Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HKIE Bowtie PDF
HKIE Bowtie PDF
Uploaded by
NOOR DIANA KHAIRUDDINOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HKIE Bowtie PDF
HKIE Bowtie PDF
Uploaded by
NOOR DIANA KHAIRUDDINCopyright:
Available Formats
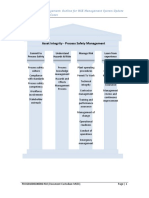
Bow-tie Modellingg in
Effective Safety Risk Control
Lisa Shi
Senior Consultant
5 June 2009
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Objectives
To appreciate the bow-tie concept and its underlying relationship with the
risk management system
To share the key elements for effective safety risk control
To illustrate the key steps of constructing bow-tie model and how it can be
used to strengthen the existing safety management system
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Common Risk Terminologies
Hazard: Any situation that has a potential to cause harm
Risk = Frequency/Probability x Severity
Risk management is the process of:
Making decisions about accepting or altering risks.
Restricting and maintaining risks within tolerable limits at
proportionate cost where elimination of risks is not possible
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Risk Management is about
What can go wrong?
How bad can it get?
How often?
Is it acceptable?
How can we prevent recurrence of incident based on latest available
technology?
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Common Hazard Identification Technique
HAZard and OPerability Studies (HAZOP)
St t d What-IF
Structured Wh t IF Technique
T h i (SWIFT)
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Failure Modes, Effects and Criticality Analysis (FMECA)
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Why do you need a model?
Satisfying legislative requirements
Meeting client operational needs
Complying with international standards or good practices
Evaluating design options
Add
Addressing
i specific
ifi safety
f t concern
Supporting frequency and consequence estimation
Demonstration of as low as reasonably practicable (ALARP)
Identifying safety critical items and systems
Prevent incident from recurrence etc
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Selection of Approach and Level of Details
Objective / subjective
Simple / complex
Technical / non-technical
One-off assessment / continual improvement
Q lit ti / quantitative
Qualitative tit ti / semi-quantitative
i tit ti
Life cycle approach
Novelty
Uncertainty
Stakeholders concern
Cost and business factors
Organisation structure
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Selection of Approach
To make a demonstration means to show, justify or make the case /
argument through the information given
You should clearly identify in the safety report all safety critical events
and the associated initiators. Safety critical events are those that
dominate the contribution to risk, so they should be identified by your risk
analysis
Safety critical events are key to identifying suitable control and protection
measures for preventing hazardous events or limiting their consequences.
However, the failure of these protection measures must also be
considered in assessing whether the residual risks are ALARP or whether
more needs to be done.
[HSE Guidance on Preparing Safety Report 1999]
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Common Difficulties and Pitfalls
Each tool has its strengths and weaknesses, and is not always obvious
which to select
Hard to select a single tool to satisfy all needs e.g. satisfying both
legislative requirements and operational needs at a time
Problems in communicating risks with senior management, frontline and
the public
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Common Difficulties and Pitfalls
Increasing size and inconsistent application of risk register
Tend to focus on hazards only; there is not enough focus on the actual
effectiveness of controls and how they relate to accident sequence
Unclear
U l responsibilities
ibiliti ffor th
the managementt off controls
t l
Often used to justify not to do something
Misunderstanding or misapplication of quantitative risk assessment
Fails to link the critical controls to safety management system
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
ALARP Principle
Unacceptable
Region
ALARP or
tolerability
Region
Broadly
acceptable
region
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Individual Risk Contour Plan and Societal Risk
Criteria for a PHI in HK
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
What is Bow-tie?
