Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hand Acupuncture Therapy PDF
Uploaded by
Papadopoulou Zwh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views86 pagesOriginal Title
Hand Acupuncture Therapy.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views86 pagesHand Acupuncture Therapy PDF
Uploaded by
Papadopoulou ZwhCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 86
TByive! Acupuncture
Ice) >) ee
|
Hand Acupuncture Therapy
Qiao Jinkin
ted by Wang Tai
pratt 2002
jing 2006
‘second Pi
tone Fat
: inuplfww-fip-com.cn
ent adie
info@ip.comen
falesafip.com
ISBN 7-119-03
‘Foreign Languages Press, B
Published by Fore
24 Bsivanahuang Road, Be!
Disrasedky Cina nerasionl Hook Taig Cape
35 Chegongzhuang Xilu, Bejing 100044, Chi
PO, Box 399, Beijing, China
Printed in the People's Republic of hima
PREFACE,
As treasure of traditional Chinese medicine, hand acupune
ture is @ physiotherapy to prevent and teat dseises: The hand
reveals — through changes f g (vital), colo and outward ap
Bearance — physologcal and pathological dsurbances nthe Boog
‘The same changes also reveal the cause and dlagnosis ofthese dice
‘eases. Treatment for prevention or cure can then Be applied By
stimulating certain acupuncture points or areas ofthe hand trou
‘scupuneture, massage or other therapies.
‘and acupuncture therapy consists of two procedures: Diagno-
through observing the hand: and treatment, though applying
acupuncture and massage. The clinical practice of observing the
and can be traced tothe Zhou Dynasty (c, Lith eentury-256 BC)
ere it was called palmisty or the holographic diagram of Ji
Gong (nine divisions) and Ba Gua (eight trigrams). Diagnosis
through observing the hand developed further in the Qin and Han
Dynasties (221 BC-AD 220). The publication of the ancient
medical classics — such a The Yellow Emperor's Canon of Medi
cine, Classic of Difficult Diseases and so on — better defined and
éstablished the theories of Zana (nteml organs) and Jingluo
(meridians and collaterals) After that, observing the hand reached
‘an even higher standard. Through this historical progression, hand
‘scupunetue therapy developed into an important branch of tradi
tional acupuncture
Over the past 20 years — following the establishment and de-
velopment of the biological holographic principle and holographic
embiyo theory —a diagnostic and therapeutic system developed for
local acupuncture that combined the diagnostic diagram of the
yranice became incre
0d appre uncture eTaPY ren
a aquired modern Do
jeveloped ster of hand acupuncture ther
6 thot Si ha
ae ete VOT eg
thos ee ron diseases.
toe und wed a vast amount
es aac cnn
work of is spot tem out so that th might beg
ie that agent wads
etd i fate est popes that this book will prove helpfy ‘oe
eects |
Eee
=
near therapy
0 Fnlin
September 1995
CONTENTS
CHAPTER | INTRODUCTION
Section | Definition of Hand Acepunctire Therapy
1nd Development of Hand Acupuncture
CHAPTER 2 THEORIES OF HAND
Section
I
Links
ks
ACUPUNCTURE
THERAPY
ina onthe Palm
the Palm and Diseases
2 Meridians
2 Meridianal Muscles
2 Merdianal Skin
Embryo System for
pic Principle and the Holograpic
nan Holographic Embryo System
ICATION, NAME AND INDICATIONS OF
HAND ACUPUNCTURE POINTS
x! Acupuncture Poi
sdianal Hand Acupang
sn bows Mer cine
ite
Be a nes of Hind HOPESINC Eni
on 3 Pins 2 Ar acupunsie
Be casawamiovriscnosis
Ceara re Donon eT .
Seon Os ’
1 ia corte Pl 4
1 eo Pal “
ni
Bert Py pation Hernia &
Sein 2 Hand EE Coord The ndtons
1 Aico a Anpesance in Holosoptic Ay ©
1 Changes
onthe Has
a Remas s
uapran 5 HAND ACUPUNCTURE THERAPY INTR9,
BEN sonics Ac
fon 1 Therapeutic Mebods Applied to Acupu
sete etd
1 Acopunctre 5
I, Bleeding Therapy
I, Moxibosion
I, Aqus-acopuncture
Y, Electroacopuncture
YI Photo-acupuncture
VIL Massage
VIL Magnetic Therapy
Section 2 Hand Acupuncture Therapy Indications and Con
‘nindicaions
I Indications of Hand Acupunctare Therapy ‘
TL Contrsndicaions of Hand Acupuncture Therapy
Section 3 Principles for Selection of Acupuncture Points ad
Holographic Arcas i
1 According tothe Involved Organs |
ta Diferental Diagnosis of Syndromy
we Poings. 4
Aeconig othe Thies of ang nd
wal Chinese Medicine Tae
unctions of Acupuncture Points
Theories of Traditional Chinese
Treatment of Fining Conse by
esate The
Cases of Fainting Dering Nec
TI. Manifestations of Fainting Dr men
Treatment of Fainting
1. Pre
[Needing in Hand
Needing
ention of Fainting During Needing
CHAPTER 6 CLINICAL A\
PUNC
Common Di
es ofthe Res
PPLICATION OF HAND ACU.
RE THERAPY
Section
Dis
ascular System
ean disease
tive System
2. Peptic ulcer of stomach and duodenum
3. Acute enteritis
$.Chronie
5.
stipation
sags 2 38
a
B
a
"
7
16
8
8
8
%0
3
2
8
3
a
8s
comneaorsri
Sines STK)
so.ctti rine ys
Die lis
Dies Frome
2 enor penta SY
Se rev (DH Sen)
ig pyelonepitis
rsas tte Nervous Sse
sieia
Anemia easi8
Falah
4 seule of sok
$ saguele of rein ins
6 Newralisciice
1 Facil aby
Facil spasm hn
Geog of he greater occipital nerve
10 Senile dementia
Spam of diaphragmatic muscles
IL ifxtious Diseases
Lnfuenza
2. German measles
3. Whooping cough
4.Pulmonary tuberculosis
5.Viral hepatitis
‘6 Bacillary dysentery
See SRE E SESS ES e ewes eeesssssesses7F
Seetion 2 Common Disorders Related wo Surgery
Cori tery and Ortho-
| Postoperative sonal dststion
2. Hyperplasia of breast,
3.Hemontoids
&. Acute lumbar sprain
5 Shit necke
{6.Cerviel spondylosis
7 Petar of shoulder
8 Stain ofthe lamba muscle
9.Prolapse of limbar intervertebral dae
10-Heel pain
1Speain of the ankle joint
12.Chronie appendicitis
1B Prolapse of the rectum
14. External humeral epicondylitis
15.Hyperplastc spondylitis
don 3 Common Bi
LDysmenortiea
25 of Gynecology
ofuseleukorrhea
3-Palvicinflamastion
4.Chronic cerviitis
5. Uterine contraction pain after childbirth
6 Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
7-Hiysteromyoma
8-Amenonthea
‘on-4 Common Pediatrie Diseases
Persistent pneumonia in children
2 Diarchea in children
3.Asthmain children
$.Convalsion in children
5.Anorexa in cildeen
6.Bed-wetting in cildeen
s
seston Coy and Tet
|e sfotum 9)
onus
3 tacome
Spee
anes
erg tits
Sepsis
so,croni sinus
1 Ns ty sensation in hat
1 Nn ody et
13. Aeue consis
Heenan
15 Teoh
Rosca dees
mercer
Tesora ewsleit
ea P eommon Disses ofthe Skin
Urticaria
2.Cutaneous pruritus
3. erpes zoster
Beem
5 Newrodermaiis
6 Acne
Secion 7 Diseases Duc to Bodily Dysfunction
{.lasomnia
2 Tred neck and shoulder muscles
4.Copiopia (eye fatigue)
4 Reduction of vitality
‘REFERENCES
snails
esi op the Bye, Nose, By,
aysete er of the EN Ea, Oy 4
}
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
Section | Definition of Hand
Acupuncture Therapy
‘What is hand scupuneture therapy? Before answering that
sion, ita tout someting fm common expen
in daily life Ms
A toothache and its
al swelling may have been caused by
using the teth to crack open too many melon seeds over long
period of induced by mental agaravation
common Chinese saying goes: tooth-
i nota serious illness, bu the suffering it produces can drive
a patient de
3 it might have be
conceened and knowl-
nd applying pressure to the Hukon
Point 'snuff-box,” a depression between the first and sebond mets
pal bones of the palm) for two to thre minutes to relieve the
Pain. Why? The explanation ha a solid basis in medical theory. As
mentioned in textbooks oa Traditional Chinese Medicine, the Hega
(L14) point ofthe hand's ¥ large intestine meridian les in
the Hukow area, So pressure applied at this point stimolates the
ation of i and blood, transmitting vital information through
meridian to the face and to the oral cavity to relieve the tooth=
ache and local swelling, This follows the principle cited in the
“Indications of Four Main Poin in Vere” to instuct inthe elini=
cal practice of Chinese acupuncture: “Choose the Hegu point for
. sa
er ows”
. ofthe ee joa Chinese Medicine gy
eine Se af Tricor th Following gy
“Tao os :
fe,on the meray
eee re or mosivan Pag
0 Mad. Masse ato cre seaes sna eh
meee
Telieyg he
sans te ody =<
ai oe entation of the body, the p
ae
(@) As 2 gin colo Seng EXE
"taagond (C8) | New point fr ash
a Re
Stats afr 9)
Fi 6 Points for hand ecapunetns eeu of hand)
1. Point for pain of medial malleolus
Location: At the junction of the skin onthe back of the hand! and
skin of the palm, on the radial side ofthe metacarpophalangeal joint
of tmumb,
Indication: Ankle pain.
