Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flexible AC Transmission System
Uploaded by
Satya SahaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Flexible AC Transmission System
Uploaded by
Satya SahaCopyright:
Available Formats
What is Flexible AC Transmission System (FACTS)?
A Flexible AC transmission System refers to the system consisting of power electronic devices
along with power system devices to enhance the controllability and stability of the transmission
system and increase the power transfer capabilities. With the invention of thyristor switch,
opened the door for the development of power electronics devices known as Flexible AC
transmission systems (FACTS) controllers. Basically the FACT system is used to provide the
controllability of high voltage side of the network by incorporating power electronic devices to
introduce inductive or capacitive power in the network.
4 Types of FACTS Controllers
Series Controllers: Series Controllers consists of capacitors or reactors which introduce
voltage in series with the line. They are basically variable impedance devices. Their
major task is to reduce the inductivity of the transmission line. They supply or consume
variable reactive power. Examples of series controllers are SSSC, TCSC, TSSC etc.
Shunt Controllers: Shunt controllers consist of variable impedance devices like
capacitors or reactors which introduce current in series with the line. Their major task is
to reduce the capacitivity of the transmission line. The injected current is in phase with
the line voltage. Examples of shunt controllers are STATCOM, TSR, TSC, SVC.
Shunt-Series Controllers: These controllers introduce current in series using the series
controllers and voltage in shunt using the shunt controllers. Example is UPFC.
Series-Series Controllers: These controllers consist of a combination of series
controllers with each controller providing series compensation and also the transfer real
power along the line. Example is IPFC.
2 Types of Series Controllers
Thyristor controlled series capacitor (TCSC): Thyristor controlled series capacitor
(TCSC) uses silicon controlled rectifiers to manage a capacitor bank connected in series
with a line. This allows utility for transferring more power on a specified line. It generally
consists of the thyristors in series with an inductor and connected across a capacitor. It
can work in the blocking mode where the thyristor is not triggered and current passes
through the capacitor only. It can work in the bypass mode where the current is bypassed
to the thyristor and the whole system behaves as a shunt impedance network.
Static Series Synchronous Compensators: SSSC is simply a series version of
STATCOM. These are not used in commercial applications as independent controllers.
They consist of synchronous voltage source in series with the line such that it introduces
a compensating voltage in series with the line. They can increase or decrease the voltage
drop across the line.
2 Parallel Controllers
Static Variable Compensators: Static variable compensator is the most primitive and
first generation of FACTS controller. This compensator consists of a fast thyristor switch
controlling a reactor and/or shunt capacitive bank to provide dynamic shunt
compensation. They generally consist of shunt connected variable impedance devices
whose output can be adjusted using power electronic switches, to introduce capacitive or
inductive reactance in the line. It can be placed at the middle of the line to increase the
maximum power transfer capability and can also be placed at the end of the line to
compensate for variations due to load.
3 Types of SVC are
1. TSR(Thyristor Switched Reactor): It consists of a shunt connected inductor whose
impedance is controlled in a gradual manner using a Thyristor switch. The Thyristor is
fired at angles of 90 and 180 degrees only.
2. TSC(Thyristor Switched Capacitor): It consists of a shunt connected capacitor whose
impedance is controlled in a stepwise manner using a Thyristor. The manner of control
using the SCR is same as that of TSR.
3. TCR(Thyristor Controlled Reactor): It consists of a shunt connected inductor whose
impedance is controlled by the firing angle delay method of SCR wherein the firing of
Thyristor is controlled causing a variation in the current through the inductor.
STATCOM(Static Synchronous Compensator) : It consists of a voltage source which
can be a DC energy source or a capacitor or a inductor whose output can be controlled
using a Thyristor It is used to absorb or generate reactive power.
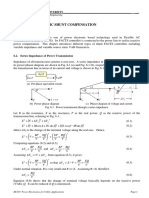
A Series-Shunt Controller- Unified Power Flow Controller:
They are a combination of STATCOM and SSSC such that both are combined using a common
dc source and provide both active and reactive series line compensation. It controls all the
parameters of the AC power transmission.
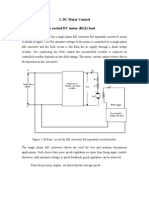
Steady-State Voltage Control using SVC for Flexible AC Transmission Systems
In order to generate Zero crossing voltage pulses we need digitalized voltage and current signals.
