Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Distribution Management of Hindustan Unilever LTD PDF
Distribution Management of Hindustan Unilever LTD PDF
Uploaded by
Anup BishnaniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Distribution Management of Hindustan Unilever LTD PDF
Distribution Management of Hindustan Unilever LTD PDF
Uploaded by
Anup BishnaniCopyright:
Available Formats
A Study on Distribution
Management of
Hindustan Unilever Limited
SubmittedTo
Prof.SGovindrajan
By
PRADEEPNARAIN
g08075
SANJEEVKUMARJHA
g08086
SATADRUBAGCHI
g08088
SOUMITRADHALI
g08090
TARUNKUMARSAHA
g08095
Content
Page
1. IntroductionHindustanUnileverLimited
2. DistributionNetworkofHUL
2.1.EvolutionoverTime
2.2.DetailOverview
12
4. InitiativestakentoImprovetheDistributionNetwork
14
5. FieldForceManagement
16
6. AnalyticalFramework
18
7. FinancialAnalysis
26
8. References
33
3. ChannelDesign
1.IntroductionHindustanUnileverLimited
Hindustan UnileverLimited(HUL),formerlyHindustanLeverLimited (itwasrenamedin lateJune
2007asHUL),isIndia'slargestFastMovingConsumerGoodscompany,touchingthelivesoftwoout
of three Indians with over 20 distinct categories in Home & Personal Care Products and Foods &
Beverages.Theseproductsendowthecompanywithascaleofcombinedvolumesofabout4million
tonnesandsalesofnearlyRs.13718crores.
HUL is also one of the country's largest exporters; it has been recognised as a Golden Super Star
TradingHousebytheGovernmentofIndia.
The mission that inspires HUL's over 15,000 employees, including over 1,300 managers, is to "add
vitalitytolife."HULmeetseverydayneedsfornutrition,hygiene,andpersonalcarewithbrandsthat
helppeoplefeelgood,lookgoodandgetmoreoutoflife.ItisamissionHULshareswithitsparent
company, Unilever, which holds 52.10% of the equity. The rest of the shareholding is distributed
among360,675individualshareholdersandfinancialinstitutions.
HUL's brands like Lifebuoy, Lux, Surf Excel, Rin, Wheel, Fair & Lovely, Pond's, Sunsilk, Clinic,
Pepsodent,Closeup,Lakme,BrookeBond,Kissan,KnorrAnnapurna,KwalityWall'sarehousehold
names across the country and span many categories soaps, detergents, personal products, tea,
coffee,brandedstaples,icecreamandculinaryproducts.Theseproductsaremanufacturedover40
factoriesacrossIndia.Theoperationsinvolveover2,000suppliersandassociates.HUL'sdistribution
network comprisesabout 4,000redistributionstockists,covering 6.3millionretailoutletsreaching
theentireurbanpopulation,andabout250millionruralconsumers.
WehaveanalyzedthedistributionnetworkofHULfromthefollowingaspects:
1. EvolutionofHULsdistributionnetwork
2. Transportation&Logistics
3. ChannelDesign
4. Initiativestakenforchannelmembermanagement.
5. Fieldforcemanagement
6. AnalyticalFramework
7. FinancialAnalysis
2.DistributionNetworkofHUL
2.1.EvolutionoverTime
TheHULsdistributionnetworkhasevolvedwithtime.ThefirstphaseoftheHULdistribution
networkhadwholesalersplacingbulkordersdirectlywiththecompany.Largeretailersalsoplaced
directorders,whichcomprisedalmost30percentofthetotalorderscollected.Thecompany
salesmangroupedalltheseordersandplacedanindentwiththeHeadOffice.Goodsweresentto
thesemarkets,withthecompanysalesmanastheconsignee.Thesalesmanthencollectedand
distributedtheproductstotherespectivewholesalers,againstcashpayment,andthemoneywas
remittedtothecompany.
The focus of the second phase, which spanned the decades of the 40s, was to provide desired
productsandqualityservicetothecompany'scustomers.Inordertoachievethis,onewholesalerin
eachmarketwasappointedasa"RegisteredWholesaler,"astockpointforthecompany'sproducts
inthatmarket.Thecompanysalesmanstillcoveredthemarket,canvassingforordersfromtherest
ofthetrade.HethendistributedstocksfromtheRegisteredWholesalerthroughdistributionunits
maintained by the company. The Registered Wholesaler system, therefore, increased the
distributionreachofthecompanytoalargernumberofcustomers.
Thehighlightofthethirdphasewastheconceptof"RedistributionStockist"(RS)whoreplacedthe
RWs. The RS was required to provide the distribution units to the company salesman. The second
characteristic of this period was the establishment of the "Company Depots" system. This system
helpedintransshipment,bulkbreaking,andasastockpointtominimisestockoutsattheRSlevel.In
therecentpast,asignificantchangehasbeenthereplacementoftheCompanyDepotbyasystemof
thirdpartyCarryingandForwardingAgents(C&FAs).TheC&FAsactasbufferstockpointstoensure
that stockouts did not take place. The C&FA system has also resulted in cost savings in terms of
direct transportation and reduced time lag in delivery. The most important benefit has been
improvedcustomerservicetotheRS.
The role performed by the Redistribution Stockists includes: Financing stocks, providing
warehousing facilities, providing manpower, providing service to retailers, implementing
promotional activities, extending indirect coverage, reporting sales and stock data, demand
simulationandscreeningfortransitdamages.
2.2.DetailOverview
ThedistributionnetworkofHULisoneofthekeystrengthsthathelpittosupplymostproductsto
almostanyplaceinthecountryfromSrinagartoKanyakumari.Thisincludes,maintainingfavorable
trade relations, providing innovative incentives to retailers and organizing demand generation
activitiesamongahostofotherthings.EachbusinessofHULportfoliohascustomizedthenetwork
to meet its objectives. The most obvious function of providing the logistics support is to get the
companysproducttotheendcustomer.
DistributionSystemofHUL
HUL's products, are distributed through a network of 4,000 redistribution stockists, covering 6.3
millionretailoutletsreachingtheentireurbanpopulation,andabout250millionruralconsumers.
There are 35 C&FAs in the country who feed these redistribution stockists regularly. The general
tradecomprisesgrocerystores,chemists,wholesale,kiosksandgeneralstores.HindustanUnilever
provides tailor made services to each of its channel partners. It has developed customer
management and supply chain capabilities for partnering emerging selfservice stores and
supermarkets.Around2,000suppliersandassociatesserveHULs40manufacturingplantswhichare
decentralizedacross2millionsquaremilesofterritory.
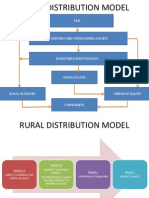
(Fig.1SchematicofHULsDistributionNetwork)
DistributionattheVillages:
The company has brought all markets with populations of below 50,000 under one rural sales
organisation.Theteamcomprisesanexclusivesalesforceandexclusiveredistributionstockists.The
teamfocusesonbuildingsuperioravailabilityofproducts.InruralIndia,thenetworkdirectlycovers
about50,000villages,reaching250millionconsumers,through6000substockists.
(Fig.2RuralDistributionModelofHUL)
HUL approached the rural market with two criteria the accessibility and viability. To service this
segment, HUL appointed a Redistribution stockist who was responsible for all outlets and all
businesswithinhisparticulartown.Inthe25%oftheaccessiblemarketswithlowbusinesspotential,
HULassignedasubstockistwhowasresponsibletoaccessallthevillagesatleastonceinafortnight
andsendstockstothosemarkets.Thissubstockistdistributesthecompany'sproductstooutletsin
adjacentsmallervillagesusingtransportationsuitabletointerconnectingroads,likecycles,scooters
ortheageoldbullockcart.Thus,HindustanUnileveristryingtocircumventthebarrierofmotorable
roads. The company simultaneously uses the wholesale channel, suitably incentivising them to
distributecompanyproducts.Themostcommonformoftradingremainsthegrassrootsbuyandsell
mode.ThisenablesHULtoinfluencetheretailersstocksandquantitiessoldthroughcreditextension
and trade discounts. HUL launched this Indirect Coverage (IDC) in 1960s.Under the Indirect
Coverage(IDC)method,companyvanswerereplacedbyvansbelongingtoRedistributionStockists,
whichservicedaselectgroupofneighbouringmarkets.
DistributionattheUrbancentres:
Distribution of goods from the manufacturing site to C & F agents take place through either the
trucksorrailroadsdependingonthetimefactorfordeliveryandcostoftransportation.Generally
the manufacturing site is located such that it covers a bigger geographical segment of India. From
theC&Fagents,thegoodsaretransportedtoRSsbymeansoftrucksandtheproductsfinallymake
thelastmilebasedonthelocalpopularandcheapmodeoftransport.