2. Point for chest pain
Location: At the junction of the skin on the back of the and
and skin of the palm, on the radial side of the phalangeal joint of
thumb,
Indications: Chest pain, vomiting and diarrhea.
3. Point for eye pain
Location: At the junction of the skin on the back of the hand
nd skin of the palm, on the ulnar side of the phalangeal joint of the
thumb.
Indication: Eye pain.
4, Point for shoulder pain
ofthe skin on the back of the hay
: son
“essen ee me
Indetons: Ace sri fh itp igen
s ‘se of an intervertebral mi rec
finde Ae yer pain 1 rs
Was y TT ote fox pn th act
FE inne eck one Location: Between te fourth and ith me
; Be facies cracd cation: atween the forth and ith mctacrpopba
feo eg of it Plager an | J inet emer eee
skin ofthe alm
nications: Seiten and pain nthe hip and butocks
intestinal pain, appendicitis, vit for pain i the throat and tooth ache
inde OE pach ston B
Temi is pane he jos sve ee rueose
ofthe kne ina the top of the hea« indications a
Crate eaten etka | al Oem een ni
Teeraeai lt atl so pate)" rt cm
Location: Between the scond and hind metcarpophal
ile BOE yagi eadace and pain athe 0p of egy, | jin closer tthe omer joint ee
ad inn be wep (oes) Indians SU eck and peck sprain
Peet union of sn onthe ack of pg) Pon forums
Ipptnotie pala, one radial side ofthe First phalangenjgg | Losson: On thera side ofthe eendetntor digitorum, o8
ae the ulnar side ofthe four exter digitorum and Leon pon
er ro
ne eap tn f e Indications Lumbago a pain ofthe ler back
i 35 ottorpaof semana neste
Be ce of bein onthe ecko hehinday| glo Abe MHPN Duce Leging Fan ang
[kin ofthe palm, on the radial side of the first phalangeal join Indications: Chronic gastritis, peptic uleer and indigestion,
“Tite ing. 16 Point for asthma and cough
Mdicaon:Painin the perineum Location: Inthe pl onthe lr side of te matacarpopilan
'9,Point for pain in the back ofthe head
Location: Atthe junction of the skin on the back of the handank
tions: Bronchitis, cou
and asthma,
" shin ofthe palm, the ulnar side of the frst phalangeal join of ite 17 Poin for bed-wettng and frequent urination
= Location: On te palmar side of the ite finger, at the midpoint
Tndications: Pain in the back of the head and tonsils of its second phlangeal crease
10. Point for back pain Indications: Bed-wetting and frequent urination.
| Location: Atthe junction of the skin on the back of the handanl 8: Runt li i Ta
ratio tlnar side of the metacerpophalangeilfill Location: At the midpoint between the point for stomach and
gin, intestine pain and Daling (PC 7) point.
eth drel vrs crease,
econ: A fond presre From any cue
infor of middle finger atthe mj
20 Poi FP gv dorsum of mile ing "Point gi
igh over ,
Piet ete demon on WD Wen
sa
neon: sh
a atts dee exum of the band, 1 cun prox
tin On and ots acrpoptalge
insane
io
Tati: Atte intn fhe As arpa! one a pg
Jom dl order ofthe ther prominence.
Indication: Malaria.
Point oftnsits
ea The pln, atthe midpoint of the ulnar border fy
esacaplbone
Tndeton Tnslits and sre thos.
25, oie for emergency treatment
ossdon: About 02 eun fom the border of nail ofthe mis
finger.
a Indication: Coma.
26, Point to control epilepsy
‘Location: At the middle point of the border between the thea
“znd iypothenar prominence
Indication: Epilepsy and fainting,
_ 2. Point ofthe spleen
On the palmar side of thumb, at the midpoint ofit
F|
High fever and diseases of the eyes,
at
in,
Indications: Diseases of spleen and stomach, and timers
28, Point ofthe smal inenine
“Location: On the palmar sie of index finger, atthe midpoint of
‘he crease between its frst and second phalangeal bones
Indication: Diseases of small intestine
29, Point ofthe large intestine
Location: On the palmar side ofthe index Fnge, at the midpoint
Df the crease between its second and third phalanges bene,
Indication: Diseases of the large intestine.
30. Point of Sanjian
‘Location: On the palmar side of middle Finger, atthe midpointot
Tease between is first and second phalangeal bone
Indications: Diseases in chest, abxomen and pelvis eavity.
31. Point ofthe heart
Location: On th
point ofthe ce
nna side othe mide finger, atthe mi
ewe i second and third plalngeal bone
Indication: Diseases ofthe heat and Blood venel
32. Point of the liver
Location: On the palma side of sng fing, a the midpint of
the crease between is it and second panel be,
Indieation: Diseaes of the lve and gallate
33, Peintof the
Location: On the
the crease between its second and thd pala
2, a the midpoint of
eal one,
Indication: Diseases ofthe respiratory system.
34, Point of Mingmen (life gate)
Location: On the palmar side ofthe ltl finger, atthe midpoint
of the
Indi
© between its frst and second phalangeal bone.
ion; Diseases of reproductive system,
Point of the kidney (night urination)
Location: On the palmar side of litle finger, at the midpoint of
the crease between its fist and second phalangeal bone,
Indication: Diseases of kidney.
36. Dagukong (EX-UE 5)
Location: On the dorsal side of thumb,
the midpoint ofits in-
see hy |
Section 3 Points and Areas of Hand
Holographic Embryo System for
Local Acupuncture
UE?)
ints on the dorsum ofeach In recent years, sever! schools of acupuncture inthe holographic
‘and third or the fourth and fifth mene ‘embryo system have been established with different views. How-
ever, the opinions of the different schools can be organized into
the wrist crease and metaca
between CR three groups
{nthe first group. the traditional diagram of Ba Gus for hand die
‘agnosis and treatment of diseases continues to be apptied in clinical
practice’ in the second group, changes in ines on the palm ae taken
hig _into account to diagnose and treat diseases; and in the thd group, &
lag) combination of the “palm massage” diagram used in Western coun
tries and the “hand diagnosis diagram” of Zhang Yansheng used at
China is applied in clinical practice to make diagnosis according t0
i, color and appearance of hand.
