Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 2: Solid Fossil Fuel (Coal) Lecture 8: Coal Mining
Uploaded by
Brijesh BhartiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 2: Solid Fossil Fuel (Coal) Lecture 8: Coal Mining
Uploaded by
Brijesh BhartiCopyright:
Available Formats
1|P a g e
Module 2: Solid Fossil Fuel (Coal)
Lecture 8: Coal Mining
Keywords: Extraction of coal, types of mining, equipments of mining, stripping
IITKharagpurNPTELWebcourse
2|P a g e
2.2. Coal Mining
Introduction:
The technology required for recovering coal from the earth crust and transporting it into coal
processing unit, is the vital step of the coal mining. This technology is based on the following
operations:
1. Extraction of coal: the method used to break out the coal deposit into smaller lumps
2. Material handling: transportation of coal from the production locality.
3. Ventilation: the development of proper air circulation system within the mine
4. Ground control: to control and prevent the sagging of the underground or surface opening
developed during extraction of coal.
There are two broad categories for mining of coal
a) Surface mining
b) Underground mining
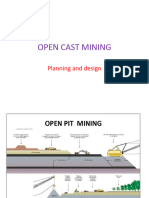
Surface mining
Surface mining is generally used when the coal seams are found within 200 ft below the earth
surface. Very big utilities and machineries are used for removing soil and rocks to expose the top
layer of coal. After extraction of coal, the rocks and soils are returned to fill up the holes of the
mine and the whole surface on the ground is properly revived to its original state and can be used
for cultivation, industrialization etc. This process is comparatively less expensive compared to
underground mining.
IITKharagpurNPTELWebcourse
3|P a g e
The prime considerations for this technique are geographic location, thickness and removal of
inter-seam waste and overburden and quality of the coal to be produced. Much of the overburden
contains layers of shale, limestone or sandstone and must be blasted before it can be removed.
After the overburden is removed coal is usually drilled and blasted, then loaded into coal haulers
with a shovel. Removal of overburden is called stripping and hence it is called strip-mining. The
types of surface mining are
a) area mining or modified open-pit mining
b) contour mining
c) mountain top removal
d) auger mining
Area mining is applied in relatively flat coal seams, where they are expanded in large area at
different depths. In this type of mining, overburden is removed by scrapers and placed outside
the mining area and loaded into trucks. Mining begins with drilling and blasting waste rocks to
expose the coal seams. Coal is removed and transported. The size and depth of the pit are
increased as mining progresses. This mining is adapted for the case when several seams lie in
parallel.
Contour mining and mountain top removal are used in hilly areas. Contour mining creates a shelf
or bench on the side of the hill. The mountain top mining process involves the removal of upto
1000 vertical feet of overburden to expose underlying coal seams. The overburden is often
scraped into the adjacent valley which is called a valley fill. Overburden is the soil and rocks to
be removed to expose the coal seams.
IITKharagpurNPTELWebcourse
4|P a g e
Augur mining is another type of surface method where overburden removal is uneconomic,
where terrain is too steep for overburden removal and where the underground method is
impractical or unsafe. It involves boring of large diameter holes into more or less horizontal coal
beds. In this method, exposed surface of the coal is drilled and removed by means of an auger.
Single, dual or triple auger heads can remove upto 90 inches of coal for a distance of about 200
ft.
Underground mining
When a coal seam does not appear near to the surface, it must be extracted by underground
process. Different underground methods may be classified as 1) room and pillar, 2) longwall.
Room and pillar is a mining technique in which the coal is extracted across a horizontal plane
making horizontal arrays of rooms and pillars to support the roof created due to extraction. In
this type of mining, the methods may be either continuous or conventional. The main differences
between the two methods are in the nature of equipments and the face of operation. In
continuous mining, the cycle begins with the continuous sumping cut into the coal face by a
continuous cutter or miner. A shuttle car is positioned behind the miner to receive and transport
the cut coal to the belt feeder. When the shuttle car is filled up, it moves away and the next
shuttle car is fed by the new cut and the cycle is continued.
In conventional mining, the breaking out of the coal from the face is done by cutting, drilling and
blasting operation. At the beginning, the cutting machine cuts a 3-4 meter slice horizontally
across the room width and then moves out to the next place to be cut. Then the drilling machine
moves in and drills holes into the cut face. This is followed by the blasting operation. Now the
IITKharagpurNPTELWebcourse
5|P a g e
area is examined for safety for entering the loading machine and shuttle car. The cars come in for
loading the coal cut.
The system of rooms and crosscuts driven in the production panels divides the panels into a
series of coal pillars. These coal pillars are extracted by the methods that allow the mining
operation to retreat toward the panel entries. Since methane gas may accumulate into the caves, a
ventilation arrangement is done by circulating air through the caves.
Longwall mining is a typical form of underground coal mining where a long wall of coal is
mined in a single piece of around 34 km long and 250400 m wide. Longwall mining has a
greater production activity than room and pillar arrangement and is safer, as mining is done
beneath a complete overhead steel canopy that moves forward as the face of coal deposit is
mined.
Three pieces of equipment are fundamental for modern longwall mining: armored face
conveyors, powered supports and the coal cutting machine. The cycle of face operations is based
on the movement of this equipment. The armored face conveyors are erected along the coal face
and are connected to a power support with the help of hydraulic jacks. The cutter loaded usually
slides along the top of the conveyor and breaks out a 20-30 in coal strip. The broken coal chunks
are carried by the conveyor.
Other methods
Shortwall mining is an alternative method which uses the equipments of both room and pillar
and longwall mining. The shortwall layout is similar to the longwall panels except that the panel
width is 150-200 ft wide. A continuous miner loading shuttle cars substitute for the cutter-loader
face conveyor system. Shortwall mining is applied to relatively shallow coal seam.
IITKharagpurNPTELWebcourse
6|P a g e
Hydraulic mining uses large amount of water at high pressure to break and convey the coal
from the working area. It is usually applied for a relatively thick coal seam. Jets of water are
directed tangentially to the coal face for breaking coal lumps.
Modification of the equipments and methods for underground mining system to overcome the
difficulties of mining is a great challenge for the future. Remotely controlled longwall and
continuous miners may be adopted for higher productivity and improve safety.
References:
1. Fuels and combustion, S. Sarkar, 2nd edition, Orient Longman Ltd., 1990.
2. McGraw Hill Encylopedia of Science & Technology, no. 4, 9th edition, McGraw Hill,
2002.
3. Elements of practical coal mining, 2nd edition, byD. F. Crickmer (Editor), David A.
Zegeer (Editor) Society for Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration, Inco.,1981.
IITKharagpurNPTELWebcourse
You might also like
- Lecture F4Document12 pagesLecture F4Shakeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXVIII, Sept. 1910 The New York Tunnel Extension of the Pennsylvania Railroad. The East River Tunnels. Paper No. 1159From EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXVIII, Sept. 1910 The New York Tunnel Extension of the Pennsylvania Railroad. The East River Tunnels. Paper No. 1159No ratings yet
- Coal Mining: Coal Mining Is The Process of Extracting CoalDocument20 pagesCoal Mining: Coal Mining Is The Process of Extracting CoalsunilsinghmNo ratings yet
- Underground Mining Methods Choice of MethodsDocument8 pagesUnderground Mining Methods Choice of MethodsSheshu BabuNo ratings yet
- Underground Mining Methods Choice of MethodsDocument8 pagesUnderground Mining Methods Choice of MethodsAjeet Kumar100% (1)
- 12 Teknologi Batubara (Edit)Document24 pages12 Teknologi Batubara (Edit)Zul BafaroNo ratings yet
- Methods and Technologies of Coal Mining-Basic ConceptsDocument36 pagesMethods and Technologies of Coal Mining-Basic ConceptsBinayNo ratings yet
- Anthracite MiningDocument75 pagesAnthracite MiningMuhamad HandokoNo ratings yet
- EgyE-Coal Written Report - FredDocument14 pagesEgyE-Coal Written Report - FredFrederick MadridNo ratings yet
- 9-Coal Mining CompleteDocument60 pages9-Coal Mining CompleteAchmad Rasyidi89% (9)
- Underground Haulage Selection: Shaft or Ramp For A Small-Scale Underground MineDocument6 pagesUnderground Haulage Selection: Shaft or Ramp For A Small-Scale Underground MineluisparedesNo ratings yet
- Surface MiningDocument35 pagesSurface MiningBhisma Hayana100% (3)
- Coal MiningDocument113 pagesCoal MiningNaniNo ratings yet
- COALMININGMETHODSDocument10 pagesCOALMININGMETHODSProf. Umesh BondeNo ratings yet
- Coal Mining Methods - EMFI SummaryDocument0 pagesCoal Mining Methods - EMFI SummaryCharles BinuNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document12 pagesModule 4Sipra SamuiNo ratings yet
- Underground Mining (Soft Rock)Document2 pagesUnderground Mining (Soft Rock)Ernie246No ratings yet
- UMM (Underground Mining Method)Document115 pagesUMM (Underground Mining Method)Irvan0% (1)
- (Hal 1-49) UMM (Underground Mining Method)Document64 pages(Hal 1-49) UMM (Underground Mining Method)Andi Kurniawan100% (1)
- Coal Mining Methods: DR M K ShuklaDocument24 pagesCoal Mining Methods: DR M K ShuklaJagdish KesarwaniNo ratings yet
- Underground Coal MiningDocument9 pagesUnderground Coal MiningSiddharth MohananNo ratings yet
- Coal Mining MethodsDocument10 pagesCoal Mining MethodsFarhan AliNo ratings yet
- Vocational Training ReportDocument32 pagesVocational Training ReportManish KujurNo ratings yet
- Report 2Document3 pagesReport 2madherchodgroup1No ratings yet
- Longwall Mining Is A Form of UndergroundDocument31 pagesLongwall Mining Is A Form of UndergroundNaniNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 1 - Pengenalan Pertambangan IndonesiaDocument67 pagesKuliah 1 - Pengenalan Pertambangan IndonesiapramaNo ratings yet