Powerful technique in risk and control measures assessment
Structured
St t d approach
h for
f risk
i k analyis
l i off events
t where
h quantification
tifi ti is i nott possible
ibl or
desirable
Combines causes and consequence
q analysis
y into one diagram.
g The diagram
g when
plotted resembles a bowtie
The theory behind the bow-tie approach could be found in the Swiss Cheese model
of Reason and concepts of layer of protection
Earliest mention of concept by ICI in 1979 and Royal Dutch/Shell Group was the first
company fully integrate the method into business practices
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Swiss-cheese Model for Accident Causation
Each slice of cheese represents a safety barrier or precaution relevant to a particular hazard
HAZARD
Incident
James T
J T. Reason
R (1997)
(1997),
Managing the Risks of
Organizational Accidents
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Case Study Bhopal Disaster in India
Background
December 1984
MIC tank alarms had not worked for 4 years
Vent gas scrubber had been out of service
for 5 months
Missing of slip-blind plate
Leaking carbon steel valve
Event
Exposing more than 500,000 people to toxic
gas and an estimate of 25
25,000
000 died
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Case Study Bhopal Disaster in India
Major Findings
Plant production process and MIC storage
Work conditions and reduce expense
Culture difference
Serious communication problems and management gaps
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Case Study Bhopal Disaster in India
Equipment failure happened just before the incident was not the only cause of the
incident
HAZARD
Lack of
Equipment emergency
failure response plans
Lack of skilled
operators due to the
staffing policy
Explosion
Reduction of
safety
Insufficient
management
maintenance of
the plant
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Case Study Bhopal Disaster in India
Many accidents could be prevented by identifying a series of preventable
events and their causes
We need to focus not only on the quantity of controls but also the quality
of controls (ensure critical parts of the system are implemented and
managed properly!!!)
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
What is Bow-tie?
Critical Activity/Task
Inspection
Maintenance
Operations
C
THREAT O
H N
A S
Z E
A THREAT
TOP Q
R EVENT
U
D E
S N
C
THREAT
RECOVERY E
PREPAREDNESS S
PREVENTIVE MEASURES
BARRIERS
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
What are the advantages of bow-tie diagram?
Just learn it first, develop one and then ask!
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Common Hazard Information in Hazard Log / Risk
Register
Hazard ID
H
Hazarddddescription
i ti
Cause
Consequence
Control measure
Probability / frequency
Severity
Risk ranking
Risk owner
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Bow-tie Construction (Example)
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Bow-tie Construction (Example)
Hazard Any situation that has a potential to cause harm
Top Event The release of hazard.
Threat Any possible cause that will potentially release a hazard and
result in a undesirable top event.
Preventive A protective measure to prevent threat(s) from releasing a
Barrier hazard
hazard.
Recovery A preparedness measure to recover or reduce risks if the top
Measure event occurs or measure to limit the severity of the outcome.
Consequence Condition/event(s) that result from the release of hazard / top
event.
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Steps for Bow-tie Modelling
1. Develop a bow-tie model to show the problem clearly including HAZARD and TOP EVENT
2. Identify the THREATS that can cause the problem
3. Display the BARRIERS to prevent the problem occurring
4. Describe the potential CONSEQUENCES
5. Identify the RECOVERY MEASURES required should the problem occur
6. Identify ESCALATION FACTOR and ESCALATION FACTORS CONTROL
7. Identify TASKS and RESPONSIBILITIES
8. Link the controls to SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Example Identify Hazard and Top Event
Hazard: Trackside Works
Top Event: Trackside Worker Struck/Crushed by Train
Knot = hazardous event.
Wh t we dont
What d t wantt to
t
happen
HAZ01 -
Trackside Works
(Trackside
Worker
Struck/Crushed
by Train)
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Example Identify Threats
Enter the threats that could cause the event to occur (left hand side),
for example
Driver/track machine operator error
Worker error inattention
Unsafe / inappropriate system of work employed by workers
Inappropriate lighting
SPAD
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Example - Identify Consequences
Enter the consequences of the event occurring (right hand side)
Fatality
Injury
Damaged equipment
Etc
Etc.
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Example Identify Preventive Barriers
Enter the barriers to prevent the event occurring (between threat and top event)
Driver/track machine Competence Health & Wellness Regular Train / machine
operator error Random D&A testing
assurance Program briefings/induction operating procedures
Worker error - Work Group
inattention Fenced areas/barriers Hi Vi vest Medical standards Staff vigilance Use of train horn
Supervision
Unsafe /
Inappropriate system
Competence Engineering work Safe working method Safety inspections /
of work employed by Job safety analysis
assurance rules statements audits
workers
HAZ01 -
Trackside Works
(Trackside
Worker
Struck/Crushed
Inappropriate lighting Engineering work
Train lights by Train)
rules
Competence
assurance, Train crew
Signal Passed at
Signal sighting training, Train Health & Wellness
danger Catch/trap points Train stop
committee operating procedures Program
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
......