Newdistributionchannels
ProjectShakti
This model creates a symbiotic partnership between HUL and its consumers. Started in the late
2000,ProjectShaktihadenabledHindustanLevertoaccess80,000ofIndia's638,000villages.HUL's
partnership with Self Help Groups(SHGs) of rural women, is becoming an extended arm of the
company's operation in rural hinterlands. Project Shakti has already been extended to about 12
states Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Chattisgarh, Uttar
Pradesh, Orissa, Punjab, Rajasthan, Maharashtra and West Bengal. The respective state
governments and several NGOs are actively involved in the initiative. The SHGs have chosen to
partner with HUL as a business venture, armed with training from HUL and support from
government agencies concerned and NGOs. Armed with microcredit, women from SHGs become
directtohomedistributorsinruralmarkets.
Themodelconsistsofgroupsof(1520)villagersbelowthepovertyline(Rs.750permonth)taking
microcredit from banks, and using that to buy our products, which they will then directly sell to
consumers.Ingeneral,amemberfromaSHGselectedasaShaktientrepreneur,commonlyreferred
as'ShaktiAmma'receivesstocksfromtheHULruraldistributor.Afterbeingtrainedbythecompany,
the Shakti entrepreneur then sells those goods directly to consumers and retailers in the village.
Each Shakti entrepreneur usually service 610 villages in the population strata of 1,0002,000. The
ShaktientrepreneursaregivenHULproductsona`cashandcarrybasis.'
ThefollowingtwodiagramsshowtheProjectShaktimodelasinitiatedbyHUL.
ProjectStreamline
To cater to the needs of the inaccessible market with high business potential HUL initiated a
Streamlineinitiativein1997.ProjectStreamlineisaninnovativeandeffectivedistributionnetwork
forruralareasthatfocusesonextendingdistributiontovillageswithlessthan2000peoplewiththe
help of rural substockists/Star Sellers who are based in these very villages. As a result, the
distributionnetworkdirectlycoversasofnowabout40percentoftheruralpopulation.
Under Project Streamline, the goods are distributed from C & F Agents to Rural Distributors (RD),
whohas1520ruralsubstockistsattachedtohim.Eachofthesesubstockists/starsellersislocated
in a rural market. The substockists then perform the role of driving distribution in neighboring
villages using unconventional means of transport such as tractor and bullock carts. Project
Streamline being a cross functional initiative, the Star Seller sells everything from detergents to
personalproducts.
Higherqualityservicing,intermsoffrequency, creditandfulllineavailability,istobeprovidedto
ruraltradeaspartofthenewdistributionstrategy.
ThediagraminthenextpageshowsthemodelofProjectStreamline.
HindustanLeverNetwork(HLN)
It is the company's arm in the Direct Selling channel, one of the fastest growing in India today. It
alreadyhasaboutseverallakhconsultantsallindependententrepreneurs,trainedandguidedby
HLN'sexpertmanagers.HLNhasalreadyspreadtoover1500townsandcities,covering80%ofthe
urban population, backed by 42 offices and 240 service centres across the country. It presents a
rangeofcustomisedofferingsinHome&PersonalCareandFoods.
The New Compensation plan for HLN partners provides new exciting ways of earning substantial
income in addition to offering rewards like revenue sharing through the innovative concept of
pools
MotherDepotandJustinTimeSystem
Inordertorationalisethelogisticsandplanningtask,aninnovativestephasbeentheformationof
theMotherDepotandJustinTimeSystem(MDJIT).CertainC&FAswereselectedacrossthecountry
to act as mother depots. Each of them has a minimum number of JIT depots attached for stock
requirements.AllbrandsandpacksrequiredforthesetofmarketswhichtheMDandJITsservicein
a given area are sent to the mother depot by all manufacturing units. The JITs draw their
requirementsfromtheMDonaweeklyorbiweeklybasis.
LeveragingInformationtechnology
HULcustomersareservicedoncontinuousreplenishment.ThisispossiblebecauseofITconnectivity
across the extended supply chain of about 2,000 suppliers, 80 factories and 7,000 stockists. This
sophisticated network with its voice and data communication facilities has linked more than 200
locationsalloverthecountry,includingtheheadoffice,branchoffices,factories,depotsandthekey
redistributionstockists.TheyhavealsocombinedbackendprocessesintoacommonSharedService
infrastructure, which supports the units across the country. All these initiatives together have
10
enhanced operational efficiencies, improved the service to the customers and have brought us
closertothemarketplace.
RSNetInitiative:
TheRSNetinitiative,launchedin2001,aimsatconnectingRedistributionStockists(RSs)throughan
internetbasedsystem.ItnowcoversstockistsoftheHome&PersonalCarebusinessandFoods&
Beveragesincloseto1200townsandcities.Togethertheyaccountforabout80%ofthecompany's
turnover. RS Net is one of the largest B2B ecommerce initiatives ever undertaken in India. It
provides linkages with the RSs own transaction systems, enables monitoring of stocks and
secondarysalesandoptimisesRSsordersandinventoriesonadailybasisthroughonlineinteraction
on orders, despatches, information sharing and monitoring. The ITpowered system has been
implemented to supply stocks to redistribution stockists on a continuous replenishment basis.
Today, the sales system gets to know every day what HUL stockists have sold to almost a million
outletsacrossthecountry.InformationonsecondarysalesisnowavailableonRSNeteveryday.
RSNetispartofProjectLeap.ProjectLeapbeginswiththesupplierrunsthroughthefactoriesand
depotsandreachesuptotheRSs.ThisensuresHULsgrowthbyensuringthattherightproductis
available at the right place in the right quantities and at the right time in the most costeffective
manner. Leap also aims at reducing inventories and improving efficiencies right through the
extendedsupplychain.
RSNethascomeasaforcemultiplierforHULWay,thecompany'sactionplantonotonlymaximise
the number of outlets reached but also to achieve leadership in every outlet. RS Net has enabled
stockists to place orders on a Continuous Replenishment System. This in turn has unshackled the
fieldforcetosolelyfocusonsecondarysalesfromthestockiststoretailersandmarketactivation.It
hasalsoenabledRSstoprovideimprovedservicetoretailoutlets.Simultaneously,HULisservicing
theruralmarket,keyurbanoutlets,andthemoderntradeasasingleconcern.
AdexaiCollaborationsuite
In 2000, HUL identified improved supply chain management as a critical business priority and
launched a comprehensive initiative, Project Leap, tasked with increasing supplier/distributor
responsiveness,reducinginventorybuffers,andoptimizingplanningandscheduling.HULchosethe
AdexaiCollaborationsuiteforfacilitatingcentralizedmonitoringoftheSCM,livecustomer/supplier
collaboration, and integrating demand and distribution planning with production scheduling. With
theaggregatedviewofdataprovidedbytheiCollaborationsuite,HULwasabletocombinesalesand
11
distributioneffortsonthediverseproductlines,whichresultedinsignificantsavingsonthecostside
for inventories and distribution. HUL updates inventory positions, shipments and customer orders
onadailybasiswiththesesoftwarepackagesandcangetapulseonthemarketrealtime.
(Fig.3HULsTurnoverComparedwithCompetitors,2006)
(Fig.4HULsMarketLeadershipacrossvariousFMCGCategories)
12
3.ChannelDesign
HindustanLeverLimited(HUL)hastwotypesofchannelselling
i.
Regular(traditional)retailchannel,
ii. DirectSellingChannelinthenameofHindustanLeverNetwork(HLN).
HUL has a well entrenched high distribution model which comprises of C&FAs, Redistribution
Stockists,wholesalersandretailers(asshownearlier).HindustanUnilever'sdistributionnetworkis
recognizedasoneofitskeystrengths.ItsfocusesonProductavailability,Brandcommunication,and
higherlevelsofbrandexperience.
HULsSalesBreakupthroughdifferentchannels:
Sales Break-up Through Different Channels
7%
33%
60%
Modern Retail
Urban General Trade
Rural Areas
ChannelStructure(SpecialFocusisonJamshedpur)
Typically,thegoodsproducedineachoftheHUL's40factoriesaresenttoadepotwiththehelpofa
carryingandforwardingagent(C&FA).Thecompanyhasitsdepotineverystateofthecountry.The
C&FA is a third party and gets servicing fee for stock and delivery of the products. In each town,
thereisatleastaredistributionstockist(RS)whotakesthegoodsfromtheC&FAandsellsthemto
retail outlets. In Jharkhand the C&FA is in Ranchi and Jamshedpur is serviced by 3 Redistribution
StockistsatSakchi(M/sOmPrakashAgarwal),BistupurandParsudih.
