems in longitudinal torsional and lateral
modes -Matrix methods of solution-normal modes - Orthogonality principle-Energy methods,
Introduction to vibrations of plates
Dynamics of rotating machinery
9 Hours
Unit IV
Vibration Control
Introduction Reduction of Vibration at the Source - Control of Vibration by Structural design
Material Selection Localized additions Artificial damping Resilient isolation, Vibration isolation
Vibrations measurement on lathe
9 Hours
Unit V
Condition based Maintenance Principles and Applications
Introduction - Condition Monitoring Methods - The Design of Information system, selecting methods
of monitoring, Machine condition monitoring and diagnosis Vibration severity criteria Machine
maintenance techniques Machine condition monitoring techniques Vibration monitoring techniques
Instrumentation systems Choice of monitoring parameter
Acoustic testing, Active noise and vibration control
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
278
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Textbooks
1.
2.
Singiresu S. Rao, Mechanical Vibrations, Prentice Hall Publish, New Delhi,2010.
J. S. Rao , Vibratory Condition Monitoring of Machines, Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi,
2000.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
K. J. Bathe and F. I. Wilson, Numerical Methods in Finite Element Analysis , Prentice Hall of
India, New Delhi, 1978.
J. P. Den Hartog Mechanical Vibrations,Crastre press, 2007.
Science Elsevier, Hand Book of Condition Monitoring, Elsevier Science, 1996.
NPTEL:http://nptel.iitm.ac.in/courses/Webcourse-contents/IIT-%20Guwahati/ve/index.htm
www.conditionmonitoringsystem.com/
279
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M013 MECHANICAL BEHAVIORS OF MATERIALS
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge on Mechanical Behavior of Material at various environmental and load
conditions
To make students to understand the significance of temperature variation and fatigue loading on
material property
At the end of the course students will be able to consider material failure through temperature,
fatigue stress and fracture for selection of materials for any specific application
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
(e) The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team.
(g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for
entry-level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Relate the mechanical properties of materials to their structure.
Select materials for structural applications.
Solve realistic and/or fundamental problems relating to the mechanical behavior of materials for
individual solutions and tests.
Work in teams for the materials selection in design.
4.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
35
35
35
35
Remember
Understand
30
30
30
30
Apply
35
35
35
35
Analyze/Evaluate
--
--
--
--
Create
--
--
--
--
100
100
100
100
Total
13
Test 1*
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
13
Neatly draw stressstrain curve for a ductile material.
State Hook's Law.
Define true stressstrain.
Give the dimensions of Charpy and Izod impact test samples.
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
280
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
Define ductile fracture.
Define fracture toughness.
What is theoretical cohesive strength of solids?
What are the two standards of the minimum creep rate?
What is a Burger's vector?
What is the need for tensile testing?
What is Orowan's modification?
What is homologous temperature?
Define Super plasticity.
Which test is used to measure toughness?
Define Endurance Limit.
What is Dislocation?
What are the various methods to increase fatigue strength?
Draw Goodman diagram for fatigue loading.
What is Bauschinger Effect?
What are Whiskers?
List at least two factors that promote transition from ductile to brittle fracture?
What are the three forms of crystal structures for common metals?
Mentions two types of dislocations.
What is Curie point?
What are orthotropic materials?
What is TRIP steel?
Name the factors that affect KIC test.
List strengthening mechanism in solids.
Understand
1.
Why is Rockwell hardness test widely used in industries?
2. Differentiate between fatigue and creep failures.
3. Differentiate between slip and twin.
4. Why Interatomic bonds in HCP Materials are stronger than those in FCC crystals?
5. Why FCC Materials have low work Hardening rate?
6. Why bulb filaments made of single crystals?
7. Why Annealing is done after cold working?
8. Differentiate between Edge and Screw dislocation.
9. Specific strength of materials is very high when they are in fiber size but lower when
they are in bar form Why?
10. Why fatigue strength decreases as size of a part increases beyond around 10 mm?
11. Draw the Goodman straight line and the soderberg straight line for designing under fatigue loads.
12. What do you understand by coaxing?
13. Differentiate between cold working and Annealing.
14. Compare tension test and torsion test in terms of the state of stress and strain developed.
15. Differentiate between Ausforming and Martempering
16. How is SN curve constructed?
Apply
1.
The flat bar shown in figure- 1is 10 mm thick and is pulled by a
force P producing a total
change in length of 0.2 mm. Determine the maximum stress developed in the bar. Take E= 200
GPa.
281
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Fig.1
2. Rocket motor casings may be fabricated from either of two steels:
(a) low alloy steel yield 1.2 GPa toughness 70 MPam,
(b) maraging steel yield 1.8 GPa toughness 50 MPam
The relevant Code specifies a design stress of yield/1.5.
Calculate the minimum defect size which will lead to brittle fracture in service for each material, and
comment on the result.
3. The bar of rectangular cross-section, w x b, is edge-cracked and loaded by a tensile force, N, and a
bending moment, M. Consider the equilibrated distribution of yield stress across the ligament and
hence show that plastic collapse may be caused by any combination of M and N which satisfies: m + n (n + 2 ) = ( 1 - )2
where = a/w ; n = N/bwS y ; m = 4M/bw2 Sy
4.
5.
6.
Discuss about slip planes and slip direction (slip system) in FCC,BCC and HCP metals.
The toughness of a 700 MPa yield structural steel is estimated to be 140 MPam.
What size and mass of SEN bend test specimen is necessary, and what capacity of testing machine
would be required?
Assume fracture at = 0.5.
Estimate the life of the component of the previous problem with an initial crack size of 5 mm, if
the material yield is 250 MPa. Assume a plastic configuration factor of ( 1 - )
Unit I
Basic Concept of Material Behavior
Elastic deformation Permanent deformation Fracture : Tensile, Creep, Fatigue, Embrittlement
Basis for linear elasticity Anisotropic linear elasticity Rubber elasticity Viscoelasticity
Dislocations Yield strength of a perfect crystal Edge dislocation Screw and Mixed dislocation
Twining Properties of dislocation Dislocation geometry and crystal structure Interaction of
moving dislocation
Dislocation climb.
9 Hours
282
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit II
High Temperature Deformation of Crystalline Material
Creep mechanism Dislocation glide at low temperature, Differential flow creep mechanisms Creep
in two phase alloys Independent and sequential process Deformation mechanism maps
Engineering aspects of creep design Super plasticity Hot working of metals: Dynamic Recovery
and recrystalization
Interaction of creep with fatigue.
9 Hours
Unit III
Tensile Fracture at Low Temperature and Embrittlement
Theoretical strength of a crystalline solid Theories of low temperature tensile fracture Relation
between bonding, crystal structure and fracture mechanism Mode I, Mode II,Mode III Brittle fracture
Ductile fracture, Embrittlement characteristics and mechanism Metal Stress corrosion cracking
Hydrogen
Ductile to brittle transition temperature (DBTT).
9 Hours
Unit IV
Strengthening Mechanisms
Work hardening, Boundary strengtneing,solid solution strengthening, particle hardening, Deformation
of two phase aggregates,strength,Microstructure and processing patented steel
wire,Martesite,Ausforming,Precipitation hardening in aluminum alloys TRIP (Transformed induced
plasticity) steel,Maraging steel, shape memory alloys Metallic glass and nano crystalline materialsAustempering
9 Hours
Unit V
Fracture and Fatigue
Importance of Fracture Mechanics, Griffith Fracture Theory, Crack Driving Force & Energy Release
Rate, Modes of fracture, Stress intensity factors Crack propagation in the presence of a notch
Material design for fracture toughness High temperature fracture modes Mechanism maps Failure
in super plastic materials Characteristics of fatigue fracture Fatigue crack growth rates Paris Law
Cyclic stress Strain behavior Creep Fatigue interaction
Corrosion fatigue.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
Thomas H Courtney, Mechanical Behavior Materials, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt
Ltd., New Delhi, 2000.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
R. W. Hertzberg, Deformation and Fracture Mechanics of Engineering Materials, John Wiley &
Sons, New Delhi,2000.
M. A. Meyers and K. Chawla, Mechanical Behavior of Materials, Prentice Hall of India, New
Delhi,2001.
George E. Dieter, Mechanical Metallurgy, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New
Delhi, 2007.
Metals Hand Book, Vol.11, Failure Analysis and Prevention, American Society for Metals, 2002.
F. A. Mcclintock, and A. S. Argon (eds.,): Mechanical Behavior of Materials, Addison Wesley
Reading,Mass, New Delhi,1966.
283
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M014 DESIGN OF MECHANICAL DRIVES
3 0 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To impart the knowledge on how to design the mechanical components like belt, gears, bearing,
shaft etc
To know the principles and working of various types of mechanical drives
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(d) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of engineering design. Understanding the
concept generation, design optimization and evaluation. Knowing the fundamentals of intellectual
property rights. Students will be able to effectively design various engineering components and
make process plan for the production,
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programs.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Understand the fundamental philosophy of mechanical drives.
Selection of mechanical drives for given application.
Design the mechanical drives for given machine.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
14
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze / Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I
25
30
20
25
-100
Test II
25
30
20
25
100
Model
Examination
25
30
20
25
-100
Semester End
Examination
25
30
20
25
-100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
14
Name the types of drives.
State uniform pressure theory.
Define factor of safety.
Name the different types of clutches.
Why a positive clutch is used?
Discuss the various types of power threads.
Define friction drive and speed drive.
What are the materials used for lining friction surface?
Define pressure angle.
What is disk brake?
List the different types of bearings.
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
284
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
Define contact angle.
What is meant by self locking brake?
Define module.
Define diametral pitch.
Define dynamic load rating.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Identify the parameters to design the clutches.
How do you express the life of a bearing?
List the advantages of gear drives compared to chain drives.
How does the function of a brake differ from that of a clutch?
What are the thermal considerations in brake design?
What condition must be satisfied in order that a pair of spur gears may have a constant velocity
ratio?
7. How the shaft and arms for spur gears are designed?
8. What is herringbone gear? Where are they used?
9. What is Tredgolds approximation about the formative number of teeth on bevel gear?
10. What are the various forces acting on warm and worm gears?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
How the shaft and arms for spur gears designed in gear box?
How to design the clutches for automobiles?
A weight is brought to rest by applying brakes to the hoisting drum driven by on total energy
observed by the brake.
Why are two universal joints often used when there is angular misalignment between two shafts?
Analyze / Evaluate
1.
2.
Design a bevel gear for transmit the power of 100 kW
Suggest the suitable design for the universal coupling
Unit I
Introduction
Power Transmission systems: General considerations, principal types, comparative study of different
drives, applications, limitations.
Design of shafts
9 Hours
Unit II
Design of Speed Drives
Design of spur, helical, bevel and worm gears. Design of speed gear boxes, standardization of spindle
speeds, speed diagrams, selection of bearings, design of housings, lubrication considerations, selection
of servo and stepper motors, timing belts.
Design of flat, V belt and rope drives
9 Hours
285
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit III
Design of Feed Drives
Requirements, types, feed drive using feed boxes, design of power screws, lead screws, selection of
recirculating ball screws, LM guide ways, rotary indexing drives, cam drives, applications, feeding
mechanisms in automated plants, pneumatic feed units, Principles
Design of rack and pinion
9 Hours
Unit IV
Design of Friction Drives
Partial friction drives, couplings, clutches, toothed clutches, unidirectional clutches, safety clutches,
drum, disk brakes, design principles.
Design of centrifugal clutch
9Hours
Unit V
Variable Speed Drives
Need, different types, applications. Case studies- Design of feeding mechanisms for automation,
Design of headstock, Design of cam drive for automate, Selection of timing belt for a CNC machine
Design of tailstock
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Text book
1.
Shigley's, Mechanical Engineering Design, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd.,
Series in Mechanical Engg., New Delhi, 2010.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, PSG College of Technology, Design Data Book, DPV
Printers, 2009.
Jack A. Collins, Henry R. Busby, and George H. Staab , Mechanical Design of Machine
Elements and Machines Jhon Wiley & Sons - New Delhi,2009
Robert L. Norton, Machine Design, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2010.
Alfred Hall (Author), A. Holowenko (Author), H. Laughlin Schaum's Outline of Machine DesignTata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2000
Mehta N. K., Machine Tool Design Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New
Delhi,2010
286
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M015 ENGINEERING INNOVATION
(Common to all branches)
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To establish and maintain competitive advantage in the industrial environment through making
students capable of applying their innovative and creative skills
To secure skills in using various tools to create, innovate and implement new ideas to improve the
technology in which they work
To make them skilled in protecting their ideas through various available intellectual property rights
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(d) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of engineering design. Understanding the
concept generation, design optimization and evaluation. Knowing the fundamentals of intellectual
property rights. Students will be able to effectively design various engineering components and
make process plan for the production.
(g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for
entry-level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Procedural approach to make and implement creative ideas.
Working as a team to the organisational and New Product development.
Applying TRIZ to improve the product and process.
Filing their ideas under Intellectual Property Rights protection.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
15
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
40
30
30
--100
30
30
40
--100
Model
Examination*
30
30
40
--100
Semester End
Examination
30
30
40
--100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
15 *
What are all the four inputs to Innovation?
Define innovation continuum.
What are all the steps to convert an Idea into a Concept?
What are all the types of Innovation?
What is top down innovation?
What is Bottom up innovation?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
287
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
What are all the stages of system approach to the innovation process?
What is ICI stage?
Define concept.
What are all the characteristics of an innovator?
What are all the expectation of creative people?
What are all the characteristics of a leader to encourage creativity?
What is brainstorming?
Define psychological inertia.
What is TRIZ?
What is input and output of a technique?
Define contradiction for a technical problem.
What is idealization?
Write any four contradictions of a TRIZ matrix.
What are all Intellectual properties?
What is the life period of a Patent?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
Differentiate Invention and Innovation.
How important is an Idea?
How concept is differentiated from an Idea?
Differentiate Invention from Innovation.
How innovations are differentiated?
Why improvement of product platform is necessary?
Why bottom up innovation is challenging than top down?
What are all the considerations for an innovation process?
Why process models are required?
When is the ICI stage ends? and Why?
Why is knockout analysis important?
How do you measure success of an Innovation?
How important is the brainstorming?
What are all the advantages of young people in creative environment?
How to identify a creative innovator?
What do you expect from management as an innovator?
What are all the characteristics you have to prove as a creative leader?
How can team creativity be promoted in a group or an organization?
How important is the criticism in the life of an innovation?
Suggest a few areas in which quality circle can be formed in your environment.
How contradictions are identified?
How each type of contradictions are differentiated?
How to find ideality?
How standard solutions are found out?
Why is IPR protection important?
What are all the steps of filing a patent application?
What is patent infringement?
How copyright is different from other IPRs?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
Propose an idea to make an innovation around you.
Identify the type under which your innovation is falling.
How are you going to convert your innovation as a group creativity?
288
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Give your strategic planning to complete ICI stage.
Suggest one topic for conducting brainstorming to improve your innovation.
How are you going to form your team and what are all your expectations to select teammates?
Can you use TRIZ for creating an idea for your innovation? if so write contradictions and given
standard solution in the matrix.
Under which IPR category your innovation is falling?
Unit I
Perspectives on Innovation
Innovation Continuum, Sources of Innovation, conditions for successful innovation, Innovation types
and product classes Innovation Matrix, Classification, Top Down innovation, Bottom up
innovation, Independent innovators
Team innovation
8 Hours
Unit II
Innovation Process
Process Considerations, Process Models, Limitations, Idea Concept Invention stage, Lateral
Thinking, Brainstorming, Pre Project stage, Measuring Success, Project Stage
Product launch
Individual and Team Creativity
Selecting creative people, Characteristics of Innovators, Expectation of creative people, Creative
leadership, Building on ideas, Team creativity and organization, Criticize others ideas
Quality circle
8 Hours
Unit III
New Product Development
Introduction, Models, Product Planning, Product Strategy, Competing with other products,
Withdrawing products, Market Research - Testing, Discontinuous New Products, Technology Intensive
Products, Managing New Product Development Team
Case Study
9 Hours
Unit IV
Product Innovation through TRIZ Theory to Resolve Inventive Problems
Origin of TRIZ - Theory to Resolve Inventive Problems Problem formulation and functional analysis
Concept of ideality contradiction : Physical and technical 39 contradicting parameters
contradiction matrix 40 Inventive principles 76 standard solutions technology evolution trends
Case studies
10 Hours
Unit V
Managing Intellectual Property
Intellectual Property Rights, Patents - Introduction, Search, Writing Documents, Fees and Forms,
International Classification. Licensing, Patent trolls and Myths, Technology Transfer - Importance,
Models, Inward Transfer.
10 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
289
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Textbook
1.
Gerard H. (Gus) Gaynor, Innovation by Design, American Management Association, 2002.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Paul Trott, Innovation Management and New Product Development, Pearson Education Limited,
New Delhi,2004.
Leigh L. Thompson, Hoon-Seok Choi, Creativity and Innovation in Organizational Teams,
Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, USA, 2006.
John Adair, Leadership for Innovation, Kogan Page Limited, USA, 2007.
Robert W. Weisberg, Creativity - Understanding Innovation in Problem Solving, Science,
Invention, and the Arts, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., USA, 2006.
www.triz-journal.com
290
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M016 AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS
(Common for EIE, EEE and MECH Engineering branches)
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge to the students in the principles of operation and constructional details of
various Automotive electronic components and subsystems
To impact knowledge to students in various electronic subsystems of Automobile Engineering
At the end of the course, the students will be able to have a sound knowledge of the vehicles and
the mechanisms involved in the starting systems, ignition systems and an engine control systems
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
(j) The graduates can become job-givers rather than just job-seekers.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
Graduates can able to diagnose and troubleshoot if any malfunction occurs in the electronic control
systems on automobiles.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
16
Blooms Taxonomy
(New version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I*
Test II*
30
40
30
--100
30
40
30
--100
Model
Examinations*
30
40
30
--100
Semester End
Examination
30
40
30
--100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
What is meant by distributor less ignition system?
What is the function of detonation sensor?
What is the purpose of using wheel sensor in ABS?
List the sources of exhaust gas emissions from the automobiles that affect the environmental
conditions.
5. State four advantages of a pre-engaged starter when compared with an inertia type.
6. What is dwell angle?
7. What is the function of electromagnetic sensors in electronically sensed ABS?
8. Define Total vehicle dynamics.
9. What is the purpose of Vehicle navigation system?
10. Write the components of Embedded system.
16
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
291
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
What is meant by inductive charging?
What is meant by black box fault finding?
What are Euro Norms?
What is meant by telematics?
What is the concept of CAN with signal format?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
Differentiate between a solenoid switch and relay switch
Whether the petrol fuel injection is different from diesel fuel injection? How does it differ?
Write any two advantage of bosch compact alternator.
Write the two important methods in pre computerized ignition system to advance the ignition
timing?
Difference between MAF and MAP sensors.
Why do we use Hall Effect sensors in automotive application?
How do you obtain the quantity of fuel to be injected in electronic engine management system?
Differentiate throttle body and MPFI injection systems.
Why acceleration enrichment of fuel is needed?
Why a D.C series motor is preferred for the starting system of automobiles?
Why an artificial intelligence system used in automobiles?
Why digital displays are multiplexed.
Differentiate between active and passive safety.
Where the cruise control system used in vehicles?
Why we are using multi cylinder engine rather than using a larger single cylinder of similar cubic
capacity?
Apply
1.
2.
Calculate chemically correct air fuel ratio for complete combustion of octane (C8H18).
Design a Electric circuit for automatic seat adjuster, power window , auto lock and for parking
assist sensor.
Unit I
Automotive Electricals and Electronics:
Power train system (air system, fuel system (carburetor and diesel fuel injection, ignition system,
exhaust system .Auxiliary systems (cooling, lubrications and electrical system), Transmission system
(front, rear and 4 wheel drive, manual , automatic transmission, differential). Braking system (Drum,
disc, hydraulic, pneumatic), Steering system (rack and pinion, power steering)
Electromagnetic clutch, braking system ABS.
10 Hours
Unit II
Need for Electronics in Automotive Systems
Basic electrical components and their operations in an automobile: Power train sub system (Starting
system, charging system- ignition systems-electronic fuel control), Chassis sub system ( TCS & ESP)
Comfort and safety sub system ( airbags, seatbelt tensioners, cruise control-, parking). Performance
(speed, power, torque), Control (emission, fuel economy, drivability and safety) & legislation
(environmental legislation for pollution and safety norms).
Safety -night vision , lane departure warning.
10 Hours
292
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit III
Introduction to Embedded System
Embedded System Definitions: Components of embedded systems.
Hardware Module: Microprocessor, Microcontrollers, On chip peripherals: Program memory (PM) ,
Data memory(DM), Parallel port structures, Timer, Input capture & Output compare units, ADC,
PWM, Introduction to an embedded board.
Software Module : IDE Getting started: Creating new project, creating new files, adding files to
project, compile, build, debug and simulation of a project. Embedded system programming: Uploaders, ISP, ROM Emulators, In-circuit emulators.
Debug Interfaces: BDM and JTAG.
10 Hours
Unit IV
Embedded System in Automotive Applications
Engine Management System Gasoline/ diesel system, various sensors used in system- electronic
transmission control- Vehicle Safety System Electronic control of braking and traction Body
electronics System level test- Anti spinning Engine Interaction systems - Software calibration
using engine and vehicle dynamometers- Environmental test for electronic control unit- Application of
control elements and control methodology in automotive system.
Infotainment systems, navigation systems
10 Hours
Unit V
Embedded System Communication Protocols
Introduction to control networking- Communication protocols in embedded system- SPI, I2C , USB
Vehicle communication protocols- Introduction to CAN, LIN, FLEXRAY
Communication protocol: MOST, KWP2000
10 Hours
Total: 50 Hours
Text book
1.
Tom Denton, Automobile electrical and electronics systems, SAE Publishers, 2004.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
William D. Ribbens, Understanding Automotive Electronics, Newnes Publishing, 2003.
Ronald K. Jurgon, Automotive Electronics Handbook, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt
Ltd., New Delhi, 1999.
BOSCH, Automotive Hand Book, 6th edition.
William T. M Automotive electronics systems.
Barry Hollembeak, Automotive Electricity, Electronics and Computer Controls, Delmar
Publishers, 2001.
293
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M017 MICRO-ELECTRO MECHANICAL SYSTEMS
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To get an exposure in the application of MEMS for various domains
To impart knowledge on MEMS with their manufacturing techniques
To create exposure to packaging techniques of MEMS
Make students to scale up and scale down the physical quantities of micro system
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology
subjects and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
e) The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team.
i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Adequate to use the desired products in complex environments.
Identify the materials based on its application.
Choosing the suitable fabrication technique.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
17
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
40
30
30
--100
40
30
30
--100
40
30
30
--100
40
30
30
--100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
17
Define MEMS
Classify the micro actuator techniques.
What is meant by comb drive?
What is meant by up scaling and down scaling?
What is meant by wafer?
What is the use of silicon compounds?
State the application of quartz.
What is meant by lithography?
Differentiate between positive resist and negative resists.
Mention any three piezo electric material.
State the application of silicon nitride.
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
294
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
What is meant by etching?
List the various CVD techniques for silicon compounds.
What do you meant by LIGA?
What do you menat by SLIGA?
Define Class 10.
What do you meant by clean room?
What are the limitations of bulk micro manufacturing?
State the general consideration in packing design.
What is the need of packaging in MEMS?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
How the SMA actuation differs from Piezo actuation?
How the sensors are classified based on MEMS?
How silicon atoms are located in (111), (100), (110) plane.
How the photolithography process is carried out?
How atoms are located in silicon crystal?
How the polycrystalline silicon is made?
How Microsystems packaging is classified?
How the hardness is achieved by various heat treatment processes?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
How will you choose a suitable material for industrial application?
On what basis the micro pump works?
Estimate the different scaling factors for the various components?
How you perform the surface bonding?
Unit I
Introduction
Introduction to MEMS and Microsystems, typical products, Microsystems and micro electronics
applications of Microsystems in automobile and other industries, working principle of Microsystems
types of micro sensors, Micro actuation techniques MEMS with micro actuators micro pump
micro motors micro valves micro grippers micro accelerometers, micro fluids
MEMS gyroscope, electrostatic fluid accelerator
9 Hours
Unit II
Materials for MEMS and Microsystems
Substrates and wafer active substrate materials, silicon as a substrate material, silicon compoundssilicon dioxide, silicon carbide, silicon nitride, polycrystalline silicon, silicon piezo-resistors, Gallium arsenide, quartz, - piezoelectric crystals polymers as industrial materials, polymers for
MEMS and Microsystems, conductive polymers Langmuir-Blodgett films, packing materials.
Glass, tungsten film and Sillimanite
9 Hours
Unit III
Fabrication Processes
Photolithography photoresists and application, light sources, phoresist development, removal and
postbacking, Ion implantation, diffusion, oxidation process, chemical vapor deposition-working
295
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
principle, chemical reactions, rate of deposition, physical vapor deposition sputtering, deposition by
epitaxy, etching- chemical etching and plasma etching.
Electron beam lithiography and HF etching
9 Hours
Unit IV
Micromanufacturing
Bulk micromanufacturing- etching, isotropic and anisotrotpic etching, wet and dry etching, surface
micro machining, LIGA process- general description materials, electroplating, SLIGA process,
Process design- photolithography, thin film fabrication, geometry shaping.
Micro cutting and chemical mechanical planarization
9 Hours
Unit V
Microsystem Packaging
Mechanical packaging of microelectronics, Micro system packaging general considerations, three
levels of packaging-die level, device level and system level, interfaces in microsystem packaging,
essential packaging technologies, three dimensional packaging, assembly of Microsystems, selection of
packaging materials, signal mapping and transduction.
Zero level packaging
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
Tai- Ran Hsu, MEMS & Microsystems Design and Manufacture, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing
Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2010.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
N. P. Mahalik, MEMS, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi,2010
Gardner, W. Julian, K. Varadan Vijay and O. Awadelkarim, Osama, Micro sensors MEMS and
Smart Devices, Jhon Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2001.
Gad-el-Hak, Mhamed, The MEMS Handbook, CRC Press 2002.
S. Fatikow, U. Rembold, Microsystem Technology and Microrobotics, SpringerVerlag, Berlin,
Heidelberg, 1997.
E. H. Tay, Francis and W. O. Choong , Micrfluids and Bio MEMS applications, Springer, 2002.
296
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M018 NANO-TECHNOLOGIES
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To impart the students to be an expert in advanced technology in the society
To develop the students to acquire overall sound knowledge in nano materials
To make the students to know the applications of Nano materials in various fields
Make the students to select suitable nano fabrication process
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Adequate to ensure the suitable material for all tasks
Analysis the various crystal structures and bonding processes
Identify the materials based on micro structures
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
18
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
40
30
30
--100
40
30
30
--100
40
30
30
--100
40
30
30
--100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
18 *
What are the important constituents of thin films?
What is called nano?
What is the unit of nano?
What is nano particle?
What is known as quantam dots?
Which is called as micro crystalline silicon?
What is called quasi crystal?
What are the various types of quasi crystal?
Define nano crystalline.
Mention the main methods to create nano particles.
Which ball mill is used in attrition method?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
297
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
What is called pyrolysis method?
Which process is said to be as wet chemical technique.
What is the use of centrifugation?
What is the use of nano material in fuel cell?
Mention any three current nano technology applications.
Mention any three nano machining techniques.
What is called top up nano fabrication?
What is called bottom up nano fabrication?
What are the various modes in Scanning probe microscopy?
Define piezo force mode.
What is called Magnetic Force Mode?
What is the difference between nanotech, biotech and synthetic biology?
What is nano medicine?
What is the principle adopted in sol-gel process?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
How the nano materials are classified?
How the high energy ball mill used to produce nano materials?
In what way the nano materials helpful in various fields?
Whether LIGA process is suitable to fabricate nano structures?
Can we use quantam material in nano fabrication processes?
Is it necessary to inspect the nano particles in each step during production?
Apply
1.
2.
How the nano material is choose for particular application?
On what basis the production process of nano material is selected?
Unit I
Introduction to Nanomaterials
Amorphous, Crystalline, microcrystalline, quasicrystalline and nanocrystalline materials- historical
development of nano materials-problems in fabrication and characterization of
nano materials.
Optical properties of nano materials
9 Hours
Unit II
Production of Nanomaterials
Methods of production of nanomaterials, Sol-gel synthesis, Inert gas condensation, Mechanical
alloying or high-energy ball milling, Plasma synthesis, and Electro deposition.
Chemical vapour deposition
9 Hours
Unit III
Application of Nanomaterials
Applications in Electronics, Chemical, Mechanical engineering industries-Use of nanomaterials in
automobiles, aerospace, defense and medical applications Metallic, polymeric, organic and ceramic
nanomaterials.
Application of nano in food and agriculture industry
9 Hours
298
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit IV
Nanofabrication and Machining
LIGA, Ion Beam Etching, Molecular Manufacturing Techniques - Nano Machining Techniques, Top/
Bottom up Nano fabrication Techniques, Quantum Materials.
Molecular motors, electro chemical micro machining
9 Hours
Unit V
Inspection of Nanomaterials
Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) - Contact Mode, Tapping Mode, Scanning Tunneling Mode
(STM). Advanced Scanning Probe Microscopy Electrostatic force Mode (EFM)- Magnetic Force
Mode (MFM)- Scanning Thermal Mode (STM), Piezo Force Mode (PFM). Scanning Capacitance
Mode (SCM), Nanoidentation.
Biosensing with nanopores
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
Mark Ratner and Daniel Ratner, Nano Technology, Pearson Education, New Delhi, 2003.
Bharat Bhushan, Springer Handbook of Nano Technology, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg,
New york 2004.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
J. Tlusty, Machining Processes and Equipment, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi,2000
Rebecca L. Johnson, Nanotechnology, Learner Publication company, 2006.
Richard Booker and Eary Boysen, Nanotechnology, Weily Publications, 2008.
Ampere A TSeng Nanofabrication fundamentals and application, World Scienticfic Co, Pvt, Ltd,
Singapore, 2008.
http://www.nanotech-now.com/
299
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M019 DESIGN OF AIR - CRAFT STRUCTURES
4 0 0 4.0
OBJECTIVES
To learn the basics of aircraft systems, structures and components
To get exposure to the aircraft and aerospace industry
To understand the applicability aspects in Aircraft design
To acquire the theoretical and practical knowledge to design the aircraft structures
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1. Skill to learn the new development in Aircraft component design and analysis.
2. Skill for modeling and analysis using aircraft structural software.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I*
Test II*
30
20
20
30
-100
30
20
20
30
-100
Model
Examinations
30
20
20
30
-100
Semester End
Examination
30
20
20
30
-100
19
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
19
What are the types of frames?
Define Plane truss and Space truss? Give some examples.
What are the methods used to analyze the plane & space frames?
What are the assumptions made in analyzes of a truss?
What is cantilever truss? What is simply supported truss?
What are the primary and secondary stresses in the analysis of a truss?
Define: Continuous beam.
What are the advantages of Continuous beam over simply supported beam?
Define: Moment distribution method. (Hardy Cross method).
Define: Stiffness factor.
Define: Distribution factor.
Define Flexural Rigidity of Beams.
Define: Constant strength beam.
Define: Composite beam.
Define: Proof Resilience.
*The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
300
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
Write the formula to calculate the strain energy due to torsion
Write the Castigliano s first theorem.
Define : Maxwell Reciprocal Theorem.
Define : Modulus of resilience.
What is slenderness ratio ( buckling factor)? What is its relevance in column?
What are the limitations of the Euler s formula?
List out different theories of failure
Define: Maximum Shear Stress Theory. ( Tresca s theory)
Define: Plasticity ellipse.
What are the real-time difficulties of structural damages?
Write the Eulers formula for different end conditions.
What shape is more suitable for nose of aircraft?
What are the trouble suiting methods in design of aircraft structure?
What is ADL analysis in aircraft structural damage?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Differentiate short and long column.
Compare the unit load method and Castigliano s first theorem
Differentiate the statically determinate structures and statically indeterminate structures?
Differentiate maneuver load and actuator load.
Why inertia load in the aircraft engine?
How to select the suitable materials for design the aircraft skin.
Why super plastics are used to make the skin of aircraft?
Apply
1. Find the strain energy per unit volume, the tensile stress for a material is given as 150 N/mm .
Take E = 2 x10 N/mm .
2. Find the strain energy per unit volume, the shear stress for a material is given as 50 N/mm . Take
G= 80000 N/mm .
Analyze/ Evaluate
1. Design of wing of new aircraft structural model.
2. Select the suitable materials for nose point of the aircraft
3. Design new structural profile for the aircraft to reduce the thrust force.
Unit I
Introduction
Overview of the Aircraft Design Process: Introduction, phases of Aircraft Design, Aircraft Conceptual
Design Process, Conceptual Stage, Preliminary Design, Detailed Design,
Design methodologies
3Hours
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Review of Hookes Law, Principal stresses, Equilibrium and Compatibility, Determinate Structures, St
Venants Principle, Conservation of Energy, Stress Transformation
Stress strain relations
4Hours
301
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Introduction to Aircraft Structures
Types of Structural members of Fuselage and wing section Ribs, Spars, Frames, Stringers, Longeron,
Splices, , Types of structural joints, Types of Loads on structural joints.
Sectional properties of structural members and their loads
5 Hours
Unit II
Aircraft Loads
Aerodynamics Loads, Inertial Loads due to engine, Actuator Loads, Maneuver Loads, VN diagrams,
Guest Loads, Gust Loads, Ground Loads, Ground Conditions, Miscellaneous Loads.
6 Hours
Aircraft Materials and Manufacturing Processes
Material selection criteria, Aluminum Alloys, Titanium Alloys, Steel Alloys, Magnesium Alloys,
copper Alloys, Nimonic Alloys, Non Metallic materials, Use of Advanced materials smart materials,
Manufacturing of A/C structural members , Overview of Types of manufacturing processes for
composites, Sheet metal Fabrication , Machining, Welding, super plastic Forming and Diffusion
Bonding
Composite materials
6 Hours
Unit III
Structural Analysis of Aircraft Structures
Theory of Plates - Analysis of plates for bending, stresses due to bending, plate deflection under
different end conditions, Strain energy due to bending of circular, rectangular plates, plate buckling,
compression buckling, shear buckling, Buckling due to in plane bending moments, Analysis of
stiffened panels in buckling, Rectangular plate buckling, Analysis of stiffened panels in post buckling
of sheel panels for Buckling, Compression loading, Shear Loading / Shell Shear Factor,
Circumferential Buckling Stress
Sample exercises& example Problems
12 Hours
Unit IV
Theory of Beams Symmetric Beams in pure Bending, Deflection of beams, Unsymmetrical Beams
in Bending, Plastic Bending of beams, Shear Stresses due to Bending in Thin Walled Beams, Bending
of Open Section Beams, Bending of Closed Section Beams, Shear Stresses due to Torsion in Thin
Walled Beams.
Sample exercises & example Problems
12 Hours
Unit V
Airworthiness and Aircraft Certification
Definition, Airworthiness Regulations, Regulatory Bodies, Type certificate, General Requirements,
Requirements Related to Aircraft Design Covers, Performance and Flight Requirements, Airframe
Requirements, Landing Requirements, Landing Requirements, Fatigue and Failsafe requirements,
Emergency provisions, Emergency Landing requirements.
Real time case study-aircraft certification
7 Hours
302
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Aircraft Structural Repair
Types of Structural damage, Nonconformance, Rework, Repair, Allowable Limit, Repairable Damage
Limit, Overview of ADL Analysis, Types of Repair, Repair Considerations and Best Practices.
5 Hours
Total: 60 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
Daniel P. Raymer, Aircraft Design A Conceptual Approach, American Institute of Aeronautics
and Ast; 2006
Michael Niu, Airframe Structural Design, Adaso Adastra Engineering Center, 2006.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Dave Anderson, Introduction to Flight, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd.,
New Delhi,2008.
Lan moir, Allan Seabridge, Aircraft Systems: Mechanical, Electrical and Avionics Subsystems
integration, Wiley, 2008.
Michael Niu, Aircraft stress Analysis and Sizing, Technical Book Co., 2005.
Roger D . Schaufele, the Elements of Aircraft Preliminary Design, Aries Publications, 2000.
Dale Hurst, Aircraft Structural Technician, Avotek publishers, 2001.
303
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M020 FLEXIBLE MANUFACTURING SYSTEMS
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To emphasis the importance of group technology, cellular manufacturing systems - significance
and impact in manufacturing areas
To introduce the basics and components of FMS to the learners
To enlighten the students about the engineering aspects of Robots and their applications
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
1.
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and
technology
subjects and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
2.
3.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Implementation of Group technology.
Able to apply different scheduling methods.
Knowledge on use of robotics in FMS.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
20
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
45
30
25
--100
45
30
25
--100
40
35
25
--100
40
35
25
--100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
20 *
Classify the types of production processes.
Define flexible automation.
Mention some advantages of flexible automation.
What is meant by programmable automation?
Define fixed automation.
State few reasons for automation.
Define part family.
Define group technology.
What is PFA?
Which features are considered for form code in OPTIZ coding?
What factors are influencing the best machine arrangement in cells?
Write the digit sequence followed in OPTIZ coding system.
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The
remaining 10 marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated
for 50 marks.
304
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
What is cellular manufacturing?
List the advantages of cellular manufacturing.
What are the types of machine cells?
List out the types of machine cell design.
Name few coding systems used for parts identification.
What are the components of FMS?
Name different types of FMS.
State few FMS layout configurations.
List the planning and design issues of FMS.
Depict the FMS loop layout.
Why scheduling is required in FMS?
Mention few benefits of FMS.
What are applications of AS/RS?
Define scheduling.
What are the two basic categories of automated storage systems?
Define accuracy and repeatability.
Classify robot based on work volume.
How do you specify a robot?
What is meant by work volume?
What is the function of a gripper?
What is the use of an end effectors?
What is work cell control?
Name different types of robot cell layout.
What is a Range in sensors?
What is the meaning of proximity sensing?
What is Tactile Sensor?
Define spatial resolution.
What parameters are considered in deigning robot cell?
What are the objectives of AS/RS?
Understand
1. What is the difference between product layout and process layout?
2. How the part families are formed?
3. What is the difference between hierarchical structure and chain type structure in a classification
and coding system?
4. What are the typical objectives when implementing cellular manufacturing?
5. What is the difference between virtual machine cell and formal machine cell?
6. How to select proper material handling system for FMS?
7. When do we use knowledge based scheduling?
8. Differentiate AS/RS and Carousel storage system.
9. Whether AGVs are preferred to use in FMS? If yes why?
10. How do you classify robots from the view points of applications of FMS?
11. How robot can be used in assembly?
12. What is the difference between repeatability and accuracy in a robotic manipulator?
13. Why simulation FMS is necessary?
14. What parameters are considered in deigning robot cell?
305
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Apply
1.
Develop the form code ( first five digits ) in the OPTIZ system for the parts illustrated below
2.
Using notation scheme for defining manipulator configurations, draw diagrams of the following
robots:
a) TRT, b) VVR, c) VROT
3.
The linear joint of a (type L) certain industrial robot is actuated by a piston mechanism. The length
of the joint when fully retracted is 600mm and when fully extended is 1000mm. If the robots
controller has an eight bit storage capacity, determine the control resolution for this robot.
Unit I
Introduction and Flexible Manufacturing Cell
Types of production, characteristics, applications, Flexibility in machining systems, need for FMS,
Flexible Automation, where to apply FMS technology. Characteristics, Flexible Machining systems,
achieving flexibility in machining systems, Machine cell design, quantitative techniques.
Levels of automation
9 Hours
Unit II
Group Technology
Part families, parts classification and coding, types of classification and coding systems. Machine cell
design: The composite part concept, types of cell designs, determining the best machine arrangement,
benefits of group technology
Rank order clustering
9 Hours
306
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit III
Flexible Manufacturing Systems
Components of an FMS, types of systems, FMS work stations. Material handling and storage system:
Functions of the handling system, FMS layout configurations. Material handling equipment AS/RS.
Planning, scheduling and control of FMS - Scheduling - Knowledge based scheduling - Hierarchy of
computer control - Supervisory computer.
FMS planning and design issue, Sizing the FMS
9 Hours
Unit IV
Computer Software, Simulation and Database of FMS
System issues - Types of software - specification and selection - Trends - Application of simulation software - Manufacturing data systems - data flow - CAD/CAM considerations - Planning FMS
database.Area of application of FMS
9 Hours
Unit V
Robotic technology and Applications
Joints and links, common robot configurations, work volume, types of robot control, accuracy and
repeatability, other specifications, end effectors, sensors in robotics.Characteristics of robot
applications, robot cell design, types of robot applications: Material handling, processing operations,
assembly and inspection
Work cell Control and Interlocks
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
Mikell P. Groover, Automation Production Systems and Computer Integrated
System, Prentice Hall of India, PTR Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2007.
Manufacturing
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Nanua Singh, Systems Approach to Computer Integrated Design and Manufacturing, John Wiley
and Sons, 1998.
Joseph Talvage and Roger G. Hannam, Flexible Manufacturing systems in practice, Marcel
Dekker Inc., NewYork, 1987
S. R. Prasad, R. Prabhakar and S. Dhandapani, Intelligent Flexible Autonomous Manufacturing
Systems, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2000
N. K. Jha, Handbook of Flexible Manufacturing Systems, Academic Press Inc., 1998
Satya Ranjan Deb, Robotics Technology and Flexible Automation, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing
Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2001
307
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M021 COMPUTER INTEGRATED MANUFACTURING
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To learn the basics of CAD/CAM integration and concept of the group technology
To have a exposure to various automation principles
To know the network management and installation and the DBMS concepts
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and
technology
subjects and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
(c) The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in
various materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting,
fabrication, machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of
the course, students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable
component in industry.
(g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Able to determine the part family of the given part.
Handle the given material to finish the part within specified time.
Generation of the GT code for the given part.
Able to develop the database system for the Manufacturing Industry.
Installation of the LAN systems.
Interconnect the multiple manufacturers using MAP technology.
Design of storage system for the given set of components in the company.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
S. No.
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
40
35
35
35
Remember
Understand
35
25
25
25
Apply
20
30
30
30
Analyze/Evaluate
--
--
--
--
Create
--
--
--
--
100
100
100
100
Total
21
Remember
1.
2.
3.
21
Define CIM.
What do you mean by MAP?
List out the structures of coding system available.
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
308
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
What is meant by CAPP? Mention the approaches of it.
What is the key machine concept in cellular manufacturing?
What are the elements of CIM?
What are the objectives of CIM?
State the major areas of CIM.
Define process planning.
What are the functions of process engineering?
State the steps in process planning.
What are the factors affecting process planning?
Define CAPP.
Write down the equipment/devices used in Factory Data Collection Systems.
Write any two benefits of FMS.
Define Group Technology.
List out the stages in Group Technology.
Define Part families.
What are the methods available for solving problems in GT?
List out the premises for the developed of DCLASS code.
What is Production flow analysis?
What are the applications of GT?
What are the results of Process Planning?
Gives the major objectives of a Production Management Systems (PMS).
Define SFC.
What are the primary functions of SFC?
What are the phases of SFC?
What Bar code consists?
What are the types of Bar code?
What is Direct attached Storage?
What are the types of SFC?
Define flexible manufacturing systems.
What arc the objectives of FMS?
What is Local Area Network(LAN)?
What are the reasons for using LAN?
What are the features of LAN?
What is topology?
What are the advantages of LAN?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
What do you understand by the term islands of automation?
Why the GT code is used in the manufacturing industry?
Compare the different types of automatic identification technologies.
Differentiate between the variant process planning and generative process planning approaches.
How the Shop Floor Control is achieved?
Why Generative approach is mostly preferred than Variant CAPP?
Compare the Manufacturing Automation Protocol and Technical Office Protocol.
Apply
1.
Develop the form code (First five digits) in the Opitz system for the part illustrated in figure.
309
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
2.
Apply rank order clustering technique to the part-machine incidence matrix to identify logical part
families and machine groups. Parts are identified by letters and the machines are identified
numerically
Parts
Machines
A
B
C
D
E
F
1
1
1
2
1
1
3
1
1
4
1
1
5
1
1
6
1
1
1
3.
A roller conveyor moves tote pans in one direction at 150 ft/min between a load station and an
unload station, a distance of 200 ft. The time to load parts into a tote pan at the load station is 3 sec
per part. Each tote pan holds 8 parts. In addition, it takes 9 sec to load a tote pan onto the conveyor.
Determine: (a) spacing between tote pan centers flowing in the conveyor system and (b) flow rate
of parts on the conveyor system. (c) Consider the effect of the unit load principle. Suppose the tote
pans were smaller and could hold only one part rather than eight. Determine the flow rate in this
case if it takes 7 sec to load a tote pan onto the conveyor (instead of 9 sec for the larger tote pan)
and it takes the same 3 sec to load the part into the tote pan.
Unit I
Introduction
The meaning and origin of CIM- the changing manufacturing and management scene - External
communication - islands of automation and software-dedicated and open systems-manufacturing
automation protocol introduction to CAD/CAM integration
Reliability and precision in automation
9 Hours
310
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit II
Group Technology and Computer Aided Process Planning
History of group technology- role of G.T. in - part families - classification and coding - DCLASS and
MICLASS and OPITZ coding systems-facility design using G.T. - benefits of G.T-cellular
manufacturing. Process planning - role of process planning in CAD/CAM integration - approaches to
computer aided process planning - variant approach and generative approaches - CAPP and CMPP
process planning systems.
Facility layout planning
9 Hours
Unit III
Shop Floor Control and Flexible Manufacturing System(FMS)
Shop floor control-phases -factory data collection system -automatic identification methods- Bar code
technology-automated data collection system. FMS-components of FMS - types -FMS workstation material handling and storage systems- FMS layout -computer control systems-application and benefits
Introduction to AS/RS
9 Hours
Unit IV
CIM Implementation and Data Communication
CIM and company strategy - system modeling tools -IDEF models - activity cycle diagram CIM open
system architecture (CIMOSA)- manufacturing enterprise wheel-CIM architecture- Product data
management-CIM implementation-software. Communication fundamentals- local area networks topology -LAN implementations - network management and installations. - PDM Tools
9 Hours
Unit V
Open System and Database for CIM
Open systems-open system inter-connection - manufacturing automations protocol and technical office
protocol-(MAP/TOP).Development of databases -database terminology- architecture of database
systems-data modeling and data associations -relational data bases - database operators - advantages of
data base and relational database.
OSI model-different types of layer
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
Mikell. P. Groover, Automation, Production Systems and computer integrated manufacturing,
Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2007.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
P. Radhakrishnan , S. Subramanyan and V. Raju, CAD/CAM/CIM, New Age International (P) Ltd.,
New Delhi, 2000.
S. Kant Vajpayee, Principles of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, Prentice Hall of India, 2003.
Roger Hanman, Computer Intergrated Manufacturing, Addison Wesley, 1995.
Mikell. P. Groover and Emory Zimmers Jr., CAD/CAM, Prentice Hall of India , New Delhi 1998.
http://nptel.iitm.ac.in/courses/Webcourse-contents/IIT
Delhi/Computer%20Aided%20Design%20&%20ManufacturingII/index.htm
311
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M022 NON TRADITIONAL MACHINING PROCESSES
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To study the advanced machining processes
To understand the difference between traditional and unconventional machining processes
To know the principles and working of various nontraditional processes based on mechanical,
electrical, electrochemical and thermal energy
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(c) The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in
various materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting,
fabrication, machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of
the course, students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable
component in industry.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Knowledge about advanced machining processes.
Selection of a nontraditional machining process for the given application.
Evaluation of material removal rate of a given process.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
40
40
20
--100
30
50
20
--100
Model
Examination*
40
40
20
--100
Semester End
Examination
40
40
20
--100
22
23
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
23
Name few unconventional machining processes.
Expand the terms; MRR. IEG, ECM, EDM and USM.
What is an abrasive?
Mention the abrasives used in mechanical energy based processes.
Name the electrolytes used in EDM.
State any two characteristics of a good dielectric fluid.
What is the use of dielectric fluid?
List out the main parts of AJM process.
Write down the function of sonatrode.
Mention four applications of unconventional machining.
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
312
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
Name the parts of plasma arc machining.
What is the principle of EDM?
Expand LASER.
What are the tool materials preferred for EDM and ECM processes?
State two applications for LBM.
What are the advantages of chemical machining?
Write two limitations of WJM process.
What is MRR?
Name the power circuits used in EDM.
What are the types of LASERS?
Define: Plasma.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
Identify the processes that can machine electrically conductive materials.
Identify the processes in which plastic materials can be machined.
Compare electrolyte and dielectric fluid.
How EBM differs from PAM?
How material removal takes place in EBM process?
In which process frequent short circuiting will happen?
Identify the parameters those mostly influence surface quality of a plasma arc machined part.
How ECG differs from ECM?
In what way the spark produced in ECM and EDM differ from each other?
How the grinding wheel used in ECG, is able to conduct electricity?
Why two types of mirrors are used in producing LASER light in Ruby laser?
What is the principle of material removal in ECM?
How water can machine hard materials like metals?
State the mechanism of metal removal in electro chemical grinding.
How electrochemical honing differs from conventional honing.
How to produce plasma?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Why short circuiting happens in ECM?
Knowing all the parameters of EDM process how to arrive the material removal rate?
In which cases the chemical machining can be conveniently applied?
Which method can give better surface finish, an EDM or an EBM? Justify.
How to find out the material removal rate for a metal and an alloy machined using ECM?
Unit I
Introduction
Unconventional Machining Process Need Classification Energies employed in the processes
Brief overview of all techniques AJM, WJM, USM, EDM, ECM, EBM, LBM, PAM.
Future of non-conventional machining processes
9 Hours
Unit II
Mechanical Energy Based Processes
Abrasive Jet Machining Water Jet Machining Ultrasonic Machining.. Working Principles
equipment used Process parameters Material removal rate-Variation in techniques used
Applications.
313
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Abrasive-water jet machining
9 Hours
Unit III
Electrical Energy Based Processes
Electric Discharge Machining- working Principles-equipments-Process Parameters- Material removal
rate - electrode / Tool Power Circuits-Tool Wear Dielectric Flushing Wire cut EDM
Applications-Recent developments in Electro discharge machining.