- Longwall MiningDocument42 pagesLongwall MiningNaniNo ratings yet
- Question No: 61: Room and Pillar MethodDocument12 pagesQuestion No: 61: Room and Pillar MethodashikNo ratings yet
- Surface Mining: MineralDocument3 pagesSurface Mining: MineralAndalio JkeiNo ratings yet
- Surface Mining MethodsDocument34 pagesSurface Mining MethodsGeorge MudzimuNo ratings yet
- Longwall MiningDocument6 pagesLongwall MiningGiancarlo Calderon AmesquitaNo ratings yet
- Coal India NationalisationDocument8 pagesCoal India NationalisationAshutosh MondalNo ratings yet
- 1-a-OPEN CAST MINING Design and PlanningDocument52 pages1-a-OPEN CAST MINING Design and Planningjimcorbett099No ratings yet
- Open Cast Mining - 979 PDFDocument21 pagesOpen Cast Mining - 979 PDFAbdul JabbarNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii-Sub Structure ConstructionDocument38 pagesUnit Iii-Sub Structure Constructionumamaheswari skNo ratings yet
- 2 - ClassificationDocument38 pages2 - Classificationluch33savesNo ratings yet
- Highwall Mining With A Focus On Design OptimizationDocument12 pagesHighwall Mining With A Focus On Design OptimizationbikamlnclNo ratings yet
- Cut & Fill StopingDocument13 pagesCut & Fill StopingJasmeet Singh SalujaNo ratings yet
- 1-Open Cast Mining MethodsDocument20 pages1-Open Cast Mining Methodsjimcorbett099No ratings yet
- Surface Mining MethodsDocument15 pagesSurface Mining MethodsMatthew Butler50% (2)
- Application of Highwall Mining in IndiaDocument12 pagesApplication of Highwall Mining in IndiaSatish kumarNo ratings yet
- Coal Mining MethodsDocument2 pagesCoal Mining MethodsIzhar JiskaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Surface MiningDocument90 pagesChapter 2 Surface Miningrishav baishya100% (3)
- Surfacemining 151016201725 Lva1 App6892Document19 pagesSurfacemining 151016201725 Lva1 App6892vigneshNo ratings yet
- Coal MiningDocument13 pagesCoal MiningSirad HirsiNo ratings yet
- Art 3A10.1007 2Fs40789 015 0071 4Document65 pagesArt 3A10.1007 2Fs40789 015 0071 4ryithanNo ratings yet
- Supported Stoping MethodDocument46 pagesSupported Stoping Methodabhimanyu choudharyNo ratings yet
- Introduction UG Mine SafetyDocument58 pagesIntroduction UG Mine Safetygiyat_prcNo ratings yet
- Mining MethodsDocument78 pagesMining Methodsفردوس سليمانNo ratings yet
- Caving Mechanisms of Loose Top Coal in Longwall Top Coal Caving Mining Method 2014 International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining SciencesDocument11 pagesCaving Mechanisms of Loose Top Coal in Longwall Top Coal Caving Mining Method 2014 International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Scienceskatta_sridharNo ratings yet
- Open-Cast Mining MethodDocument56 pagesOpen-Cast Mining Methodogala oscar100% (2)
- Coal MiningDocument36 pagesCoal MiningZUBAID HASAN 1907026No ratings yet
- 16.shortwall Mining-D M Gokhale, WCLDocument6 pages16.shortwall Mining-D M Gokhale, WCLkatta_sridharNo ratings yet
- Underground Mining - Unsupported MethodsDocument15 pagesUnderground Mining - Unsupported MethodsPuvanendran GajananNo ratings yet
- Underground Haulage Selection 1Document6 pagesUnderground Haulage Selection 1Zusica WigunnaNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Underground Stoping Methods - IIDocument68 pagesA Presentation On Underground Stoping Methods - IIANSHUL YADAV100% (1)
- LN11 MN3111 Coal Mining Methods PART1Document29 pagesLN11 MN3111 Coal Mining Methods PART1Alfredtungu PiusNo ratings yet
- In-Plant Coal Handling System of Captive Power Plant at H W P, Manuguru - K. Murugappan - A.C. Mohana Rao - M.S.N. SastryDocument6 pagesIn-Plant Coal Handling System of Captive Power Plant at H W P, Manuguru - K. Murugappan - A.C. Mohana Rao - M.S.N. SastrygurumoorthiNo ratings yet
- Stowing and CavingDocument14 pagesStowing and CavingPrabhu Prasad100% (1)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (64)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- Why Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeFrom EverandWhy Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (699)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (223)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanFrom EverandThe Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanNo ratings yet
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeFrom EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (19)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogFrom EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- The Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- The Big, Bad Book of Botany: The World's Most Fascinating FloraFrom EverandThe Big, Bad Book of Botany: The World's Most Fascinating FloraRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)