Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IV Fluids Chart PDF
IV Fluids Chart PDF
Uploaded by
Miguel Cuevas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
IV fluids chart.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageIV Fluids Chart PDF
IV Fluids Chart PDF
Uploaded by
Miguel CuevasCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
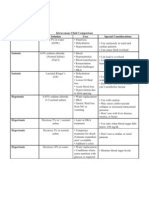
Intravenous Fluid Comparison
Type Solution Uses Special Considerations
Dextrose 5% in water Fluid loss Use cautiously in renal and cardiac patients
Isotonic (D5W) Dehydration Can cause fluid overload
Hypernatremia
Shock Can lead to overload
0.9% sodium chloride Hyponatremia Use with caution in patients with heart failure or
Isotonic (Normal Saline) Blood transfusions edema
(NaCl) Resuscitation
Fluid challenges
DKA
Dehydration Contains potassium, dont use with renal failure
Burns patients
Isotonic Lactated Ringers Lower GI fluid loss Dont use with liver disease, cant metabolize lactate
(LR) Acute blood loss
Hypovolemia due to
third spacing
Water replacement Use with caution
Hypotonic 0.45% sodium chloride DKA May cause cardiovascular collapse or increased
(1/2 normal saline) Gastric fluid loss intracranial pressure
from NG or vomiting Dont use with liver disease, trauma, or burns
Hypertonic Dextrose 5% in Later in DKA Use only when blood sugar falls below 250 mg/dL
normal saline treatment
Temporary treatment Dont use n cardiac or renal patients
Hypertonic Dextrose 5% in normal for shock if plasma
saline expanders arent
available
Addisons crisis
Water replacement Monitor blood sugar levels
Hypertonic Dextrose 10% in water Conditions where
some nutrition with
glucose is required
You might also like
- Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Part I: Emergency Department (ED)Document8 pagesNovel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Part I: Emergency Department (ED)Uzumaki K100% (1)
- IV Solution Cheat SheetDocument13 pagesIV Solution Cheat Sheetisapatrick8126100% (4)
- NarcanDocument1 pageNarcanKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- IV Solutions Reference Chart (Uses & Effects)Document1 pageIV Solutions Reference Chart (Uses & Effects)jkbills94% (17)
- Lab Normals Chart For NursesDocument2 pagesLab Normals Chart For NursesRavneetKalkatNo ratings yet
- Eliquis Drug Bib CardDocument1 pageEliquis Drug Bib CardTee Wood100% (1)
- IV Solution Cheat SheetDocument1 pageIV Solution Cheat Sheet'Jessie' Poquiz100% (2)
- Monthly Crash Cart InventoryDocument4 pagesMonthly Crash Cart InventoryMenGuitar100% (1)
- IVF Table of Commonly Used IV SolutionsDocument3 pagesIVF Table of Commonly Used IV SolutionsKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- GMO Investigator Kit ManualDocument84 pagesGMO Investigator Kit ManualMariela LopezNo ratings yet
- RFF TB Units 1 6Document89 pagesRFF TB Units 1 6Lucia Silva0% (1)
- Emergency DrugsDocument17 pagesEmergency Drugsapi-3853350100% (12)
- Table of Commonly Used IV SolutionsDocument3 pagesTable of Commonly Used IV Solutionsmara514081% (16)
- 24 Emergency DrugsDocument7 pages24 Emergency DrugsApple BelicanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Fluid and Electrolytes ChartsDocument7 pagesChapter 14 Fluid and Electrolytes ChartsBNA_RN100% (3)
- Medical Surgical Nursing Common Drugs and Its AntidotesDocument2 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Common Drugs and Its AntidotesJhannNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DrugsDocument12 pagesCardiovascular DrugshannahcoNo ratings yet
- Ecart DrugsDocument1 pageEcart DrugsKarla JaneNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument14 pagesDrug Study On Emergency Drugsjcarysuitos100% (4)
