0% found this document useful (0 votes)
654 views1 pagePhysics Essentials for Students
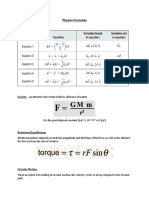
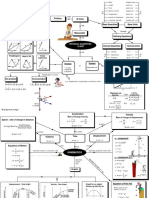
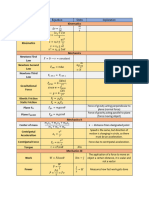
1. This document provides a physics cheat sheet covering common units, conversions, formulas for motion, forces, energy, and circular motion.
2. Key motion formulas include equations for constant velocity, constant acceleration, projectile motion, and two-dimensional motion.
3. Important force formulas include gravity, friction, springs, buoyancy, and drag.
4. Key energy formulas distinguish between kinetic and potential energy, and cover different types of energy including mechanical, thermal, electrical, and more.
Uploaded by
Muhammad Pathan AbroCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
654 views1 pagePhysics Essentials for Students
1. This document provides a physics cheat sheet covering common units, conversions, formulas for motion, forces, energy, and circular motion.
2. Key motion formulas include equations for constant velocity, constant acceleration, projectile motion, and two-dimensional motion.
3. Important force formulas include gravity, friction, springs, buoyancy, and drag.
4. Key energy formulas distinguish between kinetic and potential energy, and cover different types of energy including mechanical, thermal, electrical, and more.
Uploaded by
Muhammad Pathan AbroCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd