Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chaptertour Jordantidgwell
Chaptertour Jordantidgwell
Uploaded by
api-349648754Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chaptertour Jordantidgwell
Chaptertour Jordantidgwell
Uploaded by
api-349648754Copyright:
Available Formats
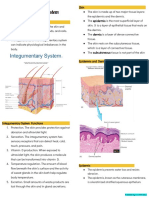
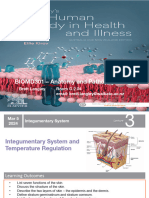
Integumentary System
Learning Target I can create a model and use it to discuss the function of the integumentary
system.
Proficiency Descriptor Definition
4 Proficient I can create a model and use it to discuss the functions of the integumentary
system.
3 Developing I can compare and contrast the structure and function of the epidermis and
dermis.
2 Basic I can define the anatomy and physiology of each accessory structure of the
skin.
1 Minimal I can document the general functions of the skin.
0 No Evidence No evidence.
P116-126
You may also use http://www.innerbody.com/anatomy/integumentary#full-description as a resource
List the general functions of the skin
Provides protective covering
Helps regulate body temperature
Retards water loss from deeper tissues
Houses sensory receptors
Synthesizes various biochemicals
Excretes small quantities of wastes
Where is the epidermis? Outer layer of the skin
What is the difference between the different layers?
The dermis is thicker than the epidermis and includes connective tissue consisting of
collagenous and elastic fibers, epithelial tissue, smooth muscle tissue, nervous tissue,
and blood.
What is the general function? Protection
Differentiate between thick and thin skin. Which layer?
Thick - Dermis
Thin - Epidermis
Which layer is most superficial?
Epidermis
What type of tissue do you find here?
Epidermis: Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Vascular or nonvascular?
Nonvascular
Where is the dermis?
What is the general function of the dermis?
What type of tissue is it comprised of?
Connective Tissue, Epithelial Tissue, Smooth Muscle Tissue, Nervous Tissue, and Blood
Vascular or nonvascular?
Vascular
Where is the hypodermis or subcutaneous layer? The last layer of the skin
What type of tissue? Adipose
What is its function? Insulation
What cells are responsible for producing the pigment for skin color determination? Melanocytes
What is the pigment called that determines skin color? Melanin
Do you have a lot of this pigment or a little? How do you know? I have more because I have darker
hair
What determines how much you have? Hair color, where you live, environment, etc
What is the function of melanin? To protect against harmful UV rays
Describe anatomy and physiology of each accessory structure of the skin.
hair follicle
explain the purpose of the arector pilli muscle - when cold, makes hair stand up on
end
What is hair made up of? Kerotin
Where is hair not present? Palms of hands, soles of feet, lips, nipples
sebaceous gland
What does this produce? Sebin
what is the purpose for it? Gives hair nutrients
sudoriferous gland
What are the different gland types? Apocrine and Eccrine
What are their differences? Apocrine is present at puberty and produces smelly sweat
and Eccrine releases water and other waste
What type of sweat is produced by an eccrine gland? Water
Where is it usually found? Pores
What type of sweat is produced by an apocrine gland? Smelly sweat
Where is it usually found? Hair follicles
Explain why someone would call the skin a blood storage unit and how this relates to homeostasis. -
Blood goes there whenever is needed and can stay there as long as its needed
How does the skin regulate body temperature? Vasoconstriction and Vasodialation
What is vasodilation? When blood vessels expand and release heat through pores
What is vasoconstriction? When blood vessels constrict and make heat go to core because of being
cold
What are the characteristics of
a first degree burn? Red, irritated
a second degree burn? Wet, red, yellow, hurts the worst
a third degree burn? Charred, nerves are dead, no repair
If there was a cut into the dermis how would your body respond? (3 or 4 parts) - skin repairs itself
and melanin is pushed up through the dermis
A superficial epidermal wound is healed how? Rapid cell division
What type of cells are responsible for cleaning a wound? White blood cells
You will need to know the following:
epidermis
Stratum corneum
Stratum lucidum (when?)
