Professional Documents
Culture Documents
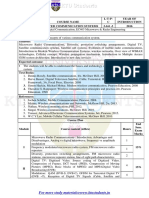
Wireless Communications EX 751: Lecture: 3 Year: IV Tutorial: 0 Part: II Practical: 1.5
Uploaded by
BineilKcThapa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pagesyllabus
Original Title
Wireless Comm
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsyllabus
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageWireless Communications EX 751: Lecture: 3 Year: IV Tutorial: 0 Part: II Practical: 1.5
Uploaded by
BineilKcThapasyllabus
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
3.7.
Types of smallscale fading (flat, frequency selective, fast, slow),
WIRELESSCOMMUNICATIONS RayleighandRiceanfadingdistribution
EX751 4. ModulationDemodulationmethodsinmobilecommunications(4 hours)
Lecture :3 Year :IV
Tutorial :0 Part :II 4.1. Review of amplitude (DSB, SSB, VSB) and angle (frequency, phase)
Practical :1.5 modulationsanddemodulationtechniques
4.2. Reviewoflinecoding,digitallinear(BPSK,DPSK,QPSKs)andconstant
CourseObjectives: envelop (BFSK, MSK, GMSK) modulation and demodulation
To introduce the student to the principles and building blocks of wireless techniques
communications. 4.3. Mary(MPSK,MFSK,QAMandOFDM)modulationanddemodulation
techniques
1. Introduction (2hours) 4.4. Spread spectrum modulation techniques, PN sequences, direct
1.1. Evolution of wireless (mobile) communications, worldwide market, sequenceandfrequencyhoppedspreadspectrums
examples 4.5. Performancecomparisonofmodulationstechniquesinvariousfading
1.2. Comparisonofavailablewirelesssystems,trends channels
1.3. Trends in cellular radio (2G, 2.5G, 3G, beyond 3G) and personal
wirelesscommunicationsystems 5. Equalizationanddiversitytechniques (4hours)
5.1. Basicsofequalization.Equalizationincommunicationsreceivers,linear
2. Cellularmobilecommunicationconcept (4hours) equalizers
2.1. Frequencyreuseandchannelassignmentstrategies 5.2. Nonlinear equalization, decision feedback and maximum likelihood
2.2. Handoffstrategies,types,priorities,practicalconsiderations sequenceestimationequalizations
2.3. Interference and system capacity, cochannel and adjacent channel 5.3. Adaptive equalization algorithms, zero forcing, least mean square,
interference,powercontrolmeasures recursiveleastsquaresalgorithms,fractionallyspacedequalizers
2.4. Gradeofservice,definition,standards 5.4. Diversitymethods,advantagesofdiversity,basicdefinitions
2.5. Coverageandcapacityenhancementincellularnetwork,cellsplitting, 5.5. Space diversity, reception methods (selection, feedback, maximum
sectoring,repeaters,microcells ratioandequalgaindiversity)
5.6. Polarization,frequencyandtimediversity
3. Radiowavepropagationinmobilenetworkenvironment (12hours) 5.7. RAKEreceiversandinterleaving
3.1. Freespacepropagationmodel,radiatedpowerandelectricfield
6. Speechandchannelcodingfundamentals (4hours)
3.2. Propagation mechanisms (largescale path loss) Reflection, ground
6.1. Characteristics of speech signals, frequency domain coding of speech
reflection,diffractionandscattering (subbandandadaptivetransformcoding)
3.3. Practicallinkbudgetdesignusingpathlossmodels. 6.2. Vocoders (channel, formant, cepstrum and voiceexcited ), Linear
3.4. Outdoor propagation models (LongleyRice, Okumura, Hata, Walfisch predictivecoders(multipulse,codeandresidualexcitedLPCs),Codec
andBertoni,microcell) forGSMmobilestandard
3.5. Indoorpropagationmodels(partition losses,longdistancepathloss, 6.3. Review of block codes, Hamming, Hadamard, Golay, Cyclic, Bosh
multiplebreakpoint,attenuationfactor) ChaudharyHocquenghgem(BCH),ReedSolomon(RS)codes
3.6. Small scale fading and multipath (factors, Doppler shift), Impulse 6.4. Convolutional codes, encoders, coding gain, decoding algorithms
