Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary of Port Folio
Summary of Port Folio
Uploaded by
Nagendra SahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summary of Port Folio
Summary of Port Folio
Uploaded by
Nagendra SahCopyright:
Available Formats
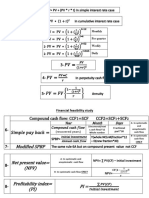
Summary: Portfolio Management
Portfolio Management
Risk Return
Standard deviation(σ)* Required return (CAPM) Available Return
OR (When return considers risk factor) (When return do not considers risk factor)
Variance (σ2)** Required return = RF + β security (RM - RF) Dividend + Value appreciation
Return = Price at beginning
Overall risk Where, RF = Return Risk free
RM = Return Market OR
β security = systematic risk (in time) D1 + (P1 - P0)
= P0
When, CAPM< Available Return = Buy
*Normally calculate Std. Dev.(σ) for overall risk.
CAPM>Available Return = Sell
plus **Consider variance as overall risk at the time of CAPM = Available Return = Hold
calculation of systematic and unsystematic risk. i.e. Expected Return (or Average Return)
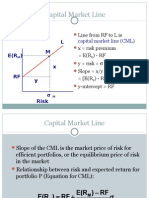
Security Market line is a graphical representation of CAPM.
Systematic Risk Unsystematic Risk On Security On Portfolio
= β2security X σ2market = σ2Security - Systematic risk (Say, Security A) [Say, Portfolio consists of Security “A” and “B”]
Alternative-1: Alternative-1:
(It cannot be diversified because (It Can be diversified because (When different possible Returns are given with their probabilities)
it depend upon economy) it is specific to firm) [when information about proportion of investment
Expected or Average Return on security “ A” = has been given]
Even β is a systematic risk, we
do not calculate β when question OR we can say, (Possible Return-1 X Probability-1)
ask for calculation of systematic σ2Security = Systematic +
risk. Because we have to unsystematic risk + (Possible Return-2 X probability-2) R portfolio = (RA WA + RB WB)
calculate systematic risk in “%” + (Possible Return-3 X probability-3)
term. But β is in times term. + ( … … ………… X …………..) Where, RA & RB = Return on security A & B.
WA = Proportion of security A with Total
Suppose EBT is 1.5 times of Alternative-2 investment.
EAT, and EAT is 12% then what (When different possible Returns are given without probabilities) WB = Proportion of security B with Total
is EBT? investment.
Here, EBT = EBT X EAT Expected or Average Return on security = Alternntive-2:
i.e. EBT = (1.5 X 12%) = 18%. (when no information about investment given)
CA. Nagendra Sah Email: ca_npsah@icai.org
Summary: Portfolio Management
For Second Method see, (Possible Return-1 + possible Retunr-2 + possible R.-3 + ….) RA + RB + … …
Correlation coefficient Return Portfolio
No. of Return No. of return
=
Standard Deviation (σ)
On one Security On Portfolio
[Say, Portfolio consists of Security “A” and “B”]
σ portfolio = √ Variance (σ )
2
Alternative-1: Alternative-1:
(When different possible Returns are given with their probabilities)
σ portfolio = √(σA WA) + (σB WB) + 2 (σA WA) (σB WB) rAB
Variance (σ2) = (Possible Return 1 - mean return) X Probability-1
Where, σA & WB = Standard deviation of security A and B,
+ (Possible Return 2 -mean return) X probability-2
+ (Possible Return 3 -mean return) X probability-3 WA & WB = Proportion of Security A and B,
+ ( … … ……… - …………….. .) X …………
Alternative-2: rAB = Correlation coefficient of A with B.
(When different possible Returns are given without their probabilities)
(Possible R 1-Mean R) + (Possible R 2 - Mean R) + … … … Alternative 2: (when, rAB = +1)
No of items σportfolio = (σA WA) + (σB WB)
Alternative 3: (when, rAB = -1)
σportfolio = (σA WA) - (σB WB)
Co-variance :
Correlation coefficient (r):
The value of Correlation Coefficient (r) must fall between -1 to +1.
If “rAB” is positive it will signify that returns in security A are increasing while in the security B also they are increasing.
If “rAB” is Negative it will signify that returns in security A are increasing while in the security B they are decreasing.
If correlation is “-1” i.e. perfect negative, overall risk can be brought to “nil”
CA. Nagendra Sah Email: ca_npsah@icai.org
Summary: Portfolio Management
And in this case proportion of one security =
σ one security
σ one security + σ other security
If correlation is other than “-1” i.e. say +0.5, -0.2, 0, +1 etc. overall risk can not be brought to nil but it can be minimize,
And in this case proportion of one security =
σ one security - Co-variance (one with other)
σ2 one security + σ2 other security - 2 Co-variance (one with other)
Coefficient of determination (r2):
According to sharp, Variance explained by the market index is systematic risk and unexplained variance is the unsystematic risk.