keratinocytes
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum basale
melanocyte
dermis
dermal papillae
subcutaneous layer
blood vessels
hair follicle
sebaceous glands
arrector pili
sudoriferous glands
eccrine
apocrine
adipose tissue
You might also like
- A Private Hospital - ZarqaDocument73 pagesA Private Hospital - ZarqaFarhadNo ratings yet
- Mirror Therapy - Practical Protocol For Stroke Rehabilitation, 2013Document25 pagesMirror Therapy - Practical Protocol For Stroke Rehabilitation, 2013Nacho Castro Izquierdo75% (4)
- UNIT 1 - Orientation To The Human Body Study GuideDocument6 pagesUNIT 1 - Orientation To The Human Body Study GuideEgi Rivas100% (1)
- Integumentary WebquestDocument3 pagesIntegumentary Webquestsamantha57% (14)
- Lukegarbett Bloodtypingscenario1Document2 pagesLukegarbett Bloodtypingscenario1api-340693501No ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument44 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisBulborea Mihaela100% (1)
- Psoas Muscle of The SoulDocument19 pagesPsoas Muscle of The SoulJanez Kozamernik100% (5)
- Chaptertour AlexandriabeersDocument3 pagesChaptertour Alexandriabeersapi-342509632No ratings yet
- Chaptertour DavidbognarDocument3 pagesChaptertour Davidbognarapi-342605368No ratings yet
- SkinDocument15 pagesSkinSnikitha SaiNo ratings yet
- CPD (Skin Anatomy & Physiology)Document25 pagesCPD (Skin Anatomy & Physiology)Shahida H. AbdulmajidNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Integumentary SystemDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Integumentary SystemLaraib HabibNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument10 pagesIntegumentary Systemapi-318236712No ratings yet
- Bio 2 Unit 4 Exam ReviewDocument16 pagesBio 2 Unit 4 Exam Reviewkassandraw24No ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument11 pagesUntitled PresentationAman VermaNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument11 pagesUntitled PresentationAman VermaNo ratings yet
- Skin and Fascia Lec 2Document42 pagesSkin and Fascia Lec 2Javaid mukhtarNo ratings yet
- Midterm PcosDocument14 pagesMidterm Pcosjohnbiel.barsana26No ratings yet
- 10 - Skin and AppendagesDocument58 pages10 - Skin and AppendagesMycah Averey AmierolNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Mary Jane T. Cabataña, RN Instructor, MC1Document28 pagesIntegumentary System: Mary Jane T. Cabataña, RN Instructor, MC1Paul CliffordNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument56 pagesIntegumentary SystemSamantha Kaye ReclaNo ratings yet
- Seeley's Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 5 Seeley's Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 5Document6 pagesSeeley's Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 5 Seeley's Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 5Kaiser GarridoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System ReportingDocument49 pagesIntegumentary System Reportingalmira garciaNo ratings yet
- 09 IntegumentDocument58 pages09 Integumentkim kaiNo ratings yet
- Barlis The Integumentary SystemDocument30 pagesBarlis The Integumentary SystemBlackKnight ZeusNo ratings yet
- INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Reviewer SHS General Biology 2 PDFDocument14 pagesINTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Reviewer SHS General Biology 2 PDFKeiNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues MedicalDocument44 pagesAnimal Tissues MedicalNOELIE IBACARRANo ratings yet
- SKINDocument30 pagesSKINShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Dermis WorksheetDocument2 pagesDermis Worksheetxcupcakex122006No ratings yet
- SESSION 13 - Integumentary System ENGLISH IIDocument39 pagesSESSION 13 - Integumentary System ENGLISH IImzunigamendivil148No ratings yet
- Integumentary System 2023Document14 pagesIntegumentary System 2023Maria AndinoNo ratings yet