TheHULmanagementrealizedcertainproblemswiththeexistingsalesmodel.First,themodelwas
not viable for small towns with small population and small business. HUL found it expensive to
appoint one stockist exclusively for each town. Secondly, the retail revolution in the country has
changedthepatternthecustomersshop.Largeretailselfserviceshopsarebecomingcommonplace.
13
In response of these problems, HUL redesigned its sales and distribution channel and the new
systemisknownas'diamondmodel'inthecompany.Atthetopendofthediamond,therearethe
selfserviceretailstoreswhichconstitute10%ofthetotalFMCGmarket.Themiddle,fatterpartof
thediamondrepresentstheprofitcenterbasedsalesteam.Inthebottomofthepyramidistherural
marketing and distribution which accounts for 20% of the business. As a result of the new
distributionplanthecompanyhasplannedtoreducethenumberofRSinsmalltowns.
RedistributionStockists:
TotalnumberofRSinJamshedpur=3(atSakchi,Bistupur,Parsudih).Thisisgoingtobereducedto
onlyonewitheffectfromnextmonthofthisyear.
Sales Margin: 4.76% which includes cash discount, unloading expenses from depot,
distributionexpensestoretailers,incentiveschemes&otherincidentalexpenses.
Modesoftransportused:Rickshaw,tempo.
Incentiveschemes:Before2000holidaypackagesandtoursbutafter2000nononmonetary
incentiveforRS.
Software systems and Information System: UNIFY 8.3 (Developed by IBM & CMC). This
softwareneedstobesynchronizeddailyandthesystemupdatesanyinformation/incentive
schemes/salesfiguresetctoandfromthecommonsharedplatform.
AreasofOperations:MarkedforeachoftheRS.
SellingOperations:RSssellsthegoodsto
o
Wholesaler(gets1.5%max.discountfromRS)
Retailers(gets1.0%max.discountfromRS)
Wholesaler:
GetscashdiscountsandotherschemespromotedbyHUL(getspointsunderVijetaScheme).
Retailers:
TotalretailerbaseinJamshedpur:Approximately1070.
SalesMargin:Dependsontheproduct
o
Soap,detergents
8%onMRP
Cosmetics
10%onMRP
Fooditems
8%onMRP
14
Incentiveschemes:
Companyprograms(SchemeDiscounts+CashDiscounts)
TPRschemesbasedonSales(1%to4%)
Vijetaschemeisnotforretailers.
FieldSalesForce:
To meet the everchanging needs of the consumer, HUL has set up a distribution network that
ensures availability of all their products, in all outlets, at all times. This includes, maintaining
favourable trade relations, providing innovative incentives to retailers and organizing demand
generationactivitiesamongahostofotherthings.
TheimportantactivitiesthatHULfieldsalesforcedoesare(i)targetchasingand(ii)reportingona
dailybasis.AccountinformationismaintainedonpalmtopsgivenbyHUL.Duringourresearchand
informalsurveyofHULfieldsalesforce,wecametoknowthatforthelasttwoyears,trainingisnot
beinggivenatalltothesalesforce.
HULhaslimitedthenetworkchannelsellingtocategoriesofHome&PersonalCare(HPC)andFood
products with exclusive brands for this channel. That is, these particular brands (products) are all
exclusivetoHLN,specificallydevelopedfortheDirectSellingchannel,andnotavailableintheretail
channel. The general trade comprises grocery stores, chemists, wholesaler, kiosks and general
stores.HindustanUnileverserviceseachwithatailormademixofservices.
4.InitiativestakentoImprovetheDistributionNetwork
HULhastakenthefollowinginitiativestoimproveitsdistributionnetwork:
Setting up of a fullscale sales organisation comprising key account management and
activationtoimpact,fullyengageandservicemodernretailersastheyemerge.
ServicingChannelpartnersandcustomerswithcontinuousdailyreplenishment.
LeveragingscaleandbuildingexpertisetoserviceModernTradeandRuralMarkets.
Delayeringofsalesforcetoimproveresponsetimesandservicelevels.
Revamping of its sales organisation in the rural markets to fully meet the emerging needs
andincreasedpurchasingpoweroftheruralpopulation.HULsdistributionnetworkinrural
India already directly covers about 50,000 villages, reaching about 250 million consumers
throughabout6,000substockists.
15
Implementationofsupplychainsystemthatconnectsstockistsacrossthecountry,andalso
includesabackendsystemconnectingsuppliers,allcompanysitesandstretchingrightupto
stockists. IT tools have been deployed for connectivity across the extended supply chains.
BackendprocesseshavebeencombinedintoacommonSharedServiceinfrastructure.
LaunchingofProjectShaktithroughwhichthe companyisable toextenditsoperationsin
villages. HUL has also included several NGOs and state governments as the initiative helps
ruralwomentoimprovetheirfinancialposition.
LaunchingofHULNetworktoleveragethechannelofdirectsellingbypresentingcustomised
offeringsin11homeandpersonalcareandfoodcategories.Startedin2003,italreadyhasa
baseof300,000consultantsacrossthecountry.
StartingoffranchisedLakmeBeautySalonsandAyushTherapycentrestoofferstandardised
services, in line with the strategy to leverage the equity of its brands through relevant
services.
Finding out Innovative ways to reach out to its consumers, particularly in rural areas by
leveragingnonconventionalmedialikewallpaintings,cinemavans,weeklymarkets(haats),
fairsandfestivals.
InitiatingtheconceptofSuperValueStores(SVS)inurbanareastopartnertraditionalstores
to provide a range of services ranging from managing their inventory to setting up POS
(pointofsale)banners.Inadditiontothis,toboostuptraditionalretailinthefaceincreasing
inroads made by large, modern retailing chains like Spencers, Reliance Fresh etc (where
HULissqueezedharderfordiscounts),HULstartedrestructuringsomeoftheselectedSVSs
intotheformofselfserviceretailshopsalamodernretails.Thisistoprotect&maintainthe
competitiveadvantagethatHULhasoveritsbiggestcompetitorsintheothermarkets(e.g.,
P&G),withitsverydeepdistributionreachthroughtraditionalretail.
LaunchingtheUnicareschemewithupmarketpharmaciesandretailerstosaleitspremium
brands.
Undertakingseveralinitiativesfortraditionalchannelsinordertoimproveitscapabilitiesat
thefrontendbydevelopingskillsforstockists'salesforce.Under'ProjectDronacharya',the
FMCGmajorcontinuouslyimpartedtrainingtoover10,000stockistsalesmen.
Launching of several promotional schemes for existing wholesalers and distributors. For
instance,ithasstartedtheVijetaRishtaJeetKaschemelastyeartoprovideaplatformfor
thewholesalerandHULtogrowthebusinessbyearningpointsandredeemingthem.
16
5.FieldForceManagement
TheworkingcycleofatypicalHULfieldforcememberisfrom21stofeverymonthtothe20thofthe
nextmonth.Duringthisperiodheisgivenvarioustargetsthathelpstoachievecompanyobjectives
andgiveshimachancetoprovehisperformancerelativetoother.
Tostartwiththefieldforcememberisgivenaparticularareaandhisresponsibilityistocatertoall
theretailersinthatarea.Whiledecidingtheareaforeachmemberofthefieldforce,thecompany
makessurethattheoperatingareaofeachfieldmemberdoesn'toverlapwithhisothercolleagues.
TherearevariousmethodsusedbythecompanytoincentivizethefieldforceMonetaryandNon
Monetary.
InHUL,thefieldforceisevaluatedusingQOC(QualityofContribution).Itconsistsof4components
1.SecondarySale(Maxpoints=2.5)
2.Eco(Maxpoints=0.5)
3.Focus(Maxpoints=0.5)
4.FCS(MaxPoints=0.5)
SECONDARY
ECO
QOC
FOCUS
FCS
17
Secondary Sale Based on the operating area, each member is given a specific target in terms of
value(e.g.,Rs.15lacs)fortheoperatingmonth(21st20thofnextmonth).Ifheachieves100%of
thetargethegets2.5points,ifheachieves95%targethegets1.5points.Thesepointsareusedto
addtothetotalQOCscoreaswellaslinkedtomonetaryincentive.