Micro electro discharge machining
9 Hours
Unit IV
Chemical and Electro-Chemical Energy Based Processes
Process principles of Chemical machining and Electro-Chemical machining -Etchants-maskantstechniques -Process Parameters Material removal rate -Applications-equipments-Electrical circuitProcess Parameters-Electro chemical grinding, Electro chemical honing and Electro chemical
deburring Applications.
Pulsed electro chemical machining
9 Hours
Unit V
Thermal Energy Based Processes
Laser Beam machining, Plasma Arc Machining - Principles Equipment - Electron Beam Machining.
Principles Equipment - Types-Beam control techniques- Material removal rate - Applications.
Laser enhanced etching
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
P. K. Mishra, Non Conventional Machining, Narosa Publishing House,New Delhi, 2007.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
G. F. Benedict. Nontraditional Manufacturing Processes, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, 1987
P. C. Pandey and H.S.Shan, Modern Machining Processes, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing
Company Pvt Ltd.,New Delhi, 2008.
Mc Geough, Advanced Methods of Machining, Chapman and Hall, London
Paul De Garmo, J.T.Black, and Ronald.A.Kohser, Material and Processes in Manufacturing
Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 2007.
Vijaya Kumar Jain, Advanced Machining Processes, Allied Publishers Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 2005.
314
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M023 ADVANCED CASTING PROCESSES
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
At the end of this course the student should be able to understand the need for special casting
processes
To understand the principles, tools and possible defects in each casting process
To understand the knowledge on process capabilities of various special casting processes
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
a)
The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in
various materials. To make students understand requirements and methodologies to be followed in
casting, fabrication, machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the
end of the course, students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a
desirable component in industry.
i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Gain more knowledge in basics of sand types and properties, pattern and core preparation,
moulding methods etc in casting processes.
Selection of suitable casting process based on shape and size of the component and their
applications.
Interpret interrelationship between various types of advanced casting process like investment
casting, centrifugal casting, full mould casting etc.
Able to enlighten the causes and remedies for the casting defects in various casting process.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S.No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
40
35
25
--100
30
40
30
--100
35
40
25
--100
35
40
25
--100
24
25
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
25
Write the basic steps in the casting process.
Write the advantages of casting process.
What are the functions of a riser in the green sand mould?
Write the advantages and limitations of wood as the pattern material.
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
315
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
Name the materials used for pattern making.
Define the terms core print, chaplets and chills.
Give four applications of shell moulded castings.
Write the factors to be considered in design of casting.
Discuss the various pattern allowances.
How does curing agent added to sand mix in shell moulding?
Name the tests used in the shell molding process.
Write down the sand mix for shell molding.
Name three lubricants used in shell molding process.
What is the function of mould release agent?
What is meant by expendable pattern?
Name four materials suitable for making pattern in investment casting process.
What does autoclave means in foundry operations?
List out the properties needed for a ceramic core.
Name the parameters that control the ceramic shell mould process.
What are the methods employed in removal of wax pattern.
How the control is applied in De-Lavaud process?
What is called as silica gel? Write its usage.
List the factors affecting selection of die material.
What is meant by 'slip' and 'raining' as applied to centrifugal casting?
What are the major problems of carbon-di oxide process?
Name atleast four investment casting alloys.
List out the castings produced by centrifugal casting.
Need the casting process by which hollow castings are produced.
What are the process variables in centrifugal casting?
State the use of 'ejector pins' in die casting.
Name the metal injection mechanisms followed in die casting.
What is called as melt loss in die casting?
List the pattern materials for carbon-di oxide process.
State any two advantages of CO2 process.
List out the process parameters in full mould process.
Name the process control variables of squeeze casting.
Give the limitations of squeeze moulding method.
What are the various types of cores used in die casting?
What is vacuum die-casting?
What is meant by pre expanded polystyrene?
Name four products made by electro slag casting process.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
Write the differences between pattern and core.
Compare the different types of sand moulds.
State the necessity for allowances to a pattern.
Why the binder is added to molding sand?
Write the requirements of a good pattern.
What is the aim of inspection and testing of castings?
What is the necessity of sand testing?
State the ways of improving sand permeability.
What type of mould is used for making a frustum of cone?
How the blow holes and cracks inside the casting can be inspected?
Only metal patterns are used in shell mould casting processes. Why?
What is meant by stuccoing? When is it used?
316
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
How the shell thickness can be controlled?
What type of sand is used in shell molding? Why?
In what way the shell molding process is advantageous than sand casting?
State the purpose of additives, fillers and resins in the preparation of wax pattern.
Why firing of shell is carried out?
Compare the process of hot and cold chamber metal injection mechanism
What is called as 'G factor'? Give its importance.
How the core is removed from castings?
Write down the significance of centrifugal force in casting process.
Why venting is necessary in die-casting and how it is achieved?
Why cooling of dies is necessary during their operation?
Give the purpose of providing coating over polystyrene pattern.
Why the full mould process is called so?
Compare the process of pressure die casting and permanent mould casting.
Compare the process of true centrifugal, semi centrifugal and centrifuged casting.
Why permanent moulds are preheated before operations?
Why there are two entry points in centrifugal casting?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
Prepare a list of 15 well known castings used for household, industrial or art applications.
Compare the specific features and process capabilities for the Investment, Shell molding and
Centrifugal casting processes
Identify the pattern material and type of pattern based on the application requirements of the
following components:
a. Toys
b. Rocker arm
c. Valves
d. Safety tools
e. Gears
f. Engine block
g. Brake drum
Unit I
Introduction
Introduction to sand casting - Types of sands - Sand properties - Moulding methods: Manual and
machine - Pattern and its types - Materials - Allowances - Cores and types - Sand reclamation - Casting
defects - Inspection and testing - Need for special casting processes - Applications.
Methods of constructing patterns - characteristics, ingradients and additives of moulding and core
sands
9 Hours
Unit II
Shell Molding
Introduction to the process - Machines - Patterns and materials - Hot coating, warm coating, and cold
coating processes - Sand, resin and other materials - Process parameters characteristics of shell mould
- castings - Defects and their causes in moulds and cores - Hot box and cold box processes - ABC
process
Recent trends in Shell casting and applications
9 Hours
317
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit III
Investment Casting
Process - Pattern and mould materials - Block mould and ceramic shell mould - Advantages and
limitations - Mercast and Shaw processes - CLA process - CLV process - Plaster moulding process Magnetic molding process.
Process capability of investment casting and applications
9 Hours
Unit IV
Centrifugal and Die Casting
Centrifugal process - Types: Centrifugal, semi-centrifugal and centrifuged casting processes Calculation of rotating speed of the mould - Equipment - Dies for permanent mould castings Pressure die casting - Die casting machines: Immersed plunger type and gooseneck process - Design
considerations for die casting methods - Low pressure die casting.
Cleaning and finishing of centrifugal and die-castings and applications
9 Hours
Unit V
Continuous Casting, CO2 and Full Mould Processes
Introduction to continuous castings - Reciprocating mould process - Direct chill process - Casting of
steel, aluminum, brass material in continuous casting - CO2 mould / core hardening process - Full
mould process - Principles Applications
Other special process - squeeze casting, slush casting and electro slag casting processes.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
P. L. Jain, Principles of Foundry Technology, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd.,
New Delhi, 2009.
A. K. Chakrabarti, Casting Technology and Cast Alloys, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2005.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
ASM International Handbook Committee, ASM Handbook Volume 15:Casting, ASM
International, 2008
Howard F. Taylor, Meston C Fleming & John Wulff, Foundry Engineering, Wiley Eastern
Limited, New Delhi, 1993.
Jain Dharmendra, Foundry Technology, CBS Publishers & Distributors, 2007.
Peter Beeley. Foundry Technology, Butterworth-Heinemann, 2001.
http://www.scribd.com/doc/15885832/Metal-Casting-Full-Lecture-Notes
318
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M024 METAL FORMING
3
0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in various Materials.
To understand requirements and methodologies to be followed in forming and fabrication of
engineering materials.
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology
subjects and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
(g) Graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
Manufacturing a desirable component in industry.
Solve realistic and/or fundamental problems relating to the Forming processes.
Work in teams for the design and manufacturing.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I*
Test II*
30
40
30
--100
30
40
30
--100
Model
Examinations*
30
40
30
--100
Semester End
Examination
30
40
30
--100
26
27
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
27 *
Define Slip and twinning.
What is meant by Strain rate?
Classify the metal forming process.
State the features of different types of rolling mill.
What is the advantage of tandem rolling?
List the parts made by shape rolling.
Define forge ability.
Give the advantages and drawbacks of forging process.
What is upset forging?
What are the advantages of isothermal forging?
Define extrusion.
What is tubular extrusion?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
319
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
Define extrusion ratio.
What is impact extrusion?
Define tube drawing.
What is spring back?
Give the advantages of sheet metal forming
Define deep drawing.
What is press brake?
What is metal spinning?
Define stretch forming.
Define blanking and piercing.
What is meant by high energy rate forming?
Give some application of metal spinning process and explosive forming.
Define the term super plasticity.
Define fine blanking.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
What is the difference between rolled plate and sheet?
Why roller leveling necessary?
What is the difference between cold, warm and hot forging?
Hoe does extrusion varies from rolling and forging?
What is the difference between extrusion and drawing?
Why metal is cold worked?
How press forging differ from drop forging?
Why cold rolling is done by four high rolling mill?
How hydraulic presses are compare with mechanical press?
Why number of passes required rolling a steel bar?
How the metal is prepared for drawing operation?
How can the cutting force be reduced in sheet metal operation?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
How can u tell whether a certain part is forged or cast?
Rolling reduces the thickness of plates and sheets. However it is possible to reduce the thickness
by simply stretching the material .Would this be a feasible process?
What changes would you expect in the strength, hardness, and ductility of metal after being drawn
through dies?
What is the purpose of heat treatment in forging?
A block of lead 25 mm X 25mm X 150 mm is pressed between flat dies to a size 6.25 mm X 100
mm X 150 mm. If the uniaxial flow stress is 6.9 MPa and =0.25 determine the pressure
distribution over the 100 mm dimension and the total forging load.
Determine the maximum possible reduction for cold rolling a 300 mm thick slab when =.08 and
the roll diameter is 600 mm. What is the maximum reduction on the mill for hot rolling when =
0.5?
Calculate the rolling load if steel sheet is hot rolled 30 percent from a 40 mm thick slab using a
900 mm diameter roll. The slab is 760 mm wide. Assume =0.30.The plane strain flow stress is
140 MPa at entrance and 200 MPa at the exit from the roll gap due to the increasing velocity.
320
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit I
Theory of Metal Forming
Metallurgical aspects of metal forming slip twining - mechanics of plastic deformation effects of
temperature strain rate-microstructure and friction in metal forming spring back effect yield
criteria and their significance classification of metal forming processes.
Various methods of analyzing the metal working processes (slip-line field theory, upper bound solution,
stab methods)
9 Hours
Unit II
Forging and Rolling Processes
Principle-classification equipment, tooling-processes parameters and calculation of forces during
forging and rolling processes Ring compression tests Post forming heat treatment Defects(cause
and remedy) applications.
Residual stresses in forging, driving torque and power in rolling
9 Hours
Unit III
Extrusion and Drawing Processes
Classification of extrusion processes tool, equipment and principle of these processes influences of
friction Extrusion force calculation Defects and analysis Rod/wire drawing tool equipment
and principle of processes defects Tube drawing and sinking processes Mannesmann processes of
seamless pipe manufacturing.
Hydrostatic extrusion, tandem wire drawing
9 Hours
Unit IV
Sheet Metal Forming Processes
Classification conventional and HERF processes Presses - types and selection of presses
formability diagram formability of sheet metals Principle, process parameters equipment and
application of the following processes Deep drawing, spinning - stretch forming, plate bending, press
brake forming Explosive forming electro hydraulic forming magnetic pulse forming.
Rubber hydro form process
9 Hours
Unit V
Recent Advances
Super plastic forming electro forming fine blanking P/M forging Isothermal forging highspeed
hot forging -high velocity extrusion.
Orbital forging, liquid metal forming
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
R. Narayanasamy, Metalworking Technology, Prentice Hall of India , New Delhi,1999.
B.L. Juneja, Fundamentals of metal forming processes , New Age International (P) Ltd,New
Delhi,2006.
321
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Dieter, Mechanical Metallurgy, McGraw-Hill , Revised Edition 2007.
Serope Kalpakjian, Manufacturing engineering and Technology , Pearson Publishing Co.,New
Delhi, 2001.
William F. Hosford & Robert M. Caddel, Metal forming , (Mechanics & Metallurgy), Prentice
Hall of India, New Delhi, 1990.
Sinha and Prasad, Theory of metal forming and metal cutting, Dhanpat Rai Pub (p) Ltd. 1999.
Rao P.N, Manufacturing Technology, TMH Ltd., 2007. (Revised Edition).
322
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M025 PROCESS PLANNING AND COST ESTIMATION
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To introduce the process planning concepts
To make cost estimation for various products after process planning
To know the importance of machining time for various operations
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry- level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
Understand the various process planning approaches and commercial packages. Prepare a process
planning flowchart for an industrial component.
Estimating the machining time for various operations.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
28
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
30
40
30
--100
30
40
30
--100
Model
Examination*
30
40
30
--100
Semester End
Examination
30
40
30
--100
Remember
1. What is meant by process planning?
2. State the general approaches to process planning
3. Define breakeven point.
4. List out commercially available CAPP systems
5. Define standardization
6. What do you mean by simplification?
7. Define Cost Estimation
8. List out some methods of costing.
9. What are the components of a job estimate?
10. What is ladder of cost?
11. Give some example for administrative expenses.
12. What is meant by overhead expenses?
13. Who are called indirect labour?
14. What you mean by Depreciation?
28
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
323
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
15. Define Depreciation due' to Physical Decay.
16. The cost consists of prime cost and factory expenses is known as _____
17. Define Shear Loss.
18. What do you mean by tong hold loss?
19. Write the equation for estimation of machining time.
20. Define tear down time
21. List the various data required to make a cost estimate.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
What is the effect of simplification?
What are the factors affect process planning?
Compare manual process planning with computer aided process planning.
State the importance of realistic estimates.
What are factors for calculating the probable cost of the product?
Differentiate between estimating and costing in terms of organizing department.
Process material is direct material (True / False)
How to determine the direct labour cost?
When do you prefer allocation of overhead expenses by unit rate?
In what aspect the direct differ with indirect expenses?
Differentiate hot forging and cold forging
Write down some depreciation situation due to functional conditions.
In general what is the amount of scale loss considered?
State the significance of speed in machining time
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
State the applications of Break even analysis.
What do you mean by Break-even point in terms of sales value?
Which type of cost estimation is applied in construction industry?
Write down the importance of costing.
Type of depreciation where a machine is to be replaced while it is functioning is known_______.
How do you evaluate the machining time for shaping?
Unit I
Process Planning
Types of Production - Standardization, Simplification - Production design and selection - Process
planning, selection and analysis - - Steps involved in manual experience based planning and computer
aided process planning - Retrieval, generative - Selection of processes analysis- Breakeven analysis.
Introduction to group technology
9 Hours
Unit II
Estimating and Costing
Importance And Aims Of Cost Estimation - Functions Of Estimation - Costing - Importance And Aims
Of Costing - Difference Between Costing And Estimation - Importance Of Realistic Estimates Estimation Procedure.
Introduction to method study, work study
9 Hours
324
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit III
Elements of Cost
Introduction - Material Cost - Determination of Material Cost Labour Cost - Determination of Direct
Labour Cost - Expenses - Cost of Product (Ladder of cost) Problems- Analysis of overhead expenses
- Factory expenses - Depreciation - Causes of depreciation - Methods of depreciation - Administrative
expenses - Selling and Distributing expenses - Allocation of overhead expenses - problems.Introduction to cost accounting theory only
9 Hours
Unit IV
Product Cost Estimation
Estimation in forging shop - Losses in forging - Forging cost Problems - Estimation in welding shop Gas cutting : Material cost, Labour cost and finish on cost Problems Estimation in foundry shop Estimation of pattern cost and casting cost Problems
Methods & types of estimates
9 Hours
Unit V
Estimation of Machining Time
Importance of machine time calculations - Estimation of machining time for Lathe operations Estimation of machining time for drilling, boring, shaping, milling and grinding operations - Problems.
Estimation of machining time for planning operations simple problems only
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
R. Kesavan, E Elanchezhian and B Vijaya Ramnath, Estimating and Costing New Age
International Publications, 2008.
B. P. Sinha, Mechanical Estimating and Costing, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt
Ltd., 2001.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
S. K. Mukhopadhyay,Production Planning and Control-Text and cases,PHI Pvt. Ltd 2007.
Chitale.A.V. and Gupta.R.C., Product Design and Manufacturing, PHI, ,2000.
R.S and Tailor, B.W, Operations Management, PHI, , 2003.
T. R. Russel Banga & S. C. Sharma ., Mechanical Estimating and Costing, Khanna Publishers,
New Delhi, 2007.
325
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M026 INDUSTRIAL ROBOTICS
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To analyze robot manipulators in terms of their kinematics, control.
Enable to program and control an industrial robot system that performs a specific task.
To discuss various applications of industrial robot systems.
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
c)
The graduates will be able to learn various techniques available to make shapes and designs in
various materials. Students will be understood the methodologies to be followed in casting,
fabrication, machining, materials, metallurgy and forming of engineering materials. At the end of
the course, students will be able to select and perform suitable method of producing a desirable
component in industry.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Able to identify the configuration of a robot.
Identifying a suitable robot for a given application.
Can do simple programming of robot.
Able to determine the end effector position by analyzing the kinematics.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Test 1*
Test 2*
Model
Examination*
Semester End
Examination
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
40
30
30
--100
40
40
20
--100
30
40
30
--100
30
40
30
--100
29
30
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
30 *
What is a manipulator?
Define robot arm.
Give the standard definition for an industrial robot.
State the laws of robot.
Expand: PUMA, SCARA and UNIMATION.
What is accuracy?
What is work volume of a robot?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
326
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
Name the drive systems used for a robot.
Classify industrial robots.
Mention few application areas of an industrial robot.
Name the components of a machine vision system.
What is proximity sensor?
What is touch sensor?
What is force sensor?
Name the methods used to estimate the cost in implementing a robot.
What are types of robot programming?
What is a teach pendant?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
Differentiate accuracy and repeatability.
How to increase the accuracy of a robot arm?
Why the payload is calculated with load at the outer position of the arm?
Can robots completely replace the human efforts in industry? Why?
Why RCC is required?
Which application is easiest to program for a robot?
What kind of end effector is required to stack the glass plates? Why?
A LPG cylinder is to be arc welded using a robot; how to program it for automation?
Electric drives are not suitable robots handling inflammable products. State the reason.
State the differences between proximity and touch sensors.
Why force sensor is needed for a robot?
What are the job opportunities available in a robot assisted automation?
Why safety is important in robot zone?
State the usage of teach pendant compared to programming method
Where to apply inverse kinematics?
When the forward kinematics is advantageous?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
A frame F has been moved 9 units along x-axis and 5 units along the y-axis of the reference frame.
Find the new location of the frame.
A point P(7, 3, 2)T and it is subjected to the transformation described (i0 rotation of 90 about zaxis. (ii) followed by a rotation of 90 about y-axis (iii) followed by a translation [4 -3 7]. Find the
coordinates of the point relative to the reference frame.
Calculate the inverse matrix of the following transformation matrix:
A cool drink bottling company needs to utilize robot in the packing section. How to do it? Justify
your answer.
Write a program to flange drilling operation using VAL programming.
What type of robots can be applied in inspection? Give reasons.
Unit I
Introduction
Definition of a robot scope of industrial robots, Robot anatomy robotics and automation, law of
robots, specification of robots, resolution, repeatability and accuracy of manipulator. Classification of
robots and justifying the use of robots. Drive mechanisms hydraulic, electrical, pneumatic drives.
Economic and social issues
9 Hours
327
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit II
Robot Control and Kinematics
Power transmission systems and control - mechanical transmissions method Rotary to rotary, rotary to
linear conversions - rotary problem- remote centered compliance devices. End effectors vacuum,
magnetic and air operated grippers.
Robot Kinematics- Forward Kinematics, Inverse Kinematics and Differences Forward Kinematics
and Reverse Kinematics of Manipulators with Two, Three Degrees of Freedom (In 2 Dimensional),
Four Degrees of Freedom (In 3 Dimensional) DH matrices.
Micro motor and micro gripper
9 Hours
Unit III
Robot Sensors and Vision Systems
Sensors types tactile sensors, proximity and range sensors, contact and non-contact sensors,
velocity sensors, touch and slip sensors, force and torque sensors.
Robotic vision systems, imaging components, image representation picture coding, object
recognition and categorization, visual inspection, robot cell, design and control layouts.
Performance characteristics of a robot
9 Hours
Unit IV
Robot Programming and Artificial Intelligence
Robotics programming: Teach Pendant Programming, Lead through programming, Robot
programming Languages VAL Programming Motion Commands, Sensor Commands, End effecter
commands, and Simple programs. Basics Goals of Artificial Intelligence.
Simple programs for drilling operations using VAL
9 Hours
Unit V
Industrial Applications
Application of robots in machining - Welding - Assembly - Material handling - Loading and
unloading-CIM-hostile and remote environments. Inspection and future application-safety, training,
maintenance and quality. Economic analysis of robotics. SCARA robots, wheeled robots, Bipedal
robots (humanoid robots), hexapod robots.
Robot cell
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
M. P. Groover, Industrial Robotics Technology, Programming and Applications, Tata McGraw
Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2001.
D. Richard, Klafter, A. Thomas, Chmielewski and Michael Negin, Robotics Engineering An
Integrated Approach, Prentice Hall of India , New Delhi, 2001.
References
1.
2.
3.
K. S. Fu, R. C. Gonzalez and C. S. G. Lee, Robotics Control, Sensing, Vision and Intelligence,
Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2003.
Yoram Koren, Robotics for Engineers, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New
Delhi, 2004.
James G. Keramas, Robot Technology Fundamentals, Cengage Learning, 2011.
328
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
4.
5.
Subir Kumar Saha., Introduction to Robotics, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt
Ltd., New Delhi, 2008.
http://nptel.iitm.ac.in/video.php?subjectId=112101099.
329
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M027 RAPID PROTOTYPING
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To provide knowledge of methods for the manufacturing of prototypes from computer based
models
To understand the entire process of direct manufacturing from the creation of computer based
models to their physical realization
To understand the various methods of manufacturing and their merits, demerits and applications
To impart students to convert CAD models in to real life engineering components
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Prototyping the models of real world engineering parts.
Assess the Effect of process parameters in RP process.
Development of model using various RP processes.
RP of Tools using RP techniques.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
31
Blooms Taxonomy
(New version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I*
Test II*
30
40
30
--100
30
40
30
--100
Model
Examinations*
30
40
30
--100
Semester End
Examination
30
40
30
--100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
31 *
Define Rapid prototyping.
State triangulation algorithm.
What is the importance of Time compression engineering or concurrent engineering?
State the various types of RP processes.
What are the different geometric modeling techniques.
Define Vertex-to-vertex rule.
How rapid prototyping processes are classified?
What are the process parameters affecting model creation in Stereolithography?
Define Tesselation.
What are the Different RP formats available?
What are the process parameters affecting model creation in Direct Metal Laser Sintering?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
330
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
State the limitations of LOM.
List out the materials used in LOM and SLS.
What are the process parameters affecting model creation in FDM, LOM, SGC & 3DP?
What is photopolymerisation?
What is support materials used in RP processes?
What is the atmosphere used in SLS model creation?
Define Solid ground curing.
List the materials used for the following RP processes:
i) Stereo lithography
ii) FDM iii) LOM
iv) SGC v) 3DP
Write the various types of RP processes.
What is Solid ground curing process?
Define Rapid prototyping.
Write the disadvantages of STL process.
List the materials used in direct metal laser sintering process.
Name some neutral file format used for slicing of parts.
Which method is used for curing of parts made by FDM process?
What is the significance of maintaining higher temperature at the nozzle?
List some of the medical applications using RP models.
What is Rapid Tooling?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
What are the limitations of wireframe and surface modeling over Solid modeling?
How a solid model is developed using Constructive Solid Modeling?
How the parts made by FDM process are superior to other RP processes?
Why are post processing operations necessary for RP processes?
Why support materials not necessary in SLS process?
Distinguish between Direct and Indirect tooling.
How the Rapid prototyping processes are classified?
Is it significant to use more number of layers in STL process?
How STL Files are created?
How the photo polymerization process occurs in STL?
How Solid ground curing is carried out?
How information flows from data creation to STL file formatting across an RP system?
How models are developed by material addition and material removal process?
Why carbon dioxide atmosphere is necessary in SLS process?
How lateral distortion of paper prototype by water absorption is prevented in LOM?
Why RP process generated models are preferred in medical applications?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
How process parameters affect surface finish, dimensional accuracy of parts manufactured in
stereolithography process?
Evaluate the effect of process parameters in Selective Laser Sintering Process?
Which RP process will you prefer for manufacturing the given components(fig 1&2)? Justify your
selection based on economy and dimensional accuracy?.
331
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Fig 1
Fig 2
Unit I
Introduction
Need for time compression in product development, Product development conceptual design
development detail design prototype RP Data Formats - Information flow in a RP system Generation of STL file- Steps in RP- Factors affecting RP process- Materials for RP- applications of
RP- RP in Indian scenario.