On the basis of personal experience and study, the author thinks
thatthe last group isthe most reasonable and seientifi in its clinical
Practice and theoretical foundations. After rectifying and modifying
the < achieved by the specialists in the third group, the author
ions: Febrile diseases and pain. has organized the hand holographic embryo system for local acu
Say pices ie
Tear four points onthe palmar side ofthestiad ye ums new sonnet he sone ote bse ome Hager
jofeach hand, at the midpoint of their proximaliniy an the midpoint of the wrist crease. It is used to represent the
anterior midline of the body and the vertical axis in the body. The
end, the corresponding areas of head, nose, mouth, esophagus,
stomach, kidney, reproductive organs and perineum are arranged in
Secondly, most people have four basic lines on their palms that
a
xie (EX-UE 9)
a Thee are four points onthe dorsal sid of exchhly
the junction between the skin on the back of the hand ag
am ost proximal tothe border of all webs beeen
ig a point at each tip of the 10 fingers, 0. of
free edge of nail.
diseases, hypertension and revival oly
indetning oresrnN TSO of gy
very i es called heaven
Be Te il Ne oblique one tavehg thy
Ter sent te eh nae
Neen eens scarecr line hena 1,82)
Bere nama Dein OE Tne (od ig lil
Ae ae mine oF al 8 call Yoh ng
7
. fate ine.
See
on ene te ran body sd reno te rma
Se pcs 0 he Sr of Md ee
Bd ote Real uPper and Love back ag
ee ptt sls of he and a8 ond ae
(ere 7).
1. Head area
Location: Around the palma cease atthe bas of mide ings
Indications: Diseases ofthe top of the head, forehead and both
temples CTaiyang point)
Location: On the vertical midline ofthe head area and just below
the forehead,
Indications: Diseases ofthe nasal septum or nasal cavity.
3. Eye area
Location: Below the head are, beside the nose area and not
‘beyond the interosseous spaces on both sides ofthe third metacarpal
bone
Ind
ation: Disorder of visual acuity and diseases of the eyes,
Location: Below
area heside the nose area and above the
Indication: Diseases ofc
5. Mouth area
Location: Below the nose area and around the nterseeton ofthe
the heaven line (heart line)
cheeks, tongue, oral mucosa
.en the heaven line [hear ine} and the human being Tine (head
with its proximal end asthe cardia area
ses ofthe esophagus cardia, nec, thyroid and
Location: Around the midpoint of the vertical palmar midline
Indications: Diseases of stomach, cardia, pylorus and Guode=
8. Kidney area —
Location: Next to the vertical palmar midline, on both
-
center ofthe stomach 4
wn the 8 an
“tne io ase. the
pete renal pels. adrenal slang
es: DE ag
csi B08
al Fett oS Ne ons gg
ee ofthis area on both
ee oct tne ower pret
ns te get db Ne 1 Porn gh
ec pepe th cena pg
er pe prosiate eae served. Th 7
sens Bint band is ObSeVEd. The Upper peg
mie lower portion represents the teine gen
ase dvi) the central ponten
iS oe
(ee Fit.) 2
Pipe vee
Figo
Indications: Diseases of promate gland, testis, ependidymis,
seminal vesicle, and spermatic dct in male: and dacaces of wer
‘vagina, oviduct and ovary in female -
10, Trachea tea
Location: A vertical rectangular are from the web between the
ring and litle Finger tothe heaven fine (heat Hine]. Diseases of ung
tnd trachea are shown inthis area (se Fig, 8)
Indication: Diseases of trachea.
left chest and lung
Location: On the left side of the trachea area
‘ons: Diseases of the left chest, bronchus, lung, pleura,
and upper back,
Area of right chest and lung,
on: The midline ofthis area is coineides with the upper
a
pat bone distal 10 the fea
ers ott gs
sinensis, a
mt
i hrzoal rca over Pe
Pease SPC PEN hc mage
of palm) 1 represent both sides fay
meeases of mbar spinal CTU and ae Mi
at ngular area surrounded by the
mld ge, hman Ns
eo ine (ie fine] as its three edges. The my
a geet feof he ve,
se ipso eM Fea hay
TSS awn te Heaven ie fea ey
Se hint witt cone saa ae a
se past tough ceo ee
erica fine drawn along the interOsseOus space betwee
‘hones of the middle and ring
“Indication: Diseases of spleen.
"16. Gallbladder area
1 Location: The centr of this area is at the intersection of aby.
gaps blower rosina) age otra
earth line fife line]) and a vertical |
trachea area. It is lower than (proximal to) the spleen ara.
Diseases of gallbladder and biliary ducts.
“Ateas ofthe upper, middle and lower abdomen
Location: The center of the upper abdomen area is at the ine
i tangential line of the human being {head line) aii
ythrough the trachea are. The vertical midinea!
inte
n ein ine fe
ea
tea
|
‘the hypothenar prominence is divided ino three segments to divide
the abdomen into the upper, middle and lower divisions (se Fig, 8).
Tadieations: Diseases in the organs of the abdomen such a the
pancress peritoneal membrane, sal intestine, appendix, stomach,
find ascending, transverse and descending colon,
‘Aconigue characteristic ofthe right half of te palm is that iis
‘readess and tailless” (tha is, it nchades only the rank of mn
by) to represent the organs between the neck and perinesm. TRE
corresponding arees of internal organs om the left half ofthe palm
are mentioned as follows. First of all, the palmar surface of the
proximal segment of the index finger is divided into three equal
‘Vertical portions
18. Area for dreaminess
Location: In the left one-third of the proximal segment of index
Indications: Insomnia and dreaminess.
19. Area for insomnia
Location: In the right one-third of the proximal segment of in-
dex finger
Indications: Insomnia, sleepiness and nervous status.
20. Area for hypertension
Location: In the left one-third of the proximal segment of mid=
dle fin
Indication: Hyper
21. Area for hyp
Location: In the rig
snt one-third ofthe proximal segment of mid=
dle finger
Indication: Hypotension.
2, Area for dizziness
Location: In the middle one-third of the proximal segment of
middle finger.
Indications; Dizziness, Co poisoning and fainting
23, Area for fatigue
Location: In a square area left to the intersection of the heaven
line [heart line] and the interosseous space between the metacarpal
8
lll
idle FEE
yan. NE ESTAS OF Days
ation.
food suPPly
non the Fight border of ha,
us
Bia print
ied gan re ao the a
re emi, 221 TSOTE AM hr ggg
the anos
6. Rectum ae
cto: Po oy
ert i Tl represent the left and right get
ae nerd and media sides 9 "eft nd ish seg
27, Area for deficiency of ‘
Toeation Disa othe heart area, on the junction ofthe sig
thebeck ofthe hand and skin ofthe palm over the medial suc
the proximal segment of thamb.
Tnication: Diseases with deficiency of vita
28, Heart area
fe eda oo
‘eaten
sninent area from the tip of the thy
‘The vertical midline ofthis area
‘Location: The thenar prominence is di
‘potions with the medial one bigger than the lateral one to reprsa
into two veri
the right and left heart (both ventricle and auricle) respectively
ar prominence is die
14 into tree equal transverse portions and the upper one
ais the left heart and the middle one-third isthe arf
30. ren for theta
Location: Inthe lower oe thie of the ltr oneal.
then prominence feet
‘ndiation: Rheumatism, catching cold and commen cold
wineold type _ ete
31. Blader area
Location: Th area is around the intersection ofthe interosseous
spsce between the metacarpal Bone ofthe inex and mile ger
andthe midline ofthe thenar prominence. nd its Blom he Re
‘ea. The urethra area Is below this wea, he steese
Indications: Diseases of unary system inching
der, eta and 50 on nae
32, Skin area
Location: Directly below the area for yperension, tthe ne
ction of its midline andthe ight bord ofthe thenar prominene
Indication: Allerpe dermatitis, czema, purpura, subcutaneous
33. Area of the left shoulder and arm
Location: Ina area ofthe pal left oa vertical line dawn from
the lft end of the basal crease of index finger tothe human being
fine [head line
Ingicatons: Diseases of et shoulder and arm,
the right shoulder and arm
Inthe ight to vertical ine drawn
Tine (heart line},
cations: Diseases of
sree ofthe lft eat
Location: In the central area ofthe left surface of the proximal
niddle Finger.
ions: Diseases of left outer meatus and eardrum, ots
media, and perforated eardrum.