- P9mi9p6lx - Lesson 3.3-The Integumentary System 3Document23 pagesP9mi9p6lx - Lesson 3.3-The Integumentary System 3Precious RoxasNo ratings yet
- (Ayuste's Group) 1) A Complete Gut and Segmentation Complete GutDocument30 pages(Ayuste's Group) 1) A Complete Gut and Segmentation Complete Gutjoseph tanNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument46 pagesIntegumentary SystemFrancis MacasioNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument8 pagesIntegumentary SystemTabay, Stephanie B.No ratings yet
- Integumentary System - Pptx-For Fundamentals of Zoology 2020Document25 pagesIntegumentary System - Pptx-For Fundamentals of Zoology 2020Islam SamirNo ratings yet
- Science Notes The SkinDocument5 pagesScience Notes The Skinapi-615817090No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Plant and Animal Tissues 3Document14 pagesLesson 1 Plant and Animal Tissues 3mauilucero978No ratings yet
- 04 The Integumentary SystemDocument37 pages04 The Integumentary SystemRuthie MendozaNo ratings yet
- 1st SCT Part 2Document48 pages1st SCT Part 2teeboyakegbesolaNo ratings yet
- Skin Anatomy: Prof: Shekhar TeliDocument21 pagesSkin Anatomy: Prof: Shekhar TeliShekhar TeliNo ratings yet
- Lec Anaphy Mid RevDocument33 pagesLec Anaphy Mid RevLOTIVIO VIKTORIANo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument51 pagesIntegumentary SystemAuza Moses IbrahimNo ratings yet
- UOW BIOMD301 3 - Integumentary System and Temperature RegulationDocument60 pagesUOW BIOMD301 3 - Integumentary System and Temperature Regulationnandani ramNo ratings yet
- 09 - Skin and Its AppendagesDocument61 pages09 - Skin and Its AppendagesArjohn VegaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument90 pagesIntegumentary SystemJennyreen LenonNo ratings yet
- Tiomico - BSP 2A - Integumentary SystemDocument8 pagesTiomico - BSP 2A - Integumentary SystempiescesNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: Dermatology ExaminationDocument28 pagesThe Integumentary System: Dermatology ExaminationCasey EngelNo ratings yet
- Skin Crash Course (Graphic Organizer)Document2 pagesSkin Crash Course (Graphic Organizer)Elliot SynderNo ratings yet
- Anaphy-Integumentary SystemDocument8 pagesAnaphy-Integumentary SystemRapa PedzNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Practical The Skin NGUDocument22 pages4.5 Practical The Skin NGUAya OsamaNo ratings yet
- L1,2,3 - Intro, Anatomy, Language of Dermatologydr. Almontaser BellahDocument102 pagesL1,2,3 - Intro, Anatomy, Language of Dermatologydr. Almontaser BellahTOMMYNo ratings yet
- Skin LayersDocument3 pagesSkin LayersCrackmcat CrackmcatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 The Skin and The Integumentary SystemDocument2 pagesChapter 6 The Skin and The Integumentary SystemMardie ArcesNo ratings yet
- The Following Notes Are References According To Figures and Tables in Gartner and Hiatt (2 Edition, 2001)Document5 pagesThe Following Notes Are References According To Figures and Tables in Gartner and Hiatt (2 Edition, 2001)gerginNo ratings yet
- Histology by - Dr.abdirahman Gagajir 1Document40 pagesHistology by - Dr.abdirahman Gagajir 1HusseinNo ratings yet
- Cor 007 Module 17Document12 pagesCor 007 Module 17Camille ManlongatNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Midterms Reviewer 1Document31 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Midterms Reviewer 1Zucc mahnut100% (1)
- Connective TissueDocument38 pagesConnective TissueAryan DesaiNo ratings yet
- Skin 2020Document60 pagesSkin 2020Yousef KhallafNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine SystemMaclharenn TiquiNo ratings yet
- Integumentary NotesDocument5 pagesIntegumentary NotesRiyue KreoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument15 pagesIntegumentary SystemmonkeysaltaccNo ratings yet
- Chapter II IntegumentaryDocument9 pagesChapter II IntegumentaryTitoMacoyTVNo ratings yet