The voltage signal from the mains is taken and is converted into pulsating DC by bridge rectifier
and is given to a comparator which generates the digital voltage signal. Similarly the current
signal is converted into the voltage signal by taking the voltage drop of the load current across a
resistor. This AC signal will be again converted into digital signal as the voltage signal. Then
these digitalized voltage and current signals are sent to the microcontroller. The microcontroller
will calculate the time difference between the zero crossing points of voltage and current, whose
ratio directly proportional to the power factor and determines the range in which the power is. In
the same manner using Thyristor switched reactor (TSR) also zero cross voltage pulses can be
generated for voltage stability improvement.
You might also like
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsFrom EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Facts 2 MarksDocument14 pagesFacts 2 MarksBharath Raj100% (1)
- Introduction To FACTS: Alternating Current Transmission System (FACTS) Devices in Power Grids. FACTS AllowDocument4 pagesIntroduction To FACTS: Alternating Current Transmission System (FACTS) Devices in Power Grids. FACTS AllowsameekshaNo ratings yet
- Static VAR Compensation (SVC)Document2 pagesStatic VAR Compensation (SVC)Vedant KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: EighthDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank: EighthprakashNo ratings yet
- FACTS Question BankDocument7 pagesFACTS Question BankAnbarasan AnnamalaiNo ratings yet
- Solid State Drives Short BookDocument48 pagesSolid State Drives Short BookGomathi Raja MNo ratings yet
- Eee-Vi-Power System Analysis and Stability (10ee61) - Notes PDFDocument119 pagesEee-Vi-Power System Analysis and Stability (10ee61) - Notes PDFLatisha CarterNo ratings yet
- EE6603-PSOC Question BankDocument15 pagesEE6603-PSOC Question BankAnonymous sdfoA3No ratings yet
- Facts QuestionsbankDocument7 pagesFacts Questionsbankjaackson10No ratings yet
- PS7202-Flexible AC Transmission Systems PDFDocument5 pagesPS7202-Flexible AC Transmission Systems PDF1balamanianNo ratings yet
- SUBJECT: Elective-I Flexible A.C. Transmission Systems (FACTS) Question Bank Unit-I:Introduction To FactsDocument4 pagesSUBJECT: Elective-I Flexible A.C. Transmission Systems (FACTS) Question Bank Unit-I:Introduction To FactsJagadish Babu KondraguntaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Live - Power SystemDocument27 pagesElectrical Live - Power SystemashishNo ratings yet
- EE1401 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL - Two Marks Questions and Answer & QBDocument16 pagesEE1401 POWER SYSTEM OPERATION AND CONTROL - Two Marks Questions and Answer & QBAmruthNo ratings yet
- Prist University: Question BankDocument7 pagesPrist University: Question BankJhon LouisNo ratings yet
- Important Questions - APS - IDocument3 pagesImportant Questions - APS - IAakash MehtaNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument2 pagesFinalgobinathNo ratings yet
- EE2036-FACTS Question Bank For Two UnitsDocument7 pagesEE2036-FACTS Question Bank For Two UnitsSaran ArunNo ratings yet
- EE2036 2 MarksDocument19 pagesEE2036 2 MarksSaravanan RameshNo ratings yet
- Mlp-Ee 51Document11 pagesMlp-Ee 51prasad357No ratings yet
- Facts 3Document14 pagesFacts 3gjk1236596100% (1)
- Power System Analysis-BE (PT) NEWDocument13 pagesPower System Analysis-BE (PT) NEWMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- Real and Reactive Power Flow Control With Upfcconnected To A Transmission LineDocument7 pagesReal and Reactive Power Flow Control With Upfcconnected To A Transmission LineSravan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ee 1352 Power System Analysis Question and AnswersDocument7 pagesEe 1352 Power System Analysis Question and AnswersSandhosh RajaNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Facts (Part-A & Part-B)Document5 pagesUnit-1 Facts (Part-A & Part-B)Udaya KumarNo ratings yet
- Power Quality 2 Marks and 16 MarksDocument6 pagesPower Quality 2 Marks and 16 MarksBala MuruganNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Objectives of Series and Shunt CompensationDocument51 pagesCH 4 Objectives of Series and Shunt CompensationclydeNo ratings yet