ECO/WidthpackTargetThisisusedforthepenetration/reachofcertainproductsintheexisting
market.ThefollowingisatypicalECOtargetassignedtoafieldforceagent:
LuxInternational
105outletsx1SKU
PearsSoap
135outletsx1SKU
Rin
104outletsx1SKU
BreezeSoap
100outletsx1SKU
Theoutletsmentionedarewithintheoperatingareaofthepersonand1SKU=Rs.27/.Basedon
thistheFieldpersoncalculatesnumberofpacksheshouldselltotheretailers.Theconcernedagent
receivesthistargetaround25thofeachmonthandhastocompletethistargetwithinthe5thdayof
next month. Upon completion he gets additional 0.5 points added to his QOC score along with
monetary incentive associated with it. However if this is not met within 5th, he looses the
opportunity.
Focus/DepthPacktargetThisismainlyusedtoincreasethesalesvolumeofcertainproducts.A
typicalFocustargetisgivenbelow:
LuxInternational
Rs20,640/@Rs6/perunit
LifeBuoy
Rs70,220/@Rs10/perunit
Wheel
Rs99,000/@Rs10/perunit
BreezeSoap
Rs27,000/@Rs10/perunit
This target needs to be achieved within 20th of next month. Upon achieving the target the field
personisawarded0.5pointswhichisthenaddedtohisoverallQOCscore.
FieldCapabilityScore(FCS)Inthiscomponent,thefieldforcepersonsarerequiredtoensurethat
the scheduled visit/outlet billing is such that at least 15 items are demanded per order. If this is
achieved the retailer gets a discount of 1% on the billed amount and on the other hand the field
person gets an additional score of 0.5 which is added to his QOC score. Each scheduled visit per
outlet is one per week. For example if there are 100 outlets within the operating area of a field
personthenthenumberofvisitperweekis100andtotalnumberofvisitpermonth=100x4=400.
18
Thesalespersonisrequiredtoachieve90%successratetoget0.5pointsforhisQOCscoreandat
least65%forasatisfactoryperformance.
NonMonetaryMethods
TheotherpurposeoftheQOCscoresistohighlighttheperformanceofthefieldpersonamonghis
peers. Based on the QOC various awards are distributed to the field persons at the end of every
month. These awards are also known as MOC Star awards. MOC stands for Monthly operating
Cycle.
IfQOCscore>4.5Thepersoniseligiblefor7staraward
IfQOCscore>4Thepersoniseligiblefor5staraward
IfQOCscore>3.5Thepersoniseligiblefor3staraward
In the event of exceptional performance, management representatives from the regional office
cometothezonalofficetodistributetheawards.Thephotographoftheawardwinnersisdisplayed
intheofficeasasourceofinspirationforothersalesperson.
TargetSettingMechanismandmonitoring
Theregional officemonitorstheperformanceofvariouszones.Athoroughanalysisisdoneatthe
end of each month and based on that the weak products are identified or those for which the
demandhasweakened.ThisisthebasisofsettingECOandFOCUStargetsforthefieldpersons.Each
fieldpersonisgivenapalmtopwhereinhecanfeedtheentriesonthespotwherethetransactionis
done.Thissolvesbasicallythetwopurposes
a)Thefieldpersonisfreedfromthetedioustaskofmaintainingcumbersomerecordsandcanthen
concentrateonthejob(thusITisreplacingsomeofthefieldforceorotherchannelmembers),
b)Thesolditemisimmediatelyupdatedinthecompanyinformationsystem.
6.AnalyticalFramework
WetriedtoanalyzeHULsdistributionnetworkinthelightof20mostsignificantvariablesthataffect
the distribution part of channel management for any organization in the business of marketing &
sellingofgoods.Thevariables,theirexplanationsandtheirimpactontheHULsdistributionnetwork
aregivenbelow
1. NumberofConsumers
In retail business dominated by traditional stores like Kirana Stores etc (Indian retail business
falls in this category), higher the no. of consumers, higher will be the no. of channel
intermediaries.Theimplicationofthisisthattherewillbemanylayersinthechannelinsucha
19
situationandmanagingsuchacomplexdistributionnetworkbykeepingtabsoneveryplayerwill
be a huge task. Moreover, Transport & Logistics (T&L) support provided by the organization
needstobewellorganized.
ImplicationforHUL
HULskeystrengthliesinmanagingitsdistributionnetworkinIndia.HULisIndiaslargestFMCG
company with unmatched distribution network, which is built over a century focusing on
traditional retail. HUL's distribution network comprises about 4,000 redistribution stockists,
covering about 6.3 million retail outlets reaching the entire urban population, and about 250
million rural consumers in India. Its said that HUL is able to touch the lives of about 2 out of
every 3 Indian consumers. This achievement is due to the sheer strength of its distribution
network(productsshouldbegoodasalways,otherwisetheywillfindnobuyersinthelongrun).
Foracomparison,P&G,worldslargestFMCGmajor,doesnotfinditsnameinthelistoftop5
FMCGmajorsinIndiaasitsstrengthliesinmanagingmodernretail(biggestexample,WalMart),
butnottraditionalretail.
2. GeographicDispersionofConsumers
Again,thisiscloselyrelatedwiththepreviousvariable,moresoinalarge,geographicallydiverse
country like in India. With the increase in this dispersion level, more intermediaries and more
layersarerequiredinthedistributionnetworksoastoeffectivelyreachthelength&breadthof
the country. Obviously the T&L management for such an organization would be critical to
accomplishthis.
ImplicationforHUL
For a country as geographically diverse as India, panIndian presence & market leadership can
only be possible when products reach even the remotest parts of the country. HUL is very
successfulinachievingandmaintainingthisreachduetoitsdistributionnetwork.
3. FrequencyofPurchase
If the frequency of purchase is high, then transport intensity in the last mile (i.e., from
distributortoretailers)increasesmanifold.ForFMCGproducts,asathumbrulewecantakethat
themeantimebetweentwopurchasesis~90days.Withtheintroductionofsmallerformfactor
packagingforFMCGgoods(Re.1/shampoosachetsbeingaverygoodexample),thetransport
intensityincreasedfurther.
20
ImplicationforHUL
HUL has about 4000 redistribution stockists, who supply to approx. 6.3 million outlets across
India.Sincemanufacturingisdoneat40plantsaroundthecountry,rationalizingthelogisticsand
planningisahugetask.AninnovativestepinthatregardhasbeentheformationoftheMother
DepotandJustinTimeSystem(MDJIT).CertainC&FAswereselectedacrossthecountrytoact
as mother depots. Each of them has a minimum number of JIT depots attached for stock
requirements. All brands and packs required for the set of markets which the MD and JITs
serviceinagivenareaaresenttothemotherdepotbyallmanufacturingunits.TheJITsdraw
theirrequirementsfromtheMDonaweeklyorbiweeklybasisandsupplytostockistsinthat
area,who,inturn,supplytoretailers.
4. TendencytoPostponePurchase
Ifthetendencytopostponepurchaseislesser,thentheproductwillbeeasiertodistribute.For
example,products/serviceslikeFireExtinguishers,LifeInsuranceetc.aresuchthatthoughthese
are needed, the overall tendency for the consumers is to postpone the purchases these
products/services can be termed as necessary evil. For this kind of products, regular
reinforcementinthemindsofconsumersbecomesnecessary,salesfieldforcebecomescritical
anduseofexpertfieldforceiscommonplace.
ImplicationforHUL
Since FMCG products are used regularly and these products are not necessary evils,
distributionnetworkofHULdoesnotrequireanyexpertfieldforcetosellitsproducts.Onlythe
recent diversification of HUL into Home Water Purification business (Pure It brand) needs
dedicatedfieldsalesforce.
5. LevelofFamiliarity/Knowledge(ofconsumer)abouttheProduct
Iftheleveloffamiliarityofconsumerwiththeproductishigher,lowerwillbetheimportanceof
fieldsalesforceandhigherwillbetheimportanceofchannel.
ImplicationforHUL
SinceFMCGgoodsareverymuchfamiliartoconsumers,channelanditsdifferentmembersare
very much important to HUL and field sales forces function is mostly limited to channel
managementandensuringavailabilityofproducts.
21
6. DegreeofBrandLoyalty
If the consumers are more brand loyal, then less push will be required from the channel
memberstoselltheproductsastherewillbesufficientpullordemandfromtheconsumers.
Thisimpliesthatforproductswithloyalcustomerbase,effortsfromthechannelmemberscan
bemuchlesserforfinalofftaketohappenwhichinturnleadstolessermarginstothechannel
members for those products. For faster moving products (mostly due to brand pull), retailers
maynotbeaversetoslightlylessermarginsasrotationoftheproductsishighandthushis/her
ROIisprotected.
RetailersROI=
M arg in Rotation
Investment
ForaFMCGplayerwithanonestablishedbrand,marginstochannelmembersandpointofsale
(POS)advertisingarebothimportant.
