Professional Documents
Culture Documents
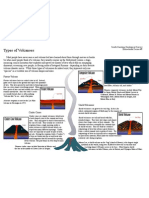
Types of Volcanoes
Uploaded by
bjmandiaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Volcanoes
Uploaded by
bjmandiaCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Volcanoes
Types of Volcanoes Geologists generally group volcanoes into four main kindscinder
Geologists generally group volcanoes into four main kindscinder cones, composite volcanoes, shield volcanoes, and lava domes.
cones, composite volcanoes, shield volcanoes, and lava domes.
Cinder cones
Cinder cones Cinder cones are the simplest type of volcano. They are built from
Cinder cones are the simplest type of volcano. They are built from particles and blobs of congealed lava ejected from a single vent. As
particles and blobs of congealed lava ejected from a single vent. As the gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small
the gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small fragments that solidify and fall as cinders around the vent to form a
fragments that solidify and fall as cinders around the vent to form a circular or oval cone. Most cinder cones have a bowl-shaped crater
circular or oval cone. Most cinder cones have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit and rarely rise more than a thousand feet or so above
at the summit and rarely rise more than a thousand feet or so above their surroundings. Cinder cones are numerous in western North
their surroundings. Cinder cones are numerous in western North America as well as throughout other volcanic terrains of the world.
America as well as throughout other volcanic terrains of the world.
Composite volcanoes
Composite volcanoes Some of the Earth's grandest mountains are composite volcanoes
Some of the Earth's grandest mountains are composite volcanoes sometimes called stratovolcanoes. They are typically steep-sided,
sometimes called stratovolcanoes. They are typically steep-sided, symmetrical cones of large dimension built of alternating layers of
symmetrical cones of large dimension built of alternating layers of lava flows, volcanic ash, cinders, blocks, and bombs and may rise as
lava flows, volcanic ash, cinders, blocks, and bombs and may rise as much as 8,000 feet above their bases. Some of the most conspicuous
much as 8,000 feet above their bases. Some of the most conspicuous and beautiful mountains in the world are composite volcanoes,
and beautiful mountains in the world are composite volcanoes, including Mount Fuji in Japan, Mount Cotopaxi in Ecuador, Mount
including Mount Fuji in Japan, Mount Cotopaxi in Ecuador, Mount Shasta in California, Mount Hood in Oregon, and Mount St. Helens
Shasta in California, Mount Hood in Oregon, and Mount St. Helens and Mount Rainier in Washington.
and Mount Rainier in Washington. Most composite volcanoes have a crater at the summit which contains
Most composite volcanoes have a crater at the summit which contains a central vent or a clustered group of vents. Lavas either flow through
a central vent or a clustered group of vents. Lavas either flow through breaks in the crater wall or issue from fissures on the flanks of the
breaks in the crater wall or issue from fissures on the flanks of the cone. Lava, solidified within the fissures, forms dikes that act as ribs
cone. Lava, solidified within the fissures, forms dikes that act as ribs which greatly strengthen the cone.
which greatly strengthen the cone. The essential feature of a composite volcano is a conduit system
The essential feature of a composite volcano is a conduit system through which magma from a reservoir deep in the Earth's crust rises
through which magma from a reservoir deep in the Earth's crust rises to the surface. The volcano is built up by the accumulation of material
to the surface. The volcano is built up by the accumulation of material erupted through the conduit and increases in size as lava, cinders,
erupted through the conduit and increases in size as lava, cinders, ash, etc., are added to its slopes.
ash, etc., are added to its slopes.