- "Emergency Drugs": Pictures/ Generic Name Brand Name/ Classification/ Stock Dose/ Indication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument7 pages"Emergency Drugs": Pictures/ Generic Name Brand Name/ Classification/ Stock Dose/ Indication Nursing ResponsibilitiesJohn Balgoa100% (2)
- Fluid ElectrolytesDocument6 pagesFluid ElectrolytesKareem Mae Pines RaborNo ratings yet
- Drug CalculationsDocument78 pagesDrug CalculationsNader Smadi100% (9)
- Different Iv FluidsDocument2 pagesDifferent Iv FluidsBeverly DatuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument15 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsDennise Juayang100% (1)
- PEDIA PresentationDocument195 pagesPEDIA PresentationKatrina Lim-HatagueNo ratings yet
- Drug Computations 1Document9 pagesDrug Computations 1Alex Olivar100% (1)
- Digoxin Drug CardDocument1 pageDigoxin Drug CardMahsa Ahmadzadeh100% (2)
- Saunders Comprehensive Review Nclex - Fluids - ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesSaunders Comprehensive Review Nclex - Fluids - Electrolytesissaiahnicolle100% (1)
- HaemodialysisDocument98 pagesHaemodialysisKo Zin100% (1)
- Emergency DrugsDocument47 pagesEmergency DrugsBesiman100% (1)
- Crash Cart Drugs 1Document23 pagesCrash Cart Drugs 1Kristiina MakinenNo ratings yet
- Insulin, Regular (Humulin R)Document1 pageInsulin, Regular (Humulin R)ENo ratings yet
- Week 10 Drug Card - Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)Document2 pagesWeek 10 Drug Card - Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)RCurry09No ratings yet
- AmiodaroneDocument2 pagesAmiodaronekumaninaNo ratings yet
- DKA (Diabetic Ketoacidosis)Document3 pagesDKA (Diabetic Ketoacidosis)Hassan.shehri83% (6)
- Captopril Drug StudyDocument1 pageCaptopril Drug StudyRachel Mae Dente AcedillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesFrom EverandNursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid ComparisonDocument1 pageIntravenous Fluid ComparisonKristine Faith AzcuetaNo ratings yet
- Types of Intravenous FluidsDocument4 pagesTypes of Intravenous FluidsMhaye Ruiz Genturalez RN100% (2)
- IV Fluids Chart-1Document1 pageIV Fluids Chart-1rodtanchoNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte TherapyDocument6 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Therapygilpogs100% (1)
- Types of SolutionDocument3 pagesTypes of SolutionfwarqueenNo ratings yet
- 1IV FluidDocument31 pages1IV FluidManeesha KhalseNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Therapy - NCM 106Document8 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Therapy - NCM 106Hana CyrilNo ratings yet
- I.V Cheat Sheet!Document2 pagesI.V Cheat Sheet!Audrey LeonarNo ratings yet
- Pocket Card - IV Fluids - December 2023Document6 pagesPocket Card - IV Fluids - December 2023Evieta CallysthaNo ratings yet
- IV Fluids - January 2019Document6 pagesIV Fluids - January 2019Benjamin NgNo ratings yet
- IV FluidsDocument6 pagesIV FluidsAr-jay PorrasNo ratings yet
- Pocket Card - IV Fluids - September 2021Document6 pagesPocket Card - IV Fluids - September 2021NeweeJoonYowNo ratings yet
- IV Fluids: CrystalloidsDocument6 pagesIV Fluids: CrystalloidsGlaiza BartolomeNo ratings yet
- REPORTDocument15 pagesREPORTMacen OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Chart Larutan IVDocument3 pagesChart Larutan IVparji santosaNo ratings yet
- Nur2731 3rd Semester Final ReviewDocument196 pagesNur2731 3rd Semester Final Reviewjanet rooseveltNo ratings yet
- Iv Fluids and Solutions With Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument33 pagesIv Fluids and Solutions With Nursing ResponsibilitiesJennie JalemNo ratings yet
- Iv SolutionsDocument12 pagesIv SolutionsRinalyn BalderramaNo ratings yet
- Intravenous FluidsDocument19 pagesIntravenous Fluidsblack pink in ur area 21100% (1)
- IV Fluid Cheat SheetsDocument8 pagesIV Fluid Cheat SheetsNhietz SeraNo ratings yet
- What Are IV FluidsDocument7 pagesWhat Are IV FluidsKATHLEEN MARIE MONTA�ONo ratings yet