Introduction to geometric modeling wireframe, surface and solid modeling
9 Hours
Unit II
Stereolithography
Classification of RP systems, Stereolithography systems Principle process parameters process
details machine details, Applications Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) system Principle
process parameters process details machine details, Applications.
Application of stereolithography in bio-medical engineering
9 Hours
Unit III
FDM and LOM
Fusion Deposition Modeling Principle process parameters process details machine details,
Applications Laminated Object Manufacturing Principle process parameters process details
machine details, Applications.
Case study on FDM in evaluation and testing of sukhoi super jet landing gear
9 Hours
Unit IV
SGC, 3DP and LENS methods
Solid Ground Curing Principle process parameters process details machine details,
Applications. 3 Dimensional printers Principle process parameters process details machine
details, Applications, and other concept modelers like thermo jet printers, Sanders model maker, JP
system 5, Object Quadra system. Laser Engineering Net Shaping (LENS) - Ballistic Particle
Manufacturing (BPM) Principle.
Manufacturing RC car parts with 3D printing
9 Hours
Unit V
Rapid Tooling and Applications of RPT
Introduction to rapid tooling Direct and indirect method - Software for RP STL files, Magics,
Mimics. Application of Rapid prototyping in Medical field, manufacturing and automotive industries.Rapid prototyping finishing processes
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
332
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Textbook
1.
Chua Chee Kai, Leong Kah Fai and Lim Chu Sing, Rapid Prototyping: Principles and
Applications, World Scientific Publishing Company, Singapore, 2010.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
D. T. Pham and S. S. Dimov, Rapid Manufacturing, Springer-Verlag, London, 2001.
Paul F. Jacobs: Stereo Lithography and other RP & M Technologies, SMENY, 1996.
Frank W. Liou, Rapid Prototyping and Engineering Applications: A toolbox for prototype
development CRC Press- Technology and Engineering, 2007.
Terry Wohlers, Wohlers Report 2000, Wohlers Associates, USA, 2000.
J. G. Conley, Rapid Prototyping and Solid Free Form Fabrication, Journal of Manufacutring
Science and Engineering, vol. 19, Nov 1997, pp 811-815.
333
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M028 WELDING TECHNOLOGY
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the basic concepts, working principles of welding and special welding processes.
To learn different welding methods and its applications.
To acquire knowledge about welding symbols, welding design, and welding automation.
To learn destructive, non destructive testing and inspection of welded joints.
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(g) Graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for entry-level placement
in Mechanical Engineering
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes
(j) The graduates can become job-givers rather than just job-seekers
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices
SKILL SET
1
2
3
Able to select the welding process.
Able to understand welding symbols.
Select the suitable testing method for welded joints.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
32
Blooms Taxonomy
(New version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Test I*
Test II*
30
40
30
Model
Examinations*
30
40
30
Semester End
Examination
30
40
30
30
40
30
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
--100
--100
--100
--100
Remember
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
32
Define welding process.
What are the advantages of welding process?
List the various welding positions.
List the various types of welding joints.
What is arc length?
What are the different types of arc welding?
Name the commonly used gases in gas welding.
Define weldability.
List the function of fluxes.
What is filler material?
What is explosive welding?
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
334
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
List the important safety measures to be taken in welding shop.
Write the various welding defects.
State the application of soldering process.
How the weld bead is indicated by the weld symbol?
What are the advantages of submerged arc welding?
Name any three welding NDT methods.
Name any four welding destructive testing methods.
Name any two under water welding application.
List any six welding application.
What are the different methods of arc initiation?
What is the abbreviation of DCSP and DCRP?
What are the advantages of using robots in welding?
What is the use of fluxes?
What is key hole?
What are the different types of tracking?
Understand
1 Why edge preparation is necessary?
2 How the arc is produced in arc welding?
3 When will you use DCSP welding?
4 When will you use DCRP welding?
5 How CI welding differ from MS welding?
6 How fluxes are applied in arc and gas welding?
7 When filler rod is required in welding process?
8 What are the factors to be considered for the selection of welding rod?
9 What is the difference between submerged arc welding and TIG welding?
10 Why cleaning of welding surface is necessary?
11 How resistance welding is differ from arc welding?
12 What do you understand by the term heat balance?
13 How solid state welding differ from arc welding?
14 State the basic differences between resistance welding and arc welding?
15 Distinguish between welding, brazing and soldering.
16 What is the difference between TIG and GMAW welding?
17 How CI welding differ from MS welding?
18 What is tool tipping and how is it done?
19 List any five welding process designation.
20 What is the use of backing plate in submerged welding?
Apply
1
2
3
Draw a double V butt joints for a 50mm thick mild steel plate and represent the same with
welding symbols.
Find out the correct welding process to make a tube having 150mm Bore and 500mm length from
1.5mm thick stainless steel sheet and state the reason for selection.
Suggest suitable inspection method to check welding quality for the following components
a) Boiler
b) Tank
335
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit I
Basics and Principles of Welding Process
Welding classification types of weld joints-weld position- edge preparation- fluxes- filler rodsafety aspects in welding - gas welding arc welding electrode: types, selection, coding -shielded
metal arc welding, GTAW, GMAW, SAW, Resistance welding (spot, seam, projection, percussion,
flash types) atomic hydrogen arc welding.
Thermit welding
9 Hours
Unit II
Special Welding Processes
Electron beam and Laser beam welding plasma arc welding stud welding friction welding
explosive welding ultrasonic welding roll bonding-diffusion bonding cold welding welding of
plastics.- brazing and soldering
Underwater welding
9Hours
Unit III
Weld Design and Metallurgy
Welding symbols: welding dimension, No. of examination, area of examination, brazing symbol, NDT
symbol welding design : selection of joint, selection of weld type- allowable strengths of welding,
allowable strengths of weld under steady loads, allowable fatigue strengths of welds, design of welds
subjected to combined stresses, weld throat thickness.Welding Metallurgy: Metallurgy of steel, melting
of electrode and parent metal, solidification of weld metal, gas absorption, gas metal reaction, slag
metal reaction, surface phenomena and solid state reaction- weldability
Weldability of cast iron, steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloys
9 Hours
Unit IV
Automated Welding
Automation welding automation welding operation, structure analysis classification of welding
automation Introduction to welding robots robotic welding system types of welding robots- Robot
selection mechanics Design of welding robots Joint tracking system
Introduction to welding fixtures
9 Hours
Unit V
Weld Defects and Inspection and Testing of Welding
Weld defect Surface defects, subsurface defect Sources of weld defect Arc, resistance and
friction welding process defects Introduction to inspection and testing of welds Types of testing &
inspection : Visual inspection and measurement, Destructive Testing Tensile Tests, Impact Tests,
Bend Tests, Break Tests, Etch Tests - Non-Destructive Testing Liquid Penetrant Testing, Magnetic
Particle Testing, Eddy Current Testing, Radio Graphic Testing, Magneto Graphic Testing, Ultrosonic
Testing, Acoustic Emission Testing, Tightness test - Testing of pipe, plate, boiler, drum, tank
destructive testing methods.
Acceptance levels of arc welding defects
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook(s)
1. Little, Welding technology, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2004.
336
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
R. S. Parmer, Welding Processes & Technology, Khanna Publishers, New Delhi, 2008.
R. S. Parmer, Welding Engineering & Technology, Khanna Publishers, New Delhi, 2008.
O. P. Khanna, A text book of Welding Technology, Dhanpat rai publications (II- edition) - New
Delhi, 2002.
Metals Hand Book, Volume 6, ASM, 2001.
www.weldingtypes.net/
337
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M029 INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To study production system and various layouts
Acquire knowledge in process planning and control
To study work and work measurement
To Gather knowledge in inventory control
To know system analysis and maintenance
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
(g) The graduates will become equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary for
entry- level
placement in both Mechanical Engineering as well as IT companies.
(h) He graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility and
will display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and upgradation.
(i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education
Programmes.
SKILL SET
1
2
3
4
5
6
Ability to perform the process planning and control.
Expertise in the work-study analysis and work sequence.
Able to act as the best inventory manager.
Will able to manage and maintain the system as well the human resources in any level company.
Will have overview idea to set the new company and maintain the systems.
Expertise in the system analysis and maintenance.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
33
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
30
40
30
--100
30
40
30
--100
Model
Examination*
30
40
30
--100
Semester End
Examination
30
40
30
--100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
33
What is industrial engineering?
List out the roles of industrial engineer.
What is the production and manufacturing?
What are the types of layout?
Methods to design the workstation?
what is process planning?
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
338
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
Define group technology.
What is the use of SIMO chart?
what is work sampling?
what is micro motion and macro motion study?
What is inventory?
What do you mean by ABC analysis?
What is mean by just in time in manufacturing?
Define KANBAN technique.
What are the recent developments in system analysis and maintenance?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
How the Production system Sequences?
How Factors affecting production system and productivity?
Types of Various layouts
What is process planning, production planning and various charts?
How to do the Workplace management and utilization of optimum manpower
Where to apply the ABC analysis?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
Will able to Perform the production management.
Will able to set the production system as well as to manage the system.
Will able to perform industry working evaluation and streamline the processes.
Will aware about System related repairs & maintenance and issues.
Unit I
Production System
Industrial engineering - Concept, History and development, Applications, Roles of Industrial engineer.
Production management, Industrial engineering versus production management, operations
management. Production system Analysis, Input output model, Productivity, Factors affecting
productivity. Plant layout, Process layout, Product layout, Combination layout, Fixed position layout,
Flow pattern, Workstation design
Plant layout procedure.
9 Hours
Unit II
Process Planning and Control
Process planning definition, procedure, Process selection, Machine capacity, process sheet, process
analysis, process chart symbols, outline process chart, flow process chart. Group technology
functional and group layout, classification and coding system, formation of component family.
Production planning, economic batch quantity, loading, scheduling.Production control dispatching,
routing. Progress control bar, curve, gantt chart, route & schedule chart, line of balance
Case studies in process planning.
9 Hours
Unit III
Work Study
Work study definition, need, advantages, objectives of method study and work measurement, method
study procedure, flow diagram, string diagram, multiple activity chart, operation analysis, analysis of
motion, principles of motion economy, design of work place layout & ergonomics, therbligs, SIMO
339
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
chart, stop watch procedure, micro & macro motion study. Predetermined motion time system, work
sampling principle, procedure.
Problems
9 Hours
Unit IV
Inventory Management
Inventory control, classification, management, objectives, functions. Economic order quantity,
inventory models, ABC analysis, Material Requirement Planning(MRPI), Manufacturing Resource
Planning(MRP II), Operating cycle, Just in Time manufacturing system, KANBAN technique, lean
manufacturing, Supply chain management. Material handling functions, principles, Engineering and
economic factors, Material handling equipment selection, maintenance, types,
Principle of unit load and concept of containerization and palletisation
9 Hours
Unit V
System Analysis and Maintenance
System concept - system analysis, systems engineering, techniques, applications. Value analysis aim,
technique, procedure, advantages, value engineering, value control, types of values. Re-engineering,
Business process re-engineering. Plant maintenance objectives, importance, maintenance engineer
duties, functions and responsibilities. Types breakdown, scheduled, preventive, predictive. Plant
maintenance schedule,
Recent developments in maintenance
9 Hours
Total : 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
O. P. Khanna, Industrial Engineering and Management, Dhanpat Rai and Sons, New Delhi, 2008
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
J. A. Tompkins and J. A. White, Facilities planning, John Wiley, 2010.
Benjamin W. Neibel, Motion and time study, Richard .D .Irwin Inc., 2006.
Hamdy M. Taha, Operations Research, an Introduction, McMillan Co.,2008.
Lee J. Krajewski, Larry P.Ritaman, Operations Management ,Addison Wesley,2007.
Ravi Shankar, Industrial Engineering and Management, Golgotia Publications Pvt Ltd, New
Delhi, 2009.
340
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M030 PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To introduce the mathematical foundations on theory of probability and to apply the concept
present in the often encountered discrete and continuous probability models
To acquire knowledge on the concepts of correlation and regression, for the application of
problems in engineering
Describes the fundamental principles of hypothesis testing
To demonstrate an ability to design and conduct experiments using one way and two way
classification and ANOVA analysis
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
a)
An ability to be familiar with fundamentals of probability, random variable and distributions thus
acquire the capability to applying them in decision making.
b) The graduates will be able to acquire the knowledge, capability of analyzing and solving any
concept or problem associated with heat energy dynamics and utilization. Students will be able to
understand the working concepts of thermal engineering.
d) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of engineering design. Understanding the
concept generation, design optimization and evaluation. Knowing the fundamentals of intellectual
property rights. Students will be able to effectively design various engineering components and
make process plan for the production.
e) An ability to participate and succeed in competitive examinations.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
To develop the skill to think logically and critically using probability concepts.
To acquire the knowledge in hypothesis testing for small and large samples.
Ability to collect, understand, organize and analyze data for decision making using statistical
techniques.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
35
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Test I34
Test II1
Model
Examination1
Semester End
Examination
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
Create
Total
20
40
30
10
100
20
40
30
10
100
20
40
30
10
100
20
40
30
10
100
Remember
1. Define Probability
2. Define Random Variable.
35
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
341
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
3. Write the formula for Exponential Distribution.
4. Normal Distribution and Normal Probability curve is ------ shape and symmetrical about the line --5. State types of Two - Dimensional random variable.
6. The coefficient of correlation lies between -------.
7. State kinds of problems of tests of hypothesis.
8. What is the Level of Significance usually employed in testing of hypothesis.
9. The t-distribution ranges from ---------.
10. State one use of Chi-Square Distribution.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
If A and B are events in S such that P (A B)=1/4, P( A )=2/3 and P(A B)=3/4. Find P( A /B).
State Bayess theorem.
State the central limit theorem.
If X is a uniform random variable in [-2, 2], find the p.d.f. of X and var(X).
State any two properties of Poisson process.
( x2 + y 2 )
The joint pdf of the R.V. (X,Y) is given by f(x,y) = K xy e
,x>0, y>0. Find
the value of K and prove also that X and Y are independent.
The joint probability function (X , Y ) is given by P(x,y) = k(2x + 3y),
x = 0,1,2; Y = 1,2,3 Find marginal distribution.
What is the importance of confidence limits in testing of hypothesis ?
State 2 differences between CRD and RBD.
Name the basic principles of experimental design.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
If at least one child in a family of three children is a boy, what is the probability that all three are
boys.
In a class of 100 students 75 are boys and 25 are girls. The chance that a boy gets a first class is
0.25 and the probability that a girl gets first class is 0.21. Find the probability that a student
selected at random gets a first class.
The overall percentage of failure in a certain examination is 40. What is the probability that out of
a group of 6 candidates at least 4 passed the examination.
In a newly constructed township, 2000 electric lamps are installed with an average life of
1000 burning hours and standard deviation of 200 hours. Assuming the life of the lamps follows
normal distribution, find the number of lamps expected to fail during the first 700 hours.
From a sack of fruits containing 3 oranges, 2 appls and 3 bananas, a random sample of 4 pieces of
fruit is selected. If X is the number of oranges and Y is the number of apples in the sample, find P
( X +Y 2 ) .
The two equations of the variables X and Y are x = 19.13 - 0.87y and
y = 11.64 - 0.50x. Find the correlation co-efficient between X and Y.
What is the importance of confidence limits in testing of hypothesis ?
40 people were attacked by a disease and only 36 survived. Will you reject the
hypothesis that the survival rate , if attacked by this disease is 85% in favour of the
hypothesis that it is more , at 5% level of significance.
What is the Use of F- distribution.
When do you use paired t-test.
342
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Analyze/ Evaluate
1. A given lot of IC-chips contains 2% defective chips. Each is tested before delivery.
The tester
itself is not totally reliable. Probability of tester says the chip is good when it is really good is 0.95
and the probability of tester says chip is effective when it is actually defective is 0.94.If a tested
device is indicated to be defective, what is the probability that it is actually defective ?
2. A passenger arrives at a bus stop at 10.00A.M,knowing that the bus will arrive at sometime
uniformly distributed between 10.00A.M and 10.30A.M.What is the probability that he will have to
wait longer than 10 min ? If at 10.15A.M the bus has not yet arrived, what is the probability that he
will have to wait atleast 10 additional minutes ?
3. In a certain factory turning razor blades, there is a small chance of 1/500 for any blade to be
defective. The blades are in packets of 10. Use Poisson distribution to calculate the approximate
number of packets containing i) 1 defective ii) 2 defective blades respectively in a
consignment of 1000 packets.
4.
X and Y are two R.Vs having joint density function
1
( 6 x y ); 0 < x < 2 , 2 < y < 4 .
f ( x, y) = 8
0 : otherwise
Find
5.
i) P ( X < 1 Y < 3), ii ) P ( X + Y < 3)and iii ) P ( X < 1 / Y < 3) .
If X and Y are independent random variables each normally distributed with mean as 0 and
variance as
find the density function of
y
r = x 2 + y 2 and = tan 1 .
x
6.
The table below gives the number of aircraft accidents that occurred during the various days of the
week. Test whether the accidents are uniformly distributed over the week.
Days
: Mon
Tue
Wed
Thur
Fri
Sat
No.of accidents:
14
18
12
11
15
14
7. A certain drug is claimed to be effective in curing cold. In an experiment on 500 persons with
cold, half of them were given the drug and half of them were given the sugar pills.The patients
reaction to the treatment are recorded in the following table.
Helped
Harmed
No effect
Drug
150
30
70
Sugar pills
130
40
80
On the basis of this data,can it be concluded that the drug and sugar pills differ significantly
in curing cold?
8. Random samples of 400 men and 600 women were asked whether they would like to have a school
near their residence.200 men and 325 women were in favour of the proposal . Test the
hypothesis that the proportion of men and women in favour of the proposal are same , at 5% level
of significance.
9. An experiment was designed to study the performance of 4 different detergents for
fuel injectors: Engine 1
Engine 2
Engine 3
Totals
Detergent A
45
43
51
139
Detergent B
47
46
52
145
Detergent C
48
50
55
153
Detergent D
42
37
49
128
Totals
182
176
207
565
Looking on the detergents as treatments and the engines as blocks ,obtain the appropriate analysis of
variance table and test at the 0.01 level of significance whether there are differences in the detergents
or in the engines.
343
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
10. Analyse the variance in the following Latin Square of yields (in kgs) of paddy where
A,B,C and D denote the different methods of cultivation.
D122
A121
C123
B122
B124
C123
A122
D125
A120
B119
D120
C121
C122
D123
B121
A122
Examine whether the different methods of cultivation have given significantly
different.
Unit I
Probability and Random Variable
Axioms of probability - Conditional probability - Total probability - Bayes theorem - Random variable
- Probability mass function - Probability density functions - Properties- Moments
Moment generating functions and their properties
9 Hours
Unit II
Standard Distributions
Binomial, Poisson, Geometric, Uniform, Exponential, Gamma, Weibull and Normal distributions and
their properties Problems
Functions of a random variable
9 Hours
Unit III
Two Dimensional Random Variables
Joint distributions - Marginal and conditional distributions Covariance - Correlation and Regression Transformation of random variables
Central limit theorem (Without proof)
9 Hours
Unit IV
Testing of Hypothesis
Sampling distributions Testing of hypothesis for mean, variance, proportions and differences
Chi-square and F distributions
.
9 Hours
Unit V
Design of Experiments
Analysis of variance One way classification Two way classification
Latin square
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1. T. Veerarajan, Probability, Statistics and Random Processes, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing
Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi , 2006.
2. R. A. Johnson, Miller and Freunds Probability and Statistics for Engineers , Pearson Education,
New Delhi, 2009.
344
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
References
1. R. E. Walpole , R. H. Myers, R. S. L. Myers and K. Ye , Probability and Statistics for Engineers
and Scientists , Pearsons Education, New Delhi , 2002.
2. S. Lipschutz and J. Schiller , Schaums outline Series - Introduction to Probability and Statistics ,
Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 1998.
3. S. C. Gupta and J. N. Kapur , Fundamentals of Mathematical Statistics , Sultan Chand, New
Delhi,1996.
4. S. Ross, A first Course in Probability , Pearson Education, New Delhi , 2002.
345
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M031 MARKETING MANAGEMENT
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To introduced to key marketing ideas and phenomena, especially the core theme of delivering
benefits to customers
To impart skills in marketing analysis and planning
To communicate knowledge on management and also about basic concepts of supply chain
management due to logistics levels
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology
subjects and thus acquire the capability to applying them.
(k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
Skill to apply the new Management techniques in Marketing , project and real time applications.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
36
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
40
30
30
--100
40
30
30
--100
Model
Examination*
40
30
30
--100
Semester End
Examination
40
30
30
--100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
36 *
Define Marketing management
Define the project
What is meant by marketing mix
Basic criteria of segmentation
Reduce it to a set of manageable tasks
Define pricing
Functions of product development
Name any few market strategy
What is meant by portfolio analysis
How to classify pricing methods
Define supply chain management
Why branding is required?
Name any two basis of market segmentation.
Distinguish between marketing and sales.
What are the buy phases? State the importance of pricing?
Define pull strategy.
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
346
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
List out the constitutes of good marketing research.
How do you classify industrial products?
Write any four public relation tools.
What is a brand? How do you build brand identity?
What trends are taking place in channel dynamics?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
What are the characteristics of an effective marketing mix?
How can informal communication among various departments in an organization facilitate the
marketing function?
Why should a company attempt to emotionally engage its customers
Of the various roles played by consumers in the decisions making process, which one is more
important and why?
Why is it important for a company to study its environment?
What are the important requirements for commissioning a good research?
What are the essential conditions in designing a questionnaire to elicit a correct response from the
respondent?
Define Marketing Management.
Define the terms: Exchange and Transactions.
Give one example of each of the following: Places and Ideas to be marketed.
Brief Selling Concept
What is mean by strategic marketing plan
Which are the different types of customers?
Explain competition power used to motivate channel members?
In which organization structure a company can avoid geographic or customer duplication?
Give the difference between transformational and transactional leadership.
What is mean by profit margin quota and give its importance.
State the critical success factors for making distribution strategy effective.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
How do customers or clients come into the program?
How alpha and beta testing methods are adopted for market testing of business goods?
Discuss the regulatory framework for businesses in India? How do these regulations affect
multinational companies that are doing business in India?
4. What constitutes good marketing research?
5. What are the objectives of salesmanship?
6. How do consumer characteristics influence buying behavior?
7. What are the emerging opportunities and challenges to a marketer of consumer durables.
8. What factors would you consider in determining the sample size for a marketing research study?
9. How alpha and beta testing methods are adopted for market testing of business goods?
10. Critically analyze the importance of marketing department relationships with other functional
departments in the organization.
Unit I
Introduction
Marketing: Definition, Marketing process, Core concepts, The Marketing Environment, Marketing
Mix, Philosophies of Marketing
Consumer markets Vs business markets.
9 Hours
347
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit II
STP and Buyer Behaviour
Segmentation: Levels, Importance, Process, Bases of Segmentation Targeting - Positioning
Consumer Behaviour: Decision making process, Buying roles, Influencing factors
Organizational Buyer behaviour
9 Hours
Unit III
Product and Pricing
Product: Meaning, Types of Goods, Product hierarchy, New Product Development: Process, Pricing:
Meaning
Types, methods, issues
9 Hours
Unit IV
Marketing Strategy
Marketing Plan: Components Marketing Strategy: Formulation and Implementation, Portfolio
analysis, BCG Matrix, GEC Grid.
Marketing research: importance, process.
9 Hours
Unit V
Promotion and Distribution
Promotion: Promotion Mix, Advertising: Importance, Sales Promotion: Importance, Methods:
Customer oriented, Trade oriented Marketing Channels: Channel levels, Channel Members, Roles,
Channel Management, Retailing: Trends in Retailing
Logistics and supply chain management
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
Phillip Kotler, Principles of Marketing: A South Asian Perspective, Pearson Education, New
Delhi, 2010.
References
2.
3.
4.
5.
V. S. Ramasamy and S. Namakumari, Marketing Management: Global Perspective Indian
Context, Macmillan Publishers India, 2009.
Donald S. Tull and Del I. Hawkins, Marketing Research: Measurement and Method, Prentice
Hall of India, New Delhi, 2010.
Rajan Saxena, Marketing Management, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., New
Delhi, 2009.
www.ocw.mit.edu/courses/sloan-school-of-management/15-810 marketing- management- fall2004/lecture-notes
348
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M032 ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIORS AND MANAGEMENT
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To enable the students to understand the perspectives of management
To give an insight about the functions of management like planning, organizing, staffing, leading,
controlling
To familiarize the students with organizational culture and help them to manage change
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(e) The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team.
(h) The graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility and will
display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and up gradation.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Select the best alternative by proper Decision making.
Influence and moderate the work behavior of different personalities.
Solving complex issues by adopting proper conflict management styles.
Develop a conducive organizational culture.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Test 1*
Test 2*
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
40
40
20
--100
40
40
20
--100
Model
Examination
40
40
20
--100
Semester End
Examination
40
40
20
--100
37
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Define management.
List the functions of managers.
What do you mean by policy?
What is staffing?
State the functions of attitude.
What is group dynamics?
Differentiate Strong from Weak cultures.
What is the role of change agent?
Understand
1.
2.
37
Describe the Evaluation of management.