- PE LessonPlanDocument4 pagesPE LessonPlanNarasimman DonNo ratings yet
- WWW Universityquestions inDocument8 pagesWWW Universityquestions inagreykatoNo ratings yet
- Anna University Affiliated Colleges Be Eee Semester Vi Ee2353 - High Voltage Engineering Unit - Iover Voltages in Electrical Power SystemsDocument6 pagesAnna University Affiliated Colleges Be Eee Semester Vi Ee2353 - High Voltage Engineering Unit - Iover Voltages in Electrical Power Systemspvanitha143No ratings yet
- Voltage Compensation: Reyes, Sabaña, Sombrado, Valenzuela and VivoDocument17 pagesVoltage Compensation: Reyes, Sabaña, Sombrado, Valenzuela and VivoFreddie MendezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 FactsDocument5 pagesUnit 2 FactsHarris RajNo ratings yet
- Power System Control-1Document6 pagesPower System Control-1Venkatesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Subject Code: Ee 1005 Subject Name: Power Quality: What Are The Causes Due To Short Circuit in TheDocument22 pagesSubject Code: Ee 1005 Subject Name: Power Quality: What Are The Causes Due To Short Circuit in TheChetan KotwalNo ratings yet
- IUBAT-International University of Business Agriculture and TechnologyDocument8 pagesIUBAT-International University of Business Agriculture and TechnologyMd Hasibur RahmanNo ratings yet
- T&DDocument5 pagesT&DMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- Unified Power Flow ControlDocument9 pagesUnified Power Flow ControlpavanNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Power and Distribution TransformerDocument8 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Power and Distribution Transformermaniking1No ratings yet
- Sri Jayachamarajendra College of EngineeringDocument13 pagesSri Jayachamarajendra College of EngineeringFernando Desengkie SangmaNo ratings yet
- New QBhve3yearDocument29 pagesNew QBhve3yearArun SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Ee2036 - Flexible Ac Transmission System: 2 Marks and 16 Marks-Question BankDocument27 pagesEe2036 - Flexible Ac Transmission System: 2 Marks and 16 Marks-Question Bankgunasekaran RajendranNo ratings yet
- EE 466 Power System Protection: University of HailDocument22 pagesEE 466 Power System Protection: University of Hailselvithimmarajan@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Flexible AC Transmission SystemDocument2 pagesFlexible AC Transmission SystemNehaPriyadarshniNo ratings yet
- 2nd Mid Assingnment QuestionsDocument3 pages2nd Mid Assingnment QuestionsSatya TejaNo ratings yet
- EE 2402 - QB ProtectionDocument7 pagesEE 2402 - QB ProtectionArun Bharath RajaNo ratings yet
- HV Mcq'sDocument9 pagesHV Mcq'sasfandyar khanNo ratings yet
- Department of Eee Question Bank: Sub Code: Ee1004 Sub Name: Power System Transients Year: Iv SEM: ViiiDocument8 pagesDepartment of Eee Question Bank: Sub Code: Ee1004 Sub Name: Power System Transients Year: Iv SEM: Viiiqais652002No ratings yet
- Ee 1351 Power System AnalysisDocument31 pagesEe 1351 Power System AnalysisStephen Kenth La GuerreNo ratings yet
- QUESTIONBANK EcadDocument19 pagesQUESTIONBANK EcadVarsha WaingankarNo ratings yet
- EE2036 Flexible AC Transmission Systems Two Mark Question and AnswersDocument15 pagesEE2036 Flexible AC Transmission Systems Two Mark Question and Answersanshuman nayakNo ratings yet
- RSM Nagar, Kavaraipettai - 601 206: R.M.K. Engineering CollegeDocument1 pageRSM Nagar, Kavaraipettai - 601 206: R.M.K. Engineering CollegeRojaNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 Circuit Breakers (Switchgear and Protection)Document84 pagesUnit-6 Circuit Breakers (Switchgear and Protection)sujithNo ratings yet
- Integration of Green and Renewable Energy in Electric Power SystemsFrom EverandIntegration of Green and Renewable Energy in Electric Power SystemsNo ratings yet
- Facts: Flexible A.C Transmission SystemDocument29 pagesFacts: Flexible A.C Transmission SystemVenkatesh PalakaluriNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document118 pagesUnit 1Susmita AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- Transient Stability of A Two-Machine Transmission System With Power System Stabilizers (PSS) and Static Var Compensator (SVC) NewDocument26 pagesTransient Stability of A Two-Machine Transmission System With Power System Stabilizers (PSS) and Static Var Compensator (SVC) Newkrishnendu maitraNo ratings yet