of the right ear
ihe central area of the right surface of the proximal
s
ee ght outer me
of id enses ofthe right ts ay
ise 2
mea ofthe ead (occipital bone)
5 STA ne dorsal surface of thumb an ay,
tpl heath
es
a
Fig. 10
38. Spine area
Location: Along the tendon of the e
finger. 4
‘ndications: Diseases of cervical, thoracic and lumbar spit
9. Cervical spine
‘On the dorsal surface of hand, around the mea
censor muscle of mid
joint of mide finger
Indications: Diseases of evi pine and both shoe
40, Thoracic spine area TT oe
Location: Below the area of the cervical spine, in an area over
the upper tee fits of he extensor tendon oe mi age
Indications: Dees fhe thre esa
41. Lumbar m Ae
Location: In an area over the
lower two-fifths of the exten
tendon of the middie fi
above the dorsal wrist
and
Indications: Diseases of waist
lumbar muscles and lumbar and
sacral bones \
Back atea
Location: The whol
of hand represents
of bara bod Th
the dor
the left b
represents
. Diseases of the
Fott
(CHAPTER 4
p OBSERVATION DIAGNgg,.
| diagnosis includes many di
n_diagnosis aenoste
ition of the ae Ee Seger, shape of
and pattems of palmar lines acegrget
i raat palit. BECAUSE Of the liniag te
tecigues used in hand diagnosis wie Se
I, Shape of the Palm
“Round palm: A round palm is usually found in people yy
p, abundant energy, indomitable will, and an extovegy
disposition. People with round palms seldom sg
es eaused by emotional disturbance or mental depts
2),
palm: A square palm is usvally found in people mt
‘health, a conscientious attitude toward work, an ae
© with a stubborn disposition at times. They x
fiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases inti
' 4
Fate Fata
3. Spoon-shaped palm: A spoon-shaped palm with thick west
and base of the fingers is usualy found in people with an opene
‘minded temperament, vigorous physical strength and self-confidence,
Ifadkicted to tobacco or aleohol, these people may be susceptible to
lumbago and to being easly agitated and to early aging. (see Fig 14)
4, Rectangular palm: A rectangular palm with thin palmar mas:
cles is usually found in people who tend tobe introverted, nervous,
high-strang, sensitive and fearful. They are susceptible to poor
‘memory and weak vitality due to poor health (see Fig. 15)
1. Thickness of the Palm
ety ou
Poe uraty end arene
metho palm with rigid ens
Da eany ea nope with poor dics
Be aly mds oor wi or arbi
se tc pala nication of tig
Ihsan toner bad a0 hin pal gp
Bee reoere Liver ay
eee snice ond cg ose
eka
ate cm
me
ea =
Ill. Veins on the Palm
Sr palagea jin ae visually found in people wig
Sear ie feces. These people a susceptible oh
pon bool and venous neu, Dat henge
fens muy gradual subside and disappear and the hemontogy
Temorhcds may sop afr the hard feces inthe intestine aoe
voided
JV. Color of the Palm
The normal hand has a palm that is pink or light red ince
Tistous, mois, elastic and powerful in grasping an object. Once
‘mar color tums darker or lighter for any reason other than vee
“eichanges or mental, physical or chemical influences —peopl i
ly show some deterioration in their health
“A pale palm indicates diseases of the lung, A datk ple
without luster indieses dems
Indicates abnormal bl
final problems. A eren
hee
stomach and spleen. The golden yellow palm ndlestes iver daronea
A crimon (deep red) palm ifieates an excessivenes of heat fre
A pale or dark blue palm indieates anemia, Blood stasis. Myperten
sion, hypot
rpotension. heart dieses, out ota invisible hemor
and the diagnosis ofthese diseases may be made withowe ooh
the abnormal color change can be found in the three mai ines on
the palm. Engorged veins on a dal palm indicate bemontiihs A
network of capillaries on the palm indicates a defceney of
patches om the thenar and y=
poth ine larly known a8 “innabar pal”
indicates a past history of hepatitis, and 50 is als ealled a “tver
palm" Ifthe patches are dark purple in colo t indicates persistent
hepatitis with most iver cells destroyed, Red ates nay al a=
pear on the nts witha deficiency of vitamin C. The
pl may he bright sed in the coloe of patients with system pts
The cancer patients may be in a color of Toes (ye:
“ w hemetherapy the color of the
ack palm and fingers indicates
limbs.
of disease due to the
Section 2. Hand Diagnosis by Observation of
Holographic Areas
nosis is based on Traditional Chinese Medicine theory
ssis. Location of diseases for application of
Hand diag
of observation dia
a
‘ |.
sy cirog cx
jacupanctie er the hand. The naked eye ye i
“Pt en a blo in pe
eri of diseases. sand
by he ha
i se agnosis aid ony
Ce te Tol Chase lg
ned
on di
cbcertion a
= as simple, objet, Fela, sap,
gon with other Observation diagno
sr BOSS ii,
res of Traditional Chinese Meq
diagnostic meast
ae I latent disease
mes) Diagnosis can reveal diseases in time 4p
ortherteit progress.
a eth
icine iy
ba
J, Analysis of the Five Colors and
Their Indications
Hupanskincolor consists of ive basic colors, blu, ee,
tite and Back, and these colors represen th five intemal mye
iver heat, spleca, lung and kidney. Lustrous and most, they
ofthe normal human hand is tinted with these five colors. Thal
‘ofthe palms redder, moister, and more delicate than the skinol
bck ofthe hand. The above-mentioned normal appearance of
‘skin ofthe hand indicates that its owner is a person with sfcer
‘esseoe, gi lood and Jinye (body fluid), nocmal functions of Zag
fu and balanced yin and yang
Ta patients, abnormal colors may appear, with one cult
(Bominance over the others, either very dull and dark or ext
bright. Ancient physicians divided abnormal colors ino fie
of blue, red, yellow, white and black to indie
-
roups of syndromes (pattems of disease
indians ot fie cass Saeseh. Thi he ea
1. Blue Indicates a cold syndrome,
syndronte or convulsion sysrome
Red: Indicates a hot syndrome. A. dark ced color indicates an
excensve hot symone ad a ght rel enor ees decent
ain syome. blood stasis
1 wee en ae ee
olor red indicates the febrile or Blood-
s. such as the hot syndrome, blood heat, blood
heat, and accumulation of heat
light red color indicates impaired
functions and poor vitality of Zangfu, including a disease with defi
ciency of superficial yang, disease in an early stage, chronic disease
inal e- and mild febrile disease
4, Dee A deep color always indicates an excessive sym
‘drome” or heat syndrome. For example, in patients with the “Liver
pili,” dhe skin over the thenar and hypothenar prominence i red
with scattered dark red spots and patches beeause much eat has
late! in the live, known as “excessiveness of ive fire” In
patients with habitual constipation over the years, a simi coloe
change and red patches,— eaused by the accumulation of heat 9
2
ai
ae
ihe hypothenst Prominence, tp pr the jy
color r¢ ating Mt
Mpa, the color ted in the jype"™@h yyy
Se ra eon se ee
i ed cao nthe pan
:
with dryness and pain jn _
nage mon sa
emgrered over the dark red pharyny fe a
Hem conesiveP30eenie dsene, age Hngh
indicate a eisturbance of Blood quality,
i gal Fresh 14 08 €¥Yhere on th py viscosity, contaction of capitan, seduetag
Bee ning) Seas a
ap haetinapiinme ee ‘Any disturbance of blood quality ean cause inate
emorhaging 8 caused by openly 5x blood circulation slows to the portant
er apots are different from the soca gt anaes
joma), although they 1ook similar, "8g
Th apearance of ie and ppl aetna ood ee
— a, atea of occiput of head, area of cervical spine and
the Duzhui (DU 14) aes onthe pan ndieat pote god eats
pete tee eciomtnsing 2S sped and he yqgam inthe ai. 1fmany uso pple band von ee al
= thete over the palm, patients may be sscepthle to robo ot
Peer A purplish color wv indices) He ane Ba, a hoa ave oo
Pairs apears in subeutaneous capillaries to show hoped stove mentioned disturbance of blood quality and increase of blood
Gil bood stasis, poor blood circulation or blood coagules ont. Black (ad
ig
1): A black of dark gray color on the palm
and finges (except the thumb) indicates an increase of blood li
Spready cured, the operation incision or wound is almost helgiy, cumulated i the body to cause fatigue, lack of energy and reduction
“andthe black pigmented areas of the skin of a rather argesing, of mental power because the patient doesnot engage in enough
"presenti the corresponding regions of the body. "=
physical exercise to consume their excessive nutrients.