Coefficient of determination shows that, “(r2) %” of variance in security is explained by Market index.
Hence we can say that, Systematic risk = r2 X σ2 security and Unsystematic risk = (1- r2) X σ2security
Beta:
On Security On portfolio Project
Market line
Security market line Capital market Line Characteristic line
Security Market line is a graphical representation of CAPM. Expression:
Expression: Character line (required return) = Alpha + β security X RM
Required return = RF + β security (RM - RF)
Variable fix Variable fix Variable fix fix variable
i.e. Ans is in this form: Req. Return = 10 + β security X 5 i.e. Ans is in this form: Character line(Req. Return) = 4 + 1.5 X R M
CA. Nagendra Sah Email: ca_npsah@icai.org
Summary: Portfolio Management
Alpha:
Alternative-1: Alternative-2:
(When Risk free return given) (When Risk free return not given)
Alpha = Available Return Security - Required return CAPM Alpha = Available Return Security - β security X RM
i.e. Available return - {RF + β security (RM -RF)} i.e. Available return - { RF + β security (RM - RF)}
CA. Nagendra Sah Email: ca_npsah@icai.org
You might also like
- KSU Trumpet Syllabus 2017Document72 pagesKSU Trumpet Syllabus 2017Vini EbiNo ratings yet
- FileDocument2 pagesFileHola Hola71% (7)
- Corporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandCorporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Acid Base For StudentsDocument15 pagesAcid Base For StudentsPlan studyNo ratings yet
- Instrument Transformer Appli Guide AbbDocument124 pagesInstrument Transformer Appli Guide AbbkapilNo ratings yet
- Chap 012Document26 pagesChap 012NazifahNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Report On Basecamp PricingDocument9 pagesCase Analysis Report On Basecamp PricingKumar AnandNo ratings yet
- Modicon Unity Pro Program Languages Structure Ref ManualDocument698 pagesModicon Unity Pro Program Languages Structure Ref Manualobi SalamNo ratings yet
- Infinity - Acheron Cascade (2d20)Document153 pagesInfinity - Acheron Cascade (2d20)Ricardo OkabeNo ratings yet
- CORPORATE FINANCE - Chap 11Document4 pagesCORPORATE FINANCE - Chap 11Nguyễn T. Anh Minh100% (1)
- Capital Market Line (Rohit)Document33 pagesCapital Market Line (Rohit)agrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- Finance 70391: Topic 9: The Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument45 pagesFinance 70391: Topic 9: The Capital Asset Pricing ModelShiyun QiuNo ratings yet
- Risk, Return and Portfolio Theory - A Contextual Note: Samithamby SenthilnathanDocument11 pagesRisk, Return and Portfolio Theory - A Contextual Note: Samithamby SenthilnathanGen AbulkhairNo ratings yet
- R P - P - + C: Chapter Seven Basics of Risk and ReturnDocument13 pagesR P - P - + C: Chapter Seven Basics of Risk and ReturntemedebereNo ratings yet
- S4 - Portfolio Theory - UnlockedDocument24 pagesS4 - Portfolio Theory - UnlockedAYUSHI NAGARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document14 pagesChapter 5Mohamad SyafiqNo ratings yet
- 2 QuizDocument5 pages2 QuizAnandapadmanaban Muralidharan MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Management: Statical Analysis For Single SecurityDocument5 pagesPortfolio Management: Statical Analysis For Single SecurityJenneey D RajaniNo ratings yet
- Lezione 4Document42 pagesLezione 4gio040700No ratings yet
- Ch24 ShowDocument46 pagesCh24 ShowMahmoud AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Risk and Return Risk and ReturnDocument30 pagesRisk and Return Risk and ReturnKIM RODANo ratings yet
- 20220910171232HCTAN008C8-Topic 8-Risk ReturnDocument105 pages20220910171232HCTAN008C8-Topic 8-Risk Returnnicholas wijayaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4-WebCampus Risk and ReturnDocument6 pagesCh. 4-WebCampus Risk and ReturnEng Stephen ArendeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - 6 - Cost of CapitalDocument22 pagesLecture 5 - 6 - Cost of CapitalmaxNo ratings yet