ImplicationforHUL
AsHULenjoysleadershippositioninmanyFMCGsegmentslikeSoaps,Detergents,PersonalCare
productsetcwithstrongbrandswithcontinuouspull,HULhaslesstoworryaboutmarginsto
channelmembersorPOSadvertising.Butthissituationcanchangeconsiderablyinthefaceof
riseofasignificantcompetitorhavingalmostthesamereachasHULhas(e.g.,ITCasitseating
intoHULsmarketsharecontinuouslysinceitenteredFMCGsegment).
7. PurchasedonImpulse
Theimpulsepurchaseproductslikechocolates,toffees,colas,icecreamsetc.followSaysLaw
whichstatesthatSupplyCreatesDemand,implyingavailabilityoftheseproductsarethemost
critical aspect for these to be sold and consumed. This stresses on the fact that T&L for these
productsbecomesveryimportant.
ImplicationforHUL
HULhasonlyoneproductinthisimpulsepurchasecategoryKwalityWalls(icecream).HULis
#2afterAmulinthisFMCGsegment.Toincreasethisbrandssale&marketshare,availability,
visibilityandconsumermindsharehastobeincreasedandimprovedaswell.
8. LevelofInvolvement(LOI)
Level of involvement (i.e., time & effort spent by the consumer) generally depends on the
product cost. If LOI is higher, lower is the importance of availability and more critical is the
22
supply of information as consumer decision process depends more on elaborate information
search.
ImplicationforHUL
AsFMCGproductsaregenerallyLowInvolvementProducts,HULhastobothermoreonensuring
availabilityoftheproducts,ratherthansupplyofinformation.
9. PurchasedasaBasketofGoods
Theproductswhicharegenerallyboughttogetherbyconsumersasabasketofgoods(e.g.,Rice,
Flourpowder,Cookingoiletcatthebeginningofthemonth)aretobemadeavailabletogether
forfinalofftake.
ImplicationforHUL
ThisaspectpartlyappliestoHULsproductsassomeproductslikeshampoos,soaps,detergents
mayfallinabasket.EfficientdistributionnetworkofHULensuresavailabilityofallsuchproducts
ateachsellingpoint(individualretailer).
10. Speed&ComplexityofDecisionMakingProcess
Ifthespeedislow,thenthecomplexityofthedecisionmakingprocessishigherandgreateris
theimportanceoffieldsalesforceandthesalespersonsskill,knowledgeandquality.
ImplicationforHUL
ForFMCGproducts,complexityofdecisionmakingprocessisnotthereandso,speedofdecision
makingishigh.ThismeansthatforHUL,fieldsalesforceisoflimitedfunctionalusage.
11. PresentofExpertInfluencerintheDecisionMakingProcess
Roles of sales field force vary depending upon whether expert influencer (e.g., doctors) is
present in the process or not. If present, then consumer buying behavior may become
subcontractedandtheexpertinfluencerbecomesanothercustomerofthenetwork,apartfrom
the enduser. In that situation two groups of sales force are needed to cater to both the
segments.
ImplicationforHUL
ForFMCGgoods,roleofexpertinfluencerislimited.Butcompaniestrytoassociatebrandswith
regulatory bodies/authorities and show advertising with experts commenting upon superior
virtues of a product in an attempt to make the buying behaviour shift from picking/variety
23
seekingtosubcontractedandmakeconsumersmoreloyaltothebrand.ThesearetrueforHUL
also(e.g.,PondsIntitute).
12. ElementofCrisisPurchaseExists
If element of crisis purchase exists in the buying decision of a product (for example, bulbs &
tubes),thenitsavailabilitybecomescritical.
ImplicationforHUL
None of the products of HUL fall under this category. Nevertheless, availability of products of
HULisnecessaryforotherreasons.
13. ElementofRiskAversionExists
If the level of involvement of the consumer in buying decision process is higher, risk taking
tendency of the consumer will be lower or consumer will be more risk averse. In such a
situation,channelmemberscanunsellabrandbygivingexplicitorimplicitsuggestions. This
implies that in such a case, selling depends on many cases how the company is taking care of
channelmembers(keepingthemhappy)suchthattheyarenotluredbyothercompetitorsor
directedbygrievancessoastounsellthebrand.ThissituationisprevalentmostlyinConsumer
Durables(likeTV,Refrigeratorsetc.).InFMCGgoods,thesituationdoesnotexistperse.
ImplicationforHUL
HULisnotaffectedforitsFMCGproductsbythisvariable.ForwaterpurifierPureIt,thiscan
haveconsiderableimpactifitssalestartstohappenthroughchannelmembersratherthanby
fieldsalesforceasishappeningnow.
14. PerishabilityoftheProduct
Iftheproductisperishable(havingsmallshelflife;examplesnewspaper,milk,fruitsetc),then
thedimensionofspeedinreachingtheendconsumersbecomescritical&T&Lassumesgreat
significanceforthecompany.
ImplicationforHUL
The FMCG products that HUL sells are not perishable by nature, but have limited life. So this
aspectisnotcriticalforHUL.
15. TimeBandAssociatedwiththePurchaseoftheProduct
If there is seasonality/cyclicity for the demand or purchase of the product (examples
newspaper, milk are most on demand in the 1st three hours of the day; cooking oil, rice etc
24
grocery items are most on demand in the 1st week of the month), then high T&L and
infrastructuralrequirementsareneededforthelastmileforthetimebandwhendemandis
maximum. It is possible to have idle capacity in the areas mentioned above outside the peak
requiredtimeband.
ImplicationforHUL
ForsomeoftheproductsofHUL,theabovestatedvariableissignificant.Forexample,inFood
segment,BrandedAttaAnnapurna;insegmentslikeLaundryDetergents,Shampoo&HairOil
etc. this element of demand time band exist to a certain extent. This underscores the
importance of T&L for HUL as the transport intensity between distributors and retailers
increasesinthe1st&4thweekofamonthfortheproductsmentionedabove.Thisisoverand
abovetheregularreplenishmentofstocksatretailersdonebydistributors.FestivalslikeHolietc.
may also increase the demand for personal care items like soaps, shampoos etc for a short
periodanddistributionnetworkshouldbegearedupnottomissanysuchopportunity.
16. Fungibility
Fungibility is the property of a good or a commodity whose individual units are capable of
mutualsubstitution.Examplesofhighlyfungiblecommoditiesarecrudeoil,wheat,orangejuice,
preciousmetals,andcurrencies.Fungibility hasnothing todowith theabilitytoexchangeone
commodityforanotherdifferentcommodity.Itrefersonlytotheeaseofsubstitutionofoneunit
ofacommoditywithanotherunitofthesamecommodityforallintentsandpurposes.
Fungibilityisdifferentfromliquidity.Agoodisliquidandtradableifitcanbeeasilyexchanged
for money or for another different good. A good is fungible if one unit of the good is
substantiallyequivalenttoanotherunitofthesamegoodofthesamequalityatthesametime
and place. It is said that commodities are fungible, goods tangible, services intangible,
experiencesmemorable&transformationsareeffectual1.
As an example, one Rs. 100/ bank note is interchangeable with another. Cash is fungible. A
barrelofWestTexasIntermediatecrudeoilisfungible(directexchange)withanotherbarrelof
thesamecrudeoil.Oil(ofthesametype)isfungible.
Fungibilitydoesnotimplyliquidity,andliquiditydoesnotimplyfungibility.Jewelscanbereadily
bought and sold (the trade is liquid), but individual diamonds, being unique, are not
interchangeable (diamonds are not fungible). Indian rupee bank notes are interchangeable in
London (they are fungible there), but they are not easily traded there (they are not liquid in
London).Incontrasttodiamonds,goldcoinsarefungible.Theyarealsoliquid,especiallyundera
25
gold standard. The combination of fungibility and liquidity is one of the reasons why gold has
successfullyservedasmoneyforthousandsofyears.
Further,afungiblethingcanbecomenonfungibleundersomecircumstances.Forexample,an
old coin or a currency note may assume a value which is way above its face value due to
historical reasons or due to some defects in it which makes it unique from others from a
viewpointwhichseesitdifferentlythanitsintendedpurpose.
Theoutcomeofproductfungibilityisthatthemorefungibleaproduct becomes,higher isthe
chancethatpartsofthedistributionchannelitcanbereplacedbyIT.Agoodexampleofthisis
dematerialization(Demat) routeforsharetrading nowwherethereisnophysicalexistenceof
shares.
ImplicationforHUL
As branded FMCG goods are not fungible per se (branding is done to decommoditize &
differentiatetheproduct),theimportanceofchannelmemberswillcontinue.