9. Light coffee: A light coffee color usually appears deep
14, Yellow: The palm of patients with iver and gallbladder
‘skin of the palm to indicate a disease that has been candy
diseases is usually yellow in color, particularly remarkable in pa
tients with jaundice. In some infants, jaundice is hereditary in
| 10; Bue: The symbolic color ofthe liver, blue indicates sg se hens doce ee ee
ecco oa ee a ee
‘nd adjusted by the liver.” The presence of somebl in nature, but a severe infant jaundice stil indicates a igh suseeD>
iundemeath the skin indicates blood stasis inthetiat_gblity to diseases of live, gallbladder and blood system. In general
1 yellow palm indicates chronic diseases with a long clinical
hvhie: In general, bluish white indicates sevemp® course. For example, yellow inthe throat ars indicate chronic
fgi or an attack of bitter cold. In patients pharyngitis. Yellow rough skin im the stomach area indicates
| i
sae Macos ofthe stomach may he
insincere
Shs (HE OTK EY 29 dk yy
as es 1 9s gg
inte boy. oy
een Dark PTE aS deg
ree al disturbance in the body, etsy
sa ann on
temas ced DY 2a jet Pea
Moe and dark gray: In general, dark py
inthe contents ofthe blood to
al
Io
“~|
sai of
substan
17, Dak
Ee eabeutaneons henorshog
caused
diseases rk coffee color usually
‘Dark coffe: A da LY appears ing
dpiedtspine andihe Dachui (DU 14) area and one g
pain caused by an attack of wind orb,
ord
ee rag
cra
oor
ofcerial
nd voit
‘circulation of gi and blood.
1B, Pgmetton (2 ots and a2 of pigmentagy
tation may appear everywhere inthe skin of pat
nd impsinentof physique. Areas of pigmentation may lng
Geiehandtonfcate impaired functions of eoespondine
Wit te exception of birthmarks, newborn babies seldge ge
ties ofpiemenatin o tet skin, but hese sreas may page
tepestand increase in number and size coring aging beta
Ietabolie burden on the liver graduslly increases, decreaing
Aili to tori. Areas of pigmentation may also appear gy
Holographic areas following a continuous impairment of ema
tributed in the sing
=
ct
Aancions ofthe body. Pigment is evenly c
(pier the body in people with good healt, vigorous metabolisg a
‘Bilzoed fictions among their organs, but pigmented sp wi
[Patches may appear in holographic areas of the hand folowingan
Jmpairment, attack of disease and decrease inthe cee
jand blood,
‘ and Appearance in
Motogvophic Aras onthe Han ea Sag
Diagnosis of Syndromes 7
1, Head area
White around the crease ofthe metaarpophal
mig finger indicates a headache. the wie eolet weet
the middle segment ofthe crease i indies a heaache tole pee
hea and vortex of head if white is ated only nthe letra one
creas it indicates migraine om the ft sie of he head ten
in the right half i indicates migraine on the ight side of the tony
The presenee of some blu, purplish red or Bush purple Meat eee
sels undemeath the white skin in youth indiates ths the he oaga
and dizziness is caused not only by stagnation of but alsa by blood
stasis. The starvation ofthe bein de to decreased blood eteaaton
inthe head with poor blood supply tothe brain may cause heals
and dizziness,
2. Area for dizziness
‘The presence of a dark oF light red light or dark brown, or any
dark color spreading upward from the bottom to the tp of this
‘whole area [See Chapter 3] indicates that the patients susceptible to
vertigo and dizziness caused by deficiency of qi or excessiveness of
yin, The spread of a red color from this whole area to neatby areas
sion and for hypotension indicates dizziness with die
che, usually caused by the upward rush of blood,
ctivity of liver yang or “hepatic hypertension” (due to dys-
function of iver). A dark purple color inthis area indicates dizziness
due to p ul hypoxia ofthe brain. The presence ofa
yellowish brown calluslike papule (occasionally coffee or light
) on the palmar side of the proximal segment of mide
le fing es a persistent dizziness
3 hypertension i
The presence of & red patch inthis area with clear-cut margins
indicates hypertension caused by an upward tush of blood or hyPes=
for hyp.
hy
blood supply a
yellow in c
a
——
also own 8 “Repti hyper
HE yin I hype Ay
ea nares ists cena tng
a
eel a4 indicts
jan dot 9° hl
ae ones of bret, arena,
ness of Hibs. * hae
iit nd ight €3®)
{sometizes slightly bulsing) inthis ay,
Foe lectom oor
Blood congestion of eyes. A gray gat ly
mi skin in tis area indicates blurred yiigg My
eying of eyes. 11 some be blOod vessels cyl
ema gay or eTyish ClO! andthe yess geet
2 tay suffer from impairment ty
rate pats ™2Y of vsong
Bereta dco nln ssc a
‘blood circulation "a
6, Nose area
SNe elon tis area indicates temporary nl in
te patents are suffering from an inflammation in the nas oad
tmeendarcgy color sometimes covered th Fine ies, nde
atrophic tints.
7. Mouth area
isis a holographic area of both the mouth and oral casi
“Show thc condition and diseases. A white color in this aren.
| eaesinflammation with pain, and a dark purple, dark gray oro
‘indicates chronic and relapsing pharyngitis.
: Tooth and cheek areas
;pesence ofa white spot or small patch located in cenit
‘his area indicates inflammation with pain in the ome
‘The purity of the white matches the severity file
ithe whiter the skin in the tooth area looks, theme
Is ext
ee
peseop ert
“The conjunction ofthe esophagus and stomach isthe cardi, and
the part of the stomach next to the kidney isthe stomach funds
White, shiny and de
sed skin in the whole area indicates defi-
ney and coldness of the stomach. Whit, shiny and bulging skin
rer this area indicates edema of gastric mucosa. Yellow, rough and
callus-like thickening of gastric mucosa or chronic
gastritis ove! area, Dark red color in this area indicates con=
eistive inflammation or congestion of the gastric mucosa due to heat
i the stomach. Patients may suffer from acid reflux, heartburn and
baa breath. Dark depressed skin present in a local region ofthis area
jadicates atrophic gastritis. Bulging skin in local region ofthis area
‘pith a dark or blackish brown color underneath the skint indicates
chronic peptic stomeah leet.
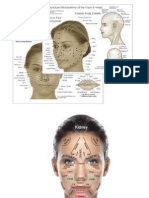
M1, Kidney area
White in this
kin indie
wea indicates deficiency of kidney a, and patents
nay sues impotence and prematore ejaculation of semen and —i8
exes wcatnessin the lower back andthe leg pinkcorisht
ret eotor on the surface ofthe skin all over this area india
and patients may suffer from sexual
Sfaorders. A dark purple color or dark red color wih some SS
tint all over this area indicates deficiency of kidney yin and sis
°
-
ciency of kidney yang,
ye BOW SOW ng
pa he Eipaate CHO Nephi of Moe ‘eatie
eel cerns dy
oy my
eos .
ie
ad. Red at
enema eines prostat, 4
aes, te presence Of OMe (OF Several roy
# perpen certain arts of this ar oe
me ing potion of the UteTWS. The presence
Grotickened iyperplastic) red color inthis
1,
A werings
but it
is or inthis area sme
fame niece tn ten damp-eot has acum
Ppt: yew orate
Seman cinch
Bainter nr
Fepmensinezms sr ia
ation wi a ove Sc neg
‘eystonthe sume sid.
Bree
ee
Sn ros A promncne
retire iicacs een
trachea in febrile diseases, and patien er from dey ou
Batty neni op spt Te prsencesr ee
erties cues oa
‘Paticats to spitup yellow sputum with sticky lumps.