- IV Fluids TheoryDocument13 pagesIV Fluids TheoryFRESY TRI SUGIANTONo ratings yet
- Syndrome of Inapropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH)Document15 pagesSyndrome of Inapropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH)Asrul Rahim100% (1)
- RenalGenitourinarySlides 23C 2020 3 Banvir 2cDocument490 pagesRenalGenitourinarySlides 23C 2020 3 Banvir 2cBanvir SinghNo ratings yet
- Icru 38Document14 pagesIcru 38Ronald Koeman Casique Useche100% (2)
- IFPMA Technology Transfer 2015 WebDocument28 pagesIFPMA Technology Transfer 2015 WebpratikNo ratings yet
- Sf1 - 2017 - Grade 9 (Year III) - BonifacioDocument4 pagesSf1 - 2017 - Grade 9 (Year III) - BonifacioHelenLanzuelaManalotoNo ratings yet
- 1.125742 S1 M5 5351 c4591001 Fa Interim Discontinued PatientsDocument112 pages1.125742 S1 M5 5351 c4591001 Fa Interim Discontinued PatientsElvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Alkylhalide 145 PDFDocument33 pagesChapter 6-Alkylhalide 145 PDFKishore KishoreNo ratings yet
- Onychomycosis Treatment and Prevention of Recurrence - 2018Document44 pagesOnychomycosis Treatment and Prevention of Recurrence - 2018Rodrigo Valenzuela MontesNo ratings yet
- DeltaOhm HD98569 Portatif PH Iletkenlik OksijenDocument5 pagesDeltaOhm HD98569 Portatif PH Iletkenlik OksijenEnisNo ratings yet
- SPT Phase 2 DeloadDocument18 pagesSPT Phase 2 DeloadJoel Alejandro Castro CasaresNo ratings yet
- Pan Malayan Insurance Corp. vs. Court of AppealsDocument3 pagesPan Malayan Insurance Corp. vs. Court of AppealsbrendamanganaanNo ratings yet
- Bromide in Drinking-Water PDFDocument15 pagesBromide in Drinking-Water PDFSalem GarrabNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Schools Division of PalawanDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Schools Division of PalawanMarbert GarganzaNo ratings yet
- Virtual Autopsy in Forensic Medicine-00085892Document4 pagesVirtual Autopsy in Forensic Medicine-00085892Fitri Amelia RizkiNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Contagion Movie Assessment 1Document5 pagesRunning Head: Contagion Movie Assessment 1swathim123No ratings yet
- BP Energol GR XP 460Document10 pagesBP Energol GR XP 460meldesastreNo ratings yet
- Buyers' Guide: Multi-Slice CT ScannersDocument181 pagesBuyers' Guide: Multi-Slice CT ScannersvitapabloNo ratings yet
- Catholic Social Teaching in PovertyDocument4 pagesCatholic Social Teaching in Povertyapi-266512667No ratings yet
- 11913-Article Text-58597-1-10-20220915Document6 pages11913-Article Text-58597-1-10-20220915dba.dbaNo ratings yet
- FLORES-Activities For Module 1Document4 pagesFLORES-Activities For Module 1Maureen FloresNo ratings yet
- Competency Gap Analysis Questionnaire - 1.1Document2 pagesCompetency Gap Analysis Questionnaire - 1.1Tracey MorinNo ratings yet
- Major ProjectDocument24 pagesMajor Projectmithu134567No ratings yet
- A&EP - 02 - Sample CalculationsDocument11 pagesA&EP - 02 - Sample CalculationsCesar AguirreNo ratings yet
- Book Reviews: Paediatric AudiologyDocument2 pagesBook Reviews: Paediatric AudiologyHarshit AmbeshNo ratings yet
- Shop Supplies: Alphabetical Table of ContentsDocument56 pagesShop Supplies: Alphabetical Table of ContentsAparecidaMarquesNo ratings yet
- Manualspectrafuge 16 DDocument16 pagesManualspectrafuge 16 DTan Hung LuuNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Studies and LiteratureDocument5 pagesReview of Related Studies and LiteratureJoanalyn Lata100% (5)
- UntitledDocument468 pagesUntitledIndesign IndeNo ratings yet
- PBSP Signature AssessmentDocument45 pagesPBSP Signature Assessmentapi-297261081No ratings yet
- OOS - 2021 - 22 - UAE SST TERM 3 - LESSON 2 - 21st Cetury Infrastructure and Smart Initiatives-AnswerkeyDocument3 pagesOOS - 2021 - 22 - UAE SST TERM 3 - LESSON 2 - 21st Cetury Infrastructure and Smart Initiatives-AnswerkeyLiterally just ReysNo ratings yet