- Rules 2nd TermDocument4 pagesRules 2nd TermMohamed AbbasNo ratings yet
- Risk ReturnDocument34 pagesRisk ReturnchandanNo ratings yet
- Risk, Return, & The Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument19 pagesRisk, Return, & The Capital Asset Pricing ModelElyza BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Portfolio QuestionsDocument6 pagesPortfolio QuestionsHarsh RajNo ratings yet
- EC3333 NotesDocument25 pagesEC3333 Notesxqhuang99No ratings yet
- Corporate Finance: Overview of Risk & ReturnDocument21 pagesCorporate Finance: Overview of Risk & ReturnManmeet Kaur SandhuNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Management & Analysis: 1. UtilityDocument10 pagesPortfolio Management & Analysis: 1. UtilityMarie Remise100% (1)
- Risk Return Relationship and Portfolio Theory-1Document65 pagesRisk Return Relationship and Portfolio Theory-1kelvinyessa906No ratings yet
- Portfolio - Lecture 4 - CAPMDocument50 pagesPortfolio - Lecture 4 - CAPMPhuc Hong PhamNo ratings yet
- Investment Management Set 18 Portfolio ImmunizationDocument16 pagesInvestment Management Set 18 Portfolio ImmunizationPaul WangNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Risk Aversion and Capital Allocation To Risky AssetsDocument20 pagesLecture 4 Risk Aversion and Capital Allocation To Risky AssetsLuisLoNo ratings yet
- FINS5513 Lecture 3A: Capital Allocation and Optimal Risky PortfoliosDocument37 pagesFINS5513 Lecture 3A: Capital Allocation and Optimal Risky Portfolios萬之晨No ratings yet
- 2assetallocation (9) 1vmodr11cDocument61 pages2assetallocation (9) 1vmodr11cGabriel PodolskyNo ratings yet
- Aide Memoire: FTX3044F - TEST 2 (Chapters 5 - 12)Document18 pagesAide Memoire: FTX3044F - TEST 2 (Chapters 5 - 12)Callum Thain BlackNo ratings yet
- MBA 643 - NotesDocument1 pageMBA 643 - NotesSandeepNo ratings yet
- Risk and Return: Erna L, PHDDocument44 pagesRisk and Return: Erna L, PHDReffika WatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Risk, Return Financial Asset PortfolioDocument16 pagesChapter 2 Risk, Return Financial Asset PortfoliortNo ratings yet
- Topic 4.1Document3 pagesTopic 4.1arp140102No ratings yet
- S5 Risk Return Online VersionDocument20 pagesS5 Risk Return Online Versionconstruction omanNo ratings yet
- Formula For Financial Market Theory AMENDEDDocument7 pagesFormula For Financial Market Theory AMENDEDHansNo ratings yet
- Session 12 PDFDocument50 pagesSession 12 PDFANKIT AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Slide 7Document17 pagesSlide 7Akash SinghNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument16 pagesMidtermNicole ReintegradoNo ratings yet
- FM Lecture 3Document33 pagesFM Lecture 3ski_leo82No ratings yet
- FM Chapter 4Document16 pagesFM Chapter 4mearghaile4No ratings yet
- Portfolio Risk and Return Part 1Document34 pagesPortfolio Risk and Return Part 1Frédé AmouNo ratings yet
- Mean Variance Portfolio TheoryDocument22 pagesMean Variance Portfolio TheoryPsyonaNo ratings yet
- Asset Pricing Principles: Charles P. Jones, Investments: Principles and Concepts, Twelfth Edition, John Wiley & SonsDocument34 pagesAsset Pricing Principles: Charles P. Jones, Investments: Principles and Concepts, Twelfth Edition, John Wiley & SonsGeorgina AlpertNo ratings yet
- 5 Return & RiskDocument23 pages5 Return & RiskOmar Faruk 2235292660No ratings yet
- Chapter11 Stock Valuation and RiskDocument39 pagesChapter11 Stock Valuation and RiskprojectonamlonNo ratings yet
- Security Analysis & Portfolio Management: Dr. Hemant ManujDocument13 pagesSecurity Analysis & Portfolio Management: Dr. Hemant ManujHasan NabeelNo ratings yet
- Risk and Return Risk and ReturnDocument33 pagesRisk and Return Risk and ReturnIxhaq motiwalaNo ratings yet
- Risk and Returns: Guico, Nikki Andrea C. BFM01Document40 pagesRisk and Returns: Guico, Nikki Andrea C. BFM01NikkiAndreaCarononganGuicoNo ratings yet