Explain patterns of management Analysis.
*
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
349
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Discuss the Planning Process.
Explain the process of formulating career strategy of an employee.
Compare and contrast Maslows and Herzbergs motivation theory.
Describe the personality attributes influencing Organizational Behaviour.
Predict the problems involved in creating and sustaining an organizational culture.
Explain organization development intervention strategies.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
If you were the chief executive officer of a large corporation, how would you institutionalize
ethics in the organization?
Formal organization is the intentional structure of roles and informal organization is a network of
personal and social relations. Comment
Design a performance appraisal matrix for a production Engineer.
Many other disciplines have contributed to the discipline of Organizational Behaviour. Justify.
Validate why values are important in understanding behaviour of people.
High cohesiveness in a group leads to higher group productivity. Comment.
Construct a proforma for studying the satisfaction level of employees as influenced by the culture
of the organization.
Illustrate with an example, why change is an ongoing activity in an organization.
Unit I
Management Overview:
Management - Definition, nature and purpose, Evolution of management, patterns of management
Analysis, Functions of managers, management and society - Operation in a pluralistic society, Social
responsibility of managers, Ethics in managing.
9 Hours
Unit II
Management Functions - I
Planning: Objectives, Types, Steps, Process, policies. Organizing - Nature and purpose,
Departmentation, Line and staff, Decentralization. Staffing - Selection, performance appraisal, career
strategy.
9 Hours
Unit III
Management Functions-II
Leading - Human Factor in managing, Behavioral models, Creativity and innovation. Motivation
theories. Leadership - Ingredients of Leadership, Styles. Communication. Controlling control
Techniques.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Organizational Behaviour
Meaning and importance of Organizational Behaviour, challenges and opportunities for Organizational
Behaviour, Attitudes Job satisfaction, personality and values. Perception, Groups and Teams, conflict
management.
9 Hours
Unit V
Organizational culture and Dynamics
Organizational Culture Definition, Functions, creating and sustaining culture, creating an Ethical
Organizational culture. Organizational change forces for change, managing change, change agents,
350
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
resistance to change, approaches to managing organizational change, Organizational Development in
intervention.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
Herold Koontz and Heinz Weihrich, Essentials of Management, Mc Tata Graw Hill, New Delhi,
2010.
References
1.
2.
Robbins, Judge, Sanghi, Organizational Behaviour, Pearson, New Delhi,2009
Fred Luthans, Organizational Behaviour, Tata McGraw Hill New Delhi,2009
351
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M033 PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To Gain knowledge on the principles of management for all kinds of people in all kinds of
organizations
To have basic knowledge on international aspect of management
To have a clear understanding of the managerial functions like planning, organizing, staffing,
leading and controlling
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
(e) The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team.
(h) The graduates will develop capacity to understand professional and ethical responsibility and will
display skills required for continuous and lifelong learning and up gradation.
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Expertise on responsibilities of a Manager.
Expertise on Organizational Hierarchy and Staffing.
Familiar with various Motivational Theories.
Familiar with budgets and controlling techniques.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1*
Test 2*
30
40
30
--100
30
40
30
--100
Model
Examination*
30
40
30
--100
Semester End
Examination
30
40
30
--100
38
39
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
39 *
What is Management?
What are all the characteristics of Management?
What are all the role of management in Organisation?
Who is the father of Scientific Management?
What is scalar chain?
What are all the functions of management?
What is partnership?
What is private limited company?
Define planning.
What are all the objectives of planning?
What are all the different types of planning?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
352
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
35.
36.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
Mention the required reasons for the need of policies.
Classify budgets.
What is MBO?
What is planning premises?
Define organising.
List out the steps involved in organisation process.
State the kinds of organisational charts.
What are the types of departmentation?
What is matrix structure?
List out the sources of authority.
What is staff authority?
What is decentralization?
What are the steps involved in manpower planning?
What is stress interview?
What is performance appraisal?
What is Halo effect?
What is managerial grid?
List down the human factors in managing.
Define creativity.
What is SCAMPER tool?
What is meant by brain storming?
Define Motivation?
Name the steps involved in motivation process?
What are the types of motivation?
Mention the various types of communication in organisation.
What is control?
What are the characteristics of control?
What is feed forward control?
What is management by expectation?
Define budget.
What are the classification of Budget?
What is zero base budget?
What is PERT and CPM?
What are the factors affecting productivity?
Define OR.
What is Value analysis?
What is polycentric attitude?
What is geocentric attitude?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Write some important functions of top management.
Write the demerits of sole trading.
What are all the problems of partnership?
Give an example of public and private limited companies.
What are all the guidelines for objective setting?
What are all the benefits of Management by Objective?
When the strategy planning fails?
What are the practices made in making effective premising?
How to evaluate the importance of a decision?
What do you understand by effective organising?
How informal organisation characteristics differ from formal organisation?
353
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
State the advantages and disadvantages of departmentation by enterprise function.
Give a note on departmentation by customers.
Compare line and staff authority.
What are all the disadvantage of decentralization?
Differentiate recruitment and selection.
How to make an effective appraisal?
What are all the sources of an organisational conflict?
Differentiate innovation and invention.
How can be harmonizing objectives achieved?
What are the important assumptions made on Y theory?
Mention the importance of motivation.
Differentiate motivation and satisfaction.
Why is budget control important?
How PERT and CPM in used?
How to use MIS for middle management?
How to calculate ROI?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
In addition to a paid job, where else might a person develop managerial experience?
In recent years, many employers seek out technically trained job candidates who also have studied
management. What advantages do you think employers see in a technical person studying
management?
Why do large companies encourage many of their employees to think like entrepreneurs?
What do you think might be advantages of making business executives adhere to a code of ethics
as do physicians and lawyers?
During weather emergencies such as a severe ice storm, some companies send out an alert that
only essential employees should report to work. Explain why managers should or should not stay
home on such emergency days.
What is your reaction to the following statement made by many business graduates? It may be
nice to study ethics, but in the real world the only thing that counts is money.
Give examples of rights that you think every employee is entitled to.
Some business owners make a statement such as, Were too busy to bother with strategy. We
have to take care of the present. What might be wrong with their reasoning?
How might the use of Internet search engines help you make better decisions on the job?
Describe the general approach a firm of five real-estate developers might take to use the nominal
group technique for deciding which property to purchase next.
Why would a heavy equipment company like Caterpillar hire a Ph.D. in economics as the CEO?
Gantt charts have been around for almost 100 years, and they are now implemented with software.
Why do Gantt charts have such staying power?
An important part of management is dealing with people. Where is the human touch in any of the
techniques described in the subject?
How can a manager tell whether an employee is resisting change?
Unit I
Historical Development
Definition of Management Science or Art Management and Administration Development of
Management Thought Contribution of Taylor and Fayol Functions of Management
Types of business organization
9 Hours
354
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit II
Planning
Nature & Purpose Steps involved in Planning Objectives Setting Objectives Process of
Managing by Objectives Strategies, Policies & Planning Premises- Decision-making
Forecasting
9 Hours
Unit III
Organizing
Nature and Purpose Formal and informal organization Organization Chart Structure and Process
Departmentation by difference strategies Line and Staff authority Benefits and Limitations DeCentralization and Delegation of Authority Staffing Selection Process - Techniques Managerial
Effectiveness
Human resource development
9 Hours
Unit IV
Directing
Scope Human Factors Creativity and Innovation Harmonizing Objectives Leadership Types
of Leadership Motivation Hierarchy of needs Motivation theories Motivational Techniques Job
Enrichment Communication Process of Communication Barriers and Breakdown Effective
Communication
Electronic media in Communication
9 Hours
Unit V
Controlling
System and process of Controlling Requirements for effective control The Budget as Control
Technique Information Technology in Controlling Use of computers in handling the information
Productivity Problems and Management Control of Overall Performance Direct and Preventive
Control Reporting The Global Environment Globalization and Liberalization
International management and global theory of management
9 Hours
Total: 45 hours
Textbook
1.
Herald Koontz and Heinz Weihrich, Essentials of Management, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing
Company Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, 2009.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Koontz, Principles of Management, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt Ltd., 2008.
JAF Stomer, Freeman R. E and Daniel R Gilbert, Management, Pearson Education, 2004.
Joseph L Massie Essentials of Management, Prentice Hall of India, (Pearson), 2003.
Fraidoon Mazda, Engineering Management, Addison Wesley, 2000.
Tripathy PC and Reddy PN, Principles of Management, Tata McGraw-Hill, 1999
355
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M034 OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES FOR ENGINEERING APPLICATIONS
3 1 0 3.5
OBJECTIVES
To Understand the art of optimization for obtaining the best results under given resources -Men,
Machine, Materials, Energy and Money).
To develop analytical Skills for solving industrial and real world problems.
To Understand various nonlinear/non-traditional optimization techniques for solving real word
engineering Problems.
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
i) The graduates will have sound foundation for entering into higher education programmes.
k) The graduates are expected to have knowledge of contemporary issues and modern practices.
SKILL SET
1.
Skill to apply the new optimization techniques in Manufacturing, Design and real time
applications.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No
1
2
3
4
5
40
Blooms Taxonomy
(New version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze/ Evaluate
create
Total
Test I*
Test II*
20
20
20
30
10
100
20
20
20
30
10
100
Model
Examinations*
20
20
20
30
10
100
Semester End
Examination
20
20
20
30
10
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
40 *
What is meant by objective function?
Define design variables
Define constraints.
What are the types of optimization
Define golden selection method
Define direct search method.
What the software development in optimization
Define Lagrange multiplier.
What are the different Evolutionary Optimization Techniques?
Define parameters input to optimization.
Define algorithm
What are the basic steps in optimizations?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
356
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Difference between single and multi objective function.
Why multi-objective functions needed?
Difference between discrete and continues variables.
Why mutation in GA?
Difference between single and multi-crossover in GA.
What are the new developments in Optimization?
Difference between Newton and Cauchy method.
Difference between constraint and unconstraint problem.
What is better searching method? Why?
Is optimization works outside the boundary? Why?
Classify optimization constraints.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
How to validate the optimization techniques results?
Apply GA algorithm for CNC Machine parameter optimization.
Apply GA algorithm to parameter optimization of any non-traditional machining process.
Apply PSO for designing of helical spring
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
Using DE method for finding optimum shaft diameter of given rod.
Can find the minimum cost for the given tolerance problem. Give an example.
Using GA techniques, find the optimum scheduling for a material purchasing company.
Create
1.
2.
Develop the new optimization techniques algorithm for the Gear design problem.
Developing new concept to improve the performance of GA/SA/PSO algorithm.
Unit I
Single Variables Optimization Techniques
General Characteristics of mechanical elements, adequate and optimum design, principles of
optimization, formulation of objective function, design constraints Classification of optimization
problem Classification of optimization techniques. Single variable Techniques of unconstrained
minimization: Dichotomous search Fibonacci method - Golden section - Interpolation methods.
Quadratic and cubic interpolation
9 Hours
Unit II
Multi - Variable Optimization Techniques
Multi-variable techniques - Direct search methods: Random search Hooke and Jeeves Simplex
method Descent methods Cauchy method- Newtons method Introduction to constrained
optimization techniques- Concept of penalty function Lagrange multiplier - Introduction to Multi
objective optimization
Software development
9 Hours
357
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit III
Evolutionary Optimization Techniques
Genetic algorithms, Simulated Annealing techniques, Particle swarm optimization, Ant colony
algorithm, Differential evolution - Implementation of algorithm using Software- MATLAB GA,SA
Program.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Engineering Applications
Design optimization: Design of simple axial, transverse loaded members for minimum cost, maximum
weight Design of shafts and torsionally loaded members Design of springs, Gears. Implementation
of algorithm.
Design of Leaf Spring, Epicycloids gear-train Optimization.
8 Hours
Unit V
Engineering Applications
Optimal tolerance allocation, scheduling optimization and operating parameters optimization for CNC
Machine Tool.
Implementation of algorithm using software
10 Hours
Total: 45 + 15 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
Singiresu S. Rao, Engineering Optimization Theory and Practice, New Age International
Publications, 2010.
Jasbin. S. Arora, Introduction to Optimum Design, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Pvt
Ltd., Singapore, 2006.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Kalyanamoy Deb, Optimization for Engineering Design Algorithms And Examples, Prentice Hall
of India, 1995.
D. E. Goldberg, Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization and Machine, Barnen, AddisonWesley, New York, 1989.
R. Saravanan, Manufacturing Optimization Through Intelligent Techniques, CRC Press, Taylor
and Francis Publications, Florida, USA, 2006.
Dimitris Bertsimas, John N. Tsitsiklis , John Tsitsiklis , Dimitris Bertsimas , John Tsitsiklis,
Introduction to Linear Optimization , 2000.
Dimitri P. Bertsekas, Nonlinear Programming, Edition II, 2000.
358
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O0PA NANO SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge on nanoscience and technology
To create an awareness on the nanomaterials
At the end of the course the students are familiar with nanomaterials and their applications
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Making to learn properties of nanomaterials metals.
Study the different types of techniques used to develop the nanomaterials.
Understanding the various applications of nanomaterials in day-to-day life.
Utilization of nanomaterials into medical and industries to develop technology.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S.No
1
2
3
4
5
6
Blooms
Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Total
41
41
Test 1
Test 2
Model
Examination
Semester End
Examination
25
25
20
20
10
-
25
25
20
20
10
-
20
25
20
20
15
-
20
25
20
20
15
-
100
100
100
100
Remember
1. Define nanoscale.
2. Give the differences between nano and thin materials.
3. Give the usage of nanomaterials in medical field.
4. What are the techniques used to find properties of materials?
5. What are the day-to-day life applications of nanomaterials?
6. What do you mean by total energy of the system?
7. What do you mean by top down and bottom up approach?
8. How physical properties vary while converting the material into nano size?
9. What is SWCNT and MWCNT?
10. What are the applications of CNT?
11. Mention the general characterization techniques of nanomaterials.
12. How electron microscopy differ from scanning electron microscopy?
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted to 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
359
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
Define diffraction.
Write the different diffraction techniques to analyse the properties of nanomaterials.
What is meant by surface analysis of nanomaterials?
What are quantum dots?
Write the importance of self-assembly technique.
What is organic FET?
State the principle of LED.
Why nanomaterials are used as energy storage device?
Write the bio medical applications of nanomaterials.
List the advantages of nanomaterials as compared to bulk materials.
Which is having high efficiency among injection and quantum cascade laser?
Write the uses of FET.
What is nano magnet?
Mention the applications of nanomagnets in industries.
Write the advantages of nano robot in medical field.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
How the nano dimension particle varies with bulk one?
Explain the different classifications of nanostructures.
Elucidate the significance of MWCNT over SWCNT.
Explain structural, electrical, mechanical properties of nanoscale materials.
What are the applications of CNT?
Why the electrical properties are more important as compared to other properties of
nanomaterials?
How nanomaterials are produced by machining process?
Give the importance of vapor phase deposition method for the production of nanomaterials.
Explain the sol-gel technique of nanomaterial production.
How the nanomaterials are analyzed in scanning electron microscopic technique?
Elucidate how nanomaterials are produced by template method?
List the general classifications of characterization methods of nanomaterials.
Explain how FTIR is used to analyze the bonding in nanomaterials?
Why the TEM is widely used than SEM? Explain.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of TEM?
Explain the quantum confinement in semiconductor nanostructures.
Explain the different fabrication techniques of nanoscale materials.
Explicate in which way thermally annealed quantum well technique is better than epitaxial
growth technique?
Explain the electro statically induced quantum dots and quantum wire technique.
Why semi conducting nano material is more important than other nanomaterials?
What are the advantages of nanomagnetic materials?
How nanomaterials are used in organic FET?
Why the organic LEDs are manufactured from nanomaterials?
How nanomaterials are used in quantum cascade laser?
Why nano photo voltaic fuel cells are used?
Explain the bio medical applications of nanodevices.
Apply
1.
2.
Clarify the effects of nanometer length scale of particles.
Give the reason for the effect of nanoscale dimensions on various properties.
360
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
Explain how the size of the particle will effect on their mechanical and structural properties of
the material?
Why sol gel method is used widely to synthesis nanomaterials?
Templating method is better than physical vapor deposition method to synthesis
nanomaterials. Why?
Why ordering of the nano system is more important? Give reason.
Explain how nanomaterials are characterized by imaging techniques?
Why diffraction techniques are used to characterize the nanomaterials?
Explain how nanomaterials are analyzed by transmission electron microscope?
Clarify the differences between self-assembly and self-organization.
Explain how organic light emitting diode overcomes the drawback of LCD?
How we can use CNT as a storage device in battery?
Why nanomaterials are used in optical memory devices?
How we can store nano particles?
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Distinguish between SWCNT and MWCNT.
Compare organic FET and organic LED.
Why nano structured particles are found in potential applications?
Give the relation between properties and applications of nano particles.
Explain with relevant example about the synthesize of nano structured materials employing
self-assembly and template based methods.
Analyze the relation between magnetic and nanomaterials.
Unit I
Nano Scale Materials
Introduction-classification of nanostructures, nanoscale architecture effects of the nanometer length
scale changes to the system total energy, changes to the system structures effect of nanoscale
dimensions on various properties structural, thermal, chemical, mechanical, magnetic, optical and
electronic properties.
Differences between bulk and nanomaterials and their physical properties.
9 Hours
Unit II
Nanomaterials Synthesis Methods
Fabrication methods top down processes milling, litho graphics, machining process bottom-up
process vapor phase deposition methods, plasma-assisted deposition process, colloidal and solgel
methods methods for templating the growth of nanomaterials ordering of nanosystems, selfassembly and self-organization.
Magnetron sputtering process to obtain nanomaterials.
9 Hours
Unit III
Nano Characterization Techniques
General classification of characterization methods analytical and imaging techniques microscopy
techniques - electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy,
atomic force microscopy diffraction techniques spectroscopy techniques-X-ray spectroscopy.
Electrical properties of nanomaterials.
9 Hours
361
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit IV
Inorganic Semiconductor Nanostructures
Quantum confinement in semiconductor nanostructures - quantum wells, quantum wires, quantum dots,
super lattices fabrication techniques requirements, epitaxial growth, lithography and etching,
electrostatically induced dots and wires, quantum well width fluctuations, thermally annealed quantum
wells and self-assembly techniques .
Quantum efficiency of semiconductor nanomaterials.
9 Hours
Unit V
Nanodevices And Applications
Organic FET- principle, description, requirements, integrated circuits- organic LEDs basic
processes, carrier injection, excitons, optimization - organic photovoltaic cells- carbon nano tubesstructure, synthesis and electronic properties -applications- fuel cells- nano motors -bio nano particlesnano objects.
Applications of nano materials in biological field.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
3.
4.
Robert W. Kelsall, Ian W. Hamley, Mark Geoghegan, Nanoscale Science and Technology, John
Wiley and Sons Ltd, 2005.
T. Pradeep, NANO: The Essentials Understanding Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, McGraw
Hill Education (India) Ltd, 2007.
Handbook of Nanoscience, Engineering and Technology, Kluwer publishers, 2002.
B. Wang, Drug Delivery: Principles and Applications,Wiley Interscience 2005.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Michael Kohler, Wolfgang Fritzsche, Nanotechnology: An Introduction to Nanostructuring
Techniques, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.2004.
William Goddard, Donald .W.Brenner, Handbook of Nano Science Engineering and Technology,
CRC Press, 2004.
Bharat Bhushan, Springer Handbook of Nanotechnology, 2004.
Charles P Poole, Frank J Owens, Introduction to Nanotechnology, John Wiley and Sons, 2003.
Mark Ratner, Daniel Ratner, Nanotechnology: A Gentle Introduction to the Next Big Idea, Prentice
Hall, 2003.
362
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O0PB LASER TECHNOLOGY
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge on laser principles
To create expertise on the applications of laser in various engineering fields
At the end of the course the students are familiar with generation and applications of laser in
various engineering fields
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Study the basic principle of laser and different types of lasers.
Analyze the function resonant cavity.
Describe the various techniques involved in the laser materials and determine the
Performance of laser materials.
Determine the measurement of distance, length, velocity, acceleration, current,
Voltage and atmospheric effect.
Design different types of lasers and apply in the medical field.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S.No
1
2
3
4
5
6
Blooms
Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1
Test 2
Model
Examination
Semester End
Examination
25
25
20
20
10
-
25
25
20
20
10
-
20
25
20
20
15
-
20
25
20
20
15
-
100
100
100
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
What is a laser? How the basic laser action is achieved?
Distinguish between spontaneous emission and stimulated emission.
What is population inversion?
Mention the important characteristics of laser.
How four level laser is more efficient than the three level laser?
What is a resonant cavity?
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted to 20 and Model Examination will be converted
to 20. The remaining 10 marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal
assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
363
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
What role does an optical resonant cavity play in a laser?
What are the host materials for solid lasers?
Mention the different techniques involved in lasers.
Define atmospheric effect.
How will you measure the distance using laser?
What is the basic principle behind the holography?
Mention the medical applications of lasers.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Write the conditions needed for laser action.
What is meant by pumping of atoms?
How optical excitation occurs in three level lasers?
What is the principle of laser action?
Compare the activator and host materials for solid lasers.
Distinguish between Czochralski and Kyropoulous techniques.
How will you determine the velocity of laser source?
List the applications of laser in welding and cutting.
Why laser is called as non-material knife?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
The first line of the principal series of sodium is the D line at 580 nm. This corresponds to a
transition from the first excited state (3p) to the ground state (3s). What is the energy in electron
volts of the first excited state?
What is the ratio of the stimulated emission and spontaneous emission at a temperature of 250oC
for the sodium D line?
Calculate the threshold condition for the ruby laser in which the appropriate parameters are as
follows: o =4.3x 1014 Hz; o=1.5x1011 Hz; no= 1.76; sp= 4.3x10-3 s; photon=6x10-9s.
A He-Ne laser emits light at a wavelength of 632.8 nm and has an output power of 2.3mW. How
many photons are emitted in each minute by this laser when operating?
Calculate the wavelength of emission from a GaAs semiconductor laser whose band gap
energy is 1.44 eV.
Analyze
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Why laser beam should be monochromatic?
How the population inversion happening in lasers?
Write the reaction for excimer laser action.
Which method is used to achieve population inversion in a dye laser?
Why we cannot use ordinary light source for LIDAR?
How the optical disk data storage plays a vital role in computer memory storages?
Evaluate
1.
2.
The life time of the excited state (2p) for spontaneous emission is 1.6x 10-9s. The energy
difference between the excited state (2p) and the ground state (2s) is 10.2eV. Find the value of
stimulated emission coefficient during a transition from an excited state (2p) to the ground state.
A laser beam can be focused on an area equal to the square of its wavelength (2). For a He-Ne
laser, = 6328. If the laser radiates energy at the rate of 1mW, find the intensity of the focused
beam.
364
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
3.
Transition occurs between a metastable state E3 and an energy state E2 just above the ground state.
If emission is at 1.1m and E2= 0.4x10-19J, find the energy of the E3 state.
Unit I
Laser Fundamentals
Introduction - principle - spontaneous emission - stimulated emission - population inversion-Pumping
mechanisms - characteristics. Types of lasers principle, construction, working, energy level diagram
and applications of dye laser chemical laser excimer laser.
Laser action.
9 Hours
Unit II
Threshold Condition
Einstein coefficients A and B spontaneous life time light amplification principle of laser action
laser oscillations resonant cavity modes of a laser.
Conditions involved in laser production.
9 Hours
Unit III
Laser Materials
Activator and host materials for solid lasers - growth techniques for solid laser materials - Bridgman
and Stock-Berger technique advantages and disadvantages - Czochralski and Kyropoulous techniques
merits and demerits.
Techniques of producing laser.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Laser in Science
Introduction harmonic generation stimulated raman emission self focusing laser and ether drift
rotation of the earth photon statistics.
Applications of Laser in ranging.
9 Hours
Unit V
Laser in Industry
Introduction Applications in material processing: laser welding hole drilling laser cutting laser
tracking Lidar laser in medicine.
Applications of Laser in sensors.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
K.Thiyagarajan and A.K.Ghatak, LASER:Theory and applications. Macmillan India Limited,
2000.
M. N. Avadhanulu, An Introduction To Lasers Theory And Applications, S. Chand Publisher,
2001.
References
1.
2.
K.P.R.Nair, Atoms, Molecules And Lasers, Narosa Publishing House, 2009.
K. R. Nambiar ,Lasers: Principles Types And Applications , New Age International Publications,
2006.
365
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
3.
4.
Alphan Sennaroglu, Solid-State Lasers And Applications, CRC Press, 2006
Bela A Lengyel, Introduction to Laser Physics, John Wiley and Sons, 1966.
366
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O0PC ELECTRO OPTIC MATERIALS
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge on electro-optic materials
To develop fundamental understanding of various electro-optic materials in communication
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Understanding the mechanism involved in the laser action.
Knowing the birefringence and optical property of the material.
Implementing the above phenomenon for modulators.
Realize the special optical properties of the system.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S.No
1
2
3
4
5
6
Blooms
Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1
Test 2
Model
Examination
Semester End
Examination
25
25
20
20
10
-
25
25
20
20
10
-
20
25
20
20
15
-
20
25
20
20
15
-
100
100
100
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Define laser action.
Give the properties of LASER.
Differentiate between stimulated and spontaneous emissions.