Shield volcanoes
Shield volcanoes Shield volcanoes, the third type of volcano, are built almost entirely of
Shield volcanoes, the third type of volcano, are built almost entirely of fluid lava flows. Flow after flow pours out in all directions from a
fluid lava flows. Flow after flow pours out in all directions from a central summit vent, or group of vents, building a broad, gently sloping
central summit vent, or group of vents, building a broad, gently sloping cone of flat, domical shape, with a profile much like that of a warrior's
cone of flat, domical shape, with a profile much like that of a warrior's shield. They are built up slowly by the accretion of thousands of highly
shield. They are built up slowly by the accretion of thousands of highly fluid lava flows called basalt lava that spread widely over great
fluid lava flows called basalt lava that spread widely over great distances, and then cool as thin, gently dipping sheets. Lavas also
distances, and then cool as thin, gently dipping sheets. Lavas also commonly erupt from vents along fractures (rift zones) that develop
commonly erupt from vents along fractures (rift zones) that develop on the flanks of the cone. Some of the largest volcanoes in the world
on the flanks of the cone. Some of the largest volcanoes in the world are shield volcanoes. In northern California and Oregon, many shield
are shield volcanoes. In northern California and Oregon, many shield volcanoes have diameters of 3 or 4 miles and heights of 1,500 to
volcanoes have diameters of 3 or 4 miles and heights of 1,500 to 2,000 feet. The Hawaiian Islands are composed of linear chains of
2,000 feet. The Hawaiian Islands are composed of linear chains of these volcanoes including Kilauea and Mauna Loa on the island of
these volcanoes including Kilauea and Mauna Loa on the island of Hawaiitwo of the world's most active volcanoes. The floor of the
Hawaiitwo of the world's most active volcanoes. The floor of the ocean is more than 15,000 feet deep at the bases of the islands. As
ocean is more than 15,000 feet deep at the bases of the islands. As Mauna Loa, the largest of the shield volcanoes (and also the world's
Mauna Loa, the largest of the shield volcanoes (and also the world's largest active volcano), projects 13,677 feet above sea level, its top
largest active volcano), projects 13,677 feet above sea level, its top is over 28,000 feet above the deep ocean floor.
is over 28,000 feet above the deep ocean floor.
Lava domes
Lava domes Volcanic or lava domes are formed by relatively small, bulbous
Volcanic or lava domes are formed by relatively small, bulbous masses of lava too viscous to flow any great distance; consequently,
masses of lava too viscous to flow any great distance; consequently, on extrusion, the lava piles over and around its vent. A dome grows
on extrusion, the lava piles over and around its vent. A dome grows largely by expansion from within. As it grows its outer surface cools
largely by expansion from within. As it grows its outer surface cools and hardens, then shatters, spilling loose fragments down its sides.
and hardens, then shatters, spilling loose fragments down its sides. Some domes form craggy knobs or spines over the volcanic vent,
Some domes form craggy knobs or spines over the volcanic vent, whereas others form short, steep-sided lava flows known as
whereas others form short, steep-sided lava flows known as coulees.
coulees.
.
You might also like
- Best Answer - Chosen by VotersDocument2 pagesBest Answer - Chosen by VotersJovz BumohyaNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument15 pagesTypes of VolcanoesSally PocamasNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Types of VolcanoesDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Different Types of VolcanoesBenes Salamanca BolascoNo ratings yet
- HGGGGDocument8 pagesHGGGGBea Ashley VosotrosNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes Everything You Need To KnowDocument5 pagesVolcanoes Everything You Need To KnowDevraj H SNo ratings yet
