Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8 Closed Feed Water Heater PDF
8 Closed Feed Water Heater PDF
Uploaded by
Shiraz KhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8 Closed Feed Water Heater PDF
8 Closed Feed Water Heater PDF
Uploaded by
Shiraz KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Vapour Power Cycles
Prof. U.S.P. Shet , Prof. T. Sundararajan and Prof. J.M . Mallikarjuna
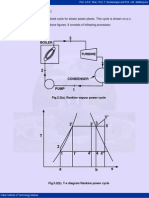
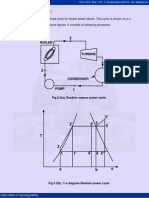
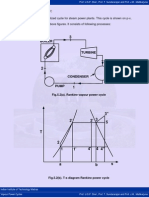
5.8 Closed Feed Water Heater:
TURBINE
(1-m1)
II
1 kg
BOILER
PUMP
m1 kg
6
3
CONDE
NSER
4
x
m1
2
1
3
DRAINCOOLER
2
1 kg
(a)
1 kg
4
3
T
2
m1 kg
6
(1-m1) kg
s
(b)
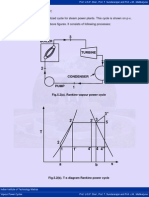
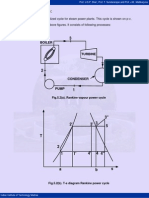
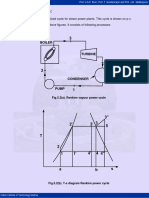
Fig.5.8. Closed feed water heater
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
PUMP
Vapour Power Cycles
Prof. U.S.P. Shet , Prof. T. Sundararajan and Prof. J.M . Mallikarjuna
Regeneration here is single stage, while turbine is of two stages. The extracted steam
of mass m1 kg is completely condensed in the heater and this liquid is first passed
through a drain cooler and then enters the condenser where it mixes with the main
condensate of mass (1-m1) kg. This liquid from the condenser is first heated from state
2 to state x in the drain cooler and then from state x to state 3 in heater. If we assume
perfect heat exchange in water heater, then the feed water as well as the condensate of
the extracted steam will leave the feed water heater at state 3. Similarly in the drain
cooler, the liquid coming from heater will get cooled to the temperature t2 of the
condensate from the pump.
Let, m1 = mass of extracted steam per kg steam supplied to the turbine.
Heat balance for drain cooler gives,
m1 (h 3 - h 2 ) = 1(h x - h 2 )
h x = h 2 + m1 (h 3 - h 2 )
Heat balance for feed heater gives,
m1 (h 6 - h 3 ) = (h 3 - h x ) = h 3 - h 2 - m1 (h 3 - h 2 )
m1 {(h 6 - h 3 ) + (h 3 - h 2 )} = (h 3 - h 2 )
m1 =
h3 - h 2
h6 - h2
Since, h 2 h1
m1 =
th =
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
h 3 - h1
h 6 - h1
(h 5 - h 7 ) - m1 (h 6 - h 7 )
(neglecting pump work)
(h 5 - h 3 )
You might also like
- ME Chapter 2Document1 pageME Chapter 2allovid50% (2)
- ME Chapter 1Document3 pagesME Chapter 1allovid50% (12)
- Elements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 5Document6 pagesElements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 5allovid0% (1)
- Reactor Design IIDocument68 pagesReactor Design IIKORAMA KIEN0% (1)
- ch08 1 40Document55 pagesch08 1 40Hadi Sobian100% (2)
- Lecture 3 - Improving Performance - RegenerationDocument6 pagesLecture 3 - Improving Performance - RegenerationIslamic world 360No ratings yet
- MEET 223 Module 6Document22 pagesMEET 223 Module 6Kurt PalacioNo ratings yet
- 11 Mercury Steam Binary VCDocument3 pages11 Mercury Steam Binary VCSekhar Babu PendyalaNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Regenerative Feed Heating in A Steam Power PlantDocument9 pagesPerformance Analysis of Regenerative Feed Heating in A Steam Power PlantDhenil ManubatNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 Thermo-IIDocument13 pagesLecture5 Thermo-IIAhsan RehmanNo ratings yet
- MSE 321 Engineering Thermodynamics & Heat Transfer: Problem 1Document4 pagesMSE 321 Engineering Thermodynamics & Heat Transfer: Problem 1Indran KunusilinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Văn TrầnNo ratings yet
- E0722836 PDFDocument9 pagesE0722836 PDFWangunNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Power Plant: Submitted by Safa Omardeen 808000383 Submitted On March 12, 2008Document8 pagesSteam Turbine Power Plant: Submitted by Safa Omardeen 808000383 Submitted On March 12, 2008Charlotte BNo ratings yet
- اسئلة امتحان الثرموDocument19 pagesاسئلة امتحان الثرموIRAQ iiNo ratings yet
- ENGRD 221 - Thermodynamics (Prof. N. Zabaras) Prelim IDocument9 pagesENGRD 221 - Thermodynamics (Prof. N. Zabaras) Prelim IMurat TülekNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecyclePrasad KhatiNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycletpplantNo ratings yet
- Applied Termo 122424Document4 pagesApplied Termo 122424rjrahul25No ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleamdevaNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleamdevaNo ratings yet
- PVT Diagram Rankine CycleDocument4 pagesPVT Diagram Rankine CycleEnny Rosmawar PurbaNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleAtanu Brainless RoyNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleRishabh VermaNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleamdevaNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecyclePrasad KhatiNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleRishabh VermaNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - Rankinecycledurga345No ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument4 pagesRankine Cyclerishav43No ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Regenerative Power Cycle and PlantDocument23 pagesTopic 6 - Regenerative Power Cycle and PlantMike MikeNo ratings yet
- Chap7 1Document10 pagesChap7 1Cm EtcmNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Vapour Power Cycles Session 4 NotesDocument19 pagesUnit - 4 Vapour Power Cycles Session 4 NotesFlamboyantAttittudeNo ratings yet
