Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antimicrobial Procedure
Uploaded by
Kadesh Hanah McCarthy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesProcedure for Antimicrobial
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProcedure for Antimicrobial
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesAntimicrobial Procedure
Uploaded by
Kadesh Hanah McCarthyProcedure for Antimicrobial
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
PHYTOCHEMICAL SCREENING FOR SECONDARY PLANT METABOLITES
Extraction of Fresh Plant Material
1.1 Weigh 100g dried ground plant in an Erlenmeyer flask
1.2 Treat sufficient 80% ethyl alcohol to completely submerge the material
*Note the volume alcohol used
1.3 Stopper the flask and keep the material soaked for 24-48 hours.
1.4 Filter through buchner funnel with gentle suction.
1.5. Rinse the flask and plant material with fresh portions of alcohol.
1.6 Transfer washings and plant material to the funnel, combining the washings with the first filtrate
1,7 Apply gentle suction to complete collection of the plant extract.
1.8 Discard the plant residue.
1.9 Concentrate the filtrate under vacuo at temperature below 50°C to about 20mL, Measure the exact
volume of the concentrated extract.
Prior to use, shake the turbidity standard vigorously on a mechanical vortex
mixer;
This standard can be kept up to 6 months, if stored in tightly sealed
screwcapped tube in the dark
The broth culture
Preparation of the nutrient broth
Refer to label for the preparation of 1000 mi solution.
Take a loopful of bacteria, gram positive or gram negative, from the culture
slant and inoculate in 50m! nutrient broth;
Incubate the culture broth for 18-24 hours at 35°
Observe the culture broth for turbidity, indicative of microbial growth
Adjusting the turbidity of the inoculum
The adjusted turbidity serves as the inoculum for the microbial
assay. This will serve as the inoculum which will be swabbed onto
agar plates.
Use within 15 minutes after adjusting the turbidity.
Aseptically transfer 5 mi of the culture broth in sterile screw-capped tubes.
Agitate on a vortex mixer the bacterial suspension and immediately compare
against the 0.5 Mcfarland standard prepared.
If the bacterial suspension does not appear to be of the same density as the
Mcfarland standard, adjust the turbidity by adding sterile saline solution or
culture broth and subsequently compare the resulting turbidity to the standard,
sheet of white paper on which 2 sharp
-
| rei acusting inocu tarbsity against a MiFavand bavi sulfate standacd
Preparation of plates
Prepare plates depending on the number of test organism and replications
fequired. Common practice requires 2 replicates for each extract and for
each test organism.
Pour approximately 15 ml of melted nutrient agar into dry and sterile petri
dishes. Let the medium solidify
Moisten a sterile cotton swab into the test organism (inoculum) suspension,
Use cotton swab with wooden applicator handles. Dip a sterile cotton swab
into a suspension of the test organism/inoculum. Press and rotate the
moistened swab firmly against the inside walll of the tube just above the fluid
level to remove the excess liquid
Cotton swabbing
Aseptically swab the test organism into a solidified nutrient agar by streaking
the swab over the entire surface of the agar plate ‘3X, rotating the plate 60
degrees after each application to ensure an even distribution of the inoculum
Figure M4, Swabbed agar plate
on the surface of the medium.
Let the swabbed plates stand for 5 minutes.
per disc diffusion method
Materials:
Screw-capped tube of test organism
Nutrient agar
Forcep
6 mm or 13 mm paper disc, sterilized in petri dish (Pack disc in sets of 10)
Using the forceps pick out one paper disc and immerse the paper disc into
the plant extract.
Lay the moistened filter disc gently on the seeded agar plate.
Figure M7. Placing paper discs
conte the agar plate
Gently tap disc with forcep to ensure maximum full contact of the dic with the
agar medium,
Incubate the plates inverted.
Technique for handling the paper disc and moistening with the plant extract:
With the forcep on one hand and the petri dish containing the serilized filter
discs on the other hand, open the dish and pick out one paper disc with the
forcep.
Immerse the disc into the assay solution.