- Ifm-Chapter 3 - Risk and Return 2 (Slide)Document50 pagesIfm-Chapter 3 - Risk and Return 2 (Slide)minhhien222No ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing ModelDocument8 pagesCapital Asset Pricing ModelSana NoorNo ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing Model (Ch-6)Document15 pagesCapital Asset Pricing Model (Ch-6)Neha SinghNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Management and Mutual Funds: Aalap ShahDocument34 pagesPortfolio Management and Mutual Funds: Aalap ShahSohrab ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Multi-Factor Asset Pricing: and More On The HomeworkDocument25 pagesMulti-Factor Asset Pricing: and More On The HomeworkMadihaBhattiNo ratings yet
- Risk and Return: RETURN: If You Buy An Asset of Any Sort, Your Gain (Or Loss) From That Investment Is Called TheDocument15 pagesRisk and Return: RETURN: If You Buy An Asset of Any Sort, Your Gain (Or Loss) From That Investment Is Called TheFear Part 2No ratings yet
- Formula For Financial Market TheoryDocument6 pagesFormula For Financial Market TheoryHansNo ratings yet
- Risk and ReturnDocument31 pagesRisk and ReturnnidamahNo ratings yet
- Ch03-5 Portifolio Theory - Risk Return AnalysisDocument113 pagesCh03-5 Portifolio Theory - Risk Return AnalysismupiwamasimbaNo ratings yet
- Lind17e Chapter02 TBDocument22 pagesLind17e Chapter02 TBdockmom4No ratings yet
- Gross Domestic Product-An Analysis: ContentsDocument4 pagesGross Domestic Product-An Analysis: ContentsSumeet ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- CASE DIGEST - GR No. 75362Document4 pagesCASE DIGEST - GR No. 75362Juvy CambayaNo ratings yet
- Imel7002 L3Document115 pagesImel7002 L3就爱吃饭团No ratings yet
- Focgb3 Ak Utest VG 3Document2 pagesFocgb3 Ak Utest VG 3Gyurácz GyulaNo ratings yet
- Matias B. Salvador Memorial Elementary School Table of Specification in Esp Iv Third Periodical Test (3 Quarter)Document2 pagesMatias B. Salvador Memorial Elementary School Table of Specification in Esp Iv Third Periodical Test (3 Quarter)Guia Marie Diaz BriginoNo ratings yet
- Eggbeater 1 Exploded View JAN22CDocument1 pageEggbeater 1 Exploded View JAN22CAlejandroz GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Gas Phase Catalysis by ZeolitesDocument36 pagesGas Phase Catalysis by ZeolitesHenrique SouzaNo ratings yet
- ISO 31000:2018 Structure: Session - 2 (A)Document35 pagesISO 31000:2018 Structure: Session - 2 (A)kanchana rameshNo ratings yet
- Heidelberg Linoprint CV (Ricoh Pro c7100) 69391Document1 pageHeidelberg Linoprint CV (Ricoh Pro c7100) 69391ArlindPacukuNo ratings yet
- Abstract 3D PrintingDocument2 pagesAbstract 3D PrintingMichael MatshonaNo ratings yet
- Wind-Turbine AerodynamicsDocument6 pagesWind-Turbine AerodynamicscharlesNo ratings yet
- ChEg 5193 Lecture 7 Interest and InvestmentDocument28 pagesChEg 5193 Lecture 7 Interest and InvestmentGammachisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 StratManDocument41 pagesChapter 4 StratManRujean Salar AltejarNo ratings yet
- Special Forms of PaymentDocument38 pagesSpecial Forms of PaymentAVelino PagandiyanNo ratings yet
- Cost Management in PM CoursesDocument167 pagesCost Management in PM CoursesJM DunandNo ratings yet
- Bloomberg - LeetCodeDocument8 pagesBloomberg - LeetCodeTuhin KunduNo ratings yet
- Small Porch SwingDocument26 pagesSmall Porch SwingEngr Saad Bin SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Cake MakingDocument382 pagesCake MakingTarak Zayani100% (1)
- JusMundi PDF Claimant S V Respondent S Icc Case No 14431 Initial Interim AwardDocument14 pagesJusMundi PDF Claimant S V Respondent S Icc Case No 14431 Initial Interim AwardthhekmpsryvlfvwuvtNo ratings yet
- Deber 3Document5 pagesDeber 3MartinNo ratings yet
- OpenSource SoftwareDeclarations IO enDocument29 pagesOpenSource SoftwareDeclarations IO enCesarFierroMontalbaNo ratings yet
- W9 Lesson 7 Introduction To MySQL - PresentationDocument29 pagesW9 Lesson 7 Introduction To MySQL - PresentationWendellNo ratings yet