- Rumus Perhitungan Turbin UapDocument17 pagesRumus Perhitungan Turbin Uapricki yusufNo ratings yet
- C W PDV DV V V W PV VDocument4 pagesC W PDV DV V V W PV VRizwan Ullah BaigNo ratings yet
- Term Project Final Report: Thermodynamics IiDocument27 pagesTerm Project Final Report: Thermodynamics IiTaylan KaraçelikNo ratings yet
- Makalah Termodinamika IIIDocument33 pagesMakalah Termodinamika IIIdata laptop asusNo ratings yet
- Thermo CycleDocument59 pagesThermo CycleDries CaersNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document13 pagesLab 1Joseph Villariza LapidoNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 RankinecycleAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 RankinecycleJohn FredyNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Rankine Cycle:: BoilerDocument4 pages5.2 Rankine Cycle:: BoilerSasi GunaNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Rankine Cycle:: BoilerDocument4 pages5.2 Rankine Cycle:: BoilerVidyut KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 - RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 - RankinecycleAnonymous BHBWQIcClNo ratings yet
- 2 Rankinecycle-2Document4 pages2 Rankinecycle-2Anonymous gS6JtOfaNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 RankinecycleSami UllahNo ratings yet
- Development of Chilled Water Turbine Inlet Air Cooling Model For Enhancement of Turbine PerformanceDocument8 pagesDevelopment of Chilled Water Turbine Inlet Air Cooling Model For Enhancement of Turbine PerformanceAklilu BahetaNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 RankinecycleMantript SinghNo ratings yet
- 2 RankinecycleDocument4 pages2 Rankinecyclesoubhadra nagNo ratings yet
- Thermo CEPDocument9 pagesThermo CEPm.sheraz malikNo ratings yet
- ME 5129 - Principles of Thermal Energy Conversion: Exergy (Second Law) Analysis of Plant CyclesDocument14 pagesME 5129 - Principles of Thermal Energy Conversion: Exergy (Second Law) Analysis of Plant CyclesAnandNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Regenerative Feed Heating in A Steam Power PlantDocument9 pagesPerformance Analysis of Regenerative Feed Heating in A Steam Power PlantMurthy VvnNo ratings yet
- Week 08 Ideal Regenerative CycleDocument49 pagesWeek 08 Ideal Regenerative CycleJohnCris B. FornilosNo ratings yet
- Clp301: Che Lab 1-Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer Lab Semester Ii, 2020 - 2021Document8 pagesClp301: Che Lab 1-Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer Lab Semester Ii, 2020 - 2021Ajeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Climbing Film Evaporator: I. CHE 1014 II. SB92Document14 pagesClimbing Film Evaporator: I. CHE 1014 II. SB92Khalid M MohammedNo ratings yet
- 2nd Law of ThermoDocument13 pages2nd Law of ThermoTomiwa TolaseNo ratings yet
- Exp08 HtoDocument9 pagesExp08 HtoRITZ SANDYNo ratings yet
- Heating TancksDocument3 pagesHeating TancksAya ZeggariNo ratings yet
- Co1 PS PDFDocument2 pagesCo1 PS PDFanon_476594787No ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger-1Document4 pagesHeat Exchanger-1ahmed hatemNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument7 pagesLiterature ReviewNikyleNo ratings yet
- Ice - Chapter 3Document1 pageIce - Chapter 3allovidNo ratings yet
- Ice - Chapter 4Document2 pagesIce - Chapter 4allovidNo ratings yet
- Ice - Chapter 2Document1 pageIce - Chapter 2allovidNo ratings yet
- Water Calculation WorksheetDocument2 pagesWater Calculation WorksheetallovidNo ratings yet
- CAM Design: Cycloidal MotionDocument1 pageCAM Design: Cycloidal MotionallovidNo ratings yet
- Ice - Chapter 4Document2 pagesIce - Chapter 4allovidNo ratings yet
- Elementds in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 12Document6 pagesElementds in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 12allovidNo ratings yet
- Elements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 2Document6 pagesElements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 2allovid100% (1)
- Elements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 14Document6 pagesElements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 14allovidNo ratings yet
- The Dot and Cross ProductDocument9 pagesThe Dot and Cross ProductallovidNo ratings yet
- Elements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 11Document6 pagesElements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 11allovidNo ratings yet
- Elements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 6Document6 pagesElements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 6allovidNo ratings yet
- Elements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 3Document6 pagesElements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 3allovidNo ratings yet
- Elements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 16Document6 pagesElements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 16allovidNo ratings yet
- Elements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 2Document6 pagesElements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 2allovid100% (1)
- Elements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 15Document6 pagesElements in Machine Design (J.T.) Module 15allovidNo ratings yet