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Example Identify Recovery Measures
Enter the recovery measures to mitigate against the consequences
First aid provisions Communication and Fatality
Emergency Plan Emergency protection
and training command control
HAZ01 -
Trackside Works
(Trackside
Worker
Struck/Crushed
byy Train)) Communication and First aid provisions
Emergency protection Emergency Plan Injury
command control and training
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Hierarchy of Control Consideration
Elimination Controls
Preventive Controls
Reduction Controls
Mitigation Controls
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Key Factors Affecting Quality of Controls
Importance
Relevance
Specificity
Effectiveness
Reliability
Compliance
p
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Other Considerations in Bow-tie Models
Escalation Factor- Condition that leads to loss of preventive barrier(s) or
loss of recovery preparedness measure(s)
Escalation Factor Control - Control(s) put in place to manage conditions
that lead to loss of preventive barrier(s) or recovery preparedness
measure(s)
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Outputs of Bow-tie Modelling
Better understanding of incident/accident sequences
Easy to conceptualise and visualise
Better communication process, especially between different levels of the organisation
Helps to prioritise the importance of control measures, support the managers /
g
managements need to oversee a broad spectrum
p / scope
p / different types
yp of risk that
they own
Link the safety critical activities back to the Safety Management System and effective
monitoring and control of risks
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Link the tasks to barriers back to SMS
How will the barrier fail?
Can we improve the effectiveness of control?
What tasks or actions do we need to do to make sure the control
continues to work?
Who is currently doing the task?
Is the staff competent for doing the task?
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
Key Notes for Bow-tie Modelling
Understanding of existing risk decision making process
D
Decision
i i fframework
kbbased
d on stakeholder
t k h ld and d operational
ti l needs
d should
h ld
be developed to maximise the strength of each tool
Develop
p links between risk register
g and bow-tie diagrams
g
Develop criteria for evaluating barrier effectiveness and importance
The bow-tie model is not intended for use in quantification of risks,
however, it supports frequency and consequence analysis and allow
detailed quantified risk analysis to be developed
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
For more information, please contact:
Lisa Shi
T +852 2287 9351
F +852 2845 2616
E lisa.shi@lr.org
The Lloyds Register Group
works to enhance safety and
approve assets and systems at
sea, on land and in the air
because life matters.
Technical Seminar for HKIE and HKARMS
LLOYDS REGISTER RAIL
You might also like
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsFrom EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Bow Ties in Risk Management: A Concept Book for Process SafetyFrom EverandBow Ties in Risk Management: A Concept Book for Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyFrom EverandGuidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- Exxon - OIMS - Framework - Brochure PDFDocument20 pagesExxon - OIMS - Framework - Brochure PDFeayujigNo ratings yet
- Asset Integrity Process Safety Management Improvements PDODocument15 pagesAsset Integrity Process Safety Management Improvements PDOMash Harthy100% (2)
- Safety Critical Elements / Equipment (SCE) Management ProcessDocument61 pagesSafety Critical Elements / Equipment (SCE) Management Processfredo405100% (14)