response model of multipath channel, multipath measurements, (Viterbiandothers)
parametersofmobilemultipathchannel(timedispersion,coherence 6.5. TrellisCodeModulation(TCM),Turbocodes
bandwidth,Dopplerspreadandcoherencetime)
You might also like
- Wireless Ms Zaiba Ishrat - TEC-801Document27 pagesWireless Ms Zaiba Ishrat - TEC-801seemarahulNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Course OutlineDocument3 pagesWireless Communication Course OutlineabdiNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument3 pagesCourse OutlineIhsan ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Course Description - 16B1NEC832 - MIMO-OFDM APPLICATION TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATION-1Document3 pagesCourse Description - 16B1NEC832 - MIMO-OFDM APPLICATION TO WIRELESS COMMUNICATION-1swapnilNo ratings yet
- Data Communication EG 2211 CT: Course DescriptionDocument3 pagesData Communication EG 2211 CT: Course DescriptionPadam BistaNo ratings yet
- NptelDocument3 pagesNptelAbhay GargNo ratings yet
- 5th Sem - Ece - CurriculumDocument10 pages5th Sem - Ece - Curriculumdhindsaharmanjatt2003No ratings yet
- ECE220 Principles CommunicationDocument2 pagesECE220 Principles Communicationraghav dhamaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: LP-EC1451 LP Rev. No: 02 Date: 05/12/2009 Page 01 of 06Document6 pagesLesson Plan: LP-EC1451 LP Rev. No: 02 Date: 05/12/2009 Page 01 of 06Lokesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- 31 Ec647Document2 pages31 Ec647armen zarNo ratings yet
- Data Communication LessonsDocument6 pagesData Communication LessonsSeniorankNo ratings yet
- Large-Scale Empirical Model For A 2.4 GHZDocument4 pagesLarge-Scale Empirical Model For A 2.4 GHZirfanahmed446470No ratings yet
- Course Outline: International Islamic University MalaysiaDocument3 pagesCourse Outline: International Islamic University MalaysiaEng-Ahmed ShabellNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communications Design FundamentalsFrom EverandMobile Communications Design FundamentalsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Principles of Communication (3-0-2)Document3 pagesPrinciples of Communication (3-0-2)Anil MarsaniNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication BIT471CO: Year: IV Semester: VIIIDocument4 pagesWireless Communication BIT471CO: Year: IV Semester: VIIIDewsun RiseonNo ratings yet
- APznzaYc 47yFiR3aqYmtKbgOEoIjB2y5F5mFrMjDiibpfdPFcR FkGSxW1zEMWfX5PHZZcJ0PlBE0Z LX012mrL0PKpyvsyGe5q TGEl61Bu9izwz 87gUbYN7A0FUpiA2Y HWr2IJ BetaeflgBR1nawSCycWcfQbMmoyH88xqlvyOAXp VjCXF9O3wn9eum191KyfaHv0pfmRWf1hiDocument2 pagesAPznzaYc 47yFiR3aqYmtKbgOEoIjB2y5F5mFrMjDiibpfdPFcR FkGSxW1zEMWfX5PHZZcJ0PlBE0Z LX012mrL0PKpyvsyGe5q TGEl61Bu9izwz 87gUbYN7A0FUpiA2Y HWr2IJ BetaeflgBR1nawSCycWcfQbMmoyH88xqlvyOAXp VjCXF9O3wn9eum191KyfaHv0pfmRWf1hiCHIRAG JINDALNo ratings yet
- EC404 Advanced Communication SystemsDocument2 pagesEC404 Advanced Communication SystemsanupvasuNo ratings yet
- IWCC Lession Plan 2022Document2 pagesIWCC Lession Plan 2022jraviskdNo ratings yet
- MIMO OFDM for Wireless LANsDocument256 pagesMIMO OFDM for Wireless LANsAhmed FadulNo ratings yet
- ExtcDocument15 pagesExtcapi-236544093No ratings yet
- CS6301 - Analog and Digital Communication (ADC) PDFDocument122 pagesCS6301 - Analog and Digital Communication (ADC) PDFSoumitra BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Multi-Carrier and Spread Spectrum Systems: From OFDM and MC-CDMA to LTE and WiMAXFrom EverandMulti-Carrier and Spread Spectrum Systems: From OFDM and MC-CDMA to LTE and WiMAXNo ratings yet
- SSC Unit 01 IntroductionDocument32 pagesSSC Unit 01 Introductionadnan MengalNo ratings yet