- Mahaquizzer 2005 Ans PDFDocument7 pagesMahaquizzer 2005 Ans PDFSatya SahaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Garden For Family FarmingDocument15 pagesNutrition Garden For Family FarmingSatya SahaNo ratings yet
- Systems Design Interview Study GuideDocument18 pagesSystems Design Interview Study GuideSatya Saha100% (1)
- Flexible AC Transmission SystemDocument3 pagesFlexible AC Transmission SystemSatya SahaNo ratings yet
- Using Data Mining For Screening Tax ReturnsDocument10 pagesUsing Data Mining For Screening Tax ReturnsSatya SahaNo ratings yet
- Java ModuleDocument30 pagesJava ModuleSatya SahaNo ratings yet
- English ThesisDocument4 pagesEnglish ThesisSatya Saha75% (4)
- Slides Ch2 Devices PDFDocument28 pagesSlides Ch2 Devices PDFSatya SahaNo ratings yet
- White Spaces PDFDocument8 pagesWhite Spaces PDFSatya SahaNo ratings yet
- Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor FundamentalsDocument20 pagesBrushless DC (BLDC) Motor FundamentalsEdo007100% (1)
- Advanced Control Systems: Maharaja Surajmal Institute of TechnologyDocument1 pageAdvanced Control Systems: Maharaja Surajmal Institute of TechnologySatya SahaNo ratings yet
- Energies 11 01491Document41 pagesEnergies 11 01491GuiNo ratings yet
- 978 613 8 91055 8 PDFDocument309 pages978 613 8 91055 8 PDFEr Sayan ParamanikNo ratings yet
- Facts: Flexible A.C Transmission SystemDocument29 pagesFacts: Flexible A.C Transmission SystemVenkatesh PalakaluriNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics - Kits PDFDocument31 pagesPower Electronics - Kits PDFGaganVishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power ControlDocument21 pagesReactive Power ControlKhurram Hashmi100% (2)
- Shunt CompensationDocument13 pagesShunt CompensationDeptiranjan MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power Compensation Technologies PDFDocument21 pagesReactive Power Compensation Technologies PDFTovar ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Facts by SVC (Flexible Ac Transmission)Document4 pagesFacts by SVC (Flexible Ac Transmission)scribsunilNo ratings yet
- Transient Stability Improvement of SMIB With Unified Power Flow ControllerDocument78 pagesTransient Stability Improvement of SMIB With Unified Power Flow ControllerRagesh OdungattuNo ratings yet
- Blocking Reactor As Part of SVC System - GEA-32012 - 161202 - R002 - HR PDFDocument11 pagesBlocking Reactor As Part of SVC System - GEA-32012 - 161202 - R002 - HR PDFPriscilla VasconcelosNo ratings yet
- SVC A02-0100Document16 pagesSVC A02-0100Christian NgalaNo ratings yet
- SVCDocument92 pagesSVCDiego MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Facts PPTDocument20 pagesFacts PPTHaripriya k aNo ratings yet
- 2015 Summer Model Answer Paper PDFDocument26 pages2015 Summer Model Answer Paper PDFRohit BariNo ratings yet
- Reactive Power CompensationDocument12 pagesReactive Power CompensationSyed Muhammad Munavvar Hussain100% (5)
- Voltage Drop Control in Transmission Line Atbara-Portsudan 220 KVDocument72 pagesVoltage Drop Control in Transmission Line Atbara-Portsudan 220 KVirfanWPKNo ratings yet
- MHO Distance Protection SettingDocument17 pagesMHO Distance Protection SettingAdhyartha KerafNo ratings yet
- PsocDocument1 pagePsocGayan ShashiNo ratings yet
- Facts 3Document14 pagesFacts 3gjk1236596100% (1)
- 663Document96 pages663ramesh epiliNo ratings yet
- D StatcomDocument29 pagesD StatcomSai Pranahita Bhaskarapantulu100% (1)
- Devices, Circuits, and Applications: Flexible AC Transmission SystemsDocument40 pagesDevices, Circuits, and Applications: Flexible AC Transmission SystemsAtiq Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Theory of Load CompensationDocument4 pagesTheory of Load CompensationBOOPATHI YADAVNo ratings yet
- Review of Reactive Power Compensation TechnologiesDocument79 pagesReview of Reactive Power Compensation TechnologiesRadu BabauNo ratings yet
- PSOC 2 Marks With AnswerDocument10 pagesPSOC 2 Marks With AnswerAnbalagan GuruNo ratings yet
- FACTs Controllers NotesDocument17 pagesFACTs Controllers NotesrajashekarmandiNo ratings yet
- Facts & Power SystemsDocument60 pagesFacts & Power SystemsSree ShobhaNo ratings yet
- Converter-Based FACTS ControllersDocument11 pagesConverter-Based FACTS Controllerssrikanth velpulaNo ratings yet
- DRPCDocument7 pagesDRPCSelvaraj JohnNo ratings yet