Sinn this ea indiates dry cough withost sputum caedty dy
heat. The presence of some red and white alternating nodules ink
sipuive broncits. White ove «depreved abe nae
Aeliciency of lung qi or Feivei (a consumptive die
Similar to pulmonary tuberculosis). The presemedl
iy
Red overati
hi
his arcing
their tenis ale
dometigt
some smal dark cofee oF purple pointed ny
and infisting margins of he knw ncaa
Nd Afea of left chest (ang)
‘The holographic spots ctresponding 4
bronchus and breast are all distributed tn the qe gies ing
ith ocenent
oF probably in
"leh half of thi area exe
trachea aea, an iregular pape a =
brownish yellow or coer
color indicates chronic bronchi. A papue ecg
(not really a blood vessel) inthis atea indicates brane eee
bronchiectsis, The
presence of s horizontal brown bar similar toa snallege genet
cn
fom ches da) aes sng he cee ea a
above the waist res incites pulmenay ong
15. Aral
chest lung}
‘Observation diagnosis in this area is smart tha in the ere
left chest (lung). except for the diference insides ofthe cone
sponding on
6, Wais
pits in the segment of the heaven.
Tine (hear line} within this area indicates eauma of the waist oF
deformity of lumbar vertebrae inthe comtesponding location, White
(sometimes on bulging skin) along both sides of the heaven lin
indicates lu
‘and soreness of waist. The whiter the skinin his
e severe the pain and soreness the patient may
The presence of « dominant red color altemating with
some white tint indicates lumbago eaused by trauma or muscular
strain in the corresponding region ofthe waist: Blue blood vessels
the heaven line ofthis white rea indi-
of coldness and poor blood supply
area looks, the m
suffer f
whole spleen area is evenly depressed. Flat skin in a white,
grayish white or whitish blue color indicates deficiency oF defi
cient-coldness of spleen. Ifthe area is much more depressed, and
al
ite and the subcutaneous tissue jg,
weinerion my be already excise “ory
fe wis ona
re tprenomerslyColertcmen and C, 05% novogg
elobuln, bran tssue fluid, saline solution, distil yg
one and desoxycortisone. :
(Chinese herbs: Injection solutions of Dangeui (Chingy
sro! Huanglian (Coptidis rhizome), Huangqi (Asmgy
{(satidis root) and Danshen (Salvia root
jc method
skin around the points is sterilized for injection oft
f 1-2 ml with No. 4 needle is used to inject
(0 sont cca
on
ater lca
se Gace” yon cate eae
Moy Cue of women Ss ge
‘oi nd hr wtean Ga
iu one therapeutic comrse conn of teem eT rd,
at should be arranged between Heatments
re Npoi for siention, oa
(1) The skin around the points a wel ag.
for injection must be carefully seized to prneaan ts
(2) For inection of drug or heb cape neon
reaction. a skin test should be done before the men nie ale
(3) Before injection of deg te dee
ological actions, contraindication precast
(4) Aqua-acupuncture is conaindienes
and it shouldbe prescribed with care to weak and eget
(5) Altemative points should be sled in gph ee
treatment in succession.
V. Electroacupuneture
After insertion of a needle into an acupunctae point, # weak
clecrical current is sent through the needle to prevent and te
diseases. The intensity of electrical stimulation may be adjusted for
achieving s better therapeutic effect according tothe nant and
severity of the disease. This is an effective therapy o teat asthma
and pain cl
1. Therapeutic methods “
(1) Necdies are inserted into selected pois in succession.
Q) Beiove the electricity of the elesoacupunctre mash
tumed on, the output current of the machine is tumed down i
wire is connected to the needle handles
se pnt re 9 80 BUEHILSag
peers the electrical x
imeyen the machine is turned ent i
Ye med eee ni
ee tl SIMO ppg
ins ty ro vn Pong
Since PPC ot eda may
Beets conc of 10 ruck ogee
x ation of the electrical stimu
eats and patients with pain oo °°
‘younger patient in oF pee
h OME fe srr in cIGEEN and weak ety
fe poits fr atention gi 7
former ezust be gradually increased: 4
“a ce intolerable discomfort. nig
ersten an mete 1 of he cond
“po oso into ban her
may
Mgeuvacupunctre is contraindicated in the
nnd weak patients. = of
YL. Photo-acupuncture
Prowarupmeture — also called laser irradiation they —
Apis laser stimulation to hand acupuncture points. A ga gg
(eapy appar of low potential, such as a HeNe (Hetium Ney
Tecer apparatus or Ar laser apparatus, is used in the treatment, Ty
“Guanes of the new brands of laser machines have been inereagl
{fom 24 10 10-15. Therefore, the scope of application ofthis ee
[bology hasbeen greatly widened, Today, the HeNe laser transning
is widely used in clinical practice.
A Therapeutic methods
Before applying laser irradiation, the apparatus should e
and the pointers of all scales turned to the °T
-—
position 2h. a steady red laser beam eas oe a saa
wes ee
ance eee
cae
iret soe
ay After the Weatment is finished, thee
umned down tothe "0" level and the eecteal soa é
eis turned off scant
* Points for atention Bsns
{iy The laser transmitter should be kept in
‘vent dust moisture and shock, 7
(a) Ii the apparatus is not used for lon
egolaly turned on and warmed up fo one on
008 repair to pre
Sime sho
iron he ch ont
Inthe acute stage, white spots
te rahe ara. In th Be te Spot may
infection a
land Chinese herbs should be prescribed. in
2, Bronchial asthma
[Pathogenesis and clinical manifestations)
This allergic disease is characterized by
bronchiole spasm, mucosal edema and lu
a
Paroxysmal at
ing fi shrinp or egg, or having an infection ofthe eg
iat Some preliminary symptoms may appcer befor an
the disease These include cough, chest distress, itching,
Aad seezing, Later, patients may suer from more seereaip
toms Such as severe chest distress, dyspnea, tightness in tas
foreed to stay in sitting position and even cyanosis and eodgme
Inertial patients. Bach atack may last for hours or afew
{Hand diagnosis)
“A dark blue color may appear over an uneven skinintheoae
Ofthe trachea ates. Some findings similar to those of bones
Pefoand in patients with a severe infection in the lng
{Selection of points}
Pist-choice points: New point for asthma and Yoji(LU IM
c
peci and most PR
uo
hung and trache:
lung asa supplemental tres
Yigg, _ Re redler seed ats no apa
Wsecontan PR S208 LL 1D. Doing NY WwiPOR Poe gn or 15 con Ble eae en ea
econ Eee rain, seco oct and the Pressing maneuver of mage ea
Fea counties aticd 8 te pin gy Sone
cough Yo point and point for throat: bleeding therapy ss My tens with # severe at sc of asthma, oxy and panne
the toshang point and the pressing maneuve of manage ge crs shoud be sministered
thumb atthe trachea area tig
‘lie with i
eae 43. Preumonta
Inpatients wits acute bronchitis and severe
ipatogeness and clinical manifestations]
Preonninis an aca infecon of the ng. aby
tin the winter and spring, The
chills, high fever chest pain,
m. Its common in youths
et go
Bat dope
semsing ih
(secon ofp
eee rine 5
spots are found in red orared
iegu (LI 4), point of lung, point for chest.