- VOLCANOESDocument10 pagesVOLCANOESYesha ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Volcanic EruptionsDocument22 pagesChapter 5 Volcanic EruptionsreesespufffNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument10 pagesTypes of VolcanoesRobert MestiolaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Midterm Lesson 2-2022Document44 pagesEarth Science Midterm Lesson 2-2022April Rose MarasiganNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument75 pagesVolcanoesMeleen ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- What Is Volcanism?Document49 pagesWhat Is Volcanism?Claire LouisNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 VolcanoesDocument13 pagesUnit 8 VolcanoesMaria Fe IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Volcano: Go To Australian Volcanos Go To Volcanic Hazards and Case Studies Go To Volcano TypesDocument14 pagesVolcano: Go To Australian Volcanos Go To Volcanic Hazards and Case Studies Go To Volcano TypesTulika ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Types of Volcano 4Document25 pagesTypes of Volcano 4Jaypee CarlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Volcanic EruptionsDocument19 pagesChapter 5 Volcanic EruptionsreesespufffNo ratings yet
- VolvanoDocument6 pagesVolvanoZarinaNo ratings yet
- 3 Types of Volcanic ConesDocument2 pages3 Types of Volcanic ConesKirsten Colin BermejoNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes The Ultimate Book: Experience the Heat, Power, and Beauty of VolcanoesFrom EverandVolcanoes The Ultimate Book: Experience the Heat, Power, and Beauty of VolcanoesNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument15 pagesTypes of VolcanoesJensen Kay NorteNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument6 pagesVolcanoesRoger Corre RivaNo ratings yet
- Volcano WorksheetDocument1 pageVolcano WorksheetJavier100% (1)
- Classification of VolcanoesDocument5 pagesClassification of Volcanoesmark.mendozaNo ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes Fact FileDocument2 pagesTypes of Volcanoes Fact FileLily Anne CerilloNo ratings yet
- VOLCANODocument69 pagesVOLCANOchristinaNo ratings yet
- VulcanismDocument35 pagesVulcanismrheeaNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument4 pagesVolcanoMargie AbogadoNo ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes: Shield VolcanoDocument17 pagesTypes of Volcanoes: Shield VolcanoRomeo Gabitanan JrNo ratings yet
- Features of A VolcanoDocument46 pagesFeatures of A Volcanoジェーン サラNo ratings yet
- VOLCANO NotesDocument17 pagesVOLCANO NotesAlexander LahipNo ratings yet
- VOLCANOESDocument65 pagesVOLCANOESPrincess Alyssa BarawidNo ratings yet
- VOLCANESDocument10 pagesVOLCANESJahnisel A. CordovaNo ratings yet
- What Is A VolcanoDocument3 pagesWhat Is A VolcanoDarlyn Llabore SueltoNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument42 pagesVolcanoesEllecarg Cenaon CruzNo ratings yet
- CH - 7 VolcanoesDocument5 pagesCH - 7 VolcanoesAawaz ek, Aaghaz hai, Andolan hai, Nav Nirman kaNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes NotesDocument13 pagesVolcanoes NotesNavya RaiNo ratings yet
- Cinder Cone Volcanoes:: Active VolcanosDocument1 pageCinder Cone Volcanoes:: Active VolcanosZwennie Liane Roquites CaburnayNo ratings yet
- Ol.6: Volcanoes and Volcanic HazardsDocument29 pagesOl.6: Volcanoes and Volcanic HazardsSalman Bin TariqNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument1 pageTypes of VolcanoesДраган ГрчакNo ratings yet
- 04 Hawaii VolcanoesDocument26 pages04 Hawaii VolcanoesJobanie AmadhayNo ratings yet
- What Is A Volcano?Document4 pagesWhat Is A Volcano?Sriram SusarlaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 (q3)Document22 pagesWeek 1 (q3)Jesseryl MargalloNo ratings yet
- Abdullah VolcanoesDocument9 pagesAbdullah VolcanoesMariam MagdyNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 - Module 1 VOLCANOESDocument39 pagesQuarter 3 - Module 1 VOLCANOESRubeliza LawengNo ratings yet