Define continuous and discrete time signals.
Define anisotropic media.
What is an acoustic optic effect?
Define a liquid crystal.
Mention the different types of polarizing devices.
Give examples for direct and indirect band gap materials.
Highlight the usage of a NLO material.
42
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted to 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
367
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
How the population inversion state in laser is achieved?
Give examples for continuous and discrete time signals.
Elucidate the importance of coherence in laser action.
Why birefringence property in an optical material is formed?
In which effect KDP crystal is working?
How the codirectional coupling occurs?
List out the conditions in which the NLO property of a material emerges.
What is the purpose of switching to quantum mechanics from classical mechanics?
Why we prefer LCD displays rather than CRT displays?
What are the advantages of injection laser diode?
Apply
1. Find the intensity of a laser beam of 10mW power and having a diameter of 1.3 mm. Assume the
intensity to be uniform across the beam. Given: P=10mW, d= 1.3 mm.
2. Discuss the three level pumping scheme for laser action.
3. Why is the optical resonator required in lasers?
4. Where can we find the practical applications of wave plates?
5. How to elevate the contrast ratio in display devices which uses in the nematic structures?
6. Non linearity in glasses occurs. Justify the argument.
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
Compare ordinary and laser light properties.
Differentiate wave refractive index and ray refractive index.
Differentiate longitudinal and transverse electro optic effects.
Bring out the importance of electro optic devices.
Unit I
Basics of Lasers
Introduction Einstein coefficients laser beam characteristics spontaneous and stimulated emission
population inversion - light amplification threshold condition laser rate equations two level laser
three level laser mode selection transverse mode longitudinal mode.
Spatial and temporal coherence.
9 Hours
Unit II
Wave Propagation in Anisotropic Media
Introduction double refraction polarization devices - Nicol prism Glan-Thomson prism
retardation plates Soleil Babinet compensator Plane waves in anisotropic media wave refractive
index - ray refractive index - ray velocity surface index ellipsoid.
Optical activity.
9 Hours
Unit III
Electro Optic Effect
Introduction KDP crystals longitudinal mode phase modulation amplitude modulation
transverse mode. Acousto-optic effect small Bragg angle diffraction large Bragg angle diffraction
codirectional coupling contradirectional coupling - applications.
Modulators.
9 Hours
368
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit IV
Non Linear Optics
Introduction self focusing phenomenon second harmonic generation phase matching
birefringent phase matching quasi phase matching frequency mixing. Semiconductors
measurement of third order optical non-linearities in semiconductors.
Frequency doubling nature of materials.
9 Hours
Unit V
Electro Optic Devices
Introduction light emitting diode direct and indirect band gap materials homo junction hetero
junction advantages disadvantages applications. Injection laser diode characteristics
advantages disadvantages. Liquid crystal displays dynamic scattering field effect advantages
disadvantages.
Optoelectronic devices.
9 Hours
Total 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
3.
Ajoy Ghatak and K. Thyagarajan, Optical electronics, Cambridge University Press, 7th reprint
2006.
B. Somanathan Nair, Electronic devices and applications, Prentice - Hall of India private limited,
2010.
Frank L. Pedrotti, S. J. Leno S. Pedrotti and Leno M. Pedrotti, Introduction to optics, Pearson
Prentice Hall, 2008.
References
1.
2.
3.
Ji - ping Huang and K.M.Yu, New Non Linear Optical Materials, Nova, Science Publishers, 2007.
J .D. Wright, Molecular crystals, Cambridge university press, 2nd edition, 1995.
R .W. Munn (Ed) and C. N. Ironsid, Molecular crystals, Blackie Academic & Professional,
Glassgow,1993.
369
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O0PD VACUUM SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To impart a sound knowledge on the vacuum science
To develop the necessary background to perform projects involving vacuum and deposition
techniques
At the end of the course the students are familiar with the various vacuum deposition
technologies employed in the various engineering fields
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a) The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Understanding the fundamentals of vacuum technology.
Understanding the various measuring instruments of vacuum.
Utilization of various components to create high vacuum.
Utilization of various components to measure the vacuum
Solution for the problems connected with high vacuum.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S.No
1
2
3
4
5
6
Blooms
Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1
Test 2
Model
Examination
Semester End
Examination
25
25
20
20
10
-
25
25
20
20
10
-
20
25
20
20
15
-
20
25
20
20
15
-
100
100
100
100
Remember
1. Define the term mean free path.
2. Give the pressure ranges of low and medium vacuum.
3. State Avogadros law.
4. List out the assumptions of kinetic theory.
5. What are the types of pump used to create vacuum?
6. What are the gauges that are used to measure the vacuum?
7. Name the direct reading gauges and indirect reading gauges.
8. Name the operation limits of penning gauge.
9. Name the ultra high vacuum gauges.
10. List out the methods of leak detection.
43
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted to 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
370
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
Give the importance of baffles and traps.
Mention the gauges that can measure ultra high vacuum.
Define throughput.
Give the Ohms law of vacuum technology.
Name the sorbent materials that have widespread use in vacuum production.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
How will you measure the pumping speed in a vacuum unit?
How will you seal the substance outside to maintain high vacuum?
Why does constant volume method have the disadvantage in measuring the pumping speed?
Differentiate between the pirani gauge and penning gauge.
Differentiate the primary gauges from secondary gauges.
How is the pumping speed measured?
How does a rotary pump produce a low pressure?
Derive the relation between the effective pumping speed and conductance of the evacuation pipe.
Explain the designing of UHV evacuation systems.
How are the vacuum surfaces cleaned?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
How will you deposit the material from the plasma etching method?
Why is cold cathode ionization gauges preferred to hot cathode gauges?
Explain the applications of turbomolecular pump.
A vacuum chamber has a volume of 100 litres and an operating gas load of 7.5 x 10-5 torr-lites/sec.
The desired operating pressure is 7.5 x 10-8 Torr. Connections between the chamber and diffusion
pump and the diffusion pump and rotary pump are to meet good design practice (assume
SE/SD=1/5). Calculate the pumping speed at the chamber, the minimum connecting pipe
conductance and the minimum speed required for the backing pump together with the minimum
diffusion pump speed required to meet these requirements.
Surface to volume ratio plays a major role in pumping systems. Why?
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
Why is the diffusion pump widely used in scientific instruments?
Oil diffusion pump system can be used as a high vacuum pumping system. Why?
Compare real and virtual leaks.
Unit I
Vacuum Systems
Introduction units of vacuum kinetic aspects of gases in a vacuum chamber physical parameters
at low pressures classification of vacuum ranges gas flow at low pressures throughput and
pumping speed flow rate and conductance.
Evacuation rate out gassing gas flow turbulent flow.
9 Hours
Unit II
Production of Vacuum
Classification of vacuum pumps rotary vane pumps roots blowers diffusion pumps molecular
drag and turbo-molecular pumps sorption pumps gettering and ion pumping cryopumping
measurement of pumping speed.
Noble pumps for inert gases.
9 Hours
371
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit III
Pressure Measurement
Classification of gauges mechanical gauges McLeod gauge thermal conductivity gauges Hot
cathode ionization gauges Bayard - Alpert gauge cold cathode ionization gauges Penning gauge
magnetron gauge.
Measurement problems in partial pressure analysis.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Vacuum Materials and Leak Detection
Sources of gases and vapours materials for vacuum system vacuum seals vacuum valves traps
and baffles leak detection pressure test spark-coil test leak testing using vacuum gauges
halogen leak detector mass-spectrometric leak detector.
Special design considerations glass to metal seals high voltage metal feedthrough.
9 Hours
Unit V
Applications of Vacuum Systems
Design considerations vacuum system for surface analysis space simulators vacuum
based coating units for thin film deposition thermal evaporation sputtering process chemical
vapor deposition - metallurgical applications.
Plasma etching pulsed vapour deposition PE chemical vapour deposition.
9 Hours
Total 45 Hours
Textbooks
1. Rao V.V, Ghosh T.B, Chopra K.L, Vacuum science and technology, Allied Publishers Limited,
2005.
2. Dorothy M. Hoffman, John H. Thomas, Bawa Singh, Handbook of Vacuum science and technology,
Elsevier Science & Technology Books, 1997.
References
1. David M. Hata, Introduction to vacuum technology, Pearson Printice Hall, 2007.
2. John F. O'Hanlon, A users guide to vacuum technology, John Wiley & Sons, 2003.
3. Chambers.A, Modern vacuum physics, Chapman & Hall, CRC Press, 2005.
372
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O0PE SEMICONDUCTING MATERIALS AND DEVICES
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To improve knowledge on semiconducting materials
To develop the necessary understanding of semiconducting materials and their applications
At the end of the course the students are familiar with various semiconducting materials and their
applications
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology
subjects and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Understanding the mechanism involved in the semiconductors.
Knowing the current components and current gain of the material.
Implementing the above phenomenon for transistors.
Realize the special properties of the semiconductors.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S.No
1
2
3
4
5
6
Blooms
Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Total
Test 1
Test 2
Model
Examination
Semester End
Examination
25
25
20
20
10
-
25
25
20
20
10
-
20
25
20
20
15
-
20
25
20
20
15
-
100
100
100
100
Remember
1. What properties are desirable in semiconductors?
2. Explain the Kronig-Penny model.
3. Define drift current density.
4. What is meant by breakdown?
5. Explain the minority carrier distribution in p-n junction diode.
6. Define temperature effect.
7. What is the basic principle of bipolar junction transistor?
8. Define current crowding.
9. What are optoelectronic devices?
44
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted to 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
373
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
10. Describe the operation of a laser diode.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
How does conductivity of a semiconductor change with rise in its temperature?
How does the thickness of the depletion layer in a p-n junction vary with increase in reverse bias?
How does the energy gap in an intrinsic semiconductor vary, when doped with a pentavalent
impurity?
Explain the mobility effects on carrier density.
What do you understand by the term holes in a semiconductor? Explain how they move under
the influence of electric field.
What is the a.c response of the p-n diode?
How is the solar cell functioning?
Apply
1. In general what is the relation between density of states and energy?
2. What is meant by the term, doping of an intrinsic semiconductor?
3. Give the ratio of the number of holes and the number of conduction electrons in an intrinsic
semiconductor.
4. Write the function of base region of a bipolar junction transistor.
5. Sketch the energy bands of a forward-biased degenerately doped pn junction and indicate how
population inversion occurs.
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
What types of charge-carriers are there in a n-type semiconductor?
What are the disadvantages of using laser diode?
What are the defect levels in semiconductors?
Consider an optical cavity. If N>>1, show that the wavelength separation between two adjacent
resonant modes is =2/2L.
Unit I
Properties of Semiconductor
Energy bands allowed and forbidden energy bands Kronig Penny model electrical conductivity in
solids based on energy bands - band model electron effective mass concept of holes in
semiconductor density of states extension to semiconductors.
k-space diagram.
9 Hours
Unit II
Carrier Transport Properties
Carrier drift drift current density mobility effects on carrier density conductivity in semiconductor
carrier transport by diffusion diffusion current density total current density breakdown
phenomena avalanche breakdown.
Graded Impurity Distribution.
9 Hours
Unit III
P-N Junction Diode
Qualitative description of charge flow in p-n junction boundary condition minority carrier
distribution ideal p-n junction current temperature effects applications the turn on transient and
turn off transient.
374
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Charge storage and diode Transients.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Bipolar Junction Transistor
Introduction to basic principle of operation the modes of operation amplification minority carrier
distribution in forward active mode non-ideal effects base with modulation high injection emitter
band gap narrowing current clouding breakdown voltage voltage in open emitter configuration
and open base configuration
Frequency Limitations.
9 Hours
Unit V
Opto Electronic Devices
Optical absorption in a semiconductor, photon absorption coefficient electron hole pair generation solar cell homo junction and hetero junction - Photo transistor laser diode, the optical cavity,
optical absorption, loss and gain - threshold current.
Photoluminescence and Electroluminescence.
9 Hours
Total 45 Hours
Textbooks
1. Donald A Neamen, Semiconductor physics and devices, Tata McGraw Hill, 2007
2. Albert Malvino,David J Bafes, Electronic Principles, Tata McGraw Hill, 2007
References
1.
2.
Kevin F Brennan, The Physics of Semiconductors, Cambridge University Press, 1999.
Micheal Shur, Physics of Semiconductor Devices, Prentice Hall of India, 1999.
375
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O0YA
POLYMER CHEMISTRY AND PROCESSING
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge on the basic concepts and importance of polymer science, chemistry of
polymers and its processing
To make understand the principles and applications of advanced polymer materials
Knowledge and application of different polymers and its processing
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Understanding the various types of polymers and its industrial application.
Compute the efficiency of polymer materials.
Development of eco-friendly materials.
Realize the advantages of nanocomposites polymers.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S.No
1
2
3
4
5
6
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I
Test II
Model
Examination
Semester End
Examination
20
20
30
20
10
100
20
20
30
20
10
100
10
20
30
20
20
100
10
20
30
20
20
100
Remember
1. Define polymer and degree of polymerization.
2. What is functionality of a polymer? Give example.
3. What is the nomenclature of a polymer?
4. Discuss the addition and chain growth polymerization with example.
5. What is copolymerization? What are the different types of copolymers?
6. Write the mechanism of addition polymerization.
7. Explain briefly the various constituents of a plastic, with example.
8. Distinguish between thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics.
9. List the various additives in processing of plastics. What are their functions?
10. Explain homogeneous and heterogeneous polymerization.
11. Write the differences between melt and interfacial polycondensation.
12. Briefly explain about emulsion polymerization.
The marks secured in the Test I and II will be converted to 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining
10 marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
376
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
Explain compression and extrusion moulding of plastics with diagram.
What is extrusion and injection moulding? Discuss with diagram.
Name any four compounding ingredients of plastics. Write their functions with example.
What is calendaring?
Write short account on reinforced plastics.
Outline the method of lubrication of plastic material.
Explain about crosslinking and blowing agents with examples.
Write an account of flame retardant polymers.
Write short notes on melt, dry and wet spinning process.
Give the classification of foaming polymers with examples.
Explain with examples the relationship between structure and properties of polymers.
Describe about coordination and ring opening polymerization.
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Write the important of plasticizers and UV stabilizers?
Compare addition and condensation polymerization reaction with example for each type .
Give the classification of foaming polymers with examples.
Suggest different types of additives for preparing reinforced polymers?
What are the different types of polymeric resins?
Give the significances of antioxidants and antiozonants additives.
What are the functions of ingredients of polymers?
List the importance of cross- linkers.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
How polymers are classified based on source and application?
What are the polymers that can be calendared into sheets?
Give examples for thermosetting and thermoplastic polymers.
What are the polymers suited for compression and injection moulding?
What are the articles produced by blow moulding?
Analyze / Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
What are the polymers suitable for insulations?
Write the special properties of teflon?
How the vinyl chloride is converted into polymer?
How nylon 6 is prepared?
What is the process involved in manufacturing cellophane sheets?
What are the different zones involved in simple extrusion polymer process?
Bring out the differences between thermoforming and vacuum-forming process?
Unit I
Principles of Polymer Science
Polymerization reactions - types examples - degree of polymerization and average molecular weights.
Thermoplastics and thermosetting resins - examples. Electrical - mechanical - thermal properties
related to chemical structure. Insulating materials - polymer alloys - composites.
Importance of glass transition temperature.
9 Hours
377
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit II
Polymerization Mechanism
Addition polymerization - free radical mechanism - cationic and anionic polymerization copolymerization - condensation polymerization nylon 6,6, ring opening polymerization nylon 6,
coordination polymerization -. Preparation, properties and industrial applications of polystyrene and
bakelite.
Application of industrial polymers.
9 Hours
Unit III
Polymerization Techniques
Homogeneous and heterogeneous polymerization bulk polymerization- PMMA,PVC, solution
polymerization - polyacrylic acid, suspension polymerization-preparation of ion exchange resins,
emulsion polymerization-synthetic rubber. Melt solution and interfacial polycondensation. Salient
features, advantages and disadvantages of bulk and emulsion polymerization.
Preparation of biodegradable polymers.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Additives for Polymers
Moulding constituents-fillers, plasticizers, lubricants, anti-aging additives, antioxidants, antiozonants,
UV stabilizers, flame retardants, colorants, blow agents, crosslinking agents -functions-significance
with suitable examples and applications in industrial processing.
Ecofriendly sustainable additives.
9 Hours
Unit V
Polymer Processing
Compression injection - extrusion and blow mouldings. Film casting - calendering. Thermoforming
and vacuum formed polystyrene, foamed polyurethanes. Fibre spinning - melt, dry and wet spinning.
Composite fabrication - hand-layup - filament winding and pultrusion.
Application of fibre reinforced plastics.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
V. R. Gowarikar, N. V. Viswanathan and Jayadev Sreedhar, Polymer Science, New Age
International (P) Ltd., New Delhi, 2003.
Joel R. Fried, Polymer Science and Technology, Prentice Hall of India (P). Ltd., 2005.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
F. W. Billmeyer, Text Book of Polymer Science, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2007.
Barbara H. Stuart, Polymer Analysis, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2002.
George Odian , Principles of Polymerization, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2004.
R. J. Young and P. A. Lovell, Introduction to Polymers, Nelson Thornes Ltd., 2002.
378
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O0YB ENERGY STORING DEVICES AND FUEL CELLS
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To make students understand the concept and working of different types of batteries and to
analyze batteries used in electric vehicles
To make students learn about the concept of fuel cells, its types and to relate the factors of
energy and environment
Students develop the skill of analyzing various energy storing devices and fuel cells at the end
of the semester
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Understanding the various types of cells and energy storage devices.
Compute the efficiency of cells.
Development of eco-friendly energy sources.
Realize the advantages of energy storage and fuel cells.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
S.No
1
2
3
4
5
6
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I
Test II
Model
Examination
Semester End
Examination
20
20
30
20
10
100
20
20
30
20
10
100
10
20
30
20
20
100
10
20
30
20
20
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
What are dry cells?
What are alkaline batteries?
State Ohms law.
Write the functions of ultra-capacitor.
Is lead acid battery thermodynamically reversible cell?
Differentiate between electrochemical and electrolytic cells.
Name the electrolyte present in the Li battery.
Mention the role of heart pacemaker in cardiology.
Classify the types of fuel cell.
Differentiate between diode and electrode.
The marks secured in the Test I and II will be converted to 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining
10 marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
379
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11.
12.
13.
14.
What is meant by redox reaction?
What are the advantages of H2-O2 fuel cell?
Name the factors which are affecting the efficiency of fuel cell.
What are eco-friendly cell?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
How do you assess the life cycle of fuel cells?
What is the role of impurities in photovoltaic cells?
How do you convert the chemical energy into electrical energy?
Suggest any two secondary storage devices for automobiles.
What types of cells are used in space applications?
Construct the alkaline fuel cell.
How do you harvest the energy from tides?
What are natural geysers?
Differentiate between photo electrochemical and photovoltaic cells.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
What are passive solar heat collectors?
What are active solar heat collectors?
Lithium battery is the cell of future - Justify.
Write the anodic reaction and cathodic reactions of NICAD battery.
Is the dry cell follows thermodynamic reversibility rule?
What types of vehicles typically use methanol?
What are the economic impacts of using hybrid electric vehicles?
Analyze / Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
How does a fuel cell differ from traditional methods of energy generation (like batteries)?
What are the feedstocks can be used to make biodiesel?
What is DuPonts experience in fuel cells?
How the biomass is converted into biofuel?
What are the effects of gasoline and ethanol emissions on the environment?
What are the effects of diesel and biodiesel emissions on the environment?
How do you obtain ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass?
What is meant by green technology?
Unit I
Batteries
Characteristics - voltage, current, capacity, electricity storage density, power, discharge rate, cycle life,
energy efficiency, shelf life. Primary batteries- zinc-carbon, magnesium, alkaline, manganous dioxide,
mercuric oxide, silver oxide batteries-Recycling/Safe disposal of used cells.
Document the various batteries and its characteristics used in mobile phones and lap tops.
9 Hours
Unit II
Batteries for Electric Vehicles
Secondary batteries- Introduction, cell reactions, cell representations and applications- lead acid,
nickel-cadmium and lithium ion batteries - rechargeable zinc alkaline battery. Reserve batteries: Zincsilver oxide, lithium anode cell, photogalvanic cells. Battery specifications for cars and automobiles.
Development of batteries for satellites.
9 Hours
380
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit III
Types of Fuel Cells
Importance and classification of fuel cells - description, working principle, components, applications
and environmental aspects of the following types of fuel cells: alkaline fuel cells, phosphoric acid, solid
oxide, molten carbonate and direct methanol fuel cells.
Fuel cells for space applications.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Hydrogen as a Fuel
Sources of hydrogen production of hydrogen- electrolysis- photocatalytic water splitting biomass
pyrolysis -gas clean up methods of hydrogen storage- high pressurized gas -liquid hydrogen type metal hydride hydrogen as engine fuel features, application of hydrogen technologies in the futurelimitations.
Cryogenic fuels.
9 Hours
Unit V
Energy and Environment
Future prospects-renewable energy and efficiency of renewable fuels economy of hydrogen energy
life cycle assessment of fuel cell systems. Solar Cells: Energy conversion devices, photovoltaic and
photoelectrochemical cells photobiochemical conversion cell.
Bio-fuels from natural resources.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
3.
M. Aulice Scibioh and B. Viswanathan, Fuel Cells: Principles and Applications, University Press,
India, 2006.
F. Barbir, PEM fuel cells: Theory and practice,Elsevier, Burlington, MA, 2005.
M. R. Dell Ronald and A. J. David, Understanding Batteries, Royal Society of Chemistry, 2001.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
M. A. Christopher Brett, Electrochemistry: Principles, Methods and Applications, Oxford
University, 2004.
J. S. Newman and K. E. Thomas-Alyea, Electrochemical Systems, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, 2004.
G. Hoogers, Fuel Cell Handbook, CRC, Boca Raton, FL, 2003.
Lindon David, Handbook of Batteries, McGraw Hill, 2002.
H. A. Kiehne , Battery Technology Hand Book,. Expert Verlag , Renningen Malsheim, 2003.
381
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O0YC CHEMISTRY OF NANOMATERIALS
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge on the basic concepts and importance of nanochemistry including synthesis
To make students understand the principles and applications of nanomaterials
Knowledge about the characterization and applications of nanomaterials
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
Understanding the various methods of synthesis and characterization techniques of nanomaterials.
Compute new preparation methodologies.
Utilization of nanomaterials in various emerging fields.
Realize the importance of nanoscience and its applications in day to day life.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S.No
1
2
3
4
5
6
Blooms
Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I
Test II
Model
Examination
Semester End
Examination
25
25
20
20
10
100
25
25
20
20
10
100
15
25
20
20
20
100
15
25
20
20
20
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
What do you mean by nano?
Define nanotechnology.
Define nanoscience.
Define top down and bottom up approach.
Define nanostructured material. Classify nanomaterials and give examples for them.
List any four day to day commercial applications of nanotechnology.
Write down any four challenges that are faced by researchers in nanotechnology.
Define carbon nanotube.
Define bucky ball.
Define nanocomposite. What are the types of nanocomposites?
List any four material characterization techniques.
List any four bottom up approaches for the synthesis of nanopowders.
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted to 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
382
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
What is biomimetic approach?
Explain Feynmans statement.
What is the dimension of quantum dot?
Explain the principle behind lithography.
Mention the different types of lithography.
What is meant by photolithography?
Explain the principle behind vapour phase deposition.
What is meant by chemical vapour deposition?
Explain sputtering.
What is meant by plasma enhanced CVD?
What is meant by bubblers?
Explain the principle behind MOVPE.
What are colloids?
What is nanosafety?
What is meant by surface induced effect?
How are nanomaterials defined?
What are the uses of nanoparticles in consumer products?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
What is the difference between nanoscience and nanotechnology?
When and where Feynman delivered his lecture on nanotechnology and what is the name of his
classical lecture?
What are the induced effects due to increase in surface area of nanoparticles?
What are the advantages and disadvantages in mechanical synthesis of nanopowders?
What are the characteristics of nanoparticles that should be possesed by any fabrication technique?
On what principle mechanical milling is based on?
How is LPE used to obtain nanowire or nanorods?
How is the template used to obtain nanowire or nanorods?
What is the role of nanotechnology in water purification?
Differentiate self-assembly from self-organisation.
How nanoparticles are stored?
List the important physical and chemical properties of nanomaterials?
How are nanomaterials detected and analysed?
How are nanomaterials prepared for biological testing?
What are the physical and chemical properties of nanoparticles?
How are nanoparticles formed?
Discuss the health effects of nanoparticles?
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Why do we want nanotechnology in our life?
What is the role of nanotechnology in medicinal field?
Expand AFM.
What is the grain size range of nanostructure materials?
Differentiate top-down from bottom-up approach needed for nanosynthesis.
Why do nanostructured particles find potential applications?
How nanostructured particles are used in health applications?
383
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Compare the relative merits of chemical, physical, biological and hybrid methods for the
preparation of nanomaterials.
Compare the relative merits of the usage of photons and particles in lithography.
Differentiate glow discharge from RF sputtering.
How can we reduce/save our energy resources by using nanotechnology?
What is the relation between properties and applications of nanoparticles?
What is the current status of nanoscience and nanotechnology?
What are the potential harmful effects of nanoparticles?
