Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Checklist LC OL Maths
Uploaded by
Edel QuinnCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Checklist LC OL Maths
Uploaded by
Edel QuinnCopyright:
Available Formats
Leaving Cert Maths O/L Checklist
What you need to know off by heart going into exam
Paper 1
Question 7 and 8 Differentiation and Functions, do first? Predictable
f(x) or f:x is the same as y, f(x) is the same as dy/dx
dy/dx = Slope (of tangent at any point so differentiate for all these questions)
Turning points (Max and Min) Let dy/dx = 0
Solve for x, sub back in for corresponding y
Same method for curve Increasing ( > 0 instead of = 0) and Decreasing (< 0)
First principles
When to use (u)(v), u over v, chain rule (power outside of bracket)
Differentiate for speed, differentiate twice for Acceleration, at greatest height
speed = 0
Graphs like will have 2 curves never touching line x = -2 (because f(-2)
is undefined. (because when you sub in -2 you get )
Periodic graphs (graphs which repeat a pattern):
period is the distance the graph extends along the x-axis before it starts repeating
range is the lowest and highest point the graph goes along the y-axis e.g. [-2, 1]
Complex numbers
Anywhere you get i sub in -1 (so anywhere you have i its the same as -1)
4 + 3i = modulus formula = 4 + 3
z = change sign of i number
Argand diagram numbers on the x-axis, is on the y-axis
One complex number over another multiply top and bottom by the conjugate of
the bottom
Arithmetic
Distance, Speed, Time triangle
Percentage Error
Multiply by percentage to get percentage of
To divide an amount in a ratio e.g. 1:3 get and of amount (multiply)
Finding Income Tax
Compound Interest Formula from Log Tables:
Final Amount = Principal(1 + i)t (no. of years)
Also used for depreciation or reducing balance with instead of +
Algebra
Any equation with an x, x and a number is a quadratic equation! Tidy up to
ax2 bx c = 0 and solve using brackets (x )(x ) or else - b formula. Forming a
quadratic equation given 2 solutions (roots): x2 sum of roots + product of roots
Indice rules Page 21 Log Tables ( = power of a half, minus powers = one over
the number, power of 0 = 1 etc)
If given equation with , square both sides to get rid of
f(3) = 0 Sub in 3 for x into given function and let equal 0, gives point (3, 0)
May 2013 E. Quinn
Simultaneous Equations, if not both linear (has x2 or xy) rearrange to get x = or y
= and sub this value in to other equation to solve
To get rid of fraction cross multiply (or multiply by common denominator)
To solve inequalities ( or ) treat as equation =, keeping x positive
N = natural numbers, Z = integers (+ and whole numbers), Q = rational numbers
(fractions), R = real numbers including irrational numbers (not fractions e.g. 2)
Prime number can only be divided by itself and 1
Factor is a divisor (number that divides into)
Sequences and Series
A sequence is arithmetic if there is a common difference (d) between terms. A
sequence is geometric if there is a common ratio between terms (common divisor)
e.g. 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 has common ratio of 2
Finding nth term use Tn formula log tables Tn = a + (n - 1)d
Finding sum or total of all terms use Sn formula (now a series)
Quadratic sequences have the same 2nd difference e.g. 1, 4, 9, 16 have a difference
of 3, 5, 7 which have all have a 2nd difference of 2.
Formula for quadratic sequence not in Log Tables an2 + bn + c (like quadratic
equation). The coefficient of n2 (a) is half 2nd difference.
Paper 2
Area and Volume
Trapezoidal Rule given in Log Tables can be simplified as:
equal width/2(1st + last + 2(remaining offsets))
Area = cm, Volume = cm
Perimeter = length all around
Area of a square = (side), Area of a rectangle = length breadth,
Area of parallelogram = base height, Area of triangle = half base height
Volume of a box = length breadth height
Be very familiar with formula page from Log Tables, remember arc/sector page
The Line
Must use Length formula when needing length of line (or given PQ), unless
perfectly horizontal or vertical can count length along X or Y axis.
Slope formula in Log Tables or if drawn can use rise/run (turn into y = mx + c if
getting slope from equation with no points, slope is m)
Parallel = Slopes are the same
Perpendicular = Same but turned upside down, sign changed (when you
multiply 2 perpendicular slopes you get 1)
Equation of a line (need point (x1, y1) and slope m). Can draw a line if equation is
in form y = mx + c, where m is the slope and c is the y intercept.