- Most of Volcanoes/ Earthquakes and Formation of Mountains Occurs Along With?Document63 pagesMost of Volcanoes/ Earthquakes and Formation of Mountains Occurs Along With?Imee TiloNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument26 pagesTypes of VolcanoesMatt PayawalNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument15 pagesTypes of VolcanoesYogendra PatilNo ratings yet
- Mary Drury - VOLCANOES TemplateDocument11 pagesMary Drury - VOLCANOES TemplateMary DruryNo ratings yet
- Power Point Volcanic EruptionDocument18 pagesPower Point Volcanic Eruptionwandi primaNo ratings yet
- Volcanic LandformsDocument16 pagesVolcanic LandformsLielet MatutinoNo ratings yet
- Volcano (Students)Document20 pagesVolcano (Students)Wamm MadlaNo ratings yet
- Want To Stay On Top of All The Space NewsDocument2 pagesWant To Stay On Top of All The Space Newsapi-241769903No ratings yet
- Volcanoes and EarthquakesDocument104 pagesVolcanoes and EarthquakesAlleli AspiliNo ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes (g9 Lesson)Document16 pagesTypes of Volcanoes (g9 Lesson)Salvierrah BengNo ratings yet
- (Title) : Grade 9 ScienceDocument13 pages(Title) : Grade 9 ScienceJoTanlogonOcate-AmbongNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes-How It Is FormedDocument55 pagesVolcanoes-How It Is FormedHenry JacobNo ratings yet
- VolcanismDocument60 pagesVolcanismGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- Quinbigan NHS Radar 1-2Document2 pagesQuinbigan NHS Radar 1-2bjmandiaNo ratings yet
- Major Final Outputs (Mfos) Key Result Areas (Kras) Objectives Performance Indicators Outputs MovsDocument12 pagesMajor Final Outputs (Mfos) Key Result Areas (Kras) Objectives Performance Indicators Outputs MovsDom Ricafranca Cueto100% (3)
- ActionDocument10 pagesActionbjmandiaNo ratings yet
- G12 Ap 11Document3 pagesG12 Ap 11Caleb BiagNo ratings yet
- G12 Ap 11Document3 pagesG12 Ap 11Caleb BiagNo ratings yet
- Dr. Jose P. RizalDocument5 pagesDr. Jose P. RizalbjmandiaNo ratings yet
- Nick JoaquinDocument2 pagesNick JoaquinbjmandiaNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding Worksheet1Document2 pagesCovalent Bonding Worksheet1sheikhaamirhussainNo ratings yet
- Survey Instrument For School Heads and Teachers Teaching MAPEHDocument812 pagesSurvey Instrument For School Heads and Teachers Teaching MAPEHbjmandiaNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- LRMS Child Protection Committee Nov 2013 PDFDocument13 pagesLRMS Child Protection Committee Nov 2013 PDFbjmandiaNo ratings yet
- The Two BrothersDocument1 pageThe Two BrothersJone Castillo100% (3)
- 4 SDO SHS Implementation Team TORDocument2 pages4 SDO SHS Implementation Team TORbjmandiaNo ratings yet
- Workshop On SHS Implementation Planning Batch 4: Goals and ObjectivesDocument10 pagesWorkshop On SHS Implementation Planning Batch 4: Goals and ObjectivesbjmandiaNo ratings yet
- 2 Tracer StudyDocument6 pages2 Tracer StudybjmandiaNo ratings yet
- Functions of Public Schools District Supervisor PSDS Education Program Supervisor EPS With Assigned DistrictsDocument1 pageFunctions of Public Schools District Supervisor PSDS Education Program Supervisor EPS With Assigned DistrictsbjmandiaNo ratings yet
- 6 Conditions For Determining DepED SHS in 2016Document2 pages6 Conditions For Determining DepED SHS in 2016bjmandiaNo ratings yet
- Cub Bio Lesson01 Activity1 Pop Density Worksheet AnswersDocument1 pageCub Bio Lesson01 Activity1 Pop Density Worksheet AnswersbjmandiaNo ratings yet
- 12 Partnerships For Senior High SchoolDocument18 pages12 Partnerships For Senior High SchoolbjmandiaNo ratings yet
- TLE and Techvoc List of Specializations and PrereqsDocument2 pagesTLE and Techvoc List of Specializations and PrereqsbjmandiaNo ratings yet
- BEIS Performance Indicators - DefinitionsDocument7 pagesBEIS Performance Indicators - Definitionsbjmandia100% (1)