17. DegreeofCustomizationPossible
Degreeofcustomizationdirectlyaffectseconomiesofscale;higherthecustomization,lesserthe
economiesofscale.Also,criticalityofsalesfieldforceincreaseswithcustomizationlevelsofthe
offering.
ImplicationforHUL
ForFMCGproductsofHUL,whicharemassproduced,suchcustomizationsarenotpossibleand
thus with higher economies of scale, lower criticality of field forces from the standpoint of
customizationofproductofferings,costsarelowerintheserespectswithHUL.
18. NegativeorPositiveReinforcingProduct
Negative reinforcing products are those which are bought to avoid/reduce the problem (ex.
insurance, washing machine, car battery etc). Positive reinforcing products are those which
gratify the senses (ex. Perfumes, Chocolates, Vacation etc). Shopping experience becomes a
criticalaspectforpositivereinforcingproductstoreaffirmthepositivefeelings.
ImplicationforHUL
Axe & Rexona deodorants are distinctly positive reinforcing products from HUL, including
others like Lux, Lakme etc. So these are seen in most shopping malls etc. with high visibility
displaystoreaffirmthefeelings.Consumersarewillingtopayhigherforthesebrands.
26
19. Value/VolumeRatio(ValueDensity)oftheProduct
Thisratioisveryimportantforboththecompanyandtheretailerforitstwocriticalaspects
T&L cost and retailer ROI/sq. cm (retailers are actually in real estate business in true sense).
Highertheratio,betteritisforbothcompanyandtheretailerashigherratiosignifieslesserT&L
costperunitvolumetransportedforthecompanyandgreaterROIperunitofshelfspaceforthe
retailer.
ImplicationforHUL
IngeneralforFMCGgoodsandforHULaswell,valuedensityisrelativelylower.Inadditionto
this fact, increasing trend towards using smaller pack sizes increases the packaging density
(increased packaging density increase cost to some extent, but favours mechanized handling
greatly,reducinghandlingcosts).Sincevaluedensityisless,transportationcostswillbehigher
andthusitisofeconomicsensetohavemanufacturingplantslocatedclosuretomajormarkets.
ThisisthereasonHULhasvariousmanufacturingplants(40intotality)locatedacrossIndia.This
is a pointer to the fact most of the major FMCG players (including HUL) use contracted
manufacturing dispersed across the geographic spread so as to lower transportation cost
component.
7.FinancialAnalysis
We have taken data from CMIE database while analyzing the performance of marketing & sales
(including distribution) functions of HUL and comparable companies. By comparable, we mean
those companies whose main economic activity, as defined in the CMIE database, is the same as
HULs.Forexample,maineconomicactivityofHULasdefinedinthatdatabaseisCosmetics,toilet
preparations, soap & washing prep. Obviously, one major FMCG company in India, ITC, does not
comeunderthispurviewasitsmajoreconomicactivityisTobaccobusinesswhichisnearly85%ofits
totalrevenue.Butforthesakeofcomparison,wehaveincludedITCalsoasitsnontobaccoFMCG
businessrevenueinFY08wasRs.2511Cr.,nearlyashighasNirma,thesecondlargestplayerafter
HULinHULschosencategory.Butthefiguresforadvertising,marketing&distributionexpensesof
ITC as percentages to its total sales may not be directly comparable to those figures of HUL as
product categories are different and the impact of above mentioned variables on these two
companyssales&distributionfunctionisdissimilar.OthermajorFMCGplayersnotincludedinthe
analysis are Nestle, Amul, Britannia & Tata Tea, which are mostly into the Food & Beverages
27
segmentwhereHULhasrelativelylesserpresence(ProcessedFoods&Icecreamsegmentstogether
constituteonlyapproximately5%ofHULstotalsales).InTea,HULispresentsignificantly,though.
Inthefollowingpagesadvertising,marketing&distributionexpensesofmajorFMCGgoods(inHULs
categorymostly)arebeingshown.Itistobeunderstoodherethatmarketingexpenseshereinclude
commissions, rebates, discounts, sales promotional, expenses on direct selling agents &
entertainmentexpenseswhereasdistributionexpensesincludeoutwardfreight.
Exhibit1:AnnualSpendinAdvertising,Marketing&DistributionfunctionsinFY08
Sl.
Company Name
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Annual
Rs. Crore
Mar-08
Annual
Rs. Crore
Mar-08
Sales
Advertising
expenses
HUL
14937.88
1422.9
Nirma
Dabur
Colgate-Palmolive
Reckitt Benckiser
P&G Home
Godrej
Emami
P&G Hygiene & Health
Henkel
Henkel Marketing
ITC
2651.15
2128.17
1597.3
1334.76
1079.57
922.78
586.42
556.02
430.33
417.79
21467.38
40.96
248.1
256.51
207.85
119.45
61.4
102.92
57.95
0
0
427.83
Advert. Exp.
As % of
Sales
9.53
1.54
11.66
16.06
15.57
11.06
6.65
17.55
10.42
0.00
0.00
1.99
Annual
Rs. Crore
Mar-08
Marketing
expenses
6.07
71.87
21.4
0
9.34
44.31
42.37
27.46
40.85
40.94
65.64
68.17
Annual
Rs. Crore
Mar-08
Marketing
Distribution
Exp. As %
expenses
of Sales
0.04
731.41
2.71
1.01
0.00
0.70
4.10
4.59
4.68
7.35
9.51
15.71
0.32
136.91
66.84
35.36
55.88
70.54
32.27
14.86
37.24
16.4
17.63
548.4
Dist. Exp.
As % of
Sales
4.90
5.16
3.14
2.21
4.19
6.53
3.50
2.53
6.70
3.81
4.22
2.55
Exhibit2:AdvertisingExpensesaspercentageofSales
Advertising Expenses as % of Sales
20.00
17.55
18.00
16.06
Advertising Exp. as % to Sales
16.00
15.57
14.00
11.66
12.00
11.06
10.42
10.00
9.53
8.00
6.65
6.00
4.00
1.99
1.54
2.00
0.00
0.00
Henkel
Henkel
Marketing
0.00
HUL
Nirma
Dabur
ColgateReckitt
Palmolive Benckiser
P&G
Home
Godrej
Emami
P&G
Hygiene &
Health
ITC
28
We can see here that Nirma, Godrej & Henkel (ITC also) have less advertising expenses (as % to
sales)thanHUL.Importantly,Henkelhaszeroadvertisingexpensesin2008,whichmayexplainthe
factthatawarenesslevelinconsumersforHenkelbrandsislow.HULadvertisingisdonemainlyin
case of soaps (for example Dove; done mainly to reaffirm that its not a soap!), shampoos,
deodorants (Axe), laundry detergents (Surf Excel, Rin) etc. With the introduction of home
waterpurifier(PureIt),considerableadvertising&promotionalexpenseshavegoneintoit.
Oflate,weseeverylittleofNirmaadvertisements.Thisisapparentfromitsadvertisingexpenseas
% to sales, which is very low (only 1.54%). ITC is altogether a different story. Cigarettes & other
tobacco related products which constitute approx. 85% of its sales, all relate to intoxication or
habitual consumption patterns having intensely brand loyal consumers and thus almost no
advertising(surrogateadvertisingisdone)isneededeithertoreaffirmthebrandsorintroducenew
consumers to the brands (there is regulatory angle as well). Current consumers of these tobacco
products are the biggest advertising agents that ITC has and of course, they do it voluntarily and
without knowing what theyre doing. But while moving faster into nontobacco FMCG business
ridinghighonitsstrengthofdistributionnetworkmatchingorsurpassinginsomecasesthatofHUL,
ITC has started aggressive advertising campaigns (Fiama Di Wills shampoo, Vivel soap,
Sunfeastbiscuits,Bingosnacksetc),directlyfocusingonmarqueebrandsofHULlikeSunsilk&
Lux,increasingtheheatonBritanniaforbiscuitsandtakingonKurkure&othersnacksandchips
fromPepsi,Cokeandothers.
Advertising expenses as percentage to sales is highest for Emami, which owns brands such as
Navratnahairoil&talc,Boropluscream&talc,HimaniFastRelief,Fair&Handsome,SonaChandi
Chawanprash,Menthoplusetc,eachofwhichisadvertisedheavilyinthemassmedia(e.g.,TV)with
famous & expensive celebrity endorsers like Amitabh Bachchan, Kareena Kapoor, Govinda etc. On
the other hand, we see regular advertising streams for Colgate toothpastes and other oral care
products, in which category ColgatePalmolive is the market leader. ReckittBenckiser advertises
considerablyforitsbrandslikeHerpic,Mortein,Vanish,Clearasil,Dettol,Strepsilsetc,whichisthe
reasonforitshighadvertisingcostaspercentageofsales.