- Chaptertourskeletalsystemp JoshuahansonDocument2 pagesChaptertourskeletalsystemp Joshuahansonapi-349648558No ratings yet
- Digestivesystemintroduction JoshuahansonDocument1 pageDigestivesystemintroduction Joshuahansonapi-349648558No ratings yet
- Joshuahanson RespiratoryintroDocument3 pagesJoshuahanson Respiratoryintroapi-349648558No ratings yet
- Joshuahanson Bloodtypingscenarios2Document2 pagesJoshuahanson Bloodtypingscenarios2api-349648558No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Integumentary System Lab: BackgroundDocument5 pagesUnit 4 Integumentary System Lab: Backgroundapi-349648558No ratings yet
- Unit2chaptertour JoshuahansonDocument3 pagesUnit2chaptertour Joshuahansonapi-349648558No ratings yet
- Staff DirectoryDocument12 pagesStaff DirectoryTimNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of FLUNARIZINEDocument10 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of FLUNARIZINEAccung BuccuNo ratings yet
- PerioPruv The Next Big Thing - PPD Nov 11Document1 pagePerioPruv The Next Big Thing - PPD Nov 11Carolyn WilkinsonNo ratings yet
- A Digital Inclusion Project For Older PeopleDocument1 pageA Digital Inclusion Project For Older PeopleMauricio AraujoNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal Neuralgia 2Document48 pagesTrigeminal Neuralgia 2mszlazak4179No ratings yet
- COMPLICATII TARDIVE DUPA INJECTAREA DE ACID HIALURONIC IN SCOP ESTETIC SI MANAGEMENTUL LOR Ro 399Document21 pagesCOMPLICATII TARDIVE DUPA INJECTAREA DE ACID HIALURONIC IN SCOP ESTETIC SI MANAGEMENTUL LOR Ro 399tzupel4No ratings yet
- Look Great Naked!: Big-O Sex SecretsDocument162 pagesLook Great Naked!: Big-O Sex SecretsShahryar Rizvi100% (1)
- Hoja Seguridad Dromus BLDocument7 pagesHoja Seguridad Dromus BLClaudia hernandezNo ratings yet
- Regulatory and Pharmacological Basis of Ayurvedic FormulationsDocument349 pagesRegulatory and Pharmacological Basis of Ayurvedic FormulationsSNo ratings yet
- Bunion: Strengthening Foot Muscles To Reduce Pain and Improve MobilityDocument1 pageBunion: Strengthening Foot Muscles To Reduce Pain and Improve Mobilitymucki_provokatorNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument68 pagesSeminarcr5wjqrpm5No ratings yet
- TruCal Lipid en GB 6Document7 pagesTruCal Lipid en GB 6mnemonicsNo ratings yet
- Yakult SupplementDocument7 pagesYakult SupplementLuisRodriguezNo ratings yet
- The Vodka Diet Edit 12.20Document114 pagesThe Vodka Diet Edit 12.20Late Knight GamingNo ratings yet
- 7721 (25) NeurotraumaDocument72 pages7721 (25) NeurotraumanewazNo ratings yet
- IV ScriptDocument3 pagesIV ScriptRica AcuninNo ratings yet
- (Ebook pdf) Hazzard's Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology, 8th ed 8th Edition Kevin P. High - eBook PDF all chapterDocument54 pages(Ebook pdf) Hazzard's Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology, 8th ed 8th Edition Kevin P. High - eBook PDF all chapteradiletsigen100% (7)
- BLOOD and CIRCULATIONDocument11 pagesBLOOD and CIRCULATIONKert trocioNo ratings yet
- Introduction Feng ShuiDocument58 pagesIntroduction Feng Shuihunky11100% (3)
- RGDOC Updated 11 August 11Document229 pagesRGDOC Updated 11 August 11foong_niNo ratings yet
- Wurzel 2016Document8 pagesWurzel 2016prolanis pkmmulyoharjoNo ratings yet
- AO - ICV - Forms CorrectedDocument14 pagesAO - ICV - Forms CorrectedFhebie Jevalyn DioayanNo ratings yet
- Jadwal DokterDocument7 pagesJadwal DokterfranciaNo ratings yet
- Review: Emilio Perucca, Piero Perucca, H Steve White, Elaine C WirrellDocument12 pagesReview: Emilio Perucca, Piero Perucca, H Steve White, Elaine C WirrellFernandoNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Anti Doping 2000 2015 PDFDocument4,506 pagesEncyclopedia of Anti Doping 2000 2015 PDFLeandro NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic Drug InteractionsDocument40 pagesPharmacokinetic Drug Interactionsabdullah2020No ratings yet