- 2EC444 Wireless CommunicationDocument1 page2EC444 Wireless CommunicationDhaval PatelNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Channel Models: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandMultiple-Input Multiple-Output Channel Models: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- WSN Unit 2Document14 pagesWSN Unit 2Sandeep Kumar MekapothulaNo ratings yet
- Advanced 3G and 4G Wireless MobileDocument2 pagesAdvanced 3G and 4G Wireless MobileApoorva AakarshNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication SyllabusDocument2 pagesMobile Communication Syllabusflampard24No ratings yet
- WWW - Nptel.iitm - Ac.in Syllabus Syllabus PDF 117103016Document3 pagesWWW - Nptel.iitm - Ac.in Syllabus Syllabus PDF 117103016Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- An Enhancement On The Traditional Concept Wherein The Radio Is and Its, Is Able To, and Is Capable of FollowingDocument25 pagesAn Enhancement On The Traditional Concept Wherein The Radio Is and Its, Is Able To, and Is Capable of FollowingAnusha Somavarapu100% (1)
- Bece307l Wireless-And-Mobile-Communications TH 1.0 0 Bece307lDocument3 pagesBece307l Wireless-And-Mobile-Communications TH 1.0 0 Bece307lyv5pgh7z84No ratings yet
- Bece306l - Digital-Communication-Systems - TH - 1.0 - 71 - Bece306l - 66 AcpDocument2 pagesBece306l - Digital-Communication-Systems - TH - 1.0 - 71 - Bece306l - 66 AcpMansi MalaykaNo ratings yet
- Csi ZG520 Course HandoutDocument7 pagesCsi ZG520 Course Handoutdeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Radio Research and Implementation ChallengesDocument2 pagesCognitive Radio Research and Implementation ChallengesMisfa SusantoNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communications and NetworksDocument3 pagesWireless Communications and NetworksNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- A Unified Approach To The PerformanceDocument18 pagesA Unified Approach To The PerformanceTerim ErdemlierNo ratings yet
- BOS Final - 4 Sem - 18EC42Document4 pagesBOS Final - 4 Sem - 18EC42‡ ‡AnuRaG‡‡No ratings yet
- Mel ZG520 Course HandoutDocument7 pagesMel ZG520 Course HandouteadaladarenuNo ratings yet
- List of ElectiveDocument21 pagesList of ElectiveANUJ100% (2)
- Pcs PDFDocument2 pagesPcs PDFDisha SinghNo ratings yet
- ECE Elective SyllabusDocument34 pagesECE Elective SyllabusPratyush ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Techniques and Applications in Radar Image ProcessingFrom EverandDigital Signal Processing Techniques and Applications in Radar Image ProcessingNo ratings yet
- Detail MIMO Wireless CommunicationsDocument4 pagesDetail MIMO Wireless Communicationsshakeel1900No ratings yet
- Course Name: Advanced DWDM Duration: Three Days Course ObjectiveDocument3 pagesCourse Name: Advanced DWDM Duration: Three Days Course ObjectiveSumit DuttNo ratings yet
- Program of Electrical and Computer Engineering Wolaita Sodo University, College of EngineeringDocument4 pagesProgram of Electrical and Computer Engineering Wolaita Sodo University, College of EngineeringkattaswamyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of MIMO Wireless CommunicationsDocument371 pagesFundamentals of MIMO Wireless CommunicationsYuvaraj BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Eight SemDocument1 pageEight Semapi-19497192No ratings yet
- Wireless and Mobile Communications: InstructorDocument43 pagesWireless and Mobile Communications: InstructorRaja Iftikhar HaiderNo ratings yet
- Multiple Antenna Technique OverviewDocument51 pagesMultiple Antenna Technique Overviewsyafrilrifai007No ratings yet
- EE4188 Wireless Communications - OBTLDocument7 pagesEE4188 Wireless Communications - OBTLAaron TanNo ratings yet