- Zip Grade 50Document1 pageZip Grade 50bjmandia100% (2)
- 44 - Synchronized Election Calendar For Supreme Pupils Government SPG and Supreme Students Government SSG For SY 2017-2018Document1,959 pages44 - Synchronized Election Calendar For Supreme Pupils Government SPG and Supreme Students Government SSG For SY 2017-2018bjmandiaNo ratings yet
- PDS-Work Experience SheetDocument2 pagesPDS-Work Experience SheetCes Camello100% (1)
- Region IVDocument2 pagesRegion IVbjmandiaNo ratings yet
- Secondary 1 Express English Paper 1 & 2Document15 pagesSecondary 1 Express English Paper 1 & 2Menon HariNo ratings yet
- Copy of HW UMTS KPIsDocument18 pagesCopy of HW UMTS KPIsMohamed MoujtabaNo ratings yet
- BrainPOP Nutrition Quiz242342Document1 pageBrainPOP Nutrition Quiz242342MathableNo ratings yet
- June 2019Document64 pagesJune 2019Eric SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Time Sheets CraneDocument1 pageTime Sheets CraneBillie Davidson100% (1)
- Sialoree BotoxDocument5 pagesSialoree BotoxJocul DivinNo ratings yet
- FS011 Audit Plan Stage 2Document2 pagesFS011 Audit Plan Stage 2Ledo Houssien0% (1)
- SpectraSensors TDL Analyzers in RefineriesDocument8 pagesSpectraSensors TDL Analyzers in Refineries1977specopsNo ratings yet
- 20 Best Cognac CocktailsDocument1 page20 Best Cognac CocktailsHL XanticNo ratings yet
- Expressions of QuantityDocument5 pagesExpressions of Quantitybenilde bastidaNo ratings yet
- Molarity, Molality, Normality, and Mass Percent Worksheet II Answer Key 11-12 PDFDocument3 pagesMolarity, Molality, Normality, and Mass Percent Worksheet II Answer Key 11-12 PDFGerald KamulanjeNo ratings yet
- Prestress 3.0Document10 pagesPrestress 3.0Jonel CorbiNo ratings yet
- A-V300!1!6-L-GP General Purpose Potable Water Commercial Industrial Hi-Flo Series JuDocument2 pagesA-V300!1!6-L-GP General Purpose Potable Water Commercial Industrial Hi-Flo Series JuwillgendemannNo ratings yet
- Government of Tamilnadu Directorate of Legal Studies: Inter-Collegeiate State Level Moot Court Competition-2022Document30 pagesGovernment of Tamilnadu Directorate of Legal Studies: Inter-Collegeiate State Level Moot Court Competition-2022Divya SrinimmiNo ratings yet
- Sand Casting OverviewDocument166 pagesSand Casting Overviewsamurai7_77No ratings yet
- Grade 11 - Life Science - November Paper 2-1 - MemoDocument8 pagesGrade 11 - Life Science - November Paper 2-1 - MemoJustinCase19910% (1)
- Epilepsy 2 AAN 2018Document12 pagesEpilepsy 2 AAN 2018Eashaa KumarNo ratings yet
- 5 Keto Pancake RecipesDocument7 pages5 Keto Pancake RecipesBai Morales VidalesNo ratings yet
- PNFDocument51 pagesPNFMuhamad Hakimi67% (3)
- Bonsai TreesDocument19 pagesBonsai TreesMayur ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- Exterior Wall PrimerDocument2 pagesExterior Wall PrimerAsian PaintsNo ratings yet
- Iso 2281 1990Document8 pagesIso 2281 1990jesus torresNo ratings yet
- Factors Associated With Early Pregnancies Among Adolescent Girls Attending Selected Health Facilities in Bushenyi District, UgandaDocument12 pagesFactors Associated With Early Pregnancies Among Adolescent Girls Attending Selected Health Facilities in Bushenyi District, UgandaKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- 13 Methods To Increase Your Conditioning - Strength by SkylerDocument5 pages13 Methods To Increase Your Conditioning - Strength by SkylerMarko Štambuk100% (1)
- Non-Binary or Genderqueer GendersDocument9 pagesNon-Binary or Genderqueer GendersJuan SerranoNo ratings yet
- Z0109MN Z9M TriacDocument6 pagesZ0109MN Z9M TriaciammiaNo ratings yet
- Toolbox Talks - Near Miss ReportingDocument1 pageToolbox Talks - Near Miss ReportinganaNo ratings yet
- MoringaDocument24 pagesMoringaobengappiahk100% (2)
- MPX-200 Service Manual PDFDocument90 pagesMPX-200 Service Manual PDFvivijaNo ratings yet
- Osma Osmadrain BG Pim Od107 Feb 2017pdfDocument58 pagesOsma Osmadrain BG Pim Od107 Feb 2017pdfDeepakkumarNo ratings yet