EX-UE
% 1), area of the chest and
[herpetic methods
Regular acupuncte is
plied atthe St
is perform
plied at all fist-choiee points, bledi
an point, and massage or application
chea area and area of chest and
[Remarks}
Seriously il patents should be treated with the antibiotics and
Chinese herbs as well as the hand acupuncture therapy mentioned
Aove,
seal manifesto)
sia disease of th brome wi
everile anatomical dilatation and deforma ty
Ts aly «complication involving yo te
se thatelternve not Deen ented wig cat
rae ernst ty psy erie any
tronic bronchitis or bronchial asthma, Commag ing
atacks of coughing, spitting of ae aa
Beers mt
iecsiny se ncreed ng nangaer nat
aay aa
[Band diagnosis) )
In patients with bronchiectasis, some dark re
ait trachea area and the holographic
Fresh esp in his aren indicat fresh hemor
pois indicate «history of hemoptysis in the past hehe
[Selestion of point]
Fist-hoice points: Yujt (LU
lung
Secondary points: Trachea area,
(Therapeutic methods]
Regular acupuncture is applied atthe point of
Laogong points withthe needle slanting from Yuji ne
for application of a purging maneuver. Blecding ig
tee-dged neve is performed atthe point of lang aie net
acupuncture has been applied. The massage or magnet teat
performed inthe trachea and lung areas and tthe pote
‘supplemental treatment. Z
[Remarks]
Bronchiectasis is a stubborn cisease resistant to atau
Therefore, a combined therapy of the Western medicine and Tsk
tional Chinese Medicine should be adopted to teat pales
Severe hemoptysis and infection. At the same time, patients shill
‘be put in 4 Trendelenburg's position for expectorating spuunsl
Rove,
of the ba
10), Laogong C8) ast
3 af. and pont feng
Wag
PEO,
=
nesis 370 Cf many chronic diseases of the lung, pulmo:
fs 20m disease involving reduced clastic of lung
eee sang volume and impairment of respiratory
spot
(Past
Se ot te mes. Conic onreae a
LS emo pe of fe deer Ne
F crrniod wah be pee y aaa
geno # ee Gporiness of breath during o after some exertion,
‘fom dyopuea el saceie a
gets
ea
ae sem
ye exacerbated in winter or after a severe ng
sitio isenosis}
Hd gras may apes inthe tach area and the
Sek be st
[selesion of points]
(et hoie points: Ye (LU 10), point for asthma and point of
WS scondary points: Bronchu
(sea)
TTerapentc methods)
eglar acupuncture is applicd at Yuji point and point for
asta; the thee-edged needle i use to bleed 3-4 drops of blood
foie pinta lng. At the same time, the pressing massage with
tnd is performed in the bronchus area and bilateral areas of
dean ung.
(Remarks)
Pains musty their bes to maintain their health prevent any
ss ofthe common cold and control lng infection. significant
sey of oxygen should be given to patients with severe cyanosis.
area and area of chest and lung.
n
‘vial
I, Disease of the Cardiovascuty
Sy
[.Fyperteniedsense
PPubobcns ardliin! manxany
Triste common syndrome wi an
Be sestonttysyemic gn boca
Beli ie tyrone of bor
i
teste ary tnd mcaisse <
wth drgs shuld be adsinisred optic ge ante
Ilan digo) ere
Sore wit fe dc red 0 yelow nod
Briere. Sotered whnerron
Steck tocnacs vier
mine
© Duta cont
hee
high loo pressure, andthe spes also may bo sagt eg
sdiziness. Red oF dark red spots indicate renat penta
Tang prio of time. Yellow nodules indicate pene 28
am Persistent. ype
Pesto:
ee
aa
[Therapeutic methods)
hong (PC 9), Hoos S12) ag,
‘UE 11), point for
Panty
fea for dizziness, ™
2. Hypotensive disease
[Pathogenesis and clinical manifestation]
tn patients with hypotension, biood pressure may belowert=
i
0 mm of systole pressure and 40-50 mil
estrone of OT Symons of the diese ae dn
aati Pres nia,
se
wei A), spears inthe aren fr hypotension
ni
Point to raise blood pressure and area for
Het ey: Arca fr dizziness and ard for insomnia.
Mc |
[Thee rare is applied atthe point 10 raise blood pres-
ar aco rformed in the areas for hypotension, dizziness
ee ssa is
Sisco
ary heart disease
4 Gerona clinical manifestation
Cie oe = ree
Bs case by 2
Eoin
fea major 790%
eee segments ofthe
Steet sos,
Sapa ies
Pea ciagosi]
Intent with coroner
deal ese ean be seen inthe cet
ene ofthunb,An regular ptch of red altering with whi
Great intichea aca Some whit spots orpitsmay eppearin he
‘ex for poor blood supply. Bluish white spots in this area indicate
spc
[ekcton of points]
Firsi-choice points: Shaof
thet
Supplement points: Heart area and area for poor blood supply
Ps
se with ischemia
sclerosis and induced by over
erfull stomach or an attack of
isease i a sudden onset of a
pain behind the upper, middle
radiating pain spreading
ease, a small hard varicose
of the metacarpophalangeal
HPS), Shaochong (HI9) and point
v
[Mrerapeutic methods)
Regular acupunctre is applied a Shagry
py capped at Shaochong point and mace
Ieart area and area for poor Blood supply
[Remarks}
“Tho onset ofthe disease is sulden, so
te administered i time. Patents with sey
be transported immediately © a hospita)
Poin
200 epee
. ro |
‘reste
Smpioms include dyspnee, palpitations of Ine hee Ct
peso pain, vertigo, profuse swentng oe
exacerbated by over fatigue and mental stress eS
Tad dagen
A sting fie pots repre in
panacea A wit cor
(Sesion in
(PC8) and heart area.
Seely pins Ara fo
Mery mets
Hegilar acupuncture is applied at Shaofu and Guanchongpa, |
4nd massage or application of magnet therapy is performed ate
‘teas for insomnia and dizziness and also atthe Laogon pte
calming the mind
ions)
By adi
the hear areas
extended segment gt
pophalngcl crap
*PDEAS over the arene
GATS), Guanchong (1, Lange
‘insomnia and area for dierines,
$. Cardiac arrhythmia
{Pathogenesis and clinical manifestations}
Common cardiac arrhythmia involving sinus amythnia
y, abnormally slow heartbeat (bradyeardia,
cart Beale Ee ee wof the vegetative Nervous system,
ptm ca dso os
ee one ane
ir ron f te He re sy sw are darker
ei ert Beat
locks sion of points] 9), heart area and point of
(Soest 8) and Shaochong (HT 9) P
if methods]
is applied at Shaochong point; and mas-
cf ea performed inthe her ate
aagnet therapy 18 Pe
‘speor ag
6 myocorai I manifestations}
oe
Py
a
-rongshons (I 1)
erapetie methods)
Bde hry 02k prick oF an cup
rennin piss) Sacco yo eh
Far, and massage with thumb is performed jee OM ang ty
Ie epee set end at Lecgong oe haga
‘[Remarks} i
Pats with mild my certs an be cue yy
ture therapy lone, but severe myocarditis meng
thw aconbire they of este medi aa
GineseNedine Patents win everesymprns er ae
Irani ese ck ety
tne
Poor blogg
Z,
reg
7.Chronie rheumatic heart disease
[Pathogenesis and clinical manifestations
Chronic heumatic heart disease with deform
alvesis te result of acote rheumatic heart disease
ante valves ofthe heart are often involved to cause
valve opening, valvular insufficiency or both in
‘ilar lesions may produce hemodynamics, hear
insufficiency and congestive heart failure
palpitations ofthe heart, dyspnea, covtin
‘The cases ofrheumatic heart disease are sill unknowns
isthought closely related to rheumatic fever ae
(Hand diagnosis}
Some dark red or dark blue spots are found inthe area
Yalve (nea the metacarpophalangeal crease inthe heat) ag
dark blue color appears in the area for siteumetism, :
Y ofthe,
Temas
‘Combination, .
"murmin,ag
Patents mays
1 and shortness
{Selection of points)
Bisi-choice points: Shaochong (HIT 9), Laogong (PC8) is
of heart and area for rheumatism. -
Secondary points: Heart area and area of mitral valve |
ic methods}
parce ll Schon.
ge oe wh (a ore
SE et ae cf, sina eg
ot in the Bear ee for
manifestations ofthe disease ae very complicated,
get plenty of rest and avoid tiredness Cita
= eardiac insufficiency of heart file shou be
ts yw) EOE SS ae
M1. Diseases of the Digestive System
4. Gastritis
oe ona o ce ee
aay SOiery diarthea, Patients with severe ate gistitsmay lio
Ce. ‘on and acidosis, Patients with chron gastritis
ea cen, dl jy
unget
el
have fever deer
ray suffer from
somiing and
(Hand diag
In patients
cue pte ooo
Te ice th wie pes each
co 1 inthe ind ebgeon mc
aetiomach, In patients with chronic sti me wisp te
sesame omach ce, ell hiked ist
seen svc indes cone hype ei i
a on over alge eof =
Ee its}
—
thoi pom Poin orpinol
Wailaogong (EX-UE 8).
omach and intestine 9d
acy points: Stich a0 7 F opp
ernest metho]
Proeipnene plod he pi opin
tos abi nn Wlsogone PO 0 50. may! mg
Fateh es 6 o8 oF uper sans
2.Pepte leer of stomach and dodenim
Tbunegenesi and clinical manifestation)
sia dase in EE 9 0M Gch an ag
cased by lonastantng indigestion, exireme fem
Set dyfncion ofthe vegttve nervous syxem, Py
aif from eeglar epigastric pai, regusiaton op sett
beehng aves end vomiting
(Hand diagnosis)
Inpatients wih an ule in thei stomach oF duodenum,
redarblacksh brown color may sppeas nermcsth the pat
skinoverthe stomach and duodenum areas. A blackish ewe
indets that ler akeady have healed up. The presence of
ite round pathos aleraing with some small rsh ed sens
those areas indicates possiiliy of bleeding over the ult
sure.