Unit I
Nanoworld
Introduction History of nanomaterials concepts of nanomaterials size and confinement effects
nanoscience nanotechnology Moors law. Properties electronic, optical, magnetic, thermal,
mechanical and electrochemical properties. Nanobiotechnology molecular motors optical tweezers.
First industrial revolution to the nano revolution.
9 Hours
Unit II
Synthesis of Nanoparticles
Introduction hydrolysis-oxidation - thermolysis metathesis - solvothermal methods. Sonochemistry:
nanometals - powders of metallic nanoparticles - metallic colloids and alloys - polymer metal
composites - metallic oxides - rare earth oxides - mesoporous materials - mixed oxides. Sono
electrochemistry - nanocrystalline materials. Microwave heating - microwave synthesis of nanometallic
particles.
Magnetron sputtering process to obtain nanomaterials.
9 Hours
Unit III
Types and Functionalization of Nanomaterials
Polymer nanoparticles, micro, meso and nanoporous materials. Organic inorganic hybrids, zeolites,
nanocomposites, self-assembled monolayers, semiconductor quantum dots, nanofibres, supramolecular
nanostructures. functionalization of nanomaterials stabilization methods. Reactivity of -functional
groups on ligand shells.
Implications of nanoscience and nanotechnology on society.
9 Hours
Unit IV
Physical and Chemical Characterization
Electron microscopes: scanning electron microscope (SEM) transmission electron microscope (TEM)
atomic force microscope (AFM): working principle instrumentation applications. UV-visible
spectroscopy: principle instrumentation (block diagram only) applications. FT-IR spectroscopy:
introduction instrumentation (block diagram only) applications merits and demerits.
Nanoscience and technology research institution.
9 Hours
Unit V
Applications of Nanomaterials
Nanocatalysis, colorants and pigments, self-cleaning lotus effect, anti-reflective coatings,
antibacterial coatings, photocatalysis, nanofilters for air and water purifiers. Thermal insulation
aerogels, smart sunglasses and transparent conducting oxides molecular sieves nanosponges.
384
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Harnessing nanotechnology for economic and social development.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
3.
C N R Rao, Nanoworld An Introduction to Nanoscience and Technology, Jawaharlal Nehru
centre for advanced scientific research, Bangalore, India, 2010.
C N R Rao, A Muller and A K Cheetham, The Chemistry of Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Properties
and Applications, Vol. 1 & 2, John-Wiley and Sons, 2005.
T Pradeep, Nano: The Essentials, Understanding Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 1st Edn., Tata
Mcgraw Hill publishing company, 2007.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
Geoffrey A Ozin, Andr C Arsenault , Nanochemistry: A Chemical Approach to Nanomaterials,
Royal Society of Chemistry, 2009.
G B Sergeev, Nanochemistry, 1st Edn.,Elsevier, 2006.
S Chen, Functional Nanomaterials: A Chemistry and Engineering Perspective (Nanostructure
Science And Technology), Springer,2010.
Yury Gogotsi, Nanomaterials Handbook, Taylor and Francis group, USA, 2006.
385
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O0YD
CORROSION SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge about the various types of corrosion and its mechanism
To make students understand the various methods of corrosion control, corrosion testing and
monitoring
Students acquire the basic knowledge about corrosion and its control.
PROGRAM OUTCOME
a)
The graduates will become familiar with fundamentals of various science and technology subjects
and thus acquire the capability to applying them
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Understand why corrosion related problems are complex and interrelated in the engineering field.
Compare the mechanism of dry corrosion and electrochemical corrosion to support corrosion
minimizing techniques in metals and its alloys.
Characterize and analyze different forms of corrosion and its study techniques.
Classify and understand about the relationship between corrosion and its environment.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S.No
1
2
3
4
5
6
Blooms
Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I
Test II
Model
Examination
Semester End
Examination
25
25
20
20
10
100
25
25
20
20
10
100
15
25
20
20
20
100
15
25
20
20
20
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
What is corrosion?
What are the types of corrosion?
Define dry corrosion. Explain the mechanism.
Explain the mechanism of electrochemical corrosion.
What are the units to measure corrosion rate?
Galvanic corrosion. Discuss.
Describe the Pourbaix digrams of Mg, Al and Fe and their limitations.
List out the different forms of corrosion. Explain.
What are inhibitors?
The marks secured in Test I and II will be converted to 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
386
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
Explain the mechanisms of various corrosion scale formation and its types.
Write the working principle of Tafel polarization techniques.
How polarization and impedance techniques used to measure the corrosion products?
Define cathodic protection. List its types.
What are non-electrochemical and electrochemical methods of corrosion testing and monitoring?
What is Tafel linear polarization?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Explain why corrosion rate of metal is faster in aqueous solution than atmosphere air?
What are the factors influencing the corrosion rate? Explain.
Discuss the Pilling-Bedworth rule.
Differentiate between electrochemical and dry corrosion.
How inhibitors are used to protect the corrosion rate of the metal? Explain.
What are consequences of Pilling-Bedworth ratio?
List the difference between filliform corrosion and pitting corrosion.
Apply
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Compare the effects of corrosion products.
Why pitting corrosion is localized corrosion? Explain.
Describe alternatives to protective coatings.
Identify different forms of corrosion in the metal surface.
Explain how we could reduce corrosion of metals.
What are the measures to be taken to reduce corrosion fatiques?
What are the major implications of enhanced techniques of corrosion product analysis?
Analyze/ Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
List reasons why it is important to study of corrosion.
How Tafel polarization and impedance techniques used to measure the corrosion products?
Explain how we could reduce corrosion of metals?
Unit I
Introduction to Corrosion
Importance and cost of corrosion spontaneity of corrosion passivation - importance of corrosion
prevention in various industries - the direct and indirect loss of corrosion- galvanic corrosion: area
relationship in both active and passive states of metals - Pilling Bed worth ratio and its consequences units of corrosion rate - mdd and mpy - importance of pitting factor - Pourbaix digrams of Mg, Al and
Fe and their advantages and disadvantages .
Corrosion of metals by other gases.
9 Hours
Unit II
Forms of Corrosion
Different forms of corrosion - uniform corrosion-galvanic corrosion, crevice corrosion, pitting
corrosion, intergranular corrosion, selective leaching, erosion corrosion, stress corrosion- high
temperature oxidation, kinetics of protective film formation and catastrophic oxidation corrosion.
Industrial boiler corrosion, cathodic and anodic inhibitors
9 Hours
387
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit III
Mechanisms of Corrosion
Hydrogen embrittlement- cracking, corrosion fatigue - filliform corrosion, fretting damage and
microbes induced corrosion. Mechanisms of various corrosion scale formation - thick layer and thin
layer - insitu corrosion scale analysis.
Analyze the rust formation in mild steel using weight loss method
9 Hours
Unit IV
Cathodic and Anodic Protection Engineering
Fundamentals of cathodic protection - types of cathodic protection systems and anodes. Life time
calculations - rectifier selection. Stray current corrosion problems and its prevention. Coating for
various cathodic protection system and their assessment- inhibitors - corrosion of steels. Anodic
protection-Design for corrosion control.
Role of paints and pigments to protect the corrosive environment
9 Hours
Unit V
Corrosion Testing and Monitoring
Corrosion testing and monitoring - electrochemical methods of polarization- Tafel extrapolation
polarization, linear polarization, impedance techniques-Weight loss method - susceptibility test
testing for intergranular susceptibility and stress corrosion.
Analyze the instruments for monitoring the corrosion.
9 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
3.
Zaki Ahmad, Principles of Corrosion Engineering and Corrosion Control, Elsevier Science and
Technology Books, 2006.
R. Winstone Revie and Herbert H. Uhlig, Corrosion and Corrosion Control: An Introduction to
Corrosion Science and Engineering, John Wiley & Science, 2008.
Mars G. Fontana, Corrosion Engineering, Tata McGraw Hill, Singapore, 2008.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
ASM Hand Book, Vol. 13, Corrosion, ASM International, 2005.
Pierre R. Roberge, Hand Book of Corrosion Engineering, McGraw Hill, New York, 2000.
Denny A. Jones, Principles and Prevention of Corrosion, Prentice Hall Inc., 2004.
A.W. Peabody, Control of Pipeline Corrosion, NACE International, Houston, 2001.
388
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O001 ENTREPRENEURSHIP DEVELOPMENT I
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVE
To gain knowledge on basics of Entrepreneurship
To gain knowledge of business entity, source of capital and financially evaluate the project
To gain knowledge on production and manufacturing system
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
e) The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team
b) The graduates can become job-givers rather than just job-seekers
SKILL SET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Entrepreneurial thinking
Innovation techniques in developing business
Legal aspects of a business
Skills on finance and cash flow
Skills on planning operations
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
45
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I
Test II
20
20
20
10
20
10
100
20
20
20
10
20
10
100
Model
Examination
20
20
20
10
20
10
100
Semester End
Examination
20
20
20
10
20
10
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
45 *
What is entrepreneurship?
What are the factors that motivate people to go into business?
Define a small-scale industry.
Define tiny industry.
Who is an intrapreneur?
State functions of SISI.
What is serial entrepreneur?
What is Technopreneurship?
What is reversal method?
What is brainstorming?
What do you mean by term business idea?
Mention any two schemes Indian government provides to the development of entrepreneurship.
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
389
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
What is a project report?
What is project scheduling?
Mention any four techniques available for project scheduling.
What is contract act?
Define MOU.
What are al the types of sources of finance for an entrepreneur?
Mention any five external sources of finance to an entrepreneur.
Classify the financial needs of an organization.
What is short term finance?
What is return on capital?
What is capital budgeting?
What is product design?
What is quality council?
What is inventory?
What is lean manufacturing?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Why is entrepreneurship important of growth of a nation?
Mention the essential quality required for someone to be an entrepreneur.
Why is motivational theories important for an entrepreneur?
How is network analysis helpful to the development of an entrepreneur?
Mention the essential requirements for a virtual capital.
How under-capitalization affects an entrepreneur.
Differentiate proprietorship and partnership.
Mention the causes of dissolution of a firm.
How important is the support of IDBI to an entrepreneur?
What are the salient features of New Small Enterprise Policy, 1991?
Why scheduling is very important for a production design?
Apply / Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
If you want to become as an entrepreneur, what will be your idea?
Select any one of the creative idea generation method and suggest an innovation that you can
implement in your business.
Write a short notes on various legal aspects that you have to consider to run you business.
How will you generate you capital and other financial supports?
In case of getting enough financial support, plan your business and plot the various stages using
any of the tools or techniques.
Create
1.
2.
3.
Draft a sample project report for your business.
Do a network analysis using PERT and CPM for your business plan.
Write a brief report to apply to a financial organization for seeking financial support to your
business.
390
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit I
Basics of Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship Competence, Entrepreneurship as a career, Intrapreneurship, Social entrepreneurship,
Serial entrepreneurship (Cases), Technopreneurship.
Entrepreneurial Motivation
6 Hours
Unit II
Generation of Ideas
Creativity and Innovation (Cases), Lateral thinking, Generation of alternatives (Cases), Fractionation,
Reversal Method, Brain storming
Utilization of Patent Databases
8 Hours
Unit III
Legal Aspects of Business
Contract Act, Sale of Goods Act, Negotiable Instruments Promissory Note, Bills and Cheques,
Partnership, Limited Liability Partnership (LLP), Companies Act Kinds, Formation, Memorandum of
Association, Articles of Association (Cases).
Business Plan Writing
10 Hours
Unit IV
Business Finance
Project evaluation and investment criteria (Cases), Sources of finance, Financial statements, Break
even analysis, Cash flow analysis.
Calculation of Return on Investment
11 Hours
Unit V
Operations Management
Importance Functions Deciding on the production system Facility decisions: Plant location, Plant
Layout (Cases), Capacity requirement planning Inventory management (Cases) Lean
manufacturing.
Project Planning
10 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
Donald F. kuratko, Entrepreneurship Theory, Process & Practice, South western cengage
learnng, USA, 2009.
References
1. Hisrich, Entrepreneurship, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi, 2005.
2. Prasanna Chandra, Projects Planning, Analysis, Selection, Implementation and Reviews, Tata
McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi, 2000.
3. Akhileshwar Pathak, Legal Aspects of Business, Tata McGraw Hill, 2006.
4. Norman Gaither and Greg Frazier, Operations Management, Thomson Learning Inc, 2007.
5. Edward De Bono, Lateral Thinking, Penguin Books, 1990.
391
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11O002 ENTREPRENEURSHIP DEVELOPMENT II
3 0 0 3.0
OBJECTIVES
The students on completion of the course will be able to
Evolve the marketing mix for promoting the product / services
Handle the human resources and taxation
Understand Government industrial policies / support provided and prepare a business plan.
PROGRAM OUTCOMES
e) The graduates develop skills to be effective members of a team
b) The graduates can become job-givers rather than just job-seekers
SKILL SET
1.
Increase in awareness of the entrepreneurship Development for engineering decisions.
ASSESSMENT PATTERN
S. No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
46
Blooms Taxonomy
(New Version)
Remember
Understand
Apply
Analyze
Evaluate
Create
Total
Test I
Test II
30
30
20
10
10
-100
30
30
20
10
10
-100
Model
Examination
30
25
20
10
10
05
100
Semester End
Examination
30
25
20
10
10
05
100
Remember
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
46
Who are Fabian Entrepreneur?
Explain the Views on Schumpeter on Entrepreneurship?
Mention the three functions of NSIC?
Narrate the role of IDBI in the development of Entrepreneurship?
What are Project Objectives?
What are the stages in a Project Lifecycle?
Give the meaning of Feasibility Report?
Explain the objective of Entrepreneurial Training?
What is Motivating Training?
Who is a Small Scale Entrepreneur?
How to develop Rural Entrepreneur?
What are the Social Problems of Women Entrepreneur?
Differentiate between entrepreneur and entrepreneurship.
What are the types of entrepreneurs?
The marks secured Test I and Test II will be converted 20 and Model Examination will be converted to 20. The remaining 10
marks will be calculated based on assignments. Accordingly internal assessment will be calculated for 50 marks.
392
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
Explain the various qualities of entrepreneur.
Briefly explain the different merchant castes in India.
What is entrepreneurship training?
Discuss any three programmes supporting women entrepreneurs.
Write a note on the role of NISIET.
What are the challenges and opportunities available in SSI's?
Understand
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Narrate any six differences between a Manager and an Entrepreneur?
Explain briefly various types of Entrepreneur?
What are the elements of EDP?
What is the role played the commercial banks in the development of Entrepreneur?
How would you Classify Projects?
What are the stages in project Formulation?
What are the target groups of EDP?
What are the major problems faced by Small Entrepreneur?
What are the problems & prospects for women entrepreneur in India?
Apply/Evaluate
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Describe the various functions performed by Entrepreneurs?
Explain the role of different agencies in the development of Entrepreneur?
Discuss the criteria for selecting a particular project?
Describe the role of Entrepreneur in the Development of Country?
Define business idea. Elaborate the problems and opportunities for an entrepreneur.
Elaborate the schemes offered by Commercial banks for development of entrepreneurship.
Explain the significant role played by DIC & SISI for the development of entrepreneurship.
Design a short Entrepreneurship development programme for farmer
Discuss the role and importance of the following institutions in promoting, training and developing
entrepreneurs in India:
Create
1.
2.
3.
All economy is the effect for which entrepreneurship is the cause"-Discuss.
Review the entrepreneurial growth by the communities of south India.
What are the problems of Women entrepreneurs and discuss the ways to overcome these
barriers?
4. Discuss the importance of small scale industries in India.
5. Critically examine the growth and development of ancillarisation in India.
6. Discuss the various sources and collection of credit information of entrepreneurs.
7. Briefly explain the recommendation and policy implication for survival of SME's.
8. Discuss the role of the Government both at the Central and State level in motivating and
developing entrepreneurship in India.
9. Developing countries like India need imitative entrepreneurs rather than innovative
entrepreneurs. Do you agree? Justify your answer with examples.
10. What are the reasons of very few women becoming entrepreneurs in a developing country like
India? Whether Indian women entrepreneurs have now made an impact and shown that they too
can contribute in economic development of the country? Discuss with examples.
11. Discuss the Culture of Entrepreneurship and its role in economic development of a nation. What
factors contribute to nurturing such a culture?
393
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
Unit I
Marketing Management
Formulating Marketing strategies, The marketing plan, Deciding on the marketing mix (Cases),
Interactive marketing, Marketing through social networks, Below the line marketing, International
marketing - Modes of Entry, Strategies (Cases).
Five P's of marketing, SSI Policy Statement
10 Hours
Unit II
Human Resource Management
Human Resource Planning (Cases), Recruitment, Selection, Training and Development, HRIS,
Factories Act 1948 (an over view)
Global Trends in Human Resource Management
10 Hours
Unit III
Business Taxation
Direct taxation Income tax, Corporate tax, MAT, Tax holidays, Wealth tax, Professional tax
(Cases).Indirect taxation Excise duty, Customs, Sales and Service tax, VAT, Octroi, GST(Cases)
Recent Trends for a Troubled Tax, professional tax slab
8 Hours
Unit IV
Government Support
Industrial policy of Central and State Government, National Institute and Agencies, State Level
Institutions, Financial Institution
Global Entrepreneurship Monitor, Excise Exemption Scheme
7 Hours
Unit V
Business Plan Preparation
Purpose of writing a business plan, Capital outlay, Technical feasibility, Production plan, HR plan,
Market survey and Marketing plan, Financial plan and Viability, Government approvals, SWOT
analysis.
Small Industry Cluster Development Programme, National Equity Fund Scheme
10 Hours
Total: 45 Hours
Textbook
1.
S. S. Khanka, Entrepreneurial Development, S. Chand & Co, New Delhi, 2010
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Hisrich, Entrepreneurship, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi, 2005.
Philip Kotler, Marketing Management, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2003.
K. Aswathappa, Human Resource and Personnel Management Text and Cases, Tata McGraw
Hill, 2007.
P. C. Jain, Handbook for New Entrepreneurs, EDII, Oxford University Press, New Delhi, 2002.
Akhileshwar Pathak, Legal Aspects of Business, Tata McGraw Hill, 2006.
394
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M0XA CONDITION MONITORING
1 0 0 1.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the basics of condition monitoring in mechanical systems
To understand the Maintenance of machine, methods of monitoring and techniques
General concept of condition monitoring, general issues of condition monitoring, Main components in
a condition monitoring system. Maintenance type, Condition based maintenance systems, Machine
maintenance techniques. Noise/sound monitoring, Crack monitoring, Leakage monitoring, Lubricant
monitoring. Machine condition monitoring techniques, Vibration monitoring techniques, selecting
methods of monitoring. Introduction, Machinery Alignment, Rough Alignment Methods, Vibration
monitoring-causes.
Total: 20 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
B K N Rao, Handbook of Condition Monitoring, Elsevier, 1996
Singiresu S Rao, Mechanical Vibrations, Pearson Education, 2004
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
J S Rao, Vibratory Condition Monitoring of Machines, Narosa publishing house, 2000
Davies, Handbook of condition monitoring: techniques and methodology, Chapman & Hall, 1998
J Hywel Williams, Alan Davies, Paul R Drake, Condition-based maintenance and machine
diagnostics, Kluwer academic publishers ,1994
www.conditionmonitoringsystem.com/
http://www.ecgcorp.com/velav/
395
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M0XB DESIGN FOR MANUFACTURE AND ASSEMBLY
1 0 0 1.0
OBJECTIVES
To study the use of tolerances in manufacturing
Application of this study to machining and casting processes
To make the student familiar with solving different problems in design modifications of the
product related to various manufacturing techniques
Tolerances: Limits and Fits, tolerance Chains and identification of functionally important dimensions Geometric tolerances. Materials choice - Influences of materials - Space factor - Size - Weight.
Introduction - Pattern, Parting line, Mould, Machined holes and cored holes. Design of castings based
on parting line considerations and minimizing core requirements. Form design of welded fabrication welding processes - stresses - Designing cast members using Welds. Form design aspects in ForgingDesign aspects of welding and forging of mechanical components.
Introduction - Design features to facilitate machining Drills, Milling cutters - Reduction of machined
area - Simplification by separation - Simplification by amalgamation. Introduction - Identification of
uneconomical design - Modifying the design - Datum features - Design for Recyclability - Design for
remanufacture.
Total: 20 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
G Boothroyd, P Dewhurst and W. Knight, Product Design for Manufacture and Assembly, Marcell
Dekker, 2002
Harry Peck, Designing for Manufacture, Pitman Publishing, 1983
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
A K Chitale and R. C. Gupta, Product Design and Manufacturing, PHI 2007
Robert Matousek, Engineering Design, Blackie & Son Limited, 1963
R Bryan , Fischer, Mechanical Tolerance stackup and analysis, Marcell Dekker, 2004
J G Bralla, Hand Book of Product Design for Manufacturing, McGraw Hill Publications, 2000
http://www.dfma.com/
396
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M0XC DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS USING TAGUCHI APPROACH
1 0 0 1.0
OBJECTIVES
By learning and applying this technique, students can significantly reduce the time required for
experimental investigation
Apply for product/process optimization
Overview of DOE and taguchi approach- common experiments and methods of analysis. Orthogonal
array- properties case studies - L -4, L-8, L-12,L-16,L-32 Orthogonal array - L-9,L-18, L-27
Orthogonal array - ANOVA-Degrees of freedom-confidence level and interval exercises.
Total: 20 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
Ranjit K Roy, Design of Experiments using the Taguchi Approach, John Wiley & sons, Inc., 2001
Ranjit K Roy, A Primer on the Taguchi Method, Society of Manufacturing Engineers, Michigan,
1990
References
1.
Genichi Taguchi, Subir Chowdhury and YuinWu, Taguchis Quality Engineering Hand Book,
John Wiley & Sons, Inc
397
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M0XD GEOMETRIC DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING
1 0 0 1.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the basics of GD&T and its practical applications
To understand the proper way to specify dimensions and tolerances, symbols, datum, position,
location, run out and profile
Introduction to Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing - Dimensioning and Tolerancing
Fundamentals -Symbols, Terms, and Rules-Datum Application, Datum feature identification-Inclined,
cylindrical datum feature. Form flatness, straightness, circularity, cylindricity - Position Maximum
Material Condition, Least material Condition - Location - Position, Coaxiality - Concentricity
Symmetry Exercises - Run out - Definition, circular runout, total runout Profile Definition,
Specifying profile, radius refinement with profile profile of conical feature.
Total: 20 Hours
Textbooks
1.
Gene R Cogorno, Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing for Mechanical Design, McGrawHill,
2006
References
1.
2.
Alex Krulikowski, Fundamentals of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing, Delmar Cengage
Learning, 1997
Gary K Griffith, Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing: Application and Inspection, Prentice
Hall
398
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M0XE INTELLIGENT OPTIMIZATION TECHNIQUES
1 0 0 1.0
OBJECTIVES
To Learn Nontraditional Optimization techniques
To develop the skill to apply the optimization techniques for real time mechanical engineering
problems.
Introduction, General Structure of GA-Selection Techniques-Constrained and unconstrained
optimization problems-Mutation operators-Cross Over Functions-Example Problems. IntroductionClassical particle swarm optimization method - Molecular Dynamics Formulation conservative and
non-conservative Environments- Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration techniques for PSOExample problems. Introduction, Types of ANN, Elements of ANN- Weight function, Threshold
Function , Hidden Layer network, Basic fundamental rules-Example for Feed forward back
propagation and perspective neural network model. Introduction, Basic steps in SA, Unconstrained and
constrained problems, Re-annealing concept, Example simple Design problems. Introduction to Ant
colony and Tabu search method- Concept Explanations- Comparison study of GA with Ant Colony and
Tabu Search Algorithm, Application Traveling Salesman problems.
Total: 20 Hours
Textbooks
1.
S S Rao, Optimization Techniques, New Age International, 2007
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
James F Kennedy, James Kennedy, Russell C. Eberhart and Yuhui Shi, Swarm intelligence,
Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 2001
M Mikki and Ahmed A Kishk, Particle Swarm Optimization: a Physics-Based Approach, Morgan
& Claypool, Jan 2008
Mohamad H Hassoun, Fundamentals of artificial neural networks, Prentice Hall of India Learning,
2010
R Saravanan, Manufacturing Optimization through Intelligent Techniques, Published by CRC
Publications, Taylor and Francis, U.S.A., 2006
399
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M0XF LEAN MANUFACTURING
1 0 0 1.0
OBJECTIVES
To acquire the general knowledge to deliver consistently high quality and value added products
and services to the customer in a lean environment
To understand the terminology relating to lean operations in both service and manufacturing
organizations
History Evolution - Toyota production system - Lean manufacturing overview - Work place
organization - Visual controls - Pull production and cellular manufacturing - Value flow pull - Value
and perfection lean Mapping the present Mapping the future - Product and process development
Value stream analysis - Over production - Waiting - Work In Progress - Transportation - Inappropriate
processing - Excess motion or ergonomic problems - Defected products - Underutilization of employees Just In Time - Kanban tooling - Total Productive Maintenance 5S - Single Minute Die Exchange Lean six sigma - Flow charting - Identifying and eliminating unnecessary steps - Setup time - reduction
approaches - Steps in implementing lean strategy Lean accounting system
Total: 20 Hours
Textbooks
1.