- 6th Semester SyllabusDocument5 pages6th Semester SyllabusmahyahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction: Kobid Karkee Kobidkarkee@kec - Edu.np Kantipur Engineering College Dhapakhel, LalitpurDocument28 pagesChapter 1: Introduction: Kobid Karkee Kobidkarkee@kec - Edu.np Kantipur Engineering College Dhapakhel, LalitpurBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- Text Completion ContextDocument4 pagesText Completion ContextBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- NewDocument2 pagesNewBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- Science FeeDocument1 pageScience FeeBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- Text Completion ContextDocument4 pagesText Completion ContextBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- Install Utorrent and Close The Application in The System Tray. Run Fix - Exe Enjoy:)Document1 pageInstall Utorrent and Close The Application in The System Tray. Run Fix - Exe Enjoy:)BineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- What Is Life ? Life Is The Most Amazaing Gift From GodDocument1 pageWhat Is Life ? Life Is The Most Amazaing Gift From GodBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-08-28 20.51.30 - 2Document1 pageNew Doc 2019-08-28 20.51.30 - 2BineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- Palmistry Guide: Understanding Lines and Mounts on Your HandDocument61 pagesPalmistry Guide: Understanding Lines and Mounts on Your HandBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- Project Management: B.E. Tribhuwan University, IOEDocument15 pagesProject Management: B.E. Tribhuwan University, IOEBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- ClassDocument1 pageClassBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing EX 753: Lecture: 3 Year: IV Tutorial: 1 Part: II Practical: 1.5Document1 pageDigital Signal Processing EX 753: Lecture: 3 Year: IV Tutorial: 1 Part: II Practical: 1.5BineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communications EX 751: Lecture: 3 Year: IV Tutorial: 0 Part: II Practical: 1.5Document1 pageWireless Communications EX 751: Lecture: 3 Year: IV Tutorial: 0 Part: II Practical: 1.5BineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- In Brief HereDocument3 pagesIn Brief HereBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- In Brief HereDocument3 pagesIn Brief HereBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 Aeronautical CommunicationDocument12 pagesCh-2 Aeronautical CommunicationBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- Ch-3 Aeronautical NavigationDocument39 pagesCh-3 Aeronautical NavigationBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- Mega RecoverykeyDocument1 pageMega RecoverykeyBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- FeasibilityDocument1 pageFeasibilityBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- HereDocument1 pageHereBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- Hybrid TransformersDocument1 pageHybrid TransformersBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- BitLocker Recovery Key 7B846EEC 12B8 4A39 8CB7 1619643B3508Document1 pageBitLocker Recovery Key 7B846EEC 12B8 4A39 8CB7 1619643B3508BineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- HereDocument1 pageHereBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- What Is Differntial EquationDocument2 pagesWhat Is Differntial EquationBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- Project Management: B.E. Tribhuwan University, IOEDocument15 pagesProject Management: B.E. Tribhuwan University, IOEBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- M Ary SignallingDocument89 pagesM Ary Signallingsukhween100% (4)
- Application of J or IDocument3 pagesApplication of J or IBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- Bexq Iv IDocument86 pagesBexq Iv IBineilKcThapaNo ratings yet
- BS en 12405-3-2015Document82 pagesBS en 12405-3-2015Doiciel100% (1)