Remove excess liquid by letting the moist paper disc to touch the inside wall
of the container of the assay solution.
IV. Reading the
say plates,
Look for a “HALO” or “Clearing” around the discs. This is known as the zone
of inhibition.
Invert the plates and with a ruler measure the diameter of each inhibition zone
in millimeters.
Express results as mm diameter zone of inhibition.
Record the diameter of the paper disc used in the assay in mm.
IV. Analyzing the results
<10 mm may be expressed as inactive
10-13 mm, partially active
14-19 mm, active
>19 mm, very active
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Work Instruction: Jar TestingDocument4 pagesWork Instruction: Jar TestingKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Chemicals InventoryDocument1 pageLaboratory Chemicals InventoryKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Minutes of The MeetingDocument3 pagesMinutes of The MeetingKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Jar Testing of Chemical DosagesDocument32 pagesJar Testing of Chemical DosagesRolando CortazarNo ratings yet
- F-REV-01a Minutes of The Meeting - Rev 0Document3 pagesF-REV-01a Minutes of The Meeting - Rev 0Kadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- May 07 Updates Minutes SampleDocument1 pageMay 07 Updates Minutes SampleKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- TASC Onboarding OrientationDocument59 pagesTASC Onboarding OrientationKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- 2020-11-07 TASC List of Participants For The Training of The 15MLD WTPDocument1 page2020-11-07 TASC List of Participants For The Training of The 15MLD WTPKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- TASC PPT FormatDocument5 pagesTASC PPT FormatKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Weekly Report SeptemberDocument16 pagesWeekly Report SeptemberKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- All Tasc Employees Management Tool Box MeetingDocument3 pagesAll Tasc Employees Management Tool Box MeetingKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- SQ Prove 600 Analytical Procedures and Appendices 2017-07-1Document267 pagesSQ Prove 600 Analytical Procedures and Appendices 2017-07-1Kadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Lockout Tagout ProcedureDocument7 pagesLockout Tagout ProcedureKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Week 2-Soft SkillsDocument16 pagesWeek 2-Soft SkillsKadesh Hanah McCarthy100% (1)
- Araga Tate Niversity: Class PoliciesDocument13 pagesAraga Tate Niversity: Class PoliciesKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Anal Chem Act 2Document7 pagesAnal Chem Act 2Kadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Christian EthicsDocument10 pagesChristian EthicsCatherine Mariae FloresNo ratings yet
- Philosophical Rational of The StudyDocument4 pagesPhilosophical Rational of The StudyKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Application LetterDocument1 pageApplication LetterKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Towards Coupling Dispersive FinalDocument9 pagesTowards Coupling Dispersive FinalKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Caffeine From Mountain DewDocument80 pagesIsolation of Caffeine From Mountain DewKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
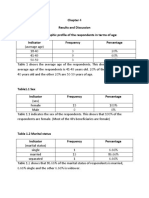
- Results and Discussion Table 1. Socio-Demographic Profile of The Respondents in Terms of Age: Indicator Frequency PercentageDocument4 pagesResults and Discussion Table 1. Socio-Demographic Profile of The Respondents in Terms of Age: Indicator Frequency PercentageKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Ideal Gas and Van Der Waals Equation of States (EOS) : Computer Simulation ExperimentDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Ideal Gas and Van Der Waals Equation of States (EOS) : Computer Simulation ExperimentKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Research J. Science and Tech. 2016 8 (4) :215-220Document2 pagesResearch J. Science and Tech. 2016 8 (4) :215-220Kadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Engr. Norberto R. Paquingan, DMDocument10 pagesEngr. Norberto R. Paquingan, DMKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- Application For OjtDocument13 pagesApplication For OjtKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- HPCDocument1 pageHPCKadesh Hanah McCarthyNo ratings yet
- 2017 Pds GuidelinesDocument4 pages2017 Pds GuidelinesManuel J. Degyan75% (4)
- ASTM Thermometers, Test Specimens and GlasswareDocument15 pagesASTM Thermometers, Test Specimens and GlasswareJoko Setio PurnomoNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)