- Safety Critical Elements ManagamentDocument34 pagesSafety Critical Elements Managamentsjarvis5100% (2)
- Question Set - Asset IntegrityDocument5 pagesQuestion Set - Asset IntegrityAmal A.No ratings yet
- RiskMetrics (Monitor)Document24 pagesRiskMetrics (Monitor)Angel Gutiérrez ChambiNo ratings yet
- PSM Auditing (Presentation)Document25 pagesPSM Auditing (Presentation)kanakarao1100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Asset Integrity Implementation Module 1Document5 pagesFundamentals of Asset Integrity Implementation Module 1SARFRAZ ALINo ratings yet
- Risk Management Module 3 SummaryDocument6 pagesRisk Management Module 3 SummaryNdomaduNo ratings yet
- Essential Practices for Creating, Strengthening, and Sustaining Process Safety CultureFrom EverandEssential Practices for Creating, Strengthening, and Sustaining Process Safety CultureNo ratings yet
- Guide for Asset Integrity Managers: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategies, Practices and BenchmarkingFrom EverandGuide for Asset Integrity Managers: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategies, Practices and BenchmarkingNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Engineering Design for Process SafetyFrom EverandGuidelines for Engineering Design for Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- H PSAF RAINALDI Process Safety PDFDocument12 pagesH PSAF RAINALDI Process Safety PDFanton100% (1)
- A Practical Approach To Managing Safety Critical Equipment and Systems in Process PlantsDocument10 pagesA Practical Approach To Managing Safety Critical Equipment and Systems in Process Plantsfredo405No ratings yet
- Intro To PSM at UI-WCP Oct 2019 (Workshop)Document60 pagesIntro To PSM at UI-WCP Oct 2019 (Workshop)Aditya SetiadiNo ratings yet
- Asset Integrity Process Safety Visible Leadership QuestionsDocument20 pagesAsset Integrity Process Safety Visible Leadership Questionsqaisarabbas9002100% (10)
- BOWtie HSE UKDocument92 pagesBOWtie HSE UKRmz ExeNo ratings yet
- OGP Asset Integrity - The Key To Managing Major Incident RisksDocument20 pagesOGP Asset Integrity - The Key To Managing Major Incident Risksdediekos100% (1)
- Hsse Asset Integrity GuideDocument73 pagesHsse Asset Integrity Guideranjitpandey100% (7)
- Asset Integrity Directive PDFDocument25 pagesAsset Integrity Directive PDFLuke Fielding100% (1)
- Preparation of A Safety CaseDocument39 pagesPreparation of A Safety Casebaaziz2015100% (2)
- UKOOA Asset Integrity Key Performance Indicator For Use in The UK OIL and GAS INDUSTRYDocument10 pagesUKOOA Asset Integrity Key Performance Indicator For Use in The UK OIL and GAS INDUSTRYEyoma EtimNo ratings yet
- AI-PS Element Guide No 10Document9 pagesAI-PS Element Guide No 10eankiboNo ratings yet
- PSM Element 1Document38 pagesPSM Element 1Mircea CaprarNo ratings yet
- Process Safety AlarpDocument20 pagesProcess Safety Alarpvisutsi100% (1)
- What Is Process Safety EngineeringDocument3 pagesWhat Is Process Safety EngineeringCLPWC100% (11)
- AI-PS Element Guide No 13Document10 pagesAI-PS Element Guide No 13rwerwerwNo ratings yet
- Safety Critical Elements - Performanace Standards EngineeringDocument4 pagesSafety Critical Elements - Performanace Standards EngineeringKarthikeyan Varathan100% (1)
- Hazid: Hazard & IdentificationDocument29 pagesHazid: Hazard & IdentificationJagan Bose100% (1)
- Process Safety CompetencyDocument32 pagesProcess Safety CompetencyFelipe Miguel Sánchez Clements100% (4)
- Process Safety Performance IndicatorsDocument30 pagesProcess Safety Performance Indicatorskanakarao1100% (2)
- Learning Lessons From IncidentsDocument37 pagesLearning Lessons From IncidentsAugusto Serrano50% (2)