- Technical Indicator Builder User Guide MT4Document24 pagesTechnical Indicator Builder User Guide MT4Eduardo NevesNo ratings yet
- Capeta 23Document55 pagesCapeta 23janof1No ratings yet
- Abrasion TestDocument7 pagesAbrasion TestMohd SyahrulizamNo ratings yet
- GNSS Processing Report for TDTV MarkerDocument9 pagesGNSS Processing Report for TDTV MarkerJoshua Paskah NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Airbus Techdata AC A321 0322Document434 pagesAirbus Techdata AC A321 0322Mario AntonioNo ratings yet
- 188524-01, DW502 DW504 La - EngDocument9 pages188524-01, DW502 DW504 La - EngCilvio LewlawskyjNo ratings yet
- SBI Online Registration Form for CINB SaralDocument1 pageSBI Online Registration Form for CINB Saralamitjainis60% (5)
- Standards Summary Sheet - ANSI A10.8-2011Document2 pagesStandards Summary Sheet - ANSI A10.8-2011DwiCahyoAgustino100% (1)
- Linear IC Voltage RegulatorsDocument11 pagesLinear IC Voltage RegulatorsJavier Avalos GallosNo ratings yet
- Registered Contractor List PPADBDocument3 pagesRegistered Contractor List PPADBGaone Lydia SetlhodiNo ratings yet
- Microscope 101: How To Safely Use A Microscope: Preparing A Wet-Mount SlideDocument2 pagesMicroscope 101: How To Safely Use A Microscope: Preparing A Wet-Mount SlideClara AbegãoNo ratings yet
- HVAC-Indoor AC-LG-Cassette 4 Way 2x2Document4 pagesHVAC-Indoor AC-LG-Cassette 4 Way 2x2Ashar HassanNo ratings yet
- Bus ID No.: E-1347: Passenger InformationDocument1 pageBus ID No.: E-1347: Passenger InformationVignesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ac6905a DatasheepDocument10 pagesAc6905a DatasheepMUSIC ELECNo ratings yet
- 300nb Fire Water Line - BEEL - 071953Document2 pages300nb Fire Water Line - BEEL - 071953irshadiiitNo ratings yet
- Nut, Double Hexagon, Self Locking: Page 1/3Document3 pagesNut, Double Hexagon, Self Locking: Page 1/3Renato WatanabeNo ratings yet
- Behringer X-TOUCH: Universal Control SurfaceDocument15 pagesBehringer X-TOUCH: Universal Control SurfaceManuel Becerra RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Q4FY23 Investor PresentationDocument49 pagesQ4FY23 Investor PresentationAradhyaNo ratings yet
- Standby Leakage Power Reduction in Digital CircuitsDocument4 pagesStandby Leakage Power Reduction in Digital CircuitsmadhuNo ratings yet
- AW169 Executive and Private Transport Brochure - Gen2020Document8 pagesAW169 Executive and Private Transport Brochure - Gen2020Lavern P. SipinNo ratings yet
- Quality Planning ProcessDocument47 pagesQuality Planning ProcessRAZOR GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Motorola Moto G (2014) ManualDocument68 pagesMotorola Moto G (2014) ManualXBNo ratings yet
- Quot - Leak Tester BP Ridwan - PTI Cosmetics - 08apr21Document6 pagesQuot - Leak Tester BP Ridwan - PTI Cosmetics - 08apr21mario gultomNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Assembly Language For x86 Processors 7th Edition Irvine Test Bank PDFDocument33 pagesDwnload Full Assembly Language For x86 Processors 7th Edition Irvine Test Bank PDFjovialtybowbentqjkz88100% (14)
- Module Chapter 4 - GE 106Document7 pagesModule Chapter 4 - GE 106Justin Roi ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- TLC Online Learning Packs Brochure 2020Document20 pagesTLC Online Learning Packs Brochure 2020trongnvtNo ratings yet
- AWM 5000 Series Microbridge Mass Airflow Sensor: Installation Instructions For TheDocument2 pagesAWM 5000 Series Microbridge Mass Airflow Sensor: Installation Instructions For ThewidsonmeloNo ratings yet
- Solis 10K PDFDocument15 pagesSolis 10K PDFVictor Rios GarciaNo ratings yet
- Isogeometric Analysis For Modeling and Simulation of Building ProcessesDocument11 pagesIsogeometric Analysis For Modeling and Simulation of Building Processes董思辰No ratings yet