MarketingExpenses
Asstatedearlieralso,marketingexpenseshereincludethefollowing
commissions
rebates
29
discounts
salespromotional
expensesondirectsellingagents
entertainmentexpensesetc.
Exhibit3:MarketingExpensesaspercentageofSales
Marketing Expenses as % to Sales
18.00
15.71
16.00
Marketing Exp. as % to Sales
14.00
12.00
9.51
10.00
8.00
7.35
6.00
4.59
4.68
4.10
4.00
2.71
2.00
1.01
0.04
0.70
0.32
0.00
0.00
HUL
Nirma
Dabur
ColgateReckitt
Palmolive Benckiser
P&G
Home
Godrej
Emami
P&G
Hygiene &
Health
Henkel
Henkel
Marketing
ITC
Here we see that the marketing expenses of HUL are among the lowest in the market (only the
second lowest after Colgate Palmolive which has very good brand pull for its Colgate
toothpastes).ThisprovesthatHULisabletomaintainconsiderablebrandpullthroughadvertising.
ITCagaincomesamongthelowestitstobaccoproductsrequireverylittlepushandhaveveryhigh
rotations.Also,ITCmostlydealswithsmallretailersanddistributors(paancigaretteshopsowners)
whohavemarginalbargainingpower.
AnotherrevelationisthatHenkel,whichhaszeroadvertisingexpenditure,hasthehighestmarketing
expenses among all others. But this strategy to push the products through the channel partners
may not be a good one for Henkel as it might be losing out for the lack of visibility and thus
consumer mind share and brands such as Margo, Fa, Neem toothpaste etc are losing out in the
market. Further, it is also a pointer to the fact that Henkels largest business share is in industrial
30
chemicals (adhesives, sealants e.g., popular brand Loctite; this segment constitute ~44% of
worldwide sales of Henkel) and for B2B, advertising per se is not that much important. For B2B ,
important is directselling approach, which generally requires negotiations, volume discounts etc,
whicharereflectedinhighestmarketingexpenses(aspercentagetosales)comparedtoothers.
P&G is in between the extremes and with considerable advertising expenses also, it is unable to
createsufficientpullforitsproductsinIndia(asevidencedbythefactthatmarketingexpensesare
also relatively higher) or its getting stuck for the lack of sufficient distribution muscle a la HUL in
traditionalretailinIndiaandsuffersfromlackofreachandavailabilityattheendconsumerlevel.
As mentioned earlier, both ColgatePalmolive and ReckittBenckiser both enjoys very good brand
loyalties and market leadership for their key brands like Colgate toothpastes and Dettol (#1 in
antiseptics),Herpic,Morteinetc.Thisiscorroboratedbythefactthatthesecompanieshavesomeof
thelowestmarketingexpenses(aspercentagetosales)inthegroup,asshowninthechart.
DistributionExpenses
Distributionexpensesincludetheoutwardfreightcosttothecompany.
Exhibit4:DistributionExpensesaspercentageofSales
Distribution Expenses as % to Sales
8.00
7.00
6.70
6.53
Distribution Exp. as % to Sales
6.00
5.16
5.00
4.90
4.22
4.19
3.81
4.00
3.50
3.14
3.00
2.55
2.53
2.21
2.00
1.00
0.00
HUL
Nirma
Dabur
ColgateReckitt
Palmolive Benckiser
P&G
Home
Godrej
Emami
P&G
Hygiene &
Health
Henkel
Henkel
Marketing
ITC
31
WehaveseenthatT&LplaysaveryimportantroleforHUL&otherswhohavepanIndianpresence
inFMCGbusiness.ColgatePalmolive,Emami&ITChassomeofthelowestdistributionexpenses(as
%tosalesfigures)&P&Ghasthehighest.HULislowerinthisrespectthanNirma&P&G,buthigher
than Henkel. This can be explained somewhat from the impact of the variable, Time Band of
purchase,ontheincreasedtransportintensityforHULinthelastmileforsomeoftheproductslike
householdpersonalcare,laundrydetergent,brandedattaetcinthefirst&lastweekofthemoth.
ITC(tobacco),Henkel(largelyB2B)aremostlyprotectedfromthisimplicationofthevariable.
AnotherimportantthingtorememberthatvaluedensityofFMCGgoodsisrelativelylower,causing
share of transportation costs in the overall cost structure to be relatively higher. This implies
dispersed manufacturing, locating manufacturing plants nearer to major markets. So one location
manufacturing to get higher economies of scale and on the other hand, trying to serve
geographically diverse markets may not be economically attractive for FMCG sector. Compared to
HULs 40 manufacturing plants across India, Nirma, the 2nd largest FMCG major in soaps and
detergents category, has 6 manufacturing plants, all located in and around Gujarat. So,
transportationcostofNirma,ifittriestocatertopanIndianmarketwillbehigher.Thisissupported
bythefactthatNirmas higherdistributioncost percentagethanHUL.ForP&G,thesamereasons
significantlyaffectitsdistributioncostwhichishighestforthegroupanalyzed.
32
8.References
1. B.JosephPine,JamesH.Gilmore(1999),TheExperienceEconomy:WorkisTheatre&
EveryBusinessaStage,PublishedbyHarvardBusinessPress,254pages.
2. HULWebsite(http://www.hul.co.in/)
3. HULCLSAConference,InvestorPresentation(24thSept.,2008).
4. ReckittBenckiserWebsite
(http://www.reckittbenckiser.com/site/RKBR/Templates/Home.aspx?pageid=1)
5. ColgatePalmoliveWebsite
(http://www.colgate.co.in/app/Colgate/IN/HomePage.cvsp)
6. EmamiGroupWebsite(http://www.emamigroup.com/Brands)
7. CMIE
8. Wikipedia
You might also like
- HUL Distribution ModelDocument19 pagesHUL Distribution ModelArpan Mehra93% (70)
- HUL Supply Chain ReportDocument56 pagesHUL Supply Chain ReportWHO IS ITNo ratings yet
- Hindustan Unilever Marketing Strategies and PoliciesDocument46 pagesHindustan Unilever Marketing Strategies and Policiesroma4321No ratings yet
- Air Waybill Form - Printable TemplateDocument1 pageAir Waybill Form - Printable Templateวชิรวิชญ์ ศรีทองกุลNo ratings yet
- HUL S&D ManagementDocument21 pagesHUL S&D ManagementKuldipak KheradiyaNo ratings yet
- Hul Distribution ModelDocument5 pagesHul Distribution ModelBhavik LodhaNo ratings yet
- HINDUSTAN UNILEVER Limited Final ProjectDocument78 pagesHINDUSTAN UNILEVER Limited Final ProjectNeeta MohanNo ratings yet
- HUL Supply ChainDocument20 pagesHUL Supply ChainAbhishesh Suman77% (13)
- Difference BW HUL and P&G Distribution Structure PDFDocument14 pagesDifference BW HUL and P&G Distribution Structure PDFRahul Mehay100% (1)
- Distribution Channel of Kohinoor CondomsDocument11 pagesDistribution Channel of Kohinoor CondomsPravah Shukla100% (1)
- IKEA's Strategic ManagementDocument38 pagesIKEA's Strategic ManagementJobeer Dahman93% (45)
- Backgrounder: 1. SchlumbergerDocument5 pagesBackgrounder: 1. Schlumbergervikri rahmatNo ratings yet
- Distribution Channels HULDocument12 pagesDistribution Channels HULnavdeep98480% (10)
- Sales and Distribution of HULDocument17 pagesSales and Distribution of HULAnkit Patodia100% (1)
- Sales and Distribution Manaagement in HULDocument18 pagesSales and Distribution Manaagement in HUL'Gitesh ⎝⏠⏝⏠⎠ Patil'No ratings yet
- Hindustan Unilever Limited (HUL)Document17 pagesHindustan Unilever Limited (HUL)priyankasinghal100% (20)
- SCM Synopsis HulDocument17 pagesSCM Synopsis HulSanjib BiswasNo ratings yet
- HUL Distribution Network (Final Presentation)Document22 pagesHUL Distribution Network (Final Presentation)angihpNo ratings yet
- VijetaDocument2 pagesVijetaPandharinath Rameshrao Chidrawar100% (1)
- Supply Chain Nanagement of HULDocument11 pagesSupply Chain Nanagement of HULsalil1235650% (4)
- Sales and Distribution - Hindustan Uni LeverDocument25 pagesSales and Distribution - Hindustan Uni LeverAthirapai75% (4)
- HUL (Supply Chain)Document19 pagesHUL (Supply Chain)rohan_jangid8100% (4)
- Competitive Strategies of HULDocument13 pagesCompetitive Strategies of HULankitpnani100% (1)
- Hindustan Unilever Pricing PolicyDocument2 pagesHindustan Unilever Pricing PolicyALLEN MATHEW JOHN100% (1)
- HUL Case With QuestionsDocument20 pagesHUL Case With QuestionsPrakash KcNo ratings yet
- Study of The Promotional Strategies of HUL LTDDocument73 pagesStudy of The Promotional Strategies of HUL LTDPawan Saini80% (5)