Area of a Triangle (perform same translation on points where one is to be (0,0)),
can use half base height if you have perpendicular height/length
To find the point of intersection of 2 lines, use Simultaneous Equations
Intersecting X axis, sub in y=0 (x, 0) vice versa for Y axis, x = 0 (0, y)
May 2013 E. Quinn
The Circle
x2 + y2 = R2 Equation of a circle with centre (0,0) and radius R
(x - 3)2 + (y - 2)2 = 16 Equation of a circle with centre (3,2) and radius 4
Diameter = twice the radius
How to find point of intersection of a line and circle (simultaneous equations)
A tangent is a line that has only one point of intersection with a circle and is
perpendicular to the radius
How to find equation of tangent (line): y- y1 = m(x - x1)
Probability
Fill boxes for number of options and multiply numbers if:
You are arranging, forming codes or passwords and are concerned with order
Put down number of boxes to be filled first and fill restrictions
If you see the word probability in the question:
No. of favourable outcomes/Total outcomes
Answer will be a fraction (or can be changed to a decimal between 0 and 1)
And means multiply (2 or more things/events, e.g. both red = P(1st red) and
P(2nd red))
Or means add (e.g. at least, can be one way or another way)
Fundamental Principle of Counting 3 starters, 4 mains have 3 4 different
combinations
Sample Space listing all the possible outcomes, could be in table form
Expected value multiply value by probability
Statistics
How to get 3 different averages/central tendency mean, mode & median
How to get 3 different measures of variability/spread range, standard deviation,
interquartile range
Can use formula on Log Tables for Mean and Standard Deviation but need to be
able to use calculator also: Mode, 2: Stat, 1-Var, Input values pressing = after
each value, AC, Shift followed by 1, 4: Var, 3: x (Standard Deviation), =
Be able to draw and read from the various graphical representations bar charts
(or more accurate histograms), pie charts, trend graphs, dot plots/line plots, stem
and leaf diagrams and scatterplots
3 distribution curves Normal/symmetrical, Skewed right/Positive skew, Skewed
left/Negative skew
Types of data: Univariate or Bivariate, Categorical or Numerical, Nominal or
Ordinal, Discrete or Continuous, Primary or Secondary
Discuss outliers, correlation (in general), ways of collecting data (surveys etc..)
Correlation coefficient is between -1 and 1 depending on shape of dots on
scatterplot strong positive close to 1, no correlation close to 0, strong negative
close to -1
Empirical Rule 68% of data 1 Standard Deviation () from the mean, 95% of
data 2() from the mean, 99.7% of data 3() from the mean
May 2013 E. Quinn
Trigonometry
Right angled triangle Pythagoras Theorem a2=b2+c2 if missing side. Sin = o/h,
Cos = a/h, Tan = o/a, label all sides of triangle opposite, hypotenuse, adjacent
Sin-1, Cos-1or Tan-1 buttons on calculator if finding missing angle
Sine Rule works for finding missing sides and angles on nearly all triangles. Must
use sides and angles opposite each other to work. Cross multiply to get on its own
If Sine Rule doesnt work, use Cosine Rule. Side a must be opposite angle A
when subbing into formula
Area of a triangle formula must use 2 sides and the angle in between these sides
If angles greater than 90, add or subtract 180 to find equivalent angles rotated.
To know whether answer is + or remember unit circle A S T C (all +, only Sin +
etc)
Enlargements
If scale factor is bigger than 1 the shape will be bigger, if it is less than 1 it will be
smaller
To draw: Draw lines from centre of enlargement through each vertex (corner),
measure and multiply by scale factor to get vertex of enlargement.
To get scale factor: Length of image side Length of original side
Area of Enlargement = Area of original (Scale Factor)2
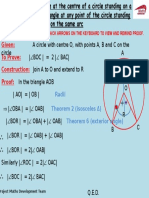
Geometry (Option 6A or 6B) A is construction or definition, B is rest of Geometry
Constructions:
Circumcircle bisect lines (could be in disguise as finding centrepoint of a circle
draw 3 chords inside and bisect, or finding a centrepoint equidistant to 3
points/vertices of triangle)
Incircle bisect angles (could be in disguise as centrepoint equidistant to all
sides/lines of triangle)
Centroid bisect lines and join midpoints (medians) to opposite vertex (corners)
Angle of 60 (an equilateral triangle) using compass and ruler
Tangent to a given circle at a given point (90 to radius)
Parallelogram given the lengths of the sides and the measure of the angles
Definitions: Theorem, Proof, Axiom, Corollary, Converse, Implies
Know 10 theorems in book/handout.