- Monthly Infoshare Meeting 02 SCE Impaired WorkshopDocument23 pagesMonthly Infoshare Meeting 02 SCE Impaired Workshopcloudno911100% (2)
- Integrity Management of Safety Critical Equipment and SystemsDocument10 pagesIntegrity Management of Safety Critical Equipment and SystemsLi QiNo ratings yet
- Asset IntegrityDocument21 pagesAsset Integrityrimas004No ratings yet
- BowTie TheoryDocument35 pagesBowTie Theorysaban2139100% (2)
- Process Safety Management Guidelines For ComplianceDocument16 pagesProcess Safety Management Guidelines For CompliancewinarnobNo ratings yet
- Section 43 - Process Hazard Analysis Protocol PDFDocument5 pagesSection 43 - Process Hazard Analysis Protocol PDFzironelNo ratings yet
- Pre Startup Safety ReviewDocument29 pagesPre Startup Safety ReviewAhsan100% (1)
- Your Quick Guide To Process Safety ManagementDocument5 pagesYour Quick Guide To Process Safety ManagementArunachalam AvanashiNo ratings yet
- AI-PS Element Guide No 6Document10 pagesAI-PS Element Guide No 6rwerwerwNo ratings yet
- Process Safety Management OutlineDocument24 pagesProcess Safety Management Outlineismailines100% (1)
- Handbook On Process Safety Integrity For Utility Operators PDFDocument135 pagesHandbook On Process Safety Integrity For Utility Operators PDFJose AlvarezNo ratings yet
- CCPS Monograph Reflections From Global Process Safety LeadersDocument29 pagesCCPS Monograph Reflections From Global Process Safety LeadersKiranNo ratings yet
- Day 5 - Hazop Procedure For CompanyDocument57 pagesDay 5 - Hazop Procedure For CompanyPablo CastroNo ratings yet
- Bow Ties and Offshore Safety StudiesDocument3 pagesBow Ties and Offshore Safety StudiesPillai Sreejith100% (7)
- 09 1HAZOPStudyTrainingCourseDocument55 pages09 1HAZOPStudyTrainingCoursehelton_bsbNo ratings yet
- OGDCL Safety Critical Elements Handbook Final PDFDocument106 pagesOGDCL Safety Critical Elements Handbook Final PDFSyed Muhmmad Hussain Shah100% (1)
- AI-PS Element Guide No 2Document7 pagesAI-PS Element Guide No 2zizu1234No ratings yet
- Fire and Explosion Hazard Management Rev 1Document36 pagesFire and Explosion Hazard Management Rev 1fxgbNo ratings yet
- Risk Based SafetyDocument6 pagesRisk Based Safetysalman ahmedNo ratings yet
- Loss of ContainmentDocument68 pagesLoss of Containmentpetrolhead1No ratings yet
- AI-PS Element Guide No 7Document10 pagesAI-PS Element Guide No 7Asad KhanNo ratings yet
- Ep 95 0300 - (Hemp)Document86 pagesEp 95 0300 - (Hemp)lsaishankar100% (1)
- PSM Compliance AuditDocument18 pagesPSM Compliance Auditkanakarao1100% (1)
- Process Safety - Barrier Management: Nageswara Rao HSSE Manager Shell Technology Center BangaloreDocument16 pagesProcess Safety - Barrier Management: Nageswara Rao HSSE Manager Shell Technology Center BangaloreÖzlem ÖzkiliçNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal PumpDocument25 pagesCentrifugal Pumpsamuad59No ratings yet
- Hazop Training GuideDocument9 pagesHazop Training GuideAli RizviNo ratings yet
- NORSOK Standard For Process DesignDocument27 pagesNORSOK Standard For Process DesignM. Faisal SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Failure RatesDocument96 pagesFailure RatesAli Rizvi100% (3)
- Fuel Storage SitesDocument268 pagesFuel Storage SitesAli RizviNo ratings yet
- API Guide To PsiDocument86 pagesAPI Guide To PsiAli RizviNo ratings yet
- Fall ArestDocument22 pagesFall ArestAli RizviNo ratings yet
- ALARP JustificationDocument8 pagesALARP JustificationAli RizviNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Selecting Appropriate Tools To Improve HSE CultureDocument24 pagesA Guide To Selecting Appropriate Tools To Improve HSE CultureSAYED100% (3)
- Hira KSBDocument2 pagesHira KSBamitNo ratings yet