Dennis P Hobbs, Lean Manufacturing Implementation, J. Ross Publications, 2004
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Jeffrey K Liker, The Toyota Way-14 Management Principles, Mc-Graw Hill, New York, 2004
Pascal Dennis, Lean Production Simplified, Productivity Press, USA, 2002
James P Womack, Daniel T. Jones, Lean Thinking: Banish waste and create wealth in your
corporation, Simon & Schuster UK Limited, Free Press, 2003
Jay Arthur, Lean Six-Sigma Demystified, Tata McGraw-Hill Company, New Delhi, 2007
Richard J Schonberger, World Class Manufacturing, Free Press, 2008
400
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M0XG SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT
1 0 0 1.0
OBJECTIVES
To acquire the general knowledge to deliver consistently high quality and value added products
and services to the customer in a supply chain environment
To understand the terminology relating to supply chain operations in both service and
manufacturing organizations
Supply Chain Fundamentals, Importance, Decision Phases, Process View. Supplier Manufacturer
Customer Chain. Drivers of Supply Chain Performance. Overview of Supply Chain Models and
Modeling Systems. Definition of Supply Chain Management (SCM), Scope, SCM as a Management
Philosophy, Functions of SCM. Distribution Network Design Role, Factors Influencing, Options,
Value Addition. Models for Facility Location and Capacity Location. Impact of uncertainty on
Network Design. Network Design Decisions Using Decision Trees. Supply Chain Network
Optimization Models. Overview of Demand Forecasting in the Supply Chain. Aggregate Planning in
the Supply Chain. Managing Predictable Variability. Managing Supply Chain Cycle Inventory.
Uncertainty in the Supply Chain Safety Inventory. Determination of Optimal Level of Product
Availability. Coordination in the Supply Chain. Cross-Functional drivers, Role of sourcing in a supply
chain, Logistics providers, Procurement process, Supplier selection, Design collaboration, Role of
Pricing and Revenue Management in a supply chain. eBusiness Framework and Role of Supply
Chain in e-Business and B2B Practices. Supply Chain IT Framework. Information Systems
Development. Packages in Supply Chain eSRM, eLRM, eSCM. Reverse and Green Supply Chain
Management.
Total: 20 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
Sunil Chopra and Peter Meindl, Supply Chain Management, Pearson Education, 2004
S G Deshmukh and R P Mohanty, Essentials of Supply Chain Management, Jaico Publishing
House, 2009
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Monczka, Purchasing and Supply Chain Management, Thomson Learning, 2002
Shapiro Jeremy F, Modeling the Supply Chain, Thomson Learning, 2002
Janat Shah, Supply Chain Management Text and Cases, Pearson 2009
David Simchi-Levi, Designing and managing the supply chain, Tata McGraw-Hill Editions, New
Delhi, 2000
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Supply_chain_management
401
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M0XH TOOL DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING
1 0 0 1.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the concept and basic mechanics of metal cutting
To study principles of designing Jigs, fixtures and dies for industrial applications
To understand the concept of die making procedures and Machines used for producing die
Introduction to metal cutting general motions of machine tools mechanics of metal cutting chip
formation friction and temperature. Principles of jigs and fixture design locating and clamping
methods devices and its objectives computer applications in fixture design and analysis.
Fundamentals of Cutting tool design - types and its properties, Tool geometry - Design of single and
multi point cutting tools Introduction selection of die sets simple and progressive die - bending die
single and double action die. Introduction principle of operation Wire cut EDM - Electrical
Discharge Machining (EDM) Electro Chemical Machining (ECM) Applications.
Total: 20 Hours
Textbooks
1.
2.
B C Sen and A. Battacharya, Principles of Metal Cutting, New Central Book Agency
C Donaldson, G H Lecain and V C Goold, Tool Design, TMH, 1978
References
1.
Richard R Kibbe, John E Neely, Roland O Merges and Warren J White, Machine Tool Practices,
Prentice Hall of India, 2003
2. J R Paquin and R E Crowley, Die Design Fundamentals, New York-Industrial Press Inc
3. Dallas B Daniel, Progressive Dies, SME, 1994
4. Smith A David, Die Design Hand Book , SME, 1990
5. P K Mishra, Nonconventional Machining, Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi, 2008
402
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M0XI TOTAL PRODUCTIVE MAINTENANCE
1 0 0 1.0
OBJECTIVES
It is essential for a practicing engineer to have an understanding of the total productive
maintenance, Mechanical Systems, Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Maintenance, etc
To have a clear idea of the advanced maintenance systems. The paper aims at providing the
students the basic ideas in these areas
Defining TPM- Need & Objectives, Benefits- Stages of implementing TPM- Tools in TPM- Equipment
Maintenance - Mechanical Systems Maintenance- Hydraulic and Pneumatic System Maintenance Electrical & Electronic Parts. Routes of Autonomous Maintenance-Initial cleaning- eliminating sources
of dirt- inspection & lubrication standards- General inspection- Autonomous inspectionStandardization & Autonomous Management. Establishing a Maintenance Plan-Preliminary
considerations- Systematic method- Maintenance Plan and schedule planning-schedule of Plant shut
downs- Production machines Maintenance practice - Machine Reconditioning - Maintenance
Management Evaluation. Planned Maintenance- Understanding & Restoring Basic conditionsMaintenance Informative System- Periodical Maintenance- Predictive Maintenance- Lubricant
analysis- Breakdown Reduction. Maintenance scheduling- Predictive and Preventive maintenance machine health monitoring systems- spare parts inventory and maintenance- Training & EducationOffice TPM.
Total: 20 Hours
Textbooks
1.
K Venkataraman, Maintenance Engineering and Management, PHI Learning, 2007
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Kenneth E Rizzo, Total Production Maintenance-A Guide for the Printing Industry, GATF Press,
2001
S Nakajima, Introduction to Total Production Maintenance, Productivity Press, 2003
R C Mishra & Pathak K, Maintenance Engineering & Management, Prentice Hall of India
Publication, 2002
J Juran, Handbook of Quality Control, Tata McGraw Hill Publication, 2001
O P Khanna, Industrial engineering and management, Dhanpat rai publications (pvt.) ltd, 2011
403
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M0RA DESIGN OF AUTOMOTIVE SYSTEMS
- - - 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To impart knowledge about automotive system
To learn the recent developments in clutch, gearbox, transmission systems, automotive electronics
and the students will have command over automotive system concepts and application
Recent developments in Vehicle Structure and Engines - types of chassis - types of frames
materials - unitized frame body construction - Design of Engine Components - Material for
various engine components - valves, valve springs and flywheel - Clutch and Brakes - calculation
of critical parameters of clutches - Pressure distribution in brakes - internally expanding brakes disc brakes - Transmission Systems - parameters - differential, axle shafts and gear box Suspension and Steering System - Oscillation and smoothness of ride - Automotive electronics
Sensors in automobiles - engine management system - Case studies on automotive design -
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
www.antya.com/detail/Automotive-Technology/80736.
www.gtubooks.com/Automobile-Engineering
http://www.inderscience.com/browse/index.php?journalCODE=ijvd
http://ameusc.wordpress.com/2008/03/04/international-journal-of-vehicle-design-is-live-in-ejournals/
http://www.ijat.net/
404
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M0RB GEOMETRIC MODELING OF CAD
- - - 3.0
OBJECTIVES
Understand the intricate nature of CAD system and the methods of representation of wireframe,
surface, and solid modeling systems
Understand the mathematical basis for geometric modeling of curves and surfaces and their
relationship with computer graphics
Gain experience in design projects involving multiple
CAD Systems and Graphics Transformations - subsystems of CAD - hardware and software Networking of CAD systems - generative, cognitive and image processing graphics - static and
dynamic data graphics - Transport of graphics data - graphic standards - Mathematical Representation
of Curves and Surfaces - Wireframe models - parametric representation of curves - curve manipulation
- surface models - Mathematical Representation of Solids - boundary representation - constructive solid
geometry - solid manipulations - Visual Realism and Computer Animation - Model cleanup - hidden
line/surface/solid removal - shading and colors - Computer and Engineering animation - Animation
types and techniques - design applications - Product Design and Development - Mass Property
Calculations - geometric properties - mass property evaluation - design and engineering applications Assembly modeling - Testing mating conditions - Assembly load conditions - Assembly analysis.
Reference
1. http://www.idav.ucdavis.edu/education/GraphicsNotes/Transformations/Transformations.html
2. http://nptel.iitm.ac.in/courses/Webcoursecontents/IITDelhi/Computer%20Aided%20Design%20&% 20ManufacturingI/index.htm
405
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M0RC DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS
- - - 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To understand the details of various design methods
To understand the details of factorial design
To know the concept of regression models
Students will be able to conduct research effectively
Guidelines for designing experiments - applications of experimental design - Sampling and Sampling
Distributions - Randomized Designs - Experiments with a Single Factor Design - Analysis of Variance
- Model Adequacy Checking - Determining Sample Size - Regression Approach to the Analysis of
Variance - Factorial Designs - Two-Factor Factorial Design - General Factorial Design - Blocking in a
Factorial Design - 2k Factorial Design - Block Designs - Three-Level and Mixed-Level Factorial and
Fractional Factorial Designs - Regression Models Linear Parameters - Hypothesis Testing in
Multiple Regression - Confidence Intervals - Prediction of New Response Observations - Regression
Model Diagnostics - Testing for Lack of Fit.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
www.wiley.com/college/montgomery
http://www.inderscience.com/browse/index.php?journalID=351&year=2009&vol=1&issue=1
http://www.emeraldinsight.com/journals.htm?articleid=840145
http://www.statease.com/articles.html
406
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology | Regulation 2011
11M0RD INDUSTRIAL SAFETY
- - - 3.0
OBJECTIVES
To anticipate, identify, evaluate, and control workplace hazardous conditions and practices
To develop effective safe operating procedures and comprehensive safety and health programs
To address identified hazards, conditions, and practices in a cost effective manner
To support employees and managers in developing a positive organizational safety culture
To measure and evaluate occupational safety and health performance
Energy source Fires Fire extinguishers types and handling. Personal protective equipments
n e e d - Types electricity and chemical Industrial Hygiene House keeping Machine
Guarding and its types - applications Safety in welding and Gas cutting material handlingExplosive chemicals handling and storage Testing of such chemicals. Hazards and its types Release of hazardous materials Thermal power plant Atomic power plant mining industries
Fertilizers petroleum refinery Guide lines for setting standards for safe equipments and safe
operation in the above industries.-Types of organization Safety committee EHS policy Safety
education - Employee participation on safety motivation - First aid Principles and methods
Training. Legal aspects of Industrial safety Factories act Mines act pollution control acts for
water air and land child labour and women employee acts- OSHAS 18001-207.
References
1.
2.
3.
4.
http://www.OSHA.gov
http://me.queensu.ca/undergraduate/laboratory/safety.php
International Journal of Reliability, Quality and Safety Engineering
International Journal of Injury Control and Safety Promotion
407
You might also like
- Lifting operations procedureDocument81 pagesLifting operations procedureAria Imam Ambara100% (3)
- Diploma in Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesDiploma in Mechanical Engineeringidforemon6898No ratings yet
- Frequency Analysis Using Catia V5Document41 pagesFrequency Analysis Using Catia V5Vasudha Ballarapu100% (1)
- Zte Bts ManualDocument136 pagesZte Bts ManualDiwakar Mishra100% (2)
- Syllabus - Mining Machinery EngineeringDocument7 pagesSyllabus - Mining Machinery EngineeringSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Mtech Result 10Document28 pagesMtech Result 10Anju P. RajuNo ratings yet
- 3 MDM Curriculum AsOn 04nov2011Document25 pages3 MDM Curriculum AsOn 04nov2011Vamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- MechanicalDocument186 pagesMechanicalश्रीराज् कथलियिल्No ratings yet
- Course Curriculum For The New Programme (B.Tech.) W.E.F. 2013 BatchDocument9 pagesCourse Curriculum For The New Programme (B.Tech.) W.E.F. 2013 Batchteju1996coolNo ratings yet
- s1 MtechDocument12 pagess1 MtechAnju P. RajuNo ratings yet
- Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University final year exam scheduleDocument6 pagesDr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University final year exam scheduleNihal SinghNo ratings yet
- B - Tech - 2015 T - TableDocument34 pagesB - Tech - 2015 T - TablePradeep T G ThekkedathNo ratings yet
- University of Calicut (Abstract) : Contd ..2Document46 pagesUniversity of Calicut (Abstract) : Contd ..2BITTU KUMARNo ratings yet
- KSOU Distance Education ProgramsDocument9 pagesKSOU Distance Education ProgramsPramod AroraNo ratings yet
- JNTU B.Tech Supply Exam Timetable 2012Document5 pagesJNTU B.Tech Supply Exam Timetable 2012Dustin PetersonNo ratings yet
- Iii Year I Sem.r09Document4 pagesIii Year I Sem.r09chakradhar_jallaNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University HyderabadDocument4 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University HyderabadMukesh BishtNo ratings yet
- BTech Mech Curriculum & Syllabi (2008-09 Onwards)Document105 pagesBTech Mech Curriculum & Syllabi (2008-09 Onwards)Raghav SarinNo ratings yet
- JNTU Exam TimetableDocument6 pagesJNTU Exam Timetablerocky4bestNo ratings yet
- Iii Year I Sem.r09Document5 pagesIii Year I Sem.r09Kolan Vamshi Kiran ReddyNo ratings yet
- Jntuworld: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University:: KakinadaDocument5 pagesJntuworld: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University:: KakinadaSai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Contffi (I, Iili#il,: Phyi2ItDocument13 pagesContffi (I, Iili#il,: Phyi2ItRahul SoniNo ratings yet
- Signature: COMPETENCY MATRIX (ODD Sem 2013-2014)Document10 pagesSignature: COMPETENCY MATRIX (ODD Sem 2013-2014)rajasekaran2323No ratings yet
- Mechanical CurriculumDocument103 pagesMechanical CurriculumPremsai Tadisetti100% (1)
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University KakinadaDocument4 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University KakinadaSrinivas DevulapalliNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. (H) SyllabusDocument42 pagesB. Tech. (H) SyllabusMahendra DhadweNo ratings yet
- Mechanical EngineeringDocument36 pagesMechanical EngineeringChandan Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Engineering Curriculum Structure Semester WiseDocument26 pagesEngineering Curriculum Structure Semester WisemasoodmuhidNo ratings yet
- Shri Shankaracharya Technical Campus, Bhilai: B.Tech. (Mechanical Engineering), Semester: 6Document19 pagesShri Shankaracharya Technical Campus, Bhilai: B.Tech. (Mechanical Engineering), Semester: 6Ashutosh girdharNo ratings yet
- 31 RevisedDocument5 pages31 RevisedSrimanthula SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Aeronautical EngineeringDocument16 pagesGujarat Technological University: Aeronautical EngineeringumodiNo ratings yet
- Spread of Mechanical Engineering CurriculumDocument7 pagesSpread of Mechanical Engineering CurriculumtaridanNo ratings yet
- Department of Technical Education: GovernmentDocument1 pageDepartment of Technical Education: Governmentsoftwaretesting.cmmi6417No ratings yet
- JNTU III Year B.Tech Nov/Dec 2012 Exam TimetableDocument4 pagesJNTU III Year B.Tech Nov/Dec 2012 Exam Timetableaditya56No ratings yet
- PI 5th Sem-1Document8 pagesPI 5th Sem-1svyas7872No ratings yet
- 2 T.E. Mechanical EngineeringDocument50 pages2 T.E. Mechanical Engineeringpatil_raaj7234100% (1)
- III - YEAR - I - SEM.R09 - KLSDLKSDHFLSDKFHSDKHFLSJKDHFJSHDJKSHDJFSHJDocument5 pagesIII - YEAR - I - SEM.R09 - KLSDLKSDHFLSDKFHSDKHFLSJKDHFJSHDJKSHDJFSHJanandnavzsNo ratings yet
- B.Tech (Mechanical Engineering) - M.Tech (CAD/CAM) - M.Tech (Machine Design) - Doctorial ProgrammesDocument21 pagesB.Tech (Mechanical Engineering) - M.Tech (CAD/CAM) - M.Tech (Machine Design) - Doctorial ProgrammesAbhishek PrasadNo ratings yet
- Mid Sem 1112Document9 pagesMid Sem 1112Harsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Production EngineeringDocument39 pagesProduction EngineeringkeepingbusyNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: B.E Sem-V (All Branch) Subject Code/Teaching/Examination SchemeDocument8 pagesGujarat Technological University: B.E Sem-V (All Branch) Subject Code/Teaching/Examination SchemeBhavesh PipaliyaNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering 2006 Sem I & IIDocument21 pagesCivil Engineering 2006 Sem I & IIArjun KrNo ratings yet
- JNTU R20 B.Tech - Mechnaical Engineering III IV Year Course Structure SyllabusDocument126 pagesJNTU R20 B.Tech - Mechnaical Engineering III IV Year Course Structure SyllabusHema TharunNo ratings yet
- IITB MTech Manufacturing Engineering Program StructureDocument1 pageIITB MTech Manufacturing Engineering Program StructureKunal ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Ic3 8Document62 pagesIc3 8Akshay TanotraNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument74 pagesPDFHARISHKOTHARU48No ratings yet
- EEE 2 3 4 Year 2011-12 PDFDocument61 pagesEEE 2 3 4 Year 2011-12 PDFCharan Priya MangipudyNo ratings yet
- Be Ece 04082014Document275 pagesBe Ece 04082014sumellanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus B.tech. Electronics KUDocument72 pagesSyllabus B.tech. Electronics KUdavarshahNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University:: KakinadaDocument6 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University:: KakinadaSai Ranganath BNo ratings yet
- Sathyabama University Mech Syllabus (Highlighted Copy)Document109 pagesSathyabama University Mech Syllabus (Highlighted Copy)Reginald YesuthasanNo ratings yet
- Direct 2nd Year ITI MCVC RulesDocument6 pagesDirect 2nd Year ITI MCVC RulesPankaj KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Anna University Affiliated Institutions Automobile Engineering CurriculumDocument97 pagesAnna University Affiliated Institutions Automobile Engineering CurriculumDhileepan KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Practical Control of Electric Machines: Model-Based Design and SimulationFrom EverandPractical Control of Electric Machines: Model-Based Design and SimulationNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Micromachining for Nanofabrication, MEMS and NanotechnologyFrom EverandElectrochemical Micromachining for Nanofabrication, MEMS and NanotechnologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Embedded Mechatronic Systems, Volume 1: Analysis of Failures, Predictive ReliabilityFrom EverandEmbedded Mechatronic Systems, Volume 1: Analysis of Failures, Predictive ReliabilityNo ratings yet
- Engineering Applications: A Project Resource BookFrom EverandEngineering Applications: A Project Resource BookRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (1)
- Anna University Report FormatDocument7 pagesAnna University Report Formatdilip_66690% (10)
- Orthographic ProjectionsDocument14 pagesOrthographic ProjectionsSanthana BharathiNo ratings yet
- Ansys Training Book.Document15 pagesAnsys Training Book.Sarath Babu SNo ratings yet
- CAT 2009 solved questionsDocument11 pagesCAT 2009 solved questionsVpn PrasadNo ratings yet
- The Great Depression PDFDocument2 pagesThe Great Depression PDFSanthana Bharathi100% (1)
- Anna University Report FormatDocument25 pagesAnna University Report FormatJaya Seelan100% (1)
- Stress Analysis CATIADocument27 pagesStress Analysis CATIARanga NathNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Multicrop CutterDocument6 pagesFabrication of Multicrop CutterSanthana Bharathi50% (2)
- Am Cat QuestionsDocument19 pagesAm Cat QuestionsRahul ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- GSTDocument16 pagesGSTSanthana BharathiNo ratings yet
- Opportunity Costs and Ecological BenefitsDocument20 pagesOpportunity Costs and Ecological BenefitsSanthana BharathiNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2 MarksDocument23 pagesThermodynamics 2 MarksSanthana BharathiNo ratings yet
- OOAD ConceptsDocument3 pagesOOAD ConceptsSanthana BharathiNo ratings yet
- Data StructuresDocument5 pagesData StructuresSanthana BharathiNo ratings yet
- AMCAT Test SyllabusDocument9 pagesAMCAT Test SyllabusNetrapal RajputNo ratings yet
- AMCAT Test SyllabusDocument9 pagesAMCAT Test SyllabusNetrapal RajputNo ratings yet
- CNC NotesDocument21 pagesCNC NotesradhiostrokesNo ratings yet
- Important Questions in Operating SystemsDocument6 pagesImportant Questions in Operating SystemsSanthana BharathiNo ratings yet
- CAT 2005 Solved PaperDocument14 pagesCAT 2005 Solved PapertoshgangwarNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Interview QuestionsDocument9 pagesMechanical Interview QuestionsSanthana BharathiNo ratings yet
- CAT 2009 solved questionsDocument11 pagesCAT 2009 solved questionsVpn PrasadNo ratings yet
- JPEG Image Compression Standard ExplainedDocument24 pagesJPEG Image Compression Standard Explainedfmail667No ratings yet
- Alarm ManagementDocument22 pagesAlarm ManagementAnshul SinghalNo ratings yet
- New Features For INSITE 8.1.0: 1. Installation and Compatibility A. Upgrade CapabilityDocument6 pagesNew Features For INSITE 8.1.0: 1. Installation and Compatibility A. Upgrade CapabilityMisael CaffarelNo ratings yet
- Bombas de Agua PaiDocument17 pagesBombas de Agua PaiEver Rivera50% (2)
- Pup News LetterDocument24 pagesPup News LetterArielle RamirezNo ratings yet
- CoatingDocument16 pagesCoatingPubg fansNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Unconfirmed Transaction Hack ScriptDocument2 pagesBlockchain Unconfirmed Transaction Hack ScriptScott BradleyNo ratings yet
- أ. د / ﻴ اﺮﺑاﺮ ﺎﻄﻟا ،ةﺮﻜﺴ ﺔﻌﻣﺎﺟ ﺮﺋاﺰ ا - Brahimit@Live.Fr:Document23 pagesأ. د / ﻴ اﺮﺑاﺮ ﺎﻄﻟا ،ةﺮﻜﺴ ﺔﻌﻣﺎﺟ ﺮﺋاﺰ ا - Brahimit@Live.Fr:الاستادة بختةNo ratings yet
- Lec8 PDN System UpDocument30 pagesLec8 PDN System UpLoiLeVanNo ratings yet
- Lukjanenko LabyrinthDocument198 pagesLukjanenko LabyrinthStDeepBlueNo ratings yet
- Op-3-65. Checklist For Jack-In-Pile Supervision: Work Instructions For EngineersDocument4 pagesOp-3-65. Checklist For Jack-In-Pile Supervision: Work Instructions For Engineersjinwook75No ratings yet
- Info Iec62271-203 (Ed1.0) en DDocument11 pagesInfo Iec62271-203 (Ed1.0) en DdvamseeramNo ratings yet
- 22LS350S, 350T, 359S, 359T, 3500, 3510, 3590Document52 pages22LS350S, 350T, 359S, 359T, 3500, 3510, 3590Kiran VeesamNo ratings yet
- GD10L IR Open Path Hydrocarbons PDSDocument2 pagesGD10L IR Open Path Hydrocarbons PDSNelson PucheNo ratings yet
- ch05Document13 pagesch05Engine Tuning UpNo ratings yet
- A1 Principles of Teaching - Ans.KeyDocument11 pagesA1 Principles of Teaching - Ans.KeyJam Uly Gasty100% (2)
- Apsheet QRDocument697 pagesApsheet QRinxdrajaya20No ratings yet
- Electrical OFFICE WAREHOUSE FREEWOOD - PERMIT 2 - Part3Document1 pageElectrical OFFICE WAREHOUSE FREEWOOD - PERMIT 2 - Part3David BarrientosNo ratings yet
- LPG Cylinder Rate ChartDocument4 pagesLPG Cylinder Rate ChartBest Movie scenesNo ratings yet
- Amit Rana: C-607, IFCI Colony Paschim Vihar New Delhi 110063Document4 pagesAmit Rana: C-607, IFCI Colony Paschim Vihar New Delhi 110063rana_pooja20No ratings yet
- Hunter Catalog em PDFDocument236 pagesHunter Catalog em PDFpsmanasseNo ratings yet
- DS2 Series 380V Servo Drive: Fast Reference ManualDocument43 pagesDS2 Series 380V Servo Drive: Fast Reference Manualspectra-tw100% (1)
- Siemens Arrester Hand Book PDFDocument120 pagesSiemens Arrester Hand Book PDFRatilal M JadavNo ratings yet
- Nirosta 4104: Krupp EdelstahlprofileDocument2 pagesNirosta 4104: Krupp EdelstahlprofileLuis MayorgaNo ratings yet
- LT 14701r1.3 20220223 AG90 Specifications SheetDocument4 pagesLT 14701r1.3 20220223 AG90 Specifications SheetArani Davila TineoNo ratings yet
- Residential Enclosure Options for Surface and Flush MountingDocument26 pagesResidential Enclosure Options for Surface and Flush MountingramadhanNo ratings yet
- Open Source Frequency Counter DIY Kit 10Hz-250MHzDocument10 pagesOpen Source Frequency Counter DIY Kit 10Hz-250MHzBruno Santos de Miranda100% (1)
- FlangeDocument10 pagesFlangeNurul LailyahNo ratings yet