Might need to prove sides are equal. Think triangles and prove congruency. Need
to know:
Congruent triangles equal (need 2 sides and an angle SSA, AAS or SSS)
Similar/Equiangular all angles the same, sides are in proportion (1:2 etc)
Isosceles, equilateral and scalene triangles
May 2013 E. Quinn
You might also like
- Have Yourself A Merry Little Christmas SATBDocument3 pagesHave Yourself A Merry Little Christmas SATBEdel QuinnNo ratings yet
- Can't Help Falling in ChordsDocument4 pagesCan't Help Falling in ChordsEdel QuinnNo ratings yet
- Soprano-Score and PartsDocument15 pagesSoprano-Score and PartsEdel QuinnNo ratings yet
- Junior Cert Music Marking SchemeDocument12 pagesJunior Cert Music Marking SchemeEdel QuinnNo ratings yet
- Theorem 14 ProofDocument3 pagesTheorem 14 ProofEdel Quinn100% (1)
- Theorem 19 ProofDocument1 pageTheorem 19 ProofEdel QuinnNo ratings yet
- Long DivDocument29 pagesLong DivEdel QuinnNo ratings yet
- Empirical RuleDocument1 pageEmpirical RuleEdel QuinnNo ratings yet
- De DannanDocument1 pageDe DannanEdel QuinnNo ratings yet
- Gaudete! Christus Est Natus.: No XIV Piae Cantiones 1582 Arr D G Mason 1997Document4 pagesGaudete! Christus Est Natus.: No XIV Piae Cantiones 1582 Arr D G Mason 1997Edel QuinnNo ratings yet
- Oliver ScriptDocument40 pagesOliver ScriptEdel Quinn80% (5)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Quant Checklist 343 by Aashish Arora For Bank Exams 2023Document91 pagesQuant Checklist 343 by Aashish Arora For Bank Exams 2023kumaripallavi725No ratings yet
- Cavite State University: Cavite College of Arts and TradesDocument7 pagesCavite State University: Cavite College of Arts and TradesNiel Ian LunaNo ratings yet
- My Homework Lesson 4 Round To The Nearest TenDocument8 pagesMy Homework Lesson 4 Round To The Nearest Tendwvujqsmg100% (1)
- Annotated BibliographyDocument8 pagesAnnotated BibliographyArbilei de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Imo Sample Paper Class-3Document2 pagesImo Sample Paper Class-3Riddhi100% (4)
- Floyd WarshallDocument6 pagesFloyd WarshallciaoasdasdNo ratings yet
- Father of GeometryDocument11 pagesFather of GeometrymohammedismayilNo ratings yet
- Examens Eng PDFDocument250 pagesExamens Eng PDFMajid KhanNo ratings yet
- H2 Mathematics 2017 Preliminary Exam Paper 1 Question Ans Er All Uestions (100 Marks) 1Document14 pagesH2 Mathematics 2017 Preliminary Exam Paper 1 Question Ans Er All Uestions (100 Marks) 1Emmanuel Elijah ErNo ratings yet
- Unconstrained Multivariable OptimizationDocument42 pagesUnconstrained Multivariable OptimizationAliyya DhiyaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Feb 2016Document44 pagesTutorial 2 Feb 2016No NameNo ratings yet
- Summary T3 2023Document2 pagesSummary T3 2023Hussin HamidonNo ratings yet
- Weighted Regression in ExcelDocument1 pageWeighted Regression in Exceldardo1990No ratings yet
- Spatial Referencing: Faculty of Applied Engineering and Urban Planning Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument43 pagesSpatial Referencing: Faculty of Applied Engineering and Urban Planning Civil Engineering DepartmentMohammed Al MaqadmaNo ratings yet
- Floating Point RepresentationDocument18 pagesFloating Point RepresentationVishnu BhanderiNo ratings yet
- Math9 LAS Q4 W4Document6 pagesMath9 LAS Q4 W4Jay PeeNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Coefficient Quantization On The Performance of A Digital FilterDocument17 pagesThe Effect of Coefficient Quantization On The Performance of A Digital FilterKanza FatimaNo ratings yet
- Pre - Calculus: Quarter 2 - Module 2Document19 pagesPre - Calculus: Quarter 2 - Module 2kimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Definition and Equation of A CircleDocument47 pagesDefinition and Equation of A Circlesaira claire cayetanoNo ratings yet
- Discrete Logarithms in Finite Fields: Alice BobDocument10 pagesDiscrete Logarithms in Finite Fields: Alice BobguruannamalaiNo ratings yet
- Monte Carlo Simulations ExcelDocument164 pagesMonte Carlo Simulations Exceljijo morijoNo ratings yet
- Stat - 992Document16 pagesStat - 992Siam ShawNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Topic: Searching/Sorting: Input FormatDocument10 pagesAssignment 2 Topic: Searching/Sorting: Input FormatkalluNo ratings yet
- Functions, Limits and Continuity: X G F X G X FDocument5 pagesFunctions, Limits and Continuity: X G F X G X FKenny KenNo ratings yet
- Matrix Analysis For Scientists and Engineers by Alan J LaubDocument172 pagesMatrix Analysis For Scientists and Engineers by Alan J LaubJulio Cesar Barraza Bernaola91% (11)
- q6 DSA - Q10Document6 pagesq6 DSA - Q10Sumanth_YedotiNo ratings yet
- Towards an ω-groupoid model of Type Theory: Based on joint work with Ondrej RypacekDocument33 pagesTowards an ω-groupoid model of Type Theory: Based on joint work with Ondrej RypacekΓιάννης ΣτεργίουNo ratings yet
- Group C Assign 23Document4 pagesGroup C Assign 23Siddhesh MhatreNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Notes (Just Statements)Document16 pagesAlgebra 2 Notes (Just Statements)mmmellyyyyNo ratings yet
- EE341 FinalDocument4 pagesEE341 FinalLe HuyNo ratings yet