- Improving Outcomes For Breast Cancer SurvivorsDocument280 pagesImproving Outcomes For Breast Cancer SurvivorsHồ Q. ThuậnNo ratings yet
- FNCE3004 International Finance Semester 1 2024 Miri Sarawak Campus INTDocument16 pagesFNCE3004 International Finance Semester 1 2024 Miri Sarawak Campus INTAlex chiewNo ratings yet
- IIM Bangalore Study ReportDocument27 pagesIIM Bangalore Study ReportvishalNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects of NursingDocument29 pagesLegal Aspects of NursingKamranKhan100% (1)
- Group Assignment - Personal FinanceDocument23 pagesGroup Assignment - Personal FinanceArthur OmbatiNo ratings yet
- IFE Level 4 Certificate in Fire Science and Fire SafetyDocument9 pagesIFE Level 4 Certificate in Fire Science and Fire SafetyDebayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- Final Report - Aashita SabharwalDocument41 pagesFinal Report - Aashita SabharwalAashita Sabharwal100% (1)
- Akzo Nobel Risk ManagementDocument53 pagesAkzo Nobel Risk ManagementdhanuNo ratings yet
- GOOD PRACTICE GUIDE - Control of Pollution and Noise From Demoition and Construction SitesDocument18 pagesGOOD PRACTICE GUIDE - Control of Pollution and Noise From Demoition and Construction SitesTengLiJinNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Non Performing Loans The Case of Ethiopian BanksDocument169 pagesDeterminants of Non Performing Loans The Case of Ethiopian BanksEdlamu AlemieNo ratings yet
- Project Report On BHARTI AXA Life InsuraDocument50 pagesProject Report On BHARTI AXA Life InsuraArvindSinghNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence: Expanding MyDocument20 pagesEmotional Intelligence: Expanding MyArvie ChavezNo ratings yet
- Constructionsafety IEEDocument29 pagesConstructionsafety IEESamNo ratings yet
- 613v1-Principles and Practice of General InsuranceDocument18 pages613v1-Principles and Practice of General InsuranceŠ Òű VïķNo ratings yet
- How To Successfully Manage Organisational Conflicts: Presented By: Asra Badbade 2SD20BA010Document11 pagesHow To Successfully Manage Organisational Conflicts: Presented By: Asra Badbade 2SD20BA010Asra BadbadeNo ratings yet
- Risks and ChallengesDocument4 pagesRisks and ChallengesLavanth DynoNo ratings yet
- Yousefi Et Al., 2020Document14 pagesYousefi Et Al., 2020Adria ViolaNo ratings yet
- 2015 - Rubinger - Counting Techniques To Improve Accuracy in The Warehouse - WMSDocument5 pages2015 - Rubinger - Counting Techniques To Improve Accuracy in The Warehouse - WMSGeanella GarciaNo ratings yet
- 07 Standardized Work QIP V4 Fev 2021 Training MaterialDocument83 pages07 Standardized Work QIP V4 Fev 2021 Training Materialawdhut kulkarniNo ratings yet
- CSR - IIA Practical Guide PDFDocument22 pagesCSR - IIA Practical Guide PDFMudit KothariNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 - Health and Safety Policy - Final Draft - August 2018Document76 pagesCase Study 1 - Health and Safety Policy - Final Draft - August 2018lonnyNo ratings yet
- Ch-7 - Risk AnalysisDocument32 pagesCh-7 - Risk AnalysisDebayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- Pub Engineering Insurance and Reinsurance enDocument38 pagesPub Engineering Insurance and Reinsurance enMuhammad Fazriansyah100% (1)
- MRD Sample TemplateDocument4 pagesMRD Sample TemplatePrashant KarpeNo ratings yet
- HE - Household Services CGDocument20 pagesHE - Household Services CGLily PoraqueNo ratings yet
- Symmetry 11 00340 PDFDocument16 pagesSymmetry 11 00340 PDFSilvya BerlianNo ratings yet
- CHE135 - Ch1 Intro To Hazard - MII - L1.1Document26 pagesCHE135 - Ch1 Intro To Hazard - MII - L1.1muhammad izzulNo ratings yet
- DRR Lesson 6.1Document56 pagesDRR Lesson 6.1Leo EspinoNo ratings yet