{Selection o points}
Fist-
You might also like
- Acupuncture Treatment of AsthmaDocument6 pagesAcupuncture Treatment of Asthmariteandritual100% (2)
- Misc Protocols Acu PDFDocument136 pagesMisc Protocols Acu PDFFarooq Bin Mahfooz100% (2)
- Korean Hand AcupunctureDocument81 pagesKorean Hand AcupunctureKarl100% (4)
- The Silver Bullet The KOSA (Korean Orthodox Saahm Acupuncture) - NeedleLess AcupunctureDocument57 pagesThe Silver Bullet The KOSA (Korean Orthodox Saahm Acupuncture) - NeedleLess AcupuncturePowChoy83% (12)
- Auricular Acupuncture 2013 SummerDocument89 pagesAuricular Acupuncture 2013 Summerdoringrama100% (3)
- Limb MicrosystemsDocument1 pageLimb Microsystemsdrprasant100% (1)
- Pain Control With Acupuncture - Class 2Document46 pagesPain Control With Acupuncture - Class 2Hector Rojas100% (1)
- MK Sastry .Fundamentals of TCM DiagnosticsDocument148 pagesMK Sastry .Fundamentals of TCM DiagnosticsEdison halim100% (1)
- TCM ReferencesDocument24 pagesTCM ReferencespelizNo ratings yet
- Scalp Acupuncture Effective For Stroke - New Study: Published by HealthcmiDocument2 pagesScalp Acupuncture Effective For Stroke - New Study: Published by HealthcmiEdison halimNo ratings yet
- Chinese Auricular Therapy, Bai XinghuaDocument243 pagesChinese Auricular Therapy, Bai Xinghuagamisemas100% (7)
- Acupuncture Meridians and Acupuncture PointsFrom EverandAcupuncture Meridians and Acupuncture PointsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- Scalp Acupuncture Theory and Clinical Applications: Yuxing LiuDocument0 pagesScalp Acupuncture Theory and Clinical Applications: Yuxing Liuitsik12886100% (2)
- Adv Acu Tech 1 - Exam 1 Study NotesDocument15 pagesAdv Acu Tech 1 - Exam 1 Study Notesg23164100% (1)
- Acupuncture - 07 - Pulse DiagnosisDocument44 pagesAcupuncture - 07 - Pulse DiagnosisLeonardo Bassani100% (3)
- Acupuncture in Neurological ConditionsDocument181 pagesAcupuncture in Neurological ConditionsDrRudresh Sajjan67% (3)
- Post Stroke Scalp AcupunctureDocument64 pagesPost Stroke Scalp AcupunctureJosé Mário91% (11)
- Basic Su Jok TherapyDocument10 pagesBasic Su Jok Therapytalhahameed8580% (5)
- The Officials2Document41 pagesThe Officials2shamsorahNo ratings yet
- Article Bahuang PointsDocument3 pagesArticle Bahuang PointsmudrahoraNo ratings yet
- Adv Acu Tech 1 - Class 1 - Jiao's Scalp AcupunctureDocument4 pagesAdv Acu Tech 1 - Class 1 - Jiao's Scalp Acupuncturesuperser123465No ratings yet
- Face AcupunctureDocument2 pagesFace AcupunctureDanadipa Bayuputra33% (3)
- Acupuncture - Parkinsons PDFDocument43 pagesAcupuncture - Parkinsons PDFFitzgerald Pacheco100% (1)
- Shanghan Lun ResumeDocument3 pagesShanghan Lun ResumeMatthieu DecalfNo ratings yet
- Scalp Acupuncture - MS1 To MS14 - Ok - Ok - OkDocument51 pagesScalp Acupuncture - MS1 To MS14 - Ok - Ok - Okmd_corona62100% (16)
- Acupuncture Formulas PDFDocument346 pagesAcupuncture Formulas PDFjorge_r_souza100% (1)
- Cookbook Acupuncture August 2015Document234 pagesCookbook Acupuncture August 2015Anonymous rS3GWcd100% (7)
- Acupuncture For BurnsDocument34 pagesAcupuncture For BurnsIvonne Flores FernándezNo ratings yet
- Intro To Zang Fu 1Document20 pagesIntro To Zang Fu 1Erica YangNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture in Clinical PracticeDocument322 pagesAcupuncture in Clinical PracticeMarthen Beck100% (5)
- RCP - Post Stroke Scalp Acupuncture Research PDFDocument64 pagesRCP - Post Stroke Scalp Acupuncture Research PDFIstiqomah Flx100% (1)
- 7 Emotions TCM PDF Part 1Document8 pages7 Emotions TCM PDF Part 1kon migelNo ratings yet
- Pocket Handbook of Particularly Effective Acupoints For Common Conditions Illustrated in ColorDocument273 pagesPocket Handbook of Particularly Effective Acupoints For Common Conditions Illustrated in ColorMohammedBilal100% (6)
- LingshuDocument428 pagesLingshuvaloraami1047100% (2)
- Master Tong Information Document PDFDocument105 pagesMaster Tong Information Document PDFKimberly100% (2)
- 1050113Tung - s Acupuncture (FB社團版)Document73 pages1050113Tung - s Acupuncture (FB社團版)Michel Sannchz100% (4)
- Dry Needling Position Paper 11.11.10 Rev. 1Document5 pagesDry Needling Position Paper 11.11.10 Rev. 1Elanghovan ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Syndrome Differentiation of Zang-Fu OrgansDocument50 pagesSyndrome Differentiation of Zang-Fu OrgansSyukri La Ranti100% (6)
- Eye Acupuncture PDFDocument8 pagesEye Acupuncture PDFLiv100% (3)
- AcupunctureDocument54 pagesAcupuncturealvaedison00No ratings yet
- Acupuncture Accordind Traditional PHDDocument13 pagesAcupuncture Accordind Traditional PHDcugarNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture - Basic Research and Clinical ApplicationDocument172 pagesAcupuncture - Basic Research and Clinical Applicationion vasile100% (1)
- Acupuncture Explained: Clearly explains how acupuncture works and what it can treatFrom EverandAcupuncture Explained: Clearly explains how acupuncture works and what it can treatNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture As NADA ProtocolDocument9 pagesAcupuncture As NADA ProtocolJoão Augusto FélixNo ratings yet
- Fifty Years of Clinical Holistic Treatment for Parkinson’s: A Unique ApproachFrom EverandFifty Years of Clinical Holistic Treatment for Parkinson’s: A Unique ApproachRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- List of Points-Acupuncture Association-Acupuncture ClassDocument10 pagesList of Points-Acupuncture Association-Acupuncture ClassAnonymous 42krkNVNo ratings yet
- An Interview With Robert ChuDocument4 pagesAn Interview With Robert ChuAnonymous uMnup2r100% (1)
- Unique Point Japanese AcupunctureDocument12 pagesUnique Point Japanese Acupuncturepustinikki100% (4)
- BATTLEFIELD ACUPUNCTURE - by Richard Niemtzow MD PHD MPHDocument12 pagesBATTLEFIELD ACUPUNCTURE - by Richard Niemtzow MD PHD MPHCarissa Nichols100% (2)
- Acupuncture PointsDocument46 pagesAcupuncture PointsM. P. Schaefer100% (1)