- Hul Distribution NetworkDocument33 pagesHul Distribution Networksalmanjimmy100% (6)
- HulDocument30 pagesHulkunal joijode100% (1)
- A Brief Study On Market Sructure and Demand Analysis of Hindustan Unilever LimitedDocument65 pagesA Brief Study On Market Sructure and Demand Analysis of Hindustan Unilever LimitedShivangi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- HUL Final ProjectDocument60 pagesHUL Final Projectsharmanmanu67% (3)
- Project On HULDocument25 pagesProject On HULArchit KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Pantaloons RetailDocument18 pagesPantaloons RetailSumit RathiNo ratings yet
- SCM DaburDocument21 pagesSCM Daburanshvaidhya0% (1)
- HUL Strategic MarketingDocument60 pagesHUL Strategic MarketingDebangan DasNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies of HulDocument57 pagesMarketing Strategies of HulHarshit JainNo ratings yet
- HUL-branding StrategyDocument59 pagesHUL-branding Strategypriyanka-telang-210876% (17)
- Hindustan Unilever Limited (HUL) IntroductionDocument3 pagesHindustan Unilever Limited (HUL) Introductionravi thapar40% (5)
- Hul Sip Report 12Document76 pagesHul Sip Report 12Nishtha Zutshi100% (1)
- Hindustan UnileverDocument24 pagesHindustan Unileverspenzik100% (5)
- A Power Point Presentation On HUL's Marketing Strategy in Rural India - FinalDocument26 pagesA Power Point Presentation On HUL's Marketing Strategy in Rural India - FinalGuddu Kumar100% (2)
- Amul StrategyDocument18 pagesAmul StrategyAkram Ul Hoque100% (12)
- Hul ReportDocument28 pagesHul ReportB.C.ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- DR Umesh SolankiDocument29 pagesDR Umesh Solankivivek guptaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HULDocument7 pagesIntroduction To HULvaibhhav1234567890100% (1)
- Strategies of HulDocument48 pagesStrategies of Hulbins157% (7)
- Indian Institute of Planning and Management: New DelhiDocument33 pagesIndian Institute of Planning and Management: New DelhiDip RanjanNo ratings yet
- A Study On Distribution Management of Hindustan Unilever Limited by Ashish AgarwalDocument32 pagesA Study On Distribution Management of Hindustan Unilever Limited by Ashish AgarwalAshish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Distribution Management of Hindustan Unilever LTD NewDocument31 pagesDistribution Management of Hindustan Unilever LTD NewNachiket JaniNo ratings yet
- A Study On Distribution Strategies of Hindustan Unilever Limited by Rajnikant GharatDocument31 pagesA Study On Distribution Strategies of Hindustan Unilever Limited by Rajnikant GharatRajnikant GharatNo ratings yet
- A Study On DistributionDocument5 pagesA Study On Distributionpranav2411No ratings yet
- Distribution Channel ReportDocument20 pagesDistribution Channel ReportVijay SharmaNo ratings yet
- HUL S&D StrategyDocument16 pagesHUL S&D Strategyakshay_abs100% (1)
- "A Study On Marketing Strategies of HLL in South India": Project ProposalDocument8 pages"A Study On Marketing Strategies of HLL in South India": Project ProposalAishwarya RajNo ratings yet
- Marketing PlanDocument59 pagesMarketing PlanSharath Shyamasunder75% (4)
- Submitted By: Hiren Gadhvi Neeraj Trivedi Shikha Agrawal Rahul Mehta Sachin PatelDocument23 pagesSubmitted By: Hiren Gadhvi Neeraj Trivedi Shikha Agrawal Rahul Mehta Sachin PatelShikha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- A Study On Sale and Distribution Management of Hindustan Unilever LimitedDocument35 pagesA Study On Sale and Distribution Management of Hindustan Unilever LimitedJakir HussainNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledkranthiNo ratings yet
- Hindustan Unilever LimitedDocument63 pagesHindustan Unilever LimitedPrashant Chaudhary100% (1)
- CA2 Marketing, Discuss Any Two Questions. Marks: 25 Case Study: Rural Distribution For The FMCG Sector - A Case Study of HLLDocument8 pagesCA2 Marketing, Discuss Any Two Questions. Marks: 25 Case Study: Rural Distribution For The FMCG Sector - A Case Study of HLLPrashant RazdanNo ratings yet
- MarketingChannel Group6Document31 pagesMarketingChannel Group6Anx19No ratings yet
- Project LuxDocument48 pagesProject LuxKing Nitin Agnihotri33% (3)
- SandeepDocument56 pagesSandeepAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Hindustan Unilever Limited: Distribution System of HULDocument3 pagesHindustan Unilever Limited: Distribution System of HULRushabh JadavNo ratings yet
- Ai - PPT 7 (Internal Control)Document30 pagesAi - PPT 7 (Internal Control)diana_busrizalti100% (1)
- Salina YeungDocument10 pagesSalina Yeungabdullah basemNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management QuizDocument3 pagesOrganization and Management QuizJisbert Pablo AmpoNo ratings yet
- The Cultural Context of EntrepreneurshipDocument8 pagesThe Cultural Context of Entrepreneurshipfansuri80No ratings yet
- Case 1Document19 pagesCase 1Ragini RangaramuNo ratings yet
- Reebok Project WorkDocument56 pagesReebok Project WorkdipanshuNo ratings yet
- Tds Party NamesDocument24 pagesTds Party NamesSunil MishraNo ratings yet
- SMCSL Reviewed Bye-Laws 11 May 2021Document23 pagesSMCSL Reviewed Bye-Laws 11 May 2021Adeyeye EniolaNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health and Safety AgentDocument2 pagesOccupational Health and Safety AgentmphatuseniNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing Trends 2020: Industry Highlights and Market TrendsDocument38 pages3D Printing Trends 2020: Industry Highlights and Market TrendsAlex BurdeNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit Scheduling Tool3Document1 pageInternal Audit Scheduling Tool3BharathNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting - ABC Vs Variable CostingDocument3 pagesCost Accounting - ABC Vs Variable CostingJaycel Yam-Yam VerancesNo ratings yet
- Oracle Hrms IndiaDocument318 pagesOracle Hrms Indiavinay_narula_4No ratings yet
- Rera BookDocument80 pagesRera BookRahul O Agrawal100% (1)
- Commercial Banks Behavior and Effect On Profitability in UaeDocument16 pagesCommercial Banks Behavior and Effect On Profitability in UaeAbdelghani RemramNo ratings yet
- (Module 10 - Module 18) MGT 101 FinalDocument453 pages(Module 10 - Module 18) MGT 101 FinalUsama KJ100% (1)
- DCCI Membership Application Form - Angel ProjectsDocument2 pagesDCCI Membership Application Form - Angel ProjectsDurban Chamber of Commerce and IndustryNo ratings yet
- Me Market-StructureDocument3 pagesMe Market-Structurebenedick marcialNo ratings yet
- Liabilities of Independent Director Under Company LawDocument19 pagesLiabilities of Independent Director Under Company LawVIPIN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Rusame33492Document1 pageRusame33492jinalpatel004No ratings yet
- The Driver Business Plan2Document16 pagesThe Driver Business Plan2AhmedHassanSharkasNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Industry of BangladeshDocument32 pagesPharmaceutical Industry of BangladeshPratikBhowmick100% (1)
- BBTX4203 Taxation II - Eaug20Document296 pagesBBTX4203 Taxation II - Eaug20MUHAMMAD ZAKI BIN BASERI STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Consultancy Procurement Document (CPD) - TPS Zemun - Procurement Support and SupervisionDocument120 pagesConsultancy Procurement Document (CPD) - TPS Zemun - Procurement Support and SupervisionSheila MaNo ratings yet
- Rate Analysis FormatDocument1 pageRate Analysis FormatShashika Sameera77% (13)
- National Highways Authority of IndiaDocument239 pagesNational Highways Authority of IndiaAnonymous eKt1FCDNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term % Midtrem Exam 20 % Result Course IdentificationDocument6 pagesMid-Term % Midtrem Exam 20 % Result Course IdentificationSukhmani KambojNo ratings yet